文章编号:1004-0609(2014)03-0631-06
阴极极化对7050铝合金应力腐蚀行为的影响
祁 星1,宋仁国1,王 超1,李 海1,乔利杰2,宿彦京2,褚武扬2
(1. 常州大学 材料科学与工程学院,常州 213164;
2. 北京科技大学 环境断裂教育部重点实验室,北京 100083)
摘 要:采用阴极极化、慢应变速率拉伸试验(SSRT)和定氢仪研究阴极极化对7050铝合金应力腐蚀行为的影响。结果表明:当阴极极化电位高于-1100 mV时,7050铝合金的应力腐蚀敏感性(Iscc)随着极化电位的负移而升高;而当阴极极化电位低于-1100 mV时,Iscc则随着极化电位的负移而下降。外加极化电位对不同时效状态7050铝合金Iscc的影响程度不同,即阴极极化对欠时效状态下铝合金的Iscc影响显著,对过时效状态铝合金Iscc的影响最小,对峰时效状态下铝合金Iscc的影响居中。铝合金的应力腐蚀机理为阳极溶解和氢脆共同作用,且氢对铝合金应力腐蚀的作用随着氢浓度的增加而增加。
关键词:7050铝合金;应力腐蚀;氢脆;阴极极化;慢应变速率拉伸
中图分类号:TG178 文献标志码:A
Effects of cathodic polarization on stress corrosion behavior of 7050 aluminum alloy
QI Xing1, SONG Ren-guo1, WANG Chao1, LI Hai1, QIAO Li-jie2, SU Yan-jing2, CHU Wu-yang2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Changzhou University, Changzhou 213164, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Environment Fracture, Ministry of Education,
University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract: The effects of cathodic polarization on stress corrosion behavior of 7050 aluminum alloy were studied by cathodic polarization, slow strain rate test (SSRT) and hydrogen determinator. The results show that the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) susceptibility (Iscc) of 7050 aluminum alloy increases with shifting negatively the polarization potential when the cathodic polarization potential is higher than -1100 mV, whereas it decreases when the cathodic polarization potential is lower than -1100 mV. The extent for the effect of polarization potential on Iscc is different among the 7050 aluminum alloys with various aging states. Cathodic polarization has greater effect on SCC of under-aged 7050 aluminum alloy than on that of over-aged 7050 aluminum alloy, and the peak aged 7050 aluminum alloy is in the middle. The SCC mechanism of aluminum alloy is a combination of anodic dissolution with hydrogen embrittlement, and the effect of hydrogen on SCC of aluminum alloy increases with increasing the hydrogen concentration.
Key words: 7050 aluminum alloy; stress corrosion; hydrogen embrittlement; cathodic polarization; slow strain rate test
7050铝合金以其密度低、强度高、弹性模量大等优点广泛应用于航空、航天等工业领域,主要用作飞机的机身框架、机翼蒙皮及衍条等[1]。然而,该合金在力学-环境交互作用下易发生应力腐蚀开裂(SCC)[2-5]。当材料在含有氯离子等腐蚀介质中发生SCC时,总是伴随着力学和电化学的协同效应[6]。目前,虽然国内外学者已经开展了一些有关力学-电化学交互作用对7000系铝合金SCC行为影响的研究[7],但是氢在SCC过程中的作用尚缺乏较为深入的定量研究。
从宏观上看,SCC机理可分为氢致开裂型和阳极溶解型两类[8-9]。然而,铝合金的SCC是氢致开裂还是阳极溶解目前尚存在争议[10]。早期人们认为铝合金的SCC机理是阳极溶解[11-12],20世纪70年代初发现有些铝合金是由氢脆引起的[13],也有研究者提出是二者的共同作用[14-15]。本文作者通过慢应变速率拉伸方法研究不同热处理状态7050铝合金在不同阴极极化电位下的腐蚀断裂行为,同时通过对试样断口进行SEM观察并且用定氢仪测试分析试样的氢浓度,初步探讨阴极极化及氢浓度对7050铝合金应力腐蚀的影响。
1 实验
1.1 材料及热处理
实验用材料为美国Alcoa公司生产的7050铝合金55 mm厚板材,化学组分(质量分数)如下:6.42%Zn,2.25%Mg,2.02%Cu,0.13%Zr,0.03%Ti,0.10%Mn,0.04%Cr,0.11%Fe,0.07%Si,其余为Al。
欠时效热处理:先将合金在470 ℃保温2 h,冷水淬火,然后在135 ℃时效8 h。峰时效和过时效处理和上述过程相同,时效时间分别为16和24 h。
1.2 SSRT实验
采用工作段标距长20 mm、直径4 mm的圆棒试样进行慢应变速率拉伸试验。取样方向为短横(S-T)向。试样用1200号砂纸进行打磨,然后用丙酮清洗,再用蒸馏水清洗并吹干,用氯丁橡胶封闭非工作段表面。装夹好试样后加载300 N左右的预紧力以消除各向的间隙。拉伸应变速率为1×10-6 s-1。这个速率小于Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金能显示氢脆效应的临界应变速率。
采用慢拉伸试验机分别在不同阴极极化电位下进行拉伸性能测试。极化电位为-1300、-1200、-1100、-1000、-900和-800 mV。试验介质为3.5%NaCl(质量分数)水溶液和干燥空气。
根据应力腐蚀敏感性计算公式对实验数据进行处理。定义应力腐蚀敏感性如下:
Iscc=1-εscc/ε0 (1)
式中:εscc为合金在腐蚀介质中的伸长率;ε0为合金在干燥空气中的伸长率。Iscc值越大,表明应力腐蚀敏感性越大;反之,Iscc值越小,应力腐蚀敏感性也越小。
1.3 氢含量分析
氢含量的测定采用EMGA-621型定氢仪,以石墨坩埚为加热体,通过脉冲加热低电压、高电流迅速升温。坩埚在高温下脱气去除杂质。样品在载气氩气流中先低温去除表面氢,然后在较高的温度下熔融后进入热导检测器进行检测,分析结果由仪器直接读出。
1.4 断口观察
断口形貌观察在JSM-6510扫描电镜上进行。
2 结果与分析
2.1 阴极极化对7050铝合金SCC的影响
3种不同时效状态7050铝合金的拉伸曲线分别见图1~3。由图1~3可见,在各种时效状态下,7050铝合金未极化时的抗拉强度均明显高于极化条件下的值;在欠时效状态下阴极极化时,拉伸曲线刚超过了屈服就开始下降,说明阴极极化大大降低了欠时效状态合金的力学性能,峰时效和过时效状态合金的力学性能也有不同程度的降低。同一时效状态合金阴极极化时,随着极化电位的负移,抗拉强度下降,而当极化电位低于-1100 mV时,抗拉强度则略有上升,但仍低于极化电位为-1000 mV时的值。上述结果表明,阴极极化对各种时效状态7050铝合金的力学性能均有显著的影响。

图1 欠时效状态7050铝合金的拉伸曲线
Fig. 1 Tensile curves of under-aged 7050 aluminum alloy

图2 峰时效状态7050铝合金的拉伸曲线
Fig. 2 Tensile curves of peak-aged 7050 aluminum alloy

图3 过时效状态7050铝合金的拉伸曲线
Fig. 3 Tensile curves of over-aged 7050 aluminum alloy
图4所示为不同时效状态7050铝合金在自腐蚀和不同极化电位下的应力腐蚀敏感性。通过电化学极化实验得出3种时效状态的自腐蚀电位:欠时效态自腐蚀电位约为-700 mV,峰时效态的约为-710 mV,过时效态的约为-730 mV。从图4可以看出,在3.5%NaCl溶液中无论哪一种热处理状态的铝合金在阴极极化电位下进行SSRT拉伸时,应力腐蚀感性均明显高于自腐蚀条件下的应力腐蚀敏感性。随着阴极极化电位的负移,应力腐蚀敏感性均呈先升后降的趋势,这是因为随着阴极极化作用增强,阴极的析氢反应逐步增加,当极化电位低于-1100 mV时,析氢反应更加剧烈,可能使更多的氢易于以气态析出[16],使得进入铝合金内部的氢含量下降,从而降低了氢脆效应。此外,欠时效状态下的7050铝合金应力腐蚀敏感性在同一极化条件下的值最大,变化幅度也最大,峰时效的上升趋势和欠时效的相近,过时效的变化程度最平缓,说明过时效状态下的7050铝合金有一定的抗应力腐蚀性能。这种差异是由于时效过后晶粒内部的结构发生了不同程度的改变[17]。对于欠时效状态的铝合金,晶粒内部主要是脱溶GP区(溶质原子的偏聚区)。这些GP区可作为可逆氢陷阱存在,合金在裂尖产生的氢原子会填充这些氢陷阱,同时位错滑移所携带的氢也会被捕获,直到饱和。氢在晶界的偏聚会大大降低晶界强度,使合金发生沿晶开裂。过时效状态的铝合金晶内析出相为η相粒子,而析出相是不可逆陷阱,氢原子无法达到饱和,因此氢不会造成晶界的过多偏聚,从而降低了氢致开裂的程度。峰时效处于中间状态,主要沉淀组织为GP区和η′相,介于以上两种情况之间[18]。
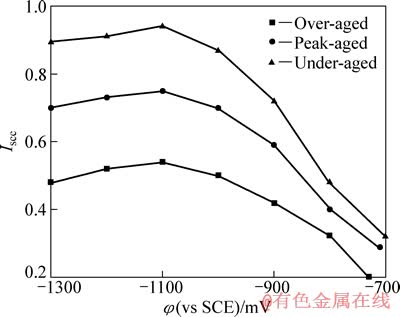
图4 不同时效状态7050铝合金的应力腐蚀敏感性(Iscc)
Fig. 4 Iscc of 7050 aluminum alloy in different aging states
2.2 氢浓度与应力腐蚀开裂的关系
表1 不同时效状态下7050铝合金的Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD)及氢浓度c*(H)
Table 1 Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD) and hydrogen concentration c*(H) of 7050 aluminum alloy in different aging states


图5 Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD)随氢浓度指数的变化
Fig. 5 Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD) vs exponent of hydrogen concentration
在开路条件下,试样的SCC以阳极溶解为主[19],为讨论方便,假定开路条件下应力腐蚀引起的塑性损失全部由阳极溶解引起,即Iscc≈Iscc(AD),且在不同阴极极化电位下Iscc(AD)是不变的。阴极极化时,而氢引起的塑性损失为Iscc*≈Iscc(H)。整个应力腐蚀开裂的Iscc=Iscc(H)+Iscc(AD)。根据Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD)的相对大小就可判定氢在高强度铝合金SCC中所起的作用及所占份额。根据Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD)随极化电位的变化就可以确定不同电位下氢在SCC中的作用。不同时效状态SCC时,也可根据Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD)来判断氢的不同作用。Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD)的值越大,说明氢的作用越大。不同时效状态Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD)的值及拉断试样氢浓度测定值c*(H)列于表1。从表1可以看出,3种时效状态随着极化电位的负移,Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD)的值都呈先升后降的趋势,拐点为-1100 mV。对Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD)和c*(H)进行拟合,得出Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD)随氢浓度指数的升高而线性增大(见图5)。设y=Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD),其线性关系为
欠时效:
y=4.7215 -4.2668 (2)
-4.2668 (2)
峰时效:
y=3.9651 -3.3571 (3)
-3.3571 (3)
过时效:
y=3.2075 -2.5328 (4)
-2.5328 (4)
由式(2)~(4)可知,氢对不同时效状态7050铝合金的应力腐蚀敏感性影响规律相同,只是影响的程度有所不同。其中,欠时效状态时氢的作用最明显,峰时效的居中,过时效的最小。故氢和7050铝合应力腐蚀敏感性有很强的关联性。
2.3 断口形貌观察

图6 欠时效状态下7050铝合金的应力腐蚀开裂断口形貌
Fig. 6 SCC fracture morphologies of under-aged 7050 aluminum alloy

图7 峰时效状态下7050铝合金的应力腐蚀开裂断口形貌
Fig. 7 SCC fracture morphologies of peak-aged 7050 aluminum alloy
不同热处理状态下的合金在空气和3.5%NaCl水溶液中以及-1100 mV阴极电位下的断口形貌如图6~8所示。由图6~8可见,3种时效制度在空气中拉伸断口均为韧窝型。欠时效断口韧窝中存在夹杂物,韧窝形状很不规则,大小差异也很明显。峰时效和过时效出现许多圆形且尺寸较小的弥散相韧窝。在3.5%NaCl水溶液中断口均为脆性韧窝断口,欠时效时已经开始出现明显脆化现象。峰时效时韧窝较为平坦,也有少量穿晶解理面的出现,过时效时仍然有较多韧窝。在-1100 mV阴极极化电位下,断口开始转为沿晶开裂。欠时效时以沿晶开裂为主,峰时效时为不规则的沿晶解理混合开裂,过时效时以穿晶准解理开裂为主,同时伴有不多的沿晶开裂。通过以上观察发现:极化电位和时效程度对高强7050铝合金的断裂形貌有显著影响,正是这种影响造成了以韧窝断口到沿晶穿晶断口的形貌变化,而其中脆化的增加以速度欠时效最为敏感,峰时效居中,过时效最慢。
3 结论
1) 外加阴极极化会增加7050铝合金的应力腐蚀敏感性,但是当极化电位负移到一定程度时(低于-1100 mV),阴极保护的作用使应力腐蚀敏感性有所下降。

图8 过时效状态下7050铝合金的应力腐蚀开裂断口形貌
Fig. 8 SCC fracture morphologies of over-aged 7050 aluminum alloy
2) 应力腐蚀敏感性与时效状态有着很强的相关性,在相同条件下,欠时效的应力腐蚀敏感性最大,峰时效的次之,而过时效的较弱。
3) 氢和阳极溶解在7050铝合金应力腐蚀过程中均起着非常重要的作用,且氢与阳极溶解引起的塑性损失的比值Iscc(H)/Iscc(AD)随氢浓度的指数的升高呈线性增大趋势。
REFERENCES
[1] 韩念梅, 张新明, 刘胜胆, 宋丰轩. 预拉伸对7050铝合金断裂韧性的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(11): 2088-2093.
HAN Nian-mei, ZHANG Xin-ming, LIU Sheng-dan, SONG Feng-xuan.Effects of prestretching on fracture toughness of 7050 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(11): 2088-2093.
[2] 张 宇, 宋仁国, 陈小明, 任建平. 7XXX系铝合金氢脆的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 材料导报, 2009, 23(5): 453-456.
ZHANG Yu, SONG Ren-guo, CHEN Xiao-ming, REN Jian-ping. Current status and trends of hydrogen embrittlement in 7XXX series aluminum alloy[J]. Materials Review, 2009, 23(5): 453-456.
[3] CHEN Song-yi, CHEN Kang-hua, PENG Guo-sheng, LIANG Xin, CHEN Xue-hai. Effect of quenching rate on microstructure and stress corrosion cracking of 7085 aluminum alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(1): 47-52.
[4] CHIELIN J, LUNGLIAO H, DAREJEHNG W. Effect of heat treatments on the tensile strength and SCC-resistance of AA7050 in an alkaline saline solution[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48: 3139-3156.
[5] OU B L, YANG J G, WEI M Y. Effect of homogenization and aging treatment on mechanical properties and stress corrosion cracking of 7050 alloys[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2007, 38: 1760-1773.
[6] 董超芳, 安英辉, 李晓刚, 生 海, 肖 葵. 7A04铝合金在海洋大气环境中初期腐蚀的电化学特性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(2): 346-352.
DONG Chao-fang, AN Ying-hui, LI Xiao-gang, SHENG Hai, XIAO Kui. Electrochemical performance of initial corrosion of 7A04 aluminum alloy in marine atmosphere[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(2): 346-352.
[7] 赵军军, 张 平, 李 奇, 原津萍. 外加电位条件下7A52铝合金应力腐蚀开裂敏感性研究[J]. 装甲兵工程学院学报, 2011, 25(5): 84-87.
ZHAO Jun-jun, ZHANG Ping, LI Qi, YUAN Jin-ping. Investigation of stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of 7A52 aluminum alloy under different applied potentials[J]. Journal of Academy of Armored Force Engineering, 2011, 25(5): 84-87.
[8] BURLEIGH T D. The postulated mechanisms for stress corrosion cracking of aluminum alloy[J]. Corrosion, 1991, 47: 90-98.
[9] KAESCHE H. Metallic corrosion-principles of physical chemistry and current problems[M]. Houston: National Association of Corrosion Engineers, 1985: 1-55.
[10] WANG D, MA Z Y. Effect of pre-strain on microstructure and stress corrosion cracking of over-aged 7050 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of alloy and Compounds, 2009, 469(1/2): 445-450.
[11] SPROWLS D O, BROWN R H. Stress corrosion mechanisms for aluminum alloys[C]//Fundamental Aspects of Stress Corrosion Cracking. Houston: NACE, 1969: 466.
[12] SPEIDEL M O. Current understanding of stress corrosion cracking growth in aluminum alloys[C]//The Theory of Stress Corrosion Cracking in Alloys. Brussels: NATO, 1971: 289.
[13] GEST R J, TROIANO A R. Stress corrosion and hydrogen embrittlement in an aluminum alloy[J]. Corrosion, 1974, 30(8): 274-279.
[14] 肖纪美. 氢与材料[J]. 稀有金属, 1985, 4(2): 2-18.
XIAO Ji-mei. Hydrogen and materials[J]. Rare Metals, 1985, 4(2): 2-18.
[15] 宋仁国, 张宝金, 曾梅光. 高强铝合金晶界偏析与氢致断裂机理的研究[J]. 航空材料学报, 1997, 17(1): 31-38.
SONG Ren-guo, ZHANG Bao-jin, ZENG Mei-guang. Investigation of grain boundary segregation and hydrogen-induced fracture mechanism in high strength aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 1997, 17(1): 31-38.
[16] 刘继华, 李 荻, 朱国伟, 刘培英. 7075铝合金应力腐蚀敏感性的SSRT和电化学测试研究[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2005, 26(1): 6-9.
LIU Ji-hua, LI Di, ZHU Guo-wei, LIU Pei-ying. Stress corrosion susceptibility of 7075 aluminum alloy studied by SSRT and electrochemical tests[J]. Corrosion and Protection, 2005, 26(1): 6-9.
[17] LI Jing-feng, PENG Zuo-wei, LI Chao-xing, JIA Zhi-qiang, CHEN Wen-jing, ZHENG Zi-qiao. Mechanical properties,corrosion behaviors and microstructure of 7075 aluminum alloy with various aging statements[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18: 755-762.
[18] 刘 军. 氢对7050铝合金短横方向慢应变速率拉伸及应力腐蚀开裂性能的影响[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 1989.
LIU Jun. The effect of hydrogen on the slow strain rate tensile properties and SCC performances on short transverse direction in 7050 aluminum alloy[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 1989.
[19] NAJJAR D, MAGNIN T, WARNER T J. Influence of critical surface defects and localized competition between anodic dissolution and hydrogen effects during stress corrosion cracking of a 7050 aluminum alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1997, 238: 293-302.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51371039);北京科技大学环境断裂教育部重点实验室开放课题资助项目(KYZ1102158C)
收稿日期:2013-04-24;修订日期:2013-09-01
通信作者:宋仁国,教授,博士;电话:0519-86330069;E-mail:songrg@hotmail.com