超声振动对电弧增材制造铝青铜合金组织和拉伸性能的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2020年第10期
论文作者:陈伟 陈玉华 温涛涛 闵文峰 张体明 封小松
文章页码:2280 - 2295
关键词:电弧增材制造;超声振动;铝青铜合金;层间温度;成形组织;拉伸性能
Key words:wire arc additive manufacturing; ultrasonic vibration;aluminum bronze alloy; interpass temperature; microstructure; tensile properties
摘 要:采用电弧增材制造技术,研究不同层间温度下有无超声振动对电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金组织及拉伸性能的影响。结果表明:在电弧增材制造的过程中,控制不同的层间温度不能抑制外延生长的柱状枝晶形成,引入超声振动后,在层间温度100 ℃下获得胞状晶组织。电弧增材制造的Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金主要由枝晶间的κII相(Fe3Al)和κIII相(NiAl)以及在α-Cu基体中析出的κIV相(富铁)组成。在含有柱状枝晶的试样中,拉伸性能均存在各向异性。在引入超声振动+层间温度100 ℃的试样中,各向异性较小并获得最佳综合拉伸性能。通过引入超声振动和控制层间温度,优化组织和拉伸性能,为高性能铝青铜合金的快速制造提供潜在方案。
Abstract: The effects of ultrasonic vibration on the microstructure and tensile properties of Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Mn-2Fe alloy produced by WAAM were studied under different interpass temperature. The results show that the control of different interpass temperature during WAAM process cannot inhibit the formation of epitaxial columnar dendrites. After the ultrasonic vibration is assisted, the cellular structure is obtained in the sample under an interpass temperature of 100 ℃. The κII (based on Fe3Al) and κIII (based on NiAl) phases are precipitated in the interdendritic regions whereas κIV (based on rich Fe) is uniformly nucleated in the α-Cu matrix. The tensile properties are anisotropic in the samples containing columnar dendrites. In samples under condition of ultrasonic vibration+interpass temperature of 100 ℃, the anisotropy is eliminated and the best tensile properties are obtained. The results indicate that WAAM fabricated the nickel aluminum bronze alloys can obtain high-performance assisted ultrasonic vibration under the right interpass temperature.
DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-37672
陈 伟1,陈玉华1,温涛涛1,闵文峰1,张体明1,封小松2
(1. 南昌航空大学 江西省航空构件成形与连接重点实验室,南昌 360063;
2. 上海航天设备制造总厂有限公司,上海 200245)
摘 要:采用电弧增材制造技术,研究不同层间温度下有无超声振动对电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金组织及拉伸性能的影响。结果表明:在电弧增材制造的过程中,控制不同的层间温度不能抑制外延生长的柱状枝晶形成,引入超声振动后,在层间温度100 ℃下获得胞状晶组织。电弧增材制造的Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金主要由枝晶间的κII相(Fe3Al)和κIII相(NiAl)以及在α-Cu基体中析出的κIV相(富铁)组成。在含有柱状枝晶的试样中,拉伸性能均存在各向异性。在引入超声振动+层间温度100 ℃的试样中,各向异性较小并获得最佳综合拉伸性能。通过引入超声振动和控制层间温度,优化组织和拉伸性能,为高性能铝青铜合金的快速制造提供潜在方案。
关键词:电弧增材制造;超声振动;铝青铜合金;层间温度;成形组织;拉伸性能
文章编号:1004-0609(2020)-10-2280-15 中图分类号:TG146.1 文献标志码:A
铝青铜合金因具有良好的强度、耐腐蚀性和耐磨性能,在船舶装置、海水处理装置等结构中具有广泛应用前景[1-2]。此外,铝青铜具有良好的焊接性,因此,常被制作成焊丝用来修复和焊接相近化学成分的结构件[3]。铝青铜还常被用作喷涂材料改善碳钢或铝合金表面的腐蚀或摩擦性能[4-5]。铝青铜合金中常添加Al、Ni、Fe、Mn等合金元素来调控综合性能,Al元素可以减重并起到固溶强化的作用,但Al元素含量大于11%(质量分数)后易形成γ2(Cu9Al4)相,材料易出现“缓冷脆性”的现象,Ni元素能提升腐蚀性能,并和Fe元素共同作用避免形成脆性相γ2,Mn元素用来增加金属的流动性[6]。传统的铸造铝青铜合金中易形成富铜的α-Cu基体相、四种金属间化合物κ相(以Fe基的κI、κII、κIV相和Ni基的κIII相)以及马氏体β相[6-7]。通常,铸造铝青铜合金在缓冷过程中会形成粗大的α-Cu晶粒,在枝晶间易形成金属间化合物,金属间化合物会降低伸长率和疲劳性能,引起晶间腐蚀等问题[8]。因此,需采用后热处理、激光喷丸、搅拌摩擦加工等方式提升铸造铝青铜的综合性能[9-11],这些后处理方式增加了铝青铜合金生产周期和制造成本。
近年来,增材制造技术因高柔性和快速响应的特点,可在较短的周期内制造出近净成形的产品而备受关注[12]。其中电弧增材制造技术(Wire arc additive manufacturing, WAAM)得益于效率高、成本低、致密度高、灵活性好等优势,成为大型构件制造的一种潜在可行方案[12]。与激光和电子束为代表的高能束热源相比,电弧热源形成的熔池尺寸更大、能量密度低,熔池的凝固行为更复杂。电子束和激光热源冷却速度能达到1×103~1×104 K/s[13-14],而电弧熔池的冷却速度通常低于1×102 K/s[15-16],更慢的冷却速度以及熔池固-液界面前沿陡峭的温度梯度,使凝固组织易形成外延生长的粗大柱状晶粒,从而引起力学性能的各向异性。
为改变这种不利的现状,诸如添加形核粒子[17-19]、引入层间轧制加工[20-21]等手段常被用来调控增材制造产品的组织和性能。与增加新元素和先增材后轧制的方法不同,超声振动产生的声流和空化效应可直接作用于液态熔池[22],实现不改变化学成分、不额外增加工序的情况下,在增材制造的过程中同步击碎初生晶核,提高形核率,实现晶粒细化的效果。近年来,已有相关研究将超声的原理引入到增材制造的过程中去。在激光增材制造技术领域,西安交通大学张安峰团队[23-24]开展了超声辅助增材制造Inconel 718、Ti-6Al-4V等合金的研究,引入超声振动后的成形件残余应力大幅下降。刘长猛团队[25]也发现超声冲击后的Ti-6Al-4V钛合金残余应力大大降低,在塑性变形和再结晶的同时作用下形成了等轴晶粒。NING等[26]开展了超声振动辅助增材制造Fe-Cr不锈钢合金,初生晶粒尺寸从未引入超声振动的7~11 μm下降至引入超声振动后的1.5~3 μm。TODARO等[27]引入超声振动后制备的Ti-6Al-4V合金中也获得了晶粒大小约为100 μm的等轴β晶粒,屈服强度比未添加超声振动的试样增加12%。在电弧增材制造技术领域,ZHANG等[28]发现在微振动工作平台下制备是Al-Mg合金气孔率降低,抗拉强度有所提升。在对钛合金[29]、不锈钢[30]的电弧增材制造过程中引入超声冲击或振动,也得到了类似细化晶粒、改善拉伸性能的报道。因此,在电弧增材制造的过程中,引入超声振动来细化微观组织、提升力学性能具有良好的可行性。
相对于传统铸造技术制备的铝青铜合金,电弧增材制造的铝青铜合金在组织和力学性能上均存在一定的区别。DING等[31]制备的Cu-8Al-6Ni-4Fe-2.0Mn合金中增材区域主要由魏氏体α相和黑色的马氏体组织组成,热处理后拉伸强度超过对应成分的铸造态合金,但伸长率相对铸造合金有所降低。SHEN等[32]研究了不同热处理参数对Cu-9Al-4.5Ni-3.5Fe-1.3Mn合金试样力学性能的影响,沉积态下存在明显各向异性,水平方向强度最高,垂直方向强度最低。通过设计多组热处理参数比较后得出(900 ℃, 2 h, WC)+(650 ℃, 6 h, AC)下处理后能降低各向异性。DHARMENDRA等[33]研究了Cu-9Al-4Fe-4Ni-1Mn合金组织形成的规律,发现金属间化合物含量明显低于铸造态,测试发现极限抗拉强度与铸造态相当,但屈服强度(约增加88 MPa)和伸长率(约增加10%)比相同成分的铸造态铝青铜合金有所提升。从以上研究可以看出,电弧增材制造的铝青铜合金沉积态下存在力学性能各向异性等问题,因此,本研究在电弧增材制造过程中引入恒定功率的超声振动,研究不同层间温度下有无超声振动对电弧增材制造铝青铜合金组织和拉伸性能的影响。
1 实验
1.1 材料和设备
本研究使用的设备主要包括两类:超声振动系统和电弧增材制造系统。超声振动系统由机架、发生器(功率3000 W)、换能器(功率2000 W)和振动工具头等组成。超声波发生器将交流电转变为高频超声信号,高频超声信号传递到换能器,换能器将其转变成同频率的机械振动,并传输到工具头,工具头将高频振动施加到工作平台上。电弧增材组制造系统包括Fronius TPS 2700型冷金属过渡焊接电源、三维工作平台、气体保护箱等。在实验的过程中,基板固定在工作平台上并随平台做高频振动,高频振动传递到液态金属熔池中,对熔池组织和性能产生影响,超声振动引入电弧增材制造过程的示意图如图1所示。

图1 超声振动引入电弧增材制造过程的示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of experimental apparatus of ultrasonic vibration assisted wire arc additive manufacturing
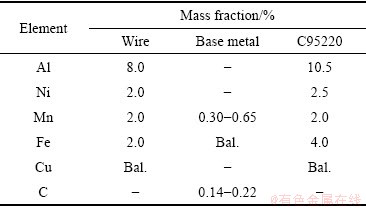
研究采用直径为1.0 mm的铝青铜焊丝,成分见表1,为方便表述,采用Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn表示。基板采用6 mm厚的Q235低碳钢,成分见表1。试验前用机械打磨的方法去除基板表面氧化膜,再用丙酮擦拭干净待用。实验前焊枪导电嘴末端至基板的距离控制在15 mm,焊丝伸出长度10 mm。经过工艺探索和优化,确定如下的电弧增材制造工艺参数:送丝速度4.0 m/min,焊接速度0.48 m/min,电压10.4 V,电流97 A,氩气流量15 L/min,提升高度1.8~2.2 mm。
表1 试验材料的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of experiment materials
研究中采用的超声发生器频率为20 kHz,超声振动功率选用2000 W恒定不变,最大振幅约为50 μm。
典型的电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金如图2(a)所示。本文选用单道多层的薄壁试样进行了组织分析和拉伸性能测试,为保证取样的完整性和分析对比的准确性,薄壁试样增材长度尺寸精确控制为120 mm,沉积高度尺寸不低于50 mm。考虑到成形精度、沉积效率以及铝青铜合金的相变温度,选择连续增材、层间温度400 ℃和层间温度100 ℃三种温度条件,研究了不同层间温度下有无超声振动对组织和拉伸性能的影响,具体试样信息及编号见表2,其中编号C1和U1试样采用连续沉积方式,测定的层间温度为范围值;U2和C2试样代表层间温度为400 ℃试样;U3和C3试样代表层间温度为100 ℃试样。由于超声振动和不同层间温度对熔池的铺展行为有影响,为保证拉伸试样的取样,不同条件下沉积总层数略有不同(表2中给出了不同参数下沉积总层数)。为尽可能精确控制层间温度,试验同时采用K型热电偶(热电偶温度记录点位于基板,在增材位置的正下方,距沉积面表层约1 mm)和手持式红外线测温仪(Smart Sensor AS872,用于实时测量增材表层温度)采集记录数据,确保两种不同方法采集的温度均达到控制值以下后,再完成后续的增材过程。
1.2 分析和表征
使用Zeiss Axio Scope A1光学显微镜(Optical Microscope, OM)、Nova Nano SEM 450和Hitachi SU 1510型扫描电子显微镜(Scanning electron microscope, SEM)、Talos f200x型透射电子显微镜(Transmission electron microscopy, TEM)观察了显微组织。用于组织观察的试样均取自于中心位置,如图2(b)中黑色虚线所示。宏观组织使用V(HF):V(HCl):V(HNO3)=1:15:5的腐蚀剂进行观察,腐蚀时间3 min左右;微观组织使用FeCl3 (5 g)+HCl (5 mL)+C2H6O (50 mL)的腐蚀剂进行观察,腐蚀时间约12 s。TEM试样先预制成厚60 μm的d 3 mm薄片,再使用体积比为V(CH3OH): V(HNO3)=3:1的电解液在-20 ℃下在Struers TenuPol-5电解双喷仪中制成。
表2 试样编号和工艺参数
Table 2 Sample number and process parameters

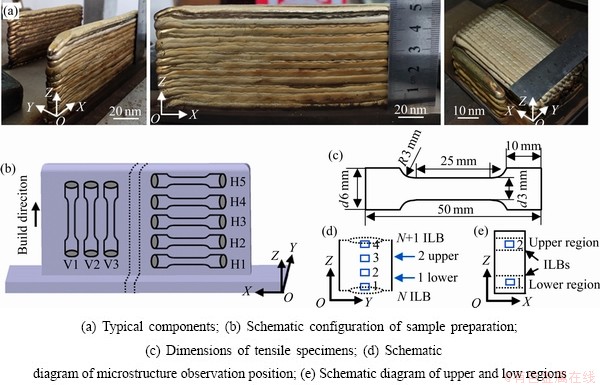
图2 电弧增材制造的Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Mn-2Fe合金实物图和取样标准及示意图
Fig. 2 Typical Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Mn-2Fe wall components produced by wire arc additive manufacturing and sample locations
研究了部分增材试样的室温拉伸性能,拉伸试样的取样位置和编号如图2(b)所示,V1~V3代表竖直方向试样位置,用于测试竖直方向的拉伸性能;H1~H5代表水平方向试样从底部到顶部的位置,用于测试水平方向上沉积高度对拉伸性能的影响,拉伸试样的尺寸如图2(c)所示。拉伸实验在Instron 8872型电子万能拉伸试验机上进行,拉伸速率0.5 mm/min,屈服强度取残余变量为0.2%时的应力。使用Hitachi SU 1510观察拉伸断口形貌。使用差示扫描量热法(Differential scanning calorimetry, DSC)测定了电弧增材制造的Cu-8Ni-2Al-2Mn-2Fe合金相变转变温度和熔化温度。此外,选用了与焊丝成分较接近的C95220铸造铝青铜合金,对比增材制造的铝青铜合金微观组织和拉伸性能的差异,C95220合金的成分见表1,拉伸试样的尺寸与增材试样保持一致。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 宏观形貌
图3所示为不同参数下电弧增材制造的Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金宏观形貌。由图3可以看出,不同层间温度和是否引入超声振动对成形能力和宏观组织具有重要的影响。在未引入超声振动的试样中,连续增材的C1试样(见图3(a))和层间温度为400 ℃的C2试样(见图3(b))中宏观形貌均可以观察到粗大的柱状晶贯穿数个沉积层,存在清晰的层带结构。在层间温度100 ℃的C3试样中,柱状晶尺寸减小,因此衬度降低,宏观下难以表征层带结构(见图3(c))。在引入超声振动后,连续增材的U1试样依旧表现为粗大的宏观柱状晶,层带结构在沉积层中隐约可见(见图3(d))。层间温度为400 ℃的U2试样中,呈现细小的柱状晶,晶粒的生长方向变得混乱,宏观下难以观察到层带结构(见图3(e))。层间温度为100 ℃的U3试样中,晶粒混乱度继续增加,宏观下同样难以观察到层带结构的存在(见图3(f))。需要特别指出的是,宏观下难以表征的层带结构,在光学显微镜下均能观察到其存在。文献[34-35]中报道增材过程中复杂的热循环和相变过程会形成两种典型的层带结构,一种是沉积过程中层与层重熔区域的熔合界面,常称作层间带(Interlayer bands, ILBs),另外一种是受热影响发生相变过程而形成的热影响层带,其位置与材料的相变转变温度、热输入量、热循环次数、沉积过程提升高度以及搭接率等参数有关。通过观察,电弧增材制造的Cu-8Al-2Ni- 2Fe-2Mn合金层带结构数量总比沉积层数少一次,仅在最后一层沉积试样中观察不到层带结构;不同参数下最后一层的沉积高度分布在2.5~2.8 mm,而相邻两条层带之间的距离约为1.8~2.2 mm,这与沉积过程中每层提升的高度相近,故宏观下观察到的层间带属于电弧热循环过程引起的重熔区与后续增材层的分界线,不属于相变引起的热影响层带。
此外,不同层间温度和是否引入超声振动对电弧增材制造的Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金成形特征有较大的影响。表2计算了各工艺参数下增材区域的有效沉积面积,可以看出,随着层间温度的降低,有效沉积面积在增加,表明降低层间温度,有利于提高液态熔池流动的稳定性,使得电弧增材的过程更稳定。在引入超声振动的连续增材U1试样中,由于过高的层间温度,超声振动使得熔池的稳定性变差,成形精度降低,有效沉积面积仅占53.9%。随着在U2和U3试样降低了层间温度,超声振动则改善了熔池的铺展行为,获得了较好的沉积精度,增加了有效沉积面积。

图3 不同参数下Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Mn-2Fe合金宏观组织形貌和有效沉积面积示意图
Fig. 3 Macro morphologies of Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Mn-2Fe alloy with different parameters and schematic diagram of effective area
2.2 微观组织和相的组成
电弧熔池形成的尺寸较大、材料的利用率高,这也是电弧增材制造沉积效率较高的原因,较大的熔池凝固过程中形成的微观组织形态更为复杂。图4显示了在未引入超声振动时不同层间温度下稳定区域两个相邻层间带之间的微观组织变化规律(Y-Z截面,组织观察示意图如图2(d)所示)。可以发现,不同的层间温度对柱状枝晶的形貌和二次枝晶的形态有较大的影响。在连续增材的C1试样中,层间温度最高,几乎所有位置的柱状枝晶均含有二次枝晶,部分区域夹杂较小的等轴晶粒。在层间温度为400 ℃的C2试样中,在层间带的上侧,柱状晶较细,二次枝晶明显较少,随着熔池高度的提升,在层间带下侧位置逐渐发展为宽大的含有二次枝晶的柱状枝晶。类似的微观组织变化规律也呈现在层间温度为100 ℃的C3试样中,更低的层间温度减少了热积累,提升了冷却速度,一次枝晶间距和二次枝晶的数量有所减小。在电弧增材制造的过程中,熔池内部的温度梯度(Temperature gradient, G)和生长速度(Growth rate, R)是时刻动态变化的[36],最终在层间带之间形成了这种具有周期性变化的微观组织。
在引入超声振动后,电弧增材制造的Cu-8Al-2Ni- 2Fe-2Mn合金微观组织发生显著的变化。在连续增材的U1试样中,过高的层间温度在超声振动的作用下,熔池在重熔区形成粗大的胞状晶粒(见图5(a1)和 (a4)中白色线所示),柱状枝晶在相邻层间带之间有被打断的现象,局部夹杂有细小的等轴晶粒,二次枝晶的数量有一定的减少,但整体的外延生长趋势没有改变。

图4 未引入超声振动下不同层间温度相邻层间带之间的微观组织(Y-Z截面)
Fig. 4 Microstructures between two adjacent ILBs without ultrasonic vibration at different interpass temperatures (Y-Z plane)

图5 引入超声振动下不同层间温度相邻层间带之间的微观组织(Y-Z截面)
Fig. 5 Microstructures between two adjacent ILBs assisted ultrasonic vibration at different interpass temperatures (Y-Z plane)
在层间温度为400 ℃的U2试样中,混杂着胞状晶和局部细长的柱状晶,二次枝晶基本消失(见图5(b1)~(b4))。在层间温度为100 ℃的U3试样中,较低的层间温度避免了热积累对晶粒尺寸和形貌的影响,最终形成不规则分布的胞状晶,晶粒的尺寸大幅减小(见图5(c1)~ (c4))。
为更直观地反映微观组织在不同沉积高度方向上的差异,图6显示了6组参数下在不同沉积高度的SEM组织图(X-Z截面,观察位置如图2(e)所示)。在连续增材的C1试样中,二次枝晶(见图6(a1))和在柱状枝晶中间形成的局部等轴晶(见图6(a2))清晰可见。在层间温度400 ℃的C2试样中,一次枝晶间距和二次枝晶的数量,均随着沉积高度的提升而增加(见图6(b1)和(b2))。在C3试样中,充分的冷却降低了二次枝晶的数量,一次枝晶间距也有所减小(见图6(c1)和(c2))。引入超声振动后,SEM下能清楚观察到连续增材的U1试样中柱状枝晶被打断的现象(见图6(d1)和(d2))。层间温度400 ℃的U2试样中柱状枝晶进一步被打断和细化(见图6(e1)和(e2))。在U3试样中,在超声振动的作用下,形成了胞状晶,并得以保留,最终阻断了柱状枝晶的形成(见图6(f1)和(f2))。此外,在C1、C2、U1和U2试样中,不同沉积高度位置的一次枝晶间距尺寸存在差别,即一次枝晶间距随沉积高度的上升而增大,过高的层间温度使得热积累严重,降低了冷却速度,给一次枝晶的生长提供了条件。在C3试样中,晶粒尺寸随沉积高度升高而增大的趋势得到了一定的缓解,U3试样中晶粒尺寸随沉积高度变化的影响较小。对试样不同位置进行测量和求均值后,测得C1、C2、C3、U1、U2和U3试样中一次枝晶间距分别约为(36.5±5.6)、(28.5±4.2)、(21.6±3.1)、(31.2±4.5)、(24.8±3.7)和(18.6±2.6) μm。
从X-Y截面的组织可以更直观地观察到晶粒尺寸的区别。典型的X-Y截面微观组织如图7所示(观察位置位于相邻层间带之间的不同高度位置,如图2(d)蓝色箭头所示),可以看出,在微观组织多是外延生长的柱状枝晶试样中,C1(见图7(a1)和(a2))和U1(见图7(d1)和(d2))试样均表现出粗大的胞状晶形貌。在C2、C3和U2试样中,靠近层间带上侧位置的微观组织为等轴晶形貌(见图7(b1)、(c1)和(e1)),二次枝晶会随熔池高度的提升而增多,横截面的微观组织呈现胞状枝晶形貌(见图7(b2)、(c2)和(e2))。在U3试样中,由于胞状晶的存在,在X-Y横截面的微观组织多为未封闭的树枝晶形貌(见图7(f1)和(f2)),且在熔池内部不同位置晶粒尺寸较均匀。
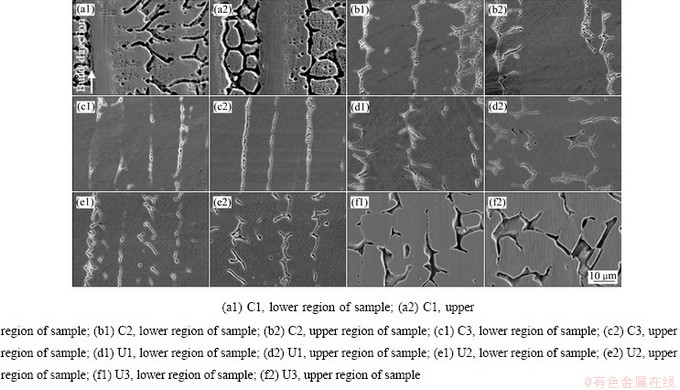
图6 各参数下不同沉积高度位置的微观组织(X-Z截面)
Fig. 6 Microstructures of deposited height at different parameters (X-Z plane)
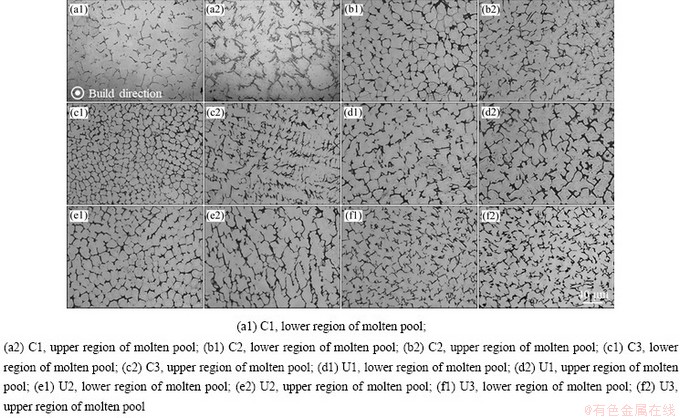
图7 各参数下相邻层间带之间不同高度位置的微观组织(X-Y截面)
Fig. 7 Microstructures of adjacent ILBs at different deposited heights parameters (X-Y plane)
图8显示了部分参数下典型特征区域的微观组织。图8(a)所示为未引入超声振动的C1试样基板与第一层沉积层的结合形貌以及微观组织,散乱的树枝晶分布在α-Cu基体中。在引入超声振动的U3试样中,基板和第一层沉积层的界面变薄,在基板附近的沉积层中形成均匀的等轴晶粒(见图8(b))。未引入超声振动的C1试样中层间带结构微观组织如图8(c)所示,在重熔区内部的柱状枝晶较细小,且二次枝晶较少,层间带的过渡区域如图8(d)所示。引入超声振动的U3试样中,层间带结构中形成的胞状晶阻断了外延生长的柱状枝晶,如图8(e)和(f)所示。层间带重熔区的组织比其他位置微观组织更细小,这主要是由于重熔区在熔池底部,有较大的冷却速度,因此形成的组织更为细小。不同参数下顶层位置的微观组织也有较大的区别,在未引入超声振动的C1试样中,顶层能观察到厚度约为200~400 μm的转向枝晶区域(见图8(g)),在转向枝晶区域内是粗大的等轴树枝晶。而超声振动加上充分冷却的U3试样中,顶层微观组织多为细小的胞状晶(见图8(h))。

图8 部分典型特征区域的微观组织(Y-Z截面)
Fig. 8 Microstructures of some characteristic regions (Y-Z plane)
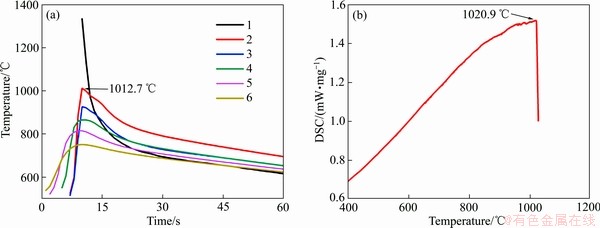
图9 电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金部分热循环曲线和DSC曲线
Fig. 9 Thermal cycles of deposited layers(a) and DSC curve(b) of Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn alloy produced by WAAM
电弧熔池从底部到顶部温度梯度G逐渐减小,生长速度v逐渐增加,G/v的数值逐渐减小,固液界面的形貌发生柱状枝晶到等轴枝晶的转变,形成了图8(g)所示的转向区域组织。图9(a)中显示了增材过程中沉积层所经历的部分热循环温度曲线,其中曲线1是第五层沉积过程中的热循环温度(将K型热电偶在增材过程中直接置于第四层上表面,测得第五层增材过程的部分温度以及后续沉积过程对该层的热循环曲线,K型热电偶最大量程约为1350 ℃,因此,不能测定实际液态熔池的温度),曲线2是第六层沉积过程对第五层的热循环影响曲线,以此类推。在曲线2中,测得最大峰值温度约为1012.7 ℃。对电弧增材制造的Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金进行了DSC测试,经计算该合金的熔化温度约为1020.9 ℃,后一次增材过程的峰值温度非常接近该合金的熔点,可以推测,后一次增材的热循环过程足以熔化顶部这层厚200~400 μm的等轴枝晶区,而发达二次枝晶为维持外延柱状枝晶的生长提供了基础[37],因此,在未引入超声振动的试样中,控制层间温度不能抑制柱状枝晶的形成,故这种转向特征区域,仅在最后一层的顶部位置得以保留。
超声振动产生的超声波空化强度IC,可以用以下公式来表达[38]:
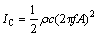 (1)
(1)
式中: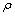 是液态密度;c是液体中超声的传播速度;f是振动频率;A是振动幅度。合金中
是液态密度;c是液体中超声的传播速度;f是振动频率;A是振动幅度。合金中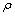 =8400 kg/m3,c=1537 m/s[39],f=20 kHz,A=50 μm。经过计算后空化强度约是5.1×108 W/cm2,远超过超声振动对熔体产生作用的最小值(不低于100 W/cm2 [35]),因此,试验过程中引入超声振动可以显著影响电弧增材制造过程中Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金的微观组织。HUNT[40]最早指出,当柱状晶前沿的等轴晶体积比率大于0.49时,即发生柱状晶向等轴晶的转变,该判断在BERMINGHAM等[17, 36]和ZHANG等[41]报道的增材制造过程中也得到了证实。层间温度100 ℃的U3最后一层试样中,细小的胞状晶组织占据了主体,充分的层间冷却,又避免了后续热循环对成形组织的影响,最终抑制了外延柱状枝晶的形成。
=8400 kg/m3,c=1537 m/s[39],f=20 kHz,A=50 μm。经过计算后空化强度约是5.1×108 W/cm2,远超过超声振动对熔体产生作用的最小值(不低于100 W/cm2 [35]),因此,试验过程中引入超声振动可以显著影响电弧增材制造过程中Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金的微观组织。HUNT[40]最早指出,当柱状晶前沿的等轴晶体积比率大于0.49时,即发生柱状晶向等轴晶的转变,该判断在BERMINGHAM等[17, 36]和ZHANG等[41]报道的增材制造过程中也得到了证实。层间温度100 ℃的U3最后一层试样中,细小的胞状晶组织占据了主体,充分的层间冷却,又避免了后续热循环对成形组织的影响,最终抑制了外延柱状枝晶的形成。
为确定电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金物相的组成,选择与焊丝成分接近的C95220铸造铝青铜合金观察了微观组织。可以看出,C95220铸造铝青铜中在枝晶间可以观察到花瓣状κI相、球状κII相以及片层状κIII相;在α-Cu的基体中,有细小的κIV相析出(见图10(a))。与铸造铝青铜合金不同,电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金在OM和SEM下均难以确定金属间化合物形貌和成分,对层间温度100 ℃的U3试样进行TEM观察发现,在枝晶间区域观察到片层状的κIII相和球状κII相。通过电子衍射图分析,得出κII相是Fe3Al相,κIII相是NiAl相。在α-Cu的基体中,高倍下能观察到细小分布的黑色κIV相(5~10 nm),采用EDS分析后发现是富铁相。电弧增材制造的过程冷却速度大于铸造的过程,且选用的焊丝中Al元素含量较少,未观察到体积较大的κI相。这与DHARMENDRA等[33]报道的电弧增材制造Cu-9Al- 4Fe-4Ni-1Mn合金结果一致。
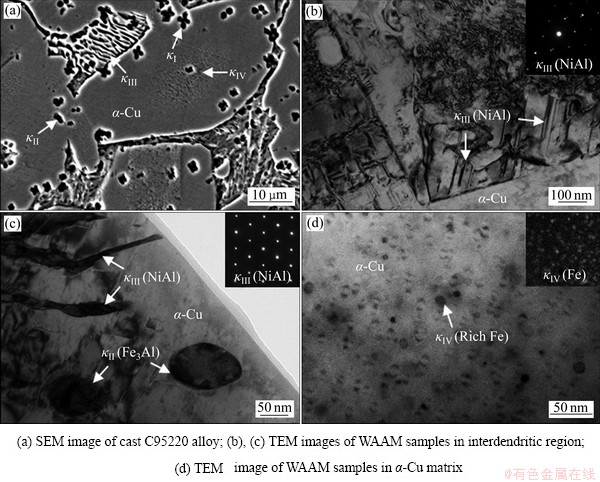

图10 C95220铸造铝青铜合金和电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金的相组成
Fig. 10 Intermetallic phases of C95220 aluminum bronze alloys and Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn alloys prepared by WAAM under different parameters
2.3 拉伸性能
根据微观组织(见图4~7)和有效沉积面积(见表2),选取微观组织相对较细小、有效沉积面积较高的U2、C3和U3试样测试了拉伸性能。取样位置和尺寸如图2(b)和(c)所示,其中水平方向H1~H5用于测试水平方向不同沉积高度对拉伸性能的影响,V1~V3用于测试竖直方向试样的性能。作为对比,也测试了C95220试样的拉伸性能。测试内容包含抗拉强度(Ultimate tensile strength, UTS)、屈服强度(Yield Strength, YS)和伸长率(Elongation, El),典型的C95220铸造铝青铜合金和电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金应力-应变曲线如图11所示,增材试样的拉伸结果汇总在表3中。从应力-应变曲线可以看出,尽管C95220合金的抗拉强度优于电弧增材制造Cu-8Al- 2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金,但电弧增材制造试样的屈服强度均高于C95220合金的,造成这两者差异的原因主要是由于C95220合金中Al、Ni和Fe含量更高,形成更多的强化相,抗拉强度占优,但铸造过程在缓慢的冷却速度形成了粗大的α-Cu基体,导致了屈服强度偏低。在U2和C3试样中,水平方向试样的抗拉强度均优于竖直方向试样,伸长率呈相反的结果,这主要是由于柱状枝晶的存在,在水平试样上,大多数的柱状枝晶晶界在标距段内垂直于拉伸载荷方向。在竖直试样上,仅有较小比例的晶界垂直于外加载荷方向,晶界的存在,提升了强度,降低了伸长率[41]。在U3试样中,拉伸性能在不同方向上的表现接近各向同性,超声振动结合较低的层间温度,形成的胞状晶组织较均匀,使得微观组织对拉伸性能的影响降低。此外,整体的抗拉强度表现出,U3>C3>U2,这主要是由于一次枝晶间距的差异造成的,粗化的α-Cu基体降低了晶界结合力,试样整体拉伸性能表现出随晶粒尺寸的减小而强度升高的趋势,但在U3试样中,拉伸强度提升的同时,伸长率并没有显著下降,超声振动加上充分的层间冷却实现了细晶强化,强度提升的同时塑性得以保留。
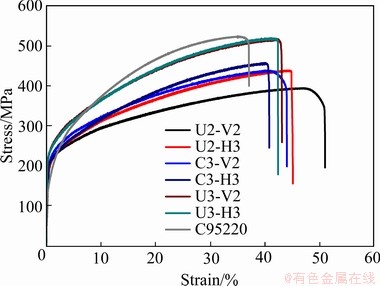
图11 典型C95220铸造铝青铜合金和电弧增材制造U2、C3和U3试样应力-应变曲线
Fig. 11 Comparison of stress-strain curves of cast C95220 alloy and U2, C3 and U3 samples
表3 不同参数下电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金的拉伸性能结果汇总
Table 3 Tensile properties of Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn alloy prepared by WAAM under different parameters
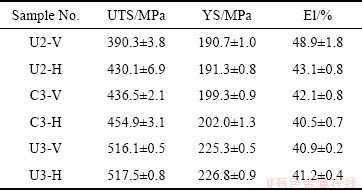
图12比较了水平方向上沉积高度位置对拉伸性能的影响规律(1~5代表取样位置从底部到顶部,见图2(b))。在含有柱状枝晶的U2和C3试样中,抗拉强度均随沉积高度的增加而缓慢降低,且在层间温度400 ℃的U2试样中,表现的更为明显。在U3试样中,不同水平高度对拉伸性能的影响不大。伸长率随沉积高度的变化没有明显的规律,抗拉强度没有随沉积高度的增加而表现出明显降低的趋势。在U2和C3试样中,一次枝晶间距随沉积高度的提升而增加(见图6),粗化的柱状枝晶是导致拉伸性能沿水平沉积高度上升而降低的根本原因。

图12 沉积高度位置对电弧增材制造U2、C3和U3试样拉伸性能的影响
Fig. 12 Effect of deposited height on tensile properties of U2, C3 and U3 samples prepared by WAAM
图13所示为U2、C3和U3拉伸试样典型的断口形貌,在U2和C3水平方向的拉伸断口中,能观察到明显的沿柱状枝晶穿晶断裂的现象,柱状枝晶晶界之间有细小的韧窝,断口表面观察到的柱状枝晶间距也随着沉积高度的增加而增大(见图13(a1)~(a3))、(b1)~ (b3)),这与抗拉强度下降的趋势保持一致(见图12)。在U2的垂直方向拉伸试样中,由于柱状枝晶较为粗大,沿枝晶撕裂的过程中,有清晰的滑移分离特征(图13(a4)中白色箭头所示),这是U2参数下垂直试样伸长率较高、且有明显的紧缩现象的重要原因(图11中应力-应变曲线所示)。在C3的垂直方向拉伸试样中,由于柱状枝晶尺寸的减小,拉伸断口中以韧窝为主,局部能观察到少量的滑移分离现象,这也符合拉伸性能测试中的强度提升但延性下降的结果(见图13(b4))。在U3试样中,不同方向和高度位置上的拉伸断口形貌较一致,均表现出细小的韧窝,验证了强度明显提升但塑性未显著下降的结论(见图13(c1)~(c4))。
综上所述,将超声振动引入电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金后,在层间温度较低的情况下,避免了热循环对微观组织的影响,抑制了外延生长的柱状枝晶,形成了胞状晶组织。对比层间温度相同的C3和U3试样,引入超声振动下的U3试样抗拉强度、屈服强度分别比C3试样提升13.3%和11.1%,且两者的伸长率相当;而在引入超声振动的不同层间温度参数下,U3试样的抗拉强度、屈服强度分别比U2试样提升19.7%和15.8%,伸长率略有下降。超声振动结合控制较低的层间温度,U3试样中拉伸性能的各向异性大幅降低,优化了电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni- 2Fe-2Mn合金的力学性能。图14总结了部分增材制造的铝青铜合金抗拉强度-伸长率关系[31-33, 43-45],对比发现,在引入超声振动的U3试样中,无需后热处理,即可获得较理想的力学性能。在以后的研究中,根据应用场景中对强度和伸长率的需求,设计焊丝成分,可实现高性能铝青铜合金的快速、高效制造。
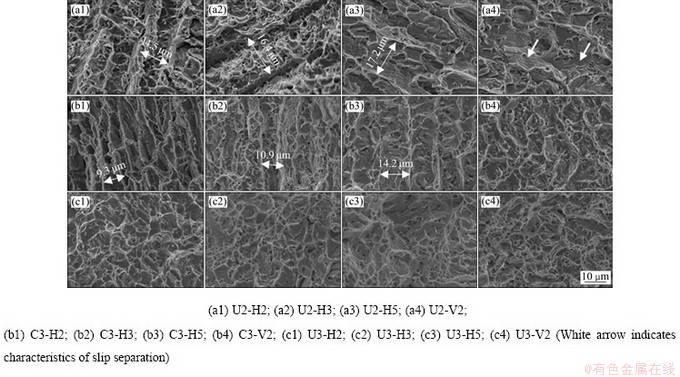
图13 不同参数下拉伸试样的典型断口形貌
Fig. 13 Typical fracture surfaces of tensile samples under different parameters
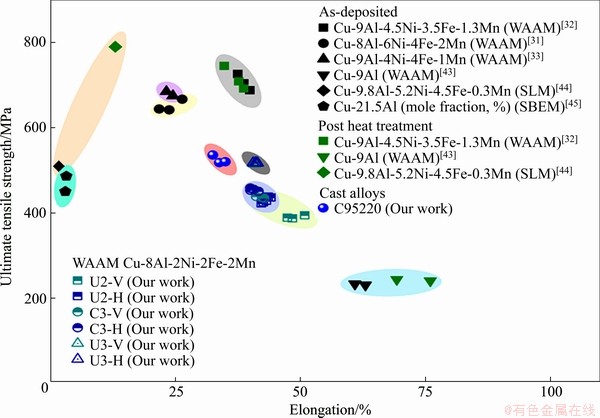
图14 部分增材制造的铝青铜合金伸长率-抗拉强度性能统计
Fig. 14 Ultimate tensile strength versus tensile elongation to failure for aluminum bronze alloys fabricated by additive manufacturing and casting technology
3 结论
1) 在未引入超声振动的电弧增材制造Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金中,控制不同的层间温度,不能抑制柱状枝晶的形成。在引入超声振动后,在较高的层间温度下,柱状枝晶有被打断的现象;在层间温度100 ℃条件下,形成了胞状晶。
2) 电弧增材制造的Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Fe-2Mn合金中,主要由枝晶间球状κII相(Fe3Al)和片层状κIII相(NiAl),以及在α-Cu基体中析出的κIV相(富铁)组成。
3) 在层间温度100 ℃和超声振动+层间温度400 ℃的试样中,拉伸性能在不同方向和不同水平沉积位置均存在各向异性,且水平方向拉伸试样抗拉强度优于竖直方向,不同水平沉积位置的抗拉强度随沉积高度增加而缓慢降低。
4) 在超声振动+层间温度100 ℃的试样中,各向异性得到有效抑制,并获得了最佳的拉伸性能,抗拉强度、屈服强度和伸长率的分别为(517.0±0.9) MPa、(226.2±1.0) MPa和41.4%±0.3%。
5) 在含柱状枝晶的水平试样断口中存在穿晶断裂,随着层间温度降低,断口中韧窝的尺寸减小,主要的断裂特征包括穿晶断裂、滑移分离和韧窝。
REFERENCES
[1] 康全飞, 胡树兵, 曾思琪, 程关坤. 船用螺旋桨材料镍铝青铜的热处理强化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(1): 107-115.
KANG Quan-fei, HU Shu-bing, ZENG Si-qi, CHENG Guang-kun. Heat treatment strengthening of nickel- aluminum bronze alloy for marine propeller[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(1): 107-115.
[2] 马 硕, 龚安华, 付立铭, 单爱党. 温轧高强韧镍铝青铜合金的组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2020, 30(1): 69-77.
MA Shuo, GONG An-hua, FU Li-ming, SHAN Ai-dang. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high strength-ductility aluminum bronze alloy produced by warm rolling[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2020, 30(1): 69-77.
[3] RAHNI M R M, BEIDOKHTI B, HADDAD-SABZEVAR M. Effect of filler metal on microstructure and mechanical properties of manganese-aluminum bronze repair welds[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(3): 507-513.
[4] 唐丽芳, 李文生, 何 玲, 胡春霞, 赵文杰, 翟海民. 冷喷涂自敏发光高铝青铜复合涂层及其摩擦磨损性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(5): 931-941.
TANG Li-fang, LI Wen-sheng, HE Ling, HU Chun-xia, ZHAO Wen-jie, ZHAI Hai-min. Friction and wear properties of cold spray self-sensitization luminescent/Cu-14Al-X composite coating [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 29(5): 931-941.
[5] 何艳艳, 李文生, 吴学军, 王大锋, 杨效田, 何 玲. 元素扩散对高铝青铜喷焊层显微组织及摩擦性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(1): 143-149.
HE Yan-yan, LI Wen-sheng, WU Xue-jun, WANG Da-feng, YANG Xiao-tian, HE Ling. Effects of element diffusion on microstructure and friction behavior of high-aluminum bronze plasma spray coating[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(1): 143-149.
[6] CULPAN E A, ROSE G. Microstructural characterization of cast nickel aluminium bronze[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1978, 13: 1647-1657.
[7] HASAN F, JAHANAFROOZ A, LORIMER G W, RIDLEY N. The morphology, crystallography, and chemistry of phases in as-cast nickel-aluminum bronze[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1982, 13: 1337-1345.
[8] 黄海友, 聂铭君, 栾燕燕, 谢建新. 连续柱状晶组织Cu-12% Al合金在3.5% NaCl和10% HCl溶液中的腐蚀行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(9): 2469-2476.
HUANG Hai-you, NIE Ming-jun, LUAN Yan-yan, XIE Jian-xin. Corrosion behavior of continuous columnar-grained Cu-12% Al alloy in 3.5% NaCl and 10% HCl solutions[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(9): 2469-2476.
[9] 李振亚, 杨丽景, 许 赪, 冒守栋, 宋振纶. 时效温度对镍铝青铜合金的硬质相演变的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(4): 766-772.
LI Zhen-ya, YANG Li-jing, XU Cheng, MAO Shou-dong, SONG Zhen-lun. Effect of aging temperature on hard phase evolution of nickel aluminum bronze[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(4): 766-772.
[10] 程光坤, 胡树兵, 曾思琪. 激光喷丸对镍铝青铜组织演变及腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(12): 2476-2485.
CHENG Guang-kun, HU Shu-bing, ZENG Si-qi. Effect of laser peening on surface characterization and corrosion resistance of nickel aluminium bronze[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(12): 2476-2485.
[11] LV Y, DING Y, HAN Y, ZHANG L C, WANG L, LU W. Strengthening mechanism of friction stir processed and post heat treated NiAl bronze alloy: Effect of rotation rates[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2017, 685: 439-446.
[12] OLIVEIRA J P, SANTOS T G, MIRANDA R M. Revisiting fundamental welding concepts to improve additive manufacturing: From theory to practice[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2020, 107: 100590.
[13] DEBROY T, WEI H L, ZUBACK J S, MUKHERJEE T, ELMER J W, MILEWSKI J O, BEESE A M, WILSON-HEID A, DE A, ZHANG W. Additive manufacturing of metallic components—Process, structure and properties[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2018, 92: 112-224.
[14] KORNER C. Additive manufacturing of metallic components by selective electron beam melting—A review[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2016, 61(5): 361-377.
[15] FACHINOTTI V, CARDONA A, BAUFELD B, BIEST O. Finite-element modelling of heat transfer in shaped metal deposition and experimental validation[J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60: 6621-6630.
[16] 李晗嫣, 陈文革, 张飞奇, 高红梅, 任澍忻. 基于CAFE模拟钛合金丝材电弧增材制造凝固过程的组织演变[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(9): 1775-1783.
LI Han-yan, CHEN Wen-ge, ZHANG Fei-qi, GAO Hong-mei, REN Shu-xin. Evolution of wire+arc additive manufactured titanium alloy during solidification process based on CAFE simulation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(9): 1775-1783.
[17] BERMINGHAM M J, KENT D, ZHAN H, STJOHN D H, DARGUSCH M S. Controlling the microstructure and properties of wire arc additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V with trace boron additions[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 91: 289-303.
[18] ZHANG D, QIU D, GIBSON M, ZHENG Y, FRASER H, STJOHN D, EASTON M. Additive manufacturing of ultrafine-grained high-strength titanium alloys[J]. Nature, 2019, 576: 91-95.
[19] MARTIN J, YAHATA B, HUNDLEY J, MAYER J, SCHAEDLER T, POLLOCK T. 3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys[J]. Nature, 2017, 549: 365-369.
[20] GU J, YANG S, GAO M, BAI J, ZHAI Y, DING J. Micropore evolution in additively manufactured aluminum alloys under heat treatment and inter-layer rolling[J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 186: 108288.
[21] MCANDREW A, ROSALES M A, COLEGROVE P, HONNIGE J, HO A, FAYPOLLE R, EYITAYO K, STAN I, SUKRONGANG P, CROCHEMORE A, PINTER Z. Interpass rolling of Ti-6Al-4V wire+arc additively manufactured features for microstructural refinement[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 21: 340-349.
[22] KOMAROV S, KUWABARA M, ABRAMOV O. High power ultrasonics in pyrometallurgy: Current status and recent development[J]. ISIJ International, 2005, 45(12): 1765-1782.
[23] 王 潭, 张安峰, 梁少端, 严深平, 张连重, 李涤尘. 超声振动辅助激光金属成形IN718沉积态组织及性能的研究[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(11): 104-109.
WANG Tan, ZHANG An-feng, LIANG Shao-duan YAN Shen-ping, ZHANG Lian-zhong, LI Di-chen. Research on as-deposited microstructure and properties of IN718 parts by ultrasonic vibration-assisted laser metal forming[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43(11): 104-109.
[24] 张安峰, 付 涛, 王 潭, 梁朝阳. 超声振动对激光熔覆及固溶时效Ti6Al4V合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(12): 85-90.
ZHANG An-feng, FU Tao, WANG Tan, LIANG Chao-yang. Effect of ultrasonic vibration on microstructure and properties of laser cladded and solution-aging treated Ti6Al4V alloys[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45(12): 85-90.
[25] ZHANG M, LIU C, SHI X, CHEN X, CHEN C, ZUO J, LU J, MA S. Residual stress, defects and grain morphology of Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by ultrasonic impact treatment assisted selective laser melting[J]. Applied Sciences, 2016, 6: 304.
[26] NING F, CONG W. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Fe-Cr stainless steel parts fabricated by ultrasonic vibration-assisted laser engineered net shaping process[J]. Materials Letters, 2016, 179: 61-64.
[27] TODARO C J, EASTON M A, QIU D, ZHANG D, BERMINGHAM M J, LUI E W, BRANDT M, STJOHN D H, QIAN M. Grain structure control during metal 3D printing by high-intensity ultrasound[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 142.
[28] ZHANG C, GAO M, ZENG X. Workpiece vibration augmented wire arc additive manufacturing of high strength aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019, 271: 85-92.
[29] GOU J, WANG Z, HU S, SHEN J, TIAN Y, ZHAO G, CHEN Y. Effects of ultrasonic peening treatment in three directions on grain refinement and anisotropy of cold metal transfer additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V thin wall structure[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 54: 148-157.
[30] JIAN L, ZHU S, CAI Z, ZHANG P, LIU J, QIN H, TONG Y. Effect of vibration on remanufacturing microstructure of FV520B stainless steel using MAG surfacing deposition technology[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2019, 48(3): 728-738.
[31] DING Dong-hong, PAN Zeng-zi, DUIN S V, LI Hui-jun, SHEN Chen. Fabricating superior NiAl bronze components through wire arc additive manufacturing[J]. Materials, 2016, 9(8): 652.
[32] SHEN C, PAN Z, DING D, YUAN L, NIE N, WANG Y, LUO D, CUIURI D, DUIN S, LI H. The influence of post-production heat treatment on the multi-directional properties of nickel-aluminum bronze alloy fabricated using wire-arc additive manufacturing process[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 23: 411-421.
[33] DHARMENDRA C, HADADZADEH A, AMIRKHIZ B S, RAM G D, MOHAMMADI M. Microstructural evolution and mechanical behavior of nickel aluminum bronze Cu-9Al-4Fe-4Ni-1Mn fabricated through wire-arc additive manufacturing[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2019, 30: 100872.
[34] HO A, ZHAO H, FELLOWES J, MARTINA F, DAVIOS A, PRANGNELL P. On the origin of microstructural banding in Ti-6Al4V wire-arc based high deposition rate additive manufacturing[J]. Acta Materialia, 2019, 166: 306-323.
[35] ZHU Y, TIAN X, LI J, WANG H. Microstructure evolution and layer bands of laser melting deposition Ti-6.5Al-3.5Mo-1.5Zr-0.3Si titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 616: 468-474.
[36] BERMINGHAM M J, STJOHN D H, KRYNEN J, TEDMAN-JONES S, DARGUSH M S. Promoting the columnar to equiaxed transition and grain refinement of titanium alloys during additive manufacturing[J]. Acta Materialia, 2019, 168: 261-274.
[37] KAPLAN M, YILDIZ A K. The effects of production methods on the microstructures and mechanical properties of an aluminum bronze[J]. Materials Letters, 2003, 57: 4402-4411.
[38] ESKIN G I, ESKIN D G. Ultrasonic treatment of light alloy melts[M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2014.
[39] SAHU R K, HIREMATH S, MANIVANNAN P V. Ultrasonic technique for concentration characterization of copper nanofluids synthesized using μ-EDM: A novel experimental approach[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 284: 429-436.
[40] HUNT J D. Steady state columnar and equiaxed growth of dendrites and eutectic[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1984, 65: 75-83.
[41] ZHANG Q, CHEN J, LIN X, TAN H, HUANG W D. Grain morphology control and texture characterization of laser solid formed Ti6Al2Sn2Zr3Mo1.5Cr2Nb titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2016, 238: 202-211.
[42] CARROLL E, PALMER T, BEESE A. Anisotropic tensile behavior of Ti-6Al-4V components fabricated with directed energy deposition additive manufacturing[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 87: 309-320.
[43] DONG B, PAN, Z, SHEN C, MA Y, LI H. Fabrication of copper-rich Cu-Al alloy using the wire-arc additive manufacturing process[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2017, 48: 3143-3151.
[44] MURRAY T, THOMAS S, WU Y, NEIL W, HUTCHINSON C. Selective laser melting of nickel aluminium bronze[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 33: 101122.
[45] WOLF T, FU Z, KORNER C. Selective electron beam melting of an aluminum bronze: Microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Materials Letters, 2019, 238: 241-244.
CHEN Wei1, CHEN Yu-hua1, WEN Tao-tao1, MIN Wen-feng1, ZHANG Ti-ming1, FENG Xiao-song2
(1. Jiangxi Key Laboratory of Forming and Joining Technology for Aerospace Components, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China;
2. Shanghai Aerospace Equipments Manufacturer Co., Ltd., Shanghai 200245, China)
Abstract: The effects of ultrasonic vibration on the microstructure and tensile properties of Cu-8Al-2Ni-2Mn-2Fe alloy produced by WAAM were studied under different interpass temperature. The results show that the control of different interpass temperature during WAAM process cannot inhibit the formation of epitaxial columnar dendrites. After the ultrasonic vibration is assisted, the cellular structure is obtained in the sample under an interpass temperature of 100 ℃. The κII (based on Fe3Al) and κIII (based on NiAl) phases are precipitated in the interdendritic regions whereas κIV (based on rich Fe) is uniformly nucleated in the α-Cu matrix. The tensile properties are anisotropic in the samples containing columnar dendrites. In samples under condition of ultrasonic vibration+interpass temperature of 100 ℃, the anisotropy is eliminated and the best tensile properties are obtained. The results indicate that WAAM fabricated the nickel aluminum bronze alloys can obtain high-performance assisted ultrasonic vibration under the right interpass temperature.
Key words: wire arc additive manufacturing; ultrasonic vibration;aluminum bronze alloy; interpass temperature; microstructure; tensile properties
Foundation item: Project(JCKY2018401C003) supported by the National Defense Basic Research Program, China; Project(20192BBH80018) supported by the Key Research and Development Plan of Jiangxi Province, China; Project(20171BCB24007) supported by the Construction Plan of Superior Science and Technology Innovation Team of Jiangxi Province, China; Project(2018ACB21016) supported by the Distinguished Young Scholars Foundation of Jiangxi, China
Received date: 2019-11-20; Accepted date: 2020-06-23
Corresponding author: CHEN Yu-hua; Tel: +86-791-3863023; E-mail: ch.yu.hu@163.com
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国防基础科研计划资助项目(JCKY2018401C003);江西省重点研发计划资助项目(20192BBH80018);江西省优势科技创新团队建设计划资助项目(20171BCB24007);江西省杰出青年基金资助项目(2018ACB21016)
收稿日期:2019-11-20;修订日期:2020-06-23
通信作者:陈玉华,教授,博士;电话:0791-3863023;E-mail:ch.yu.hu@163.com

