Article ID: 1003-6326(2005)02-0353-05
Induced effects of Cu underlayer on
(111) orientation of Fe50Mn50 thin films
WANG Lei(王 蕾), WANG Feng-ping(王凤平), LIU Huan-ping(刘还平),
WU Ping(吴 平), QIU Hong(邱 宏), PAN Li-qing(潘礼庆)
(Department of Physics, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract: Effects of Cu underlayer on the structure of Fe50Mn50 films were studied. Samples with a structure of Fe50Mn50(200nm)/ Cu(tCu) were prepared by magnetron sputtering on thermally oxidized silicon substrates at room temperature. The thickness of Cu underlayer varied from 0 to 60nm in the intervals of 10nm. High-vacuum annealing treatments, at different temperatures of 200, 300 and 400℃ for 1 h, respectively, on the Fe50Mn50(200nm)/ Cu(20nm) thin films were performed. The surface morphologies and textures of the samples were measured by field emission scan electronic microscope (FE-SEM) and X-ray diffraction(XRD). Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and Auger electron spectroscopy(AES) were used to analyze the compositional distribution. It is found that Cu underlayer has an obvious induce effect on (111) orientation of Fe50Mn50 thin films. The induce effects of Cu on (111) orientation of Fe50Mn50 changed with the increase of Cu layer thickness and the best effect was obtained at the Cu layer thickness of 20nm. High-vacuum annealing treatments cause the migration of Mn atoms towards surface of the film and interface between Cu layer and substrate. With the increasing annealing temperature, migration of Mn atoms is more obvious, which leads to a Fe-riched Fe-Mn alloy film.
Key words: Fe50Mn50 films; Cu underlayer; migration CLC number: O484.1; O484.5; O482.54
Document code: A
1 INTRODUCTION
Antiferromagnetic(AFM) materials are widely used in a spin-valve structure in combination with magnetoresistive materials for application in magnetic sensors and magnetic data storage, after a bilayer composed by a ferromagnetic(FM) and an AFM material has been used in an exchange biased spin valve[1, 2]. FexMn1-x alloys are prototypes for antiferromagnetic materials with a fcc structure in a concentration range between x=45% and x=75% at room temperature[3, 4]. The Néel temperature(TN) varies with x and reaches the maximum of about 500K at x≈50%. This relatively high TN of the alloy at equiatomic composition had made Fe50-Mn50 one of the most used materials in spin valve structure[5-7]. Even if in many applications Fe50Mn50 has been replaced by antiferromagnetic materials with higher corrosion resistance and higher blocking temperature, such as IrMn[8] and MnPt[9], it still takes the character of a model system for the investigation of the magnetic coupling at the FM/AFM interfaces.
In addition to the FM and AFM layer thickness, the exchange coupling is also found to depend on the underlayer materials in FM/Fe50Mn50 system[10-12]. In order to preserve the fcc phase in thin Fe50Mn50 films, a Cu underlayer has been used. As we know that the lattice constant of Cu is very near the one of the Fe50Mn50, the misfit between Fe50Mn50 and Cu is small and it amounts to η=(αCu-αFe50Mn50)/αFe50Mn50=-0.4%[13, 14].
Dependence of exchange coupling in permalloy/Cu/Fe50Mn50 on the Cu underlayer thickness has been investigated[15]. It is found that exchange field HE and coercivity HC are strongly related to the thickness of Cu underlayer. No exchange coupling without Cu underlayer, because the metastable phase γ-Fe50Mn50 cannot exist without transition metal underlayer. The exchange field HE at room temperature increases approximately linearly with the Cu underlayer thickness up to 30nm. The blocking temperature and the room temperature coercivity (HC) increase at small Cu underlayer thickness and saturate with further increasing Cu underlayer thickness. These phenomena are related to the changes in the microstructure of the Fe50Mn50 layer, due to the variation of Cu layer thickness. However, the effect of the Cu underlayer on the structure and composition of Fe50Mn50 remains unclear. Fully understanding the detail change of the structure and composition of Fe50Mn50 on the Cu underlayer will be helpful to technological application of spin valve magneto-resistance devices.
In this paper, we focus on the effect of Cu underlayer on the structure and composition of Fe50-Mn50 films. The dependence of the orientation of thin Fe50Mn50 films on Cu thickness and the thermal stability of the Fe50Mn50/Cu bilayer during annealing are investigated.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
Samples with a structure of Fe50Mn50(200nm)/ Cu(tCu) were deposited by magnetron sputtering on thermal oxidized silicon substrate at room temperature. The thickness of the Cu underlayer varied from 0 to 60nm in the intervals of 10nm. The base pressure was better than 2×10-4Pa and the Ar pressure was 0.45Pa. The deposition rate was 0.08nm/s for Fe50Mn50 and 0.66nm/s for Cu. The film thickness is determined by the sputtering time. High-vacuum isothermal annealing treatments for the as-deposited Fe50Mn50(200nm)/ Cu(20nm) films at the temperatures of 200, 300 and 400℃ for 1h, respectively, were performed.
The crystal structure of the films was examined by X-ray diffraction(XRD). The surface morphology and composition of the films were characterized using field emission scan electronic microscope(FE-SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). Auger electron spectroscopy(AES) was used to analyze the extent of diffusion of the Fe50Mn50(200nm)/ Cu(20nm) films annealed at 400℃.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The effects of the Cu thickness on textures of as-deposited Fe50Mn50(200nm)/ Cu(tCu) bilayer were investigated. Fig.1 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns for the Cu (tCu) films and the Fe50-Mn50(200nm) films with underlayer Cu(tCu). From Fig.1(a), it is easy to observe that the crystallization of Cu layers presented preferential (111) orientation with the increase of Cu thickness. The XRD intensity of Cu (111) peak reaches the maximum when the thickness of Cu layer is 40nm and does not increase anymore with the increase of the thickness of Cu layer. From Fig.1(b), one can find that Cu underlayer produces an obvious inducing effect on (111) orientation of Fe50Mn50 thin films. There is no obvious diffraction peak of Fe50-Mn50 (111) appears in the films without Cu underlayer. Comparing Fig.1(a) with Fig.1(b), it can be seen that the crystallization of Fe50Mn50 fcc structure along the (111) orientation presents a fluctuant change with the increasing Cu underlayer thickness. The crystallization of Fe50Mn50 fcc structure along the (111) orientation intensifies with the increasing Cu underlayer thickness from 0 to 20nm and comparatively strong and sharp diffraction peak of Fe50Mn50 (111) appears for the film grown on the underlayer of 20nm Cu. When the thickness of Cu underlayer exceeds 20nm, the XRD intensity of Fe50Mn50 (111) begins to decrease. However, the Fe50Mn50 (111) XRD peak becomes strong again when the thickness of Cu reaches 60nm. It can also be seen that the Fe50-Mn50 (111) diffraction peak position in the Fe50-Mn50(200nm)/ Cu(20nm) film has a shift to the left and is closer to the standard peak position of bulk Fe50Mn50.
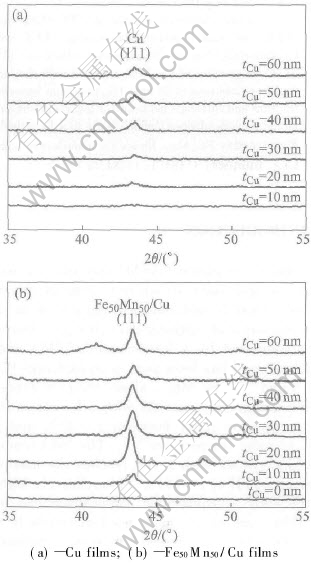
Fig.1 XRD patterns with different Cu thickness
The surface morphologies were characterized using FE-SEM. The film grew with columnar grain structure. The interface between the Cu underlayer and Fe50Mn50 layer was not sharp. This is due to a low misfit between fcc Cu (111) and fcc Fe50Mn50 (111) (less than 1 %) and close average atomic volume[16, 17]. The FE-SEM images for the Fe50Mn50/Cu films are shown in Fig.2. As can be seen, the grains of Fe50Mn50 without Cu underlayer seem to be small, while the grains of Fe50Mn50 deposited on the Cu underlayer begin to get together.With the increasing thickness of Cu underlayer from 10 to 50nm, owing to the collection of the grains on the surface of Fe50Mn50/Cu, the surface roughness of the films is enhanced. When the thickness of the Cu underlayer increases to 60nm, the surface morphology of the Fe50Mn50 film presents notable change. The grains have grown up and presented clubbed.
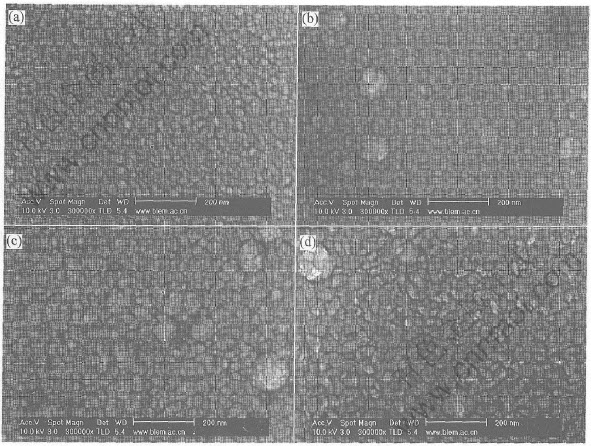
Fig.2 FE-SEM images of Fe50Mn50(a), Fe50Mn50/ Cu(20nm)(b),
Fe50Mn50/ Cu(50nm)(c) and Fe50Mn50/ Cu(60nm)(d)
From the results, it can be seen that the effects of the Cu underlayer on textures of as-deposited Fe50Mn50/Cu (tCu) films show a complex dependence on Cu thickness. Both XRD and FE-SEM indicate that the 20nm Cu underlayer has an obvious effect on (111) orientation of Fe50-Mn50 thin films. A strong and sharp diffraction peak of Fe50Mn50 (111) appears for the film. The surface of sample is smooth and a small quantity of grains combine to form a large one. When the Cu underlayer is thinner than 20nm, due to small and scattered grains of the sample, the Fe50Mn50 shows a weak XRD peak in Fe50Mn50/Cu. However, with the increasing Cu thickness, more and more grains combine to form a large one, which results in the rough surface and cave increase. These caves also lead to a lower XRD intensity. The most interesting result is observed in the Fe50Mn50/ Cu(60nm) film. Both XRD and FE-SEM results show that the film has a notable change in the structure and surface morphology. It is necessary to investigate the mechanism in our future work.
Effects of annealing on the structure of the Fe50Mn50(200nm)/ Cu(20nm) films and the thermal stability of the antiferromagnetic Fe50Mn50 layer were investigated.
The structure of the Fe50Mn50(200nm)/ Cu(20nm) and Cu(20nm) films annealed at 200, 300 and 400℃ for 1h, respectively, was also characterized by XRD. The results in Fig.3 show that with the increasing annealing temperature, the XRD intensity of Fe50Mn50 (111) decreases and the one of Cu (111) increases. Also some diffraction peaks of Mn-O presented in Fig.3(b) indicate that the oxide of Mn forms on the films.
EDX and AES were used to study the compositional distribution of Fe, Mn, and Cu in the films region. Table 1 shows the qualitative mass and atomic proportion of Fe50Mn50. Along the direction of film thickness, Fe and Mn shows the 1∶1 composition ratio. The Auger depth profile analysis for the Fe50Mn50(200nm)/ Cu(20nm) films annealed at 400℃ was carried out and the result is shown in Fig.4. As can be seen, a substantial amount of Mn atoms have migrated to the surface and migrated through the Cu layer to the substrate. And a Fe-riched Fe-Mn in the inner of the film was observed.
Table 1 Qualitative mass and atomic proportion of Mn and Fe in Fe50Mn50 film
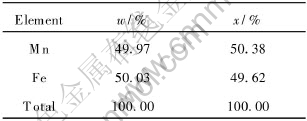
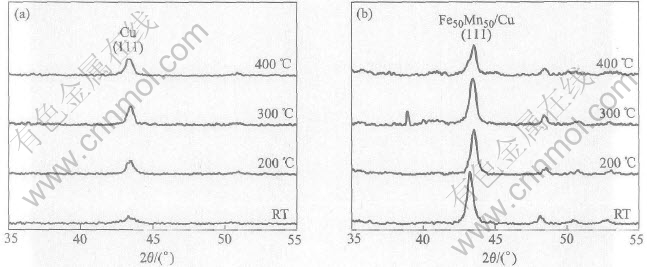
Fig.3 XRD patterns for Cu films(a) and Fe50Mn50/Cu films(b) at
different annealing temperatures for 1h
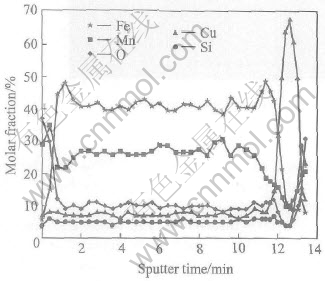
Fig.4 AES depth profile for Fe50Mn50 (200nm)/ Cu(20nm) films after annealed at 400℃
It has been observed that antiferromagnetic Fe-Mn thin film has shown to spontaneously oxidize to form a surface oxide at room temperature and 0.1Pa[18]. As the Mn atoms have been oxidized on the surface, the oxidation promotes the Mn migration towards the surface during the anneal[19]. From the results of XRD (Fig.3) and AES profile (Fig.4), it can be presumed that Mn atoms have been oxidized on the surface and Cu-SiO2 interface during annealing. At the same time, some Mn atoms have migrated through Cu layer and combined with the oxygen of substrate surface. The migration of Mn atoms leads to Fe-riched Fe-Mn in the inner of the film and then destroyed the structure of Fe50Mn50 layer, which results in the decrease of diffraction peak intensity at 400℃ as seen in Fig.3(b). The formation of Mn-O compound may have important implications for the magnetic properties of Fe50Mn50/Cu films. The migration of Mn atoms toward the surface of the film and Cu-SiO2 interface leads to the breakage of Fe50Mn50 layer composition ratio. Therefore the antiferromagnetic property Fe50Mn50 would be destroyed.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Effects of Cu underlayer on the structure of Fe50Mn50 films are studied. Cu underlayer produces an obvious inducing effect on (111) orientation of Fe50Mn50 thin films. A strong diffraction peak (111) of Fe50Mn50 appears for the films grown on the underlayer of 20nm Cu. Annealing treatment brought remarkable effects on the structure and composition of Fe50Mn50 thin film. With the increasing annealing temperature, the XRD intensity of Fe50Mn50 (111) decreases. The results of AES show that Mn atoms have migrated to the surface and Cu-SiO2 interface. The migration of Mn atoms destroys the structural and compositional properties of Fe50Mn50 layer.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors would like to thank C. Fan for his technical support.
REFERENCES
[1]Dieny B, Speriosu V S, Parkin S S P, et al. Giant magnetoresistive in soft ferromagnetic multilayers [J]. Phys Rev B, 1991, 43: 1297-1300.
[2]Nogués J, Schuller I K. Exchange bias [J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 1999, 192: 203-232.
[3]Umebayashi H, Ishikawa Y. Antiferromagnetism of γ Fe-Mn alloys [J]. J Phys Soc Jpn, 1966, 21: 1281-1294.
[4]Endoh Y, Ishikawa Y J. Antiferromagnetism of γ iron manganese alloys [J]. Phys Soc Jpn, 1971, 30: 1614-1627.
[5]Kools J C S. Exchange-biased spin-valves for magnetic storage [J]. IEEE Trans Magn, 1996, 32: 3165-3184.
[6]Lenssen K M H, de Veirman A E M, Donkers J J T M. Inverted spin valves for magnetic heads and sensors [J]. J Appl Phys. 1997, 81: 4915-4917.
[7]Tang L, Laughlin D E, Gangopadhyay S. Microstructural study of ion-beam deposited giant magnetoresistive spin valves [J]. J Appl Phys, 1997, 81: 4906-4908.
[8]Fuke H N, Saito K, Kamiguchi Y, et al. Spin-valve giant magnetoresistive films with antiferromagnetic Ir-Mn layers [J]. J Appl Phys, 1997, 81: 4004-4006.
[9]Krishnan K M, Nelson C, Echer C J, et al. Exchange biasing of permalloy films by MnxPt1 - x: Role of composition and microstructure [J]. J Appl Phys, 1998, 83: 6810-6812.
[10]Choe G, Gupta S. High exchange anisotropy and high blocking temperature in strongly textured NiFe(111)/FeMn(111) films [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 1997, 70: 1766-1768.
[11]Jungblut R, Coehoorn R, Johnson M T, et al. Orientational dependence of the exchange biasing in molecular-beam-epitaxy-grown Ni80Fe20/Fe50Mn50 bilayers (invited) [J]. J Appl Phys, 1994, 75: 6659-6664.
[12]Rypochi N, Katsumi H, Shin N,et al. Magnetoresistance and preferred orientation in Fe-Mn/Ni-Fe/Cu/Ni-Fe sandwiches with various buffer layer materials [J]. Jpn J Appl Phys, 1994, 33: 133-137.
[13]Lide D R. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics [M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1990. 4-160.
[14]PAN Wei, Sander D, LIN Minn-Tsong, et al. Stress oscillations and Surface alloy formation during the growth of FeMn on Cu(001) [J]. Phys Rev B, 2003, 68: 224419/1-224419/5.
[15]Li H Y, Li J, Yan S J, et al. Dependence of exchange coupling in Cu/FeMn/permalloy on the Cu buffer layer thickness [J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2002, 246: 1-5.
[16]Offi F, Kuch W, Kischner J. Structural and magnetic properties of FexMn1-x thin films on Cu(001) and on Co/Cu(001) [J]. Phys Rev B, 2002, 66: 064419/1-064419/10.
[17]Sander D. The correlation between mechanical stress and magnetic anisotropy in ultrathin films [J]. Rep Prog Phys, 1999, 62: 809-858.
[18]Koguchi M, Kakibayashi H, Nakatani R. Observation of Fe-Mn oxidation process using specimen transfer chamber and ultrahigh-vacuum transmission electron microscope [J]. Jpn J Appl Phys, 1993, 32: 4814-4818.
[19]Lee J H, Jeong H D, Yoon C S, et al. Interdiffusion in antiferromagnetic/ferromagnetic exchange coupled NiFe/IrMn/CoFe multiplayer [J]. J Appl Phys, 2002, 91: 1431-1435.
Foundation item: Project(19974005) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2004-12-06; Accepted date: 2005-01-18
Correspondence: WANG Feng-ping; Tel: +86-10-62333786; E-mail: fpwang@sas.ustb.edu.cn
(Edited by LONG Huai-zhong)