文章编号:1004-0609(2014)07-1812-05
激光-感应复合熔覆Cu-Fe合金涂层的结构与性能
周圣丰1,戴晓琴2,熊 征3,张天佑1,吴 超1
(1. 南昌航空大学 材料科学与工程学院,南昌 330063;
2. 南昌航空大学 信息工程学院,南昌 330063;
3. 海军工程大学 理学院,武汉 430033)
摘 要:采用激光-感应复合熔覆方法,在黄铜基材表面制备Cu-Fe合金涂层,研究涂层的显微组织与性能特征。结果表明,当激光扫描速度为3000 mm/min、粉末流量为110 g/min时,在黄铜基材上获得表面较光滑、无气孔与裂纹的Cu-Fe合金涂层。另外,Cu-Fe合金在激光-感应复合熔覆过程中发生液相分离,在涂层底部,过饱和的金属基体α-Fe呈平面状与柱状枝晶生长;在涂层中上部,直径不等的球状颗粒α-Fe镶嵌在过饱和的金属基体ε-Cu内,许多细小的白色粒状物ε-Cu在球状颗粒α-Fe内均匀弥散析出,涂层的平均显微硬度相对于基材的提高约2.8倍。
关键词:Cu-Fe合金涂层;黄铜基材;激光-感应复合熔覆;显微结构
中图分类号:TG113.1 文献标志码:A
Microstructure and property of Cu-Fe alloy coating prepared by laser-induction hybrid cladding
ZHOU Sheng-feng1, DAI Xiao-qin2, XIONG Zheng3, ZHANG Tian-you1, WU Chao1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China;
2. School of Information Engineering, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China;
3. School of Science, Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan 430033, China)
Abstract: Cu-Fe alloy coating was produced on the brass substrate by laser-induction hybrid cladding (LIHC). The microstructure and property of the coating were investigated. The results show that during LIHC when the laser scanning speed and powder feeding rate are 3000 mm/min and 110 g/min, respectively, the smooth, pore-free and crack-free Cu-Fe coating on the substrate is obtained. Furthermore, the liquid phase separation of Cu-Fe alloy takes place during LIHC. At the bottom of the coating, the supersaturated metal matrix identified as α-Fe presents the characteristics of planar growth and columnar dendritic growth. In the center of the coating, the spherical particles identified as α-Fe with different sizes are embedded in the supersaturated metal matrix ε-Cu. Large amounts of fine and white grains identified as ε-Cu phase precipitate inside the spherical α-Fe particles. As a result, the average microhardness of coating is about 2.8 times higher than that of the brass substrate.
Key words: Cu-Fe alloy coating; brass substrate; laser-induction hybrid cladding (LIHC); microstructure
铜及铜合金具有优异的导电性、导热性、塑性与韧性,在电子器件、冶金装备、航空与国防等领域具有广泛的应用[1]。但是,铜及铜合金的耐磨与抗高温氧化性能较差,大大降低了其使用寿命,从而极大地限制了其应用范围。目前,研究者采用电镀与等离子喷涂的方法提高铜及铜合金表面性能[2-3]。其中,电镀层厚度很薄,与基体呈结合力差的化学性结合;等离子喷涂层孔隙率高,与基体呈机械结合,在使用过程中易剥落。
近年来,激光熔覆层具有组织细小与致密、稀释率低、耐磨与耐蚀、与基材呈冶金结合等优点,可以表面强化与修复具有高附加值的铜及铜合金,引起了研究者的广泛关注[4-5]。但是,铜及铜合金具有良好的导热以及优异的反光性能,导致在其表面进行自动送粉式激光熔覆的难度较大。为了克服该困难,通常采用两步法,即首先采用热喷涂或粘结剂预涂的方法将熔覆粉末预置于铜合金基材表面,然后激光重熔形成镍基或钴基涂层[6-8]。虽然该方法可以明显提高铜合金基体对激光束能量的吸收率,提高涂层硬度以及与基体之间的结合强度,但是该方法效率较低,涂层的热导率偏低,与铜合金基体之间的热物理性能相差较大,易开裂。
激光-感应复合熔覆是近年来发展起来的一种新型、高效的表面强化技术。在加工效率约是单纯激光熔覆加工效率4倍的情况下,可以获得无裂纹Ni基WC涂层,其平均显微硬度达1086HV0.2,耐磨性能约是单纯熔覆层的1.42倍[9-10]。基于此,本文作者采用激光-感应复合熔覆的方法,在黄铜基材表面制备了稀释率低、无裂纹、高硬度、与基材热物理性能接近的Cu-Fe合金涂层,研究了涂层的显微结构与性能。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
实验用的基材为黄铜板,尺寸为120 mm×40 mm×5 mm,经酒精与丙酮清洗后待用。熔覆材料为专用铜-铁合金粉末,其化学成分为(质量分数):Fe 30%~35%、Si 6%~10%、Cr 3%~8%、C 1.5%~4.5%、余量为Cu,粒径为40~60 μm。
1.2 实验方法
自动送粉式激光-感应复合熔覆装置如图1所示。实验过程中激光功率为2~5 kW,激光扫描速度为900~4000 mm/min,光斑直径为5 mm,粉末流量为50~150 g/min,基材被感应加热的平均温度为1023 K,采用氩气将铜-铁合金粉末从孔径为4.5 mm的喷嘴中吹入激光-感应复合熔覆热源形成的熔池内,粉末喷嘴与基材表面法向夹角及与基材表面的距离分别为50°与15 mm。
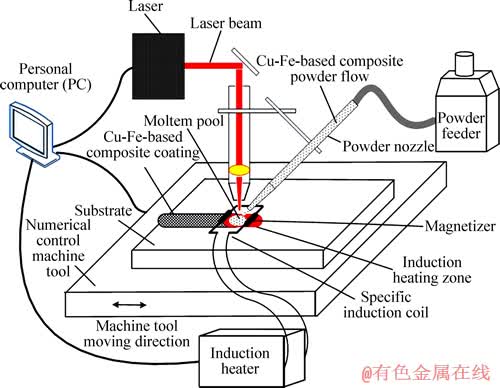
图1 自动送粉式激光-感应复合熔覆装置示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of laser-induction hybrid cladding with automatic powder feeder
实验结束后,采用着色探伤剂检测涂层的裂纹,然后沿横截面切开制备成金相试样,并用FeCl3(6 g)+HCl(12 mL)+H2O(98 mL)混合溶液腐蚀5~15 s,通过Quanta200型环境扫描电镜观测涂层的显微结构;采用X射线能谱仪测试微区化学成分;采用X’Pert PRO型X射线衍射仪分析涂层的物相结构;采用Vickers-1000型数字显微硬度计测试涂层显微硬度分布特征,载荷为1.96 N,时间为15 s。
2 结果与讨论
在本实验过程中,采用插值法获得激光-感应复合熔覆层临界状态,即根据熔覆层的宏观形貌调整激光比能(单位面积内的激光功率)与粉末面密度(单位面积内的粉末流量)[11],在临界状态附近不断插入激光功率与送粉量,以逼近准确的临界状态。实验中主要采用以下两种方法:1) 固定送粉量、光斑尺寸与激光扫描速度,通过改变激光功率来获得激光熔覆的临界条件,即保证粉末面密度不变,获得最小激光比能;2) 固定激光功率、光斑尺寸与激光扫描速度,通过改变送粉量来获得激光熔覆的临界条件,即保证激光比能不变,获得最大粉末面密度。
另外,根据周圣丰等[11]给出的关于激光-感应复合熔覆层的临界状态的定义:1) 随着激光比能的进一步降低,熔覆层的宽度变小且边部的小凹坑逐渐增多,出现不饱满的现象,因此,当熔覆层边部开始出现小凹坑时的激光扫描速度即为最大激光扫描速度;2) 随着粉末面密度的进一步增大,熔覆层中心部位的小凹坑逐渐增多,甚至相互连接成沟槽,出现烧不透的现象,因此,当熔覆层中心部位出现小凹坑时的送粉量为最大送粉量。当激光功率为5 kW时,Cu-Fe合金涂层最大的激光扫描速度与最大的粉末流量分别为3000 mm/min与110 g/min,其宏观形貌如图2所示。从图2可以看出,Cu-Fe合金涂层表面较平整与光滑,经检测无气孔与裂纹,熔覆层厚度约为1.03 mm,熔覆层宽度约为4.58 mm,稀释率约为7.5%,在可接受的范围之内。

图2 激光-感应复合熔覆Cu-Fe合金涂层的宏观形貌
Fig. 2 Macrostructure of Cu-Fe alloy coating by LIHC
图3所示为激光-感应复合熔覆Cu-Fe合金涂层的XRD谱。从图3可以看出,涂层主要由ε-Cu、α-Fe与M2C组成。
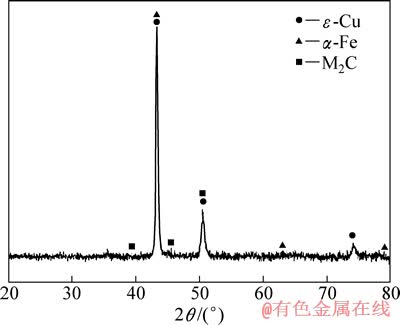
图3 激光-感应复合熔覆Cu-Fe合金涂层的XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD pattern of Cu-Fe alloy coating by LIHC
图4所示为激光-感应复合熔覆Cu-Fe合金涂层与基材界面处的显微组织。从图4可以看出,在涂层与基材的界面处,金属基体首先呈平面状生长,厚度为10~12 μm,随着离基材表面距离的增加,金属基体呈现粗大的柱状枝晶生长,柱状枝晶(标记为A)的EDS分析结果为(质量分数):73.15% Fe、7.85% Cr、1.93% Si与17.07% Cu,结合如图3所示的XRD分析结果,可以判断金属基体的主要成分为Fe,还含有大量的Cu与少量的Si与Cr,表明金属基体呈快速定向凝固的生长特征,为过饱和的固溶体α-Fe;柱状枝晶间析出物(标记为B)的EDS分析结果为76.11% Fe与23.89% Cr,表明其主要成分为Fe,还含有大量的Cr,结合如图3所示的XRD分析结果,可以判断柱状枝晶间析出物为M2C型碳化合物。
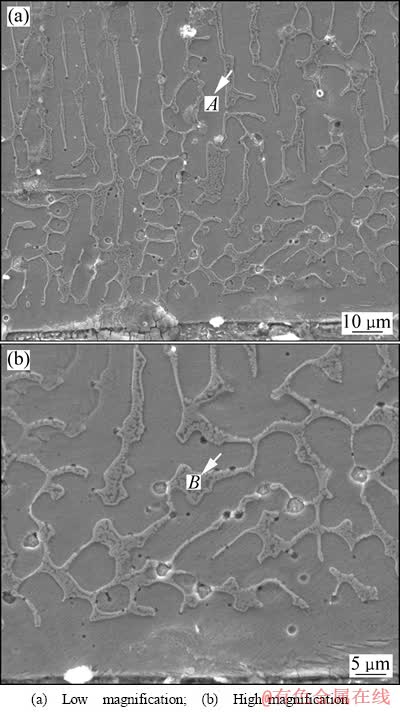
图4 激光-感应复合熔覆Cu-Fe合金涂层与基材界面处的显微结构
Fig. 4 Microstructures at interface of substrate/Cu-Fe alloy coating by LIHC
图5所示为激光-感应复合Cu-Fe合金涂层中上部的显微组织。从图5可以看出,大量球状颗粒镶嵌在金属基体内,直径在5~20 μm范围内。其中,球状颗粒(标记为C)的EDS分析结果为(质量分数):72.12% Fe、12.75% Cu、11.34% Cr与3.8% Si,金属基体(标记为D)的EDS分析结果为(质量分数):96.48% Cu、3.52% Fe。另外,在球状颗粒内部还析出了大量白色的点状晶粒。结合如图3所示的XRD分析结果可以看出,球状颗粒为α-Fe,主要成分为Fe,还含有大量的Cu与Cr,以及少量的Si不均匀地镶嵌在金属基体ε-Cu内。LU等[12]在单纯激光熔覆Cu-Fe合金涂层内也发现相似的显微组织特征。
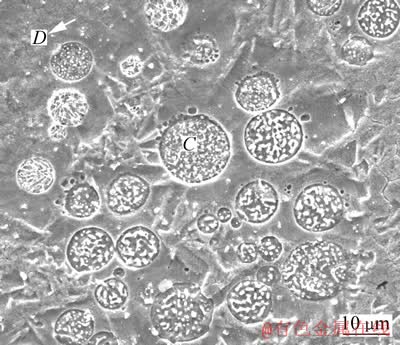
图5 激光-感应复合熔覆Cu-Fe合金涂层中上部显微结构
Fig. 5 Microstructure in the top and center of Cu-Fe alloy coating by LIHC
根据以上结果可以看出,Cu-Fe合金在激光-感应复合熔覆过程中发生了液相分离现象。这主要是因为激光-感应复合熔覆是一个快速凝固过程,激光扫描速度高达3000 mm/min,熔体的冷却速度(1×104~1×106 K/s)很大,极易过冷。根据Cu-Fe合金相图(见图6)[13],当熔池的温度降低至液相分离温度以下时,过冷熔体将处于亚稳态混溶区并会发生液相分离而分离成两个液相(富Fe相与富Cu相)。在熔池中下部,对于富Fe熔体,根据快速凝固理论,成分过冷决定着组织的生长特征,而成分过冷由温度梯度G与凝固前沿速度R的比值即G/R决定[14]。在熔池与基材界面处,温度梯度G最大,而凝固冷却速度R为0,G/R趋于无穷,铁熔体首先呈外延生长,随着离基材表面距离的增大,G减小,而R增加,G/R减小,固液界面变得不稳定,形成发达的柱状树枝晶(见图4)。在熔池的中上部,为了保持界面能最低,熔点较高而量较少的铁溶体被熔点较低而量较大的铜液相包覆而收缩成球状液滴;球状铁液滴在温度梯度与表面张力梯度的作用下,发生Marangoni运动,根据球状铁液滴直径与Marangoni运动速度的关系[15]
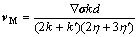 (1)
(1)
式中:k与k′分别为溶体和液滴的热导率;η与η′分别为溶体的液滴的黏度;d为液滴的直径;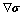 =(dγ/dT)·G为溶体与液滴之间界面张力的梯度;dγ/dT为界面张力温度系数;G为温度梯度。式(1)表明,液滴的尺寸越大,其Marangoni运动速度也越大,运动方向朝向温度较高的熔池表面。
=(dγ/dT)·G为溶体与液滴之间界面张力的梯度;dγ/dT为界面张力温度系数;G为温度梯度。式(1)表明,液滴的尺寸越大,其Marangoni运动速度也越大,运动方向朝向温度较高的熔池表面。

图6 Cu-Fe合金的二元相图[13]
Fig. 6 Binary phase diagram of Cu-Fe alloy[13]
另外,在重力场作用下,液滴要做Stokes运动,根据球状铁液滴直径与Stokes运动速度的关系[13]:
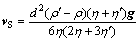 (2)
(2)
式中:g为重力加速度,ρ与ρ′分别为溶体与液滴的密度。假定在快速凝固过程中忽略熔池中熔体的其他运动形式,则熔体中第二相液滴的净运动速度为Marangoni和Stokes运动速度之和,即可写成矢量形式:
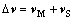 (3)
(3)
因此,在熔池的中上部,富Fe液滴的密度小于富Cu熔体的密度,富Fe液滴在Marangoni与Stokes作用下的运动方向始终向上,并且与周围其他球状液滴相互碰撞、合并与长大,使球状铁液滴直径逐渐增大,最终形成尺寸较大的液滴。当温度降至富Fe液滴的 熔点以下时,富Fe液滴开始凝固,发生共析反应γ-Fe→α-Fe+ε-Cu,即由溶质捕获导致过冷γ-Fe快速转变为过饱和的α-Fe。在室温下,Cu在α-Fe中的固溶度很小,可以忽略不计。因此,许多纳米级的白色ε-Cu在球状颗粒α-Fe的内均匀弥散析出(见图5)。因此,在Marangoni与Stokes作用力下,小液滴之间不断发生碰撞、合并与长大,再吞并小颗粒,然后迅速长大成大颗粒,并与来不及被较大颗粒吞并的小液滴一起被基体金属ε-Cu包覆起来,在涂层内形成大小不一、分布不均匀的第二相颗粒α-Fe。此外,涂层底部的金属基体α-Fe与涂层中上部的金属基体ε-Cu均为过饱和固溶体,都能有效阻碍位错的运动,导致涂层的平均显微硬度(约为280HV0.2)相对于基材提高了约2.8倍,如图7所示。
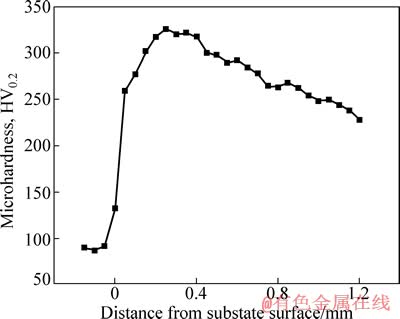
图7 激光-感应复合熔覆Cu-Fe合金涂层的显微硬度曲线
Fig. 7 Microhardness profile of Cu-Fe alloy coating by LIHC
3 结论
1) 当激光扫描速度为3000 mm/min与粉末流量为110 g/min时,采用激光-感应复合熔覆的方法在黄铜基材表面制备了无气孔与裂纹、表面较光滑的Cu-Fe合金涂层。在涂层底部,过饱和的金属基体α-Fe首先呈平面状生长,随着离基材表面距离的增加,金属基体α-Fe呈粗大的柱状枝晶生长;在涂层中部,大量直径不等的球状颗粒α-Fe不均匀地镶嵌在过饱和的金属基体ε-Cu内,许多纳米级的白色ε-Cu在球状颗粒α-Fe内均匀弥散析出。
2) Cu-Fe合金涂层的平均显微硬度达280HV0.2,相对于基材的提高了约2.8倍,其强化机理是固溶强化与析出弥散强化共同作用的结果。
REFERENCES
[1] 赵冬梅, 董企铭, 刘 平, 金志浩, 康布熙. 高强高导铜合金合金化机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2001, 11(S2): 21-24.
ZHAO Dong-mei, DONG Qi-ming, LIU Ping, JING Zhi-hao, KANG Bu-xi. Mechanism of alloying of copper alloy with high strength and high electrical conductivity[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2001, 11(S2): 21-24.
[2] 于金库, 王庚华, 刑广忠, 冯 皓. 在铜合金上获得Ni-Fe合金镀层的电镀工艺研究[J]. 燕山大学学报, 1999, 23(2): 123-125.
YU Jin-ku, WAN Geng-hua, XING Guang-zhong, FENG Hao. A study of the plating processing about the coating of Ni-Fe alloy on copper alloy substrate[J]. Journal of Yanshan University, 1999, 23(2): 123-125.
[3] 陈 健, 刘雪飘, 梁 欢. 铜及铜合金表面等离子喷涂的应用进展[J]. 金属热处理, 2010, 35(9): 98-103.
CHEN Jian, LIU Xue-piao, LIANG Huan. Research progress and application of plasma spraying on copper alloy surface[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2010, 35(9): 98-103.
[4] 余 廷, 邓琦林, 董 刚, 杨建国, 张 伟. 钽对激光熔覆镍基涂层的裂纹敏感性及力学性能的影响[J]. 机械工程学报, 2011, 47(22): 25-30.
YU Ting, DENG Qi-lin, DONG Gang, YANG Jian-guo, ZHANG Wei. Influence of Ta on crack susceptibility and mechanical properties of laser clad Ni-based coating[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 47(22): 25-30.
[5] 刘建弟, 张述泉, 王华明. 激光熔覆WC颗粒增强复合涂层的组织及耐磨性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(9): 2600-2607.
LIU Jian-di, ZHANG Shu-quan, WANG Hua-ming. Microstructure and wear resistance of laser cladding WC particles reinforced composite coatings[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(9): 2600-2607.
[6] Liu Fang, Liu Chang-sheng, Chen Sui-yuan, TAO Xing-qi, Zhang Yong. Laser cladding Ni-Co duplex coating on copper substrate[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2010, 48(7/8): 792-799.
[7] DEHM G, BANBERGER M. Laser cladding of Co-based hardfacing on Cu substrate[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2002, 37(24): 5345-5353.
[8] CHEN Sui-yuan, LIANG Jing, LIU Chang-shang, SUN Kai, MAZUMDER J. Preparation of a novel Ni/Co-based alloy gradient coating on surface of the crystallizer copper alloy by laser[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 258(4): 1443-1450.
[9] ZHOU Sheng-feng. A study of ceramic-metal composite coating prepared by laser-induction hybrid cladding technique[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2008.
[10] Zhou Sheng-feng, Huang Yong-jun, Zeng Xiao-yan, Hu Qian-wu. Microstructure characteristics of Ni-based WC composite coatings by laser induction hybrid rapid cladding[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 480(1/2): 564-572.
[11] 周圣丰, 戴晓琴, 郑海忠. 激光熔覆与激光-感应复合熔覆WC-Ni60A涂层的结构与性能特征[J]. 机械工程学报, 2012, 48(7): 113-118.
ZHOU Sheng-feng, DAI Xiao-qin, ZHENG Hai-zhong. Characteristics on structure and properties of WC-Ni60A coatings by laser cladding and laser-induction hybrid cladding[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(7): 113-118.
[12] LU Yun, HE Yi-zhu. Liquid phase separation behaviors in Cu-Fe alloy coatings synthesized by laser cladding[J]. Materials Science Form, 2010, 654/656: 1864-1867.
[13] CHEN Qing, JIN Zhang-peng. The Fe-Cu system: A thermodynamic evaluation[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1995, 26(2): 417-426.
[14] Ratke L, DIEFENBACH S. Liquid immiscible alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 1995, 15(7/8): 263-347.
[15] 冼爱平, 张修睦, 李忠玉, 刘清泉, 陈继志, 李依依. 利用Marangoni对流制备均质偏晶合金[J]. 金属学报, 1996, 32(2): 113-119.
XIAN Ai-ping, ZHANG Xiu-mu, LI Zhong-yu, LIU Qing-quan, CHEN Ji-zhi, LI Yi-yi. Preparation of homogeneity immiscible alloy by Marangoni convection[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1996, 32(2): 113-119.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50901040);江西省科技支撑计划资助项目(20122BBE500031)
收稿日期:2013-07-20;修订日期:2014-04-20
通信作者:周圣丰,副教授, 博士;电话:0791-83863026;E-mail:zhousf1228@163.com