文章编号:1004-0609(2011)05-1045-07
规则多孔铜的拉伸性能及其各向异性
彭 震, 杨天武, 李再久, 黎振华, 金青林, 周 荣
(昆明理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,昆明 650093)
摘 要:采用固-气共晶定向凝固的方法制备规则多孔铜,研究其室温拉伸性能的各向异性和气孔率对拉伸力学性能的影响,建立表征抗拉强度与气孔率和拉伸方向相关的数学模型。结果表明:规则多孔铜的拉伸性能主要取决于材料的气孔率和拉伸方向;随着气孔率的增大,规则多孔铜的拉伸性能明显下降;规则多孔铜拉伸性能呈各向异性特征,0°方向性能最好,45°方向的次之,90°方向的最差;各拉伸方向的实验数据与模型数据吻合良好。断口分析表明:规则多孔铜呈韧性断裂,拉伸断裂从孔壁处开始,最终因颈缩导致完全断裂。
关键词:规则多孔铜;各向异性;力学性能;气孔率;应力集中
中图分类号:TG146; TG115 文献标志码:A
Tensile properties and anisotropy of ordered porous copper
PENG Zhen, YANG Tian-wu, LI Zai-jiu, LI Zhen-hua, JIN Qing-lin, ZHOU Rong
(School of Materials Science and Engineering,
Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, China)
Abstract: The ordered porous copper with cylindrical pores aligned in one direction was fabricated by the solid-gas eutectic solidification process. The anisotropy of tensile properties and the porosity of ordered porous copper at room temperature were investigated. In order to discuss the effects of porosity and tensile direction on ultimate tensile strength, the stress concentration models were established. The results show that the tensile properties of ordered porous copper depend on the porosity and tensile direction. As the porosity increases, the tensile properties decrease dramatically. The anisotropy of porous copper shows that the tensile properties of ordered porous copper with 0°, 45° and 90° tensile directions are the best, better and the worst, respectively. The experimental data are well consistent with the data from the model. Through fractographic analysis, it is indicated that the ductile fracture begins at the inside walls of pores, and the eventual rupture is due to necking during the tensile process.
Key words: ordered porous copper; anisotropy; mechanical properties; porosity; stress concentration
多孔金属材料具有密度低、比强度高、刚度大、表面积大、防震、吸声、阻燃以及渗透性好等优良性能,逐渐成为航空航天、汽车、信息、建筑、军事和核能等高技术领域的工程材料[1-3]。1993年,乌克兰的SHAPOVALOV[4]提出的金属/气体共晶定向凝固法可用来制备金属基体中气孔呈圆柱形定向排列的规则多孔材料。这些气孔定向排列的多孔金属比传统的多孔金属具有力学性能上的优势,为其在力学性能上的应用提供了保障。
继乌克兰以后,美国海军研究实验室、桑迪亚国家实验室、日本大阪大学、中国清华大学以及北京科技大学开展了规则多孔材料的制备工艺和力学性能的研究。目前,固-气共晶定向凝固法制备的多孔金属的气孔率范围为15%~50%。SIMONE[5]及SIMONE和GIBSON[6]系统研究了拉伸方向与气孔轴向呈0°的规则多孔铜试样(简称0°方向)的拉伸性能,但并没有涉及其他拉伸方向的研究,没有反映其各向异性。HYUN等[7]和NAKAJIMA等[8]在对0°和90°方向试样拉伸性能的研究中发现,规则多孔铜在0°和90°方向表现出各向异性。国内刘新华等[9]和姚迪等[10]对规则多孔铜0°和90°方向压缩变形行为进行了深入的研究。而对于拉伸性能,除项亦斌等[11]对规则多孔镁0°方向的拉伸性能有所研究及陈文革等[12]将规则多孔铜与传统多孔铜的力学性能进行了比较之外,关于规则多孔铜拉伸性能的报道很少。为此,为更完善地揭示规则多孔铜的拉伸性能,更充分地表征材料的各向异性特征,本文作者对气孔率为25%~50%的材料进行0°、45°和90°方向的拉伸实验,在此基础上建立能充分反映规则多孔材料各向异性的数学模型。
1 实验
1.1 规则多孔铜的制备
采用自制的10 kg高压定向凝固设备制备规则多孔铜,所用设备如图1所示。其制备原理是发生固-气共晶转变(Liquid→Solid+gas)时,利用气体在液态金属和固态金属中的溶解度之差使过饱和气体在定向凝固过程中形成定向排列的气孔。制备时,将金属纯铜置于熔炼坩埚中,然后抽真空使熔炼炉内的气压低于10-2 Pa,再加热铸型到预设温度1 143 ℃进行熔炼,充入氢气和氩气的混合气体保温30 min后提起控制杆将铜熔液通过漏斗的倒流作用浇入内径为60 mm、高为150 mm的铸型中,最后,按预设的下拉速率进行定向凝固得到气孔定向排列于基体中的多孔铜坯料。冷却后所得铸锭坯料气孔形貌如图2所示。
1.2 拉伸实验
按GB/T228—2002设计矩形横截面比例试样如图3所示,标距为14 mm,横截面为2 mm×3 mm。使用电火花线切割机从不同气孔率材料中切割拉伸方向与气孔轴向呈0°、45°和90°的试样,用来研究该多孔材料的各向力学性能和气孔率对力学性能的影响。拉伸实验于室温在AG-IS10 KN万能实验机上进行,拉伸速率为1 mm/min,用延伸计测量拉伸位移。实验过程中记录拉伸载荷—位移曲线,分别用名义截面面积和标距值除拉伸载荷和位移得到应力和应变,从而得到该试样的拉伸应力—应变曲线。
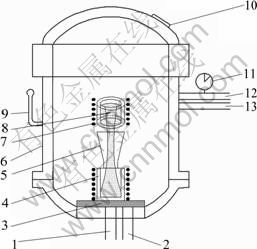
图1 规则多孔金属制备装置示意图
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of fabrication apparatus for ordered porous metals: 1—Inlet of cooling water; 2—Outlet of cooling water; 3—Copper chiller; 4—Crucible; 5—Funnel; 6—Chamber; 7—Induction-heating coils; 8—Molten copper; 9—Control bar; 10—Observation window; 11—Pressure gage; 12—Inlet of gas; 13—Outlet of gas
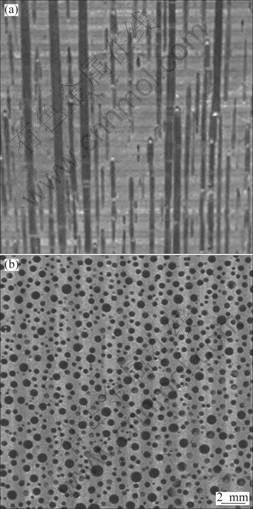
图2 规则多孔铜气孔形貌
Fig.2 Pores morphologies of ordered porous copper: (a) Vertical section; (b) Cross section
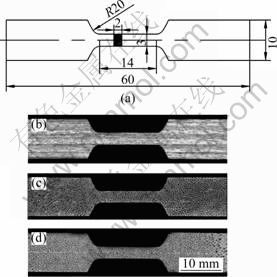
图3 拉伸试样尺寸及拉伸试样照片
Fig.3 Sizes (a) and macrophotographs in directions of 0° (b), 45°(c) and 90°(d) of tensile specimens (mm)
1.3 实验分析
直接测量规则多孔铜的质量(m)和体积(V),利用阿基米德原理计算材料的气孔率(p),如式(1)所示:
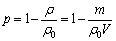 (1)
(1)
式中:ρ为所制规则多孔铜的密度;ρ0为致密铜的密度。
在应力—应变曲线上,由于没有明显的屈服平台,取σ0.2作为材料的屈服强度、最大应力作为材料的抗拉强度。在拉伸载荷达到最大值以后,试样的孔状结构使得断裂持续很长时间,气孔壁的局部区域变形严重,用断后伸长率来衡量材料的塑性不准确,因此本研究用最大应力下的应变来表征材料的塑性。
将拉伸实验后的断口在XL30ESEM-TMP扫描电子显微镜上进行扫描,观察其断口形貌。用3 g FeCl3, 10 mL HCl和100 mL H2O配制的腐蚀液对规则多孔铜进行浸蚀来观察晶界。
2 结果与分析
2.1 应力—应变曲线
图4所示为气孔率约为0.32的试样在0°、45°和90°方向拉伸得到的应力—应变曲线。由图4可以看出,规则多孔铜的拉伸应力—应变曲线的变化趋势与典型材料的拉伸应力—应变曲线的变化趋势类似。当应变小于0.005时,材料拉伸处于明显的线弹性阶段;随着载荷的进一步增大,材料发生塑性变形,此时,应力—应变曲线没有明显的屈服平台,屈服阶段不明显;进入形变强化阶段以后,材料出现均匀的塑性变形,当达到最大应力即抗拉强度以后,出现不均匀的塑性变形,最终材料断裂。
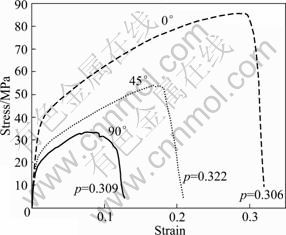
图4 试样在不同拉伸方向的应力—应变曲线
Fig.4 Stress—strain curves of samples in different tensile directions
由图4可见,规则多孔铜的拉伸曲线受实验拉伸方向的影响很大。沿0°方向拉伸时,应力—应变曲线比较光滑,与致密材料的拉伸曲线无异;而沿45°和90°方向拉伸时,在形变强化阶段以后均出现不同程度的锯齿状。这说明由于气孔轴向与拉伸方向的不同,气孔对基体产生的作用不同。沿0°方向拉伸,气孔轴向与拉伸方向相同,气孔对基体的应力集中作用微小;沿45°和90°方向拉伸时,在某个气孔或者多个气孔的孔壁处先断裂,最终完全断裂,气孔对基体的应力集中作用较大。
2.2 力学性能
2.2.1 力学性能的影响因素
图5所示为不同拉伸方向试样的力学性能随气孔率的变化。从图5可以看出,随着气孔率的增大,材料的抗拉强度、屈服强度和最大应力下的应变均下降,即材料的拉伸力学性能随气孔率的增大而降低。由气孔率的计算式(1)可知,气孔率增大,材料的实心基体减少,材料的质量减小,力学性能下降。因此,规则多孔铜的拉伸性能一方面依赖于材料的气孔率。
由图4和5(a)可以看出,规则多孔铜在0°方向的拉伸力学性能最好,45°方向的次之,90°方向的最差,这说明规则多孔铜的拉伸性能也依赖于拉伸方向,拉伸性能呈现明显的各向异性特征。导致材料呈现各向异性的原因主要有以下3个方面。
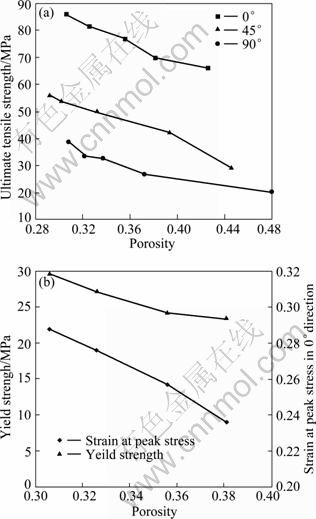
图5 具有不同气孔率的规则多孔铜试样在不同方向的拉伸性能
Fig.5 Tensile properties of ordered porous copper with different porosities in different directions: (a) Ultimate tensile strength; (b) Yield strength and strain at peak stress in 0° direction
第一,规则多孔铜沿不同方向拉伸时气孔的应力集中作用不同。45°和90°方向气孔对基体有一定的应力集中作用,而0°方向气孔对基体的应力集中作用很小[7]。
第二,规则多孔铜沿不同方向拉伸试验时的有效承载面积不同。KOVACIK[13]建立了多孔材料的规则蜂窝模型,本研究中,假设气孔在整个基体上呈正六边形分布,如图6所示。其中,d为气孔直径,c 为两气孔间的距离,A为有效承载面积。对于同一气孔率下的规则多孔铜,0°方向和90°方向的有效承载面积分别用式(2)和(3)表示。由于0≤d≤c,所以,如式(4)所示0°方向的有效承载面积大于90°方向的,致使0°方向的抗拉强度较高,90°方向的较低。
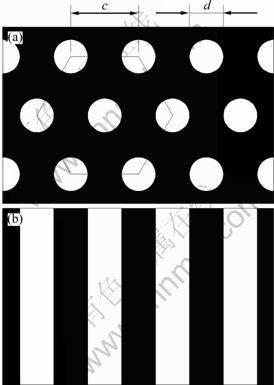
图6 规则多孔铜在不同拉伸方向的拉伸横截面
Fig.6 Tensile cross-sections of ordered porous copper with different tensile directions: (a) 0°; (b) 90°
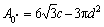 (2)
(2)
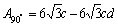 (3)
(3)
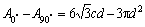 ≥0 (4)
≥0 (4)
第三,规则多孔铜的柱状晶结构使材料呈现各向异性。图7(a)和(b)分别为气孔率为0.32和0.48规则多孔铜的金相照片。由图7可以看出,固-气共晶定向凝固法制备的规则多孔铜的宏观组织为柱状晶,柱状晶的生长方向与气孔方向相同。具有柱状晶结构的材料沿柱状晶方向的拉伸性能比垂直于柱状晶方向的拉伸性能好。
2.2.2 抗拉强度的应力集中模型
BACCACCINI等[14]提出在多孔材料中可用式(5)来描述多孔金属材料的拉伸强度与气孔率之间的关系。因此,只要计算出不同拉伸方向下气孔对基体的应力集中系数,就可以建立力学模型来表征材料拉伸强度和气孔率之间的关系:
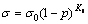 (5)
(5)
式中:σ0为致密铜的抗拉强度;σ为规则多孔铜的抗拉强度;Kt为气孔对基体的应力集中系数。
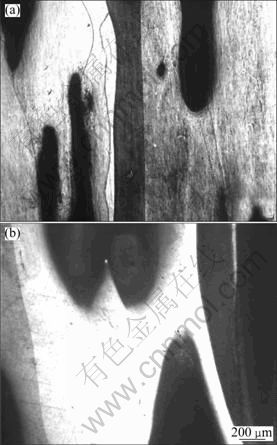
图7 不同气孔率试样的晶粒结构
Fig.7 Photographs showing grain structure with variable porosities: (a) p=0.32; (b) p=0.48
图8(a)所示为在有限宽度板拉伸中任意椭圆气孔周围基体的应力集中情况。根据经典应力集中理 论[15],应力集中系数可用式(6) 表示。当试样沿0°方向拉伸时(见图8(b)),a=r,b=∞,代入式(6)可得,Kt=1 所以,0°拉伸方向抗拉强度的应力集中模型可用式(7)表示;当试样沿90°方向拉伸时(见图8(d)),a=b=r, 那么Kt=3,则沿90°拉伸方向抗拉强度的应力集中模型可用式(8)表示;当试样沿45°拉伸时(见图8(c)),a=r, b=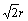 ,那么Kt=1+
,那么Kt=1+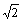 ,则45°拉伸方向抗拉强度的应力集中模型可用式(9)表示。当沿任意角方向(f)拉伸时(见图8(c)),a=r,b=r/sin f,那么Kt=1+2r/sin f,所以,任意角度拉伸时抗拉强度的应力集中模型如式(10)表示。
,则45°拉伸方向抗拉强度的应力集中模型可用式(9)表示。当沿任意角方向(f)拉伸时(见图8(c)),a=r,b=r/sin f,那么Kt=1+2r/sin f,所以,任意角度拉伸时抗拉强度的应力集中模型如式(10)表示。
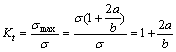 (6)
(6)
式中:σmax与圆孔尺寸a和b有关。
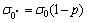 (7)
(7)
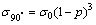 (8)
(8)
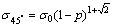 (9)
(9)
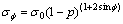 (10)
(10)
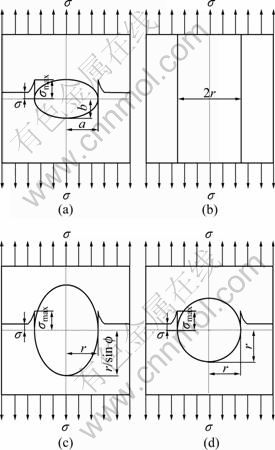
图8 规则多孔铜试样在不同拉伸方向的应力集中示意图
Fig.8 Schematic diagrams of stress concentration of ordered porous copper in different directions: (a) Parameters description and pore axis; (b) 0° direction; (c) 45° direction; (d) 90° direction
图9所示为应力集中模型数据与实验数据的拟合情况。由图9可知,0°、45°和90°拉伸方向的模型数据与实验数据吻合良好。任意角度方向的拉伸应力集中模型公式(10)是抗拉强度关于气孔率p和拉伸角度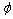 的函数,可以从理论上计算出任意角度拉伸方向下不同气孔率材料的抗拉强度,且在0°、45°和90°方向符合实验数据的变化规律。从式(7)可以看出,0°方向规则多孔铜的抗拉强度随气孔率的增大线性下降,气孔对基体的应力集中作用很小;而由式(8)和(9)可知,90°和45° 方向规则多孔铜的抗拉强度与气孔率增大呈非线性下降,气孔对基体的应力集中作用对其影响较大。
的函数,可以从理论上计算出任意角度拉伸方向下不同气孔率材料的抗拉强度,且在0°、45°和90°方向符合实验数据的变化规律。从式(7)可以看出,0°方向规则多孔铜的抗拉强度随气孔率的增大线性下降,气孔对基体的应力集中作用很小;而由式(8)和(9)可知,90°和45° 方向规则多孔铜的抗拉强度与气孔率增大呈非线性下降,气孔对基体的应力集中作用对其影响较大。
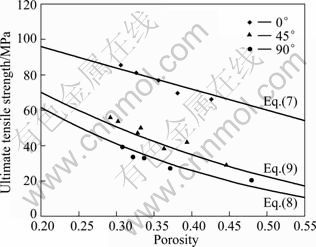
图9 应力集中模型数据与实验数据
Fig.9 Data from stress concentration model versus experimental data
2.3 断口分析
图10所示为气孔率为0.32的试样沿各方向的拉伸断口形貌。其中,图10(a1)、(b1)和(c1)所示为高倍下各断口的局部形貌,图10(a2)、(b2)和(c2)所示为低倍下各断口的整体形貌。铜是面心立方晶体结构的金属,塑性变形时有12个滑移系,具有良好的塑性变形能力[16]。HYUN等[7]的研究结果表明,0°方向有滑移线,但没有观察到韧窝。从图10中可以看出,各个方向的拉伸断口都有明显的塑性变形,都能观察到滑移线和韧窝。通常,断口上的韧窝是材料韧性断裂的标志[17],拉伸断口上明显的韧窝表明,规则多孔铜在各个方向的拉伸断裂都属于韧性断裂。通常情况下,韧窝越深越多表明材料的韧性越好。沿0°方向拉伸后试样断口的韧窝比其他两个方向的韧窝更深,更多,可以定性分析出0°方向试样的韧性最好。
由图10(a2)、(b2)和(c2)可以看出,断裂区域基体材料沿着拉伸载荷的方向存在明显的局部脊状突起,这种脊状突起是由拉伸过程中承载面积逐渐缩小而产生的颈缩所致。由断面的整体形貌可以看出,0°方向的断裂面是气孔的横截面,断裂从孔壁处向基体内进行,由于0°方向拉伸气孔应力集中作用较小,断裂由承载面积减小产生颈缩引起;45°和90°方向的断裂面都是气孔轴线所在的截面,气孔内壁应力集中最大的地方就在这个截面上,这表明规则多孔铜在45°和90°方向的拉伸断裂沿着应力集中最大的孔壁处开始,最终因颈缩导致完全断裂。
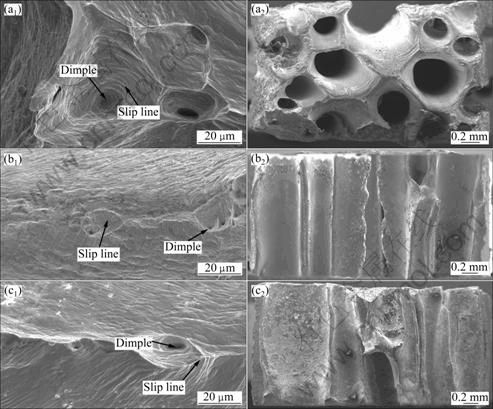
图10 规则多孔铜在不同拉伸方向的断口形貌
Fig.10 Tensile fractographs of ordered porous copper tested in different directions (Pictures at upper right show corresponding lower magnification fractographs): (a1), (a2) 0°; (b1), (b2) 45°; (c1), (c2) 90°
3 结论
1) 规则多孔铜拉伸力学性能主要取决于材料的气孔率和拉伸方向。随着气孔率的增大,拉伸性能明显下降。拉伸性能呈明显各向异性,0°方向的拉伸性能比45°和90°方向的更好,90°方向的最差。导致规则多孔铜各向异性的原因可归结为:规则多孔铜 0°方向应力集中作用最小,45°方向的其次,90°方向的最大;沿0°方向进行拉伸试验时,规则多孔铜的有效承载面积比90°方向的更大;规则多孔铜的柱状晶结构使材料具有各向异性。
2) 建立了表征规则多孔铜抗拉强度与气孔率和拉伸方向的应力集中模型,实验数据与模型数据吻合良好。0°方向规则多孔铜的抗拉强度随气孔率的增加呈线性下降,气孔对基体的应力集中作用微小,而45°和90°方向规则多孔铜的力学性能受气孔对基体的应力集中作用影响较大。
3) 断口分析表明,规则多孔铜拉伸断裂呈韧性断裂方式。断口上有明显滑移线和韧窝,0°方向比45°和90°方向规则多孔铜的塑性变形更明显。整体断口形貌表明,拉伸断裂从孔壁处开始,最终因颈缩导致完全断裂。
REFERENCES
[1] 杨雪娟, 刘 颖. 多孔金属材料的制备及应用[J]. 材料导报, 2007, 21(4): 380-383.
YANG Xue-juan, LIU Ying. Preparation and applications of porous metal material[J]. Materials Review, 2007, 21(4): 380-383.
[2] 杨亚政, 杨嘉陵. 轻质多孔材料研究进展[J]. 力学季刊, 2007, 28(4): 503-516.
YANG Ya-zheng, YANG Jia-ling. Progress in research work of light materials[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2007, 28(4): 503-516.
[3] 张华伟, 李言祥, 刘 源. Gasar工艺中金属-氢二元相图的研究[J]. 金属学报, 2005, 41(1): 55-59.
ZHANG Hua-wei, LI Yan-xiang, LIU Yuan. Study of metal-hydrogen binary phase diagram in Gasar process[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2005, 41(1): 55-59.
[4] SHAPOVALOV V I. Method of manufacture of porous articles: US, 5181549[P]. 1993-01-26.
[5] SIMONE A E. The tensile strength of porous copper made by the Gasar process[D]. Massachusetts: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1994: 44-78.
[6] SIMONE A E, GIBSON L J. The tensile strength of porous copper made by the Gasar process[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1996, 44(4): 1437-1447.
[7] HYUN S K, MURAKAMI K, NAKAJIMA H. Anisotropic mechanical properties of porous copper fabricated by unidirectional solidification[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 299(1/2): 241-248.
[8] NAKAJIMA H, HYUN S K, OHASHI K, OTA K, MURAKAMI K. Fabrication of porous copper by unidirectional solidification under hydrogen and its properties[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A, 2001, 179: 209-214.
[9] 刘新华, 姚 迪, 刘雪峰, 谢建新. 藕状多孔铜沿垂直气孔方向的压缩变形行为与本构关系[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(7): 1237-1244.
LIU Xin-hua, YAO Di, LIU Xue-feng, XIE Jian-xin. Deformation behaviors and constructive relation of lotus-type porous copper under compressive direction perpendicular to pores[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, l9(7): 1237-1244.
[10] 姚 迪, 刘新华, 刘雪峰, 谢建新. 藕状多孔铜轴向压缩变形行为与本构关系[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 18(11): 1996-2001.
YAO Di, LIU Xin-hua, LIU Xue-feng, XIE Jian-xin. Axial compressive deformation behaviors and constructive relation of lotus-type porous copper[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, l8(11): 1996-2001.
[11] 项亦斌, 李言祥, 刘 源. 定向凝固规则多孔镁的力学性能研究[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2006(S): 36-38.
XIANG Yi-bin, LI Yan-xiang, LIU Yuan. Study on mechanical properties of porous magnesium fabricated by directional solidification[J]. Special Casting and Nonferrous Alloys, 2006(S): 36-38.
[12] 陈文革, 罗启文, 张 强, 高丽娜. 定向凝固技术制备多孔铜及其力学性能[J]. 机械工程材料, 2007, 31(7): 42-44.
CHEN Wen-ge, LUO Qi-wen, ZHANG-Qiang, GAO Li-na. Fabrication and mechanical properties of porous metal copper with upward directional solidification[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 31(7): 42-44.
[13] KOVACIK J. The tensile behaviour of porous metals made by Gasar process[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1998, 46(15): 5413-5422.
[14] BOCCACCINI A R, ONDRACEK G, MOMBELLO E, MATER J. Determination of stress concentration factors in porous materials[J]. Science Letters, 1995, 14: 534-536.
[15] 航空工业部科学技术委员会. 应力集中系数手册[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1990: 235-243.
Science and Technology Committee of Aviation Industry. Manual for stress concentration factors[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1990: 235-243.
[16] 崔忠圻, 覃耀春. 金属学与热处理[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2007: 164-166.
CUI Zhong-qi, QIN Yao-chun. Metallography and heat treatment[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2007: 164-166.
[17] 刘春廷, 马 继. 材料力学性能[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009: 37-38.
LIU Chun-ting, MA Ji. Mechanical properties of materials[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009: 37-38.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金云南联合基金资助项目(u0837603)
收稿日期:2010-06-13;修订日期:2010-11-20
通信作者:周 荣,教授;电话:0871-5136755;E-mail:pzkmust@sina.com