β-钨至α-钨转变过程的研究
来源期刊:中南大学学报(自然科学版)1987年第4期
论文作者:黄慧民 陈新民
文章页码:459 - 463
关键词:α相; β相; 钨; 相变; 相变点; 亚稳相; 转变热; 转变温度; 示差扫描热法; 自燃
Key words:alpha-phase; beta-phase; tungsten; phase transformation; phase trans ormation points; metastable phases; transition heat; temperature changing; differential scanning calorimetry; spontaneous combustion
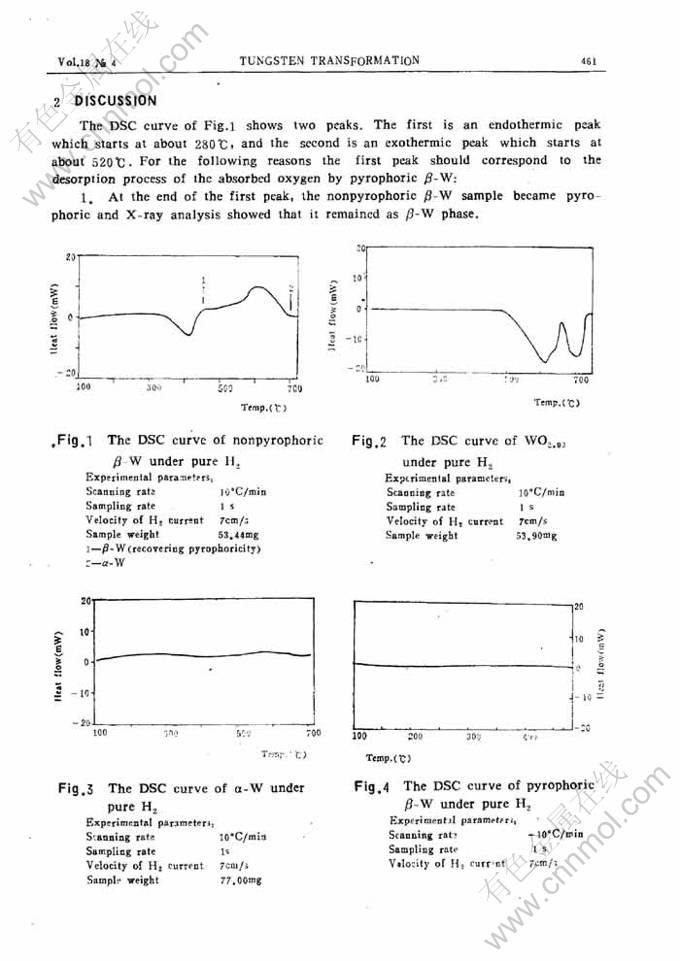
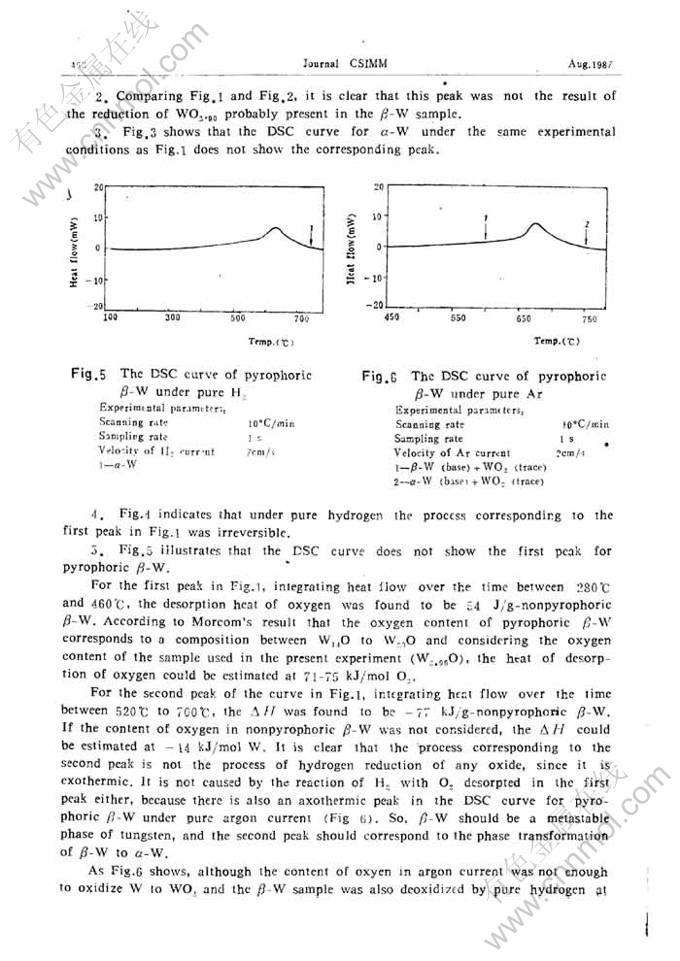
摘 要:本文以DSC法及对淬冷试样进行X射线分析的方法,研究了β-W在氢中和氩中向α-W的转变过程。非自然β-W在纯氢中升温时,约在280℃失去所吸附的氧,其解吸热为71—75kJ/mol O2。β-W至α-W的转变温度约为520℃,转变热为-14kJ/mol。这一转变过程并不一定要经由生成WO2的阶段。在纯氩中这一转变温度要比在纯氢中高。将β-W看作是由溶解氧所稳定的一种钨的亚稳相较为合适。
Abstract: In this work the β-W to a-W trandformation under hydrogen and argon, respectively, was investigated with DSC and X-ray analysis on quenched samples. Under pure hydrogen nonpyrophoric β-W loses the absorbed oxygen at about 280℃ and the desorption heat was found to be 71-75kJ/mo1 O2. The transformation temperature is about 520℃ and the transformation heat was foundto be-14 kJ/mol. The formation of WO2 is not a necessery slage for the transformation. Underpure argon the transformation temperature is higher than under pure hydrogen. It seems better toconsider β-W to be a metaphase of tungsten with some oxygen dissolved as stabilizer.