硝酸体系电解精炼高纯铜过程中氯的夹杂机制
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2020年第5期
论文作者:曹华珍 冯闻宇 张惠斌 郑国渠
文章页码:1387 - 1396
关键词:铜电解精炼;硝酸体系;氯化亚铜;夹杂机制
Key words:copper electrorefining; nitric acid system; cuprous chlorine; inclusion mechanism
摘 要:通过循环伏安法和电沉积实验研究硝酸体系电解精炼高纯铜过程中氯的夹杂机制。CV曲线中存在明显中间产物CuCl的还原峰,借此可以深入研究该夹杂物的电化学行为。实验结果表明,增加HNO3浓度虽然导致阴极电流效率略微下降,但可有效减少氯的夹杂量。在硝酸体系中电解精炼高纯铜的最佳条件是:HNO3浓度为1~2 mol/L,适宜的温度约为35 °C,电流密度不超过25 mA/cm2。在理论研究的基础上,模拟工业电解设计铜电解精炼优化实验,得到氯含量低于1 μg/g的高纯铜,且电流效率大于90%。
Abstract: A practical approach was introduced to study the inclusion mechanism of chlorine in high purity copper electrorefining from nitric acid system via cyclic voltammetry (CV) combined with electrodeposition experiments. The CV curves display an obvious reduction peak of CuCl intermediate, which can provide an insight into the electrochemical behavior of this inclusion. Experimental results show that the increase of HNO3 concentration is favorable to reducing the quantity of chlorine inclusion although there is a slight decline in cathodic current efficiency. The optimum conditions for copper electrorefining in nitric acid system are HNO3 concentration in solution of 1-2 mol/L, moderate temperature of ~35 °C with current density not exceeding 25 mA/cm2. Based on the theoretical studies, an optimized copper electrorefining experiment was designed to simulate the industrial electrolysis, by which high purity copper can be obtained with chlorine inclusion less than 10 μg/g and current efficiency higher than 90%.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 30(2020) 1387-1396
Hua-zhen CAO, Wen-yu FENG, Hui-bin ZHANG, Guo-qu ZHENG
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310014, China
Received 16 August 2019; accepted 7 April 2020
Abstract: A practical approach was introduced to study the inclusion mechanism of chlorine in high purity copper electrorefining from nitric acid system via cyclic voltammetry (CV) combined with electrodeposition experiments. The CV curves display an obvious reduction peak of CuCl intermediate, which can provide an insight into the electrochemical behavior of this inclusion. Experimental results show that the increase of HNO3 concentration is favorable to reducing the quantity of chlorine inclusion although there is a slight decline in cathodic current efficiency. The optimum conditions for copper electrorefining in nitric acid system are HNO3 concentration in solution of 1-2 mol/L, moderate temperature of ~35 °C with current density not exceeding 25 mA/cm2. Based on the theoretical studies, an optimized copper electrorefining experiment was designed to simulate the industrial electrolysis, by which high purity copper can be obtained with chlorine inclusion less than 10 μg/g and current efficiency higher than 90%.
Key words: copper electrorefining; nitric acid system; cuprous chlorine; inclusion mechanism
1 Introduction
Presently, high purity copper has attracted more and more attention due to its excellent conductivity, thermal conductivity and other properties [1,2], which endows it a wide use in many fields, including various metal targets, advanced audio cables, integrated circuit interconnects [3] and thin-film solar cells [4], etc. The preparation methods of high purity copper mainly include electrorefining (ER) [5], floating zone refining [6] and directional solidification [7]. Among these methods, electrorefining has been the most widely used method currently.
For the electrolysis technology, the common used electrolytes include sulfuric acid system and nitric acid system [8]. The preparation of high purity copper by sulphate electrolysis is a relatively mature technology. However, the sulfide ore used to produce sulfuric acid and copper sulfate is often accompanied by a variety of other impurities, such as Ag, As, Sb and Bi [9-12]. As a result, the content of impurities in sulfuric acid is 4-5 times higher than that of the same grade of synthetic nitric acid. Accordingly, the electrolyte prepared with sulfuric acid and copper sulfate is bound to contain more impurities and complicated operations for purification are unavoidable to remove these impurities before electrorefining [13-15]. At the same time, sulfur is easy to form compounds with copper, which are included in products, therefore, this method is difficult to meet the high purity requirements [16]. On the contrary, nitric acid system usually has a high purity. Moreover, copper nitrate as the electrolyte is beneficial to the oxidation of As, Sb and Bi into high-valent ions, which can effectively prevent them from precipitation on the cathode. More importantly, unlike sulfuric acid electrolyte, the nitrogen will not enter the products in nitric acid system. So, many researchers have paid much attention to the electrorefining of high purity copper from nitric acid system [17].
In our prior studies of preparing high purity copper from nitric acid system, we found that the content of most impurities was up to the standard except the chlorine, which exceeded almost 10 times of the standard level. That is to say, the nitric acid system is sensitive to chlorine. The chlorine in electrolyte mainly originates from two aspects. On one hand, Cl- is added purposely as an additive [18], which can effectively promote the dissolution of anode copper, thereby help to maintain the stability of electrolyte composition. On the other hand, the anode copper may also contain certain chlorine, which will be released to the electrolyte during electrolysis. SOARES et al [19] have given an explanation of the cathodic behavior of chlorine in sulfuric acid system, suggesting that chlorine can combine with copper to form cuprous chloride. While for the nitric acid system, there were no reports on the role of chlorine during electrorefining and systematical discussion on potential factors that would result in the chlorine inclusion.
This study aimed to investigate the cathodic behavior of chlorine in copper electrorefining from the nitric acid system and revealed the main influential factors, thus providing an efficient way to control the chlorine level in high purity copper. In order to achieve this, cyclic voltammetry was adopted to study the process of copper deposition under different conditions in the presence of chlorine, and discuss the inclusion mechanism of chlorine in the Cu layer. Combined with the electrodeposition experiments, the exact effects of chloride ion concentration, temperature, HNO3 concentration and current density on the chlorine content in products were investigated.
2 Experimental
2.1 Chemicals
All reagents used in this study were purchased from Aladdin (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., China: copper nitrate hydrate (Cu(NO3)2·3H2O, electronic grade, 99.99 wt.%), nitric acid (HNO3, electronic grade, 70 wt.%) and sodium chloride (NaCl, electronic grade, 99.99 wt.%. All aqueous solutions were prepared using ultrapure water obtained from a Millipore Milli-Q system with resistivity higher than 18 MΩ·cm.
2.2 Electrochemical measurements
The cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves were measured on a CHI660C electrochemical work- station (CH Instrument, Shanghai, China) using glassy carbon electrode (GCE, exposed area of 12.566 mm2) as working electrode, platinum plate as counter electrode (exposed area of 2.0 cm2) and saturated calomel electrode (SCE) as reference electrode. Before each test, the glassy carbon electrode was mechanically polished using 0.05 μm alumina polishing agent. The platinum electrode was washed with a piranha solution prepared by mixed H2SO4 and H2O2 in a volume ratio of 3:1 [20].
In CV study, the concentration of Cu(NO3)2 in electrolyte was controlled to be 0.1 mol/L, Cl- concentration ranged from 0 to 1 g/L. HNO3 concentration was controlled to be 0.03-4 mol/L. The potential was swept negatively from 0.5 to -0.9 V at a scan rate of 0.1 V/s. All tests were carried out at 20-50 °C.
2.3 Electrodeposition experiments
Electrodeposition of copper was performed in galvanostatic regime on a commercially available power supply, using the titanium sheet and copper plate (99%) as cathode and anode, respectively. The titanium sheet was polished by 400, 600, and 800 grit metallographic sandpaper, and then ultrasonically degreased in ethanol for 15 min. Finally, it was coated with Teflon in order to make the copper deposit only on the non-coated side of the titanium plate.
To get clear information on the chlorine inclusion, low concentration copper nitrate solutions with high Cl- content were employed in the CV study, which consisted of 0.1 mol/L Cu(NO3)2 and 0.03-4 mol/L HNO3 with Cl- concentration ranging from 0 to 1 g/L. The deposition time for all experiments was 2 h and the current efficiency under different conditions was calculated. The copper obtained by electro- deposition was detached from the cathode and rinsed thoroughly with distilled water. Then, it was dried in a vacuum oven and stored in a desiccator filled with Ar gas to prevent surface oxidation before measurements. In addition, electrodeposition experiments for simulating the industrial electrolysis were also conducted in electrolytes with 1 mol/L Cu(NO3)2 and low Cl- concentration of 0.1 g/L.
2.4 Characterization
The phase composition of the product was characterized by employing X-ray diffraction technique (XRD, RIGAKU D/Max 2550 PC) equipped with Cu Kα radiation (λ=1.54059 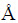 ) at 40 kV and 40 mA. The morphology and composition of the products were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, VEGA3, operated at 15 kV) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis and energy dispersive spectroscopy (Oxford EDS Inca Energy Coater 300, operated at 15 kV). Chlorine content in products prepared at high Cu2+ concentration and low Cl- concentration was characterized by ion chromatography.
) at 40 kV and 40 mA. The morphology and composition of the products were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, VEGA3, operated at 15 kV) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis and energy dispersive spectroscopy (Oxford EDS Inca Energy Coater 300, operated at 15 kV). Chlorine content in products prepared at high Cu2+ concentration and low Cl- concentration was characterized by ion chromatography.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Mechanism of chlorine inclusion
The cathodic behavior of Cl- was investigated by voltammetric and experimental studies. To get clear information on how chlorine entered the electrolytic copper and how various factors affected the inclusion of chlorine, low concentration copper nitrate solutions with high Cl- content were employed in theoretical study.
3.1.1 φ-pH diagram
φ-pH diagram of Cu2+-Cl--H2O system was made based on the thermodynamic data shown in Table 1, for the purpose of analyzing the probable reduction process of Cu2+ in acid system containing Cl-. Figure 1 demonstrates that by changing reduction potential, Cu2+ can be selectively reduced into CuCl and Cu in the range of pH<4. That is to say, the reduction of Cu2+ in this system is likely a multi-step process, involved with low-valent intermediate, i.e., CuCl.
3.1.2 Effect of Cl- on chlorine inclusion in electrolytic copper
Figure 2 presents the typical CV curves of GCE in 0.1 mol/L copper nitrate solution. For the case without Cl-, two reduction peaks are observed in the negative scanning. The weak current peak around 0 V corresponds to the underpotential reduction, while the strong peak C1 appearing at about -0.435 V is related to the reduction of Cu2+ to Cu (Eq. (1)).
Cu2++2e=Cu (1)
In the presence of Cl-, peak C1 is divided into two current peaks, C2 and C3, located at -0.450 and -0.570 V, respectively. It is noted that peak C3 is close to peak C2, both slightly negative than peak C1. Combined with the φ-pH diagram, the reduction of Cu2+ to Cu will proceed through a CuCl intermediate. Therefore, peak C2 corresponds to the reduction of Cu2+ to CuCl (Eq. (2)) and peak C3 is related to further reduction of CuCl to Cu (Eq. (3)).
Cu2++Cl-+e=CuCl (2)
CuCl+e=Cu+Cl- (3)
Some similar studies on Cu electrorefining in a sulfuric acid system have proved the existence of this cuprous intermediates [21,22]. GILEADI and TSIONSKY [23] also considered that a portion CuCl may be produced on the electrode surface via the coordination of Cu2+ and Cl-. Further reduction of intermediates CuCl leads to the appearance of peak C3; simultaneously, partial unreduced intermediates will be included by the electrolytic elementary Cu around it. Therefore, we can get some valuable information on the electrochemical behavior of intermediates CuCl in cathodic process from the evolution of peaks C2 and C3, based on which an in-depth understanding of the inclusion mechanism of chlorine can be obtained. Naturally, if the electron transfer rate of CuCl to Cu is low, excessive CuCl will be included by the rapidly produced Cu from the reduction of Cu2+.
Table 1 Reactions and their φ-pH equations in Cu2+-Cl--H2O system at 25 °C


Fig. 1 φ-pH diagram of Cu2+-Cl--H2O system

Fig. 2 CV curves of GCE in 0.1 mol/L Cu(NO3)2 solution with or without Cl- ([HNO3]=0.03 mol/L, t=25 °C)
Figure 3 shows the variation of CV curves in copper nitrate solution with different Cl- concentrations. It is noted that the peak current densities of C2 and C3 decrease sharply with the augment of Cl- concentration and their peak potentials both shift negatively. As known to all, the Cl- will combine with metal ions to produce complex species, then leading to the increase of cathodic polarization. So, with increasing the Cl- concentration, the reduction current density becomes weaker. This result further indicates the participation of Cl- in cathodic process of Cu electrorefining. Apart from this, it is noted that the potential difference Δφ between peaks C2 and C3 becomes larger with increasing the Cl- concentration, indicating that Cl- has a greater obstruction effect on the reduction of CuCl to Cu. This result reveals that more CuCl will remain in the electrolytic Cu, i.e., a high inclusion of chlorine under high Cl- concentration.

Fig. 3 CV curves of GCE in 0.1 mol/L Cu(NO3)2 solution with different Cl- concentrations ([HNO3]= 0.03 mol/L, t=25 °C)
XRD patterns of cathodic products prepared from copper nitrate system are shown in Fig. 4. The diffraction peaks denoting CuCl are clearly seen for Sample (a), which proves that the chlorine exists in copper products in the form of CuCl. It can also be seen from the XRD pattern that the presence of Cl- has an effect on the growth orientation of copper grains, making it more prone to grow along the (022) lattice plane, rather than the general (111) lattice plane.
Electrodeposition experiments were conducted to verify the role of Cl- in electrolytes on the inclusion of chlorine in electrolytic copper. Figure 5 displays the variation of chlorine content in the electrolytic copper with Cl- concentration. It can be seen from Fig. 5 that as the Cl- concentration increases, the content of chlorine in copper products increases monotonously.

Fig. 4 XRD patterns of electrolytic copper prepared from 0.1 mol/L Cu(NO3)2+0.5 mol/L HNO3 solution (t=25 °C, J=25 mA/cm2)

Fig. 5 Effect of Cl- concentration on chlorine content in electrolytic copper ([Cu(NO3)2]=0.1 mol/L, [HNO3]= 0.5 mol/L, t=25 °C, J=25 mA/cm2)
This result is consistent with the CV studies, i.e., the increase of Cl- concentration leads to more CuCl remained, which is the main source of chlorine inclusion when further reduction or dissolution of CuCl is limited. What’s more, the content of chlorine impurity in electrolytic copper increases at a large rate, for example, when it is up to 165 mg/g in the case of 1.0 g/L Cl- in electrolyte, almost 5 times as that under 0.1 g/L Cl-.
3.1.3 Effect of temperature on chlorine inclusion in electrolytic copper
Figure 6 shows the CV curves of samples at different temperatures. It can be seen that as the temperature increases, the current density peaks of C2 and C3 show an obvious increase and the peak potentials shift positively, which indicates that the two reactions can be promoted by the increased electrolysis temperature. As we know, the diffusion rate of ions in solution increases at higher temperature, which can eliminate the influence of concentration polarization and reduce the cathodic overpotential, thus making the reaction easier.

Fig. 6 CV curves of GCE in 0.1 mol/L Cu(NO3)2 solution measured at different temperatures ([HNO3]= 0.03 mol/L, [Cl-]=0.5 g/L)
However, from the comparison of peaks C2 and C3, it is noted that the increasing extents of the two current density peaks are much more different. To be specific, at a lower temperature (<30 °C), the reduction peak C2 is much higher than peak C3, i.e., the reaction of Cu2+ to CuCl is dominant under low temperatures; while for the case of higher temperature (40 °C), there is a reversal and the reduction peak C3 becomes stronger than peak C2, which indicates that the reaction of CuCl to Cu becomes significant with the increase of temperatures. The enhancement of peak C3 may result from two aspects: the fast generation of CuCl and the increased reaction rate of CuCl to Cu with temperature increment.
Figure 7 shows the effect of electrolysis temperature on the chlorine inclusion in electrolytic copper. It is observed that the temperature increment does not lead to a monotonic variation in chlorine inclusion. With the temperature rising, the content of chlorine in electrolytic copper decreases first and then reaches a minimum level at around 35 °C, after which the content of chlorine inclusion increases sharply. As mentioned above, both the generation of CuCl and the reduction of CuCl can be accelerated by the temperature increasing, which ultimately determines the quantity of chlorine inclusion. When the generation of CuCl is more dominant, it will result in the increase of chlorine in electrolytic copper. However, if the reduction of CuCl is more dominant, the fast depletion of CuCl will lead to an opposite result. From Fig. 7, it seems that the reduction of CuCl is faster than the generation of CuCl at 35 °C, so a relatively high purity copper with low chlorine content can be obtained in this condition.

Fig. 7 Effect of temperature on chlorine content in electrolytic copper ([HNO3]=1 mol/L, [Cl-]=0.5 g/L, [Cu(NO3)2]=0.1 mol/L, J=25 mA/cm2)
3.1.4 Effect of HNO3 concentration on chlorine inclusion in electrolytic copper
Figure 8 shows the CV curves at different HNO3 concentrations. An obvious inhibition effect is observed by the addition of HNO3, the cathodic current density drops and the current density peaks of C2 and C3 both have a significant shift towards negative position. This detrimental effect may be ascribed to polarization role under the strong acid condition and the strong oxidation property of HNO3, which gives rise to the oxidation and depletion of cuprous intermediate. According to the Nernst equation (Eq. (4)), the concentration decline of CuCl on cathode surface will lead to the decrease of reduction potential, i.e., the reduction potential shifts to more negative position.
 (4)
(4)
By a close comparison, it is noted that the potential difference Δφ between peaks C2 and C3 becomes larger with the HNO3 concentration increasing, which indicates that the dissolution effect of HNO3 on CuCl intermediate is much stronger, leading to a more negative deviation of C3. That is to say, the addition of HNO3 is favorable to reducing the quantity of CuCl intermediate and then limiting the chlorine inclusion.

Fig. 8 CV curves of GCE in 0.1 mol/L Cu(NO3)2 solution with different HNO3 concentrations ([Cl-]= 0.5 g/L, t=25 °C)
Figure 9 shows the influence of HNO3 concentration on the chlorine content in electrolytic copper as well as the corresponding current efficiency. It is clearly seen that the increment of HNO3 concentration leads to a sharp decrease of chlorine content in electrolytic copper (Fig. 9(a)), that is, HNO3 really has a positive role for the control of chlorine inclusion. To be specific, the quantity of chlorine in electrolytic copper is as high as 200 mg/g when the electrolyte contains 0.5 g/L Cl- and low HNO3 concentration (0.03 mol/L), which decreases to a very low level (20.1 mg/g) at HNO3 concentration up to 4 mol/L. However, high HNO3 concentration will also bring to some adverse effects, for example, the current efficiency drops gradually due to its strong oxidizing property (Fig. 9(b)). But fortunately, the current efficiency still maintains a relatively high level (>80%) at HNO3 concentration of 4 mol/L. By comprehensive consideration of the chlorine inclusion and the cathodic current efficiency, the favorable concentration of HNO3 is 1-2 mol/L.
3.1.5 Effect of current density on chlorine inclusion in electrolytic copper
Current density is also an important factor that influences the inclusion of chlorine. The experimental results of chlorine content in electrolytic copper under different current densities are presented in Fig. 10. As the current density increases, the content of chlorine in the products increases sharply. When the current density is 30 mA/cm2, the quantity of chlorine impurity is 180 mg/g, almost three times of that prepared at 15 mA/cm2. The reduction of Cu2+ to CuCl and CuCl to Cu occurs simultaneously, large current density accelerates the two reaction rates, but a portion of unreduced CuCl will be included by the rapidly generated Cu around it. Judging from the rapid increase of chlorine impurity with current density augment, the reduction rate of CuCl is slower than the generation rate of it, and this difference is particularly prominent under high current density. So, large current density is disadvantageous for the control of chlorine inclusion.

Fig. 9 Chlorine content in electrolytic copper (a) and corresponding current efficiency (b) under different HNO3 concentrations ([Cl-]=0.5 g/L, [Cu2+]=0.1 mol/L, t=25 °C)

Fig. 10 Relationship between chlorine content in electrolytic copper and current density ([Cu(NO3)2]= 0.1 mol/L, [Cl-]=0.5 g/L, t=25 °C)
3.2 Microstructures of electrorefined high purity copper
Figure 11 shows the EDS mapping images of the prepared electrolytic copper. It is clearly found that the copper fabricated from this system has a more obvious preferred orientation, which is in accordance with the XRD analysis in Fig. 4. At the same time, trace of chlorine is uniformly distributed in the electrolytic copper.
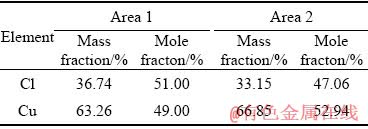
The surface morphologies of electrolytic copper are shown in Fig. 12. It is observed that many particles grow uniformly on the surface, throughout the surface of electrolytic copper. Table 2 presents the composition of the particles. As can be seen, the mole fraction of copper and chlorine in the square particles is approximate to 1:1. From this we can infer that these particles are composed of CuCl.
According to the above theoretical studies, the increase of Cl- concentration in electrolyte inevitably leads to a large quantity of chlorine inclusion. Too-high or too-low temperatures, and large current density are disadvantageous for the control of chlorine inclusion. Oppositely, the addition of HNO3 is favorable to reducing the quantity of chlorine inclusion although the cathodic current efficiency declines slightly. So, an optimized copper electrorefining experiment was designed to simulate the industrial electrolysis, in the case of 1 mol/L Cu(NO3)2 and 0.1 g/L Cl- at HNO3 concentration of 1 mol/L, electrolysis temperature of 35 °C and current density of 20 mA/cm2. For comparison, the sample under non- optimal condition was also fabricated. Figure 13 shows the SEM images of the electrolytic copper obtained under different deposition conditions. As can be seen, the quantity of CuCl particles in the product obtained under optimized condition (Fig. 13(a)) is significantly less than that of the unoptimized sample (Fig. 13(b)). This indicates that the optimized condition derived from the above study is effective for the control of chlorine inclusion in electrolytic copper. At the same time, the product obtained under the optimized condition was dissolved in nitric acid and analyzed by using ion chromatography. The result shows that the chlorine content in the product is less than 10 μg/g and the current efficiency is higher than 90%.

Fig. 11 EDS mapping images of electrolytic copper ([Cu(NO3)2]=0.1 mol/L, [Cl-]=0.5 g/L, [HNO3]=1 mol/L, t=25 °C, J= 30 mA/cm2)

Fig. 12 Surface morphologies of electrolytic copper ([Cu(NO3)2]=0.1 mol/L, [Cl-]=0.5 g/L, [HNO3]=1 mol/L, t=25 °C, J=30 mA/cm2)
Table 2 EDS data of electrolytic copper ([Cu(NO3)2]= 0.1 mol/L, [HNO3]=1 mol/L, [Cl-]=0.5 g/L, t=25 °C, J=30 mA/cm2)
4 Conclusions
(1) Inclusion mechanism of chlorine in copper electrorefining from nitric acid system was revealed by cyclic voltammetry. A distinctive reduction peak of intermediate CuCl was found during the negative scanning, which accounts for the main reason for the excessive content of chlorine.

Fig. 13 SEM images of electrolytic copper
(2) A detailed study of experimental parameters on chlorine inclusion was performed. The increase of Cl- concentration in electrolyte inevitably leads to a large quantity of chlorine inclusion, and too-high (>40 °C) or too-low (<25 °C) temperatures as well as large current densities (>25 mA/cm2) are disadvantageous for the control of chlorine inclusion. Oppositely, high nitric acid concentration can effectively reduce the chlorine content in the product although it will lead to a slight decline in cathodic current efficiency.
(3) Based on the theoretical studies, an optimized copper electrorefining experiment was designed to simulate the industrial electrolysis, which was conducted under 1 mol/L Cu(NO3)2, 0.1 g/L Cl-, 1 mol/L HNO3 with electrolysis temperature of 35 °C and current density of 20 mA/cm2. High purity copper can be prepared with chlorine inclusion less than 10 μg/g and current efficiency higher than 90%. This work thus hopefully provides an effective guideline for the industrial applications.
References
[1] KATO M. The production of ultrahigh-purity copper for advanced applications [J]. JOM, 1995, 47(12): 44-46.
[2] SHINDO Y, SHIMAMOTO S, FUKUSHIMA A. High purity copper and method of producing high purity copper based on electrolysis: US patent, 9476134 [P]. 2016-10-25.
[3] KONDO K, AKOLKAR R N, BARKEY D P, YOKOI M. Copper electrodeposition for nanofabrication of electronics devices [M]. New York: Springer, 2014.
[4] DHERE N G, GADE V S, KADAM A A, JAHAGIRDAR A H, KULKAMI S S, BET S M. Development of CIGS2 thin film solar cells [J]. Materials Science and Engineering B, 2005, 116(3): 303-309.
[5] BRUNING H, HERICY J L, LUCKE K. Production of ultra high purity copper by nitrate electrolysis and floating zone melting: General procedure and electrolytical purification [J]. Annales de Chimie—Science Des Materiaux, 1985, 10(2): 121-133.
[6] ZHU Y, MIMURA K, ISHIKAWA Y. Effect of floating zone refining under reduced hydrogen pressure on copper purification [J]. Materials Transactions, 2002, 43(11): 2802-2807.
[7] FU Ya-bo, CHEN Jie, LIU Ning, LU Yi-ping, LI Ting-ju, YIN Guo-mao. Study of ultrahigh-purity copper billets refined by vacuum melting and directional solidification [J]. Rare Metals, 2011, 30(3): 304-309.
[8] LIU Lin-hai, TAN Ding-sheng. Preparation methods of ultrahigh pure copper and their applications [J]. Shanghai Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 25(2): 60-64. (in Chinese)
[9] HAN Jun-wei, XIAO Jun, QIN Wen-qing, CHEN Dai-xiong, LIU Wei. Copper recovery from Yulong complex copper oxide ore by flotation and magnetic separation [J]. JOM, 2017, 69(9): 1563-1569.
[10] FORSEN O, AROMAA J, LUNDSTROM M. Primary copper smelter and refinery as a recycling plant—A system integrated approach to estimate secondary raw material tolerance [J]. Recycling, 2017, 2(4): 19-29.
[11] BAMPOLE D L, PATRICIA L, MULABA-BAFUBIANDI A F. Sustainable copper extraction from mixed chalcopyrite– chalcocite using biomass [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(10): 2170-2182.
[12] WANG Xue-wen, CHEN Qi-yuan, YIN Zhou-lan, WANG Ming-yu, XIAO Bing-rui, ZHANG Fan. Homogeneous precipitation of As, Sb and Bi impurities in copper electrolyte during electrorefining [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 105(3): 355-358.
[13] SALARI K, HASHEMIAN S, BAEI M T. Sb (V) removal from copper electrorefining electrolyte: Comparative study by different sorbents [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(2): 440-449.
[14] SHABANI A, HOSEINPUR A, YOOZBASHIZADEH H, KHAKI J V. As, Sb, and Fe removal from industrial copper electrolyte by solvent displacement crystallisation technique [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2019, 58(3): 253-261.
[15] XIAO Fa-xin, ZHENG Ya-jie, WANG Yong, XU Wei, LI Chun-hua, JIAN Hong-sheng. Novel technology of purification of copper electrolyte [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(5): 1069-1074.
[16] FRANCO E, LOPEZ-TORRES E, MENDIOLA M A, SEVILLA M T. Synthesis, spectroscopic and cyclic voltammetry studies of copper (II) complexes with open chain, cyclic and a new macrocyclic thiosemicarbazones [J]. Polyhedron, 2000, 19(4): 441-451.
[17] CHOI J Y, KIM D S. Production of ultrahigh purity copper using waste copper nitrate solution [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2003, 99(2): 147-158.
[18] IILHCHI M O, YOOZBASHIZADEH H, SAFARZADEH M S. The effect of additives on anode passivation in electrorefining of copper [J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 2007, 46(8): 757-763.
[19] SOARES D M, WASLE S, WEIL K G, DOBLHOFER K. Copper ion reduction catalyzed by chloride ions [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2002, 532(1): 353-358.
[20] LO Y S, HUEFNER N D, CHAN W S, STEVENS F, HARRIS J M. Organic and inorganic contamination on commercial AFM cantilevers [J]. Langmuir, 1999, 15(19): 6522-6526.
[21] VEREECKEN P M, BINSTEAD R A, DELIGIANNI L, ANDRICACOS P C. The chemistry of additives in damascene copper plating [J]. IBM Journal of Research and Development, 2005, 49(1): 13-18.
[22] SCHMIDT R, GAIDA J. Cuprous ion mass transport limitations during copper electrodeposition [J]. Chem Electro Chem, 2017, 4(8): 1849-1851.
[23] GILEADI E, TSIONSKY V. Studies of electroplating using an EQCM. I: Copper and silver on gold [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2000, 147(2): 567-574.
曹华珍,冯闻宇,张惠斌,郑国渠
浙江工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,杭州 310014
摘 要:通过循环伏安法和电沉积实验研究硝酸体系电解精炼高纯铜过程中氯的夹杂机制。CV曲线中存在明显中间产物CuCl的还原峰,借此可以深入研究该夹杂物的电化学行为。实验结果表明,增加HNO3浓度虽然导致阴极电流效率略微下降,但可有效减少氯的夹杂量。在硝酸体系中电解精炼高纯铜的最佳条件是:HNO3浓度为1~2 mol/L,适宜的温度约为35 °C,电流密度不超过25 mA/cm2。在理论研究的基础上,模拟工业电解设计铜电解精炼优化实验,得到氯含量低于1 μg/g的高纯铜,且电流效率大于90%。
关键词:铜电解精炼;硝酸体系;氯化亚铜;夹杂机制
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (LY17B030009) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China
Corresponding author: Guo-qu ZHENG; E-mail: zgq003047@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65304-3

