退火温度对淬火后冷轧5083铝合金组织及腐蚀性能的影响
罗兵辉,单毅敏,柏振海
(中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:采用金相显微镜、电镜、慢应变拉伸、阳极极化及交流阻抗测试研究退火温度对淬火后冷轧5083铝合金耐蚀性的影响。研究结果表明:冷轧后在100 ℃和150 ℃退火40 min的5083铝合金仍呈变形组织特征,在局部变形区呈现连续分布的β相(Mg5Al8),合金具有较强应力腐蚀敏感性和较弱的耐点蚀能力;在200 ℃和250 ℃退火40 min 后的合金,局部开始发生再结晶,但组织中仍包含由位错缠结而成的胞状亚组织,球状β相在晶内和晶界不连续分布,合金具有高的抗应力腐蚀和耐点蚀能力;在300 ℃和350 ℃退火40 min 的5083铝合金,为完全再结晶组织,β相又趋于连续分布,合金抗应力腐蚀和耐点蚀能力变弱。
关键词:5083铝合金;退火;点蚀;应力腐蚀
中图分类号:TG146.21 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2007)05-0802-07
Effect of annealing temperature on microstructure and corrosive properties of cold-rolled 5083 aluminum alloy after quenching
LUO Bing-hui, SHAN Yi-min, BAI Zhen-hai
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Metallography, electron microscope, slow strain testing(SSRT), potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy(EIS) were used to study the effect of annealing temperature on the corrosion feature of cold-rolled 5083 aluminum alloy after quenching. It is supposed that the high stress corrosion cracking (SCC) susceptibility results from a continuous network of β-phase and along the planes of localized deformation in alloy annealed at 100 ℃ and 150 ℃ for 40 min. The high SCC resistance of the tested alloy annealed at 200 ℃ and 250 ℃ for 40 min is related to discontinuous β-phase precipitation uniformly distribute throughout the structure in a globular form due to plenty of dislocation combinated. In condition of annealing at 300 ℃ and 350 ℃ for 40 min, a continuous network of β-phase precipitates at boundaries because of the recrystal, and the stress corrosion resistance resistance and spot corrosion become weak again.
Key words: 5083 aluminum alloy; annealing; spot corrosion; stress corrosion
5083铝合金具有中等强度、较好的延伸性以及可焊性,是一种常见的船用铝合金[1-4]。而且5083铝合金是一种热处理不可强化合金,其主要强化手段有Mg原子的固溶强化以及加工硬化[4]。同时,Mg含量超过3%的5×××系铝合金在100 ℃以上稳定化退火,容易沿晶界析出β相,从而对应力腐蚀(SCC)非常敏感[1],耐点蚀能力也弱。国内外许多学者进行了应力腐蚀和电化学腐蚀的研究[4-8],如在Al-Mg合金中添加Zn,由于在晶界形成τ相(Mg32(Al,Zn)49),从而抑制β相的析出,降低SCC敏感性;电解海水产生的活性氯对铝合金的阴极和阳极电化学极化以及腐蚀行为没有明显影响,却可提高铝合金的耐点蚀能力;Al-Mg合金在不同pH值的NaCl溶液中的不同极化电位的阻抗谱不同,表明腐蚀状态不同,但大量使用工业化生产的5083铝合金热处理对其耐蚀性影响的研究较少。为此,本文作者研究变形量为60%的5083铝合金冷轧板在不同温度退火后的耐蚀性能、力学性能和组织特征。
1 实 验
1.1 材料制备
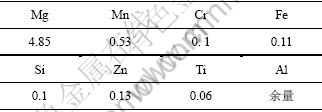
本实验采用西南铝业集团公司提供的厚度为 28 mm的5083铝合金板材,其化学成分如表1所示。
表1 5083铝合金分析成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of tested 5083 Al alloy w/%
5083铝合金在400 ℃保温1.5 h,然后经过多道次热轧至5 mm,经420 ℃/1 h固溶处理,淬火至室温,冷轧至2 mm(冷变形率为60%)。冷轧后,材料分别在100,150,200,250,300和350 ℃化退火40 min。
1.2 电化学测试
取冷轧后经不同温度退火后的片状拉伸样品,经过打磨,机械抛光,蒸馏水冲洗,无水乙醇脱脂,非工作表面用环氧树脂封涂,有效面积约1 cm2,晾干备用。交流阻抗测试在德国Thale公司的IM6e型电化学工作站上进行,扫描在开路电压下进行,频率范围为50 mHz~100 kHz,正弦度振幅为5 mV,动电位扫描测试在开路电压-0.5~0.5 mV范围内进行,扫描速度为3mV/s。本实验采用三电极测试体系,其中工作电极为待测5083合金样品,对比电极为铂电极,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE),为提高电极电位的精度,实验中引入盐桥,电解液为3.5% NaCl中性溶液。
1.3 慢应变拉伸测试
沿着轧制方向(L—T)取冷轧态以及不同温度退火40 min后的片状拉伸样品,工作部位尺寸为12 mm×3.5 mm×2 mm,在Instron 8032型电子拉伸机上进行拉伸试验,拉伸速率恒定为2.08×10-5 s-1。试验前用无水乙醇清洗试样。每种试样分为2组,分别在空气和腐蚀液(3.5% NaCl+0.5% H2O2)中拉伸,将盛装NaCl溶液的容器焊接在试样夹具上,以保证试样在整个拉伸变形过程中始终浸在腐蚀介质中。
2 实验结果及分析
2.1 电化学腐蚀
图1所示为经不同温度退火后的5083铝合金的阳极极化曲线。由图1可见,各退火温度下极化曲线均分为若干区域。如200 ℃退火后,铝电极的开路电位为EA(与腐蚀电位相当);在AB区间,电流随电位的升高逐渐增大,为铝的活性溶解区;在BC区间,电流随电位的升高几乎不变,是铝的钝化区,此时,铝合金在水溶液中会氧化,在表面形成一层电阻很大的Al2O3?H2O(即AlOOH)氧化膜,其电化学反应为[9-11]:
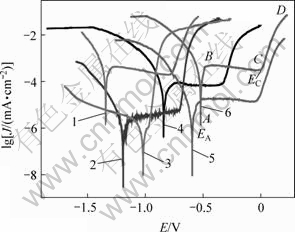
t/℃: 1—100; 2—150; 3—350; 4—300; 5—250; 6—200
图1 不同温度退火后的阳极极化曲线
Fig.1 Anodic polarization curves of 5083 alloy annealed at different temperatures
电位在C点附近是铝孔蚀诱导期;电位在CD区间,电流急剧增大,是铝电极的孔蚀阶段。因为存在Cl-,因此,在晶界等活性较高的地方容易发生溶解 反应:
AlOH+Cl-→AlOHCl+e; (4)
AlOHCl+Cl-→AlOHCl2+e。 (5)
其中:EC为铝的孔蚀电位,也就是铝电极的活化电位。经不同退火温度后,5083板材腐蚀电位如表2所示。
表2 合金经过不同温度退火后阳极极化的腐蚀电位
Table 2 Potential of 5083 alloy annealed at different temperatures
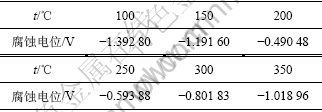
从表2可以看出,5083铝合金的腐蚀电位随着稳定化温度的升高先升高,然后下降,其中,在200 ℃退火后腐蚀电位最高,说明在200 ℃退火后耐腐蚀能力最强。
经不同温度退火后5083铝合金的交流阻抗谱如图2所示。可以看出:对于不同状态的5083铝合金,其阻抗谱都由2部分组成,即虚线上方高频的容抗弧和虚线下方低频的感抗弧。高频的容抗弧是因为形成了氧化膜覆盖在铝电极的表面,体现了氧化膜电阻的大小;低频的感抗弧是因为Cl-吸附在铝电极表面,氧化膜破坏的程度增大,表面发生了孔蚀,从而氧化膜变得不完整而产生的。膜电阻越大,电荷越难通过,耐腐蚀能力越强[11]。容抗弧的电阻R在退火温度为200~250 ℃时最高,说明合金的抗腐蚀能力在该退火温度范围内最强。
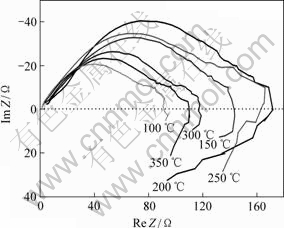
图2 不同温度退火后的交流阻抗谱
Fig.2 Impedance spectra of 5083 alloy annealed at different temperatures
2.2 金相组织及再结晶
对冷轧后分别经过100,250和350 ℃退火后的样品进行金相观察,其显微组织如图3所示。在100 ℃退火40 min后,晶粒明显沿轧制方向伸长变形(图3(a));经250 ℃退火40 min后,沿轧制方向还有很多伸长的晶粒,但开始出现再结晶晶粒(图3(b));经350 ℃退火40 min后,几乎全为再结晶晶粒(图3(c))。说明随着退火温度的升高,再结晶的程度增加,在250 ℃附近开始发生再结晶。

(a) 100 ℃;(b) 250 ℃;(c) 350 ℃
图3 不同温度退火后5083铝合金的显微组织
Fig.3 Microstructure of 5083 Al alloys annealed at different temperatures
冷轧态和不同温度退火后样品的拉伸性能如图4 所示。

图4 不同状态5083铝合金的屈服强度、抗拉强度和延伸率ε
Fig.4 Yield stress, ultimate tensile strength and total elongation of 5083 alloy under different conditions
从图4可以得出,冷轧后的样品随着退火温度的升高,屈服强度和抗拉强度不断降低,延伸率不断升高,当退火温度从250 ℃上升到300 ℃时,屈服强度和抗拉强度下降幅度很大,塑性上升程度很高,据此可认为在250 ℃开始发生再结晶。
2.3 应力腐蚀
设样品在空气中的延伸率为εa,在腐蚀液中的延伸率为εs,不同温度退火后样品在空气中和腐蚀液中的延伸率如表3所示。用延伸率的损失量εl表示应力腐蚀敏感性:εl=(εa-εs)/εa。εl越小,SCC敏感性越小;εl越大,SCC敏感性越大。冷轧态和不同温度退火后的样品的应力腐蚀敏感性如图5所示。冷轧后的样品具有最高的应力腐蚀敏感性(80%),100 ℃和150 ℃退火后应力腐蚀敏感性仍然较高(59%~65%),200 ℃和250 ℃退火后应力腐蚀敏感性较低(5%~8%),然后,随着退火温度的升高,应力腐蚀敏感性增大,300 ℃和350 ℃退火后回到较高值(40%~46%)。
表3 合金经过不同温度退火后在空气和腐蚀液中的延伸率
Table 3 Elongation of 5083 alloy under different conditions
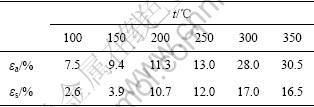

图5 不同状态的5083铝合金的延伸率的损失量
Fig.5 Loss of elongation for 5083 alloy under different conditions
对200,250和350 ℃退火后的样品在空气及腐蚀介质中拉伸断口进行电镜观察,结果如图6~8所示。

(a) 空气中;(b) 腐蚀液中
图6 100 ℃退火后样品的拉伸断口形貌
Fig.6 Fracture micrographs of 5083 alloy annealed at 100 ℃
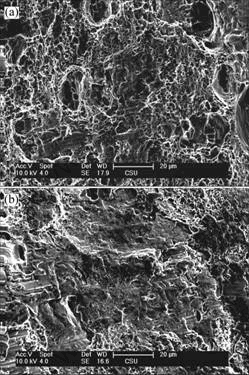
(a) 空气中;(b) 腐蚀液中
图7 250 ℃退火后样品的拉伸断口形貌
Fig.7 Fracture micrographs of 5083 alloy annealed at 250 ℃
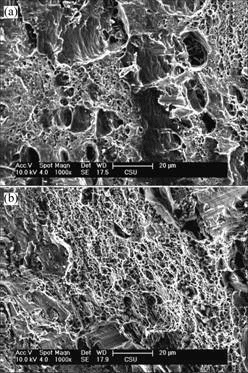
(a) 空气中;(b) 腐蚀液中
图8 350 ℃退火后样品的拉伸断口形貌
Fig.8 Fracture micrographs of 5083 alloy annealed at 350 ℃
在空气中拉伸的样品塑性较好,以韧性断裂为主;在NaCl 溶液中拉伸的样品塑性较差,以脆性断裂为主。按照氢脆断裂机制[12-17],金属浸泡在腐蚀液中时,由于金属表面成分有差异,在某些部位优先溶解,从而产生微裂缝,在裂缝中由于腐蚀液成分的变化,如氯离子浓度升高使缝隙活化,这些裂缝往往是断裂发生的优先部位。在腐蚀介质中拉伸变形时,裂缝扩展暴露出来的新鲜铝合金表面与环境中的水发生如下电化学反应[16-17]:
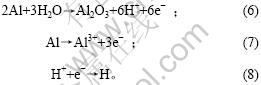
这样形成的氢原子具有活性,通过吸附、扩散输送到材料内部,沿晶界优先偏聚,导致氢脆。在2.08× 10-5 s-1的应变速率下,试样有较长的时间与介质发生反应,从而能吸收足够的氢原子,导致SCC敏感性 加大。
在5083铝合金中,β相的电极电位和α固溶体相比较低(β相的腐蚀电位为-1.15 V,α固溶体的腐蚀电位为-0.82 V[1]),在腐蚀液中为阳极而优先腐蚀。5083铝合金经过100 ℃退火后,因为退火温度低,β相只能在某些能量高的局部区域(如晶界)发生形核长大,在这些区域β相呈连续分布(图9(a)),故合金耐蚀性较弱;250 ℃退火态的5083铝合金,开始发生再结晶,因为退火温度较高,且组织中存在大量的位错(图9(b)),β相在整个合金组织中(如晶界,晶内位错缠结处)均能形核,此时,球状的β相在晶界和晶内呈弥散分布(图9(c)),从而耐蚀性提高;350 ℃退火态的5083铝合金为完全再结晶组织,组织中晶粒变大,晶界减少,晶内位错密度大大降低,在能量较高的晶界处相邻的β相发生融合长大,从而在晶界出现粗大、连续杆状分布的β相(图9(d)),在同等腐蚀条件下,晶界由于β相存在腐蚀后脱落导致更大范围基体材料腐蚀脱落。因此,在较高的退火温度时,耐腐蚀性能反而会下降。在不同温度下,β相的形态和分布发生变化,其机理有待进一步研究。
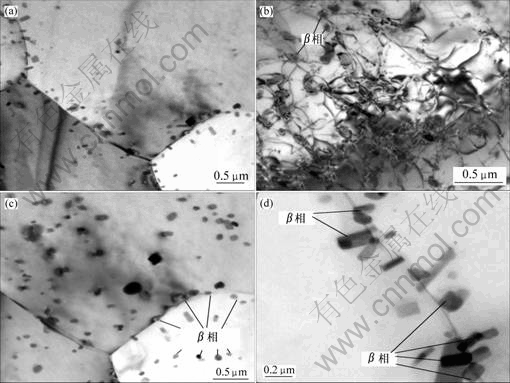
(a) 100 ℃;(b) 250 ℃;(c) 250 ℃;(d) 350 ℃
图9 不同温度退火后5083铝合金的透射电镜照片
Fig.9 TEM images of 5083 Al alloy annealed at different temperatures
3 结 论
a. 经冷变形(变形量为60%)的5083铝合金,于250 ℃退火40 min开始发生再结晶。
b. 5083铝合金在空气中拉伸以韧性断裂为主,在3.5% NaCl+0.5% H2O2溶液中拉伸以脆性断裂为主。
c. 100和150 ℃退火态的5083铝合金,β相呈连续分布,耐蚀性较弱,应力腐蚀敏感性较高;200和250 ℃退火态的5083铝合金,球状的β相在晶界和晶内呈弥散分布,从而耐蚀性提高,有较强的抗应力腐蚀能力;300 ℃和350 ℃退火态的5083铝合金β相又在晶界趋于连续分布,应力腐蚀敏感性又升高。在不同温度下,β相的形态和分布发生变化,其机理有待进一步研究。
参考文献:
[1] Chang J C, Chuang T H. Stress-corrosion cracking susceptibility of the superplastically formed 5083 aluminum alloy in 3.5% NaCl solution[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transaction A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 1999, 30(12): 3191-3199.
[2] Jones R H, Baer D R, Danielson M J, et al. Role of Mg in the stress corrosion cracking of an Al-Mg alloy[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 2001, 32(7): 1699-1711.
[3] Searies J L, Gouma P I, Buchheit R G. Stress corrosion cracking of sensitized AA5083(Al-4.5Mg-1.0Mn)[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2002, 3(396/402): 1437-1442.
[4] Popovic M, Romhanji E. Stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of Al-Mg alloy sheet with high Mg content[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2002, 76(125/126): 275-280.
[5] Carroll M C, Buchheit RG, Daehn G S, et al. Optimum trace copper levels for SCC resistance in a Zn-modified Al—5083 alloy[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2002, 3(396-402): 1443-1448
[6] 王洪仁, 吴建华, 王均涛, 等. 5083铝合金在海水中的腐蚀电化学行为及活性氯影响研究[J]. 电化学, 2003, 9(1): 60-65.
WANG Hong-ren, WU Jian-hua, WANG Jun-tao, et al. Study on the corrosion and electrochemical properties of ally AA5083 and the effect of active chlorine in seawater[J]. Electrochemistry, 2003, 9(1): 60-65.
[7] Pickens J R, Gordon J R, Green J A S. Effect of loading mode on the stress-corrosion cracking of aluminum alloy 5083[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 1983, 14(5): 925-930.
[8] 宋诗哲, 唐子龙. Al-Mg合金在不同pH值的NaCl溶液中的腐蚀行为[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 1995, 7(3): 218-224.
SONG Shi-zhe, TANG Zi-long. Corrosion behavior of Al-Mg alloys in NaCl solutions with variation of pH[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 1995, 7(3): 218-224.
[9] 宋诗哲, 唐子龙. 工业纯铝在3.5%NaCl溶液中的电化学阻抗谱分析[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护技术, 1996, 16(2): 127-132.
SONG Shi-zhe, TANG Zi-long. Electrochemical impedance spectroscope of aluminum in 3.5% NaCl solution[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 1996, 16(2): 127-132.
[10] Jones R H, Vetrano J S, Windisch Jr. Stress corrosion cracking of Al-Mg and Mg-Al alloys[J]. Corrosion, 2004, 60(12): 1144-1154.
[11] 许 刚, 曹楚南, 林海潮, 等. 纯铝在NaCl溶液中活化溶解时电化学行为研究[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 1998, 10(6): 321-326.
XU Gang, CAO Chu-nan, LIN Hai-chao, et al. Electrochemical study of active dissolution for aluminum in neutral NaCl solution[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 1998, 10(6): 321-326.
[12] 张新明, 龚敏如, 李慧中, 等. 2519铝合金薄板在不同时效状态的抗晶间腐蚀能力[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 35(3): 349-352.
ZHANG Xin-ming, GONG Min-ru, LI Hui-zhong. Effect of ageing tempers of aluminium alloy 2519 sheet on intergranular corrosion[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2004, 35(3): 349-352.
[13] Burleigh T D. The postulated mechanisms for stress corrosion cracking of aluminum alloys: A review of the literature 1980-1989[J]. Corrosion, 1991, 47(2): 89-98.
[14] 张新明, 吴文祥, 刘胜胆, 等. 退火过程中AA3003铝合金的析出与再结晶[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 37(1): 1-5.
ZHANG Xin-ming, WU Wen-xiang, LIU Sheng-dan, et al. Precipitation and recrystallization of AA3003 aluminum alloy during annealing[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2006, 37(1): 1-5.
[15] 巩伟杰. LC4铝合金应力腐蚀与腐蚀疲劳特性研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学航天与材料工程学院, 2002.
GONG Wei-jie. The stress corrosion cracking and corrosion fatigue of LC4 characteristics high pure high aluminum alloy[D]. Changsha: College of Aerospace and Material Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, 2002.
[16] 罗兵辉, 柏振海, 谢绍俊, 等. 铸造铝镁合金的应力腐蚀[J]. 中南工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 1998, 29(6): 570-572.
LUO Bing-hui, BO Zhen-hai, XIE Shao-jun, et al. The stress corrosion of casting Al-Mg alloy[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology: Natural Science, 1998, 29(6): 570-572.
[17] 褚武扬. 氢损伤和滞后断裂[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1988: 131-143.
ZHU Wu-yang. Hydrogen damage and delayed fracture[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1988: 131-143.
收稿日期:2007-03-12;修回日期:2007-04-30
基金项目:国家“十一五”科技军工配套项目(JPPT―115―2024)
作者简介:罗兵辉(1965-),男,湖南浏阳人,教授,博士,从事耐蚀材料研究
通信作者:罗兵辉,男,教授,博士;电话:0731-8830333(O);E-mail: lbh@mail.csu.edu.cn