骨组织工程用可降解多孔含银镁基支架的合成及体外性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第5期
论文作者:Hamid Reza BAKHSHESHI-RAD Ehsan DAYAGHI Ahmad Fauzi ISMAIL Madzlan AZIZ Ali AKHAVAN-FARID Xiongbiao CHEN
文章页码:984 - 996
关键词:镁基支架;生物相容性;抗菌活性;生物活性;腐蚀行为
Key words:Mg-based scaffold; biocompatibility; antibacterial activities; bioactivity; corrosion behavior
摘 要:感染是骨损伤临床治疗中常见的并发症。镁基复合材料是一种可生物降解的抗菌生物材料,已被用于减少术后感染。本文作者合成含银镁基骨组织工程支架材料,并对其进行体外表征。通过造孔剂法制备4种不同银含量(0、0.5、1、和2 wt.%) 的多孔镁基支架,用Mg-Ca-Mn-Zn-xAg (MCMZ-xAg)表示,其中x表示银含量。研究银含量对材料的孔隙结构、力学性能、生物活性和抑菌区的影响。采用X射线衍射分析(XRD)、扫描电镜(SEM)、透射电镜(TEM)和荧光显微镜对支架进行表征。体外腐蚀试验结果表明,银含量低的支架比银含量高的支架具有更好的耐腐蚀性。抗菌活性的检测结果表明MCMZ-Ag 支架具有显著抑制大肠杆菌和(E. coli) 和金黄 色葡萄球菌(S. aureus)生长的作用,且随着含银量的增加,MCMZ-Ag 支架周围的抑菌区面积逐渐增加。然而,含银量过高会增加材料的细胞毒性。总之,含0.5 wt.% Ag的支架因其具有连通的孔隙、足够的力学性能、抗菌活性和细胞黏附性能,在修复与替换受损和患病骨方面具有应用前景。
Abstract: Infection is a major potential complication in the clinical treatment of bone injuries. Magnesium (Mg)-based composites are biodegradable and antibacterial biomaterials that have been employed to reduce infection following surgical implants. The aim of present study was to synthesize and in-vitro characterize Mg-based scaffolds containing silver for bone tissue engineering. Porous Mg-based scaffolds with four silver concentrations (i.e., 0, 0.5 wt.%, 1 wt.%, and 2 wt.%), denoted by Mg-Ca-Mn-Zn-xAg (MCMZ-xAg) (where x is the silver concentration), were fabricated by the space holder technique. The effects of silver concentration on pore architecture, mechanical properties, bioactivity, and zone of bacterial inhibition were investigated in-vitro. X-ray diffractometry (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and fluorescence microscopy were utilized to characterize the obtained scaffolds. In-vitro corrosion test results indicated that the MCMZ scaffolds with lower silver content were more resistant to corrosion than those enriched with higher amounts of silver. Examination of the antibacterial activity showed that the MCMZ-Ag scaffolds exhibited superb potential with respect to suppressing the growth of Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), in the inhibition zone around the MCMZ-Ag scaffolds, with increasing in the amount of incorporated silver; however, higher amounts of silver increased the cytotoxicity. Taken together, the results of this study demonstrate that the porous 0.5 wt.% Ag-containing scaffolds with interconnected pores, adequate mechanical properties, antibacterial activity, and cell adhesion are promising with respect to the repair and substitution of damaged and diseased bones.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 984-996
Hamid Reza BAKHSHESHI-RAD1,2,5, Ehsan DAYAGHI1, Ahmad Fauzi ISMAIL2, Madzlan AZIZ2, Ali AKHAVAN-FARID3, Xiongbiao CHEN4,5
1. Advanced Materials Research Center, Department of Materials Engineering, Najafabad Branch, Islamic Azad University, Najafabad, Iran;
2. Advanced Membrane Technology Research Center (AMTEC), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor Bahru, Johor, Malaysia;
3. Department of Mechanical, Materials and Manufacturing Engineering, University of Nottingham Malaysia Campus, 43500 Semenyih, Malaysia;
4. Division of Biomedical Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada;
5. Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Received 30 July 2018; accepted 25 March 2019
Abstract: Infection is a major potential complication in the clinical treatment of bone injuries. Magnesium (Mg)-based composites are biodegradable and antibacterial biomaterials that have been employed to reduce infection following surgical implants. The aim of present study was to synthesize and in-vitro characterize Mg-based scaffolds containing silver for bone tissue engineering. Porous Mg-based scaffolds with four silver concentrations (i.e., 0, 0.5 wt.%, 1 wt.%, and 2 wt.%), denoted by Mg-Ca-Mn-Zn-xAg (MCMZ-xAg) (where x is the silver concentration), were fabricated by the space holder technique. The effects of silver concentration on pore architecture, mechanical properties, bioactivity, and zone of bacterial inhibition were investigated in-vitro. X-ray diffractometry (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and fluorescence microscopy were utilized to characterize the obtained scaffolds. In-vitro corrosion test results indicated that the MCMZ scaffolds with lower silver content were more resistant to corrosion than those enriched with higher amounts of silver. Examination of the antibacterial activity showed that the MCMZ-Ag scaffolds exhibited superb potential with respect to suppressing the growth of Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), in the inhibition zone around the MCMZ-Ag scaffolds, with increasing in the amount of incorporated silver; however, higher amounts of silver increased the cytotoxicity. Taken together, the results of this study demonstrate that the porous 0.5 wt.% Ag-containing scaffolds with interconnected pores, adequate mechanical properties, antibacterial activity, and cell adhesion are promising with respect to the repair and substitution of damaged and diseased bones.
Key words: Mg-based scaffold; biocompatibility; antibacterial activities; bioactivity; corrosion behavior
1 Introduction
Throughout the history of biomedical engineering, finding an alternative material for repairing bone defects has been a critical issue [1-3]. Magnesium (Mg) has drawn much attention as a bone substitute material due to its biodegradability, biocompatibility, and appropriate mechanical properties [4,5]. These unique properties of Mg have motivated many scientists to explore Mg-based materials for various biomedical applications, including bone tissue regeneration by means of Mg-based implants or scaffolds [6-9]. Notably, Mg-based alloys have a poor antibacterial behavior, which has limited their applications [10,11]. For example, previous studies have shown that premature failure of implants happens owing to the bacterial infection on the surface of implants, which is apt for bacterial adhesion and colonization [12]; that implant-associated infection has a risk (up to 23%) of serious fractures [13]; and that infection takes place in both the beginning stage of implantation and the whole service lifetime of implants [14]. This raises a great need to improve the antibacterial behavior of Mg-based implants [15]. For this, the antibacterial behavior of metals such as silver (Ag), titanium (Ti), zinc (Zn), gold (Au), and copper (Cu) has been employed in previous studies [11,16]. Metallic Ag, as a main reinforcement element in nanoparticles, has also offered remarkable resistance and is regarded as a vigorous antimicrobial agent [17,18].
The present study aimed to develop scaffolds based on Mg with the addition of Ca, Mn, and Zn, with a focus on identifying the influence of the addition of Ag on scaffold performance in terms of mechanical properties and antimicrobial activity [19]. Silver additives deliver antimicrobial activity to materials at relatively low concentrations, and are widely used in the textile industry and in plastic medical devices where antibacterial properties are required [20]. In addition to the inherent qualities of Ag as an anti-infective element, it has biomedical functions in the form of nanoparticles and can increase the mechanical strength of Mg scaffolds through the formation of a fine Mg-Ag phase [21]. Some strains of bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) can be easily suppressed by Ag nanoparticles [20,21]. The antibacterial characteristics of Ag result from a mechanism that alters the permeability of the bacterial outer cell membrane [10]. Some researchers maintain that silver nanoparticles can inhibit bacterial cell growth by inducing pits and gaps in the cell membrane [8]. The scaffolds to be considered herein contain Ca, which is an abundant element in the chemical composition of natural bone and can act in signal transduction [9,22]. The co-existence of Ca and Mg accelerates bone healing due to the simultaneous release of Ca and Mg ions [9,23]. Moreover, the addition of Ca to Mg with a maximum solubility of 1.34 wt.% can improve the mechanical strength through the formation of Mg2Ca precipitate in the α (Mg) phase and grain refinement of Mg [3]. Manganese (Mn) also enhances the mechanical stability of Mg via grain size refinement [8,9].
Porous scaffolds act as a template that guides the bone cells into pores to proliferate and differentiate to regenerate damaged bones. They also serve as a platform for drug delivery and body fluid transformation. The use of space holders to generate pores is an effective method for fabricating porous scaffolds [24,25]. Heat treatment burns out the space holder particles and sinters the metal compact into a porous scaffold. Pore size and porosity can be adjusted via the size and content of the space holder, respectively [1,17,26]. To the best of our knowledge, minimal research has been conducted on Mg-based scaffolds containing various amounts of silver. Here, porous scaffolds based on Mg, Ca, Mn, and Zn were created with the space holder method with Ag added in amounts ranging from 0 to 2 wt.%, and their performances were evaluated. Specifically, the effects of silver concentration on pore architecture, mechanical properties, bioactivity, and zone of bacterial inhibition were investigated.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and preparation
Powdered Mg (purity ≥99%, particle size 5-20 μm), Ag (99.5% purity, particle size ≤10 μm), Mn (99.8% purity, particle size ≤50 μm), Zn (99.8% purity, particle size ≤80 μm), and Ca (99% purity, granular size ≤1 cm) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and used as precursors. Spherical carbamide (Co(NH2)2) particles with a size of 600-800 μm (Sigma- Aldrich) were used as the space holders to fabricate the porous scaffolds. The mixture of MCMZ-xAg particles was prepared based on 1 wt.% Mn, 1 wt.% Ca, and 6 wt.% Zn, with Ag content ranging from 0 to 2 wt.%. The composite powder samples were then dried in a vacuum drying oven under an argon atmosphere at 220 °C for 2 h. To ensure fine powder mixing and particle size reduction, the samples were ground under argon gas in a planetary ball mill at 600 r/min for 5 h in a zirconia vial with a ball/powder mass ratio of 10:1 and zirconia balls with diameters of 5 and 10 mm. To generate the pore network, the composite powder samples and carbamide particles were manually mixed at a mass ratio of 60:40 to obtain homogeneity porous scaffolds. For better distribution of particles, a small amount of ethanol (2 wt.%) was added during the mixing process as a binder. The homogenous mixed powders were uniaxially compacted in a die at a pressure of 200 MPa and a crosshead speed of 2.0 mm/min into cylindrical green scaffolds with a diameter of 10 mm and a height of 15 mm. The final sintering operation was performed in two steps in a tube furnace under a high purity argon gas atmosphere: 180 °C for 2 h to remove the carbamide particles from the green compacts, then 580 °C for 2 h to increase the metallurgical bonding between composite powders (Scheme 1).
The porosity of composite scaffolds was evaluated based on the Archimedes principle. Specifically, Equation (1) represents the density (ρ) of MCMZ-xAg scaffolds in which the mass fraction (%) of Ag varies from 0 to 2, and Eq. (2) gives the total porosity (P) of porous scaffolds.
ρ=wMgρMg+wZnρZn+wCaρCa+wMnρMn+wAgρAg (1)
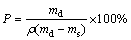 (2)
(2)
where wMg, wZn, wCa, wMn and wAg are mass fractions (%) of Mg, Zn, Ca, Mn and Ag, respectively; md and ms are the mass of sample in dry and water saturated conditions, respectively. For example, ρ has a value of 2.206 g/cm3 for MCMZ-1Ag.
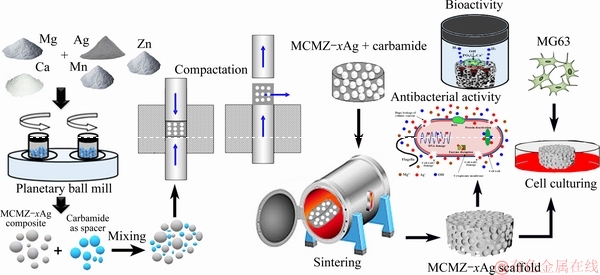
Scheme 1 Space holder method for synthesizing articulated structures
2.2 Mechanical properties
Mechanical properties were characterized by using compression tests performed at room temperature (Instron-569) using a cell with a load of 10 kN. The scaffolds were pressed along their long axes at a rate of 0.2 mm/min. At least three scaffolds of each type were examined to assess the reproducibility of test results.
2.3 In vitro corrosion behavior
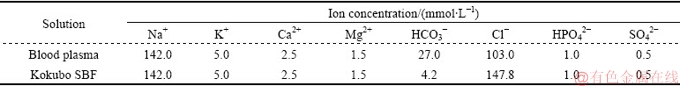
The corrosion rate of the Mg-based composite scaffolds was investigated using the electrochemical technique. The electrochemical cell consisted of Mg-based samples with a surface exposure of 0.5 cm2 as the working electrode, a platinum wire as the counter electrode, and saturated calomel as the reference electrode (SCE). The Kokubo simulated body fluid (SBF) solution with a pH of 7.44 was prepared by dissolving the reagents NaCl, NaHCO3, KCl, K2HPO4·3H2O, MgCl2·6H2O, CaCl2 and Na2SO4 into distilled water, as per Ref. [27]. Chemical composition of the Kokubo SBF was listed in Table 1, as compared to the human blood plasma [27]. Scaffolds were soaked in 200 mL of the Kokubo SBF solution for 24 h and after that, were taken out from the SBF solution, rinsed with distilled water, and dried in air. The changes in pH (pH & Ion Meters S50; Camlab) of the SBF solution were also monitored during the soaking time period. The sample impedance measurements were performed using an AC impedance system (model 2263, Princeton Applied Research), in which the initial frequency and final frequency were set to be 1×105 and 1×10-2 Hz, respectively, with an AC sine wave amplitude of 10 mV, frequency per decade of 10 Hz, and delayed before integration of 1 s. For potentiodynamic polarization measurements, a starting potential of -250 mV, final potential of 1300 mV, and scan rate of 1 mV/s were used.
2.4 In vitro antibacterial activity
The antibacterial effectiveness of the scaffolds was evaluated in the inhibition zone with the bacterial counting method, where gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus, ATCC 12600) and gram-negative Escherichia coli (E. coli, ATCC 9637) were used and counted. The size of the ring that is free from bacterial colonization indicates the extension of the antibiotic properties of MCMZ scaffolds incorporating different amounts of Ag. The test was based on the disc diffusion test, with the antibiotic gentamicin (10 μg per disc) used as a positive control. The bacteria were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h and the inhibition zone around each specimen was visually inspected. For bacterial counting, samples were placed into UV-irradiation sterilized SBF and incubated at (37±0.5) °C for 24 h with a ratio of sample surface area to medium of 1.25 cm2/mL. Subsequently, bacterial suspensions were added to the sample extracts at a volume ratio of 1:9 and the samples were kept in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 for 24 h. Then, an overnight culture of E. coli and S. aureus was diluted with broth medium and the diluted bacterial suspension of 0.1 mL was plated on agar plates and spread evenly. Viable bacteria were quantified on the agar plates after being kept in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 for 24 h.
2.5 Osteoblastic cytocompatibility
A tetrazolium-based colorimetric assay (MTT) was implemented to evaluate the cytotoxicity of MCMZ scaffolds containing Ag particles. Briefly, the culture medium was added to the scaffolds (5 mg) and incubated at 37 °C for 1 and 2 d. MG-63 cells (1× 104 cell/well) were seeded on the MCMZ-xAg scaffolds. The ratio of sample surface area to medium was 1.25 cm2/mL. Then, the extracts were collected and kept in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 for various time. Afterward, the cell medium was refreshed with 1 and 2-day extracts. The medium was removed after another 24 h and 100 μL of MTT agent (0.5 mg/mL in PBS) was inoculated into each well and kept in the incubator for 4 h. After 4 h, 100 μL of DMSO was inserted to the well to dissolve the formazan crystals. Finally, the absorbance was read at 545 nm by using an ELISA reader (Stat Fax-2100, Miami, USA) and normalized by free scaffolds culture medium as a control group [28]. Nuclear staining with DAPI (4, 6-diamidino-2-phenyl indole, blue fluorescence in live cells) was conducted to study MG63 cell reproduction. The ALP activity assay was performed on the third and seventh day to assess the influence of tetracycline on the early osteogenic differentiation of M-G63 cells. The cells were seeded at a concentration of 1×104 cell/mL placed individually in a 24-well plate. The cells were left to grow for different time at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 according to Ref. [28].
Table 1 Chemical composition of Kokubo SBF as compared to human blood plasma
2.6 Morphological characterization
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM; JSM-6380LA, JOEL, Japan) was employed to study pore morphology and detect the presence of apatite on the surface of the porous structures. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM; HT7700, Hitachi, Japan) was used to evaluate the grain size and powder morphology. Oxford energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS) analysis with an operating voltage of 20 kV was employed to determine the presence of elements. An X-ray diffractometer (Siemens D 5000) was used to investigate the phase components with Cu Kα radiation (45 kV, 40 mA). The XRD traces were recorded in a 2θ range of 20°-80° at a scanning rate of 4 (°)/min.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Structural and micrographic characterization of MCMZ-xAg scaffolds
XRD patterns of mechanically alloyed MCMZ-xAg composite powders are shown in Fig. 1(a). Weak peaks are observed in the diffractograms of the MCMZ composite powder free of silver particles due to the presence of Mg2Ca and Mg2Ca6Zn3 precipitate phases. Upon the addition of silver, a peak intensity related to Ag17Mg54 is detected in addition to those of Mg2Ca and Mg2Ca6Zn3. Note that ε-Mg54Ag17 is a non-equilibrium precipitate at room temperature with an orthorhombic structure [29,30]. The TEM image in Fig. 1(b) shows MCMZ powders containing 1 wt.% Ag prepared by the solid state mechanism followed by sintering at 580 °C for 2 h. Each agglomerate has many particles smaller than 200 nm, and homogenous spherical particles with a mean size of (67 ± 2) nm can be observed.
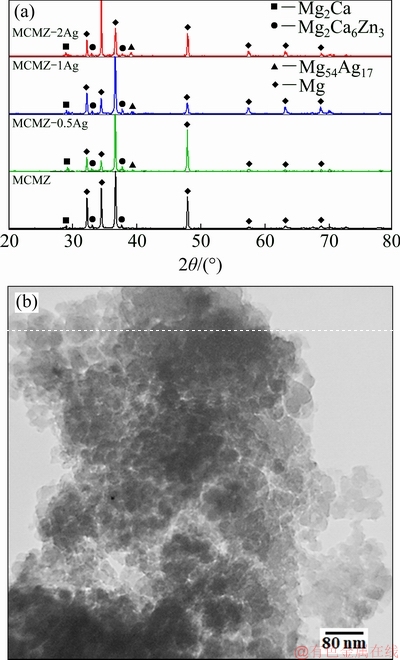
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of MCMA-xAg (a) and TEM image of MCMZ-1Ag nanopowders (b) after 6 h milling
Figure 2 shows SEM images of the MCMZ scaffolds containing Ag, which confirm the homogenous distribution of an interconnected pore network. Open-cell porosity with an appropriate pore architecture allows for biomolecules to freely move through the holes of the porous structures [1,28]. In addition, pore-scale descriptors are associated with bone ingrowth. In this study, pore features including pore morphology and pore size are consistent irrespective of the silver amount and remained intact; the porosity of 60% and pore size in the range of 600-800 μm are suitable for ontogenesis, vascularization, and bone regeneration [2,25]. Because spherical space-holder particles were extracted through conversion to gas bubbles during thermal treatment, most of the pores in the MCMZ-xAg scaffolds are connected spherical shapes [26]. In this context, a cut-off for the pore size needed to stimulate bone ingrowth that allows body fluid transport of 100-150 μm has been proposed [25]. For porous structures created from biomaterials, design factors such as pore size and interconnectivity should be optimized to help the bone scaffold lock into place, stimulate cell adhesion and growth, and increase permeability to fluids.

Fig. 2 SEM images of MCMZ-xAg scaffolds without Ag (a), with 0.5 wt.% Ag (b), 1.0 wt.% Ag (c) and 2.0 wt.% Ag (d)
3.2 Mechanical characterization of MCMZ-xAg scaffolds
Mechanical properties of porous artificial bone made from biomaterials are important for biomechanical functioning. To minimize the risk of stress-shielding in the host tissues, the mechanical strength of porous scaffolds must be comparable to that of the neighboring tissue [24,25]. Furthermore, they must have sufficient compressive strength to withstand the in vivo load before the artificial bone degrades and is gradually replaced by natural bone [9]. Nominal compressive stress-strain curves of the fabricated scaffolds with 60% porosity are shown in Fig. 3(a). The ultimate compressive strength (UCS) of the scaffolds incorporating silver is greater than that of the scaffold without containing silver ((4.0±0.2) MPa); the addition of only 0.5 wt.% Ag enhanced the UCS to more than (4.3±0.2) MPa without influencing the elongation. This can be attributed to the presence of the fine Mg-Ag precipitate phase, grain refinement, and weak basal texture. Higher Ag concentrations further improved the UCS, with the UCS of 2.0 wt.% Ag scaffolds at (4.8±0.2) MPa. This is attributed to grain refining and subsequent hindering of grain boundary sliding and dislocation motion. UCS values for all of the fabricated scaffolds were in the range of those values for bovine and human cancellous bone (compressive strength 2-12 MPa).
3.3 Corrosion behavior of MCMZ-xAg scaffolds
In the electrochemical terminology, the anodic polarization curve indicating the potential-current relationship involves a corroding metal (the fabricated Mg-based scaffolds) where loss occurs by dissolution.
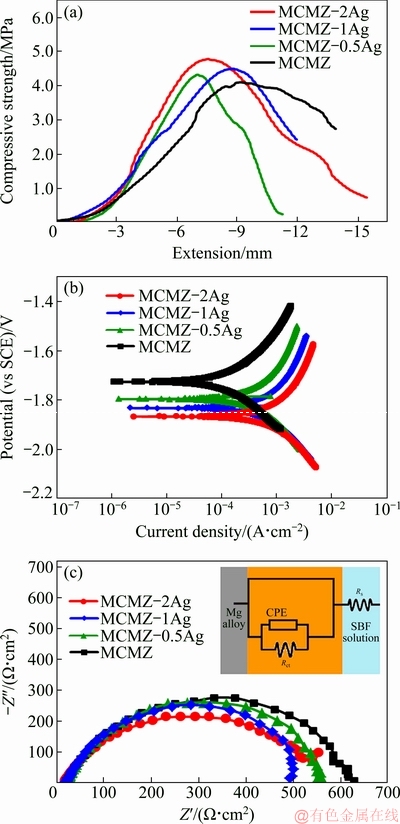
Fig. 3 Location-related instantaneous changes in compressive strength (a), potentiodynamic polarization (b) curves and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) spectra (c) of MCMZ-xAg scaffolds
The cathodic polarization curve shows the evolution of hydrogen from the reduction of water. Figure 3(b) displays polarization curves for exposure of MCMZ and MCMZ-Ag scaffolds to SBF solution. The corrosion potential of the MCMZ scaffold is more positive than that of the MCMZ-Ag scaffolds. The corrosion potential of the MCMZ scaffold is (-1726±8) mV (vs SCE), which is (71±4) mV (vs SCE) higher than that for the MCMZ-Ag scaffolds ((-1797±9) mV) (vs SCE) and implies the effectiveness of the additive elements (Zn, Ca, Mn) on corrosion resistance of the alloy. In the study on the corrosion behavior of Mg-Ca-Mn-Zn alloy, BAKHSHESHI-RAD et al [30] show that intermetallic precipitation considerably improves corrosion resistance by interrupting electron transfer. In addition, the intermetallic phases serve to prevent a continuous network structure of the anodic phases, which leads to a reduction in anodic corrosion. During corrosion in SBF, Zn and Mn additives form a passive layer on the corroding Mg layers, which hinders the penetration of chloride anions and hence increases corrosion resistance. In contrast, the incorporation of Ag nanoparticles into the MCMZ composite shifts the polarization potential in the negative direction and increases the corrosion current density (Jcorr) to slightly more than (234.2±12) μA/cm2. This change can be attributed to the electrochemical potential difference between α-Mg and Ag17Mg54 phases [29]. The electrochemical impedance spectro- scopy (EIS) analysis in Fig. 3(c) shows that the MCMZ-Ag scaffolds match well with the high- frequency capacitive loop. The high-frequency semicircle diameter determines the charge-transfer resistance (Rct) at the electrode/ electrolyte interface. Thus, the larger diameter implies more difficult charge transfer between the electrode and electrolyte. The EIS spectra of the fabricated scaffolds in a simple equivalent circuit can be used to characterize the samples, where Rs denotes the solution resistance, CPE is the electric double-layer capacitance of the passive film, and Rct is the charge transfer resistance. The figure shows that the addition of 0.5 wt.% Ag to the MCMZ composite scaffold reduces the diameter of the capacitive loop and hence lowers Rct ((520±6) Ω·cm2). However, further addition of Ag has a more negative effect on the Rct value, with the lowest value attributed to the scaffolds containing 2 wt.% Ag (Rct=(460±5) Ω·cm2).
3.4 In vitro bioactivity of MCMZ-xAg scaffolds
In vitro osteoconductivity is suggested by increased apatite apposition around the Ag-containing MCMZ scaffolds for up to 7 d in the SBF solution. Figure 4 shows SEM images of bonelike apatite aggregates formed on the surface of the scaffolds after 7 d in SBF. Plenty of apatite particles can be seen on the surface of the scaffolds due to direct exposure to SBF (Fig. 4). In addition, the mineralization of apatite particles with a spherical morphology on the scaffold pore surface might increase the mechanical integrity. Based on the SEM images, the deposition of the apatite layer appears to occur irrespective of silver content, at least for the concentrations investigated here (maximum of 2.0 wt.% Ag). EDS spectra of the scaffolds with and without Ag after immersion in SBF (Figs. 5(a) and (b)) confirm the formation of the apatite layer (Areas A and B in Fig. 4).
The most noticeable changes are the formation of P and Ca after exposure to SBF, which is related to the formation of a calcium phosphate film. The increase in the pH and hydroxyl ion concentration resulting from the prompt exchange of Ca+ and Mg2+ with H+ and H3O+ from the SBF can induce the biomineralization of apatite layers. In addition, the adsorption of calcium, phosphate, and hydroxyl ions from the SBF by the scaffolds causes the nucleation of bonelike apatite and a drop in pH due to the consumption of ions such as Ca2+ and PO43- during the process [5].
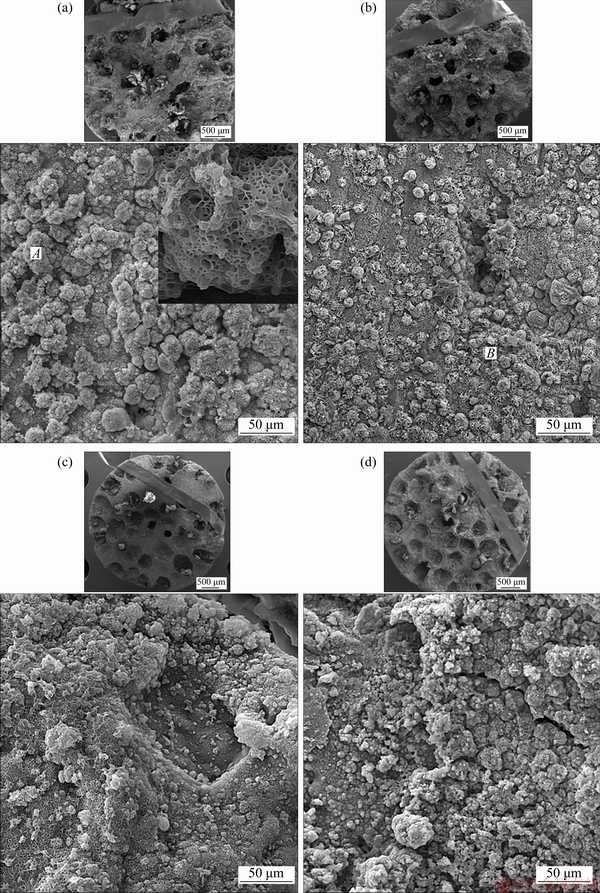
Fig. 4 SEM images of MCMZ-xAg scaffolds without Ag (a), with 0.5 wt.% Ag (b), 1.0 wt.% Ag (c), and 2.0 wt.% Ag (d) after immersion in SBF solution
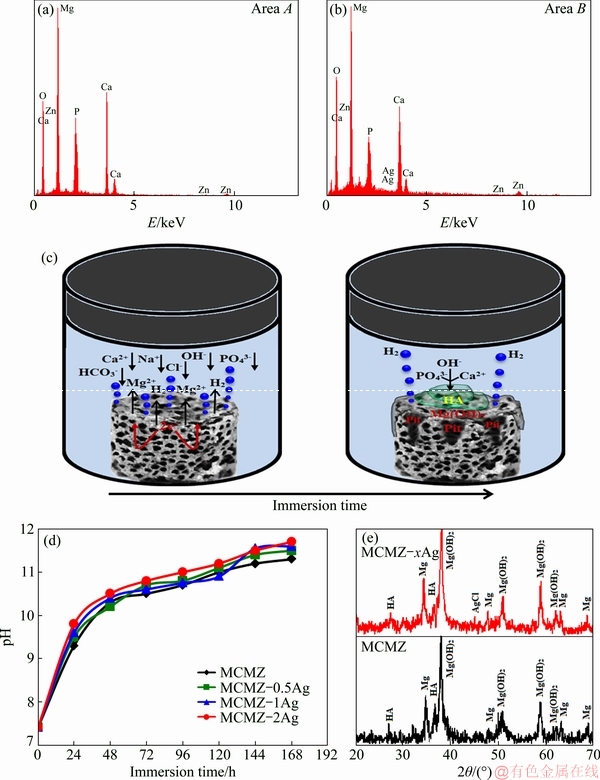
Fig. 5 EDS spectra of Areas A (a) and B (b) in Fig. 4, schematic illustration of degradation mechanism of MCMZ-xAg scaffolds in SBF solution (c), change in pH value of SBF solution (d), and XRD patterns (e) of MCMZ-xAg scaffolds after 168 h immersion in SBF solution
The formation of the apatite film on the Ag-incorporating MCMZ scaffolds provides a strong bond interface between the scaffolds and host tissue that helps the implants to lock in place. Mg-based scaffolds corrode rapidly in the electrolytic physiological environment, which limits their clinical applications. When the Mg-based scaffolds are exposed to a typical atmosphere, a protective Mg(OH)2 film develops and prevents further corrosion [30]. However, severe pitting corrosion occurs on Mg-based scaffolds in an aqueous physiological medium, because chloride ions react with the protective film to form highly soluble magnesium chloride. Finally, phosphate (PO43-) and Ca2+ in the aqueous solution react with OH- to form hydroxyapatite (HA), which accumulates on the surface of the Mg-based scaffolds (Fig. 5(c)). The corrosion reactions of Mg-based scaffolds can be summarized as follows:
Mg→Mg2++2e (Anodic reaction) (3)
2H2O+2e→H2+2OH- (Cathodic reaction) (4)
Mg2++2OH-→Mg(OH)2 (5)
Mg(OH)2+2Cl-→MgCl2+2OH- (6)
For all scaffolds, with or without Ag particles, the pH of the solution fluctuated throughout the in vitro bioactivity test (Fig. 5(d)). The pH values initially demonstrate a continuous increase over the first two days and then this increase slows through the third to seventh days and finally stabilizes at 11.35. The most stable pH value belongs to the Mg-based scaffolds without silver particles, which also exhibit the lowest degradation rate compared with the other scaffolds. The initial rise in pH is attributed to the transition of Mg to Mg2+ ions and consequent production of OH- released during the partial cathodic reaction. Thereafter, the hydroxyl ions released combine with PO43- and Ca2+ to precipitate hydroxyapatite, resulting in slowing of the increase in pH that is evident in the latter part of the pH diagram. The XRD results (Fig. 5(e)) confirm the precipitation of HA (JCPDS-PDF No. 01-071-5048) and Mg-hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) on the surface of all of the Mg-based scaffolds. For those incorporated with Ag, a silver chloride phase (JCPDS-PDF No. 01-085-1355) is observed in addition to HA and Mg(OH)2. XRD peaks observed at 2θ value of 37.5° indicate the presence of Mg(OH)2 as an alkalized layer. Nonetheless, the corrosive media can penetrate the HA coating as well as the protective alkalized layer and corrode the intact Mg. The new hydroxyl ions released from further Mg corrosion react with the products released from the dissolution of the former apatite layer (PO43- and Ca2+) to form a new HA layer. The above results demonstrate that the incorporation of Ag into the MCMZ scaffold has only a minor effect on the formation of apatite.
3.5 In vitro antibacterial activity of MCMZ-Ag scaffolds
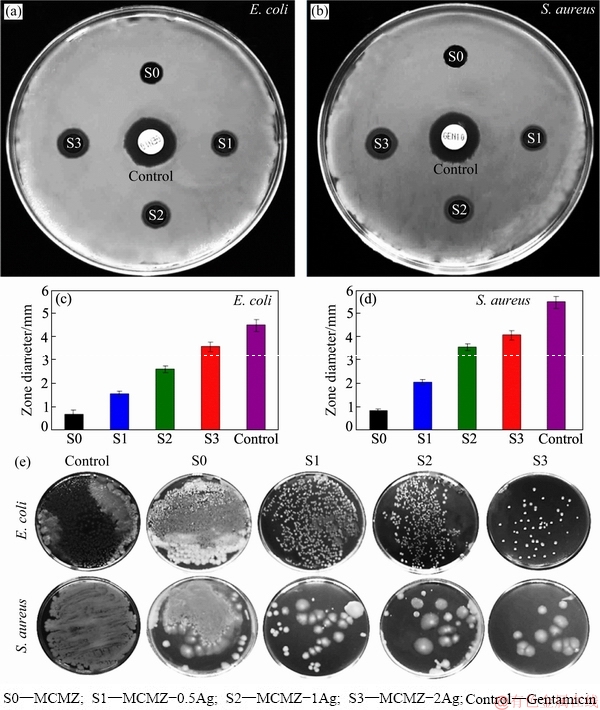
Fig. 6 Inhibition zones of MCMZ and MCMZ-Ag scaffolds against E. coli (a) and S. aureus (b) bacteria after 24 h and values of growth-inhibition zones against E. coli (c) and S. aureus (d), and photographs of antibacterial experiment with MCZM-Ag scaffolds against E. coli and S. aureus bacteria for 24 h (e)
The antibacterial activity was determined by co-culturing the MCMZ-Ag scaffolds with E. coli and S. aureus for 1 d and assessing the viability of the bacterial cells (Fig. 6). The results suggest that Ag particles can be utilized as a promising bacterial growth inhibitor in the scaffolds. The (0.5-2) wt.% Ag- containing scaffolds demonstrate more growth- inhibiting influence than the Ag-free scaffold (Figs. 6(a) and (b)), and this effect seems to be concentration- dependent as it extends to the highest concentration (2 wt.% Ag) considered here. The means sizes of the inhibition ring for E. coli for Ag free, 0.5 wt.% Ag, 1.0 wt.% Ag, and 2.0 wt.% Ag scaffolds are (0.7±0.3), (1.5±0.3), (2.7±0.4) and (3.6±0.6) mm, respectively; slightly larger inhibition rings are observed for S. aureus than E. coli (Figs. 6(c) and (d)). Figure 6(e) presents images illustrating the percent bacterial inhibition of the MCMZ scaffolds containing various amounts of Ag. The Ag-free MCMZ scaffolds have poor antimicrobial performance towards both E. coli and S. aureus while the MCMZ-Ag scaffolds considerably inhibit their growth. This is attributed to the rise of pH value throughout the degradation of Mg-based scaffolds and release of silver in the bacterial solution. In fact, high pH value of the SBF solution during the degradation of Mg-based sample leads to the bacteria membrane damage, which causes in cell death. Different kinds of microorganisms representing many biological groups have developed drug resistance, but Ag ions are known to suppress drug resistance of various bacterial cells [24]. As such, the Ag-containing scaffolds fabricated in this study can be contributed to the prevention of infection, bacterial growth inhibition, and drug resistance during the clinical usage. Even though the antibacterial effectiveness of silver has long been known and at present has been used to modulate bacterial growth in different clinical applications, the inhibitory mechanism remains largely undefined [11,16]. Possible mechanism for antibacterial performance of the MCMZ-Ag scaffolds is exhibited in Scheme 2. One possibility is that the antimicrobial activity is correlated with the released free radicals that manipulate the cell membrane and interrupt cell functions; electron transport binding to DNA is another alternative for the Ag antibacterial mechanism [20]. Another plausible argument is that antimicrobial activityresults from the interaction between silver ions and nucleophilic amino acid and thiol residues in the protein structure, causing protein denaturation and cell death [21,31]. Moreover, the release of OH- ion results in increasing pH value and alkaline environments may cause lipid peroxidation of phospholipids in bacterial membrane. This phenomenon leads to the destruction of membrane and further cellular lysis. Hence, MCMZ-Ag scaffolds present good antibacterial performance due to the release of silver ions and the formation of an alkaline environment.

Scheme 2 Schematic illustration of antimicrobial mechanisms of MCZM-Ag scaffolds in SBF solution
3.6 In vitro biocompatibility of MCMZ-xAg scaffolds
Biocompatibility is a general term used to describe a material that is compatible with living tissue. Biocompatible materials exposed to SBF do not produce toxic responses [10,32]. Measurement of cell viability and growth is the foundation for many in vitro assays of cell community response to external factors [4,25]. The in vitro cytotoxicity of Ag-incorporating MCMZ scaffolds was measured by MTT cell proliferation assay for various incubation time (Fig. 7(a)). EL-KADY et al [24] measured the maximum cytocompatible concentration of Ag ions released from scaffolds; however, the results varied depending on the type of cell/microorganism and whether the measurements were conducted in vivo or in vitro. The results from the present study show that the higher concentration scaffolds (2.0 wt.% Ag) release Ag ions into the culture medium and induce cytotoxic responses in the bone cells, whereas Ag released from the lower concentration scaffolds (0.5 wt.% Ag, 1.0 wt.% Ag) only causes minor decrease in cell proliferation. Therefore, the concentration of Ag in MCMZ scaffolds that result in a cytocompatible response from the bone cells is very narrow. The scaffolds containing 0.5 wt.% Ag develop more cells initially (1 d), but experience a slight reduction in cell viability over 4 d compared with the negative control (without Ag). Overall, the cell proliferation and cell viability of the 0.5 wt.% and 1.0 wt.% Ag-containing scaffolds are close to values noted for the negative control group.
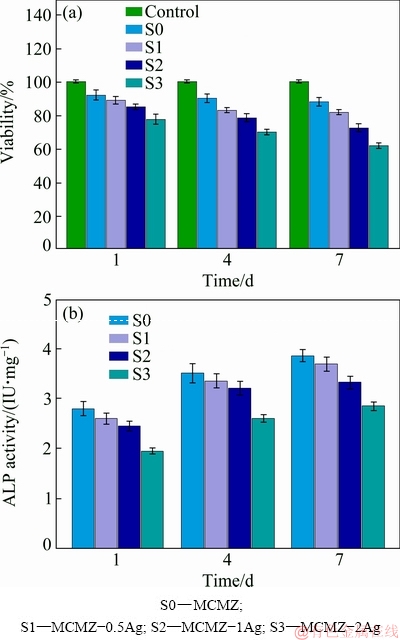
Fig. 7 Viability (a) and ALP activity (b) of MG63 cells cultured on MCMZ-xAg scaffolds for different time
The ALP activities of MG63 cells after cultivating on the MCMZ and MCMZ-Ag scaffolds for 1, 4 and 7 d are shown in Fig. 7(b). The ALP activity of MCMZ is higher than that of MCMZ-Ag scaffolds throughout the experimental period. MCMZ-0.5Ag shows slightly higher ALP activity than MCMZ-1Ag throughout culture time and the lowest ALP activity is observed from MCMZ-2Ag scaffold. ALP expression suggests that the MCMZ-0.5Ag scaffolds containing lower silver concentration benefit osteoblastic differentiation, indicating that scaffolds containing lower concentration of silver extracts suggest that they are able to promote the cell differentiation. Designing porous scaffolds that elicit appropriate cell responses (e.g., cell repopulation, cell adhesion, and differentiation) is a critical element in orthopedic research. To fulfill such expectations, cells are required to interact promptly with the scaffolds surface (the recognition process) by detecting specific receptors and attaching to the material surface. Rapid cell-material interaction strongly determines cell survival because any delay in the interaction will lead to cell death [17,18].
DAPI staining of the cells was monitored by fluorescence microscopy to determine cell attachment as well as cell viability on the surface of the fabricated scaffolds (Fig. 8). More MG63 cells interacted and attached to the (0.5-1.0) wt.% Ag-incorporating MCMZ scaffolds than to the 2.0 wt.% Ag-containing scaffold (Fig. 8(a)). Therefore, the addition of a low concentration of Ag seems to be compatible with cell attachment on scaffold surfaces. Engineering porous biomaterials elicit cell responses such as cell adhesion, cell growth, and differentiation has been a challenging element in orthopedic research. In the current study, MG63 cells were also employed to assess the cytocompatibility of MCMZ and Ag-bearing MCMZ scaffolds. Acridine orange as a versatile fluorescence dye was used to visualize the cells under a fluorescent microscope. After 2 d of culture, MCMZ and 0.5 wt.% Ag-MCMZ scaffolds (Fig. 8(b)) demonstrated greater cell-spreading with higher cell density than 1.0 wt.% and 2.0 wt.% Ag-MCMZ scaffolds. The healthy polygonal-shaped MG63 cells with their typical filopodia and flatted spindle seeded on the 2.0 wt.% Ag-MCMZ scaffold transitioned to a blurry image after 2 d, suggesting that this amount of Ag is cytotoxic. Overall, Ag incorporation into the MCMZ scaffolds had an adverse cellular response, with the 2.0 wt.% Ag significantly decreasing cell viability and adhesion. This adverse cell-biomaterial interaction might be associated with high pH and metal ions released from the 2.0 wt.% Ag-MCMZ scaffolds.
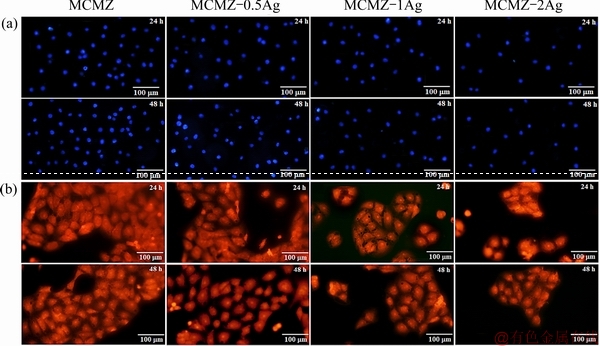
Fig. 8 DAPI staining images of MG63 cell (a) and acridine orange fluorescent staining images (b) of osteoblasts cultured for 24 and 48 h, respectively on MCMZ, MCMZ-0.5Ag, MCMZ-1Ag and MCMZ-2Ag scaffolds
The degradation rate of the 2.0 wt.% Ag-MCMZ composite scaffolds increased in the presence of Ag nanoparticles, but the increasing ion concentrations also led to higher cytotoxicity of these scaffolds to MG63 cells.
4 Conclusions
(1) The incorporation of Ag nanoparticles into the MCMZ composite scaffolds changed neither pore architecture nor porosity. The ultimate compressive strength (UCS) of the nanostructured MCMZ-Ag scaffolds was higher than the Ag-free MCMZ scaffold. The MCMZ and 0.5 wt.% Ag-MCMZ scaffolds showed higher corrosion resistance than the 1.0 wt.% or 2.0 wt.% Ag-MCMZ scaffolds.
(2) The bactericidal effect of the MCMZ-Ag scaffolds indicates that these biomaterials are strongly active against E. coli (ATCC 10536) and S. aureus (ATCC 6538 P), with the antimicrobial effect correlating with Ag content.
(3) The MTT assay confirmed the higher cell viability and cell adhesion of MCMZ and 0.5 wt.% Ag-MCMZ scaffolds than 1.0 wt.% or 2.0 wt.% Ag-MCMZ scaffolds. Hence, porous 0.5 wt.% Ag-MCMZ scaffolds with a pore size of 600-800 μm and a porosity of 60% accompanied by good antimicrobial activity meet the essential requirements for applications in bone tissue engineering.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the University of Saskatchewan and Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) for providing the facilities for this research. Also, partial financial support to this research from the Saskatchewan Health Research Foundation (SHRF) is acknowledged.
References
[1] LOPES J H, MAGALHAES J A, GOUVEIA R F, BERTRAN C A, MOTISUKE M, CAMARGO S E A, TRICHES E D S. Hierarchical structures of β-TCP/45S5 bioglass hybrid scaffolds prepared by gelcasting [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2016, 62: 10-23.
[2] MUTHUTANTRI A I, EDIRISINGHE M J, BOCCACCINI A R. Improvement of the microstructure and mechanical properties of bioceramic scaffolds using electrohydrodynamic spraying with template modification [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2010, 3: 230-239.
[3] DAROONPARVAR M, MAT M A Y, GUPTA R K, YUSOF N M, BAKHSHESHI-RAD H R, GHANDVAR H, GHASEMI E. Antibacterial activities and corrosion behavior of novel PEO/nanostructured ZrO2 coating on Mg alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 1571-1581.
[4] WITTE F. The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: A review [J]. Acta Biomaterialia. 2010, 6: 1680-1692.
[5] YAZDIMAMAGHANI M, RAZAVI M, VASHAEE D, MOHARAMZADEH K, BOCCACCINI A R, TAYEBI L. Porous magnesium-based scaffolds for tissue engineering [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2017, 71: 1253-1266.
[6] DIBA M, GOUDOURI O M, TAPIA F, BOCCACCINI A R. Magnesium-containing bioactive polycrystalline silicate-based ceramics and glass-ceramics for biomedical applications [J]. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 2014, 18: 147-167.
[7] SANCHEZ A H M, LUTHRINGER B J C, FEYERABEND F, WILLUMEIT R. Mg and Mg alloys: How comparable are in vitro and in vivo corrosion rates? A review [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2015, 13: 16-31.
[8] ZHENG Y F, GU X N, WITTE F. Biodegradable metals [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 2014, 77: 1-34.
[9] LI N, ZHENG Y. Novel magnesium alloys developed for biomedical application: A review [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2013, 29: 489-502.
[10] AGARWAL S, CURTIN J, DUFFY B, JAISWAL S. Biodegradable magnesium alloys for orthopaedic applications: A review on corrosion, biocompatibility and surface modifications [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2016, 68: 948-963.
[11] BALAMURUGAN A, BALOSSIER G, LAURENT-MAQUIN D, PINA S, REBELO A H S, FAURE J, FERREIRA J M F. An in vitro biological and anti-bacterial study on a sol-gel derived silver-incorporated bioglass system [J]. Dental Materials, 2008, 24: 1343-1351.
[12] QIN H, ZHAO Y, AN Z, CHENG M, WANG Q, CHENG T, WANG Q, WANG J, JIANG Y, ZHANG X, YUAN G. Enhanced antibacterial properties, biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance of degradable Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy [J]. Biomaterials, 2015, 53: 211-220.
[13] PARENT M, MAGNAUDEIX A, DELEBASSEE S, SARRE E, CHAMPION E, VIANA T M, DAMIA C. Hydroxyapatite microporous bioceramics as vancomycin reservoir: Antibacterial efficiency and biocompatibility investigation [J]. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 2016, 31: 488-498.
[14] LIU C, FU X, PAN H, WAN P, WANG L, TAN L, WANG K, ZHAO Y, YANG K, CHU P K. Biodegradable Mg-Cu alloys with enhanced osteogenesis, angiogenesis, and long-lasting antibacterial effects [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 27374.
[15] ROBINSON D A, GRIFFITH R W, SHECHTMAN D, EVANS R B, CONZEMIUS M G. In vitro antibacterial properties of magnesium metal against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6: 1869-1877.
[16] BAKHSHESHI-RAD H R, HAMZAH E, LOW H T, KASIRI-ASGARANI M, FARAHANY S, AKBARI E, CHO M H. Fabrication of biodegradable Zn-Al-Mg alloy: Mechanical properties, corrosion behavior, cytotoxicity and antibacterial activities [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2017, 73: 215-219.
[17] TIAN Q H, DENG D, LI Y, GUO X Y. Preparation of ultrafine silver powders with controllable size and morphology [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 524-533.
[18] CUI L Y, XU J, LU N, ZENG R C, ZOU Y H, LI S Q, ZHANG F. In vitro corrosion resistance and antibacterial properties of layer-by-layer assembled chitosan/poly-L-glutamic acid coating on AZ31 magnesium alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 1081-1086.
[19] MUTLU I. Production and fluoride treatment of Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy foam for tissue engineering applications [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 114-124.
[20] DIZAJ S M, LOTFIPOUR F, BARZEGAR-JALALI M, ZARRINTAN M H, ADIBKIA K. Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2014, 44: 278-284.
[21] KUMAR R, UMAR A, KUMAR G, NALWA H S. Antimicrobial properties of ZnO nanomaterials: A review [J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43: 3940-3961.
[22] BUZOLIN R H, MOHEDANO M, MENDIS C L, MINGO B, TOLNAI D, BLAWERT C, KAINER K U, PINTO H, HORT N. Corrosion behaviour of as-cast ZK40 with CaO and Y additions [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 427-439.
[23] MOHAMMADI F D, JAFARI H. Microstructure characterization and effect of extrusion temperature on biodegradation behavior of Mg-5Zn-1Y-xCa alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 2199-2213.
[24] EL-KADY A M, RIZK R A, ABD EL-HADY B M, SHAFAA M W, AHMED M M. Characterization, and antibacterial properties of novel silver releasing nanocomposite scaffolds fabricated by the gas foaming/salt-leaching technique [J]. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 2012, 10: 229-238.
[25] ROSETI L, PARISI V, PETRETTA M, CAVALLO C, DESANDO G, BARTOLOTTI I, GRIGOLO B. Scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: State of the art and new perspectives [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2017, 78: 1246-1262.
[26] SEYEDRAOUFI Z S, MIRDAMADI S. In vitro biodegradability and biocompatibility of porous Mg-Zn scaffolds coated with nano hydroxyapatite via pulse electrodeposition [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 4018-4027.
[27] BAKHSHESHI-RAD H R, HAMZAH E, DAROONPARVAR M, YAJID M A M, ASGARANI M K, KADIR M R A, MEDRAJ M. In-vitro degradation behavior of Mg alloy coated by fluorine doped hydroxyapatite and calcium deficient hydroxyapatite [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 24, 2014: 2516-2528.
[28] YOU F, LI Y, ZOU Q, ZUO Y, LU M, CHEN X, LI J. Fabrication and osteogenesis of a porous nanohydroxyapatite/polyamide scaffold with an anisotropic architecture [J]. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2015, 1(9): 825-833.
[29] BEN-HAMU G, ELIEZER D, KAYA A, NA Y G, SHIN K S. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of Mg-Zn-Ag alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 435-436: 579-587.
[30] BAKHSHESHI-RAD H R, IDRIS M H, KADIR M R A, OURDJINI A, MEDRAJ M, DAROONPARVAR M, HAMZAH E. Mechanical and bio-corrosion properties of quaternary Mg-Ca-Mn-Zn alloys compared with binary Mg-Ca alloys [J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 53: 283-292.
[31] ABOUDZADEH N, DEHGHANIAN C, SHOKRGOZAR M A. In vitro degradation and cytotoxicity of Mg-5Zn-0.3Ca/nHA biocomposites prepared by powder metallurgy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 1745-1754.
[32] BAKHSHESHI-RAD H R, HAMZAH E, ISMAIL A F, AZIZ M, KARAMIAN E, IQBAL N. Bioactivity, in-vitro corrosion behavior, and antibacterial activity of silver–zeolites doped hydroxyapatite coating on magnesium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 1553-1562.
Hamid Reza BAKHSHESHI-RAD1,2,5, Ehsan DAYAGHI1, Ahmad Fauzi ISMAIL2, Madzlan AZIZ2, Ali AKHAVAN-FARID3, Xiongbiao CHEN4,5
1. Advanced Materials Research Center, Department of Materials Engineering, Najafabad Branch, Islamic Azad University, Najafabad, Iran;
2. Advanced Membrane Technology Research Center (AMTEC), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Skudai, Johor Bahru, Johor, Malaysia;
3. Department of Mechanical, Materials and Manufacturing Engineering, University of Nottingham Malaysia Campus, 43500 Semenyih, Malaysia;
4. Division of Biomedical Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada;
5. Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
摘 要:感染是骨损伤临床治疗中常见的并发症。镁基复合材料是一种可生物降解的抗菌生物材料,已被用于减少术后感染。本文作者合成含银镁基骨组织工程支架材料,并对其进行体外表征。通过造孔剂法制备4种不同银含量(0、0.5、1、和2 wt.%) 的多孔镁基支架,用Mg-Ca-Mn-Zn-xAg (MCMZ-xAg)表示,其中x表示银含量。研究银含量对材料的孔隙结构、力学性能、生物活性和抑菌区的影响。采用X射线衍射分析(XRD)、扫描电镜(SEM)、透射电镜(TEM)和荧光显微镜对支架进行表征。体外腐蚀试验结果表明,银含量低的支架比银含量高的支架具有更好的耐腐蚀性。抗菌活性的检测结果表明MCMZ-Ag 支架具有显著抑制大肠杆菌和(E. coli) 和金黄 色葡萄球菌(S. aureus)生长的作用,且随着含银量的增加,MCMZ-Ag 支架周围的抑菌区面积逐渐增加。然而,含银量过高会增加材料的细胞毒性。总之,含0.5 wt.% Ag的支架因其具有连通的孔隙、足够的力学性能、抗菌活性和细胞黏附性能,在修复与替换受损和患病骨方面具有应用前景。
关键词:镁基支架;生物相容性;抗菌活性;生物活性;腐蚀行为
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Corresponding author: Hamid Reza BAKHSHESHI-RAD, E-mail: rezabakhsheshi@gmail.com; Ahmad Fauzi ISMAIL, E-mail: afauzi@utm.my
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65007-7

