DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.04.044
青藏高原地区典型土遗址冻融与盐渍耦合劣化作用分析
蒲天彪1, 2,谌文武1,吕海敏1,杜昱民1
(1. 兰州大学 西部灾害与环境力学教育部重点实验室,甘肃 兰州,730000;
2. 中国国家民族博物馆,北京,100080)
摘要:研究基于高原地区冬季降雪过程环境监测数据和多处典型土遗址的易溶盐含量与分布特征,通过对实验条件下分别掺入质量分数为0.2%的梯度增量掺入无水氯化钠和无水硫酸钠至质量分数为1%并经历冻融循环的遗址土重塑土样的风洞、崩解、弹性波速和剪切实验,揭示耦合作用下表征土遗址抗风蚀能力、抗雨蚀能力和强度等指标的劣化规律和本质原因,并对底部掏蚀、片状剥离和坍塌等高原地区典型土遗址病害形成过程以及与上述性质变化的内在联系进行剖析和阐释。研究结果表明:试样抗雨蚀能力、抗风蚀能力和强度相关指标会对耦合作用产生明显的劣化响应,因掺入盐分类型和含量的不同而表现出非线性衰减规律;相关性质的劣化为典型病害的发育提供了前提和基础。
关键词:青藏高原;土遗址;冻融;盐渍;耦合劣化
中图分类号:TU411.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)04-1420-07
Analysis on function of deterioration of typical earthen ruins under the coupling of salinized and freezing and thawing in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
PU Tianbiao1, 2, CHEN Wenwu1, L Haimin1, DU Yumin1
Haimin1, DU Yumin1
(1. Key Laboratory of Mechanics on Disaster and Environment in Western China,
Ministry of Education, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China;
2. The National Museum of Ethnology, Beijing 100080, China)
Abstract: Based on the environmental monitoring data and the analysis of the soluble salt content and distribution to several typical ruins during the process of winter snowfall in the plateau region, wind tunnel, disintegration, elastic wave velocity and shearing experiments in laboratory on remodeling sample mixed with the mass fraction of 0.2%–1% of anhydrous sodium sulfate and sodium chloride and through the freeze-thaw cycle after desalination were studied, to reveal the change rule of properties and essential reasons on those with the joint function of salinized and freezing and thawing, which characterizes the ability of ruins to resist wind erosion, rain erosion and indexes of strength. And then inner link between the forming processes of typical diseases such as detachment of bottom undercutting, surface crust and collapses was analyzed and explained. The results show that the ability of ruins to resist wind erosion, rain erosion and indexes of strength have significant deterioration response to coupling processes, which has non-linear attenuation law as mixing different typed and content of salt. In addition, the deterioration of related properties provides precondition and basis for the development of typical diseases.
Key words: Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; earthern ruin; freezing and thawing; salinized; coupling deterioration
青藏高原地势高峻,自然环境多样独特,被称为“世界第三极”,然而,恶劣的环境并没有阻止人类文明的孕育,早在距今二三万年前的旧石器时代,即有人类在今昆仑山一带活动生息。灿烂文明造就了大量文化遗存,其中不乏大量土遗址[1]。青藏高原具有辐射量大、日照蒸发强烈、气温低、积温少、日较差大和干湿分明的总体气候特征[2]。有明长城分布的青藏高原东北缘(门源、西宁、民和、贵德、互助)地区,属大陆性干旱、半干旱高原气候,具有干燥、少雨、多风、寒冷、日温差大和垂直变化显著的气候特征。土遗址是受气候影响最为显著和直接的人类历史文化遗存形式之一。在高原独特恶劣的气候控制下,区内土遗址大量发育诸如开裂、掏蚀和风化剥离等危害土遗址安全赋存的土体劣化形式。土遗址是一个复杂的开放系统,气候条件对其劣化过程的影响和控制是最为直接和突出的。国内部分学者开展了由集中降雨过程产生的干湿和盐渍复合过程的土遗址劣化规律和机理的系统研究[3-4]。QU等[5-7]进行了土遗址冻融耐久性研究,通过部分土遗址重塑样品和原状样品的冻融循环实验,初步阐明了遗址土的抗风蚀能力和抗压强度指标的变化规律。然而,对于高原地区冬季常见的降雪过程导致的冻融和盐渍共同作用下的土遗址劣化规律和机理的研究报道较少。降雪过程是青藏高原冬季普遍的一种天气过程,该过程使土遗址处于反复冻融和盐渍的复合作用之下,一方面使土遗址内部的温度场、渗流场发生改变,水分相态转变;另一方面引起其内部易溶盐分发生运移、结晶与溶解。这就会导致土体结构产生相应地调整,从而致使其物理、力学和水理等宏观性质发生与之对应的复杂响应行为。国内外同行已在关于土在冻融条件下劣化过程与机理开展了研究。SIGRUN等[8-9]研究发现冻融循环会造成土体结构的劣化,相对于黏性土,粉土对冻融等风化作用更为敏感。黄克忠[10]对冻融循环作用下青藏铁路沿线的粉质黏土进行了物理力学性质的试验分析,认为冻融循环作用不会改变应力–应变曲线的形式,只改变其弹性常数和破坏强度;KEVIN等[11]认为冻融循环对土的应力应变行为的影响受试验条件(固结、三轴等)的影响而导致不同的力学行为。但上述研究未考虑遗址土的特殊性和盐分在其中所起的作用。基于以上认识,选取遗存在青海境内的明长城遗址为典型研究对象,以对其赋存地区冬季降雪过程气候要素的分析以及遗址的盐分监测数据为基础。通过对实验条件下掺入不同含量土遗址中常见的盐分并经历冻融循环的遗址土重塑土样的崩解、稠度、风蚀速率、抗剪强度和弹性波速等指标测试,来研究冻融和盐渍双重作用下土遗址抗风蚀、抗雨蚀能力和强度的变化规律,为常见遗址劣化进程形式的发生和发展探索原因,并探讨土遗址劣化对降雪过程响应的基本途径。
1 冻融与盐渍环境分析
1.1 冻融环境特征
表1所示为遗址赋存地区冻融环境特征。从已获得的有明长城遗址分布青藏高原东北缘地区的气候资料(1980—2005年)分析可知,这些地区冬季(1,2和12月份)日平均气温较差大,最高可达20. 7 ℃;月平均降水量在0.6~3.6 mm之间,且降水形式以降雪为主;月蒸发量为36.6~88.4 mm(表1)。这充分说明在该地区冬季降雪过程中,温度、降水相态变化以及较为强烈的蒸发可为露天保存的土遗址创造充分的冻融环境,为其劣化进程提供先决条件。
1.2 典型土遗址含盐特征
对上述5个地区典型明长城遗址由底部向顶部间隔0.3 m系统采样的易溶盐测试(DSC)结果显示,遗址土易溶盐含盐质量分数在578~89 777 mg/kg之间分布,呈现自遗址根部向顶部依次减小的规律(图1);并且易溶盐中阴离子成分主要以SO42-和Cl-为主,易溶盐中SO42-质量分数为43.6%~67.3%,Cl-质量分数为6.5%~17.6%;阳离子以Na+和K+为主,其质量分数为5.9%~21.7%。依此计算分析表明NaCl和Na2SO4为遗址盐分中最为常见的离子组合形式,而且以其为代表易溶盐分的广泛分布为该区遗址土盐渍过程的发生和发展过程提供事实依据和前提。
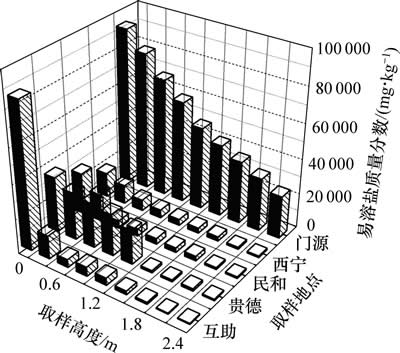
图1 典型土遗址系统采样易溶盐含量测试结果
Fig. 1 Random test results of DSC on typical earthern ruins
表1 遗址赋存地区冻融环境特征
Table 1 Feature of freezing and thawing environment in some districts with earthen ruins
1.3 遗址土的基本特征
上述土样的基本物理性质测试结果表明,其颗粒物质组成中,粉粒质量分数分布在56.31%~78.61%之间,黏粒质量分数分布在5.13%~23.20%之间,干密度位于1.47~1.78 g/cm3之间,孔隙率为32.7%~52.4%。以上遗址土的物理性质参数分布较为离散,这与其建造时所采用“因地制宜、就地取材”的夯筑原则和“人工版筑”的建造技艺是密不可分的。经概括分析,此类土多属粉土与粉质黏土的分类范畴,对冻融或盐渍作用具有较强的响应性[7]。
2 实验研究
2.1 样品制备
对取自5处典型遗址坍塌处粉粒质量分数为82.05%、黏粒质量分数为17.33%的原状土样充分碾碎后,用去离子水和分子筛联合脱盐[12]。而后向脱盐后的土体以质量分数为0.2%的梯度增量分别掺入无水NaCl和Na2SO4至1%,密封养护至盐分均匀分布于土体。最后在万能试验机下依据击实实验得到的最优含水率为14%和最大干密度为1.70 g/cm3确定土水质量,采用双向挤压法制成棱长为7.07 cm的正方体试块。
2.2 样品养护
试块置于型号为MHK-S1000温湿度控制室进行冻融循环养护,箱内温度在-40~100 ℃可调,湿度在10%~98%可调。通过反复冻结和融化,模拟试样在降雪环境下经历的冻融过程。青海诸地历年平均最低气温为-21.8 ℃,故冻融循环试验控制土体所处冻结温度为-20 ℃,冻结时间为12 h;然后定湿度融化12 h(室温20 ℃),依次进行下一个冻融循环试验,反复养护3次。
2.3 实验过程与方法
对上述完成冻融循环养护的试块采用直流下吹式多功能环境风洞分别进行风速为18,22,24,28和30 m/s携沙风不同吹蚀时间的风蚀实验,进行崩解、声波和直接剪切试验,来探索耦合作用下试样的抗风蚀、抗雨蚀能力和强度的变化规律。
3 实验结果
3.1 抗风蚀能力的变化规律
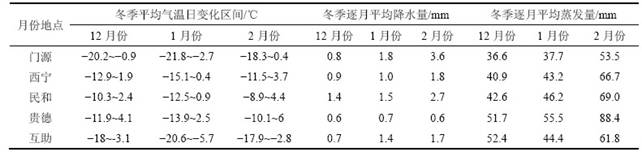
在直流下吹式风洞中进行对分别掺入质量分数为0.2%~1.0% 2种盐分并经历冻融循环试块不同风速、不同吹蚀时间的携沙风吹蚀实验。
图2所示为冻融循环后不同含盐试样18m/s风速下风蚀量变化,图3所示为冻融循环后不同含盐试样不同风速平均风蚀速率变化。从图2和图3可知:1) 掺入任意盐分试样的风蚀量随着携沙风风速和吹蚀时间的增大而呈现递增的趋势;2) 在吹蚀风速一定条件下,试样的风蚀速率随着掺入盐分质量分数的增长而呈现明显的递增趋势;3) 在相同吹蚀条件和盐分质量分数的情况下,掺入Na2SO4试样的风蚀速率增长量明显高于掺入NaCl试样的增长量。以上结果说明表征试样抗风蚀能力的物理量受携沙风风速、吹蚀时间的直接影响,其对于风速和吹蚀时间变化的响应程度取决于掺入盐分类型和含量;抗风蚀能力在冻融、盐渍耦合作用下呈现衰减的劣化规律。
3.2 抗雨蚀能力的变化规律
崩解性是指土体浸水后粒间的结构联结和强度丧失致使崩散解体的特性,崩解速度是直接表征崩解性的物理量,可以直接反映遗址土的抗雨蚀能力[13]。图4所示为冻融循环后不同含盐试样崩解速度变化。从图4可见:1) 掺入任意盐分试样的崩解速度随着掺入盐分质量分数的增大而呈现递增的趋势;2) 掺入任意盐分试样的崩解速度在0~0.4%这个区间变化较平缓,在0.4%~1.0%这个区间提高较迅速;3) 在盐分质量分
数相同的情况下,掺入Na2SO4试样的崩解速度明显高于掺入NaCl试样的崩解速度。以上结果说明试样受崩解性冻融与盐渍耦合作用的直接影响。
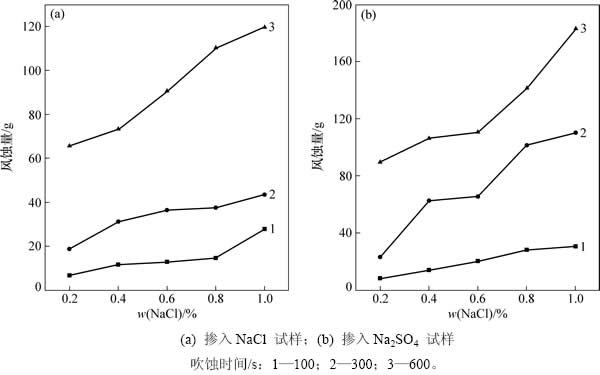
图2 冻融循环后不同含盐试样18 m/s风速下风蚀量变化
Fig. 2 Variation of wind erosion quantity of specimens mixed with different salinities after freezing and thawing cycle under wind velocity of 18 m/s
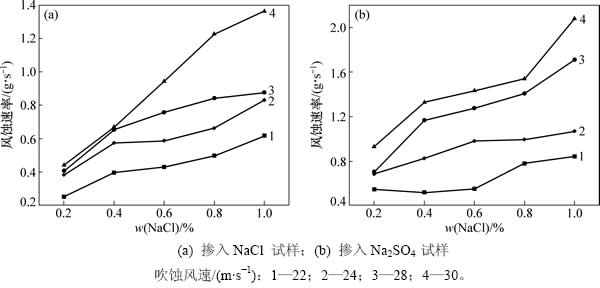
图3 冻融循环后不同含盐试样不同风速平均风蚀速率变化
Fig. 3 Variation of average wind erosion rate of specimens mixed with different salinities after freezing and thawing cycle under various wind velocities
3.3 强度的变化规律
弹性波波速作为评价岩土体物理性质和强度优劣快捷而有效的方法已经被广泛应用[14]。图5所示为冻融循环后不同含盐试样纵波波速变化。从图5可见:1) 掺入任意盐分试样的垂直层面和平行层面的纵波波速随着掺入盐分质量分数的增长而呈现递减的趋势;2) 在盐分质量分数相同的情况下,掺入Na2SO4试样的垂直层面和平行层面的纵波波速均小于掺入NaCl试样的纵波波速;3) 掺入任意盐分试样的平行层面纵波波速随着盐分质量分数升高的衰减幅度明显大于其垂直层面纵波波速的衰减幅度。上述结果表明冻融与盐渍耦合作用促使试样结构产生调整,致使试样中纵波传播速度减小,反映试样强度在耦合作用下产生衰减的行为。
图6所示为冻融循环后不同含盐试样抗剪强度变化。上述试块的平行方向的直接快剪实验表现出以下3点特征:1) 掺入任意盐分试样在相同正应力条件下试块的抗剪强度都随着掺入盐分质量分数的增大而呈现递减趋势;2) 掺入任意盐分试块的抗剪强度的衰减率都随着正应力的增大而呈现增长的趋势;3) 相同正应力条件下Na2SO4试块的抗剪强度衰减幅度都比掺入NaCl试块的大。以上表明冻融与盐渍耦合作用使试样土粒间连结程度削弱,土粒间的相对位移更加容易发生,从而表现为抗剪强度也会对耦合过程产生衰减性响应行为。
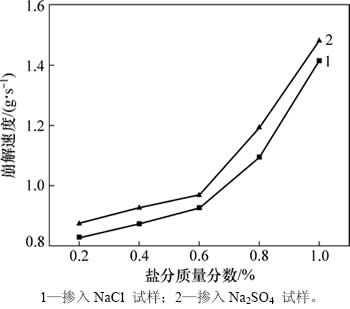
图4 冻融循环后不同含盐试样崩解速度变化
Fig. 4 Variation of disintegration rate of specimens mixed with different salinities after freezing and thawing cycle
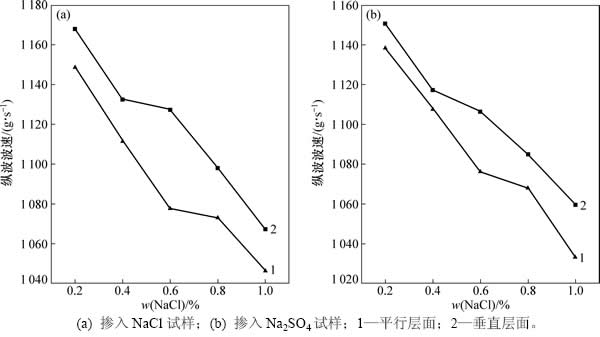
图5 冻融循环后不同含盐试样纵波波速变化
Fig. 5 Variation of vertical wave velocity of specimens mixed with different salinities after freezing and thawing cycle
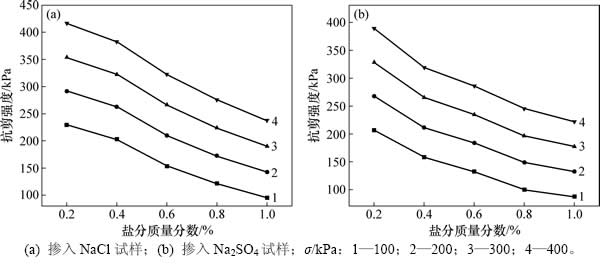
图6 冻融循环后不同含盐试样抗剪强度变化
Fig. 6 Variation of shearing strength of specimens mixed with different salinities after freezing and thawing cycle
4 分析与讨论
以青藏高原多处明长城遗址所处冻融环境为参照,以易溶盐监测结果为依据,通过经历冻融循环的不同含盐类型、数量的遗址土的风洞、崩解、弹性波速和直接剪切实验结果直接反映遗址土在冻融和盐渍耦合作用下弹性波速和抗剪强度衰减的规律。抗风蚀能力、抗雨蚀能力和强度的变化高度一致,表明土遗址对耦合作用的劣化响应非常显著。实验结果反映另一个重要特征就是Na2SO4和NaCl对耦合过程的遗址土宏观性质指标劣化响应行为表现存在较大差异。其根本原因在于结晶过程和方式的差异,Na2SO4发生Na2SO4·7H2O或Na2SO4·10H2O的吸失水结晶转化过程,导致体积膨胀与收缩,体积膨胀率可达数倍或数十倍;NaCl虽然没有像Na2SO4那样存在结晶水的得失,但具有很强的吸湿性,在湿度变化的影响下也会发生结晶 溶解的过程,与Na2SO4相比,同样会产生较小的体积膨胀和孔隙压力。
溶解的过程,与Na2SO4相比,同样会产生较小的体积膨胀和孔隙压力。
冬季降雪是青藏高原最常见的天气过程,降融雪整个过程中有气温升降、降水(固-液-气) 3种相态的转化等环境因素的变化;而对于在露天环境中保存的土遗址的影响则更显著。首先,在降雪过程中,由于环境温度的改变导致遗址中温度场改变;其次,在融雪过程中,停留在遗址表面的积雪融化入渗至其中导致其渗流场改变;最后,在渗流场、蒸发和毛细作用下,水分携带着盐分迅速向遗址表面和底部发生二维运移,同时,水分在温度场的变化下会发生固液态的相互转化,盐分在温度场的变化下发生结晶-溶解相互转化。因此,冬季反复的降雪过程导致遗址中温度场、渗流场和盐分的反复变化,使之处在反复冻融和盐渍耦合作用之下。
由遗址土在冻融和盐渍耦合作用下土遗址对耦合作用的劣化响应以及降融雪过程对土遗址的影响可知,由冬季降雪造成的反复冻融和盐渍耦合作用实质上是土遗址在水-热-盐的共同作用下水分、盐分发生运移与相态的转换过程。盐随水走,这是水盐在土体中运移的主要形式,土体中各种类型的孔隙则是水盐运移的主要通道;水盐在运移的过程受到温度的影响,在孔隙中完成相态的转化和结晶-溶解的过程。具体表现为当土体冻结时,水分由固态转化为液态,体积发生膨胀,盐分溶解度受温度的影响,部分析出发生结晶,体积亦发生膨胀;当土体融化时,水分由固态转化为液态的冰,体积发生收缩,盐分随着温度升高结晶开始溶解,体积亦收缩。这样反复叠加的膨胀-收缩的过程同时作用于土体结构,一方面使土颗粒之间失去支撑形成空缺,从而改变了颗粒骨架的联接方式;另一方面亦使土体原生隐微裂隙张开、扩大、加深与连通,形成长大裂隙,导致其土颗粒间联接力变小。因此,土体结构遭受严重破坏,随之表现出抗风蚀能力、抗雨蚀能力和强度一系类列宏观性质的劣化行为。
底部掏蚀、片状剥离和坍塌是高原地区以明长城为代表的土遗址典型且普遍发育的病害[15],上述一系列宏观性质的劣化表现为这些等典型病害普遍发育提供了佐证。遗址土体的抗风蚀能力、抗雨蚀能力和强度分别直接控制着底部掏蚀、片状剥离和坍塌病害的发生与发展进程。 底部掏蚀病害的发育过程实质上是盐分在土遗址底部发生聚集,遗址底部土体在耦合作用下,结构遭受破坏,粒间连接力变弱,致使土体抗风蚀能力降低;而后在挟沙风高速运动的砂粒的强烈撞击和磨蚀作用下脱离土骨架成为自由土粒而被搬运到它处形成空腔的过程。上述完成冻融交替的含盐试样的携沙风吹蚀实验结果是对底部掏蚀病害形成过程最好的表述。同样,片状剥离的形成是遗址表面土体增湿崩解产生蠕动泥流,经蒸发干燥作用形成龟裂状外翘结皮,与含盐土体在冻融交替环境下的抗雨蚀能力的改变有着直接的关系。对冻融交替的含盐土体的弹性波速和抗剪强实验结果则直观地表明遗址土在耦合作用下强度发生衰减的特征,为遗址坍塌病害提供直接与有力的证据。 因此,由降雪过程导致的冻融和盐渍耦合作用是控制高原地区土遗址典型病害发育和发展不可忽略的驱动力。
5 结论
1) 冬季降雪和强烈蒸发的气候特征以及遗址中易溶盐质量分数和分布特征为高原地区以明长城遗址为代表的土遗址发生冻融和盐渍耦合作用提供了前提和基础。
2) 掺入不同质量分数NaCl和Na2SO4并经历冻融循环的试样的风蚀、崩解、弹性波速和剪切室验结果揭示了遗址土其耦合作用下会发生抗风蚀能力降低(风蚀速率提高)、抗雨蚀能力减弱(崩解加速)、强度衰减(弹性波速和抗剪强度降低)的现象。
3) 在冻融交替和盐渍耦合作用下,水盐热过程使水分和盐分在遗址土孔隙中发生固液态、结晶-溶解相互转化,引发孔隙扩张,骨架软化。粒间连接变弱是导致抗风蚀、抗雨蚀能力和强度等宏观性质的劣化的本质原因。
4) 遗址土宏观性质在冻融交替和盐渍双重作用下发生劣化响应,有力地驱动底部掏蚀、片状剥离和坍塌等严重威胁土遗址病害的发育和发展。
参考文献:
[1] 丘富科. 中国文化遗产词典[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2009: 357-358.
QIU Fuke. Chinese culture heritage dictionary[M]. Beijing: Cultural Relic Press, 2009: 357-358.
[2] 吴绍洪, 尹云鹤, 郑度, 等. 青藏高原近30年气候变化趋势[J]. 地理学报, 2005, 60(1): 3-11.
WU Shaohong, YIN Yunhe, ZHENG Du, et al. Climate changes in Tibet Plateau during the last three decades [J]. Acta Geographica Sinca, 2005, 60(1): 3-11.
[3] 崔凯, 谌文武, 匡静, 等. 干湿交替与盐渍双重作用下干旱半干旱地区土遗址劣化效应[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(6): 2378-2384.
CUI Kai, CHEN Wenwu, KUANG Jing, et al. Effect of deterioration of earthern ruin with joint function of salinized and alternating wet and dry in arid and semi-arid regions[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(6): 2378-2384.
[4] 崔凯, 谌文武, 张景科, 等. 干旱区古代建材夯土特征及劣化机理研究[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2012, 44(6): 47-54.
CUI Kai, CHEN Wenwu, ZHANG Jingke, et al. Study on mechanism of degradation and feature of ancient building materials- rammed earth in arid region[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2012, 44(6): 47-54.
[5] QU Jianjun, CHENG Guodong, ZHANG Kecun, et al, et al. An experimental study of the mechanisms of freeze/thaw and wind erosion of ancient adobe buildings in northwest China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2007, 66(2): 153-159.
[6] 严耿升, 张虎元, 王晓东, 等. 干旱区土建筑遗址冻融耐久性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32(8): 2267-2282.
YAN Gengsheng, ZHANG Huyuan, WANG Xiaodong, et al. Durability of earthen architecture ruins under cyclic freezing and thawing[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(8): 2267-2282.
[7] OZTAS T, FAYETORBAY F. Effect of freezing and thawing processes on soil aggregate stability[J]. Catena, 2003, 52(1): 1-8.
[8] SIGRUN H K,  . The influence of freeze-thaw cycles and soil moisture on aggregate stability of three soils in Norway[J]. Catena, 2006, 67(3): 175-182.
. The influence of freeze-thaw cycles and soil moisture on aggregate stability of three soils in Norway[J]. Catena, 2006, 67(3): 175-182.
[9] 张虎元, 刘平, 王锦芳, 等. 土建筑遗址表面结皮形成与剥离机制研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2009. 30(7): 1883-1891.
ZHANG Huyuan, LIU Ping, WANG Jinfang, et al. Generation and detachment of surface crust on ancient earthen architectures[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(7): 1883-1891.
[10] 黄克忠. 岩土文物建筑的保护[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1998: 1-4.
HUANG Kezhong. Conservation of cultural relic and construction building of rock-soil[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 1998: 1-4.
[11] KEVIN H, ALIDA H. Weathering by wetting-drying: Some experimental results[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 1996, 21(4): 365-376.
[12] 崔凯, 谌文武, 韩琳, 等. 干旱区土遗址掏蚀区土盐渍劣化与风蚀损耗效应[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2011, 31(9): 1414-1421.
CUI Kai, CHEN Wen-wu, HAN Lin, et al. Effects of salinized deterioration and aeolian ullage on soils at undercutting area of earthern ruins in arid region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 31(9): 1414-1421.
[13] 李最雄, 赵林毅, 孙满利. 中国丝绸之路土遗址的病害及PS加固[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(5): 1047-1053.
LI Zuixiong, ZHAO Linyi, SUN Manli. Deterioration of Earthern Sites and Consolidation with PS Material along SILK ROAD of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(5): 1047-1053.
[14] GB 50021—2001, 岩土工程勘察规范[S].GB 50021—2001, The rock soil engineering reconnaissance specification[S].
[15] 蒲天彪. 青海省境内明长城保存现状分析与保护对策[J]. 文物, 2011(9): 86-90.
PU Tianbiao. Analysis of current situation and study of protection measure on Ming Great wall in Qinghai province[J]. Cultural Relics, 2011(9): 86-90.
(编辑 罗金花)
收稿日期:2015-04-10;修回日期:2015-06-10
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(52108245,41562015);2013文化遗产保护领域科学和技术研究课题(2013-YB-HT-013);冻土工程国家重点实验室开放基金(SKLFSEl201101)(Projects (52108245, 41562015) National Science Foundation of China; Project (2013-YB-HT-013) supported by the Scientific Research and Technical Project in Conservation of Cultural Heritage in 2013; Project (SKLFSEl201101) supported by the Open Foundation from Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute)
通信作者:谌文武,博士,教授,从事地质工程、岩土工程、文物保护工程研究;E-mail:sungp@lzu.edu.cn