NF-RO组合膜处理大豆乳清废水
缪畅,邱运仁
(中南大学 化学化工学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:采用芳香聚酰胺纳滤膜和反渗透膜处理模拟大豆乳清废水,研究溶液浓度、操作压力、膜面流速、pH等对渗透通量与截留效果的影响,并探讨蛋白污染膜的清洗条件。研究结果表明:在一定操作压力下,渗透通量随着料液浓度的增加而减小,随膜面流速的增加而增加;对一定浓度的原料液,在操作压力小于0.7 MPa时,渗透通量随压力的增大而增大,当操作压力大于0.7 MPa时,渗透通量不再随压力的增大而增大;大豆乳清废水的等电点pH为4.5,当pH大于等电点时,渗透通量和截留率随pH的增大而增大;芳香聚酰胺反渗透膜对纳滤透过液的NaCl截留率在90%以上;蛋白污染纳滤膜经pH=10的NaOH溶液清洗后,通量可完全恢复。
关键词:乳清蛋白;纳滤;反渗透;膜污染;废水处理
中图分类号:X703, TQ028.8 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2010)04-1623-05
Treatment of soybean whey wastewater by NF and RO membrane
MIAO Chang, QIU Yun-ren
(College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The aroma polyamide (APA) nanofiltration (NF) membrane and reverse osmosis (RO) membrane were used for the treatment of simulative industrial soybean whey wastewater. The effects of concentration, trans-membrane pressure (TMP), velocity, and pH on the permeate flux and retention were investigated, and the cleaning of the whey protein fouled membrane was also studied. The results show that the flux decreases with the increase of the concentration, and increases with the increase of the velocity at a certain TMP. The permeate flux increases with the increase of TMP when TMP is within 0.7 MPa, and the permeate flux changes little when TMP is greater than 0.7 MPa. The pH of isoelectric point (IEP) is 4.5, when the pH of the soybean whey wastewater is greater than IEP, both the flux and retention increase with the increase of pH. The removal of NaCl in the filtrate of nanofiltration is over 90% by the treatment of reverse osmosis. Water flux of the cleaned NF membrane can recover by the cleaning with NaOH solution at pH 10.
Key words: whey protein; nanofiltration; reverse osmosis; membrane fouling; wastewater treatment
大豆蛋白是通过大豆蛋白质改性加工而制成的高科技植物性蛋白质产品,因其具有很高的营养和经济价值而受到人们的青睐。乳清废水是在大豆分离蛋白过程中产生的,来源于碱溶酸沉上清和水洗等工序。乳清废水中含有少量未沉淀的大豆球蛋白、丰富的乳清蛋白和大豆低聚糖等营养价值和经济价值很高的功能性物质和一些盐类[1-3]。我国是大豆生产大国,大豆加工企业遍布全国各地,但以中小型企业居多,资金少,乳清废水的处理是各豆制品企业面临的突出问题。目前,该废水较多地是用化学生物方法处理,以降低其中的化学耗氧量(COD)和生物需氧量(BOD)。该方法不仅处理工艺复杂,且资源浪费严重,效率低,难以达到工业上废水排放的要求[3]。膜技术是近年发展起来的一门新型的分离技术,因其具有无相变、能耗少、易操作和分离效率高等一系列优点,被广泛用于食品加工业废水处理[4-5]。膜分离技术用于大豆乳清废水中大豆蛋白和低聚糖的浓缩,并通过反渗透脱盐得到RO水。采用该技术实现了资源的有效利用,变废为宝,有着极高的经济效益和社会效益。在大豆乳清废水中,由于乳清蛋白作为一种胶体物质,在过滤压差和透过水流的作用下很容易吸附在膜表面形成凝胶层,从而造成膜污染,渗透通量下降,极大地降低了膜的分离效率,因此,选择合适的膜材料并选择有效的膜清洗方法是实现膜分离技术用于乳清废水资源化处理的关键。芳香聚酰胺是一种较高性能的高分子合成材料[6],由于分子链中含有刚性苯环结构和氢键,使其具有较好的热稳定性、机械延展性和耐压密性[6-8],被广泛用作膜材料[7]。随着淡水资源日益减少,对海水进行淡化已迫在眉睫,聚酰胺反渗透膜已成为有效的海水脱盐膜[9]。游双银等[10]采用截留相对分子质量分别为1500和500的聚酰胺超滤和纳滤膜提取橄榄苦苷,橄榄苦苷的截留率达到94.41%,而且膜分离后提取液澄清透明,膜较易清洗。本文作者考察了用芳香聚酰胺纳滤-反渗透组合膜处理模拟大豆乳清废水的工艺条件,研究浓度、操作压差和pH对膜渗透通量的影响,并考察大豆乳清蛋白污染膜的清洗条件,得到了适宜的清洗工艺,可为工业生产提供指导。
1 实验
1.1 仪器与药品
仪器为:M-N2521A3型芳香聚酰胺卷式纳滤膜,压力≤1.5 MPa;2521型芳香聚酰胺卷式反渗透膜(Applied Membranes INC,USA),除盐率为98%,2种膜面积均为1.1 m2,纯水通量均为40~50 L/h;752s型紫外可见分光光度计(上海棱光技术有限公司生产);Mettler Toledo 320-S酸度计(梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司生产);DDS-IIA型电导仪(成都贝斯达仪器有限公司生产)。
药品为:大豆蛋白胨,总氮含量>9%,氨基氮含量≥2.0%,pH为6.8~7.0(杭州天和微生物试剂有限公司生产,AR级);考马斯亮蓝试剂(国药集团化学试剂有限公司生产,AR级);氢氧化钠、盐酸、氯化钠(均为AR级)。
1.2 大豆乳清废水的制备
大豆乳清废水采用碱溶酸沉法制备模拟工业乳清废水[11]。具体操作与工艺参数如下:在50 ℃将大豆蛋白胨与去离子水以1?10(质量比)均匀混合;用质量分数为40%的NaOH调节pH到8.5,恒温搅拌40 min后降温至40 ℃;用质量分数为30%的HCl调节pH到4.5,静止20 min;以转速3 000 r/min离心分离5 min得到上清液,然后加入2 g/L NaCl即为乳清废水。
1.3 分析测定方法
采用考马斯亮蓝G-250法[12]测定蛋白质含量;采用电导率测定法测定盐酸浓度。
1.4 实验装置与流程
将制备的大豆乳清废水加入储槽,通过纳滤膜浓缩分离大豆蛋白。待系统运行稳定后,考察蛋白质量浓度、操作压差和pH等对渗透通量和截留率的影响,从而确定最佳操作工艺参数,并测定纳滤浓缩液的蛋白浓度。二级纳滤的透过液用于反渗透脱盐,通过测定进出反渗透膜前后溶液电导率的变化,计算反渗透膜的盐截留率。当膜通量下降较大时,需对膜进行清洗,通过比较不同清洗剂对膜通量恢复的效果,确定最佳清洗条件。乳清废水工艺流程如图1所示。

图1 乳清废水处理工艺图
Fig.1 Flow diagram of treatment of soybean whey wastewater
2 实验结果与分析
2.1 纳滤过滤大豆乳清废水
2.1.1 蛋白质量浓度的影响
在蛋白质量浓度为0.9~5.0 g/L时,在操作温度为20 ℃、压差为0.5 MPa、流量为4 L/min和pH=8的条件下考察原料液的蛋白质量浓度对纳滤膜渗透通量和蛋白截留率的影响,结果分别如图2和图3所示。

图2 蛋白质量浓度不同时乳清废水的通量衰减曲线
Fig.2 Permeate decline of soybean whey with different concentration

图3 蛋白质量浓度对截留率的影响(一级纳滤)
Fig.3 Effect of concentration on rejection (nanofiltration for the first time)
图2所示为不同蛋白质量浓度下一级纳滤渗透通量随时间的变化。由图2可知:在初始通量均为55.30 L/(m2?h)的情况下,蛋白质量浓度越高,通量衰减越快。处理蛋白质量浓度为4.8 g/L的溶液,在开始5 min内,通量由55.30 L/(m2?h)衰减到32.73 L/(m2?h),经35 min衰减到22.73 L/(m2?h);而处理质量浓度为0.9 g/L的料液,经过45 min通量为34.55 L/(m2?h)。这是因为进料质量浓度越大,蛋白质胶体物质在膜表面的堆积和吸附越严重,造成膜孔堵塞和膜污染也越严重,使膜通量急剧下降。这与Su等[13]采用无机Al2O3膜过滤不同质量浓度的BSA溶液得到的结果较相似。另外,随着超滤的进行,通量逐渐减小并趋于稳定。这是因为膜面的吸附和浓差极化使蛋白质质量浓度逐渐增大到蛋白质的凝胶化浓度,在膜面上形成凝胶层,此时,通量主要受它控制,该时间可称为“凝胶化时间”。从图2可见:凝胶化时间为30~35 min。
图3所示为一级纳滤处理不同质量浓度蛋白液的稳定段截留率R。由图3可知:在一级纳滤时,在蛋白质量浓度为1~5 g/L时,随蛋白质量浓度增加,纳滤膜对乳清蛋白的截留率略有减小,但在此蛋白质量浓度范围内,截留率均高于88%。一级纳滤的透过液再进入二级纳滤,经检验,二级纳滤透过液中不含乳清蛋白,说明此纳滤膜对乳清蛋白有较好的截留效果。
2.1.2 操作压差(TMP)的影响
实验考察了在温度为20 ℃、流量为4 L/min和pH为8.0的条件下,处理蛋白质量浓度为2.9 g/L的乳清液时操作压差(TMP)对渗透通量的影响,结果如图4和图5所示。由图4可知:TMP较大时,膜的初始渗透通量较大,但通量衰减也较快,前5 min内,膜通量迅速衰减,然后缓慢减小并趋于稳定。这是因为随着过滤时间的增加,浓差极化现象越严重,蛋白质在膜表面吸附并逐渐形成凝胶层。
图5所示为TMP对稳定段渗透通量J的影响关系曲线。处理RO水时,通量随TMP的增加而增加,且基本呈线性关系。处理乳清蛋白液时,当TMP小于0.7 MPa时,膜的渗透通量随TMP的增加而增加,但当TMP大于0.7 MPa时,膜通量基本不再随TMP的变化而变化。这是因为TMP较低时,浓差极化和膜污染影响较小,纳滤膜渗透通量J随着TMP增大而增大;随着压差的增加,浓差极化严重,过滤阻力增大,凝胶层增厚,当凝胶层达到稳定后,膜通量主要受凝胶层控制,则出现膜的渗透通量随时间趋于稳定而与压力无关的现象[14]。并且操作压差越大,造成膜表面凝胶层的厚度越大,清洗难度及能耗也必然增大。所以,为了保持较大的通量同时又有效地减少膜污染,应该选择在临界压力下进行纳滤操作。

图4 不同压差下渗透通量的衰减
Fig.4 Decline of permeate flux with time at different TMP

图5 操作压差(TMP)对渗透通量的影响
Fig.5 Effect of TMP on permeate flux
2.1.3 膜面流速的影响
由于卷式膜的实际流通截面积未知,难以计算膜面流速,故用进料流量表示膜面流速的影响。在料液温度为20 ℃、压差0.5 MPa和pH为8.0的条件下,处理蛋白质量浓度为2.9 g/L和4.0 g/L的乳清液时流量对渗透通量的影响,结果见图6。由图6可知:随着流量的增加,透液通量增加。这是因为流量增加,膜面流速增加,有利于减小浓差极化和蛋白质在膜面的吸附和沉积,从而减小浓差极化阻力和膜污染阻力。

图6 流量对渗透通量的影响
Fig.6 Effect of volumetric flow rate on permeate flux
2.1.4 溶液pH的影响
图7所示是pH为3.5~10.8时处理质量浓度为2.9 g/L的乳清液的渗透通量与截留率关系曲线。由图7可见:当pH=4.5时,为乳清蛋白的等电点,膜的渗透通量最小,污染达到最大值。因为在等电点处,由于缺乏静电排斥力,吸附最严重,所以膜污染最 大[13, 15];当处于碱性条件时,由于高于等电点,膜荷负电,蛋白质分子间的静电排斥力增大,同时,pH 较高使得蛋白质分子溶解性增大,蛋白质分子不易在膜表面沉积形成吸附层,因此,渗透通量增大。在 pH>7时,膜的截留率可达90%以上。

图7 pH对渗透通量J和蛋白截留率R的影响
Fig.7 Effect of pH on permeate flux and rejection
2.2 反渗透脱盐
当乳清溶液经过二级纳滤后,经检验,透过液中不再含有大豆蛋白,NaCl质量浓度为1.97 g/L,说明原溶液中绝大部分NaCl透过了纳滤膜。透过的盐溶液作为反渗透的原液进行脱盐。反渗透操作压力在0.6~1.5 MPa内,运行2 h,膜的截留率均达90%以上。
2.3 膜的清洗
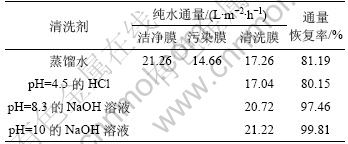
大豆蛋白作为一种胶体物质易吸附在膜表面或堵塞膜孔,导致膜污染。为了维持纳滤膜过程的正常进行,必须对污染膜进行清洗,污染膜均是在0.5 MPa下经一级纳滤质量浓度为2.9 g/L的乳清蛋白液35 min后所得的膜。考察不同清洗剂对大豆乳清蛋白污染膜的清洗效果,清洗在较低的压力下进行,具体过程如下:先用纯水测定被大豆蛋白污染的纳滤膜在0.19 MPa下的水通量,再用清洗液在0.19 MPa下循环清洗35 min,放出清洗液,然后,用纯水冲洗膜至pH呈中性,再测定清洗膜的纯水通量,并计算通量恢复率,结果如表1所示。
从表1可知:蒸馏水对污染膜有一定的清洗效果,用pH为等电点的HCl溶液清洗,对纳滤膜的通量恢复效果不理想,而用pH>8的NaOH溶液清洗可获得较好的清洗效果;用pH=10的NaOH溶液清洗蛋白污染纳滤膜,清洗膜的通量可以恢复到洁净膜的水平。
表1 清洗剂清洗效果
Table 1 Efficiency of cleaning agents
3 结论
(1) 处理一定质量浓度的乳清废水,当操作压力小于0.7 MPa时,增加操作压力,渗透通量增大,截留率也增加;当操作压力大于0.7 MPa时,通量基本不变,临界操作压力为0.7 MPa。
(2) 处理一定质量浓度的乳清废水,在等电点pH=4.5处,通量最小;pH偏离等电点越远,渗透通量越大。
(3) 在0.6~1.5 MPa内,对纳滤透过液进行反渗透脱盐,盐截留率可达90%以上。
(4) 蛋白污染膜经pH=10的NaOH溶液清洗后,其膜通量基本与洁净膜的膜通量相近。
参考文献:
[1] 徐朝辉, 万端极, 崔朝亮, 等. 膜技术在处理大豆乳清废水中的应用[J]. 中国油脂, 2007, 32(1): 68-70.
XU Zhao-hui, WAN Duan-ji, CUI Zhao-liang, et al. Application of membrane technology in the treatment of soy whey wastewater[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2007, 32(1): 68-70.
[2] 袁其朋, 马润宇. 膜分离技术处理大豆乳清废水[J]. 水处理技术, 2007, 21(3): 161-163.
YUAN Qi-peng, MA Run-yu. Treatment of soybean whey wastewater by membrane process[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2007, 21(3): 161-163.
[3] 祁佩时, 吕斯濠. 超滤法处理大豆蛋白废水及资源回收的研究[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2005, 37(8): 1138-1141.
QI Pei-shi, L? Si-hao. Soy protein wastewater treatment and resource reclamation with ultrafiltration[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2005, 37(8): 1138-1141.
[4] 周伯川, 杨帆. 膜法提取大豆分离蛋白的研究[J]. 膜科学与技术, 1998, 18(6): 22-24.
ZHOU Bo-chuan, YANG Fan. Study on extraction of SPI by membrane technique[J]. Membrane Science and Technology, 1998, 18(6): 22-24.
[5] Guu Y K, Chiu C H, Young J K. Processing of soybean soaking water with a NF-RO membrane system and lactic acid fermentation of retained solutes[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 1997, 45: 4096-4100.
[6] 周建梅. 热致液晶聚酰胺的溶解性能和热性能[J]. 应用化学, 2007, 24(12): 1458-1460.
ZHOU Jian-mei. Dissolvability and thermal property of a thermotropic liquid crystalline polyamide[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2007, 24(12): 1458-1460.
[7] Noelia S J, Ana G V, Pedro E et al. Fluorescent aromatic polyamides with urea binding sites and fluorine or dansyl signaling units[J]. Eur Polym J, 2008, 44: 3578-3587.
[8] 任晓晶, 皇甫风云, 白云东. 芳香聚酰胺纳滤膜的制备及性能研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2008, 33(6): 25-27.
REN Xiao-jing, HUANGFU Feng-yun, BAI Yun-dong. Preparation and separation performance of aromatic polyamide nanofiltration membrane[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2008, 33(6): 25-27.
[9] LIU Mei-hong, YU San-chuan, TAO Jie, et al. Preparation, structure characteristics and separation properties of thin-film composite polyamide-urethane seawater reverse osmosis membrane[J]. J Membr Sci, 2008, 325: 947-956.
[10] 游双银, 尹卫平, 张丽, 等. 聚酰胺膜在橄榄苦苷分离上的工艺研究[J]. 中成药, 2007, 29(8): 1235-1238.
YOU Shuang-yin, YIN Wei-ping, ZHANG Li, et al. Study on separation of oleuropein by polyamide membrane[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2007, 29(8): 1235-1238.
[11] 赵冬梅, 刘凌, 张京健. 豆制品生产中高浓度废水的检测与分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2006, 32(1): 68-71.
ZHAO Dong-mei, LIU Ling, ZHANG Jing-jian. Detection and analysis of the concentrated waste water from soybean processes[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2006, 32(1): 68-71.
[12] 曹稳根, 赵海泉, 焦庆才. 考马斯亮蓝与牛血清蛋白相互作用机理的研究[J]. 激光生物学报, 2008, 17(1): 32-37.
CAO Wen-gen, ZHAO Hai-quan, JIAO Qing-cai. Mechanism of the interaction between coomassie brilliant blue and bovine serum albumin[J]. Acta Laser Biology Sinica, 2008, 17(1): 32-37.
[13] Su T J, Lu J R, Cui Z F, et al. Identification of the location of protein fouling on ceramic membranes under dynamic filtration conditions[J]. J Membr Sci, 1999, 163(2): 265-275.
[14] Balakrishnan M, Dua M, Bhagat J J. Effect of operating parameters on sugarcane juice ultrafiltration: results of a field experience[J]. Sep Purif Technol, 2000, 19: 209-220.
[15] Bader M S H, Veenstra J N. Analysis of concentration polarization phenomenon in ultrafiltration under turbulent flow conditions[J]. J Membr Sci, 1996, 114(2): 139-148.
收稿日期:2009-08-06;修回日期:2009-11-06
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(20776161)
通信作者:邱运仁(1966-),男,湖南益阳人,博士,教授,从事环境工程、膜分离技术等研究;电话:0731-88876675;E-mail: qiu_yunren@yahoo.com.cn
(编辑 任楚威)