


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 2112-2117
Effect of bonding parameters on microstructures and properties during TLP bonding of Ni-based super alloy
LIN Tie-song1, LI Hai-xin1, HE Peng1, YANG Xue1, HUANG Yu-dong2, LI Liang1, HAN Leng1
1. State Key Laboratory of Advanced Welding and Joining, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China;
2. School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 9 September 2011; accepted 27 March 2011
Abstract: Ni-based alloy was transient liquid phase bonded using a BNi-2 interlayer. The effect of bonding parameters on the microstructures and mechanical properties of the joints was investigated. With the increase of bonding temperature or time, the number of Ni-rich and Cr-rich borides and the grain size of precipitation zone decrease. Higher bonding temperature or longer bonding time is beneficial to the diffusion of melting point depressant elements (B and Si) from the PZ to the base metal and atomic interdiffusion between the base metal and the joint. The chemical composition and microstructure of the joints bonded at 1170 ℃ for 24 h are comparable to the base metal. The shear test results show that both the room and elevated temperature shear-strengths of the joints increase with increasing bonding time. However, the effect of bonding time on elevated temperature tensile-shear strength is greater than on room temperature tensile-shear strength.
Key words: Ni-based alloy; transient liquid phase bonding; microstructure; tensile-shear strength
1 Introduction
With the continuous development of modern industry, especially aviation, aerospace and nuclear industry, materials with excellent performances are urgently needed [1,2]. Ni-based alloys, which have high temperature mechanical properties and good corrosion resistance, are commonly employed for manufacturing complex shapes for hot section components of aircraft engines and power generation turbines [3,4]. These components need to withstand higher temperature and stress, causing more rapid components degradation by fatigue, creep and oxidation reaction. Under most situations, it is more economical to repair damage than to completely replace the components. The most common repair method is welding [5,6]. However, welding is often found unsuitable for repairing high strength Ni-based alloys due to their high susceptibility to hot cracking during welding and post-weld heat treatment cracking [7,8]. Therefore, transient liquid phase (TLP) bonding technique, which can be used to produce joints with comparable microstructure and mechanical properties to those of the base metal, has been gaining attention for joining Ni-based alloys [9,10].
Some studies have employed TLP bonding technique to join Ni-based alloys. In order to achieve sound joints, most studies focus on the solidification behavior of residual liquated interlayer during TLP bonding process for the elimination of the eutectic [5,11-13]. The effect of bonding temperature and time on isothermal solidification of the joint has been reported [11-13]. For example, the time required to complete the isothermal solidification process can be predicted by using both analytical and numerical models [14,15]. However, few studies have been done on the effect of bonding parameters on the microstructure evolution of the joint after complete isothermally solidification. Furthermore, little information on the effect of bonding parameters on the high temperature properties of such joints has been reported.
Ni-based brazed alloys, which have both good corrosion resistance and creep strength, are commonly selected as filler metals. However, some Ni-based braze alloys containing phosphorus do not meet the requirement due to the formation of brittle nickel phosphides. BNi-2 has low liquidus temperature and high creep strength among all the Ni-based braze alloys [16]. So it is chosen as an interlayer.
In this study, Ni-based alloy was bonded using TLP bonding technique with a BNi-2 interlayer. The effect of bonding temperature and time on the microstructure of the joint was investigated, and the effect of bonding time on the properties of the joint was determined.
2 Experimental
Ni-based alloy (GH99) was used as the base metal in this investigation. The commercially available Ni-based filler alloy BNi-2, in the form of foils with thickness of 50 μm, was used as the interlayer. The nominal composition and the solidus/liquidus temperature of the base metal and interlayer are listed in Table 1. The coupons were cut into dimensions of 35 mm×6 mm×1.5 mm (overlap width of 1.5 mm) using a wire electrodischarge machine. Thereafter, the mating surfaces of the coupons were polished using No. 800 SiC paper. The polished coupons and interlayer were ultrasonically cleaned for about 30 min in a solution of acetone. Subsequently, the interlayer was placed between the mating surfaces of the cleaned coupons for TLP bonding.
Table 1 Chemical composition and solidus/liquidus temperature of GH99 alloy and BNi-2 interlayer
The TLP bonding operation was carried out in a vacuum furnace (10-4 Pa). Coupons were bonded at temperatures ranging from 1130 to 1250 ℃ for 90 min and bonding time ranging from 40 min to 24 h at 1170 ℃. The heating rate was 15 ℃/min, and cooling was done in the furnace.
The bonded samples were cut perpendicularly to the joint interface, and the cross-sections of the joints were prepared by using standard metallographic. Thereafter, the polished samples were etched in solution of 20 mL HF+30 mL H3PO4 +50 mL HNO3. The microstructures of the bonded joints were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, S-570). The composition of the joint was analyzed by electron probe X-ray microanalysis (EPMA, JXA-8600). Shear tests of the samples were performed on an Instron-1186 universal testing machine to evaluate the shear strength of the brazed joints.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of bonding temperature on microstructures of joints
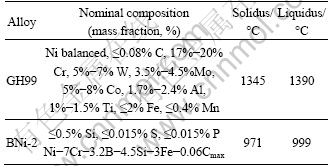
The microstructures of the joints bonded at different bonding temperature for 90 min are shown in Fig. 1. It can be seen that the joint consists of two distinct zones, isothermally solidified zone (ISZ, a zone in the middle area) and precipitation zone (PZ, a zone between ISZ and base metal). The microstructure of ISZ comprised of large and uniform grains is similar to the base metal. PZ contains a large number of white precipitates mainly distributed on the grain boundary. It displays that the closer to the center of the joints, the smaller the precipitates are, and the precipitates become larger as they are closer to the base metal.
The microstructures of the joints bonded at 1150 and 1200 ℃ for 90 min are shown in Figs. 1(a) and (b). According to the EPMA results and previous studies [3], the ISZ is mainly composed of Ni-rich and Cr-rich solid solution, and no eutectic-type solidification reaction product is formed. It implies that the diffusion of melting point depressant (MPD) elements (B and Si) from the molten interlayer into the base metal and isothermal solidification of the residual liquid are complete under the bonding conditions. According to the EPMA results, the white precipitates distributed mainly along the grain boundaries in PZ are Cr-rich and Ni-rich borides. Boron diffuses rapidly away from the molten interlayer into the base metal. The grain boundary is the preferred path for diffusion. When the solubility limit is exceeded in the base metal, Cr-rich and Ni-rich borides will form in the grain boundary. Furthermore, the number of Cr-rich and Ni-rich borides precipitates in the joint bonded at 1200 ℃ is less than that bonded at 1150 ℃. Since the solubility of boron is very low in the metal, the number of Cr-rich and Ni-rich borides is determined by the diffusivity of boron in the base metal. The diffusivities of boron in Ni-based alloy are 1.947×10-7 and 2.566×10-7 at 1150 and 1200 ℃, respectively [17]. The diffusivity of boron at 1200 ℃ is much higher than that at 1150 ℃. This can readily explain why there are smaller white precipitates in the PZ at higher bonding temperature. Furthermore, the grain size in PZ is smaller than those in ISZ and base metal. The reason is that the white precipitates which are like the second phase particles in the metal distributed along the grain boundaries hinder the growth of grains in PZ.
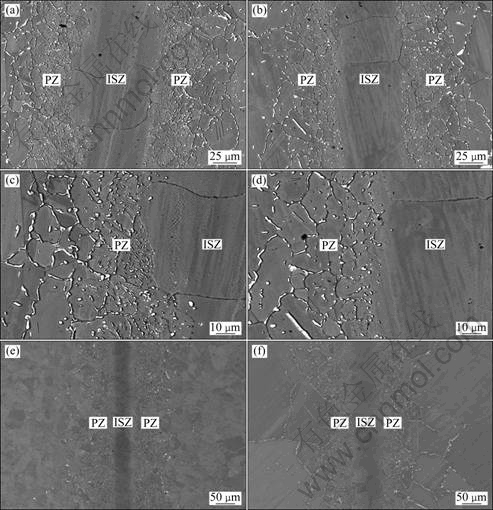
Fig. 1 SEM images showing effect of bonding temperature on microstructures of joints: (a) 1150 ℃; (b) 1200 ℃; (c) Interface of Fig. 1(a); (d) Interface of Fig. 1(b); (e) 1130 ℃; (f) 1250 ℃
To explore the effect of bonding temperature on the microstructures of the joints further, relatively low and high temperatures were taken to the experiment as a comparison. The microstructures of the joints bonded at 1130 and 1250 ℃ for 90 min are shown in Figs. 1(e) and (f). It can be seen from Fig. 1(e) that the microstructure of ISZ is similar to that of the former joint. The number of white precipitates in PZ is more than that in the joint bonded at higher temperature. Furthermore, the grains of the base metal are fine and uniform. It reveals that there is no signification change in the grain size at lower bonding temperature during the TLP bonding process. With the bonding temperature increasing from 1130 to 1250 ℃, the thickness of ISZ increases due to the dissolution of base metal into the molten interlayer. Furthermore, the number of white precipitates in PZ is significantly reduced (see Fig. 1(f)) because boron diffuses rapidly from the PZ into the base metal at higher temperature. It indicates that higher bonding temperature is beneficial for the diffusion of MPD elements from the PZ to the base metal and the uniform composition of joints. However, the grain size of the base metal increases significantly at higher temperature, resulting in the degradation of the base metal.
3.2 Effect of bonding time on microstructures of joints
The microstructures of the joints bonded at 1170 ℃ for different bonding time are shown in Fig. 2. It can be observed that the microstructures of joints also mainly consist of ISZ (comprises of Ni-rich and Cr-rich solid solution) and PZ (contains Cr-rich and Ni-rich borides). And the microstructure of PZ is greatly affected by bonding time. When the bonding time is 40 min, large quantities of white precipitates present in the PZ of the joint, as shown in Figs. 2 (a) and (c). The volume of white precipitates in the PZ decreases with increasing bonding time due to the diffusion of boron from PZ to the base metal. Furthermore, the grain size in the joints becomes uniform and the width of PZ decreases as shown in Fig. 2. When the bonding time is 8 h, the microstructure of the joints is relatively uniform, but the white precipitates distributed in the PZ are still observed (see Fig. 2(e)). When the bonding time is 24 h, the whole joint tends to be more uniform and fewer white precipitates are observed in the PZ (see Fig. 2(f)). It indicates that longer bonding time is beneficial to the diffusion of MPD elements from PZ to the base metal and the microstructure uniformity of the joints.
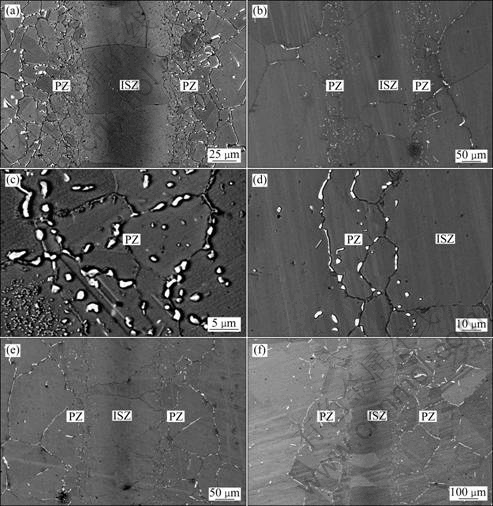
Fig. 2 SEM images showing effect of bonding time on microstructures of joints bonded at 1170 ℃: (a) 40 min; (b) 120 min; (c) Interface of Fig. 2(a); (d) Interface of Fig. 2(b); (e) 480 min; (f) 24 h
In order to determine the degree of homogeneity of elements attained as a function of bonding time and bonding temperature, the effect of TLP bonding process on the distribution of elements across the interface of the joints was studied. EPMA analysis was performed by using “line sweep” in order to monitor the quantitative changes of elements across the joint. The scan mode of the joint bonded at 1170 ℃ for 24 h is shown in Fig. 3. From the center of joints to the base metal, parallel line-scan was carried out in the regions of A, B, C and D, and then the average content of elements of each line was summed and calculated. It will be more accurate to know the distribution of the elements along the bonding joints to the base metal by contrasting their own content in the regions of A, B, C and D.
It can be seen from Table 2 that the contents of Si, which is not contained in the original base metal, are 0.96%, 0.89%, 0.94% and 0.99% in the regions of A, B, C and D, respectively. Considering the measurement error, it can be considered that the contents of Si in the four regions are basically identical. It means that Si distributes uniformly from the joint to the base metal after bonding for 24 h. Relative to the base metal away from the bonding zone, the W, Mo and other elements which are not contained in the original interlayer have been largely diffused from the base metal to the joint. According to Table 2, the four regions have similar contents of these elements. For example, the content of W in the middle of ISZ is 11.96% (region A ), and in the PZ is 13.55% (region B), while in the base metal far from the joint is about 14.3% (region D). Therefore, it can be inferred that the component of the joint is comparable to the base metal after bonding at 1170 ℃ for 24 h.
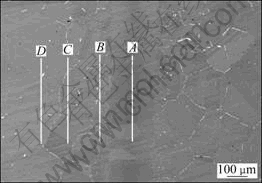
Fig. 3 Vertical line sweep mode of joint bonded at 1170 ℃ for 24 h
Table 2 Compositions of different zones in Fig. 3 (mass fraction, %)
3.3 Effect of bonding time on mechanical properties of joints
The tensile-shear strength of the joints bonded at 1170 ℃ for different bonding time is shown in Fig. 4. According to Fig. 4(a), the room temperature tensile-shear strength of the joints increases from 350 to 430 MPa with bonding time increasing from 40 to 120 min. Although the room temperature tensile-shear strength of the joints increases along with the bonding time, the growth rate is low. It indicates that the influence of bonding time on the room temperature tensile-shear strength is comparatively less. The effect of bonding time on the 900 ℃ tensile-shear strength of the joints is shown in Fig. 4(b). It can be observed that the shear strength of the joint increases from 150 to 330 MPa when the bonding time increases from 40 to 120 min. The average growth rate of tensile-shear strength at 900 ℃ is relatively fast compared to that at room temperature. It implies that the effect of bonding time on the elevated temperature tensile-shear strength is greater than that on the room temperature tensile-shear strength. The reason is that large quantities of Cr-rich and Ni-rich borides are formed in the joint bonded for short bonding time, meantime, the linear thermal expansion coefficient between the borides and the matrix is different, which results in the generation of huge stress when the tensile shear tests are performed at elevated temperature. Contrarily, the elevated temperature tensile-shear strength of the joints bonded for long bonding time is higher due to few borides in the joint.
According to the above analysis, it can be inferred that the tensile-shear strength of the joints increases further when the bonding time increases from 2 to 8 h or longer. However, when the bonding time is longer, the grains of the base metal grow seriously, resulting in the degradation of the base metal. Furthermore, the tensile-shear fracture occurs in the base metal.
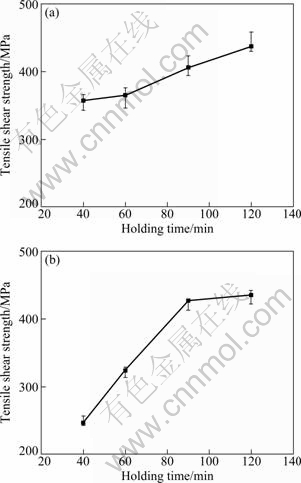
Fig. 4 Effect of bonding time on tensile-shear strength of joints bonded at 1170 ℃: (a) Room temperature tensile-shear strength; (b) Tensile-shear strength at 900 ℃
4 Conclusions
1) GH99 alloy is successfully bonded by using TLP bonding technique with a BNi-2 interlayer. The joint consists of ISZ and PZ zones. With the increase of bonding temperature, the number of white precipitates in the PZ decreases and the grain size is less than that in the ISZ and base metal. Furthermore, the composition of the joint is more uniform. However, the grains of the base metal grow significantly when the bonding temperature is 1250 ℃.
2) As the bonding time increases, the number and size of white precipitates in the PZ decrease due to the diffusion of boron from PZ to the base metal. Longer bonding time is beneficial to the atomic interdiffusion between the base metal and the joint. When the bonding time is 24 h, the chemical composition and the microstructure of the joint are comparable to the base metal.
3) With increasing bonding time, both the room and elevated temperatures tensile-shear strengths of the joint increase. However, the effect of bonding time on elevated temperature tensile-shear strength is greater than that on room temperature tensile-shear strength.
References
[1] GUO Jian-ting, ZHOU Lan-zhang, YUAN Chao, HOU Jie-shan, QIN Xue-zhi. Microstructure and properties of several originally invented and unique superalloy in China [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(2): 237-250. (in Chinese)
[2] SHI Chang-xu, ZHONG Zeng-yong. Development and innovation of superalloy in China [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(11): 1281-1288. (in Chinese)
[3] GUO Jian-ting. The current situation of application and development of superalloys in the fields of energy industry [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(5): 513-527. (in Chinese)
[4] REED R C, TAO T, WARNKEN N. Alloys-by-design: Application to nickel-based single crystal superalloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(19): 5898-5913.
[5] IDOWU O A, RICHARDS N L, CHATURVEDI M C. Effect of holding temperature on isothermal solidification rate during transient liquid phase bonding of Inconel 738LC superalloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 397: 98-112.
[6] TOKORO K, WIKSTROM N P, OJO O A, CHATURVEDI M C. Variation in diffusion-induced solidification rate of liquated Ni-Cr-B insert during TLP bonding of Waspaloy superalloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 311-318.
[7] HENDERSON M B, ARRELL D, LARSSON R, HEOBEL M, MARCHANT G. Nickel based superalloy welding practices for industrial gas turbine applications [J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2004, 9(1): 13-21.
[8] OJO O A, RICHARDS N L, CHATURVEDI M C. Study of the fusion zone and heat-affect zone microstructure in tungsten insert gas-welded INCONEL 738LC superalloy [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2006, 37: 421-433.
[9] DUVALL D S, OWCZARSKI W A, PAULONIS D F. TLP bonding: A new method for joining heat resisting alloys [J]. Welding Journal, 1974, 53(4): 203-214.
[10] LIU Ji-de, JIN Tao, ZHAO Nai-ren, WANG Zhi-hui, LIU Jin-lai, SUN Xiao-feng, GUAN Heng-rong, HU Zhuang-qi. Influence of TLP bonding on the tensile properties for a kind of nickel-based single crystal superalloy [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(2): 332-334. (in Chinese)
[11] POURANVARI M, EKRAMI A, KOKABI A H. Effect of bonding temperature on microstructure development during TLP bonding of a nickel base superalloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 469: 270-275.
[12] CAO Jian, SONG Xiao-guo, ZHENG Zu-jin, FENG Ji-cai. Effect of diffusion time on interfacial microstructure of TLP joints of DD6 single crystal superalloy [J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2011, 32(7): 13-17. (in Chinese)
[13] WANG Fei-sen, CHEN Si-jie, GAO Zeng, LIU Yan-lei, LIU Shan-guang. Effect of melting point depressant elements on the microstructures and properties of T91 steel transient liquid-phase bonding joint [J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2008, 38(11): 18-21. (in Chinese)
[14] ARAFIN M A, MEDRAJ M, TURNER D P, BOCHER P. Effect of alloying elements on the isothermal solidification during TLP bonding of SS 410 and SS 321 using a BNi-2 interlayer [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2007, 106: 109-119.
[15] McDONALD W D, EAGAR T W. Transient liquid phase bonding [J]. Annual Review of Materials Science, 1992, 22: 23-46.
[16] LEE Y L, SHIUE R K, WU S K. The microstructural evolution of infrared brazed Fe3Al by BNi-2 brazed alloy [J]. Intermetallics, 2003, 11: 187-195.
[17] WU X W, CHANDEL R S, LI H, SEOW H P, WU S C. Induction brazing of Inconel 718 to Inconel X-750 using Ni-Cr-Si-B amorphous foil [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2000, 104: 34-43.
连接工艺参数对镍基高温合金TLP连接接头组织和性能的影响
林铁松1,李海新1,何 鹏1,杨 雪1,黄玉东2,李 亮1,韩 冷1
1. 哈尔滨工业大学 先进焊接与连接国家重点实验室,哈尔滨 150001;
2. 哈尔滨工业大学 化工学院,哈尔滨 150001
摘 要:以BNi-2为中间层对镍基合金进行过渡液相连接,研究连接工艺参数对接头组织和力学性能的影响。随着连接温度的升高或连接时间的延长,沉淀区的富镍和富铬硼化物数量减少,同时沉淀区晶粒尺寸减小。较高的连接温度或较长的连接时间,有利于降熔元素(B和Si)由沉淀区向母材中的扩散和母材与连接接头间的原子互扩散。当连接温度为1170 ℃、连接时间为24 h时,可以获得与母材化学成分及组织基本相当的连接接头。剪切试验结果表明:室温和高温拉剪强度均随着保温时间的延长而增加,但连接时间对高温拉剪强度的影响要大于对室温拉剪强度。
关键词:镍基合金;过渡液相连接;微观组织;拉剪强度
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
Foundation item: Projects (50975062, 51105107, 51275135, 51021002) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (QC2011C044) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, China; Project (20112302130005) supported by Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, China; Project (20100471027) supported by the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: HE Peng; Tel/Fax: +86-451-86402787; E-mail: hitjoining@hit.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61436-2