高精度层序地层格架内的地震沉积学应用
——以哈萨克斯坦南图尔盖盆地A区为例
毛治国1, 2,樊太亮3,凌宗发4,孙伟5,李小江6,白斌1, 2,沈武显3,蒋韧3
(1. 中国石油勘探开发研究院,北京,100083;
2. 提高石油采收率国家重点实验室,北京,100083;
3. 中国地质大学(北京) 能源学院,北京,100083;
4. 中国石油对外合作经理部,北京,100007;
5. 科麦奇中国有限公司,北京,100016;
6. 中国石化江汉石油管理局 江汉分公司江汉采油厂,湖北 潜江,433124)
摘 要:在高精度层序地层格架内,应用地震沉积学方法,通过90°相位转换、地层切片和分频处理,进行地震属性趋势和钻井综合分析,研究哈萨克斯坦南图尔盖盆地A区沉积岩岩性、沉积体系及其响应特征,确定沉积微相的边界与分布范围以及单砂体的体积、厚度与规模。研究结果表明:该区河流相发育,以河床滞留沉积、边滩、河漫滩、河漫湖泊等微相为主;不同频率对地震数据的相位等特性有不同响应,刻画地质体的横向不连续性能力也有所不同,频率为20~25 Hz时对河道砂体最敏感,在地层切片上完整清晰地刻画出河道边界、宽度、延伸长度及其平面几何形态。
关键词:高精度层序地层;地层切片;分频技术;南图尔盖盆地
中图分类号:TE121.34 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2010)06-2296-09
Application of seismic sedimentology high-resolution sequence stratigraphic frameworks: Taking block A of South Turgay Basin, Kazakstan as an example
MAO Zhi-guo1, 2, FAN Tai-liang3, LING Zong-fa4, SUN Wei5, LI Xiao-jiang6,
BAI Bin1, 2, SHEN Wu-xian3, JIANG Ren3
(1. Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration & Development of PetroChina, Beijing 100083, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Enhanced Oil Recovery, Beijing 100083, China;
3. School of Energy Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China;
4. Foreign Cooperation Administration Department of PetroChina, Beijing 100007, China;
5. Kerr-McGee China Petroleum Limited, Beijing 100016, China;
6. Jianhan Oil Production Plant of Jianghan Petroleum Administration Bureau, Qianjiang 433124, China)
Abstract: Using seismic sedimentology technologies, such as 90° phasing convertion, stratal slicing and frequency decomposition, lithology and facies of sedimentary rocks in block A of South Turgay Basin in Kazakstan were studied in the high-resolution sequence stratigraphic frameworks. And the boundary and distribution range of microfacies, even to the size, thickness and scale of single sand body were confirmed. The results show that the block A develops meandering river deposit, including four microfacies, i.e., lag deposit, point bar deposit, flood-plain deposit and flood-lake deposit. And meanwhile, different frequency bands have different response features and different capabilities to characterize the horizontal discontinuity of geologic bodies in seimic data. The frequency decomposing stratal slicing (20-25 Hz) displays channel sand bodies clearly and characterizes channel boundary, width, extended length and plane geometric shape accurately.
Key words: high-resolution sequence stratigraphy; stratal slicing; frequency decomposing technology; South Turgay Basin
地震勘探技术经历了数十年的发展,已成为当今世界油气勘探的主要技术手段之一。随着油气资源勘探的逐渐深入,寻找油气田的难度逐渐增大,勘探复杂性日趋增加,油气地质理论和勘探技术也不断向前发展[1]。继地震地层学、层序地层学之后,又出现了一门新的边缘交叉学科——地震沉积学[2]。Zeng等[3-4]认为地震沉积学是利用地震水平反射的结构、外形和趋势与沉积体系地形之间关系,研究沉积岩岩性、沉积相及其沉积过程的一门学科。2005年,地震沉积学国际会议的召开,标志着地震沉积学学科体系正式建立[5-6]。地震岩石学和地震地貌学组成了地震沉积学的核心内容[7],它与地震地层学、层序地层学、沉积学等学科相关,但是,在概念、研究内容、方法技术等方面都有所不同[8]。地震沉积学的基本手段是将某个地质时间界面上的地震属性显示出来。90°相位转换、地层切片和分频解释是地震沉积学中的3项关键技 术[9-10]。地震沉积学最大的理论突破在于对地震同相轴穿时性予以重新认识[11-12]。
1 研究区地质概况
南图尔盖盆地位于乌拉尔山以东的哈萨克斯坦中部,是海西基底之上发育的中生代裂谷盆地,总面积为8×104 km2,呈南北向长轴状分布[13]。构造位置处于图兰板块东南部的乌拉尔—天山缝合线转折端剪切带,西西伯利亚盆地与中亚地块的连接部位(图1)[14]。盆地基底为断裂切割块体,具有垒-堑相间的地质结构,其主要特征是地堑内地层发育齐全,不仅发育了巨厚的侏罗系—新近系地层,局部深凹还发育三叠系,最大厚度在5 km以上。
该盆地自1983年被勘探已来,已发现大小油气田17个[15]。到目前为止,在浅层相较简单的构造圈闭中已经发现油气34亿桶。上侏罗—下白垩统河流—三角洲相砂泥岩沉积是目前南图尔盖盆地主要油气储层,整个盆地90%以上的油气藏均与该储集层有关[16]。本文以盆地上侏罗统Akshabulak组—下白垩统Arysukm组河流—三角洲相砂泥岩沉积储层为研究对象,根据现有钻井和三维地震工区分布,选择A区块开展高精度层序地层分析;在精细的等时地层格架内,进行地震沉积学和沉积微相研究,探讨砂体分布规律。
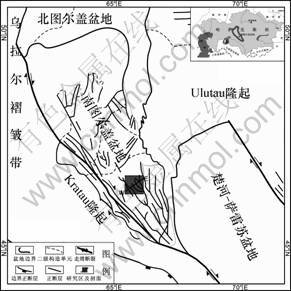
图1 研究区构造位置平面图
Fig.1 Sketch map of structural location of studied area
2 高精度层序地层格架
南图尔盖盆地基底固结于早古生代末,中—晚古生代形成碎屑岩-碳酸盐岩过渡层。中新生代经历初始张裂、断陷发育、断坳转换、坳陷发育和后期隆起等多期构造运动,盆内充填了巨厚的陆源碎屑岩和海相碳酸盐岩沉积[13]。研究层段上侏罗—下白垩统处于盆地断坳转换末期—坳陷发育早期,是盆地构造运动减弱、坳陷充填向准平原化沉积的过渡阶段。岩性以灰色粉砂岩、砂岩为主,夹薄层泥岩,沉积环境为三角洲—河流相。
三级层序作为地层的基本单元是由不整合及其与之对应的整合面所限定的,其内部不存在明显的不整合,而对四级及以上的高精度层序划分和对比实际上使用了旋回地层学和事件地层学的原理。对于陆相碎屑岩,普遍认为水进面是高频沉积旋回追踪对比最可靠和容易识别的标志[17]。
综合该区的岩芯、测井、地震资料分析,结合 井-震标定结果,在研究区进行地震、钻井层序对比,识别出6个四级层序界面,自下而上依次为SBl,SB2,SB3,SB4,SB5和SB6 (图2)。其中:SBl为沉积作用转换面;SB2,SB3,SB5和SB6为河道下切冲刷面;SB4为侏罗系顶面区域性削蚀不整合面。根据上述不同特征的层序界面,在研究区选择区域性的三维地震剖面进行合成记录标定,建立研究区上侏罗统Akshabulak组—下白垩统Arysukm组高精度层序地层格架,划分为2个三级层序、5个四级层序。这5个四级层序从下至上依次命名为SQl-1,SQ1-2,SQ1-3,SQ2-1和SQ2-2(图2)。
SQ1-1层序位于Akshabulak组下部,底界面在自然电位曲线上表现为进积叠加样式向退积叠加样式转换,在自然伽马曲线上表现为高值,其电阻率曲线表现为由中值到低值的转换面。岩性上则由下部的细粒深水沉积物突变为粗粒河道滞留沉积。
SQ1-2层序位于Akshabulak组中部,底界面在自然电位曲线上表现为由进积叠加样式向退积叠加样式的转换,其自然伽玛值为高值,电阻率曲线由中值突变为低值。层序内湖泛面对应于全区较稳定的泥岩层段,电阻率和自然电位低,自然伽玛值高。且泥岩颜色由灰色、深灰色变为绿色、浅绿色,反映水体深度的变化。
SQ1-3层序位于Akshabulak组顶部。侏罗纪末期的断坳构造转换运动是盆地内一次较强的挤压抬升运动,造成了盆地内侏罗系顶部的区域性削蚀,前白垩系构造被剥蚀、夷平,形成准平原状态,并与其后沉积的白垩系之间形成了角度不整合接触关系。研究区SQ1-3层序遭受大范围剥蚀,分布范围较小。岩性主要为灰色砂岩,夹有薄层棕红色泥岩,反映水体较浅的氧化环境。
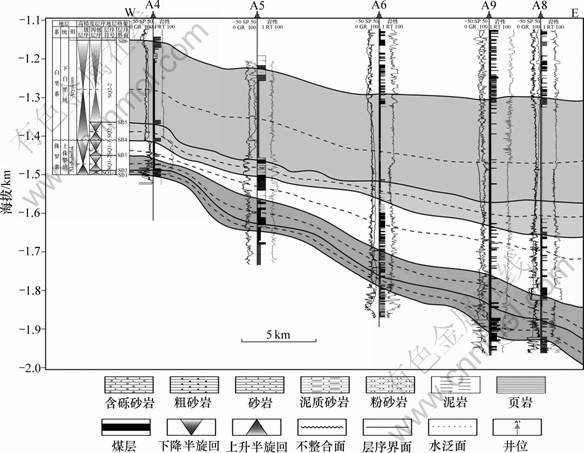
图2 南图尔盖盆地A地区上侏罗统—下白垩统高精度层序格架模式图
Fig.2 High-resolution sequence stratigraphic frames of upper Jurassic and lower Cretaceous series in block A of South Turgay basin
SQ2-1层序位于Arysukm组下部,侧向厚度变化较小,为一套全区填平补齐的地层,反映盆地开始进入坳陷沉积阶段。层序底部发育一套全区广泛分布的低位体系域灰色底砾岩,自然电位和电阻率为高值,呈漏斗形;中部发育水进体系域的厚层滨浅湖—半深湖相泥岩沉积,夹薄层砂岩,形成了区域上最大规模的稳定性标志层和良好盖层;顶部为高位体系域的三角洲—河流相砂泥互层。
SQ2-2层序位于Arysukm组上部。盆地水体变浅,主要发育一套棕红色、浅绿色泥岩,形成于滨浅湖环境,向上砂体粒度和厚度变大,逐渐过渡为三角洲—河流沉积环境。
3 高精度层序地层格架内的地震沉积学分析
地震岩性学和地震地貌学是地震沉积学的基本组成部分[5-6]。应用地震岩性学,可以将三维地震数据转换成测井曲线[18],通过岩性曲线可对储层层次上的测井资料与地震资料进行综合解释。通过地震地貌学解释,地震资料可进一步转换成带岩性标记的沉积相图像,这种图像是高分辨率沉积体系识别的基础[19]。对高精度层序地层格架内进行地震沉积学分析,不仅保证了岩性和沉积体系划分的等时性,还保证了岩性和沉积体系识别的精确性,便于准确地确定沉积微相的边界与分布范围,甚至单砂体的体积、厚度与规模。
利用地震沉积学再造高精度层序地层格架并识别沉积体系是三维地震解释方法的一个重要革新[20]。它与经典地震层序地层的差别在于其使用地震数据的水平方向性质而非垂直方向性质来生成高精度地震属性图,从而与地形地貌学联系起来。多年来,层序地层学以二维地震解释方法为基础,在地震剖面上识别同相轴和地震相,综合多个剖面解释结果对地震相作图,进而在平面上对沉积相进行解释。事实证明:许多高精度层序在地震剖面上只是被检测,并未被分辨,所以,这种方法对高精度层序地层学研究效率低且易混淆。地震沉积学提供了一种新的解决方法:在平面上成像并解释沉积体系,然后,在纵向和三维环境中研究其层序地层学含义[21-22]。这种方法不再需要用肉眼追踪单个四级、五级层序,进而恢复全盆地的高精度层序地层格架,从而大大加快了解释速度。盆地沉积物的地层切片系列提供了沉积体系在高精度层序格架内保存和演化的映像。只有特殊需要时,才有必要对高精度层序及沉积体系域进行三维作图。
3.1 90°相位转换
波形和测量振幅是地震相位谱的函数。零相位波的分辨率为强振幅的1/4,若层厚低于λ/4(λ为波长),则顶底界限很难区分,经反射相交,形成合成波;当层厚为λ/4~λ时,顶底反射可以较好区分,但合成波仍然与原零相位波相差较大。
对于单一界面和厚层地层,零相位地震数据体具有波形对称、波形对比时模糊性小、波形中心和最大振幅处与反射界面相吻合且振幅谱相同时分辨率最大等优点,因此,一般均采用零相位地震数据体进行传统地震解释。但世界各地大部分油田储层垂向厚度均较小(<λ),部分甚至小于λ/4。Zeng等[21, 23-25]发现采用90°相位波在薄层地震解释中效果更佳。
在研究区,通过90°地震相位转换,反射波主瓣位于薄砂岩层(黑轴)中心,一方面,减少了砂泥互层反射的双极性,克服了零相位波的缺点,可以较好地分辨薄砂岩层的几何形态;另一方面,地震反射由相对于地层界面对称转为地层对称,在厚度为λ内与岩性唯一对应,可以更好地对同测井曲线进行对比见 图3。
3.2 层序格架内的地层切片
有效利用地震数据平面特性的方法就是切 片[26-27]。目前能用的方法包括时间切片、沿层切片以及地层切片或等分切片,根据这些切片能可靠地识别高精度层序中的沉积体系域,进而提高层序地层学分析的可靠性和精度[28-31]。为达到最佳效果,必须根据具体的构造和地层条件选择合适的方法(图4)。
(1) 若地层是席状并且是水平的,则使用时间切片(图4(b));
(2) 若地层是席状但不是水平的,则使用沿层切片(图4(c));
(3) 若地层既不是席状的也不是水平的,则应使用地层切片(图4(d))。
研究区层段地层为楔形,因此,选用地层切片(图4(d))。选用90°地震相位转换后数据体,以高精度层序地层格架等时界面(包括层序界面SBl,SB2,SB3,SB4,SB5,SB6和水泛面)作为参考层进行层位追踪,在2个参考层之间进行等比例插值,所得的任一地层切片(沿任一地质时间)均代表了相应地质时间的地层响应。插值层位数量可根据参考层厚度及地震分辨率进行调整(图3)。对插值后的层位进行属性提取,选取其中特征较明显的部分,为后面分频处理和沉积相分析工作做准备。
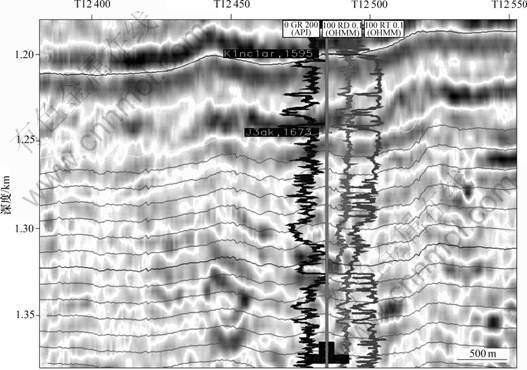
图3 研究区90°相位转换地震剖面和测井曲线综合对比图
Fig.3 Seismic section of 90° phasing convertion and logs in block A
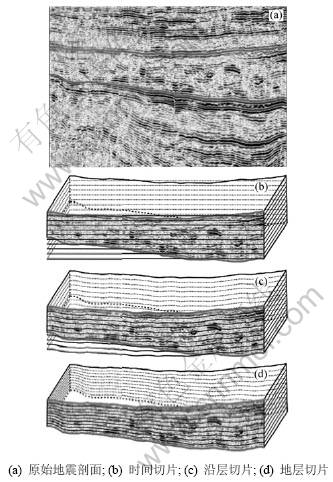
图4 实际地震资料不同切片对比图
Fig.4 Different types of slicing used in seismic sedimentology
3.3 地层切片分频处理
地震频率成分控制地震反射同相轴的倾角和内部反射结构,不同峰值反射频率对应不同的地质反射界面。在低频资料中,反射同相轴更多地反映岩性界面信息,而高频资料中,反射同相轴更多地反映等时沉积界面信息[24, 32]。因此,受地震资料频率的控制,不同频段的地震数据反映不同的地质信息,对应不同的沉积(微)相的响应。从而,在地震资料分频基础上进行综合分析,可以很好地揭示沉积岩岩性分布、沉积体系展布和沉积(微)相特征。
频谱分解是一种简单、稳定的高分辨率地震地层/构造目标或油藏成像方法,是地震属性分析中的重要组成部分[33]。在研究区,选取属性特征明显的地层切片确定时窗,对地震资料进行分频处理,得到一系列频率切片,在平面上进行观察,发现研究区目的层段河道砂体发育,多期交互叠置,物源主要来自研究区西北部,但不同频率地层切片对河道砂体响应差异明显。在SQ1-2层序内同一地层切片,频率为20~25 Hz时对河道砂体最敏感,在地层切片上能完整、清晰地刻画出河道边界、宽度、延伸长度及其平面几何形态 (图5(c)和5(d));频率为10 Hz时(图5(b))仅部分刻画出粉砂质细砂岩和粉砂岩充填的下游河道;而频率为35 Hz时刚好相反,仅刻画出以粗砂岩、中砂岩为主的上游河道(图5(e));当频率更高(50 Hz)或更低(5 Hz)时,河道基本不可见(图5(a)和5(f))。由此可见:不同频率对地震数据的相位等特性有不同响应,可刻画地质体的横向连续性能力也有所不同,进而反映不同沉积环境形成的沉积体。
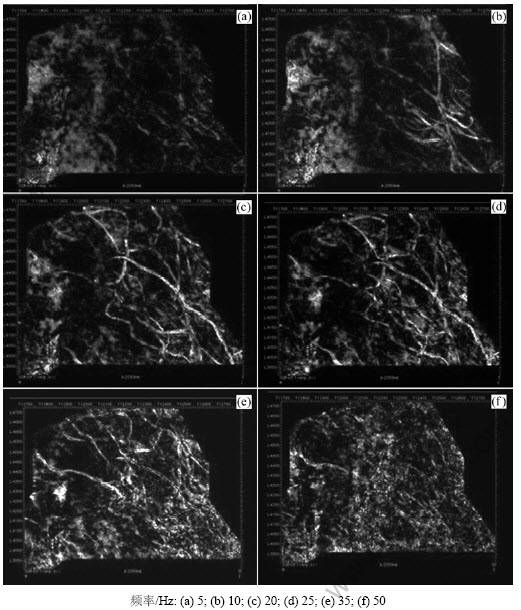
图5 SQ1-2层序内同一地层切片分频处理揭示河道带特征
Fig.5 Feature of channel belts displayed by typical separate frequency slicing in sequence SQ1-2
4 沉积微相特征及其地震沉积学解释
地震属性是对地震资料的几何学、运动学、动力学及统计学特征的一种测量,与地震数据中的时间、振幅、频率和衰减等基本信息有关,也是各种地层特征、地质现象的反映。根据本次地震沉积学分析目的,对高精度层序地层格架内的分频地层切片,在研究过程中主要提取能较好反映陆相碎屑岩岩性的振幅类和能量类属性。分频地层切片属性图显示:研究区振幅呈带状延展,河流特征明显(图6)。
对钻井进行对比,发现测井曲线多呈现箱形或钟形,沉积二元结构明显,为曲流河相典型特征,物源方向为北西—南东向,主要发育以下4种沉积微相。
(1) 河床滞留沉积。河床是河谷中经常流水的部分,岩石类型以砂岩为主,其次为砾岩,碎屑粒度是河流相中最大的。测井曲线多为箱形或钟形,自然伽玛值低,自然电位和电阻率高。该微相类型在研究区主要发育于层序界面附近。在分频地层切片属性图中,河道对应长条状黑色区域,表现出强振幅、强反射特征(图6(a))。

图6 地层切片地震属性与沉积微相解释图
Fig.6 Feature of channel belts displayed by typical separate frequency slicing
(2) 边滩。边滩又称为“点砂坝”或“内弯坝”,是河床侧向侵蚀、沉积物侧向加积的结果。沉积物以砂为主,混有砾岩、粉砂岩和黏土。测井曲线形态以尖峰状、指状为主,自然电位和电阻率高,自然伽玛低。在分频地层切片属性图中,边滩是河床凸岸能量和振幅较强的部分(图6(a))。
(3) 河漫滩。河漫滩是河床外侧、河谷底部较平坦的部分。岩性以粉砂岩为主,亦有黏土岩的沉积,在测井曲线上以指状为主。在分频地层切片属性图中,能量和振幅中等,对应河床外的绿色以及浅灰色部分(图6(a))。
(4) 河漫湖泊。河漫湖泊是河漫平原上最低的部分。洪水期河水漫溢至河床两侧河漫滩上,洪水期后,低洼地区就会积水,形成河漫湖泊。河漫湖泊以黏土岩沉积为主,并有粉砂岩出现,是河流相中粒度最小的沉积类型。测井曲线一般呈平直或微指状。在分频地层切片属性图中,河漫湖泊对应地震能量及振幅均较弱的灰色及灰白色部分(图6(a))。
由此可见:振幅类和能量类属性对由岩性变化引起的河流相敏感。通过地震属性趋势和钻井综合分析比较,分频地层切片属性可以更好地揭示沉积微相特征及其平面展布(图6(b))。
5 结论
(1) 地震沉积学是利用地震水平反射的结构、外形和趋势与沉积体系地形之间关系,研究沉积岩岩性、沉积相及其沉积过程的一门学科。其基本手段是通过90°相位转换、地层切片和分频处理,将某个地质时间界面上的地震属性显示出来。它与地震地层学、层序地层学、沉积学等学科相关,但是,在概念、研究内容、方法技术等方面都有所不同。
(2) 高精度层序地层格架内的等时层序界面和最大水泛面是最佳的参考层,所得的任一地层切片均代表相应地质时间的地层响应,在沉积相识别和分析中具有独特的优势,不仅保证了岩性和沉积体系划分的等时性,还保证了岩性和沉积体系识别的精确性,可以准确地确定沉积微相的边界与分布范围,甚至可确定单砂体的体积、厚度与规模。
(3) 研究区河流相发育,以河床滞留沉积、边滩、河漫滩、河漫湖泊等微相为主,物源方向为北西—南东向。不同频率对地震数据的相位等特性有不同响应,可刻画地质体的横向连续性能力也有所不同,频率为20~25 Hz时对河道砂体最敏感,在地层切片上可完整、清晰地刻画出河道边界、宽度、延伸长度及其平面几何形态。
致谢:
本文得到了中国石油天然气勘探开发公司薛良清、中国石油勘探开发研究院顾家裕、朱如凯、卞德智、潘校华、黄先雄、苏永地、王武和、郑俊章、朱如凯等的帮助和支持,在此一并表示衷心的感谢!
参考文献:
[1] Schlager W. The future of applied sedimentary geology[J] . Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2000, 70(1): 2-9.
[2] 董春梅, 张宪国, 林承焰. 地震沉积学的概念、方法和技术[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(5): 698-704.
DONG Chun-mei, ZHANG Xian-guo, LIN Cheng-yan. Conception, method and technology of the seismic sedimentology[J]. Acta Sedmentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(5): 698-704.
[3] ZENG Hong-liu, Backus M M, Barraw K T, et al. Stratal slicing (Part Ⅰ): Realistic 3D seismic model[J]. Geophysics, 1998, 63(2): 502-513.
[4] ZENG Hong-liu, Henry S C, Riola John P. Stratal slicing (Part Ⅱ): Real 3-D seismic data[J]. Geophysics, 1998, 63(2): 514-522.
[5] ZENG Hong-liu, Backus M M. Interpretive advantages of 90-phase wavelets (Part 1): Modeling[J]. Geophysics, 2005, 70(3): 7-15.
[6] ZENG Hong-liu, Backus M M. Interpretive advantages of 90-phase wavelets (Part 2): Seismic applications[J]. Geophysics, 2005, 70(3): 17-24.
[7] 林承焰, 张宪国. 地震沉积学探讨[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, 21(11): 1140-1144.
LIN Cheng-yan, ZHANG Xian-guo. The discussion of seismic sedimentology[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2006, 21(11): 1140-1144.
[8] 吴因业, 顾家裕, 施和生, 等. 序地层学到地震沉积学: 全国第5届油气层序地层学大会综述[J]. 石油实验地质, 2008, 30(3): 217-226.
WU Yin-ye, GU Jia-yu, SHI He-sheng, et al. From sequence stratigraphy to seismic sedimentology: Summarized from the 5th congress of oil and gas sequence stratigraphy[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2008, 30(3): 217-226.
[9] 董春梅, 张宪国, 林承焰. 有关地震沉积学若干问题的探讨[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2006, 41(4): 405-409.
DONG Chun-mei, ZHANG Xian-guo, LIN Cheng-yan. Discussion on several issues about seismic sedimentology[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2006, 41(4): 405-409.
[10] 林承焰, 张宪国, 董春梅. 地震沉积学及其初步应用[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(2): 69-72.
LIN Cheng-yan, ZHANG Xian-guo, DONG Chun-mei. Concept of seismic sedimentology and its preliminary application[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(2): 69-72.
[11] ZENG Hong-liu, Tucker F H, Lesli J W. Stratal slicing of Miocene-Pliocene sediments in Vermilion Block 50-Tiger Shoal Area, offshore Louisiana[J]. The Leading Edge, 2001, 20(4): 408-418.
[12] ZENG Hong-liu, Ambrose W A, Villalta E. Seismic sedimentology and regional depositional systems in Mioceno Norte, Lake Maracaibo, Venezuela[J]. The Leading Edge, 2001, 20(11): 1260-1269.
[13] Khalit K P, Timur K P, Michael J S, et al. Structure, evolution and oil and gas potential of the South Turgay Basin, Kazakhstan[C]//American Association of Petroleum Geologists 1997 Annual Convention. Anonymous. Dallas, USA, 1997: 690.
[14] Allen M B, Alsop G I, Zhemchuzhnikov V G. Dome and basin reofolding and transpressive inversion along the Karatau Fault System, southern Kazakstan[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2001, 158(2): 83-95.
[15] Effimoff I. Future hydrocarbon potential of Kazakhstan[C]// Wallace E. Pratt Memorial Conference on Petroleum Provinces of the 21st Century. AAPG Bulletin, 1999, 83(12): 2305.
[16] Anon. PetroKazakhstan exploration finds more oil in South Turgai basin[J]. Oil and Gas Journal, 2005, 103(8): 36-38.
[17] 顾家裕, 张兴阳. 陆相层序地层学进展与在油气勘探开发[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(5): 484-490.
GU Jia-yu, ZHANG Xing-yang. Progress in continental sequence stratigraphy and its application in petroleum exploration and development[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2004, 25(5): 484-490.
[18] 李祥权, 苏明, 张建新, 等. 三维地震技术在地质研究方面的应用[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(4): 553-557.
LI Xiang-quan, SU Ming, ZHANG Jian-xin, et al. Application of 3D seismic technique in geology study[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2008, 29(4): 553-557.
[19] 黄锋, 李志荣, 廖玲, 等. 利用地震资料进行沉积相分析[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2003, 25(3): 197-200.
HUANG Feng, LI Zhi-rong, LIAO Ling, et al. Sedimentary facies analysis using seismic data[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2003, 25(3): 197-200.
[20] 陆永潮, 杜学斌, 陈平, 等. 油气精细勘探的主要方法体系: 地震沉积学[J]. 石油实验地质, 2008, 30(1): 1-5.
LU Yong-chao, DU Xue-bin, CHEN Ping, et al. Main methods system of fine petroleum exploration: Seismic sedimentology[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2008, 30(1): 1-5.
[21] ZENG Hong-liu, Kerans C. Seismic frequency control on carbonate seismic stratigraphy: A case study of the Kingdom Abo sequence, west Texas[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2003, 87(2): 273-293.
[22] 魏嘉, 朱文斌, 朱海龙, 等. 地震沉积学——地震解释的新思路集尘机研究的新工具[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2008, 31(2): 95-101.
WEI Jia, ZHU Wen-bin, ZHU Hai-long, et al. Seismic sedimentology: A new idea for seismic interpretation and new tool for sedimentological studies[J]. Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 2008, 31(2): 95-101.
[23] Sicking C J. Windowing and estimation variance in deconvolution[J]. Geophysics, 47(7): 1022-1034.
[24] ZENG Hong-liu, Backus M M, Kenneth T B, et al. Facies mapping from three-dimensional seismic data: Potential and guidelines from a tertiary sandstone-shale sequence model Powerhorn Field, Calhoun County, Texas[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1996, 80(1): 16-46.
[25] ZENG Hong-liu, Hentz T F. High-frequency sequence stratigraphy from seismic sedimentology: Applied to Miocene, Vermilion Block50, Tiger Shoal area, offshore Louisiana[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2004, 88(2): 153-174.
[26] Kolla V, Ph Bourges J M, Urruty S P. Evolution of deep-water Tertiary sinuous channels offshore Angola (west Africa) and implications for reservoir architecture[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2001, 85(8): 1373-1405.
[27] 李秀鹏, 曾洪流, 查明. 地震沉积学在识别三角洲沉积体系中的应用[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 35(6): 625-629.
LI Xiu-peng, ZENG Hong-liu, CHA Ming. Mapping deltaic depositional systems using seismic sedimentology[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2008, 35(6): 625-629.
[28] 刘保国, 刘力辉. 实用地震沉积学在沉积相分析中的应用[J]. 石油物探, 2008, 47(3): 266-271.
LIU Bao-guo, LIU Li-hui. Application of applied seismic sedimentology in sedimentary facies analysis[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2008, 47(3): 266-271.
[29] 郭海洋, 巫芙蓉, 刘树根, 等. 地震沉积学在GA地区的初步应用[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2008, 30(5): 399-402.
GUO Hai-yang, WU Fu-rong, LIU Shu-gen, et al. The preliminary application of Seismic sedimentology in Guangan area[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 30(5): 399-402.
[30] 董艳蕾, 朱筱敏, 曾洪流, 等. 黄骅坳陷歧南凹陷古近系沙一层序地震沉积学研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2008, 26(2): 234-240.
DONG Yan-lei, ZHU Xiao-min, ZENG Hong-liu, et al. Seismic sedimentology study on Shayi sequence in Qinan Sag, Huanghua Depression[J]. Acta Sedmentologica Sinica, 2008, 26(2): 234-240.
[31] 董艳蕾, 朱筱敏, 曾洪流, 等. 歧南凹陷地震沉积学研究[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 32(4): 7-12.
DONG Yan-lei, ZHU Xiao-min, ZENG Hong-liu, et al. Study of seismic sedimentology in Qinan Sag[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Science & Technology Edition, 2008, 32(4): 7-12.
[32] 吴国忱, 康仁华, 印兴耀. 三维时频分析方法在地震层序分析中的应用[J]. 石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2000, 24(1): 81-84.
WU Guo-chen, KANG Ren-hua, YIN Xing-yao. The application of 3D time-frequency analysis in seismic sequence analysis[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China: Science & Technology Edition, 2000, 24(1): 81-84.
[33] 刘春慧, 金振奎, 刘家铎, 等. 地震数据处理技术在准噶尔盆地东部C25井西区砂体识别中的应用[J]. 矿物岩石, 2007, 27(4): 104-111.
LIU Chun-hui, JIN Zhen-kui, LIU Jia-duo, et al. Application of technique of seismic data processing to the identification of sandbody of C25 well in the eastern Junggar Basin[J]. Mineral Petrol, 2007, 27(4): 104-111.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2010-01-18;修回日期:2010-04-15
基金项目:国家重大科技专项(2008ZX0500102);国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2009CB219304)
通信作者:毛治国(1977-),男,湖北宜昌人,博士,从事层序地层与油气勘探的研究;电话:010-83598623;E-mail: maozhiguo@petrochina.com.cn