
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.12.005
锌氧压酸浸渣赋存特性与浸出毒性评价
陈永明1, 2,代杰1, 2,胡方园1, 2,李云1, 2,常聪1, 2,向长柳1, 2,何静1, 2
(1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 中南大学 难冶有色金属资源高效利用国家工程实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:锌氧压酸浸渣属于冶炼危废,其安全处置已成为制约锌系统稳定生产的重要因素。为揭示其安全利用的关键技术难题与瓶颈,采用粒度分析仪、X射线荧光分析仪(XRF)、电感耦合原子发射光谱仪(ICP-AES)、电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)、高频红外碳硫仪、X射线衍射分析仪(XRD)、矿物解离分析仪(MLA)、扫描电镜-能谱(SEM-EDS)连用技术、X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS)以及傅里叶红外光谱仪(FTIR)分析研究2种典型锌精矿氧压酸浸渣的粒度分布、化学组成、形貌特征和表面元素化学价态以及分子键结构等矿物学特性。采用热分析仪(TG-DSC)和毒性浸出程序(TCLP)分别考察锌氧压酸浸渣的着火性能和短期环境活性等安全属性。研究结果表明:氧压酸浸渣1多呈球块状,平均粒径为22 μm,主要物相为单质硫、闪锌矿、黄铁矿、石膏和石英等,其中单质硫质量分数最高,达52%;氧压酸浸渣2外形不规则,平均粒径为86 μm,主要物相为单质硫、纤铁矾、硫酸铁、闪锌矿和石膏等,其中单质硫质量分数为33%。锌氧压酸浸渣热稳定性较差,酸浸渣1的着火温度为214~291 °C,酸浸渣2的着火温度为213~240 °C;锌氧压酸浸中锌和镉元素在弱酸性条件下不稳定,酸浸渣1中锌和镉的浸出量分别超标6.45和2.55倍,酸浸渣2中锌和镉的浸出量分别超标4.37和4.80倍。
关键词:氧压酸浸渣;矿物学特征;着火点;浸出毒性
中图分类号:X758 文献标志码:A 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
文章编号:1672-7207(2020)12-3309-12
Occurrence characteristics and leaching toxicity evaluation of residues from zinc sulfide oxygen-pressure leaching process
CHEN Yongming1, 2, DAI Jie1, 2, HU Fangyuan1, 2, LI Yun1, 2, CHANG Cong1, 2,
XIANG Changliu1, 2, HE Jing1, 2
(1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. State Engineering Laboratory for Efficient Utilization of Refractory Nonferrous Metals Resources, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Zinc leaching residues(ZLR) produced from zinc sulfide oxygen-pressure leaching process were classified as hazardous waste, and its safe disposal became an important factor limiting the stable production in zinc processing system. In order to reveal the key technical problems and bottleneck in ZLR safty utilization, the particle size distribution, chemical composition, morphological characteristics and the valence of surface element as well as molecular bond structure of two typical ZLRs produced from zinc sulfide oxygen-pressure leaching process were investigated by particle size analyzer, X-ray fluorescence analyzer(XRF), inductively coupled atomic emission spectrometer(ICP-AES), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer(ICP-MS), high-frequency infrared carbon and sulfur analyzer, X-ray diffraction analyzer(XRD), mineral dissociation analyzer(MLA), scanning electron microscopy(SEM)-energy spectroscopy(EDS)technique, X-ray photoelectron spectrometer(XPS) and Fourier infrared spectrometer(FTIR). In addition, the ignition performance and short-term environmental activity of ZLRs were investigated by thermal analysis(TG-DSC) and toxic leaching procedure(TCLP), respectively. The results show that No.1 ZLR is spherical in shape, with an average particle size of 22 μm, and the phases composition mainly contains elemental sulfur, sphalerite, pyrite, gypsum and quartz. Elemental sulfur is the major component up to 52%(mass fraction). No.2 ZLR is irregular in shape and has an average size of 86 μm. It is mainly composed of fibroferrite, ferric sulfate, sphalerite and gypsum and the mass fraction of elemental sulfur is 33%. The two ZLRs have a poor thermal stability, with ignition temperature range from 214 °C to 291 °C for the No.1 ZLR and 213 °C to 240 °C for the No.2 ZLR. The leaching amounts of zinc and cadmium from the No.1 ZLR exceed the limit values by 6.45 and 2.55 times, respectively. The leaching amounts of zinc and cadmium from the No.2 ZLR exceed the limit values by 4.37 and 4.80 times, respectively.
Key words: oxygen-pressure acid leaching residue; mineralogy characteristics; ignition temperature; leaching toxicity
现代锌冶炼直接浸出工艺(氧压/常压浸出—净化—电积)取消常规湿法炼锌工艺中的氧化焙烧工序,实现了硫化锌精矿的全湿法处理,硫元素以硫磺的形式进入酸浸渣[1]。我国锌精矿直接浸出工艺每年产生约60万t酸浸渣(因渣中硫磺质量分数高,简称为高硫渣),渣中除单质硫、锌、铅、铜和银等有价组分外,还含有砷、镉和汞等毒害元素,高硫渣由于这些毒害元素的潜在浸出毒性而被归为危险废物[2-4]。因此,高硫渣的安全处置具有资源综合利用与环境保护的双重意义。
近年来,国内外关于锌冶炼高硫渣资源化利用的研究多集中在单质硫的高效回收上,回收方法主要分为化学法和物理法2大类[5-6]。化学法利用溶剂溶解高硫渣中的单质硫,再通过重结晶和热分解等工序制取硫磺产品。该类方法具有操作简单、单质硫回收率高以及硫磺产品质量好等优点,但二甲苯、四氯化碳和硫化铵等化学提取剂存在易挥发、毒性大和操作环境差等缺点。物理法利用单质硫熔点、黏度和沸点较低的特性,采用物理方式有效分离单质硫与其他矿物组分。目前,物理法中“浮选-热滤”工艺被国内锌直接浸出企业采用,但该工艺存在单质硫收率低、有价组分协同提取效果差以及毒害元素处置不彻底等缺点,迫切需要革新升级技术。对高硫渣资源化利用方法的选择主要依赖于高硫渣有价组分质量分数、物相组成和热分解特性等性质,因此,系统认知高硫渣理化特性既可为其资源化利用方法的选择提供依据,又可从某种程度上揭示其资源化利用的关键技术难题与突破口。
目前,国内外陆续出现有色行业冶炼废渣赋存状态、环境迁移转化行为及污染特性的研究报道。郭朝晖等[7]研究了某大型铅锌冶炼厂湿法炼锌二次渣中重金属元素的赋存状态和环境活性,从酸沉降、微生物作用和原电池效应等方面揭示了渣中重金属的溶出机理;MIN等[8]评价某常规锌湿法浸出渣中重金属的环境活性和潜在生态风险,探究了锌浸出渣对生态环境造成毒性的主要原因;LI等[9]在某常规湿法锌浸出渣的物化性质、物相结构及形貌特征研究的基础上,采用毒性浸出程序考察了锌浸出渣的短期环境活性。此外,铜、锑和铅等冶炼渣中重金属元素的环境迁移特性研究亦有报道[10-12],但锌氧压浸出高硫渣的综合理化特性与浸出毒性等基础数据严重缺失,尚未见相关报道。
本研究从微观和宏观层次对国内2家代表性锌氧压浸出企业所产高硫渣的矿物学特性进行表征,精细认知高硫渣中有价组分与毒害元素的质量分数组成、化学价态、微观结构等赋存特性,并考察高硫渣着火点和浸出毒性等安全属性,丰富了高硫渣基础理化特性数据库。
1 试验原料
研究所用高硫渣原料1和高硫渣原料2分别取自国内2家代表性锌精矿二段氧压酸浸工序,将采集的样品在60 °C下干燥5 h后于行星球磨机球磨30 min,所得粉末封存备用。球磨后高硫渣的外观如图1所示,因2家企业氧压浸出时的具体工艺参数及除铁策略不同,高硫渣的颜色区别明显。

图1 高硫渣物理图
Fig. 1 Physical morphology of two residues
2 分析与测试方法
2.1 赋存特性分析
2.1.1 化学组成测定
采用X射线荧光光谱(XRF,Axios,PANalytical)确定高硫渣元素种类,半定量分析元素质量分数。基于XRF检测结果,使用混酸消解高硫渣粉末,采用电感耦合原子发射光谱仪(ICP-AES,Avio 500)定量分析高硫渣中锌、铅、铜、银和铁等有价金属以及砷、镉、铬、汞和硒等毒害元素,低于ICP-AES检测线的元素采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS, ICAP RQ)进行定量分析。采用高频红外碳硫仪(CS744,USA)确定高硫渣中硫元素质量分数。高硫渣中赋存于金属硫酸盐中的硫元素以氯化钠溶液为提取剂进行提取,提取液中硫酸根用氯化钡溶液沉淀为硫酸钡,经过滤、灼烧后称质量,计算得到高硫渣中可溶性硫酸根的质量分数。采用X射线衍射仪(XRD,Rigaku ITRIII)测定高硫渣主要物相,靶材为铜靶,以10 (°)/min的速率扫描样品,衍射角范围为10°~80°,所得衍射图谱用Jade 6.0分析;采用自动矿物分析仪(MLA,FEI650,捷克)测定高硫渣中矿相种类及质量分数。
2.1.2 粒度与形貌测定
采用激光粒度分析仪(Mastersizer 2000)在湿法模式下以乙醇为分散剂测定高硫渣的粒度分布;采用扫描电镜-能谱连用技术(SEM-EDS,Tescan Mira3 Lmu, Oxford)分析高硫渣的形貌和区域元素分布。
2.1.3 分子键结构测定
采用透射傅里叶红外光谱仪(FTIR,Nicolet 6700,Thermo Fisher Scientific,USA)分析高硫渣中相关组分的分子键结构。室温下以溴化钾为背景,采用4 cm-1的分辨率对高硫渣样品红外光谱信号进行64次扫描累加,测定范围为4 000~ 400 cm-1,所得红外图谱用OMNIC软件分析。
2.1.4 表面元素化学价态测定
采用X射线光电子能谱(XPS,ESCALAB250Xi,Thermo Fisher-VG Scientific)确定高硫渣表面化学组成及S,Fe,As和Cr等变价元素的原子价态,靶材为镁靶,真空度为1×10-6 Pa。
2.2 安全属性测试
2.2.1 热稳定性评估
高硫渣中的单质硫易燃,在贮存和运输过程存在着火风险,故采用广泛使用的热重分析法[13-14]评估高硫渣的热稳定性。分析时,取高硫渣1和高硫渣2各13.200 0 mg,在热分析仪(Mettler 1100LF, Switzerland)中控制空气流量为500 mL/min,在5 ℃/min的升温速率下将物料从室温加热到700 ℃。
2.2.2 浸出毒性测试
重金属的环境风险评估常包含可浸出性测试。高硫渣在地表径流、雨水等淋滤以及自然风化的作用下会释放重金属等组分,进而影响周边的水质、土壤甚至大气。采用广泛应用的TCLP法(toxicity characteristic leaching procedure)法[15-16]测试高硫渣球磨样的浸出毒性,以简便快速地评价其重金属生态风险[17-18]。
毒性浸出实验条件为:按液固比20:1 L/kg计算所需浸提剂的体积,调节翻转式振荡装置转速为(30±2) r/min,于(23±2) ℃下振荡(18±2) h,应用压力过滤器和0.7 μm玻璃纤维滤膜对样品过滤。
浸提剂种类需根据高硫渣的酸碱度选取,高硫渣酸碱度测定参照文献[19]。水渣比为2.5:1,pH电极法测定水溶液pH。当高硫渣pH<5时选用浸提剂1 (将5.7 mL冰醋酸溶入去离子水中,再加入1 mol/L的NaOH 64.3 mL定容至1 L,用1 mol/L的NaOH 或HNO3调节溶液pH,使之保持在4.93±0.05)。当pH>5时选用浸提剂2 (将5.7 mL冰醋酸溶入去离子水中,定容至1 L,保持溶液pH在2.88±0.05)。
3 结果与讨论
3.1 化学组成
采用XRF和ICP-AES/ICP-MS对高硫渣的元素组成及质量分数进行检测,结果分别如表1和表2所示,由表1和表2可见:锌冶炼高硫渣1和2中主要元素都是S,质量分数分别高达50.81%和28.30%,并含有Zn,Fe,Pb,Cu和Ag等有价金属以及As,Cd,Cr,Hg和Se等毒害元素;高硫渣2中铁元素质量分数较高,是其显赤红色的原因;高硫渣1中硫元素的质量分数比高硫渣2的高,这与硫化锌精矿原料配置以及氧压酸浸工序的具体工艺参数有关。此外,由表2可知,高硫渣中可溶性硫酸盐质量分数较高。
表1 高硫渣XRF分析结果(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical composition of residues analyzed by XRF %
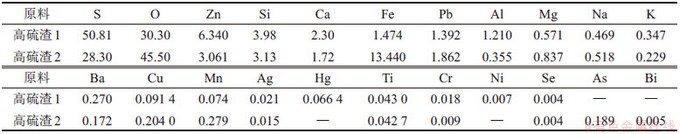
表2 高硫渣ICP-AES/ICP-MS分析结果(质量分数)
Table 2 Chemical composition of residues analyzed by ICP-AES/ICP-MS %
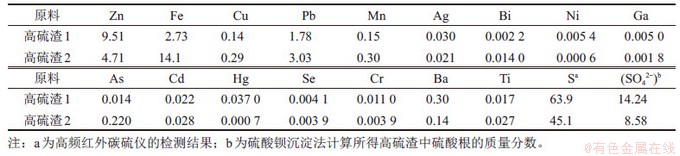
图2所示为高硫渣1和2的XRD图谱。由图2可知:高硫渣1中主要物相为单质硫、硫化锌和硫酸钙等;高硫渣2中主要物相为单质硫、硫化锌、铁矾以及石英等。
图2 高硫渣XRD图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of the two residues
高硫渣更多物相种类及质量分数分析结果如图3所示。由图3(c)可知,高硫渣1主要含有单质硫(S)、闪锌矿(ZnS)、黄铁矿(FeS2)、石膏(CaSO4·2H2O)、石英(SiO2)和石英-绢云母-硫等物相,其中单质硫质量分数最多,达52%。元素Fe和Cu分别主要以黄铁矿和黄铜矿(CuFeS2)形式存在。由图3(f)可知,高硫渣2主要含有单质硫、纤铁矾Fe(OH)SO4·5H2O、硫酸铁、闪锌矿及石膏等物相,其中单质硫质量分数只有33%;元素Fe主要物相为黄铁矿、磁黄铁矿(Fe1-xS)、纤铁矾和铁的硫酸盐,与高硫渣1中元素Fe的主要赋存物相不同,这是因为在氧压酸浸工艺条件下,铁以二价形态保留于浸出液中,再设置针铁矿中和沉铁工段,因此,高硫渣1中铁主要存在于未反应的黄铁矿中;而高硫渣2中铁以三价形式沉淀于浸出渣中,因此,高硫渣2中铁主要存在于纤铁矾和未反应完的磁黄铁矿等物相中。

图3 高硫渣背散射图、MLA彩图及矿物质量分数组成图
Fig. 3 Backscattered electron images, MLA images and mineral content images of No. 1 and No.2 residues
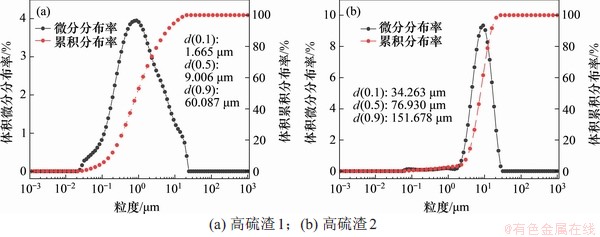
图4 高硫渣粒度分布曲线
Fig. 4 Particle size distribution curves of the two residues
3.2 粒度分布与形貌特征
高硫渣粒度分布测定结果如图4所示,由图4(a)可见:高硫渣1粒径小于1.665,9.006和22.071 μm的颗粒分别占10%,50%和90%;由图4(b)可见:高硫渣2粒径小于34.264,76.930和151.678 μm的颗粒分别占10%,50%和90%。高硫渣1和高硫渣2的体积平均粒径分别为22.071 μm和85.618 μm,高硫渣1的平均粒度小于高硫渣2的平均粒度。
高硫渣形貌和元素区域分布如图5和图6所示,由图5可见:高硫渣1以块状或团聚状存在,元素Zn和Fe呈弥散分布,S集中分布在高亮区,少部分与Zn和Fe重合,与高硫渣1中硫元素质量分数高,且主要物相为硫单质、闪锌矿和黄铁矿的结果一致,元素Cu主要以硫化物的形态集中分布。由图6可见:高硫渣2中大部分颗粒呈不规则的块状,元素S除部分独立分布在高亮区外,大部分与元素Fe和O高亮区重合,说明高硫渣2中硫元素除以单质硫形态存在外,还有较大部分以铁矾的形式存在,印证了XRD的表征结果。
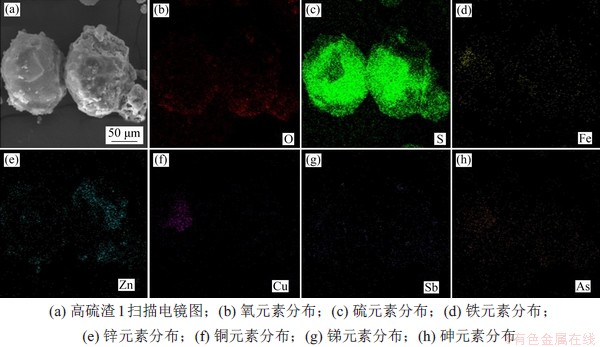
图5 高硫渣1微观形貌和元素分布
Fig. 5 Microstructure and element distribution of No. 1 residue
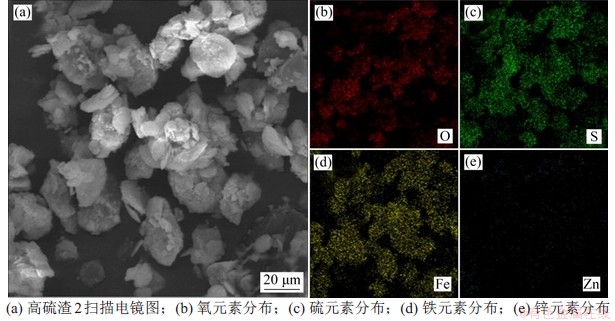
图6 高硫渣2微观形貌和元素分布
Fig.6 Microstructure and element distribution of No. 2 residue
3.4 表面化学结构
研究固废的表面物相组成及元素价态对其安全处置和利用具有重要作用,比如确定砷和铬等元素的价态分布比例有助于判断该元素的短期浸出毒性以及是否达到风险管控阈值。高硫渣X射线光电子全谱如图7所示。
由图7(a)可知:高硫渣1的表面存在O,Fe,Zn,S,As,Mg和Si等元素,由图7(b)可知:高硫渣2的表面存在O,Na,Zn,S,Mg,Al,Si和Ca等元素。
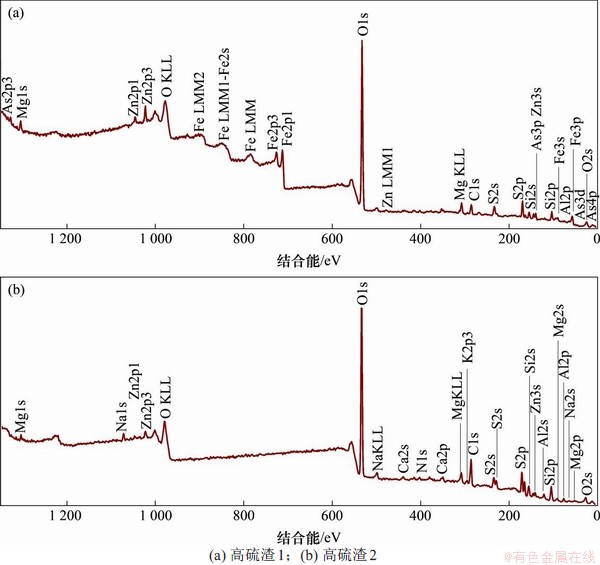
图7 高硫渣光电子全谱
Fig. 7 XPS wide scan spectrums of the two residues
为了说明2种高硫渣表面S,Fe,As和Cr等元素的价态,分别对2种高硫渣进行窄区扫描,并利用高斯-洛伦斯法对原始谱线进行拟合。图8所示为高硫渣1的S 2p,Fe 2p,As 2p3和Cr 2p分谱。如图8(a)所示,S 2p3/2主峰对应的结合能分别为162.38 eV和169.05 eV,S 2p1/2主峰对应的结合能分别为163.56 eV和170.23 eV,依次与S2-和SO42-对应[20];如图8(b)所示,Fe 2p3/2主峰对应的结合能分别为710.22,711.60和713.61 eV,Fe 2p1/2主峰对应的结合能分别为723.32,725.10和726.71 eV,依次与文献中Fe—S键[21]、Fe3+(Fe-O)和Fe3+(Fe-SO4)的Fe 2p3/2和Fe 2p1/2峰位值[22]接近,可判断高硫渣1表面的Fe以+3价和+2价共存,且以+3价为主。Fe主要以+3价形式存在这可能与渣表面吸附的Fe2+在存放和烘干过程中被氧化有关;如图8(c)所示,As 2p3特征峰值对应的结合能为1 326.85 eV,与文献[23]中As3+(As2O3)峰位值1 326.6 eV十分接近,判断高硫渣1表面的As以+3价存在;由图8(d)可见Cr 2p图谱为Zn的俄歇峰,因此未能分析出其存在价态。
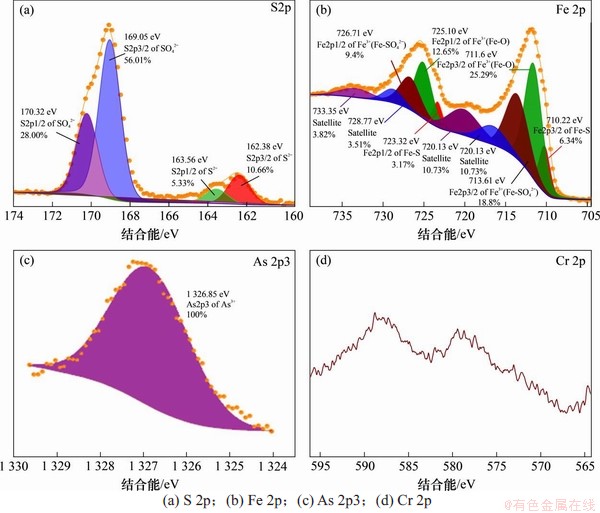
图8 高硫渣1光电子窄谱
Fig. 8 XPS narrow scan spectrums of the residue 1
图9所示为高硫渣2的S 2p,Fe 2p,As 2p3和Cr 2p分谱。由图9(a)可见:S 2p3/2主峰对应的结合能分别为163.54 eV和169.52 eV,S 2p1/2主峰对应的结合能分别为164.72 eV和170.70 eV,依次与S8和SO42-对应[20];元素As和Cd未检测出特征谱峰,可能与含砷和含镉的物相含量低、存在于高硫渣2的较内层有关。
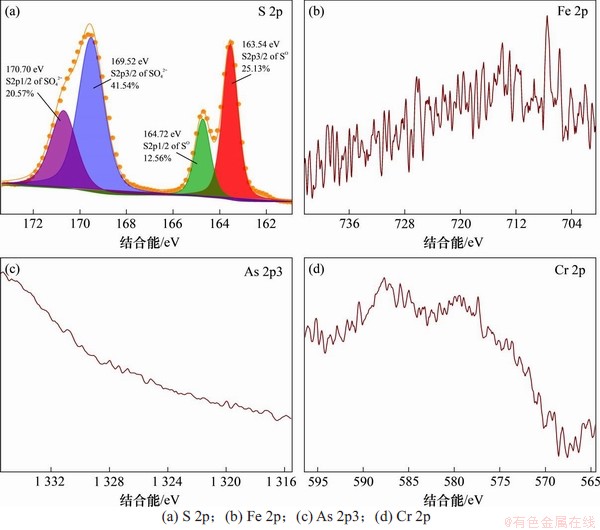
图9 高硫渣2光电子窄谱
Fig. 9 XPS narrow scan spectrums of the residue 2
3.5 分子键结构
图10所示为高硫渣1和2的红外光谱。由图10可见:在3 700 cm-1处附近的吸收带为高硫渣中以铝和镁等为主的含水硅酸盐矿物中水的O—H伸缩峰[24],与渣中含有低质量分数的绢云母、白云母和滑石等含水硅酸盐矿物相吻合。在约3 400 cm-1处显示的宽吸收带为水分子间O—H的伸缩峰[9,25],与高硫渣TG-DSC曲线在100 ℃时的分析结果吻合。在1 380 cm-1左右处的吸收带为CO32-的振动峰[9,26],与渣中质量分数较低的方解石和白云石等含碳酸根矿物对应。高硫渣在870 cm-1处附近的弱吸收和1 093 cm-1处较强的吸收带为Si—O键振动峰[9],与渣中含有SiO2的检测结果相符。高硫渣1在1 080~1 175 cm-1处的3个吸收带是重晶石族矿物中SO42-三重简并分裂的结果[26],SO42-另外的吸收频率在660 cm-1左右处[9,25],与渣中检测出铅矾等含硫酸根矿相对应。
由图10(b)可见:高硫渣2在1 000 cm-1处的较强吸收频率对应SO42-的振动,与渣中含有纤铁矾和硫酸铁等含硫酸根物相对应。单质硫中含有多个S—S键[27-28],470 cm-1左右处的峰为单质硫的S—S键伸缩峰(νS—S)[29-30]。另外,由于闪锌矿和黄铁矿等金属硫化物的特征峰在500~50 cm-1范围内[31],含铜和砷等金属的硫化物质量分数很低,所以,红外光谱图内没出现锌、铁、铜和砷等硫化物的特征峰。
分析高硫渣红外光谱,发现水和硫酸盐等物质振动带最强,而石膏和硫酸锌等矿物的存在导致高硫渣具有较强的吸水性能,因此,为防止Zn,Pb,Cd和As等重金属毒害元素的溶解释放,堆存时应保持干燥。
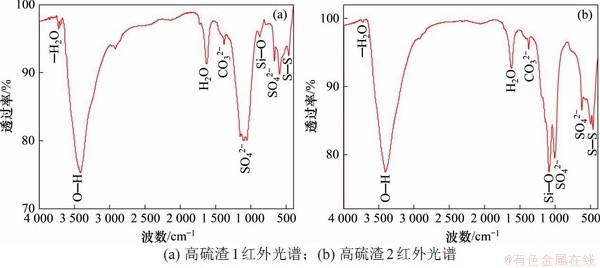
图10 2种高硫渣红外光谱图
Fig.10 FTIR spectrums of the two residues with KBr pellets
3.6 着火性能评估
高硫渣堆存时,着火点可评估堆存安全性,为其相关处置措施的制定提供参考。图11所示为高硫渣1和2的TG-DSC曲线图,结果表明,2种高硫渣均在100 ℃左右开始失水,质量损失率分别约为3%和5%;在100~200 ℃范围内高硫渣质量损失不明显,且DSC曲线显示出较尖锐的吸收峰,在此阶段,石膏和纤铁矾等物质可能失去结晶水[32];在200 ℃左右质量损失速率开始增大,并在300 ℃左右质量损失速率达到最大,说明此阶段高硫渣发生剧烈燃烧,质量损失率分别约为50%和30%,与MLA检测结果中硫磺质量分数基本一致;在300~400 ℃范围内,高硫渣的质量变化不显著;温度继续升高,高硫渣中其他组分才开始分解或燃烧,但质量损失不大,说明高硫渣中着火温度高于300 ℃的物质占比较低。
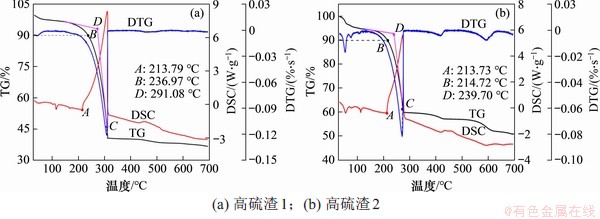
图11 高硫渣TG-DSC 曲线
Fig. 11 TG-DSC curves of the two residues
采用热重分析法研究粉样物质的着火温度时,着火点Ti的定义方法有多种。本研究分别采用固定失重法[33]、TG-DTG法[13,34]和吸放热法[35]定义高硫渣的着火点。固定失重法定义TG曲线失重10%的温度为着火点,即图11中的B点,按此定义,高硫渣1和2的着火温度分别为236.97 ℃和214.72 ℃。
TG-DTG法在图11中描述为:在DTG曲线上过峰值作垂线与TG曲线交于点C,过C点作TG曲线的切线,该切线与失重开始平行线的交点D所对应的温度定义为着火温度,按此定义,高硫渣1和2的着火温度分别为291.08 ℃和239.70 ℃。
吸放热法从传热角度定义DSC曲线上开始放热时的临界点为高硫渣的着火温度,即图11的A点,按此定义,高硫渣1和2的着火温度分别为213.79 ℃和212.73 ℃。
然而,着火点是与试验条件与可燃物本身特性有关的综合参数,实验室测定的着火点具有相对性和很强的规范性。为了更准确、全面地判断高硫渣的着火性能,应在充分了解其组成和理化性质的基础上,结合质量分数(TG)、质量分数导数(DTG)和热流(DSC)曲线综合分析外部条件对其着火性能的影响规律。
3.7 浸出毒性分析
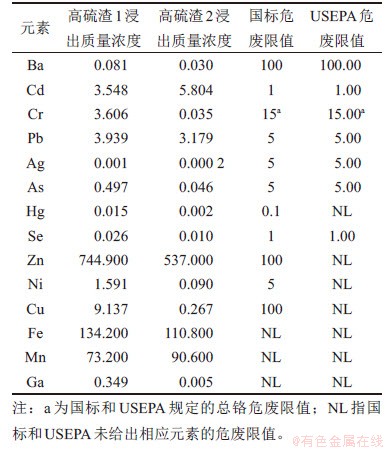
高硫渣1和2的pH分别为1.31和3.09,含水率分别为2.14%和7.71%,其TCLP法浸出浓度与美国环保署(USEPA)和国标危废判定阈值的比较结果如表3所示。由表3可见:高硫渣1和2中Cd和Zn元素浸出量严重超标,其中Cd元素分别超标2.55倍和4.80倍,Zn元素分别超标6.45倍和4.37倍,因此,高硫渣属于危险废物,需为其制定出一套科学合理、环境安全的处置和管理准则。
表3 高硫渣TCLP法毒性浸出测试结果
Table 3 TCLP test results of No. 1 and No.2 residues mg/L
4 结论
1) 高硫渣1大多呈块状或团聚状,体积平均粒径为22.071 μm,主要含单质硫(52.05%)、闪锌矿(15.94%)、石英-绢云母-硫(10.36%)、石膏(4.90%)和黄铁矿(5.78%)等矿相;高硫渣2大多呈块状或片状,体积平均粒径为85.618 μm,主要含单质硫(33.31%)、纤铁矾(19.24%)、硫酸铁(8.93%)、闪锌矿(9.58%)和石膏(3.27%)等矿相。
2) 2种渣中含有O—H键、Si—O键和S—S键等分子键以及CO32-和SO42-等离子团;高硫渣1表面的硫元素以-2价和+6价并存,铁以+2价和+3价共存,砷以+3价形式存在;高硫渣2表面存在的硫元素以0价和+6价并存。
3) 高硫渣中可燃组分含量高,热稳定性较差,在200~300 ℃时可剧烈燃烧。采用固定失重法、TG-DTG 法和吸放热法分别定义高硫渣的着火点,高硫渣1的着火点分别为236.97,291.08和213.79 ℃;高硫渣2的着火点分别为212.73,239.70和214.72 ℃。
4) 高硫渣属于危废,锌和镉元素浸出量超出危废阈值。其中,高硫渣1中锌和镉元素的浸出量分别超标6.45倍和2.55倍,高硫渣2中锌和镉元素的浸出量分别超标4.37倍和4.80倍。
参考文献:
[1] 彭容秋. 锌冶金[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2005: 67-69.
PENG Rongqiu. Zinc metallurgy[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2005: 67-69.
[2] OZVERDI A, ERDEM M. Environmental risk assessment and stabilization/solidification of zinc extraction residue: I. Environmental risk assessment[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 100(3/4): 103-109.
[3] SONER A H, ERDEM M, ORHAN R. Heavy metal pollution potential of zinc leach residues discarded in cinkur plant[J]. Turkish Journal of Engineering and Environmental Sciences, 1998, 22(3): 167-178.
[4] TURAN M D, ALTUNDOGAN H S, TUMEN F. Recovery of zinc and lead from zinc plant residue[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2004, 75(1/2/3/4): 169-176.
[5] 鲁顺利. 从高铁闪锌矿的高压酸浸渣中提取硫磺[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学冶金与能源工程学院, 2005: 4-13.
LU Shunli. Study on extracting sulfur from sulfur residues after treatment zinc sulfide concentrates with high content of iron[D]. Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology. Faculty of Metallurgical and Energy Engineering, 2005: 4-13.
[6] 朱晔. 高压有氧锌浸出渣分级与浮选试验研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学资源与环境工程学院, 2011: 8-10.
ZHU Ye. The classification and floation research oxidative pressure Zinc leaching residue[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of science and Technology. School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, 2011: 8-10.
[7] 郭朝晖, 程义, 柴立元, 等. 有色冶炼废渣的矿物学特征与环境活性[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 38(6): 1100-1105.
GUO Zhaohui, CHENG Yi, CHAI Liyuan, et al. Mineralogical characteristics and environmental availability of non-ferrous slag[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2007, 38(6): 1100-1105.
[8] MIN Xiaobo, XIE Xiande, CHAI Liyuan, et al. Environmental availability and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in zinc leaching residue[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(1): 208-218.
[9] LI Mi, PENG Bing, CHAI Liyuan, et al. Technological mineralogy and environmental activity of zinc leaching residue from zinc hydrometallurgical process[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(5): 1480-1488.
[10] POTYSZ A, KIERCZAK J, FUCHS Y, et al. Characterization and pH-dependent leaching behaviour of historical and modern copper slags[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 160: 1-15.
[11] GUO Xuejun, WANG Kunpeng, HE Mengchang, et al. Antimony smelting process generating solid wastes and dust: Characterization and leaching behaviors[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 26(7): 1549-1556.
[12] SAIKIA N, BORAH R R, KONWAR K, et al. pH dependent leachings of some trace metals and metalloid species from lead smelter slag and their fate in natural geochemical environment[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2018, 7: 348-358.
[13] 秦汝祥, 庞文华, 陶远. TG实验条件对煤氧化燃烧特性的影响分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2014, 10(5): 154-158.
QIN Ruxiang, PANG Wenhua, TAO Yuan. Effect of TG experimental conditions on the oxidative combustion characteristics of coal[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2014, 10(5): 154-158.
[14] ENGIN B, ATAKUL H. Air and oxy-fuel combustion kinetics of low rank lignites[J]. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2018, 91(2): 311-322.
[15] CHANG E E, CHIANG P C. Comparisons of metal leachability for various wastes by extraction and leaching methods[J]. Chemosphere, 2001, 45: 91-99.
[16] LU C C, HSU M H, LIN Yipin. Evaluation of heavy metal leachability of incinerating recycled aggregate and solidification/stabilization products for construction reuse using TCLP, multi-final pH and EDTA-mediated TCLP leaching tests[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 368: 336-344.
[17] UNDA-CALVO J, MARTINEZ-SANTOS M, RUIZ-ROMERA E. Chemical and physiological metal bioaccessibility assessment in surface bottom sediments from the Deba River urban catchment: Harmonization of PBET, TCLP and BCR sequential extraction methods[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 138: 260-270.
[18] ZANG Fei, WANG Shengli, NAN Zhongren, et al. Leachability of heavy metals in loess-amended dredged sediment from Northwest of China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 183: 1-7.
[19] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000: 12-14.
LU Rukun. Methods for agricultural chemical analysis of soil[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000: 12-14.
[20] JOHN F M, WILLIAM F S, PETER E S, et al. Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: a reference book of standard spectra for identification and interpretation of XPS data[M]. Minnesota: Physical Electronics, 1995: 60-61.
[21] CARVER J C, SCHWEITZER G K, CARLSON T A. Use of X‐ray photoelectron spectroscopy to study bonding in Cr, Mn, Fe and Co compounds[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1972, 57(2): 973-982.
[22] BRION D. Etude par spectroscopie de photoelectrons de la degradation superficielle de FeS2, CuFeS2, ZnS et PbS a l'air et dans l'eau[J]. Applications of Surface Science, 1980, 5(2): 133-152.
[23] TAYLOR J A. An XPS study of the oxidation of AlAs thin films grown by MBE[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 1982, 20(3): 751-755.
[24] MORGAN D J. Clay mineralogy: spectroscopic and chemical determinative methods[J]. Clay Minerals, 1995, 30(4): 421.
[25] MARTINS F M, NETO J M D R, CUNHA C J D. Mineral phases of weathered and recent electric arc furnace dust[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 154(1/2/3): 417-425.
[26] 闻辂. 矿物红外光谱学[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 1988: 61-62.
WEN Lu. Infrared spectroscopy of minerals[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 1988: 61-62.
[27] MEYER B. Solid allotropes of sulfur[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1964, 64(4): 429-451.
[28] TEBBE F N, WASSERMAN E, PEET W G, et al. Composition of elemental sulfur in solution: equilibrium of S6, S7 and S8 at ambient temperatures[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1982, 104(18): 4971-4972.
[29] 解立斌, 俞丹, 魏萌, 等. 单质硫νS-S伸缩振动的漫反射红外光谱研究[J]. 理化检验-化学分册, 2017, 53(4): 413-417.
XIE Libin, YU Dan, WEI Meng, et al. Study on the stretching vibration of sulfur(S-S) by DRIFTS[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis(Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2017, 53(4): 413-417.
[30] 赵瑶兴, 孙祥玉. 有机分子结构光谱鉴定[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 8-11.
ZHAO Yaoxing, SUN Xiangyu. Spectral identification of organic molecular structure[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003: 8-11.
[31] 刘丽华, 张培萍, 李献洲. 金属硫化物矿物的远红外光谱表征[J]. 分析测试技术与仪器, 2006, 12(1): 34-37.
LIU Lihua, ZHANG Peiping, LI Xianzhou. FTIR analysis of metallic sulfide minerals[J]. Analysis and Testing Technology and Instruments, 2006, 12(1): 34-37.
[32] QIAN Guangren, XU Xia, SUN Weimin, et al. Preparation, characterization, and stability of calcium zinc hydrophosphate[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43(12): 3463-3473.
[33] 潘峰. 煤燃烧实验中着火点确定方法分析[J]. 化工设计通讯, 2019, 45(12): 238, 252.
PAN Feng. Analysis on the determination method of ignition point in coal combustion test[J]. Chemical Engineering Design Communications, 2019, 45(12): 238, 252.
[34] LU J J, CHEN W H. Investigation on the ignition and burnout temperatures of bamboo and sugarcane bagasse by thermogravimetric analysis[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 160: 49-57.
[35] 邱建荣, 马毓义, 曾汉才, 等. 混煤着火特征温度的试验测定及模型预测[J]. 电站系统工程, 1993, 9(5): 51-54.
Qiu Jianrong, Ma Yuyi, Zeng Hancai, et al. Test measurement and modelling prediction on ignition characteristics temperature of mixed coal[J]. Power System Engineering, 1993, 9(5): 51-54.
(编辑 秦明阳)
收稿日期: 2020 -06 -16; 修回日期: 2020 -08 -30
基金项目(Foundation item):国家重点研发计划项目(2018YFC1902005) (Project(2018YFC1902005) supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China)
通信作者:何静,教授,从事有色金属清洁冶金及稀散金属综合回收研究;E-mail:he6213@163.com