网络首发时间: 2019-05-28 16:14
稀有金属 2020,44(12),1316-1324 DOI:10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.xy19050002
SnSe基热电材料的最新研究进展
陈秋凤 王秀霞 吴正森 刘呈燕 苗蕾
桂林电子科技大学材料科学与工程学院广西信息材料重点实验室
摘 要:
随着环境危机的日益加剧和能源需求的不断增加,提高能源的利用效率成为解决问题的有效途径之一。热电材料正是一类利用Seebeck效应和Peltier效应实现热能与电能之间相互转换的功能材料,有望广泛应用于废热余热回收发电以及制冷领域,从而提高能源利用效率。近年来,SnSe基热电材料因原材料丰富、环境友好和热电性能优异等优点而成为热电材料研究领域的热点。系统地分析了SnSe的晶体结构与高热电性能之间的内在关系。然后,分别综述了单晶和多晶SnSe基热电材料的特性及最新研究进展。在提高热电性能方面,针对单晶SnSe,主要通过异质原子掺杂,包括n型和p型掺杂两方面;对于多晶SnSe,一方面通过异质原子掺杂和调控织构化程度提高功率因子;另一方面通过引入纳米异质相、点缺陷和纳米孔洞等散射声子,降低晶格热导率。最后,讨论了进一步提高SnSe基材料热电性能所面临的挑战和可能的解决策略,以期为后续研究提供指导。
关键词:
热电材料 ;SnSe ;热电性能 ;单晶 ;多晶 ;
中图分类号: TB34
作者简介: 陈秋凤(1995-),女,广西北海人,学士,研究方向:硫属化合物热电材料的机制研究及热电器件的应用研究,E-mail:1556912146@qq.com; *苗蕾,教授,电话:17707733664,E-mail:miaolei@guet.edu.cn;
收稿日期: 2019-05-04
基金: 国家自然科学基金项目(51562005,51572049,51772056和51801040)); 广西自然科学基金项目(2016GXNSFBA380152和2015GXNSFFA139002); 广西大学生创新创业训练区级项目(201710595143)资助;
Recent Advances in SnSe-Based Thermoelectric Materials
Chen Qiufeng Wang Xiuxia Wu Zhengsen Liu Chengyan Miao Lei
Guangxi Key Laboratory of Information Materials,School of Material Science and Technology,Guilin University of Electronic Technology
Abstract:
With aggravating environment crisis and increasing demand for energy,improving efficiency becomes one of the key points.Thermoelectric materials are functional materials that can convert heat into electricity and vice versa by using the Seebeck and Peltier effects.It has potential to be applied in the fields of waste heat recovery and refrigeration to improve efficiency.Recently,SnSe-based thermoelectric materials were paid great attentions because of earth-abundant elements,environmentally-friendly and out-standing thermoelectric performance.Here,the relationship between structure and high thermoelectric performance was analyzed.Then,the recent advance in SnSe-based thermoelectric materials was reviewed,including foreign atomic doping(n and p-type)for single crystal and the methods to enhance power factor(foreign atomic doping and tuning of texture)and reduce lattice thermal conductivity(e.g.,nanostructured phase,point defects and nanopores)for polycrystalline.Finally,the challenges and possible solutions to further improve thermoelectric performance were discussed to give guidance for future research.
Keyword:
thermoelectric material; SnSe; thermal conductivity; single crystal; polycrstalline;
Received: 2019-05-04
Sn Se是一种具有本征低晶格热导率的化合物,在923 K时只有0.23 W?m-1 ?K-1 ,因此其表现出优异的热电性能
[1 ]
(通过无量纲因子ZT=S2 σT/(κlat +κele )来表征,其中S,σ,κlat ,κele 和T分别为Seebeck系数、电导率、晶格热导率、电子热导率和绝对温度,κlat 与κele 之和为材料的总热导率(κ))。图1所示为近年来研究较多的热电块体材料的ZT,从图1(a,b)分别可以看出,p型单晶Sn Se的最高ZT值在923 K时可达到2.62
[1 ]
,n型Sn Se晶体在773 K处的ZT最大值为2.8
[2 ]
,优于其他的热电材料。
图1 随温度变化的n型和p型块状热电材料的ZT值
Fig.1 ZT values of n-type
[1,3-9]
(a)and p-type
[2,10-18]
(b)bulk thermoelectric materials as a function of temperature(□denotes the introduction of cation vacancy)
Sn Se是常见的硫属化合物之一,具有热电性能优异、原材料丰富和环境友好等优点,使其近三年来迅速成为热电材料研究领域的热点。单晶Sn Se虽然具有优异的热电性能,但在实际应用中却面临诸多难题,比如机械加工性能差,晶体生长条件苛刻,工业放大成本高等。另一方面,多晶Sn Se块体材料因具有机械加工性能较好和容易大批量合成的特点而成为重要研究方向,但相对单晶Sn Se,多晶Sn Se的热电性能较差,因此如何提高多晶Sn Se的热电性能成为Sn Se热电材料研究的关键。本文系统综述了Sn Se晶体结构与高热电性能之间的内在关系,以及提高单晶和多晶Sn Se所采用的方法,并且针对当前研究所存在的问题提出了一些可能的解决策略,以期为后续研究提供指导。
1 Sn Se晶体结构与热电性能间的关系
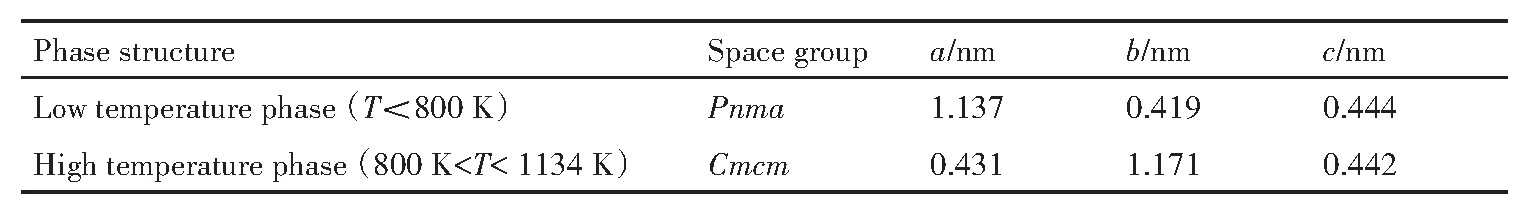
研究表明,Sn Se存在两种稳定的晶体结构(如图2所示),且都属于正交晶系,其晶胞参数如表1所示。在室温下为α相,其空间群为Pnma,可以认为是Na Cl型立方结构在三维方向扭曲后形成。该结构由强烈束缚的双层结构组成,它在a,b,c轴向的投影不同,导致其各向异性。沿bc平面内存在着厚度接近两个原子的强键合的Sn-Se键,投影视图沿b轴呈手风琴式的锯齿状,沿c轴呈扶手椅状,而沿a轴的结合力较弱(范德华力和静电吸引力)。正因此结构,导致其具有较高的Grüneisen常数(~3.13),能够通过强烈非简谐作用来散射声子,从而具有极低的晶格热导率(在a轴方向最低为0.256 W?m-1 ?K-1 )。当温度升高至800 K左右时,发生二级相变,转变为对称性更高的β相,其空间群为Cmcm。和α相类似,β也具有典型的双层结构。因为Sn Se在结构上的各向异性,导致其热电性质在a,b,c轴明显不同,比如在923 K时,在b轴方向的ZT可达2.6左右,而在a轴方向的ZT为0.8左右。
2 单晶Sn Se
Sn Se基热电材料的研究最早起源于1914年,但由于在700 K以下的电导率很低,一直被忽视。直到2014年,Zhao等
[1 ]
在Nature上报道了一种具有非常低热导率(0.23 W?m-1 ?K-1 )的单晶Sn Se,其最高ZT值在923 K时达到2.62,为当时所有热电材料的最高值,Sn Se热电性能的研究开始迅速吸引研究人员的关注,但高热电性能由高温下的β相取得,高温下Se的升华不利于Sn Se的应用,而α相的电导率因载流子浓度较低而较小,因此需要提高其载流子浓度来提高其热电性能。
表1 Sn Se基材料晶体结构的基本信息 下载原图
Table 1 Basic information of crystal structure of Sn Se-based materials
图2 Sn Se的晶体结构
Fig.2 Crystal structure of Sn Se
(a)Low temperature phase(T<800 K);(b)High temperaturephase(800 K<T<1134 K)
2.1 单晶Sn Se的热电性能优化
为了进一步提高单晶Sn Se的热电性能,采用p型或n型掺杂剂去取代Sn或Se的位置来优化载流子浓度是非常有效的方法。如图3所示为不同掺杂元素对单晶Sn Se热电性能的影响。其中,p型掺杂元素主要有Na
[19 ]
、K
[19 ]
和Ag
[20 ]
等,n型掺杂使用的掺杂元素主要为Bi
[21 ]
和Br
[2 ]
。
2.1.1 p型掺杂
理论计算
[22 ]
表明,对于p型Sn Se,如果优化载流子浓度至3.6×1019 cm-3
[23 ]
,在b轴方向ZT可达2.57。Ag掺杂
[20 ]
实验结果也表明+1价的Ag取代+2价的Sn后,电导率增加,虽然Seebeck系数相应降低,但总体功率因子增加(7.86?W?cm-1 ?K-2 )。尽管如此,Ag掺杂效率却欠佳,即提高电导率(载流子浓度)的能力有限,而且容易形成高热导率的杂相,从而增加热导率,最终,通过3%摩尔Ag掺杂
[20 ]
的样品在800 K时沿b轴方向得到的最大ZT为1.0。相比Ag掺杂,Na和K掺杂的效率则高很多,如Na掺杂
[24 ]
,随着掺杂量的增加,在723K时载流子浓度可增加至2.7×1019 cm-3 (3%Na掺杂)。尽管高载流子浓度会导致Seebeck系数降低以及电子热导率的增加,但是更高的电导率会导致功率因子的明显增大(14.5?W?cm-1 ?K-2 ),最终沿b轴方向的最大ZT为2.0。同时,通过Na掺杂,Sn Se价带中的重带参与载流子的传输,导致载流子有效质量增加,在载流子浓度一定的情况下Seebeck系数更大,有利于功率因子的提高。总而言之,通过掺杂效率较高的Na掺杂,单晶Sn Se的电学传输性能明显提升,在比较宽的温度区间实现较高的热电性能。
图3 Sn0.985Na0.015Se,Sn0.97Na0.03Se,Sn0.97Ag0.03Se,6%Bi Cl3掺杂Sn Se和Sn Se随温度变化的热电性能
Fig.3 Temperature-dependentσ(a),S(b),κ(c)and ZT values(d)for Sn0.985 Na0.015 Se
[19]
,Sn0.97 Na0.03 Se
[19]
,Sn0.97 Ag0.03 Se
[19]
,Sn0.97 Ag0.03 Se
[20]
,6%Bi Cl3 doped Sn Se
[21]
and Sn Se
[23]
2.1.2 n型掺杂
尽管本征单晶Sn Se一般为p型热电材料,但通过合适的n型掺杂后可以得到n型热电性能。理论计算表明,对于n型掺杂Sn Se
[22 ,23 ]
,如果载流子浓度为2.8×1019 cm-3 时,在a轴方向ZT可以达到~3.1。通过6%Bi掺杂单晶Sn Se
[21 ]
,不仅σ显著增加至~61.5 S?cm-1 ,而且保持了低κ(~0.29W?m-1 ?K-1 ),最终在733 K处沿b轴方向最大ZT为2.2。另外,Chang等
[2 ]
采用Br掺杂制备了具有高热电性能的n型Sn Se晶体。一方面,Br替代Sn Se晶格中的Se位后,增加了层间电荷密度的重叠(a轴方向);另一方面,连续相变增加了结构对称性,以及使原本收敛的两条传输能带分离。这两个因素导致载流子迁移率得到明显提高,同时保持了较大Seebeck系数,因此,当载流子浓度为1.2×1019 cm-3 时,在773 K下获得功率因子为~9.0?W?cm-1 ?K-2 ,热导率为~0.29 W?m-1 ?K-1 ,以及最大ZT值为2.8±0.5的记录。
3 多晶Sn Se
如前文所述,Sn Se晶体结构中层间(a轴方向)通过较弱的范德华力相结合,导致其很容易沿b-c面解理,机械加工性能较差
[25 ]
。此外,Sn Se在a和b轴均具有正膨胀性
[26 ]
,但c轴呈负膨胀特征。因此,Sn Se晶体生长过程中的温度梯度大小、坩埚容器与晶体热膨胀匹配性以及炉体降温速度等因素都可能在材料内部引发应力,促使晶体开裂
[27 ]
,导致其较难制备成大尺寸单晶
[28 ]
。这些缺点极大地阻碍了单晶Sn Se热电材料的应用。相比于单晶Sn Se,多晶Sn Se因晶粒取向性低的特点导致其各向异性并不是非常明显,甚至表现为各向同性,有利于实际应用。然而,在制备多晶Sn Se过程中常常发生Sn偏析,且很容易被氧化的情况,由于氧化层内具有高热导率的Sn O2
[29 ,30 ,31 ,32 ]
会增加其热导率,导致多晶Sn Se的热电性能并不理想。
因此,为进一步提高多晶Sn Se的功率因子(一般小于5?W?cm-1 ·K-2 )和降低热导率,进而提高热电性能,研究人员主要通过以下两个方面进行研究:(1)异质原子掺杂
[21 ,33 ,34 ,35 ,36 ,37 ,38 ,39 ,40 ,41 ,42 ,43 ,44 ,45 ,46 ]
和调控织构化程度
[47 ,48 ,49 ,50 ]
,提高功率因子;(2)引入纳米异质相
[51 ,53 ,54 ]
、点缺陷
[55 ]
和纳米孔洞
[56 ]
等散射声子,降低晶格热导率。
3.1 异质原子掺杂和调控织构化程度提高功率因子
3.1.1 异质原子掺杂优化载流子浓度和能带结构
第一性原理计算
[57 ]
表明,Sn Se基热电材料具有多导带结构,然而由于导带和价带之间的带隙较大,导致其电导率较低。另外,根据理论计算
[19 ]
可知,Sn Se的最佳载流子浓度为1×1019 ~1×1020 cm-3 ,然而实际中多晶Sn Se的载流子浓度仅为1×1017 ~1×1019 cm-3 。针对载流子浓度较低的问题,大量研究人员采用异质原子掺杂(n型掺杂和p型掺杂)的方法去提高载流子浓度。
对于n型掺杂,掺杂剂包括卤素(Cl
[33 ]
、Br
[34 ]
和I
[35 ]
),第VA族金属(Bi)化合物
[21 ]
以及多元素掺杂,如Sn Se0.87 S0.1 I0.03
[34 ]
。其中,采用熔融与热压结合的方法合成的Pb Br2 掺杂多晶Sn Se
[34 ]
样品,载流子浓度明显增加至1.86×1019 cm-3 ,电导率为(40±2)S·cm-1 ,功率因子为4.8?W·cm-1 ·K-2 ,但是由于热导率较高(0.7 W·m-1 ·K-1 ),最终ZT值在713 K时为0.54±0.1。研究发现,通过熔融和热压结合的方法制备的I掺杂多晶Sn Se样品,随着碘含量的增加,不仅载流子密度可以从2.3×1017 cm-3 (p型)增加为2.0×1017 cm-3 (n型),而且保持了Sn Se本征低热导率的特性,最终Sn Se0.97 I0.03 在773 K下获得的ZT值为1.0
[35 ]
。另外,以Bi Cl3 为掺杂物,通过熔融和等离子烧结工艺制备的Sn Se0.95 -Bi Cl3 样品,载流子浓度也明显增加
[21 ]
。与未掺杂Sn Se相比,在793 K时,其功率因子从0.1?W·cm-1 ·K-2 增加至5?W·cm-1 ·K-2 ,提高了50倍,最终ZT值为~0.7。尽管Bi Cl3 掺杂可明显提高载流子浓度,但其热导率较高,导致ZT值较低。因此,在卤素掺杂中,相比于Br和Cl掺杂,I掺杂的效果更好一些。另外,由于Sn S和Sn Se属于同类型化合物,通过在3%摩尔I掺杂的基础上固溶10%摩尔Sn S,不仅在770 K时获得了更低的热导率(~0.25 W·m-1 ·K-1 ),而且Seebeck系数也得到显著提高,最终在773 K时ZT≥1.0,进一步提高了热电性能
[35 ]
。
对于p型掺杂,主要使用的掺杂剂包括碱金属(Li
[36 ]
、Na
[37 ,38 ]
和K
[39 ]
),第IB族金属(Cu
[40 ]
和Ag
[24 ]
),第IIIA族金属(In
[41 ]
和Ge
[42 ]
),第VIA族非金属(Te)
[43 ,44 ]
和镧系元素及其化合物(La Cl3
[45 ]
)。例如,Wei等
[36 ]
采用1%Li掺杂Sn Se时,室温下的载流子浓度明显提高至3.2×1019 cm-3 ,在800 K时最大ZT值为0.5,然而,相比而言Li掺杂在提高载流子浓度方面作用有限。由于与Li+ 和K+ 相比,Na+ 的离子半径与Sn2- 较为接近,因此Na可能是3种碱金属掺杂中提高载流子浓度效果最好的。Chere等
[37 ]
研究发现在1%Na掺杂多晶Sn Se时,与未掺杂Sn Se相比,虽然Seebeck系数在300 K由480?V·K-1 降低为142?V·K-1 ,但载流子浓度提高了两个数量级,明显提高了功率因子,最终在800 K时功率因子达到5.50?W·cm-1 ·K-2 ,比未掺杂样品提高了20%~30%,获得了最大ZT值为0.8。Cai等
[38 ]
还研究了Na和K共同掺杂多晶Sn Se,结果表明,0.5%Na和0.5%K掺杂后,费米能级明显下移,并使价带中的轻带和重带顶倾向于收敛,有效增加了载流子浓度,并保持了较高的Seebeck系数,在773 K时获得~2.8?W·cm-1 ·K-2 的功率因子,最大ZT值达到1.2,明显提高了热电性能。
3.1.2 调控织构化程度提高载流子迁移率
由于Sn Se晶体在沿bc平面内存在强键合的Sn-Se键,而沿a轴是由较弱的范德华力和静电吸引力而结合,导致这类材料具有明显的各向异性。针对多晶材料,迁移率是沿晶体不同生长方向的统计平均值,但是晶粒的随机取向生长会削弱载流子的输运性能。为了充分利用Sn Se沿bc平面优异的电传输性能,需要对晶粒的取向性进行调控,使载流子尽可能沿bc平面传输,进而提高功率因子,增加ZT值。在多晶Sn Se体系中,常用的调控织构化程度的工艺有传统熔融固相反应、等离子快速烧结系统(SPS)、热压和还原气氛热处理工艺等。
Li等
[46 ]
采用熔融固相反应结合机械合金化的工艺烧结得到多晶Sn Se块体材料,其烧结过程中体现了明显的各向异性。其中在300 K时,沿垂直于压力方向和平行于压力方向的载流子迁移率分别为~30和10 cm2 ·V-1 ·s-1 ,显著提高了电导率,最终在573 K时ZT达到0.5。在Li等的制备工艺基础上,Qin等进一步运用热压工艺也成功合成多晶Sn Se,由于热压烧结过程中长时间的高压和缓慢升温可以使烧结锭块呈现强各向异性,对载流子迁移率的调控变得非常明显,最终在673 K和723 K热压得到的样品中,最大ZT值可达到0.73,结果表明,热压工艺可以有效提高多晶Sn Se的热电性能
[47 ]
。尽管热压工艺可以确保烧结成高质量的块体,但是存在耗时、耗力等缺点。为了克服这些缺点,等离子体快速热压烧结(SPS)工艺是非常好的选择。
另外,本课题组
[48 ]
通过湿化学法合成具有强各向异性的Sn Se2 纳米结构,然后以此为前驱体,经过还原气氛热处理工艺后发现,当热处理温度高于873 K时会转变为具有强各向异性的Sn Se,而且沿垂直于压力方向,ZT值在889 K时达到1.07。采用湿化学法结合SPS工艺也可以实现Sn Se的强各向异性,Shi等
[49 ]
研究结果表明,上述工艺制备的Sn0.98 Se晶体就会沿着(100)晶面具有明显的取向生长,在823 K时,载流子浓度会提高至~1.5×1019 cm-3 ,并具有较低的热导率为~0.42 W·m-1 ·K-1 ,最终Sn0.98 Se晶体得到较高ZT,约为1.36。
如上所述,通过异质原子掺杂和调控织构化程度去优化载流子浓度和迁移率能够有效地优化电输运性能。
3.2 引入纳米异质相、点缺陷和纳米孔洞等散射声子传输,降低晶格热导率
通常采用增加声子散射来降低κlat 可以有效提高Sn Se的热电性能
[50 ]
。在多晶Sn Se中引入适当的纳米杂相、点缺陷和纳米孔洞等降低晶格热导率,如纳米沉积物(岩盐型Sn Se和快离子导体Ag8 Sn Se6
[51 ]
)、单质(炭黑纳米相[52]
[53 ]
、Mo Se2
[55 ]
)等。例如,Luo等
[51 ]
利用Ag和Na双掺杂时引入纳米异质相Ag8 Sn Se6 ,由于Ag8 Sn Se6 是一种具有本征低热导率材料,它的引入使Sn Se基体形成了纳米结构,有效地增强了声子散射,与纯相Sn Se相比,Sn0.99 Na0.01 Se-Ag8 Sn Se6 样品在773 K时的热导率降低了20%。最终,Sn0.99 Na0.01 SeAg8 Sn Se6 样品在773 K处的ZT值达到1.33。另外,Wei等
[56 ]
研究发现,在多晶Sn Se中引入适当的Sn空位一方面可以增加载流子浓度,显著增强电导率和功率因子。另一方面Sn空位也会严重破坏Sn Se的结构对称性,对声子产生强烈散射,进而大幅度地降低热导率。最终,多晶Sn1-x Se在873 K时获得了一个较高的ZT值,约为2.1。除此之外,Shi等
[57 ]
在溶剂热合成的单晶Sn Se基体中成功地引入硒化铟(In Sey )纳米沉积物,由于这些纳米沉积物在后续烧结过程中发生分解后会引入纳米孔。由于纳米多孔材料可通过晶界和孔界面对声子进行散射,有效降低了晶格热导率,最终,p型Sn Se在823 K时获得较高ZT为1.7±0.2。
4 讨论与展望
与其他传统热电材料
[58 ,59 ,60 ]
相比,单晶Sn Se因具有超低晶格热导率(在923 K时为0.23 W·m-1 ·K-1 )而获得超高热电性能,被认为是一种极具应用潜力的新型半导体材料。但也面临难以生长成大尺寸单晶和机械加工性能较差等问题。与单晶Sn Se相比,多晶Sn Se具有合成相对简单、低成本以及机械加工性能较好等优点,但热电性能相对要低很多。虽然通过上述提高功率因子和降低热导率的方法,ZT值有所提高,但还需解决如下几个主要问题:第一,多晶Sn Se基材料在较高温度下因为Se的升华,会导致自身缺陷的变化,将显著影响热电性能,降低其稳定性。第二,多晶Sn Se在低温区间内性能较低,且容易生成Sn O2 等具有高热导率的杂相,导致其平均ZT值较低,不利于提高其热电器件的转换效率。因此,针对单晶Sn Se,需要结合单晶Sn Se的热膨胀特性寻找合适的坩埚来对制备工艺进行进一步优化,使单晶生长重复性好、质量可靠。另外,可结合能带工程进一步提高单晶Sn Se的热电性能。针对多晶Sn Se,应致力于解决其在高温下容易产生Se升华和生成Sn O2 等高热导率杂相的问题。可能的方法包括在范德华力层间插入阳离子阻碍Se原子的热逃逸过程,或者提升低温区的热电性能以避免工作温度过高等,来提高多晶Sn Se在实际应用中的稳定性。其中,对于Sn O2 等高热导率杂相,可通过在还原性气氛(如氢气)中进一步热处理来除去。
参考文献
[1] Zhao L D,Lo S H,Zhang Y S,Sun H,Tan G J,Uher C,Wolverton C,Dravid V P,Kanatzidis M G. Ultralow thermal conductivity and high thermoelectric figure of merit in SnSe crystals[J]. Nature, 2014, 508(7496):373.
[2] Chang C,Wu M,He D,Pei Y,Wu CF,Wu X,Yu H,Zhu F,Wang K,Chen Y,Huang L,Li J F,He J,Zhao L D. 3D charge and 2D phonon transports leading to high out-of-plane ZT in n-type SnSe crystals[J]. Science,2018,360:778.
[3] Duong A T,Nguyen V Q,Duvjir G,Duong V T,Kwon S,Song J Y,Lee J K,Lee J E,Park S D,Min T,Lee J,Kim J,Cho S. Achieving ZT=2.2 with Bi-doped ntype SnSe single crystals[J]. Nature Communications,2016,7:13713.
[4] Saramat A,Svensson G,Palmqvist A E C,Stiewe C,Mueller E,Platzek D. Large thermoelectric figure of merit at high temperature in Czochralski-grown clathrate Ba8 Ga16 Ge30 [J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2006,99:023708.
[5] Liu W S,Kim H S,Chen S,Jie Q,Lv B,Yao M L,Ren Z S,Opeil C,Wilson S,Chu C W,Ren Z F. Ntype thermoelectric material Mg2 Sn0.75 Ge0.25 for high power generation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2015,112:3269.
[6] Ning H P,Mastrorillo G D,Grasso S,Du B L,Mori t,Hu C F,Xu Y,Simpson K,Maizza G,Reece M. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of porous magnesium tin silicide prepared using pressure-less spark plasma sintering[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2015,3:17426.
[7] Hong M,Chen Z G,Yang L,Zou J. Bix Sb2 -x Te3 nanoplates with enhanced thermoelectric performance due to sufficiently decoupled electronic transport properties and strong wide-frequency phonon scatterings[J]. Nano Energy,2016,20:144.
[8] May A F,Flage-Larsen E,Snyder G J. Electron and phonon scattering in the high-temperature thermoelectric La3 Te4 -z Mz (M=Sb,Bi)[J]. Physics Review B,2010,81:125205.
[9] Zhang J,Song L,Pedersen S H,Yin H,Hung L T,Iversen B B. Discovery of high-performance low-cost ntype Mg3 Sb2 -based thermoelectric materials with multivalley conduction bands[J]. Nature Communication,2017,8:13901.
[10] Fujita K,Mochida T,Nakamura K. High-temperature thermoelectric properties of Nax CoO2-δ single crystals[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics,2001,40:4644.
[11] Brown S R,Kauzlarich S M,Gascoin F,Snyder G J.Yb14 MnSb11 :new high efficiency thermoelectric material for power generation[J]. Cheminform,2006,18:1873.
[12] Schr?der T,Rosenthal T,Giesbrecht N,Nentwig M,Maier S,Wang H,Snyder G J,Oeckler O. Nanostructures in Te/Sb/Ge/Ag(TAGS)thermoelectric materials induced by phase transitions associated with vacancy ordering[J]. Inorganic Chemistry,2014,53:7722.
[13] Girard S N,He J,Zhou X,Shoemaker D,Jaworski C M,Uher C,Dravid V P,Heremans J P,Kanatzidis M G. High performance Na-doped PbTe-PbS thermoelectric materials:electronic density of states modification and shape-controlled nanostructures[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2011,133:16588.
[14] Ma Y,Hao Q,Poudel B,Lan Y,Yu B,Wang D,Chen G,Ren Z. Enhanced thermoelectric figure-of-merit in p-type nanostructured bismuth antimony tellurium alloys made from elemental chunks[J]. Nano Letters,2008,8:2580.
[15] Fu C,Zhu T,Liu Y,Xie H,Zhao X. Band engineering of high performance p-type FeNbSb based half-Heusler thermoelectric materials for figure of merit ZT>1[J].Energy Environ Science,2015,8:216.
[16] Okamura C,Ueda T,Hasezaki K. Preparation of single phaseβ-Zn4 Sb3 thermoelectric materials by mechanical grinding process[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials,2010,51:152.
[17] Rogl G,Grytsiv A,Heinrich P,Bauer E,Kumar P,Peranio N. New bulk p-type skutterudites DD0.7 Fe2.7 Co1.3 Sb12 -x Xx (X=Ge,Sn)reaching ZT>1.3[J]. Acta Materials,2015,91:227.
[18] Olvera A,Moroz N,Sahoo P,Ren P,Bailey T,Page A,Uher C,Poudeu P F. Partial indium solubility induces chemical stability and colossal thermoelectric figure of merit in Cu2 Se[J]. Energy Environmental Science,2017,10:1668.
[19] Peng K L,Lu X,Zhan H. Broad temperature plateau for high ZTs in heavily doped p-type SnSe single crystals[J]. Energy Environmental Science,2016,9(2):454.
[20] Jin M,Shao H Z,Hu H Y,Li D B,Xu J T,Liu G Q,Shen H,Xu J Y,Jiang H C,Jiang J. Single crystal growth of Sn0.97 Ag0.03 Se by a novel horizontal Bridgman method and its thermoelectric properties[J]. Journal of Alloys&Compounds,2017,460:112.
[21] Wang X,Xu J T,Liu G Q,Fu Y J,Liu Z,Tan X J,Shao H Z,Jiang H C,Tan T Y,Jiang J. Optimization of thermoelectric properties in n-type SnSe doped with BiCl3 [J]. Applied Physics Letters,2016,108(8):083902.
[22] Hong A J,Li L,Zhu H X,Yan Z B,Liu J M,Ren Z F.Optimizing the thermoelectric performance of low-temperature SnSe compounds by electronic structure design[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2015,3:13365.
[23] Yang J,Zhang G,Yang G,Wang C,Wang Y X. Outstanding thermoelectric performances for both p-and ntype SnSe from first-principles study[J]. Journal of Alloys&Compounds,2015,644:615.
[24] Kucek V,Plechacek T,Janicek P,Ruleova P,Benes L,Navratil J,Drasar C. Thermoelectric properties of Tldoped SnSe:a hint of phononic structure[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials,2016,45(6):2943.
[25] Chattopadhyay T,Pannetier J,Schnering H G V. Neutron diffraction study of the structural phase transition in SnS and SnSe[J]. Journal of the Physics and Chemistry of Solids,1986,47(9):879.
[26] Delaire O,Li C,Hong J,May A,Ehlers G. Orbitally driven giant phonon anharmonicity in SnSe[J]. Nature Physics,2015,11(12):1063.
[27] He X,Shen H,Wang W,Wang Z,Zhang B,Li X. The mechanical and thermo-physical properties and electronic structures of SnS and SnSe in orthorhombic structure[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2013,556:86.
[28] Sassi S,Candolfi C,Vaney J B,Ohorodniichuk V,Masschelein P,Dauscher A,Lenoir B. Assessment of the thermoelectric performance of polycrystalline p-type SnSe[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2014,104(21):212105.
[29] Zhao L D,Chang C,Tan G,Kanatzidis M G. SnSe:a remarkable new thermoelectric material[J]. Energy Environmental Science,2016,9:3044.
[30] Yanagiya S,Nong N V,Xu J,Sonne M,Pryds N. Thermoelectric properties of SnO2 ceramics doped with Sb and Zn[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials,2011,40:674.
[31] Ambrosini A,Palmer G,Maignan A,Poeppelmeier K R,Lane M,Brazis P,Kannewurf C R,Hogan T,Mason T O. Variable-temperature electrical measurements of zinc oxide/tin oxide-cosubstituted indium oxide[J].Chemistry Materials,2002,14:52.
[32] Ahmed S F,Khan S,Ghosh P K,Mitra M K,Chattopadhyay K K. Effect of Al doping on the conductivity type inversion and electro-optical properties of SnO2 thin films synthesized by sol-gel technique[J]. Journal of Sol-gel Science and Technology,2006,39:241.
[33] Han G,Popuri S R,Greer H F,Lin L F,Bos J W G,Zhou W,Paul D J,Menard H,Knox A,Montecucco A,Siviter J,Man E A,Li W G,Paul M C,Min G,Sweet T,Freer R,Azough F,Baig H,Mallick T K,Gregory D H. Chlorine-enabled electron doping in solution-synthesized SnSe thermoelectric nanomaterials[J].AdvancedEnergyMaterials,2017,7(13):1602328.
[34] Li D,Tan X,Xu J,Liu G,Jin M,Shao H. Enhanced thermoelectric performance in n-type polycrystalline SnSe by PbBr2 doping[J]. RSC Advanced,2017,7:17906.
[35] Zhang Q,Chere E K,Sun J,Cao F,Dahal K,Chen S,Chen G,Ren Z F. Studies on thermoelectric properties of n-type polycrystalline SnSe by iodine doping[J]. Advanced Energy Materials,2015,5(12):126.
[36] Wei T R,Tan G,Zhang X,Wu C F,Li J F,Dravid V P,Snyder G J,Kanatzidis M G. Distinct impact of alkali-ion doping on electrical transport properties of thermoelectric p-type polycrystalline SnSe[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2016,138(28):8875.
[37] Chere E K,Zhang Q,Dahal K,Feng Cao F,Mao J,Ren Z F. Studies on thermoelectric figure of merit of Nadoped p-type polycrystalline SnSe[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2016,4(5):1848.
[38] Cai B W,Li J H,Sun H,Zhao P,Yu F R,Zhang L,Yu D L,Tian Y J,Xu B. Sodium doped polycrystalline SnSe:high pressure synthesis and thermoelectric properties[J]. Journal of Alloys&Compounds,2017,727:1014.
[39] Ge Z H,Song D S,Chong X Y,Zheng F S,Jin L,Qian X,Zheng L,Dunin-Borkowski R E,Qin P,Feng J,Zhao L D. Boosting the thermoelectric performance of(Na,K)-codoped polycrystalline SnSe by synergistic tailoring of the band structure and atomic-scale defect phonon scattering[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2017,139(28):9714.
[40] Singh N K,Bathula S,Gahtori B,Tyagi K,Haranath D,Dhar A. The effect of doping on thermoelectric performance of p-type SnSe:promising thermoelectric material[J]. Journal of Alloys&Compounds, 2016,668:152.
[41] Kim J H,Oh S,Kim Y M,So H S,Lee H,Rhyee J,Park S,Kim S. Indium substitution effect on thermoelectric and optical properties of Sn1-x Inx Se compounds[J].Journal of Alloys&Compounds,2016,682:785.
[42] Gharsallah M,Serrano-Sánchez F,Nemes N M. Giant Seebeck effect in Ge-doped SnSe[J]. Scientific Reports,2016,6:26774.
[43] Wei T R,Wu C F,Zhang X,Tan Q,Sun L,Pan Y,Li J F. Thermoelectric transport properties of pristine and Na-doped SnSe1-x Tex polycrystals[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2015,17(44):30102.
[44] Chen S,Cai K F,Zhao W Y. The effect of Te doping on the electronic structure and thermoelectric properties of SnSe[J]. Physics Review B,2012,407(21):4154.
[45] Li F,Wang W T,Ge Z H,Zheng Z G,Luo Z T,Fan P,Li B. Enhanced thermoelectric properties of polycrystalline SnSe via LaCl3 doping[J]. Materials,2018,11(2):203.
[46] Li Y L,Shi X,Ren D D,Chen J K,Chen L D. Investigation of the anisotropic thermoelectric properties of oriented polycrystalline SnSe[J]. Energies,2015,8(7):6275.
[47] Li D,Li J C,Qin X Y,Li D,Li J C,Qin X Y,Zhang J,Song C J,Wang L. Thermoelectric performance for SnSe hot-pressed at different temperature[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials,2016,46(1):1.
[48] Liu C Y,Miao L,Wang X Y,Wu S H,Zheng Y Y,Deng Z Y,Chen Y L,Wang G W,Zhou X Y. Enhanced thermoelectric properties of p-type polycrystalline SnSe by regulating the anisotropic crystal growth and Sn vacancy[J]. Chinese Physics B,2018,4(27):047211.
[49] Shi X L,Chen Z G,Liu W D,Yang L,Min Hong M,Moshwan R,Huang L Q,Zou J. Achieving high figure of merit in p-type polycrystalline Sn0.98 Se via self-doping and anisotropy-strengthening[J]. Energy Storage Materials,2018,10:130.
[50] Tang G,Wei W,Zhang J,Li Y,Wang X,Xu G,Chang C,Wang Z,Du Y,Zhao L D. Realizing high figure of merit in phase-separated polycrystalline Sn1-x Pbx Se[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2016,138(41):13647.
[51] Luo Y B,Cai S D,Hua X. High thermoelectric performance in polycrystalline SnSe via dual-doping with Ag/Na and nanostructuring with Ag8 SnSe6 [J]. Advanced Energy Materials,2019,9(2):1803072.
[53] Li J C,Li D,Xu W,Qin X Y,Li Y Y,Zhang J. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of SnSe based composites with carbon black nanoinclusions[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2016,109(17):173902.
[54] Asfandiyar,Wei T R,Li Z,Sun F H,Pan Y,Wu C F.Thermoelectric SnS and SnS-SnSe solid solutions prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering:anisotropic thermoelectric properties[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7:43262.
[55] Huang X Q,Chen Y X,Yin M,Feng D,He J. Origin of the enhancement in transport properties on polycrystalline SnSe with compositing two-dimensional material MoSe2 [J]. Nanotechnology,2017,28(10):105708.
[56] Wei W,Chang C,Yang T,Liu J Z,Tang H C,Zhang J,Li Y S,Xu F,Zhang Z D,Li J F,Tang G D. Achieving high thermoelectric figure of merit in polycrystalline SnSe via introducing Sn vacancies[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2018,140:499.
[57] Shi X L,Wu A Y,Liu W D,Moshwan R,Wang Y,Chen Z G,Zou J. Polycrystalline SnSe with extraordinary thermoelectric property via nanoporous design[J].ACS Publications,2018,12(11):11417.
[58] Guo R,Wang X,Kuang Y,Huang B. First-principles study of anisotropic thermoelectric transport properties of IV-VI semiconductor compounds SnSe and SnS[J].Physical Review B,2015,92(11):115202.
[59] Duan X K,Hu K G,Man D H,Ding S F,Jiang Y Z,Guo S C. Preparation and thermoelectric properties of Na and Al dual doped p-type Bi0.5 Sb1.5 Te3 [J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2013,37(5):757.(段兴凯,胡孔刚,满达虎,丁时峰,江跃珍,郭书超.Na和Al双掺杂p型Bi0.5 Sb1.5 Te3 热电材料的制备及性能研究[J].稀有金属,2013,37(5):757.)
[60] Zhang H,Li J T,Ding F Z,Qu F,Li H,Gu H W. Combustion synthesis of ZrNiSn Half-Heusler thermoelectric materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2019,43(4):337.(张贺,李江涛,丁发柱,屈飞,李辉,古宏伟.燃烧合成法制备ZrNiSn半哈斯勒热电材料[J].稀有金属,2019,43(4):337.)