冷坩埚连续熔化与定向凝固Ti50Al合金的温度场计算
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2012年第3期
论文作者:陈瑞润 丁宏升 杨劼人 黄锋 苏彦庆 郭景杰 傅恒志
文章页码:647 - 653
关键词:TiAl合金;冷坩埚;定向凝固;数值计算
Key words:TiAl alloys; cold crucible; directional solidification; numerical calculation
摘 要:
为了优化工艺参数和实现定向凝固,计算不同参数条件下的冷坩埚连续熔化与定向凝固Ti50Al(摩尔分数,%)合金的温度场。模型中的连续铸造通过识别运动单元的不同位置而实现。结果表明,在功率为52 kW和抽拉速度为3.0 mm/min时, 送料棒在200 s时可以完全熔化,在300 s时具有一定的过热度。当功率为52 kW时,随着抽拉速度从1.2 mm/min加快到6.0 mm/min,送料棒的过热度和熔区都减小,并且固?液界面变凹,其中在6.0 mm/min时,送料棒不能被完全熔化。当抽拉速度为3.0 mm/min时,随着功率从48 kW增加到58 kW,固?液界面位置变低且变凹,当功率为48 kW时,送料棒不能被完全熔化。当抽拉速度和功率配合恰当时,可以实现冷坩埚连续熔化与定向凝固 TiAl合金。
Abstract:
In order to optimize technological parameters and realize directional solidification, temperature fields of cold crucible continuous melting and directional solidifying Ti50Al (mole fraction, %) at different parameters were calculated. Continuous casting of the model is achieved by distinguishing the moving unit at different positions. The calculation results show that the feeding rod is entirely melted at 200 s, the melt of feeding rod has some superheat degree at 300 s under the conditions of 52 kW and 3.0 mm/min. Both the superheat degree and the molten zone of the feeding rod reduce, the solid?liquid interface becomes concave with increasing velocity from 1.2 mm/min to 6.0 mm/min when the power is 52 kW, and the outside layer of the rod cannot be melted at the velocity of 6.0 mm/min. Both superheat degree and the molten zone of the feeding rod increase, the solid?liquid interface descends and becomes concave with increasing power from 48 to 58 kW at velocity of 3.0 mm/min, and the rod cannot be melted entirely when the power is 48 kW. Cold crucible continuous melting and directional solidification of TiAl alloys will be achieved successfully when the pulling velocity and the power are matched appropriately.

![]()

Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 647-653
CHEN Rui-run, DING Hong-sheng, YANG Jie-ren, HUANG Feng, SU Yan-qing, GUO Jing-jie, FU Heng-zhi
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 9 September 2011; accepted 12 January 2012
Abstract: In order to optimize technological parameters and realize directional solidification, temperature fields of cold crucible continuous melting and directional solidifying Ti50Al (mole fraction, %) at different parameters were calculated. Continuous casting of the model is achieved by distinguishing the moving unit at different positions. The calculation results show that the feeding rod is entirely melted at 200 s, the melt of feeding rod has some superheat degree at 300 s under the conditions of 52 kW and 3.0 mm/min. Both the superheat degree and the molten zone of the feeding rod reduce, the solid-liquid interface becomes concave with increasing velocity from 1.2 mm/min to 6.0 mm/min when the power is 52 kW, and the outside layer of the rod cannot be melted at the velocity of 6.0 mm/min. Both superheat degree and the molten zone of the feeding rod increase, the solid-liquid interface descends and becomes concave with increasing power from 48 to 58 kW at velocity of 3.0 mm/min, and the rod cannot be melted entirely when the power is 48 kW. Cold crucible continuous melting and directional solidification of TiAl alloys will be achieved successfully when the pulling velocity and the power are matched appropriately.
Key words: TiAl alloys; cold crucible; directional solidification; numerical calculation
1 Introduction
TiAl alloys have attracted more attention because of their potentially attractive properties, such as low density, high melting point, good modulus retention and high oxidation resistance, making them potentially high temperature structural materials. However, TiAl alloys suffer from poor ductility and toughness at ambient temperature, high production cost and instability processing. A great deal of effort has been made to improve their properties, such as adding alloying elements, heat treatment and heat work, changing solidification route [1-4]. Among them, the directional solidification has aroused the interesting of the researchers [5]. The columnar grain sample with full lamellar microstructure has good mechanical properties. Many experiments on directional solidifying TiAl alloys have been done with Al2O3, Y2O3 or CaO crucible [6-8], whereas titanium is very active in liquid state, and will react with almost all of metals and ceramic mould, which will contaminate components, destroy microstructure and decrease mechanical properties. Directional solidification of TiAl alloys with cold crucible is a new developed technique, it not only makes full use of the advantages of cold crucible (can melt high melting point metal, no or less contamination and homogeneous structure resulting from electromagnetic stirring), but also combines with continuous casting and directional solidification, which realizes melting and solidifying integration.
During the cold crucible directional solidification, the raw materials are melted by induction heating at the upper part of crucible, and the liquid metal soft contacts with the crucible inner wall because of the electromagnetic force at the lower part of crucible. The temperature field of the melt will directly influence the shape, the position and the width of the solid-liquid (S-L) interface. The processing of melting and solidifying will affect the temperature field and the S-L interface, and further determine the metallurgy quality of the ingot. Studying temperature field is a research interesting in casting and solidification processing [9-12]. These results can provide guidance for production and further investigation. There are experimental methods and computer simulation methods in temperature field investigation. Among them, computer simulation is a very good, helpful and timesaving method. Especially for TiAl alloys, the thermocouple probe will react with liquid titanium. As cold crucible directional solidification is a new technics, no related reference on temperature field could be found.
There is a large difference in temperature field for cold crucible directional solidification and conventional solidification [13-15], that is, the feeding rod will continuously experience preheating section, induction heating section and solidifying section, and form liquid metal, the meniscus liquid and the solid state correspondingly. So, the temperature field is dynamic. In this study, in order to characterize the temperature field quantitatively, we deal with the problems of induction heating, boundary conditions, meniscus shape, melting and latent heat, and distinguishing of movement unit. Numerical calculation of temperature fields in melting and solidifying under different parameters is helpful to know about the process, control the technique, improve the metallurgy quality and get good directional solidification structure. The method of establishing the model and calculated results can be used to further investigate the temperature field, continuous casting and directional solidification.
2 Experimental
The apparatus of cold crucible directional solidification was described in Ref. [16]. The process is as follows: a feeding rod is inserted into the cold crucible from the top, and a base rod is connected with the pulling rod which is dipped into a liquid metal at the bottom. When an AC current is applied to the induction coil, a high frequency electromagnetic field is induced, and the feeding rod is heated by induction heating. With processing of induction heating, the feeding rod will be melted and separated into two parts. Because of the balance of electromagnetic pressure, liquid static pressure and surface tension, the lower liquid metal will form a liquid meniscus and some of them will soft contact with the crucible inner wall. The pulling and the supplying will be started when the liquid metal gets some superheat degree. From then on, heating transfer will change and a new S-L interface will form, and then come into a dynamic balance after some time. In this stage, the heating transfer keeps steady, and the height of the skull, the S-L interface keep steady too, as shown in Fig. 1. Ti50Al (mole fraction, %) alloys were used in this work because it is simple binary alloy.
3 Model of numerical calculation of temperature field
To solve the problem of inhomogeneous temperature that resulted from the liquid flow, the thermal conductivity is enlarged as equivalent. Because the cold crucible and the feeding rod are circular cylinders, they surround the axis symmetrically, and the angle (dθ) to the axis is taken as simulation unit. A two-dimensional circular cylinder coordinate system was used in this calculation [17].
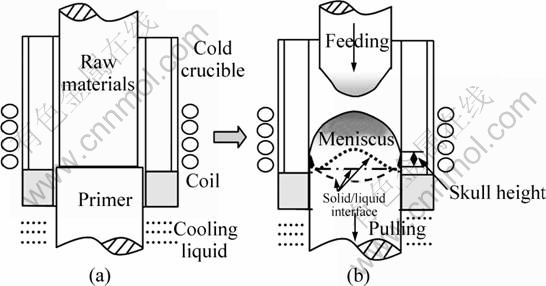
Fig. 1 Process of electromagnetic cold crucible continuous melting and directional solidification: (a) At beginning; (b) In processing
Conservation of energy (latent heat of melting is omitted) of the feeding rod can be expressed in difference equation by internal node as:
![]() (1)
(1)
where ρ, c, V are the density, specific heat capacity and volume, respectively; T is the temperature; t is time; Dt is time step; ω(i,j) is reciprocal of thermal resistance between unit i and unit j; E is radiation heat; A is convection heat; Q is heat induced by electromagnetic field.
3.1 Boundary conditions
The setting of the boundary conditions will affect the temperature field. Because the melting and the solidifying go along at the same time in cold crucible directional solidification, there are two kinds of boundary conditions, belonging to a feeding rod and a new formed rod respectively. According to the melting conditions, the boundary conditions are divided into no liquid meniscus and a liquid meniscus.
3.2 Boundary conditions of feeding rod unit before and after melting
For boundary 3, when it is a liquid boundary, because of the gap between the liquid metal and the crucible inner wall induced by the electromagnetic pressure, heat transfer is thermal radiation and thermal convection.
![]() (2)
(2)
![]() (3)
(3)
where q3 is the heat transferred by boundary 3; h is the integrated heat transfer coefficient of radiation and convection; Γ is Stephen Boltzmann constant; ε is blackness; Tc is the temperature of cold crucible.
When the feeding rod thermally radiates to the crucible inner wall, there is a reflection from the crucible inner wall to the feeding rod. So, the degree of blackness is
![]() (4)
(4)
where ε1, ε2 are the blackness of the raw materials and the cold crucible, respectively.
For the new skull boundary unit, heat transfer is thermal radiation, thermal convection and heat conduction (the skull incomplete contacts with the crucible inner wall).
![]() (5)
(5)
![]() (6)
(6)
where hc is coefficient of thermal conductivity; L(1,2) is the distance between the boundary unit and the cooling liquid; ξ is the contact ratio between the skull and the crucible inner wall.
3.3 Distinguishing of movement unit at different sections
The feeding rod will continuously experience preheating section, induction heating section and solidifying section, where there are levitation liquid section and liquid meniscus section in the induction heating section, as shown in Fig. 2.
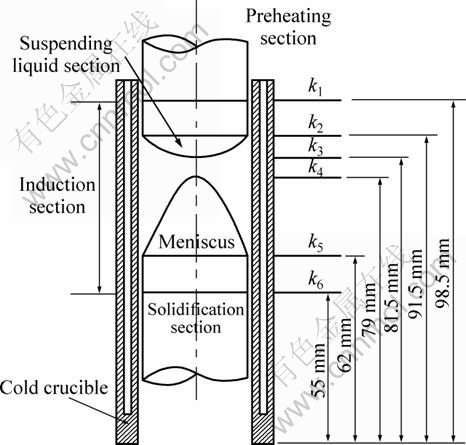
Fig. 2 Different sections of feeding rod in continuous casting
Realizing continuous movement of the calculating unit is the most important problem in the model, including distinguishing which section the movement unit is in, then adjusting heat transfer conditions correspondingly in the procedure. Based on the relationship between original position of the unit and the length of movement in the procedure, the unit can distinguish its section. The criteria for distinguishing of movement unit (i,j) in different sections are as follows.
The criterion for preheating section is
![]() (7)
(7)
The criterion for solidifying section is
![]() (8)
(8)
The criterion for induction heating section is
![]() (9)
(9)
The criterion for levitation liquid section is
![]() (10)
(10)
The criterion for liquid meniscus section is
![]() (11)
(11)
where dy is node length in axial direction; v is moving velocity of the unit, i.e., the supplying velocity for feeding rod or the pulling velocity for the new rod; dt is time step; n is the number of the time step for movement; k1, k2, k3, k4, k5, k6 are vertical coordinate values in induction heating section for signing different sections of movement unit.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Temperature field at pulling velocity of 3.0 mm/min
The calculated temperature fields at different time at the power of 52 kW and the velocity of 3.0 mm/min are shown in Fig. 3. From Fig. 3, it takes hundreds of seconds to melt Ti50Al alloys, but the liquid meniscus is not formed at 70 s; although it forms a liquid meniscus, the melt section of the feeding rod is not enough at 115 s; the feeding rod is completely melted till 200 s; the liquid meniscus has some superheat degree at 300 s. It can be seen that the movement process is a steady dynamic balance, the temperature gradient before the S-L interface is about 100 K/cm along the axis, about 110 K/cm at the boundary. The shape of the S-L interface is a little upwards on both sizes, and nearly planar. The height of the mushy zone is about 10 mm.
Compared with melting Ti6Al4V alloys [17], it takes hundreds of seconds to melt and form liquid meniscus for Ti50Al alloys, and the melting zone and superheat degree of the raw materials zone become less. The temperature gradient and mushy zone before the S-L interface become less too. Whereas, the height of the S-L interface is higher, the shape of the S-L interface is almost similar.
From the melting process and the temperature field distribution, the induction heating is started from the surface layer of the feeding rod, and then expands to the axis and both sides. This is caused by skin effect. The heating is induced in the surface layer, and then transferred to the whole feeding rod by heating conduction. From the electromagnetic field distribution in cold crucible, the maximum of magnetic flux density appears at the position slightly above the middle of the coil [18]. So, the highest temperature is at the middle of surface layer. When the base rod is pulled down at the velocity of 3.0 mm/min, the heating is transferred out more by the liquid alloys at the bottom, and the temperature field is redistributed too, as shown in Figs. 3(d-e).
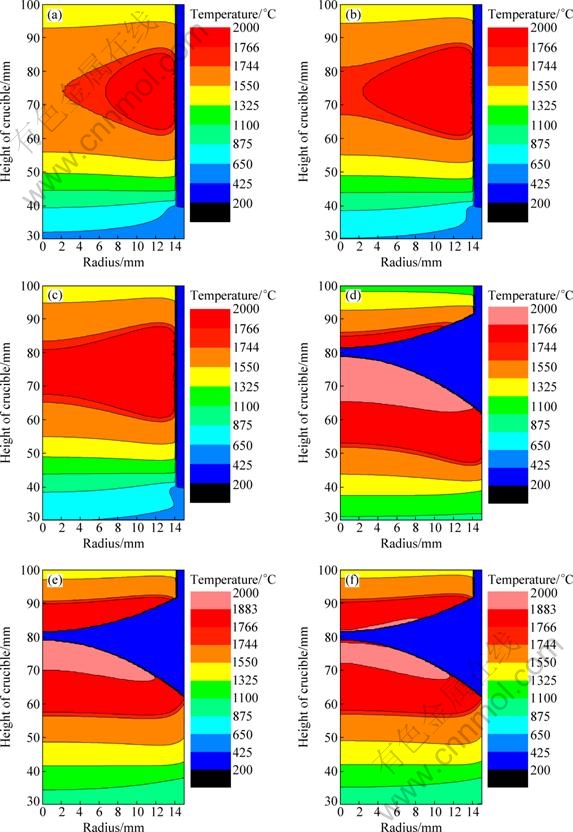
Fig. 3 Temperature fields under power of 52 kW and velocity of 3 mm/min at different time: (a) 45 s; (b) 60 s; (c) 70 s; (d) 115 s; (e) 200 s; (f) 300 s
4.2 Temperature fields at different pulling velocities
Because the velocity is one of the two key factors in directional solidification, it is necessary to calculate the temperature fields at different pulling velocities. The temperature fields are calculated when the pulling velocities are 1.2, 3.0, 4.8 and 6.0 mm/min, respectively, and the power is 52 kW. The results of calculation when the time is 300 s are shown in Fig. 4. From Fig. 4, it can be seen that with increasing the pulling velocity, the S-L interface descends and the shape of it becomes concave, and the melting zone and superheat degree of the feeding rod become less. The rod cannot be melt completely when the velocity is 6.0 mm/min. The superheat degree is the largest when the velocity is 3.0 mm/min, and then decreases with the increase of the pulling velocity. As for the effect of the pulling velocity on the temperature field, there is equilibrium between the heat transfer and induction heating. When the pulling velocity is lower, the heating induced is more than the heating transferred. Whereas, when the pulling velocity is higher, the heating induced in unit time becomes less and the heating transferred in unit time becomes more. So, with the increase of the pulling velocity, the superheat degree and the melting zone decrease, even the feeding rod cannot be melted completely when the velocity is 6.0 mm/min.
Compared with melting Ti6Al4V alloys [14], the S-L interface is at a higher position for melting Ti50Al alloys, the superheat degree of the feeding rod and the liquid meniscus are less too.
4.3 Temperature fields under different powers
Temperature gradient is another key factor in directional solidification, and it is decided by the power in cold crucible directional solidification. It is important to calculate the temperature fields at different powers. The temperature fields are calculated when the power is 48, 52 and 58 kW respectively and the velocity is 3.0 mm/min. The results of calculation when the time is 300 s are shown in Fig. 5. When the power is 48 kW, the feeding rod is only partly melted, there is no skull in the new formed ingot, and the S-L interface is planar and at higher position. As the power increases to 52 kW, the feeding rod is completely melted, the liquid meniscus becomes bigger, the superheat degree of it increases, and the S-L interface descends. When the power increases to 58 kW, the feeding rod is melted more and has a large superheat degree, the melting position reaches 95 mm, the liquid meniscus becomes bigger too, the S-L interface is at about 52 mm position and is more concave. It can be concluded that the melting zone of the feeding rod, the liquid meniscus and its superheat degree are allincreased, the S-L interface descends and becomes concave with increase of the power. Above phenomena are caused by induction heating, and the heating induced increases with the increase of the power.
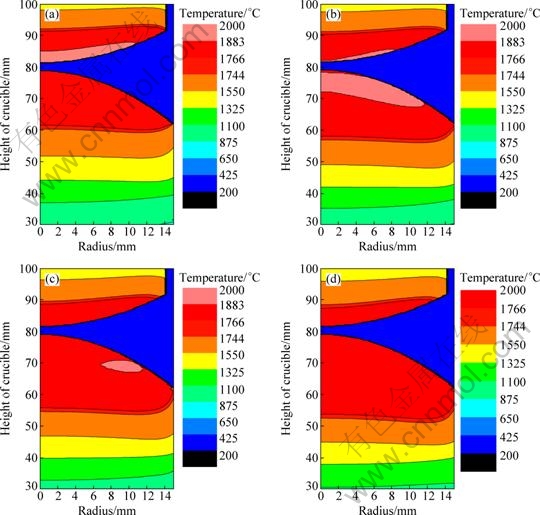
Fig. 4 Temperature fields at 300 s under different velocities: (a) 1.2 mm/min; (b) 3.0 mm/min; (c) 4.8 mm/min; (d) 6.0 mm/min
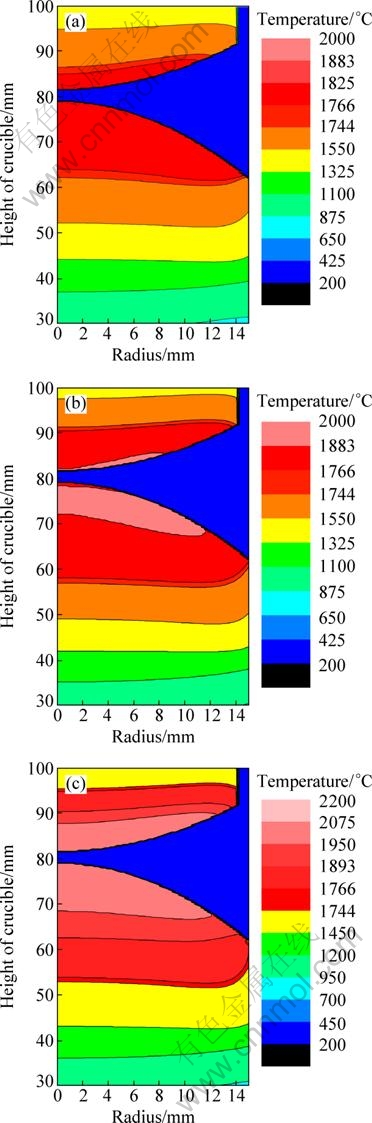
Fig. 5 Temperature fields at 180 s under different powers:(a) 48 kW; (b) 52 kW; (c) 58 kW
From above results and analyses, the temperature fields are very different under different pulling velocities and powers. Ideal melting zone of feeding rod, high superheat degree of the liquid meniscus, planar shape and appropriate position of the S-L interface can be obtained when a lower pulling velocity and a higher power are optimized and adopted. This means that cold crucible directional solidification of Ti50Al is achieved. The power of 52 kW and the velocity of 1.2 mm/min are good technical parameters for directional solidification. An ingot of Ti50Al alloys was prepared by cold crucible directional solidification at the condition of 50 kW and 1.0 mm/min, and the macrostructure is shown in Fig. 6. This experimental result almost accords with the numerical calculation result. It testifies that the model of numerical calculation of temperature field and the distinguishing of movement unit at different zones are feasible.
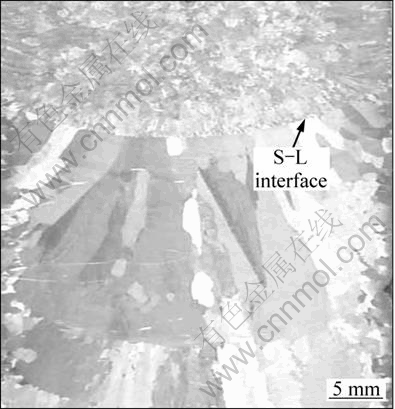
Fig. 6 Macrostructure of Ti50Al ingot prepared by cold crucible directional solidification
5 Conclusions
1) Numerical calculation results show that in cold crucible directional solidification of Ti50Al alloys, the feeding rod is completely melted at 200 s; the liquid meniscus has some superheat degree at 300 s and the temperature field keeps steady after short time during the pulling process.
2) With the increase of the pulling velocity from 1.2 to 6.0 mm/min, the melting zone and the superheat degree of the feeding rod become less, and the S-L interface becomes concave.
3) With increasing the power from 48 to 58 kW, the melting zone and the superheat degree of both the feeding rod and the liquid meniscus increase, and the S-L interface descends and becomes concave too.
4) Cold crucible directional solidification of Ti50Al can be realized from numerical simulation and experiment, the model of numerical calculation of temperature field and the distinguishing of movement unit at different zone are feasible.
References
[1] MIA J, HARDINGB R A, WICKINSB M, CAMPBELL J B. Entrained oxide films in TiAl castings [J]. Intermetallics, 2003, 11: 377-385.
[2] TJERING G L. Influence of processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of (α+β) titanium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 243: 32-45.
[3] HU D, BOTTEN R R. Phase transformations in some TiAl-based alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 2002, 10: 701-715.
[4] JIN Y G, WANG J N, YANG J, WANG Y. Microstructure refinement of cast TiAl alloys by β solidification [J]. Scripta Materialia., 2004, 51: 113-117.
[5] SAARI I H, BEDDOES J, SEO D Y, ZHAO L. Development of directionally solidified γ-TiAl structures [J]. Intermetallics, 2005, 13: 937-943.
[6] KISHIDA K, INUI H, YAMAGUCHI M. Deformation of PST crystals of a TiAl/Ti3Al two-phase alloy at 1000 °C [J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7: 1131-1139.
[7] JOHNSON D R, MASUDA Y, INUI H, YAMAGUCHI M. Alignment of the TiAl/Ti3Al lamellar microstructure in TiAl alloys by directional solidification [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 239-240: 577-583.
[8] KIM M C, OH M H, LEE J H, INUI H, YAMAGUCHI M, WEE D M. Composition and growth rate effects in directionally solidified TiAl alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 239-240: 570-576.
[9] ZHENG X S, SHA M H, JIN J Z. Experimental research and numerical simulation of mold temperature field in continuous casting of steel [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2006, 19(3): 176-182.
[10] SHEN H, YAO Z Q, SHI Y J, HU J. Study on temperature field induced in high frequency induction heating [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2006, 19(3): 190-196
[11] SU Yan-qing, XU Yan-jin, ZHAO Lei, GUO Jing-jie, FU Heng-zhi. Effect of electromagnetic force on melt induced by traveling magnetic field [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 662-667.
[12] KUND N K, DUTTA P. Numerical simulation of solidification of liquid aluminum alloy flowing on cooling slope [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(s): s898-s905.
[13] YANG Zhi-jun, ZHAO Xiao-hua, KOU Hong-chao, LI Jin-shan, HU Rui, ZHOU Lian. Numerical simulation of temperature distribution and heat transfer during solidification of titanium alloy ingots in vacuum arc remelting process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(10): 1957-1962.
[14] HA M Y, LEE H G, SEONG S H. Numerical simulation of three-dimensional flow, heat transfer, and solidification of steel in continuous casting mold with electromagnetic brake [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 133(3): 322-339.
[15] DADZIS K, EHRIG J, NIEMIETZ K, PATZOLD O, WUNDERWALD U, FRIEDRICH J. Model experiments and numerical simulations for directional solidification of multicrystalline silicon in a traveling magnetic field [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2011, 333: 7-15
[16] CHEN Rui-run, DING Hong-sheng, GUO Jing-jie, BI Wei-sheng, FU Heng-zhi. Process on cold crucible electromagnetic casting for titanium alloy [J]. China Foundry, 2007, 4(3): 190-193. (in Chinese)
[17] CHEN Rui-run, DING Hong-sheng, GUO Jing-jie, LIANG Fu-zhen, ZHANG Zi-qin, BI Wei-sheng, LIU Lin, FU Heng-zhi. Numerical calculation on effect of processing parameters on temperature field in continuous melting and solidification of Ti6Al4V alloys with cold crucible [J]. Materials Science & Technology, 2009, 17(4): 482-485.
[18] CHEN Rui-run, HUANG Feng, GUO Jing-jie, DING Hong-sheng, YANG Jie-ren, FU Heng-zhi. Electromagnetic characteristics of square cold crucible designed for silicon preparation [J]. China Foundry, 2011, 8(2): 206-211.
陈瑞润,丁宏升,杨劼人,黄 锋,苏彦庆,郭景杰,傅恒志
哈尔滨工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150001
摘 要:为了优化工艺参数和实现定向凝固,计算不同参数条件下的冷坩埚连续熔化与定向凝固Ti50Al(摩尔分数,%)合金的温度场。模型中的连续铸造通过识别运动单元的不同位置而实现。结果表明,在功率为52 kW和抽拉速度为3.0 mm/min时, 送料棒在200 s时可以完全熔化,在300 s时具有一定的过热度。当功率为52 kW时,随着抽拉速度从1.2 mm/min加快到6.0 mm/min,送料棒的过热度和熔区都减小,并且固-液界面变凹,其中在6.0 mm/min时,送料棒不能被完全熔化。当抽拉速度为3.0 mm/min时,随着功率从48 kW增加到58 kW,固-液界面位置变低且变凹,当功率为48 kW时,送料棒不能被完全熔化。当抽拉速度和功率配合恰当时,可以实现冷坩埚连续熔化与定向凝固 TiAl合金。
关键词:TiAl合金;冷坩埚;定向凝固;数值计算
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project (2011CB6055504) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: CHEN Rui-run; Tel: +86-451-86412394; E-mail: ruirunchen@hit.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61227-2

