
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.01.022
高温后花岗岩的物理力学特性试验研究
吴阳春1,郤保平1, 2,王磊3,牛新明3,王帅1,赵阳升1, 2
(1. 太原理工大学 矿业工程学院,山西 太原, 030024;
2. 太原理工大学 原位改性采矿教育部重点实验室,山西 太原,030024;
3. 中国石油化工股份有限公司 石油工程技术研究院,北京,100101)
摘要:为研究高温后花岗岩的物理力学特性与温度变化的关系,对600 ℃范围内青海共和花岗岩自然冷却后进行单轴压缩、巴西劈裂和变角剪切试验。研究结果表明:从室温~600 ℃,花岗岩质量损失率随温度升高而增大,在300 ℃之前,花岗岩体积收缩,密度变大,在300 ℃后,花岗岩体积膨胀,密度变小;从室温~600 ℃,花岗岩的抗压强度,抗拉强度和抗剪强度(内聚力)随温度升高先变大后变小,弹性模量随温度升高单调递减,在250~600 ℃时,内摩擦角随温度升高而增大;400~600 ℃可视为花岗岩从脆性向延性转变的临界温度范围。基于弹性模量的损伤因子在400 ℃之后可以较好地反映岩石强度的热损伤程度。
关键词:青海共和花岗岩;高温;抗压强度;抗拉强度;抗剪强度
中图分类号:TU45 文献标志码:A 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
文章编号:1672-7207(2020)01-0193-11
Experimental study on physico-mechanical properties of granite after high temperature
WU Yangchun1, XI Baoping1, 2, WANG Lei3, NIU Xinming3, WANG Shuai1, ZHAO Yangsheng1, 2
(1. College of Mining Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Insitu Property Improving Mining of Ministry of Education, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China;
3. Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Engineering, Beijing 100101, China)
Abstract: In order to study the relationship between the physico-mechanical properties of granite and the temperature, the uniaxial compression, Brazilian splitting and variable angle shearing experiments were carried out for Qinghai Gonghe granite within 600 ℃ after natural cooling. The results show that the mass loss rate increases with the increase of the temperature from room temperature to 600 ℃. Below 300 ℃, the volume shrinks and the density becomes larger. Over 300 ℃, the volume expands and the density becomes smaller. From room temperature to 600 ℃, the compressive strength, tensile strength and shearing strength (cohesion) of granite increase first and then decrease with the increase of temperature, and the elastic modulus decreases with the increase of temperature. From 250 ℃ to 600 ℃, the internal friction angle becomes larger with the increase of temperature. 400-600 ℃ can be regarded as the critical temperature range of granite changing from brittle to ductile. It is found that the damage factor based on the elastic modulus can well reflect the thermal damage degree of rock strength after 400 ℃.
Key words: Qinghai Gonghe granite; high temperature; compressive strength; tensile strength; shear strength
地热能因具有储量丰富、利用稳定、清洁高效的特点被世界各国认为是未来能源出路之一[1]。我国地热能开发利用“十三五”规划的发布和青海共和干热岩地热示范工程的兴起,为地热开发及研究提供了一个良好的基础。干热岩地热能主要贮藏在花岗岩内[1],高温地热田在钻井施工、人工热储建造和采热运营期间不断冷却,因此,高温或高温后花岗岩物理力学特性的研究具有一定意义。目前,高温后花岗岩的力学特性研究成果较多。如:朱振南等[2]研究了高温500 ℃范围内花岗岩遇水冷却后的物理力学特性。方新宇等[3]分析了25~1 000 ℃高温后花岗岩的抗拉强度及热损伤特性。胡少华等[4]进行了北山花岗岩热处理后的变形特性试验与损伤力学分析研究。徐小丽等[5-7]研究了高温后花岗岩单轴抗压强度及三轴抗压强度的变化规律。孙强等[8]研究了岩石高温相变及物理力学性质变化。许锡昌等[9-10]研究了高温下花岗岩的基本力学性质并进行了损伤分析,认为75 ℃和200 ℃分别为弹性模量和抗压强度的门槛温度。梁铭等[11]研究了不同冷却方式对高温花岗岩抗拉强度的影响。KUMARI等[12-14]研究了不同冷却方式对高温Strathbogie花岗岩的力学强度、渗流特性、声学响应和微观结构的作用规律。PENG等[15]研究了600 ℃内高温粗粒大理岩自然冷却后的单轴抗压强度。CHEN等[16]研究了从室温到800 ℃范围内以1~15 ℃/min的不同加热速率对花岗岩强度的影响,认为5 ℃/min的加热速率是判断花岗岩是否产生热冲击损伤的临界加热速率。目前,有关花岗岩的剪切强度及参数的研究较少,特别是高温后花岗岩的剪切强度,而实际工程失稳问题常常涉及压剪破坏。针对这一问题,本文作者以青海共和盆地干热岩地热示范工程为背景,通过单轴压缩、巴西劈裂、变角剪切试验来研究高温600 ℃范围内青海共和花岗岩的物理力学特性,以期揭示热对花岗岩强度劣化的规律,为青海共和干热岩地热开发提供指导意义。试验温度范围选取由中国地温梯度分布[17]和国内外大陆科考钻井深度[18]共同确定。
1 试验概况
1.1 试件制备
花岗岩样品取自青海共和盆地龙才沟露头地带,为印支期的灰白色中粗粒黑云母花岗岩,实测密度为2.65~2.67 g/cm3。其主要矿物成分(质量分数)如下:斜长石,40%~50%;石英,20%~25%;黑云母,5%~10%[19]。单轴压缩、巴西劈裂分别采用直径×长度为50 mm×100 mm和50 mm×25 mm的圆柱体试件,变角剪切试验采用长×宽×高为50 mm×50 mm×50 mm的正方体试件。使用水刀切割机、取芯钻机和砂带磨石机加工上述试件,其加工精度及尺寸均满足ISRM标准。试件表面光滑平整、无明显缺陷,同一状态条件下所用试件数量均为3个,试件如图1所示。

图1 试验试件
Fig. 1 Experimental specimens
1.2 试验设备
花岗岩的质量和体积分别采用精度为0.01 g的电子秤和精度为0.02 mm的游标卡尺测定。高温热处理采用SX2-12-12A型自带编程控温加热的马弗炉,温控精度为±5 ℃。力学试验采用微机控制电液伺服试验机,量程为0~600 kN。
1.3 试验步骤及方案
1) 将单轴压缩、巴西劈裂和变角剪切对应的标准试件组合后均分为7组,将每组试件称量和测量尺寸,并记录相关试验数据。2) 将其中6组试件置于马弗炉内以3~5 ℃/h的加热速率分别加热至250,300,350,400,500和600 ℃后,恒温3 h,然后从马弗炉内取出试件置于空气中,冷却至室温,并对冷却后的试件重新称重和测量尺寸,记录相关数据。最后1组试件不进行热处理,为对照组。3) 将高温处理后的6组试件和常温对照组试件依次在伺服试验机上进行单轴压缩(直径×长度为50 mm×100 mm)、巴西劈裂(直径×长度为50 mm×25 mm)、变角剪切(长×宽×高为50 mm×50 mm×50 mm)试验,其加载速率分别为0.001,0.001和0.002 mm/s。变角剪切试验采用45°,55°和65°这3个剪切角度。
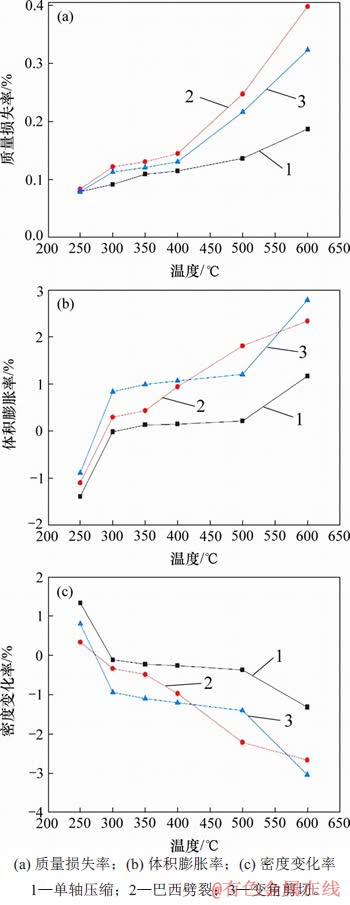
图2 高温后花岗岩物理性质与温度的关系
Fig. 2 Relationship between physical properties of granite and temperature
2 物理试验结果及分析
图2(a)~(c)所示分别为高温后花岗岩质量损失率、体积膨胀率和密度变化率与温度的关系。由图2(a)可知:试件质量损失率随温度升高单调递增,但可细分为3个阶段:300 ℃之前,质量损失率增长明显,质量减少,其原因是试件内部附着水和强结合水的逸出和蒸发。在300~400 ℃范围内,质量损失率增长缓慢,其原因是少部分弱结合水开始逸出。在400~600 ℃范围内,质量损失率明显变大,其原因是试件内部弱结合水和结构水的逸出及部分矿物热解,试件质量进一步降低。由图2(b)可知:在250~600 ℃范围内,试件体积膨胀率随温度升高单调递增,但300 ℃之前,体积膨胀率为负值,表明试件收缩,体积变小,其主要原因是受热膨胀使得试件内部的微裂纹被压密实;300 ℃之后,试件体积膨胀率为正值,试件体积变大,尤其是500~600 ℃试件体积膨胀率明显变大,主要原因是石英发生相变,由α石英变为β石英,试件体积增大。由图2(c)可知;试件密度变化率随温度升高而降低,300 ℃之前,密度变化率为正值,密度变大,300 ℃之后,密度变化率为负值,密度变小。密度是质量与体积的函数,在300 ℃之前,密度变大,说明微裂隙的压密引起的体积变小比质量降低的比例大,密度增加可以解释300 ℃之前存在一个强度强化现象。同时在500~600 ℃时试样密度降低显著,是质量变小和体积增大的共同作用的结果。300 ℃之前存在一个体积变小,密度变大的区间与徐小丽等[15]的结果一致。
3 力学试验结果及分析
3.1 单轴压缩试验
单轴压缩试验通常采用高径比为2:1的标准圆柱体试件(直径×长度为50 mm×100 mm),按一定的加载速率轴向加载至试件破裂,岩石单轴抗压强度计算公式如下:
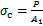 (1)
(1)
式中: 为岩石抗压强度,MPa;P为试件破坏时的最大载荷,N;A1为试件横截面积,mm2。
为岩石抗压强度,MPa;P为试件破坏时的最大载荷,N;A1为试件横截面积,mm2。
3.1.1 应力-应变曲线随温度的关系
图3所示为高温花岗岩自然冷却后全应力-应变曲线,表1所示为单轴压缩试验结果。由图3可以看出试件从加载到破坏可分为3个阶段。
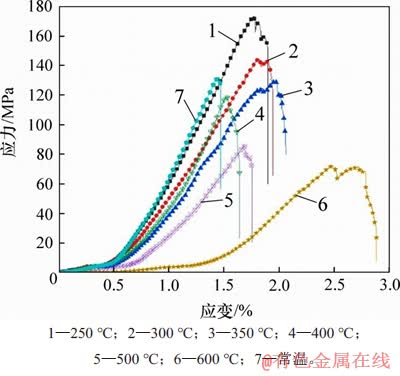
图3 高温花岗岩自然冷却后全应力-应变曲线
Fig. 3 Stress-strain curves of high temperature granite after natural cooling
1) 微裂隙压密阶段。这一阶段应力应变曲线呈上凹,该现象说明较小的应力产生较大的应变量,其主要原因是试件内部的微裂隙被压密实,压密阶段随着温度升高明显变长,表明热破裂现象随温度升高明显加剧,试件内部的微裂隙变多,特别是在500~600 ℃,微裂隙压密阶段明显变长,其本质是石英晶体发生相变,由α石英转变为β石英,这跟GE等[20]发现石英产生相变的临界温度为573 ℃相一致。
2) 弹性变形阶段。该阶段应力-应变曲线满足线性关系,即胡克定律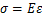 。弹性模量采用直线段的斜率表示,为切线弹性模量。
。弹性模量采用直线段的斜率表示,为切线弹性模量。
3) 屈服破坏阶段。此阶段试件表面开始出现明显裂纹,并伴随有大量的声响出现,当应力达到峰值强度时,裂纹基本贯穿整个试件,试件破坏,如图4所示。
表1 单轴压缩试验结果
Table 1 Test results of uniaxial compression experiments
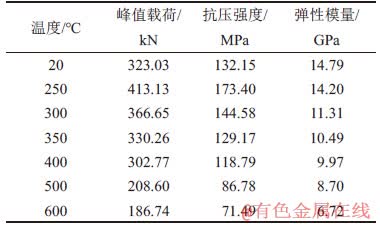

图4 单轴压缩破坏图
Fig. 4 Uniaxial compression failure picture
3.1.2 抗压强度随温度的关系
图5所示为抗压强度和峰值载荷与温度的关系图像。由图5和表1可知:高温花岗岩自然冷却后抗压强度与峰值载荷都随温度升高先变大后变小,这与徐晓丽等[7]试验发现花岗岩在200~600 ℃范围内存在强度随温度升高不降反升的异常现象相一致。在250~300 ℃范围内,试件的抗压强度比常温的高,从微观上考虑这主要是高温处理后,矿物颗粒间的热膨胀作用产生的热应力小于颗粒间的胶结力,使得花岗岩内部的微裂隙被压密实,试件抗压强度增大;300 ℃之后,颗粒间的热膨胀产生的热应力大于矿物颗粒间的胶结力,从而表现出力学性能的劣化。从宏观上解释是300 ℃内高温使花岗岩内部有限的附着水、结合水蒸发,这对强度的提升作用大于热对花岗岩的劣化作用,产生一个强度强化现象,300 ℃以后试件内部水分基本耗尽,热的劣化占主导作用,整体上体现为花岗岩力学性能劣化,这与杜守继等[21]的结论一致。试件抗压强度从室温时的132.15 MPa降低为600 ℃时的71.49 MPa,降低了60.66 MPa,衰减了45.9%。从图3可知:峰值应变由室温的1.447%增加到600 ℃时的2.480%,峰值应变增加了1.033%,增幅为71.4%。说明达到一定温度之后,随着温度的升高,热对花岗岩强度的劣化作用明显,花岗岩由脆性向延性转变。400~600 ℃的峰值应变及压密段长度有显著增长,可视400~600 ℃为花岗岩脆性向延性转变的临界温度区域。
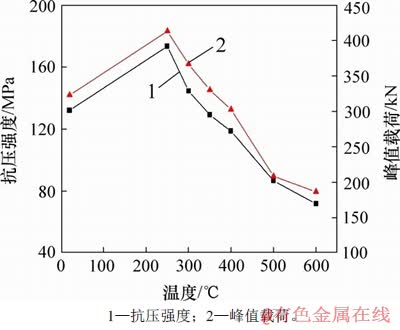
图5 抗压强度和峰值载荷与温度的关系
Fig. 5 Relationship between of compressive strength and peak load with temperature
3.1.3 弹性模量随温度的关系及损伤分析
图6所示为弹性模量及ET/E0(ET/E0定义为任意温度下的弹性模量(ET)与常温下弹性模量(E0)的比值)与温度的关系。由图6可知:随着温度升高,弹性模量单调递减,弹性模量从室温的14.79 GPa降为600 ℃的6.72 GPa,降幅达54.6%。采用ET/E0对高温花岗岩自然冷却后的弹性模量进行量纲一化处理,ET/E0反映了弹性模量随温度的变化趋势。从ET/E0可知,600 ℃的弹性模量仅为常温时的0.45倍,说明高温对弹性模量影响显著且成反比。
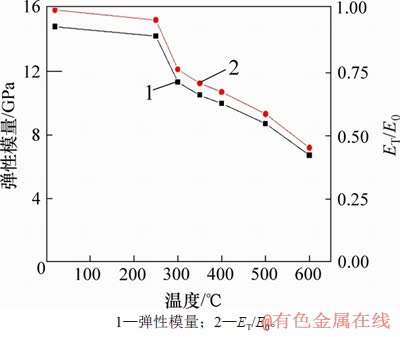
图6 弹性模量及ET/E0与温度的关系
Fig. 6 Relationship between of elastic modulus and ET/E0 with temperature
为描述高温花岗岩自然冷却后力学性能劣化程度,采用刘泉声等[10]基于弹性模量的损伤因子来定义自然冷却后花岗岩的损伤程度。损伤因子计算公式如下:
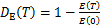 (2)
(2)
式中: 为T温度自然冷却后基于弹性模量的损伤因子;E(T)为T温度自然冷却后试件的弹性模量;E(0)为常温试件的弹性模量。
为T温度自然冷却后基于弹性模量的损伤因子;E(T)为T温度自然冷却后试件的弹性模量;E(0)为常温试件的弹性模量。
图7所示为损伤因子与温度的关系曲线。由图7可知:基于弹性模量的损伤因子随温度升高单调递增,250 ℃之后显著增大。根据单轴压缩试验结果可知:300 ℃之前因水分的蒸发和逸出,岩石抗压强度增大,水的耗散对岩石的强度变化起主要作用,热对岩石的损伤作用是次要的,故基于弹性模量的损伤因子不能很好地反映热损伤程度;300 ℃之后,热对岩石强度劣化起主要作用,故采用弹性模量的损伤因子能较好的反映热损伤的趋势,在400~600 ℃范围内,可以较好地反映热对岩石极限强度劣化的程度。
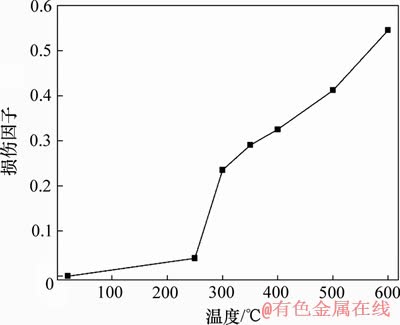
图7 损伤因子与温度关系
Fig. 7 Relationship between damage factor and temperature
3.2 巴西劈裂试验
根据弹性力学解析解可知,径向受压的圆盘,在受压平面垂直方向上存在大小相当的拉应力。试件抗拉强度可采用下式计算:
 (3)
(3)
式中: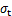 为岩石抗拉强度,MPa;D为试件直径,mm;t为试件厚度,mm。
为岩石抗拉强度,MPa;D为试件直径,mm;t为试件厚度,mm。
图8所示为巴西劈裂实物图,表2所示为巴西劈裂试验结果,图9所示为高温后花岗岩载荷-径向位移曲线,图10所示为高温花岗岩抗拉强度及峰值载荷随温度的变化。

图8 巴西劈裂实物图
Fig. 8 Picture of Brazilian splitting experiment
表2 巴西劈裂试验结果
Table 2 Test results of Brazilian spitting experiments
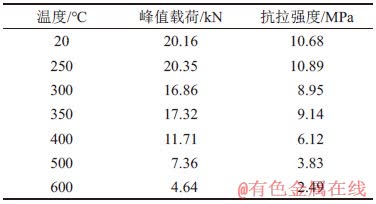
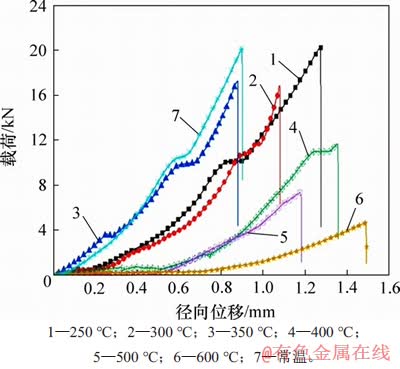
图9 高温后花岗岩载荷-径向位移曲线
Fig. 9 Load-radial displacement curves of granite after high temperature
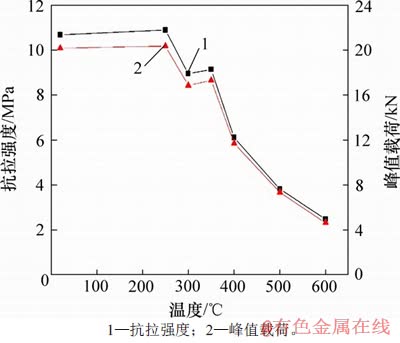
图10 高温花岗岩抗拉强度及峰值载荷与温度关系
Fig. 10 Relationship among tensile strength, peak load of high temperature granite and temperature
由图10可知:抗拉强度和峰值载荷随温度升高先变大后变小。250 ℃之前强度轻微上升与密度变化相一致,说明热膨胀产生的热应力小于颗粒间的胶结力,试件被压密实,强度提高。高温作用后花岗岩的抗拉强度从室温的10.68 MPa降为600 ℃的2.49 MPa,降幅达76.7%,这一比例说明抗拉强度受温度影响显著。
3.3 变角剪切试验
考虑承压板与剪切模具间的摩擦力,试件被剪断时,作用在破坏面上的剪应力τ和正应力σ分别为:
 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
式中:A2为剪切破坏面的面积,mm2;α为模具倾角,(°);f为承压板与模具间的滚动摩擦因数,f=1/(nd);n为滚轴数量;d为滚轴直径。
图11所示为剪切试验图。通过改变模具倾角,获得不同剪切角度下的正、剪应力,并在τ-σ坐标系中绘出,根据库仑准则:
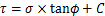 (6)
(6)
采用式(6)进行线性拟合得到岩石抗剪强度曲线,曲线的截距和斜率分别为内聚力C和内摩擦角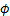 。表3所示为高温花岗岩自然冷却后剪切试验结果。
。表3所示为高温花岗岩自然冷却后剪切试验结果。

图11 剪切试验图
Fig. 11 Pictures of shear experiment
表3 高温花岗岩自然冷却后剪切试验结果
Table 3 Shear test results of high temperature granite after air cooling

3.3.1 剪切参数与温度的关系
图12所示为高温花岗岩自然冷却后抗剪强度曲线,图13所示为剪切参数随温度变化关系。从图13可知:内聚力随温度的升高先变大后变小,内摩擦角随温度升高而变大。室温~300 ℃内花岗岩的内聚力有一个明显的增长,300 ℃时达到最大值,比常温状态下增长12.116 MPa,增幅为18.5%,这是由于温度升高矿物颗粒间的热膨胀作用产生的体积膨胀将试件内部的微裂隙压密实,且热膨胀应力小于矿物颗粒间的胶结力,这样在试件整体上产生一个强化作用,300 ℃以后,受温度影响产生的热膨胀应力大于矿物颗粒间的胶结力,颗粒间胶结处产生微裂纹,试件强度产生明显降低,内聚力降低。300~400 ℃这一范围内内聚力降低显著,高达27.704 MPa,说明300 ℃后热破裂占主导作用,热对岩石强度降低作用明显。内聚力从室温的65.496 MPa降为600 ℃的28.20 MPa,降幅达56.9%。内摩擦角在250~600 ℃范围内是缓慢增大的,内摩擦角在250~300 ℃范围内增长最快,高达5.6°,可见温度变化对花岗岩剪切参数有显著影响。这一结论说明干热岩地热开发考虑温度对工程参数的选取具有实际意义。
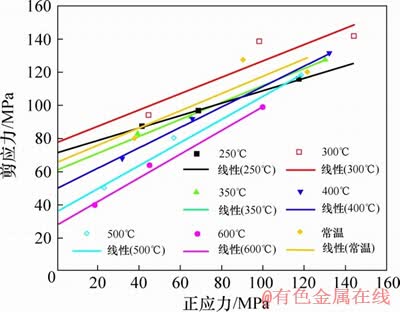
图12 高温花岗岩自然冷却后抗剪强度曲线
Fig. 12 Shear strength curves of high temperature granite after natural cooling
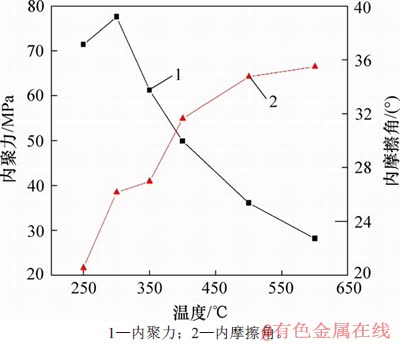
图13 剪切参数随温度变化关系
Fig. 13 Relationship between shear parameters and temperature
3.3.2 高温后剪切作用下试件变形特征分析
图14(a)~(g)所示分别为室温~600 ℃花岗岩自然冷却后的剪应力-剪应变曲线,应力-应变曲线大致分为3个阶段:压密阶段、弹性阶段、屈服破坏阶段。
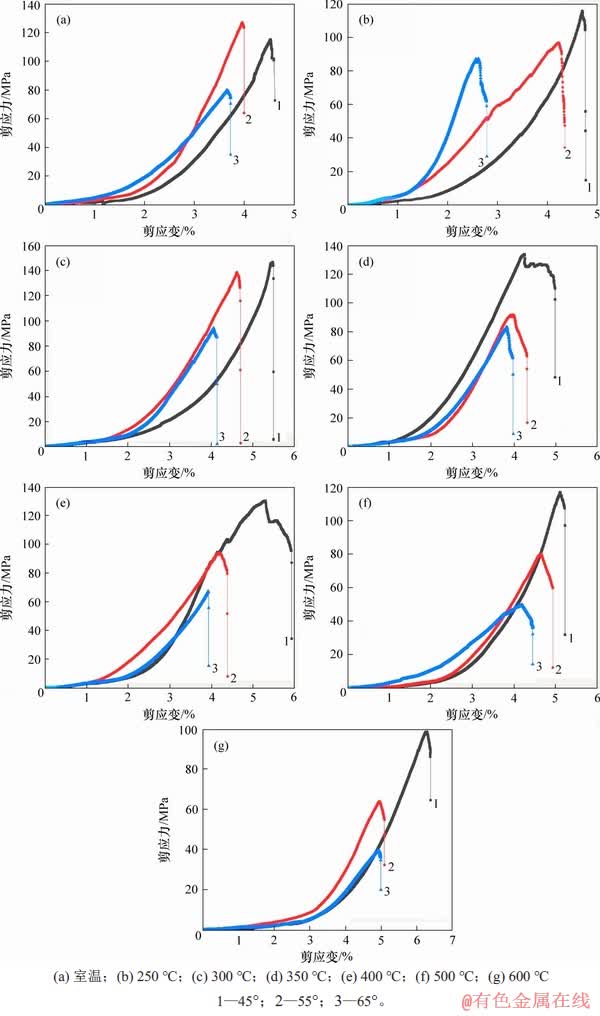
图14 高温花岗岩自然冷却后剪应力-剪应变曲线
Fig. 14 Curves of shearing stress-strain of high temperature granite after natural cooling
从图14可知:同一温度下,随着剪切角度的增大,压密阶段和弹性阶段都呈缩短的趋势,峰值剪应变变小。式(4)和式(5)可解释这一现象,随着剪切角度增大,应力分解中剪应力占比增大,在较小的载荷范围内,剪应力与正应力作用在剪切面上的摩擦力之差大于内聚力,试件破坏且破坏时对应的峰值应力、峰值应变相应变小。同一剪切角度下,峰值应变与温度的关系总的趋势是随温度的升高,峰值应变逐渐增大,但由于岩石的非均质性,矿物组分的差异,个别温度下变小,但总的趋势是符合规律的。其次,同一角度下,随着温度升高,压密段应变增大明显。根据峰值应变及压密段长度随温度的变化关系,认为400~600 ℃是花岗岩脆性向延性转变的临界温度范围。以45°剪应力-应变为例,500和600 ℃的压密段对应的应变分别约为2.5%和3.0%,增幅为20%,峰值应变分别为5.1%和6.3%,增幅为23.5%。可见500~600 ℃存在一个显著的热破裂现象,这与林睦曾[22]发现将花岗岩加热到573 ℃时,石英相变,由α-石英转变为β-石英,岩石变得疏松,强度降低相吻合。
3.3.3 高温后剪切角度对峰值应力的影响
图15所示为同一角度下峰值应力与温度的关系。从图15可知:1) 同一剪切角度下,随着温度的升高峰值正应力与剪应力都呈先增大后降低的趋势;2) 忽略岩样的差异,在同一温度下,试件的内聚力相同,但由于剪切角度不同,试件破坏时的峰值剪应力相差很大,其主要原因是:由于角度增大,根据力的分解可知剪切面上的正应力减小,相应的剪切面上的摩擦力也减小,最终表现为峰值剪应力降低。这说明必须考虑正应力对剪应力的影响,而不能简单地考虑内聚力和内摩擦角的影响。
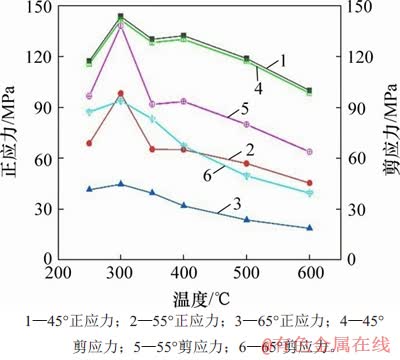
图15 同一角度下峰值应力与温度的关系
Fig. 15 Relationship between peak stress and temperature under the same shear angle
从图15可以看出:45°~55°(前10°)和55°~65°(后10°)这2个10°变化范围内,前10°相比后10°的峰值正应力和剪应力降低显著(300 ℃除外),在350 ℃时,前10°范围内,正应力降低了64.90 MPa,剪应力降低了36.45 MPa,后10°范围内,正应力降低了25.73 MPa,剪应力降低了8.53 MPa,可见前10°下正应力和剪应力的降低值分别为后10°应力差的2.52倍和4.27倍。图16所示为前后10°峰值应力降低比与温度的关系。由图16可知:除去300 ℃这一角度异常值,前后10°平均正应力差的比值为2.05,平均剪应力差的比值为2.06,同时可以看出随温度升高,峰值应力比先增大后降低,且恒大于1。这一现象说明剪切角度的低度数变化对正应力和剪应力影响显著。
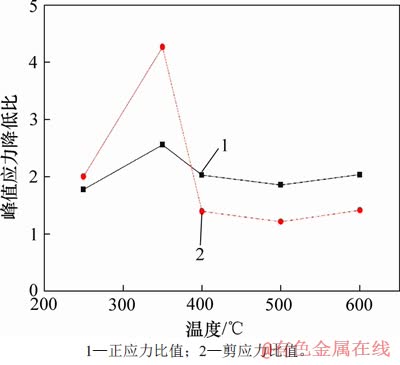
图16 前后10°峰值应力降低比和温度关系
Fig. 16 Relationship between peak stress reduction ratio (10° before and after ) and temperature
4 结论
1) 花岗岩的质量、体积和密度随温度变化大致可分为3个阶段:室温~300 ℃时,附着水和结合水蒸发,质量急剧减少,体积收缩,密度变大;在300~500 ℃时,弱结合水丧失,质量轻微损失,体积膨胀,密度变小;在500~600 ℃时,水分进一步失去,石英相变,体积膨胀,密度变小。
2) 在300 ℃之前,试件的抗压强度、抗拉强度和抗剪强度(内聚力)相较于常温试件存在一个强化区域,300 ℃以后,随温度升高,抗压强度、抗拉强度和抗剪强度(内聚力)都呈现降低趋势。弹性模量随温度升高单调递减。在250~600 ℃时,内摩擦角随温度升高单调递增。400~600 ℃可视为花岗岩从脆性向延性转变的临界温度范围。
3) 从室温~600 ℃,抗压强度、抗剪强度(内聚力)和抗拉强度分别衰减了45.9%,56.9%和76.7%,说明高温对花岗岩极限强度影响从大到小依次为:抗拉强度,抗剪强度,抗压强度。
4) 基于弹性模量的损伤因子仅在热对岩石强度劣化起主要作用的温度阶段才能较好地反映强度损伤趋势及程度。
参考文献:
[1] 许天福, 胡子旭, 李胜涛, 等. 增强型地热系统: 国际研究进展与我国研究现状[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 9(9): 1936-1947.
XU Tianfu, HU Zixu, LI Shengtao, et al. Enhanced geothermal system: international progresses and research status of China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 9(9): 1936-1947.
[2] 朱振南, 田红, 董楠楠, 等. 高温花岗岩遇水冷却后物理力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(S2): 169-176.
ZHU Zhennan, TIAN Hong, DONG Nannan, et al. Experimental study of physico-mechanical properties of heat-treated granite by water cooling[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(S2): 169-176.
[3] 方新宇, 许金余, 刘石, 等. 高温后花岗岩的劈裂试验及热损伤特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(S1): 2687-2694.
FANG Xinyu, XU Jinyu, LIU Shi, et al. Research on splitting-tensile tests and thermal damage of granite under post-high temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(S1): 2687-2694.
[4] 胡少华, 章光, 张淼, 等. 热处理北山花岗岩变形特性试验与损伤力学分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(12): 3427-3436.
HU Shaohua, ZHANG Guang, ZHANG Miao, et al. Deformation characteristics tests and damage mechanics analysis of Beishan granite after thermal treatment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(12): 3427-3436.
[5] 徐小丽, 高峰, 张志镇. 高温后围压对花岗岩变形和强度特性的影响[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(12): 2246-2252.
XU Xiaoli, GAO Feng, ZHANG Zhizhen. Influence of confining pressure on deformation and strength properties of granite after high temperatures[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(12): 2246-2252.
[6] 徐小丽, 高峰, 沈晓明, 等. 高温后花岗岩力学性质及微孔隙结构特征研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(6): 1752-1758.
XU Xiaoli, GAO Feng, SHEN Xiaoming, et al. Research on mechanical characteristics and micropore structure of granite under high-temperature[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(6): 1752-1758.
[7] 徐小丽, 高峰, 高亚楠, 等. 高温后花岗岩力学性质变化及结构效应研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2008, 37(3): 402-406.
XU Xiaoli, GAO Feng, GAO Yanan, et al. Effect of high temperatures on the mechanical characteristics and crystal structure of granite[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2008, 37(3): 402-406.
[8] 孙强, 张志镇, 薛雷, 等. 岩石高温相变与物理力学性质变化[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(5): 935-942.
SUN Qiang, ZHANG Zhizhen, XUE Lei, et al. Physico-mechanical properties variation of rock with phase transformation under high temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(5): 935-942.
[9] 许锡昌, 刘泉声. 高温下花岗岩基本力学性质初步研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2000, 22(3): 332-335.
XU Xichang, LIU Quansheng. A preliminary study on basic mechanical properties for granite at high temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2000, 22(3): 332-335.
[10] 刘泉声, 许锡昌. 温度作用下脆性岩石的损伤分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2000, 19(4): 408-411.
LIU Quansheng, XU Xichang. Damage analysis of brittle rock at high temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 19(4): 408-411.
[11] 梁铭, 张绍和, 舒彪. 不同冷却方式对高温花岗岩巴西劈裂特性的影响[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2018, 29(2): 186-193.
LIANG Ming, ZHANG Shaohe, SHU Biao. Effect of different cooling ways on Brazilian tension characteristics of heat-treated granite[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2018, 29(2): 186-193.
[12] KUMARI W G P, RANJITH P G, PERERA M S A, et al. Temperature-dependent mechanical behaviour of Australian Strathbogie granite with different cooling treatments[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 229: 31-44.
[13] KUMARI W G P, RANJITH P G, PERERA M S A, et al. Experimental investigation of quenching effect on mechanical, microstructural and flow characteristics of reservoir rocks: thermal stimulation method for geothermal energy extraction[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 162: 419-433.
[14] KUMARI W G P, RANJITH P G, PERERA M S A, et al. Mechanical behaviour of Australian Strathbogie granite under in-situ stress and temperature conditions: an application to geothermal energy extraction[J]. Geothermics, 2017, 65: 44-59.
[15] PENG Jun, RONG Guan, CAI Ming, et al. Physical and mechanical behaviors of a thermal-damaged coarse marble under uniaxial compression[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 200: 88-93.
[16] CHEN Shiwan, YANG Chunhe, WANG Guibin. Evolution of thermal damage and permeability of Beishan granite[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 110: 1533-1542.
[17] 赵阳升, 万志军, 康建荣. 高温岩体地热导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 17-20.
ZHAO Yangsheng, WAN Zhijun, KANG Jianrong. An introduction to hot dry rock (HDR) geothermal exploitation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004: 17-20.
[18] ZHAO Yangsheng, FENG Zijun, XI Baoping, et al. Deformation and instability failure of borehole at high temperature and high pressure in hot dry rock exploitation[J]. Renewable Energy, 2015, 77: 159-165.
[19] 张森琦, 严维德, 黎敦朋, 等. 青海省共和县恰卜恰干热岩体地热地质特征[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(6): 1087-1102.
ZHANG Senqi, YAN Weide, LI Dunpeng, et al. Characteristics of geothermal geology of the Qiabuqia HDR in Gonghe Basin, Qinghai Province[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(6): 1087-1102.
[20] GE Zhenlong, SUN Qiang. Acoustic emission (AE) characteristics of granite after heating and cooling cycles[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2018, 200: 418-429.
[21] 杜守继, 刘华, 职洪涛, 等. 高温后花岗岩力学性能的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(14): 2359-2364.
DU Shouji, LIU Hua, ZHI Hongtao, et al. Testing study of mechanical properties of post-high-temperature granite[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(14): 2359-2364.
[22] 林睦曾. 岩石热物理学及其工程应用[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 1991: 130-132.
LIN Muzeng. Thermal physics of rock and its application[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 1991: 130-132.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期: 2019 -03 -18; 修回日期: 2019 -05 -13
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51874207);山西省自然科学基金资助项目(201701D121131);山西省研究生教育创新资助项目(2019SY127) (Project(51874207) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(201701D121131) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province; Project(2019SY127) supported by the Graduate Education Innovation Foundation of Shanxi Province)
通信作者:郤保平,博士,副教授,从事高温岩石力学及地下工程、采矿工程研究;E-mail:xibaoping@163.com