
Microstructure, mechanical and shape memory properties of Ti-55Ta-xSi biomedical alloys
MA Yun-qing, YANG Shui-yuan, JIN Wan-jun, WANG Yun-neng, WANG Cui-ping, LIU Xing-jun
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, College of Materials, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
Received 4 January 2010; accepted 10 May 2010
Abstract: The effects of Si addition on microstructures, mechanical and shape memory properties of Ti-55Ta biomedical alloy were investigated. The results show that the microstructures consist of mainly? α′′ martensite and a little β phase, and the grain size decreases obviously with increasing Si addition. When x = 0.2, small (Ti, Ta)3Si precipitates are formed at grain boundaries. With further increasing Si content, the amount of the precipitates gradually increases. The tensile and yield strength of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys gradually increase with increasing Si addition, whereas elongation decreases. Ti-55Ta-0.1Si alloy exhibits the lowest elastic modulus and the best shape memory recoverable strain. It is revealed that the refinement of grain and the precipitation of (Ti, Ta)3Si phase are responsible to the changes of their mechanical and shape memory properties.
Key words: Ti-Ta alloy; grain refinement; tensile; shape memory effect
1 Introduction
Ti-Ni based shape memory alloys (SMAs) have been widely used as biomedical materials, such as orthodontic wire, guide wire, catheter and stent, due to their good superelasticity (SE), shape memory effect (SME), and high corrosion resistance[1]. However, since the Ni-hypersensitivity and toxicity of Ni ion have been revealed in Ti-Ni based alloys[2], the study of new Ni-free Ti-based SMAs for biomedical applications becomes necessarily needed.
It is well known that some β-Ti alloys exhibit SME as well as SE, originating from the reversible martensitic transformation between α'' martensite phase (orthorhombic structure) and β? parent phase (disordered bcc)[3], as appeared in Ti-Nb[4-5], Ti-Mo[6-7], Ti-V[8] and Ti-Ta based alloys[9-10]. However, the critical stress for slip in Ti-Nb alloys is too low to obtain good SME, Ti-Mo alloys are susceptible to ω phase embrittlement, and Ti-V alloys may not be suitable for biomedical materials due to the cytotoxicity of V element. In our previous investigation[10], Ti-55Ta alloy exhibits a good SME with 3.32% of reversible strain, and elastic modulus ranging from 66 to 75 GPa, which are much closer to the modulus of human bone as compared with that of Ti-6Al-4V[11]. Thus Ti-Ta alloys exhibit great potentials as a new Ni-free Ti-based biomedical material, considering their good SME, low modulus and even higher corrosion resistance with the present of noble element Ta. On the other hand, it is also well known that SME can be improved by alloying and thermo-mechanical treatment. BERMINGHAM et al[12] have reported that a small amount of Si addition can refine the grain size of Ti alloys. Therefore, in this study, Si element up to 0.3% (mass fraction) was added to Ti-55Ta alloy, and the microstructures, mechanical properties, as well as SMEs, were investigated. The obtained results will be beneficial for the development of Ti-Ta alloys as a new Ni-free Ti-based biomedical material.
2 Experimental
Polycrystalline buttons of Ti-55Ta-xSi (x= 0, 0.1 0.2, 0.3, %, mass fraction, the same below if not mentioned) alloys were arc-melted over six times under argon atmosphere to ensure homogeneity with high pure sponge titanium (99.65%), pure tantalum (99.9%) and pure silicon (99.99%). The mass loss during arc-melting was negligibly small. After homogenization treatment, the ingots were hot-rolled at 1 123 K to thin plates with about 1 mm in thickness. Specimens for various tests were cut from the plates by electro-discharge machine. Then the specimens were sealed in quartz tubes under argon atmosphere, and annealed at 1 073 K for 6 min followed by quenching into ice water.
The phase structure was identified by a Panalytical X’pert PRO with Cu Kα radiation. The microstructure was observed with an optical microscope (OM) after being etched in a solution of 20% HF + 10% HNO3 + 70% H2O, and with a JEOL, JXA-8100 back-scattered electron (BSE) machine. Compositions of the phase constituents were determined by electron probe microanalysis (EPMA). The martensitic transformation temperature was measured by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) (Netzsch STA 404) at heating and cooling rates of 10 °C/min. The mechanical properties and SMEs were tested by tensile method using a Galdabini Sun 2500 machine at a strain rate of 10-3 s-1. The tensile direction was parallel to the rolling direction.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure
Fig.1 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns of
Ti-55Ta-xSi (x = 0, 0.1 0.2, 0.3) alloys at room temperature, which were solution-annealed at 1 073 K and followed by ice-water quenching. All the reflection patterns can be indexed by two phases containing the main orthorhombic structure α'' phase and a little bcc structure β phase, similar to the previous investigation[10]. It can be concluded that the crystal structures of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys have not been obviously changed by Si addition. However, their microstructures appear an obvious variety, as shown in Fig.2.
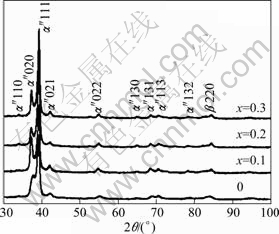
Fig.1 X-ray diffraction patterns of Ti-55Ta-xSi (x = 0, 0.1 0.2, 0.3) alloys
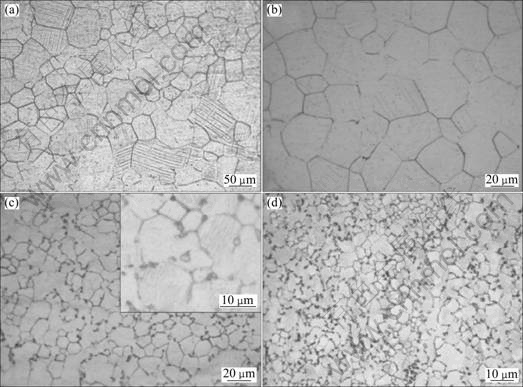
Fig.2 Optical micrographs of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys: (a) x = 0; (b) x = 0.1; (c) x = 0.2 (Inset shows high magnification optical micrograph); (d) x = 0.3
Nearly equiaxed grains are exhibited for all Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys, and the grain size decreases obviously with increasing Si content, as shown in Fig.2. Typical martensite needles can also be obviously observed. Particularly, when the Si content is 0.2%, small precipitates appear at the grain boundaries, which may be resulted from the excessive Si. The amount of the precipitates increases with increasing Si content. And the formation of this precipitate at the grain boundaries may strongly hinder the grain growth, resulting in finer grain size. According to Ti-Si and Ta-Si binary phase diagrams[13], the solubilities of Si in both Ti and Ta are very small, and Ti3Si and Ta3Si intermetallic compounds will form with excessive Si. Similar phenomenon has also been discovered in Ti-Nb-Al-Si alloys in Ref.[14], where (Ti, Nb)3Si precipitate phase was formed. Fig.3 shows the BSE image of Ti-55Ta-0.2Si alloy in the present study. The dark precipitation can be clearly observed, mainly distributing along grain boundaries. It is well known that the contrast of BSE image is closely related to the atomic number. When the elements have higher atomic number, their BSE images will be brighter, whereas be darker with smaller atomic number. In this study, the Si atomic number is obvious smaller than that of Ti or Ta. Therefore, it can be deduced that the dark precipitation has a higher Si content than the matrix phase. The chemical compositions of this precipitation cannot be accurately determined by EPMA due to its small grain size of about 1μm. However, this speculation can be confirmed by the map-scanning analysis taken by EMPA, showing a higher Si content in the precipitation, whereas almost no Si in the matrix phase due to its very small solubility in α'' phase and β phase. The chemical formula of this precipitate can be guessed to be (Ti, Ta)3Si according to (Ti, Nb)3Si in previous investigation[14]. The minor amount, small size and highly dispersed state of (Ti, Ta)3Si phases account for the absence of their diffraction peaks in X-ray patterns.
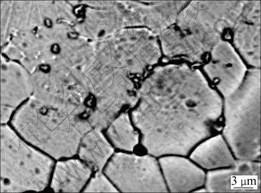
Fig.3 BSE image of Ti-55Ta-0.2Si alloy
In this study, the martensitic transformation temperatures of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys cannot be clearly detected by DSC. One possible reason is the latent heats associated with the martensitic transformation in Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys are too small to be detected. According to our previous investigation[10], the martensitic transformation temperature of Ti-55Ta alloy is around room temperature. In the present study, Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys consist of mainly α'' martensite phase and a little β phase. The intensities of the XRD diffraction peaks have no obvious change with the addition of Si, and the solubility of Si in α'' martensite phase is very small. All these information indicate that the martensitic transformation temperatures of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys are close to that of Ti-55Ta alloy, which is around room temperature.
3.2 Mechanical and shape memory properties
Fig.4 shows the stress—strain curves and mechanical properties of Ti-55Ta-xSi (x = 0, 0.1 0.2, 0.3) alloys obtained by tensile tests at room temperature. From Fig.4(a), the obvious double yielding phenomenon can be clearly observed for all experimental alloys. The first yielding is followed by the initial linear
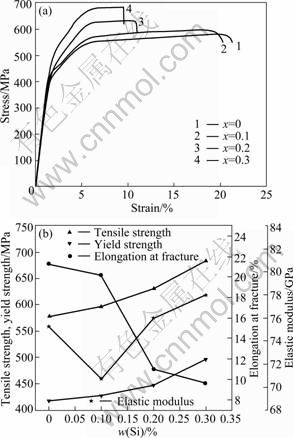
Fig.4 Stress—strain curves (a) and mechanical properties (b) of Ti-55Ta-xSi (x=0, 0.1 0.2, 0.3) alloys under solution annealed at 1 073 K
elastic deformation. Taking into account the microstructures of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys, all experimental alloys exhibit two phases containing main martensite α'' phase and a little bcc β phase. It can be deduced that the first yielding is mainly due to the reorientation of martensite variants and/or detwinning, not the stress induced martensite. The similar double yielding phenomenon has also been observed in Ti-Nb binary alloys[5] and Ti-22Nb-(2-8)Zr ternary alloys[15]. It is well known that the strain could be recovered due to SME occurrences only through the reorientation of martensitic variants and, in general, a large strain due to reorientation of martensite varies means a good shape memory recovery. Therefore, it can be deduced that Ti-55Ta-0.1Si alloy will possess a good shape memory behavior, since it exhibits the largest strain in the first yielding among those experimental alloys.
Fig.4(b) shows the mechanical properties of Ti-55Ta-xSi (x = 0, 0.1 0.2, 0.3) alloys. It can be seen that the tensile strength and yield strength both increase gradually with increasing Si content. The tensile strengths are measured to be 578, 597, 632 and 685 MPa for x = 0, 0.1 0.2, 0.3, respectively. The yield strengths, associating with the reorientation of martensitic variants and/or detwinning, are 418, 428, 448 and 497 MPa, respectively. The increase of both tensile strength and yield strength in Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys is easily understood when we remember that the grain sizes decrease greatly with increasing Si content, as more grain boundaries can effectively hinder the plastic deformation and increase the strength. At the same time, with increasing Si content, the introduction of the (Ti, Ta)3Si precipitates will also contribute to the increase of tensile and yield strength. The elongations at fracture for Ti-55Ta-xSi (x = 0, 0.1 0.2, 0.3) alloys gradually decrease with increasing Si content, which are measured to be 21.3%, 20.2%, 11.0% and 9.6% for x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, respectively. It is general accepted that the refinement of grain size will prevent the propagation of the cracks, thus resulting in good plasticity. However, in this study, the plasticity of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys gradually decreases with the decrease of grain size by increasing Si content. It can be understood that the formation of (Ti, Ta)3Si precipitations at the grain boundaries, makes the interfaces more rough, which leads to easier crack propagation.
The elastic moduli of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys are measured to be 75.3, 70.7, 76 and 78 GPa for x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, respectively. When x = 0.1, the elastic modulus abruptly decreases, then increases gradually with increasing Si content. This should be due to the grain refinement, since the grain boundaries have lower elastic modulus than grains due to high dense defects[16]. There is also a tendency to develop biomedical Ti alloys with low elastic modulus by fabricating the nano-structured Ti alloys[16]. In this study, the refinement of grain size has been achieved by the addition of Si, which may contribute to the lower elastic modulus with 0.1% Si addition. On the other hand, the brittle (Ti, Ta)3Si phase has higher elastic modulus than matrix, and it will increase the elastic modulus of the alloys. As a result, when the Si content further increases from 0.1% to 0.2% and 0.3%, the elastic modulus of Ti-55Ta-xSi increases from 70.7 GPa to 76 GPa and 78.0 GPa, due to the formation of (Ti, Ta)3Si precipitates.
The SMEs of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys were measured by tensile tests at room temperature, and the relationship between the shape recovery ratios and the residual strains is shown in Fig.5. The shape recovery ratios gradually decrease with increasing residual strains for all the experimental alloys. However, it can be clearly observed that SMEs abruptly increase when 0.1% Si is added into Ti-55Ta alloy. Then with increasing Si addition, the SMEs of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys gradually decrease. However, the addition of Si is beneficial to the SME of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys, as shown in Fig.5. It is believed that the changes of SMEs with Si content in Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys are resulted from the integrated actions of two following aspects. One is the enhancement of the strength originated from the grain refinement, which will decrease the permanent slipping strains. This factor is beneficial to the SME. Another is the increase of grain boundaries and the formation of (Ti, Ta)3Si precipitates, which will hinder the movement of martensite reorientation. This factor is negative to the SME. When x = 0.1, the SMEs abruptly increase, where the benefits of the enhancement of yield strength play a main role on the improvement of SMEs. With the further increase of Si content, the later aspect will play the main role and result in the deterioration of SME.
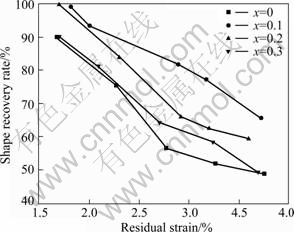
Fig.5 Relationship between shape recovery rate and residual strains for Ti-55Ta-xSi (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3) alloys
4 Conclusions
1) The microstructures of Ti-55Ta-xSi (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, %) consist of main?? α'' martensite and a little bcc β phase.
2) With increasing Si content, the tensile and yield strengths gradually increase, whereas elongation decreases. When x = 0.1, the alloy exhibits the lowest elastic modulus and the best SME among those studied alloys. With further increasing Si content, the elastic modulus gradually increases and SME decreases.
3) The refinement of grain size and the precipitation of (Ti, Ta)3Si phase are responsible to the variety of the mechanical and shape memory properties of Ti-55Ta-xSi alloys.
References
[1] XU Zu-yao. Shape memory materials [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University Press, 200. (in Chinese)
[2] SHABALOVSKAYA S A. ITIN V I, GYUNTER V E. Porous Ni-Ti-a new material for implants and prostheses [C]//Proc Int Conf Shape Memory Superelastic Tech, 1994: 7-12.
[3] NING Cong-qin, ZHOU Yu. Development and research status of biomedical titanium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2002, 10(1): 100-106. (in Chinese)
[4] FUKUI Y, INAMURA T, HOSODA H, WAKASHIMA K, MIYAZAKI S. Mechanical properties of a Ti-Nb-Al shape memory alloy [J]. Mater Trans, 2004, 45: 1077-1082.
[5] KIM H Y, SATORU H, KIM J I, HOSODA H, MIYAZAKI S. Mechanical properties and shape memory behavior of Ti-Nb alloys [J]. Mater Trans, 2004, 45: 2443-2448.
[6] KIM H Y, OHMATSU Y, KIM J I, HOSODA H, MIYAZAKI S. Mechanical properties and shape memory behavior of Ti-Mo-Ga alloys [J]. Mater Trans, 2004, 45: 1090-1095.
[7] MAESHIMA T, NISHIDA M. Shape memory properties of biomedical Ti-Mo-Ag and Ti-Mo-Sn alloys [J]. Mater Trans, 2004, 45: 1096-1100.
[8] DUERIG T W, ALBRECHT J, RICHTER D, FISCHER P. Formation and reversion of stress-induced martensite in Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al [J]. Acta Metall, 1982, 30: 2161-2172.
[9] BUENCONSEJO P J S, KIM H Y, HOSODA H, MIYAZAKI S. Shape memory behavior of Ti-Ta and its potential as a high-temperature shape memory alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 2009, 57: 1068-1077.
[10] MA Y Q, JIN W J, YANG S Y, ZHANG J B, HUANG Y X, LIU X J. Microstructure and shape memory properties of biomedical Ti-(40-65) Ta (wt. %) alloys [J]. Mater Sci Forum, 2009, 610: 1382-1386.
[11] NIINOMI M. Mechanical properties of biomedical titanium alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1998, 243: 231-236.
[12] BERMINGHAM M J, MCDONALD S D, DARGUSCH M S, STJOHN D H. The mechanism of grain refinement of titanium by silicon [J]. Scripta Mater, 2008, 58: 1050-1053.
[13] OKAMOTO H. Desk handbook-phase diagrams for binary alloys [M]. Ohio: ASM International, 2000.
[14] MASUMOTO K, HORIUCHI Y, INAMURA T, HOSODA H, WAKASHIMA K, KIM H Y, MIYAZAKI S. Effects of Si addition on superelastic properties of Ti-Nb-Al biomedical shape memory alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 438: 835-838.
[15] KIM J I, KIM H Y, INAMURA T, HOSODA H, MIYAZAKI S. Shape memory characteristics of Ti-22Nb-(2–8)Zr(at.%) biomedical alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 403: 334-339.
[16] HE G, HAGIWARA M. Ti alloy design strategy for biomedical applications [J]. Mater Sci Eng C, 2006, 26: 14-19.
生物医用Ti-55Ta-xSi合金的微观组织、力学性能及形状记忆特性
马云庆, 杨水源, 金万军, 王云能, 王翠萍, 刘兴军
厦门大学 材料学院 材料科学与工程系,厦门 361005
摘 要:研究Si元素的添加对Ti-55Ta合金的微观组织、力学性能及形状记忆特性的影响。结果表明:合金的微观组织主要由α′′马氏体相和少量β相组成;当添加Si时,合金晶粒明显细化,且当x=0.2时,合金中开始析出沉淀相,这些沉淀相主要集中在晶界处,可以阻碍晶粒长大,从而进一步细化合金晶粒。背散射电子衍射分析表明,该沉淀相为(Ti, Ta)3Si相。Ti-55Ta-xSi合金的拉伸应力—应变曲线呈现明显的双屈服现象,且随着Si含量的增加,合金的拉伸和屈服强度升高,伸长率反而减小。Si的添加可以明显改善Ti-55Ta合金的形状记忆效应,且在x= 0.1时,合金呈现出最大的形状记忆效应及最低的弹性模量。
关键词:Ti-Ta合金;晶粒细化;拉伸;形状记忆效应
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project(50771086) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(NCET) supported by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, China; Project(NCETFJ) supported by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Fujian Province University, China; Project(2009H0039) supported by Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology, China
Corresponding author: MA Yun-qing; Tel: +86-592-2189688; Fax: +86-592-2187966; E-mail: myq@xmu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60711-5