长沙地区多功能地源热泵系统的模拟与分析
李大鹏,饶政华,张翔,廖胜明
(中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:以长沙地区宾馆建筑为例,建立制冷、制热和制热水的多功能地源热泵系统模型,对多功能地源热泵系统全年运行的技术经济性能进行研究。分析多功能地源热泵系统地埋管换热器周围土壤热平衡性和系统全年能耗特点,并与传统的空气源热泵加电热水器系统进行能耗及全生命周期经济性比较。研究结果表明,与常规的地源热泵系统相比,应用多功能地源热泵系统可明显改善地下土壤全年释热量与吸热量的平衡性,运行10a后土壤温度比相同地埋管长度的常规地源热泵系统减少3.9℃;夏热冬冷地区的多功能地源热泵系统夏季的总能耗最高,冬季次之,春秋季最低;与空气源热泵加电热水器系统相比,多功能地源热泵系统总能耗可节省46%,生命周期内的费用现值节约率变化范围为7%~40%,投资回收期变化范围为5~12 a。
关键词:多功能地源热泵;生活热水;能耗;经济性;模拟
中图分类号:TK529 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)03-1221-07
Simulation and analysis of multi-functional ground source heat pump in Changsha
LI Dapeng, RAO Zhenghua, ZHANG Xiang, LIAO Shengming
(School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: A model of multi-functional ground source heat pump (MFGSHP) system integrated with cooling, heating and domestic hot water was developed. Taking a typical hotel in Changsha City as example, the techno-economic performances of MFGSHP system were studied. The heat balance of the soil around the borehole heat exchanger and the characteristic of energy consumption for MFGSHP system were analyzed. The energy consumption and life cycle economic analysis for MFGSHP system were compared to the conventional system (i.e. air source heat pump and electric water heater). The results show that the heat balance can be obviously improved by applying MFGSHP system, and the increase in soil temperature is reduced by 3.9℃ compared to the common GSHP system with the same borehole length. The energy consumption of MFGSHP in hot summer and cold winter zone is the highest in summer, moderate in winter and the least in spring and autumn. Compared with the conventional system, MFGSHP can reduce 46% of annual energy consumption, and the saving of present cost value is in the range of 7%-40% and payback period ranges from 5 to 12 a.
Key words: multi-functional ground source heat pump; domestic hot water; energy consumption; economic analysis; simulation
在夏热冬冷地区,应用地源热泵实现夏季制冷和冬季供热,是节能减排的重要措施,具有良好的环境和经济效益[1]。近年来,在国家政策法规的大力扶持和推动下,地源热泵在夏热冬冷地区正面临着重要的发展机遇,具有广阔的应用前景。然而,目前仍缺乏适用于夏热冬冷地区气候条件、地质条件、建筑特点的系统运行策略和评价体系。夏热冬冷地区冬季供热期短,地源热泵全年向土壤排放的热量远多于从土壤吸取的热量,这种土壤吸释热不平衡会导致地埋管区域土壤温度逐年升高,从而降低地源热泵系统的运行效率[2-3],已成为制约地源热泵发展的关键技术问题之一。应用制冷、制热和制热水多功能地源热泵系统,不仅可减少夏季地埋管换热器向土壤的释热量,而且还可在冬季利用热泵从土壤中吸热来制取生活热 水[4-5]。Cui等[6]以香港地区住宅为例对多功能地源热泵系统进行了研究,Li等[7]对多功能地源热泵地埋管换热器周围的土壤温度进行了数值模拟,研究表明:该系统有望缓解土壤累计吸释热不平衡的问题。然而,关于多功能地源热泵系统在夏热冬冷地区的适应性及其相关的技术经济评价方法的研究尚未有效开展。本文作者在动态能耗模拟软件TRNSYS[8]的平台上建立了制冷、制热和制热水的多功能地源热泵系统模型,并以长沙地区宾馆建筑为例对多功能地源热泵系统全年运行的技术经济性能进行了研究。本研究有助于夏热冬冷地区地源热泵系统的优化设计和推广应用,促进实现低能耗、低排放可再生能源建筑。
1 数学模型
1.1 建筑冷热负荷计算
以长沙地区某宾馆建筑为研究对象,该宾馆共3层、南北朝向,总建筑面积为2 080 m2,建筑围护结构的热工性能参数、室内空调和采暖的设计参数均按《公共建筑节能设计标准》[9]的规定选取。长沙地区典型气象年数据来自文献[10]。利用TRNSYS计算获得该建筑的全年逐时负荷(如图1所示),得到其峰值冷负荷为127.5 kW,峰值热负荷为78.5 kW,全年累积冷负荷为201 133.4 kW·h,累积热负荷为94 742.3 kW·h。
1.2 地埋管换热器设计
根据长沙地区地质特点查《地源热泵系统工程技术规范》[11]获得地埋管换热器设计所需的土壤热物性。表1所示为土壤热物性参数及地埋管设计的主要参数。根据表1给出的基本参数,采用Bernier修正的ASHRAE算法[12]计算得到该建筑冷负荷所对应的地埋管换热器总长度为5.7 km,热负荷所对应的地埋管换热器总长度为3.5 km。考虑到地源热泵系统同时用于制取生活热水,在夏季将减少地埋管向土壤的释热量,在冬季增加地埋管从土壤中的吸热量,因此确定该系统地埋管换热器总长度为3.5 km。

图1 建筑全年逐时负荷
Fig.1 Hourly load of building
表1 土壤热物性参数及地埋管换热器设计参数
Table 1 Design parameters for borehole heat exchanger

1.3 生活热水系统设计
利用地源热泵作为热源制取生活热水,构成多功能地源热泵系统,如图2所示。根据不同的运行工况可通过冷凝显热热回收或单独制热水2种方式来制取生活热水。生活热水的使用水温为40 ℃[13],日热水用水量变化曲线如图3所示[14]。若生活热水的出水温度达不到使用要求,则开启辅助电加热器进行补偿。根据以上条件,得到热水系统的设计参数(如表2所示),并计算得到生活热水贮水箱容积为9.5 m3,设循环热水的循环加热温升为5 ℃,则循环热水的设计水流量为21 450 kg/h。
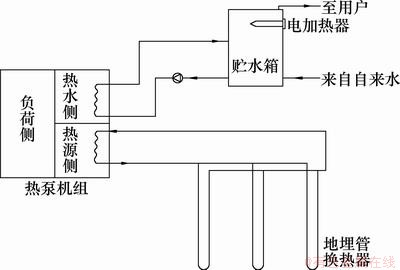
图2 多功能地源热泵系统示意图
Fig.2 Sketch of multi-function GSHP system
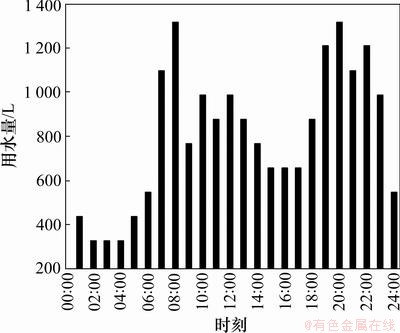
图3 热水日用水量变化曲线
Fig.3 Profile of daily domestic hot water consumption
表2 生活热水系统设计参数
Table 2 Design parameter for domestic hot water system

1.4 常规热泵机组模型
采用特性参数估计的方法建立常规水-水热泵机组模型。该模型的计算流程如下:
(1) 输入已知参数蒸发器进水温度Twi,e和流量 ,冷凝器进水温度Twi,c和流量
,冷凝器进水温度Twi,c和流量 以及确定热泵机组运行性能(制冷和制热工况)的8个特性参数(如表3所示);
以及确定热泵机组运行性能(制冷和制热工况)的8个特性参数(如表3所示);
(2) 假定热泵制冷量(或蒸发器吸热量)Qeo和冷凝器释热量(或制热量)Qco;
(3) 计算蒸发温度和冷凝温度,调用制冷剂物性参数数据库求出蒸发压力、冷凝压力、蒸发器进出口焓值、压缩机进口比容;
(4) 计算制冷剂质量流量和压缩机输入功率Whp;
(5) 计算热泵实际制冷量(或蒸发器吸热量)Qe和冷凝器释热量(或制热量)Qc;
(6) 判断 <
< (ε为一足够小的值)是否成立,若不成立,则返回第2步重新计算;反之,则输出Qe,Qc和Whp,计算结束。
(ε为一足够小的值)是否成立,若不成立,则返回第2步重新计算;反之,则输出Qe,Qc和Whp,计算结束。
表3 热泵运行特性参数最优值
Table 3 Optimum value of estimated characteristic parameters

热泵特性参数的确定方法如下:定义蒸发器进水温度和流量、冷凝器进水温度和流量及其所对应的热泵制冷量(或制热量)和功率为1个数据列;热泵产品样本中会提供多个数据列表示热泵性能,根据样本中提供的不同蒸发器进水温度和流量、冷凝器进水温度和流量计算出对应的Qe,Qc和Whp,取式(1)所示目标函数的最小值,即获得所对应的8个特性参数的最优值,并将其作为地源热泵系统的运行参数。

式中:Qcat和Wcat分别为样本中提供的与不同蒸发器进水温度和流量、冷凝器进水温度和流量对应的制冷量(或制热量)和功率;Q和W分别为计算得到的制冷量(或制热量)和功率;n为样本中数据列的总数;i为样本中的第i个数据列。
1.5 多功能热泵机组模型
在上述常规热泵模型基础上,建立制冷、制热和制热水多功能热泵机组模型,可实现热泵制冷、制热、制热水和制冷热回收4种运行工况的模拟。模型中采用了以下假设:
(1) 多功能热泵制冷、制热工况下的特性参数与常规热泵对应工况下的特性参数相同,制热水工况与制热工况下的特性参数相同;
(2) 在制取生活热水时,须首先满足建筑物冷、热负荷的需求;
(3) 制冷热回收工况下能回收全部冷凝显热。
计算过程中,需首先根据室内冷、热负荷和负荷因子f的情况确定热泵的运行工况。其中,负荷因子为单位时间内室内冷(热)负荷与热泵实际的制冷(热)量的比值,表示热泵处于制冷(热)工况运行的时间比例。热泵的运行工况可按以下3种情况确定:
(1) 当热泵制冷运行且负荷因子大于0.5时,热泵运行于制冷热回收工况,此时热泵的冷凝显热全部用于加热生活热水,模型的计算步骤如下:
(a) 通过热泵模型得到制冷量Qload,全部冷凝热Qc,冷凝显热Qc,dhw,压缩机输入功率Whp;
(b) 循环热水出水温度为:
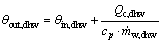
式中: in,dhw为循环热水进水温度,℃;cp为水的比热容,kJ/(kg·℃);
in,dhw为循环热水进水温度,℃;cp为水的比热容,kJ/(kg·℃); 为循环热水设计流量,kg/s。
为循环热水设计流量,kg/s。
(c) 热源侧的出水温度为:

式中: in,source为热泵热源侧进水温度,℃;
in,source为热泵热源侧进水温度,℃; 为热泵热源侧设计水流量,kg/s。
为热泵热源侧设计水流量,kg/s。
(d) 循环热水的平均水流量为:

(e) 热源侧的平均水流量为:

(2) 当热泵制冷运行且负荷因子小于0.5时,热泵运行于制冷和制热水工况共存的状态下。假设热泵在2种运行模式下热源侧的进水温度和水流量相同,此时模型的计算步骤如下:
(a) 热泵按制冷模式运行得到热泵总制冷量Qload(符号为负)、全部冷凝热Qc(符号为负)和压缩机输入功率Whp;
(b) 热泵按制热水模式运行得到蒸发器吸热量Qe,dhw(符号为正)、冷凝器释热量Qc,dhw(符号为正)和压缩机输入功率Wdhw;
(c) 利用式(2)计算循环热水出水温度;
(d) 热源侧出水温度为:

(e) 热泵的实际输入功率为:
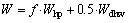
(f) 循环热水的平均水流量为:

(g) 热源侧的平均水流量为:
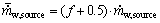
(3) 当热泵制热运行时,热泵需首先处于制热工况运行以满足建筑热负荷需求,然后在其剩余时间内运行于制热水工况来制取生活热水。模型的计算步骤如下:
(a) 热泵按制热模式运行得到热泵总制热量Qload、热源侧的吸热量Qe,hp和压缩机输入功率Whp;
(b) 热泵按制热水模式运行得到热水制热量Qc,dhw、热源侧的吸热量Qe,dhw和压缩机输入功率Wdhw;
(c) 循环热水出水温度按式(2)计算;
(d) 热源侧出水温度为:

(e) 热泵的实际输入功率为:

(f) 循环热水的平均水流量为:

(g) 热源侧的平均水流量为:
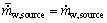
1.6 多功能地源热泵系统模型
在上述多功能热泵机组模型的基础上,耦合地埋管换热器模块、建筑负荷输入模块、生活热水贮水箱模块、气象数据输入模块以及用于参数计算的方程运算器及控制模块,建立非稳态的多功能地源热泵系统模型。图4所示为多功能地源热泵系统模型在TRNSYS中各模块连接的示意图。模型在t时刻的计算流程如下:
(1) 给定热泵负荷侧进水温度和水流量以及热源侧水流量,把地埋管换热器模块在上一时刻的出水温度作为热泵热源侧进水温度,从建筑负荷输入模块中得到t时刻室内负荷,并计算负荷因子;
(2) 利用多功能热泵模块得到t时刻热源侧出水温度和平均水流量、实际输入功率和循环热水出水温度,进而利用贮水箱模块得到生活热水供水温度;
(3) 利用地埋管换热器模块计算t时刻地埋管出水温度。

图4 多功能地源热泵系统中各模块连接示意图
Fig.4 Schematic connection of modules used for multi-function GSHP system in TRNSYS
2 结果与讨论
2.1 土壤热平衡分析
图5所示为常规地源热泵系统和多功能地源热泵系统连续运行10 a的地埋管周围土壤平均温度变化曲线。多功能系统运行10 a后,土壤平均温度为23.9 ℃,与初始地温19.3 ℃相比上升了4.6 ℃,平均每年上升0.46 ℃,并且土壤温度上升幅度有逐年减缓的趋势。常规地源热泵系统在地埋管长度分别为3.5 km和5.7 km时,系统运行10 a后,土壤温度分别达到了27.8 ℃和27.0 ℃。通过对比发现,在相同地埋管长度下,多功能系统的土壤温度比常规系统降低了3.9 ℃;即使常规系统的地埋管长度增加至冷负荷所对应的长度,其土壤温度仍比多功能系统时高3.1 ℃。可见:应用多功能系统可有效缓解夏热冬冷地区地源热泵系统的土壤吸释热不平衡问题。

图5 逐时土壤温度变化曲线
Fig.5 Hourly soil temperature profiles
2.2 系统能耗分析
多功能地源热泵系统能耗主要包括热泵能耗、地埋管环路水泵能耗、循环热水环路水泵能耗和辅助电加热器能耗。通过模拟计算,得到系统运行1 a的能耗为138 406 kW·h。图6所示为全年每月的系统总能耗。可见:该系统在夏季能耗较高,冬季能耗次之,春秋季能耗最少。这是因为夏季的冷负荷较高造成的热泵机组能耗偏高;同时,在夏季热泵运行工况中制冷热回收工况占了很大的比例,而该工况下回收的热量不能完全满足加热生活热水的要求,需要开启辅助电加热器,增加了系统能耗。在冬季或春秋季运行时,热泵在制热水工况下基本能满足生活热水的需求。

图6 逐月系统总能耗
Fig.6 Monthly energy consumption
2.3 对比分析
考虑对同一建筑采用空气源热泵满足建筑物的冷热负荷和用电热水器提供生活热水(以下简称为传统系统),通过TRNSYS对传统系统进行能耗模拟,并与多功能地源热泵系统进行能耗和全生命周期经济性对比。假设不考虑冬季结霜对热泵性能的影响,电热水器的输入功率恰好能满足生活热水需热量的要求。额定工况下空气源热泵总制冷量 130 kW,总功率44.8 kW;总制热量165 kW,总功率43.4 kW。
2.3.1 能耗对比分析
传统系统的能耗包括空气源热泵的能耗和电热水器的能耗。运行1 a后,空气源热泵的能耗为74 182 kW·h,电热水器的能耗为183 525 kW·h,总能耗为 257 707 kW·h。因此,比传统系统相比,多功能地源热泵系统可节省46%的能耗。另外,如考虑空气源热泵冬季结霜对其性能的影响,传统系统的能耗将更大,采用多功能地源热泵系统的优势将更明显。
2.3.2 全生命周期经济性对比
采用费用现值作为评价指标对2个系统在全生命周期内的经济性进行比较。费用现值由初投资和系统每年运行费用2部分组成。假设2个系统的初投资差异仅体现为地源热泵系统比传统系统增加了地埋管换热器的初投资,地埋管换热器的初投资按200 元/m计算。因此费用现值C的计算公式[15]可表示为:

式中:n为系统进行经济性分析的周期,a;C0为初投资,元;Wt为系统第t年的总能耗,kW·h;P0为第0年时的电价,元/(kW·h);d为电价的每年增长率,%;i为基准折现率,%。
假设系统生命周期为20 a,第0年电价为1元/(kW·h),电价的年增长率为6%,基准折现率为10%。图7所示为全生命周期的费用现值对比。从图7可以看出:多功能地源热泵系统在运行20 a后的费用现值(261.4 万元)比传统系统的总投资(357.8 万元)节省了96.4 万元,节约率达到了27%。多功能地源热泵系统在运行到第7年时费用现值即开始少于后者,也就是说采用地源热泵系统的投资回收期为7 a。
通过改变电价的年增长率和基准折现率,对2个系统全生命周期的费用现值进行敏感性分析。表4所示为2个系统的敏感性分析结果。可以看出:改变电价的年增长率或改变基准折现率后,多功能地源热泵系统的费用现值仍较小,费用现值节约率为7%~40%,投资回收期为5~12 a。

图7 全生命周期的费用现值对比
Fig.7 Comparison of cost present value of life cycle
表4 敏感性分析
Table 4 Sensitive analysis

3 结论
(1) 在夏热冬冷地区应用多功能地源热泵系统可明显缓解地下土壤全年释热量与吸热量的不平衡性,保证系统多年运行效果的稳定性。
(2) 在多功能地源热泵系统中,由于夏热冬冷地区冷热负荷的特点以及热泵制热水方式的不同,因此夏季系统总能耗最高,冬季次之,春秋季最低。
(3) 多功能地源热泵系统与传统系统相比,每年系统总能耗可以节省46%。生命周期内的费用现值节约率变化范围为7%~40%,投资回收期变化范围为5~12 a。
参考文献:
[1] Mustafa O A. Ground-source heat pumps systems and applications[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2008, 12(2): 344-371.
[2] Lund J, Sanner B, Rybach R, et al. Geothermal (Ground Source) heat pumps: A world overview[J]. GHC Quarterly Bulletin, 2004, 25(3): 1-10.
[3] Kavanaugh S P. Impact of operating hours on long-term heat storage and the design of ground heat exchangers[J]. ASHRAE Transactions, 2003, 109(1): 187-192.
[4] 胡松涛, 郭潇潇, 李绪泉. 地源热泵技术在生活热水供应中的应用[J]. 流体机械, 2007, 35(9): 62-64.
HU Songtao, GUO Xiaoxiao, LI Xuquan. Application of ground source heat pump to domestic hot water supply[J]. Fluid Machinery, 2007, 35(9): 62-64.
[5] Biaou A L, Bernier M A. Achieving total domestic hot water production with renewable energy[J]. Building and Environment, 2008, 43(4): 651-660.
[6] CUI Ping, YANG Hongxing, Spitler Jeffrey D, et al. Simulation of hybrid ground-coupled heat pump with domestic hot water heating systems using HVACSIM+[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2008, 40(9): 1731-1736.
[7] Li S, Yang W, Zhang X. Soil temperature distribution around a U-tube heat exchanger in a multi-function ground source heat pump system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2009, 29(17/18): 3679-3686.
[8] TRNSYS. TRNSYS 16-a transient system simulation program[R]. Madison: Solar Energy Laboratory, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 2006.
[9] GB 50189—2005, 公共建筑节能设计标准[S].
GB 50189—2005, Design standard for energy efficiency of public buildings[S].
[10] 中国气象局气象信息中心气象资料室, 清华大学建筑技术科学系. 中国建筑热环境分析专用气象数据集[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版, 2005: 51-58.
Climate Information Center, Climate Data Office of China Meteorological Bureau, Department of Building Science and Technology of Tsinghua University. China standard weather data for analyzing building thermal conditions[M]. Beijing: China Building Industry Publishing House, 2005: 51-58.
[11] GB 50366—2005, 地源热泵系统工程技术规范[S].
GB 50366—2005, Technical code for ground-source heat pump system[S].
[12] Bernier M A. Ground-coupled heat pump system simulation[J]. ASHRAE Transactions, 2001, 107(1): 605-616.
[13] GB 50015—2003, 建筑给水排水设计规范[S].
GB 50015—2003, Code for design of building water supply and drainage[S].
[14] ASHRAE. 2007 ASHRAE Handbook: HVAC Applications, chapter 49 Service water heating[M]. Atlanta: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. 2007: 11-12.
[15] 龙惟定. 建筑节能与建筑能效管理[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2005: 80-83.
LONG Weiding. Building saving energy and building energy efficient management[M]. Beijing: China Building Industry Publishing House, 2005: 80-83.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2012-03-20;修回日期:2012-06-15
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划(“863”计划)项目(2007AA05Z225);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(2010QZZD0105)
通信作者:廖胜明(1963-),男,湖南长沙人,博士,教授,博士生导师,从事新能源技术、新型热泵技术研究;电话:0731-88836936;E-mail: smliao@csu.edu.cn