DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-36485
基于硫酸-盐酸混酸体系钒电池电解液的性能优化
杨亚东1, 2, 3, 4, 5,张一敏1, 3, 4, 5, 6,唐 历2,刘 涛1, 3, 4, 5,黄 晶1, 3, 4, 5,杨 晓2
(1. 武汉科技大学 资源与环境工程学院,武汉 430081;
2. 攀钢集团研究院有限公司 钒钛资源综合利用国家重点实验室,攀枝花 617000;
3. 武汉科技大学 国家环境保护矿冶资源利用与污染控制重点实验室,武汉 430081;
4. 武汉科技大学 钒资源高效利用湖北省协同创新中心,武汉 430081;
5. 武汉科技大学 湖北省页岩钒资源高效清洁利用工程技术研究中心,武汉 430081;
6. 武汉理工大学 资源与环境工程学院,武汉 430070)
摘 要:为提高钒电池电解液的能量密度及宽温度区间稳定性,对基于硫酸-盐酸混酸支持电解质体系的电解液进行稳定性及电化学性能优化。对电解液进行钒离子及氯离子稳定性测试,发现在支持电解质配比为硫酸根浓度2.0~3.0 mol/L、氯离子浓度6.0~6.4 mol/L时,电解液钒浓度可达2.4 mol/L且四种价态的电解液均可在-20~50 ℃稳定存在10 d以上且可以有效避免氯化氢挥发。对稳定性优化后的电解液进行循环伏安及交流阻抗测试,发现在钒浓度为2.2 mol/L、硫酸根浓度为2.75 mol/L、氯离子浓度为5.8 mol/L时,电解液的电化学性能最佳。对浓度组成优化的电解液进行充放电测试,发现电解液可以在-20~50 ℃及40~80 mA/cm2稳定运行,且能量效率可达75%。
关键词:钒电池;电解液;稳定性;电化学性能
文章编号:1004-0609(2021)-06-1621-11 中图分类号:O642 文献标志码:A
引文格式:杨亚东, 张一敏, 唐 历, 等. 基于硫酸-盐酸混酸体系钒电池电解液的性能优化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(6): 1621-1631. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-36485
YANG Ya-dong, ZHANG Yi-min, TANG Li, et al. Performance optimization of electrolyte based on sulfate-chloride mixed acid for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(6): 1621-1631. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-36485
近年来,随着化石能源的逐渐消耗和环境保护要求的日益严苛,可再生能源的利用受到越来越多的关注。由于可再生能源的间歇性及波动性使得其利用面临较多的问题,因此,大规模储能装置的开发就显得尤为重要。全钒液流电池储能系统由于其具有循环寿命长,运行成本低、排放能力强、响应快、安全性高、环境友好、容量功率独立可调等特点[1-5],是间歇式可再生能源储存的首选技术之一[6-10]。
电解液作为钒电池储能系统的重要组成部分,不仅决定了钒电池的能量密度,同时决定了钒电池运行的效率及稳定性[11-13]。高浓度V(Ⅱ)、V(Ⅲ)、V(Ⅳ)电解液在低温下易发生结晶,而高浓度的V(Ⅴ)电解液在高温下易形成沉淀,其中尤其以V(Ⅴ)电解液热稳定性最差[14]。因此,需要提高电解液在高浓度下的高低温稳定性和电化学性能,从而提高钒电池的能量密度并拓宽其温度适应区间。电解液通常采用H2SO4作为支持电解质,此体系下在温度高于40 ℃时V(Ⅴ)电解液中的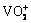 易转化为V2O5沉淀,而V(Ⅱ)、V(Ⅲ)、V(Ⅳ)电解液在温度低于0 ℃时易形成硫酸盐结晶,这极大地限制了电解液钒浓度及运行温度区间使得其能量密度被限制在18~22 W·h/L[15]。针对硫酸体系的钒电池电解液稳定性提升已进行了大量的研究,主要集中在添加剂方面。有研究者采用无机添加剂(碱金属硫酸盐、六偏磷酸钠、草酸盐、硼酸盐和卤素)作为添加剂提高了五价电解液的热稳定性,但其电化学性能提升有限[11, 16-17]。有研究者还针对含有羟基、羧基、磺酸基和巯基的有机添加剂进行了研究[18-21]。LI等[22]研究了果糖、甘露糖醇、葡萄糖和d-山梨糖醇等多元醇对电解液性能的影响,发现含d-山梨醇添加剂的电解液表现出较好的电化学性能和稳定性。WANG等[23]研究多种酸性添加剂,发现含有羧基和磺酸基团的添加剂可以明显延缓五价电解液的热沉淀,提高五价电解液的热稳定性。LIANG等[24]选择L-谷氨酸作为添加剂,提高了五价电解液的热稳定性和电化学性能,同时发现含氮基团的引入可以加快V(Ⅳ)/V(Ⅴ)电对的电极反应速率。有研究者采用含氮物质修饰电极来改善钒电池正极氧化还原对的电化学活性[25-26]。有研究表明,有羟基和羧基的添加剂会在在钒电池长期循环运行中被五价钒离子氧化,因此,羧酸类和醇类物质不适合用作钒电池电解液添加剂[27]。然而到目前为止,添加剂方面的研究并没有取得很显著的进展,电解液钒浓度只能达到1.6 mol/L且温度仅为0~40 ℃。因此,有研究者提出采用新的支持电解质体系取代硫酸体系以提高电解液性能,LI等[28]采用H2SO4和HCl的混酸作为支持电解质,该体系不仅可以大幅提高电解液能量密度而且可以拓宽电解液的运行温度区间。然而,混酸体系电解液不可避免地面临着由于氯离子的引入而导致的氯化氢挥发和氯气析出的问题。因此,需要对混酸体系电解液进行浓度组成优化,从而消除因氯离子引入而带来的隐患,同时进一步提高电解液的能量密度。
易转化为V2O5沉淀,而V(Ⅱ)、V(Ⅲ)、V(Ⅳ)电解液在温度低于0 ℃时易形成硫酸盐结晶,这极大地限制了电解液钒浓度及运行温度区间使得其能量密度被限制在18~22 W·h/L[15]。针对硫酸体系的钒电池电解液稳定性提升已进行了大量的研究,主要集中在添加剂方面。有研究者采用无机添加剂(碱金属硫酸盐、六偏磷酸钠、草酸盐、硼酸盐和卤素)作为添加剂提高了五价电解液的热稳定性,但其电化学性能提升有限[11, 16-17]。有研究者还针对含有羟基、羧基、磺酸基和巯基的有机添加剂进行了研究[18-21]。LI等[22]研究了果糖、甘露糖醇、葡萄糖和d-山梨糖醇等多元醇对电解液性能的影响,发现含d-山梨醇添加剂的电解液表现出较好的电化学性能和稳定性。WANG等[23]研究多种酸性添加剂,发现含有羧基和磺酸基团的添加剂可以明显延缓五价电解液的热沉淀,提高五价电解液的热稳定性。LIANG等[24]选择L-谷氨酸作为添加剂,提高了五价电解液的热稳定性和电化学性能,同时发现含氮基团的引入可以加快V(Ⅳ)/V(Ⅴ)电对的电极反应速率。有研究者采用含氮物质修饰电极来改善钒电池正极氧化还原对的电化学活性[25-26]。有研究表明,有羟基和羧基的添加剂会在在钒电池长期循环运行中被五价钒离子氧化,因此,羧酸类和醇类物质不适合用作钒电池电解液添加剂[27]。然而到目前为止,添加剂方面的研究并没有取得很显著的进展,电解液钒浓度只能达到1.6 mol/L且温度仅为0~40 ℃。因此,有研究者提出采用新的支持电解质体系取代硫酸体系以提高电解液性能,LI等[28]采用H2SO4和HCl的混酸作为支持电解质,该体系不仅可以大幅提高电解液能量密度而且可以拓宽电解液的运行温度区间。然而,混酸体系电解液不可避免地面临着由于氯离子的引入而导致的氯化氢挥发和氯气析出的问题。因此,需要对混酸体系电解液进行浓度组成优化,从而消除因氯离子引入而带来的隐患,同时进一步提高电解液的能量密度。
本文作者主要研究了钒浓度、硫酸根和氯离子浓度对电解液在-20~50 ℃时氯离子稳定性的影响进行研究,确定了最佳的浓度组成范围以保证钒电池的稳定运行。然后基于稳定性优化的浓度组成范围,通过考察浓度组成对电解液物化性能及电化学性能的影响,从而确定最佳的浓度组成以进一步提高钒电池的能量密度及效率。此外,对正负极电解液的电极反应动力学进行分析,阐明了浓度组成对电解液电化学性能的影响机理。
1 实验
1.1 电解液制备
实验中使用的化学试剂均为分析纯,水为去离子水。不同浓度组成的V(Ⅳ)电解液通过电解经过硫酸和盐酸活化的V2O5(纯度99.9%)进行制备,相应的V(Ⅱ)、V(Ⅲ)和V(Ⅴ)电解液则通过电解V(Ⅳ)电解液进行制备。电解过程中的电解终点通过自动氧化还原电位滴定进行确定。
1.2 电解液氯离子稳定性测试
将制备的电解液密封于玻璃瓶中,然后置于有机玻璃架中,将装有V(Ⅴ)电解液的有机玻璃架静置于50 ℃的恒温水浴锅内进行稳定性测试。每个电解液测试时间最多10 d,由于电解液在高温有可能发生氯化氢挥发,测试10 d后,再对电解液氯离子浓度进行检测。
1.3 电导率及黏度测试
电解液的电导率采用电导率仪(Seven Compact S230-K,梅特勒托利多公司)进行测量,黏度采用品氏毛细管黏度计进行测量。电解液电导率及黏度的测量温度均为25 ℃,测试结果取3次平行测试的平均值。
1.4 电化学测试
采用CHI660E电化学工作站(上海晨华仪器有限公司)上进行电化学测试,测试采用三电极系统,石墨电极(1 cm2)作为工作电极,饱和甘汞电极(SCE)作为参比电极,铂片电极(2 cm2)作为对电极。每次测试前石墨电极用SiC砂纸抛光,然后分别在乙醇和去离子水中超声清洗10 min。循环伏安(CV)测试以10 mV/s的扫描速率进行,电压范围为0.6~1.3 V。交流阻抗(EIS)测试的交流微扰电压为5 mV,频率区间为1×10-2~1×105 Hz,由高频区向低频区方向进行扫描,测试电压为0.9 V。所有电化学测试均在25 ℃的温度下进行。
1.5 电池充放电测试
电池充放电测试采用自制的单电池,单电池以Nafion 117离子交换膜为隔膜,25 cm2(5 cm×5 cm)的聚丙烯腈基石墨毡为正负电极,铜板为集流体。通过蓝电CT2001A(5 V/10 A)电池测试仪进行电池充放电,电流密度为40~120 mA/cm2。初始的正负极电解液分别为V(Ⅳ)和V(Ⅲ)电解液,电解液体积均为30 mL,电解液流速为40 mL/min。充放电测试的电压上限和下限分别为1.65 V和0.65 V。不同温度的电池性能通过将电解液储液罐置于恒温器的外部恒温场内进行测试。氯离子的循环稳定性通过测试随充放电循环过程中正极电解液的氯离子浓度变化进行监测。
2 结果与分析
2.1 电解液氯离子的静态稳定性
基于前期混酸体系电解液钒离子稳定性的测试结果,当硫酸根浓度为2.0~3.0 mol/L、氯离子浓度6.0~7.0 mol/L时,电解液钒浓度可达2.4 mol/L且四种价态的电解液均可在-20~50 ℃稳定存在10 d以上。为避免氯化氢的挥发以保证钒电池的稳定运行,对氯离子的稳定性进行研究。由于高酸度及高温更易导致氯化氢的挥发,因此氯离子的稳定性主要在于测试高温下V(Ⅴ)电解液中氯离子浓度的变化。对不同钒浓度及硫酸根浓度的V(Ⅴ)电解液热稳定性测试后的氯离子浓度进行测试,其结果如图1(a)~(c)所示。
当电解液钒浓度为1.6 mol/L时,氯离子浓度和硫酸根浓度均对稳定性测试后的氯离子浓度有显著影响。初始氯离子浓度为6.0 mol/L 时,测试后的氯离子浓度随着硫酸根浓度的增加变化较小。当初始氯离子浓度升至6.4 mol/L时,测试后的氯离子浓度在硫酸根浓度为2.0~2.4 mol/L时保持不变,但当硫酸根浓度继续上升时,氯离子浓度会出现明显下降。当初始氯离子浓度为6.8和7.0 mol/L时,在硫酸根浓度范围为2.0~3.0 mol/L时,测试后,电解液中氯离子浓度均出现显著降低,且均降低至6.4 mol/L左右。当电解液钒浓度为2.0 mol/L,初始氯离子浓度为6.0或6.4 mol/L时,电解液在10 d稳定性测试后,其氯离子浓度保持不变,这说明氯离子的稳定性有所增强。初始氯离子浓度6.8和7.0 mol/L时,电解液中氯离子浓度的变化趋势与钒浓度为1.6 mol/L的电解液一致,但整体降低程度较少。当钒浓度上升到2.4 mol/L时,氯离子浓度随硫酸根浓度增大的变化趋势与钒浓度为2.0 mol/L 的电解液基本一致,但初始氯离子浓度为6.8和7.0 mol/L时,氯离子浓度的降低程度较小。由上述分析可知,当硫酸根浓度为2.0~3.0 mol/L时,混酸体系电解液的初始氯离子浓度不宜超过6.4 mol/L,硫酸根浓度的增加不利于氯离子的稳定性,这主要是由于随着硫酸根浓度的增加氢离子的浓度也相应增加,从而使得氯化氢的挥发加强。此外,钒浓度的增加有助于提升的氯离子稳定性,这是由于引入的氯离子与五价钒离子形成了可溶性的复合结构VO2Cl(H2O)2。基于以上分析,电解液钒浓度为1.6~2.4 mol/L,硫酸根浓度为2.0~3.0 mol/L、氯离子浓度为6.0~6.4 mol/L时,可以有效地抑制氯离子的挥发。
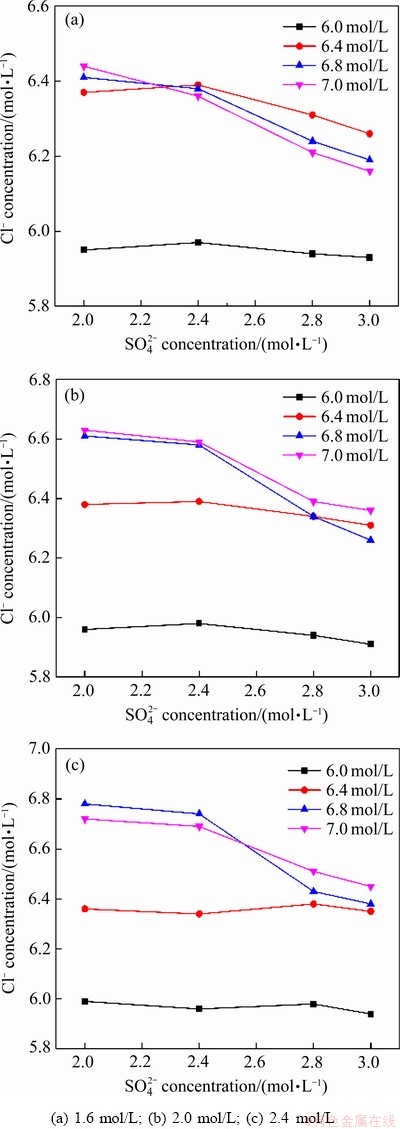
图1 不同V(Ⅴ)浓度电解液热稳定性测试后氯离子浓度随硫酸根离子浓度的变化
Fig. 1 Change of Cl- concentrations with  concentrations after stability test in electrolyte with different V(Ⅴ) concentrations
concentrations after stability test in electrolyte with different V(Ⅴ) concentrations
2.2 电解液物化性能
从上述稳定性分析的结果可见,混酸体系电解液的最佳浓度组成范围为钒浓度1.6~2.4 mol/L、硫酸根浓度2.0~3.0 mol/L和氯离子浓度6.0~6.4 mol/L。电解液作为钒电池的储能介质,不仅是氧化还原反应的活性物质,而且在充放电过程中起着重要的离子传输作用。快速的电极反应及离子传输有利于降低电解液中钒离子在电极表面的反应阻抗和极化,而电极反应及离子传输的速度分别由电解液的物化性能电导率及黏度决定。因此,需要对不同浓度组成电解液的电导率和黏度进行研究以进一步优化电解液性能。对稳定性优化后浓度组成范围的电解液电导率及黏度进行测试,其研究结果如图2所示。
V(Ⅳ)电解液的电导率随着钒浓度的增加而逐渐减小,当钒浓度从1.6 mol/L增大为2.4 mol/L时,电导率降低了32%。与之相反,V(Ⅳ)电解液的黏度随钒浓度的增大而增大。随着硫酸根浓度从2.0 mol/L升高到3.0 mol/L,电解液的电导率及黏度均逐渐增大,且分别增大了22%和51%。与硫酸根浓度相似,随氯离子浓度的增大电解液电导率与黏度均逐渐增大,两者分别增大了15%和28%。这种变化趋势主要是由于硫酸根及氯离子浓度的增加会使电解液中氢离子浓度增加,从而导致电导率及黏度的升高。从电导率及黏度的变化趋势可见,钒浓度对电导率的影响较大而硫酸根浓度对黏度的影响较大。因此,为降低电解液的浓差极化和欧姆极化,钒浓度、硫酸根浓度及氯离子浓度应分别低于2.2、2.75和6.2 mol/L。
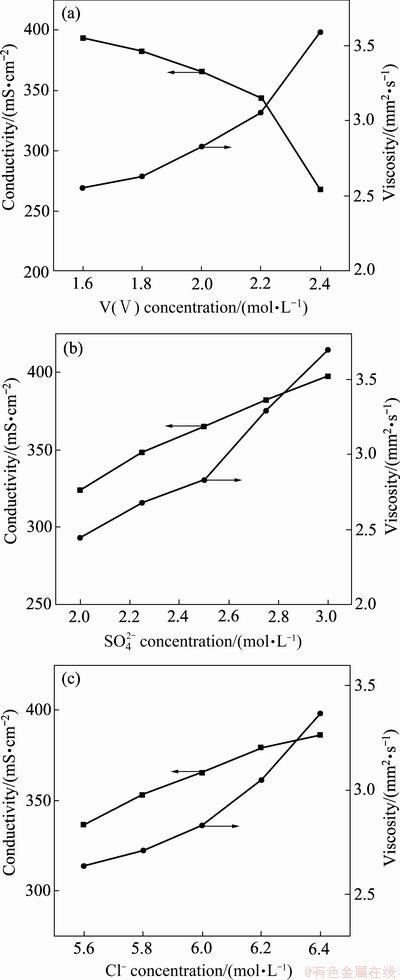
图2 不同钒浓度、硫酸根浓度及氯离子浓度的V(Ⅳ)电解液的电导率及黏度
Fig. 2 Conductivity and viscosity of V(Ⅳ) electrolyte with different vanadium concentration(a), sulfate concentration(b) and chloride ion concentration(c)
2.3 电解液电化学性能
为进一步提高电解液电化学性能,对不同浓度组成的正极电解液进行循环伏安测试,测试的循环伏安曲线如图3所示。氧化峰电流密度Jpa、还原峰电流密度Jpc和峰电位差△φp是表征电化学性能的重要参数,对循环伏安曲线进行分析拟合,其具体参数如图4所示。
随着钒浓度的增加,氧化峰电流密度Jpa和还原峰电流密度Jpc先增大后减小。当钒浓度由1.6 mol/L增大至2.2 mol/L时,Jpa和Jpc分别由72.53 mA/cm2、62.90 mA/cm2增大至102.21 mA/cm2、88.88 mA/cm2。峰电位差△φp随钒浓度增大先减小后增大,△φp在钒浓度为2.2 mol/L时最小为180 mV。这说明钒浓度的升高有利于电解液电化学活性及可逆性的提高,但当其增大到一定程度会对电化学活性产生不利影响,这可能是由于活性物质浓度和物化性能共同作用导致的。钒浓度的增大会使反应活性物质增多有利于电化学活性的增强,同时电解液黏度会增大和电导率出现降低,从而会阻碍钒离子扩散和电迁移从而增大电极反应的欧姆极化和浓差极化。当硫酸根浓度由2.0 mol/L增大到2.75 mol/L时,Jpa和Jpc变化幅度不大但当硫酸根浓度继续上升时出现明显下降,△φp变化较小维持在300 mV左右。这说明在一定的硫酸根浓度范围内硫酸根浓度的变化不会对电解液电化学活性及可逆性产生显著影响,这是由于随着硫酸根浓度的增大电解液黏度与电导率均随之增大,从而导致欧姆极化减弱、浓差极化增大。Jpa和Jpc随着氯离子浓度的增大而逐渐减小,且当氯离子浓度由5.8 mol/L增大到6.0 mol/L时,出现明显下降;△φp则在氯离子浓度为5.6~5.8 mol/L时保持不变,当氯离子浓度继续升高时,△φp则出现明显增大,这种变化趋势也是由电解液黏度与电导率变化的共同作用导致的。
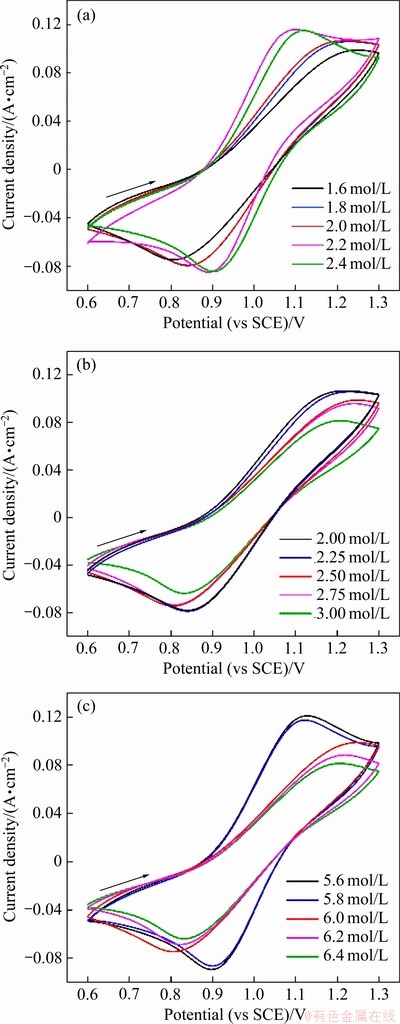
图3 不同钒浓度、硫酸根浓度及氯离子浓度的V(Ⅳ)电解液的循环伏安曲线
Fig. 3 CV curves of V(Ⅳ) electrolyte with different vanadium concentrations(a), sulfate concentrations(b) and chloride ion concentrations(c)
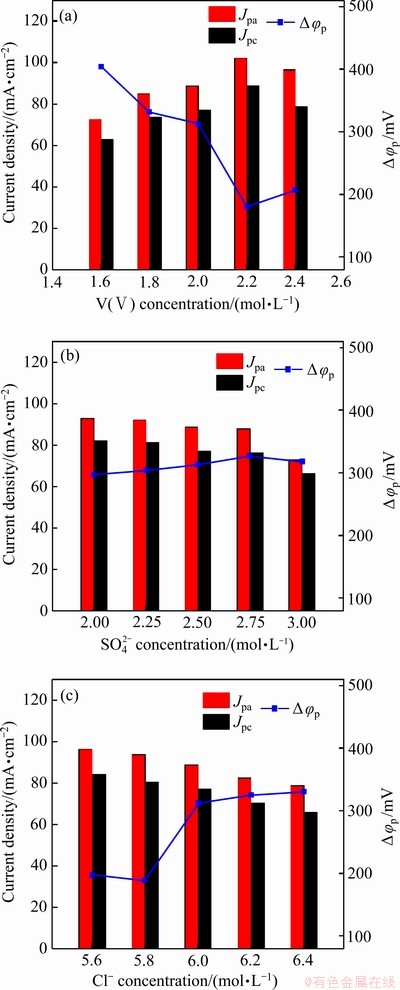
图4 不同钒浓度、硫酸根浓度及氯离子浓度的V(Ⅳ)电解液的循环伏安曲线对应的氧化峰电流密度Jpa、还原峰电流密度Jpc和峰电位差△φp
Fig. 4 Oxidation peak current density (Jpa), reduction peak current density (Jpc) and peak potential difference (△φp) of CV curves for V(Ⅳ) electrolyte with different vanadium concentrations(a), sulfate concentrations(b) and chloride ion concentrations(c)
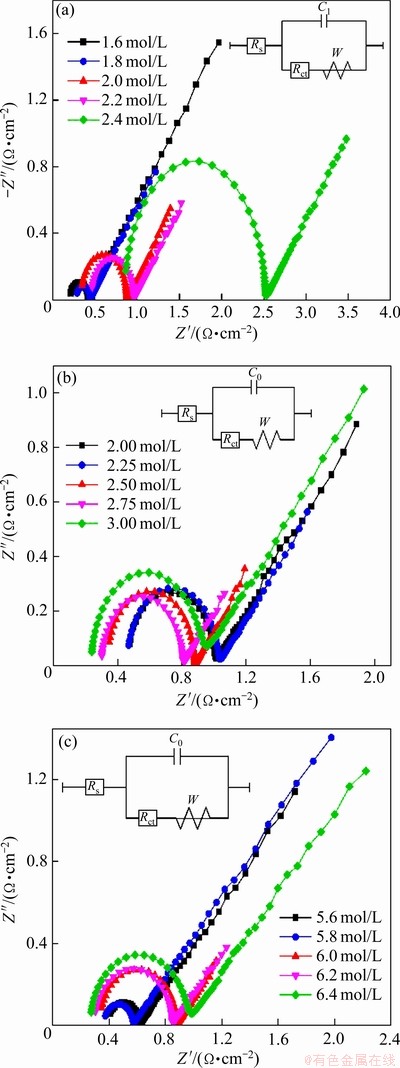
图5 不同钒浓度、硫酸根浓度及氯离子浓度的V(Ⅳ)电解液的交流阻抗图谱
Fig. 5 Electrochemical impedance spectroscopies of V(Ⅳ) electrolyte with different vanadium concentrations(a), sulfate concentrations(b) and chloride ion concentrations(c)
为进一步探究电解液电化学性能变化的机理,对电解液进行电极反应动力学分析。对不同浓度组成的电解液进行交流阻抗测试,其结果如图5所示。由图5可见,能奎斯特图谱在高频区域均呈现一个半圆而低频区为一条直线,这说明混酸体系电解液中的V(Ⅳ)/V(Ⅴ)电对的氧化还原反应由高频区的电荷传递过程以及低频区的扩散过程共同控制。能奎斯特图谱可以通过相应的等效电路模型进行拟合,其具体的拟合动力学参数溶液电阻Rs、电荷传递电阻Rct和扩散阻抗Wr如图6所示。随着钒浓度的升高,Rs、Rct和Wr均逐渐增大,Rs的增大是由于电解液电导率的降低,而Rct和Wr在钒浓度为1.6 mol/L至2.2 mol/L范围内增大较为缓慢而在钒浓度继续上升时出现明显的上升,这主要是由高浓度电解液中电极表面钒离子的吸附过程及扩散过程速度降低导致的。Rs随着硫酸根浓度的增大而逐渐减小,这是由氢离子浓度增大导致的,而Rct则在硫酸根浓度为2.0~2.75 mol/L范围内稍有下降但当硫酸根浓度由2.75 mol/L增大至3.00 mol/L时出现明显上升,这可能是硫酸根及氢离子过多使得钒离子的电化学活性下降导致的,Wr则呈现逐渐上升的趋势,这是由于硫酸根浓度过高阻碍了钒离子扩散。Rs、Rct和Wr随氯离子浓度增大的变化趋势与随硫酸根浓度的变化基本一致。
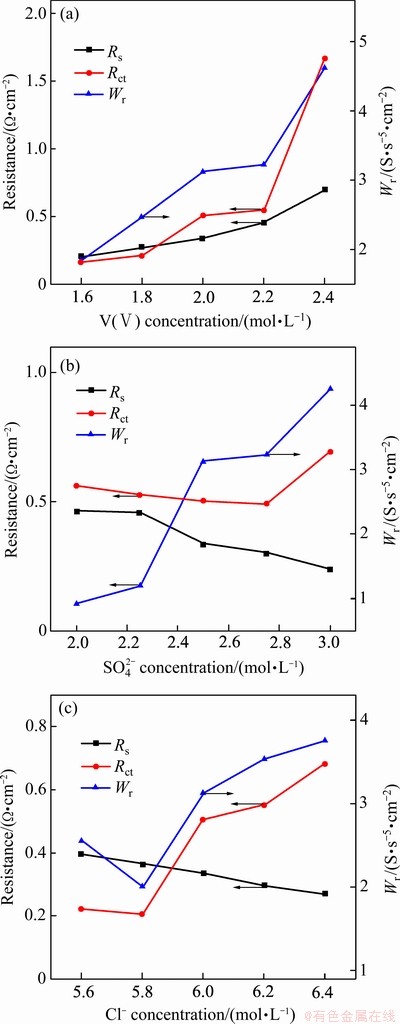
图6 不同钒浓度、硫酸根浓度及氯离子浓度的V(Ⅳ)电解液的交流阻抗图谱拟合动力学参数
Fig. 6 Dynamics parameters obtained from fitting of impedance plots for V(Ⅳ) electrolyte with different vanadium concentrations(a), sulfate concentrations(b) and chloride ion concentrations(c)
2.4 电池充放电性能
基于上述分析可知,最终选取的混酸体系电解液的最佳浓度组成为钒浓度2.2 mol/L,硫酸根浓度2.75 mol/L,氯离子浓度5.8 mol/L。为进一步评价该浓度组成电解液的电池性能及温度适应区间,对其在40~120 mA/cm2电流密度及-20~50 ℃温度范围内进行电池充放电测试,其库伦效率、电压效率和能量效率如图7所示。
库伦效率在-20~50 ℃温度范围内均随电流密度的增大而逐渐增大,高电流密度下库伦效率的提高是由充放电时间变短使得钒离子穿过膜引起的自放电减少所导致的,在50 ℃温度下库伦效率随电流密度增大的快速上升也进一步证明了该观点。库伦效率在同电流密度下随温度的升高而减小,这是由于在高温下钒离子穿过膜的速度加快导致充放电过程中自放电增多使得放电容量减少,进而使得库伦效率降低。此外,在-20 ℃温度下,电池仅能在40~80 mA/cm2电流密度范围内稳定运行,这是由于低温下钒电池极大的极化阻抗使得其在高电流密度下无法进行充放电。在-20~50 ℃温度区间内,电压效率随电流密度的增大而减小且在-20 ℃温度下降低较为显著。由于较高的电流密度会导致低温区电解液的欧姆极化,因此,电压效率随着电流密度的增大而降低。随着温度的升高,电压效率逐渐增大,这是由温度升高电解液的电导率增大而黏度减小、使得电极反应的欧姆极化与浓差极化减小导致的。能量效率作为库伦效率与电压效率的乘积,在-20 ℃和25 ℃随着电流密度的增加而减小,在50 ℃温度下,当电流密度增大至60 mA/cm2时,能量效率出现上升;但在60~120 mA/cm2电流密度范围内时,能量效率逐渐降低。这是由于库伦效率在40~60 mA/cm2电流密度范围内大幅上升,而随后其增幅相对小于电压效率的降幅。从上述分析可以发现采用该浓度组成的电解液可以在-20至50 ℃温度区间及40~80 mA/cm2电流密度范围内稳定运行且时能量效率可达75%。
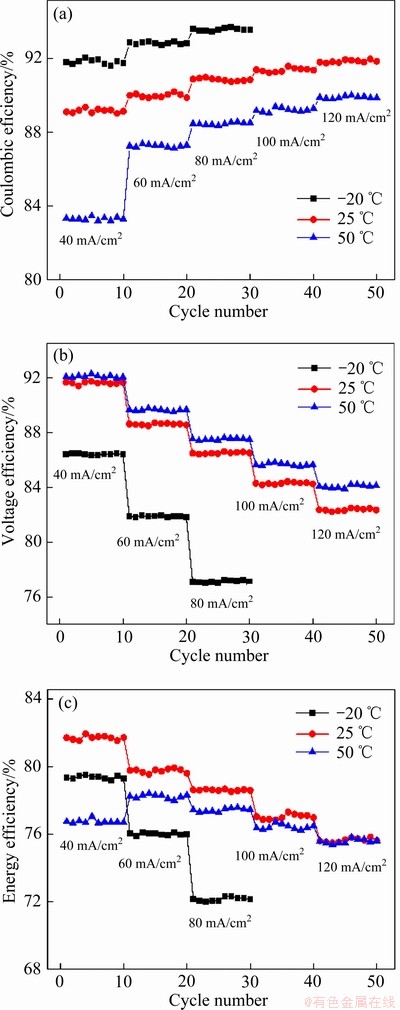
图7 不同电流密度及温度下电池循环充放电测试的库伦效率、电压效率和能量效率
Fig. 7 Coulombic efficiency (CE)(a), voltage efficiency (VE)(b) and energy efficiency (EE)(c) of charge-discharge tests at different current densities and temperatures
为进一步探究温度对电池循环充放电过程的影响,对不同温度的充放电曲线和放电容量衰减进行分析,测试结果如图8所示。随温度降低,放电电压平台下降而充电电压平台上升。由于温度升高电极反应的欧姆极化与浓差极化均减小,充放电过程的过电压降低,这与电压效率的变化规律一致。此外,温度升高电池充放电容量也相应增加,这是由于极化减小使得充电电压较低而放电电压较高,在相同截止电压下充电和放电时间延长,进而提高电池容量。放电容量衰减曲线表明放电容量保持率随着温度上升而降低,100个循环后,-20 ℃温度下的容量损失约为181 mA·h远低于在25 ℃下的468 mA·h和在50 ℃下的694 mA·h。这种现象是由于在较高温度下钒离子穿过离子交换膜而引起的自放电增多。
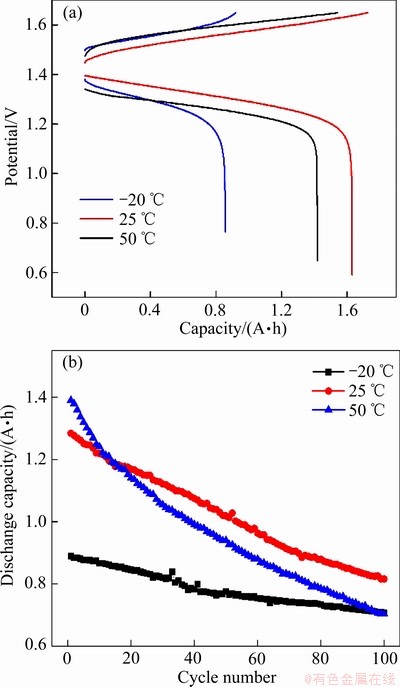
图8 不同温度下电池充放电曲线和放电容量衰减曲线
Fig. 8 Charge-discharge curves(a) and discharge capacity decay curves(b) of VRFB at different temperatures
3 结论
1) 通过对电解液氯离子稳定性、物化性能及电化学性能进行研究,进一步提高混酸体系电解液能量密度并拓宽其温度适应区间。50 ℃下氯离子稳定性表明,当氯离子浓度不超过6.4 mol/L时,可以有效避免氯化氢挥发,保证混酸体系电解液的稳定性。
2) 物化性能测试表明,电解液黏度均随钒浓度、硫酸根浓度及氯离子浓度的升高而增大,电导率则随硫酸根浓度及氯离子浓度的升高而增大,但随钒浓度的升高而减小。钒浓度为2.2 mol/L,硫酸根浓度为2.75 mol/L,氯离子浓度为5.8 mol/L的电解液的电化学性能最佳。
3) 结合物化性能及交流阻抗测试,发现电化学性能的变化受电解液黏度、电导率及电化学活性的共同影响,该浓度组成的电解液可以在-20~50 ℃温度区间及40~80 mA/cm2电流密度范围内稳定运行且能量效率可达75%。
REFERENCES
[1] ULAGANATHAN M, ARAVINDAN V, YAN Q Y, et al. Recent advancements in all-vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2016, 3: 1500309.
[2] 刘大凡, 李晓磊, 郭西凤. 全钒氧化还原液流电池的发展现状[J]. 无机盐工业, 2010, 42(8): 4-6.
LIU Da-fan, LI Xiao-lei, GUO Xi-feng. Current development status of all vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2010, 42(8): 4-6.
[3] PARASURAMANA A, LIM T M, MENICTAS C, et al. Review of material research and development for vanadium redox flow battery applications[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 101: 27-40.
[4] 尹跃龙, 李小山, 王树博. 复合添加剂对全钒液流电池正极电解液的影响[J]. 化工进展, 2011, 30: 767-769.
YIN Yue-long, LI Xiao-shan, WANG Shu-bo. Effect of complex additives on the positive electrolyte for all vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2011, 30: 767-769.
[5] ALOTTO P, GUARNIERI M, MORO F. Redox flow batteries for the storage of renewable energy: A review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 29: 325-335.
[6] 王 刚, 陈金伟, 汪雪芹. 全钒氧化还原液流电池电解 液[J]. 化学进展, 2013, 25(7): 1103-1104.
WANG Gang, CHEN Jin-wei, WANG Xue-qin. Electrolyte for all vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2013, 25(7): 1103-1104.
[7] CHO Y I, PARK S J, HWANG H J, et al. Effects of microwave treatment on carbon electrode for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Chem Electro Chem, 2016, 2: 872.
[8] 陈孝娥, 崔旭梅, 王 军. V(Ⅲ)-V(Ⅳ)电解液的化学合成及性能[J]. 化工进展, 2012, 31(6): 1330-1332.
CHEN Xiao-e, CUI Xu-mei, WANG Jun. Study on the chemical synthesis and performance of V(Ⅲ)-V(Ⅳ) electrolyte[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2012, 31(6): 1330-1332.
[9] KAUSAR N, MOUSA A, SKYLLAS-KAZACOS M. The effect of additives on the high-temperature stability of the vanadium redox flow battery positive electrolytes[J]. Chem Electro Chem, 2016, 3: 276-282.
[10] 徐 波, 齐 亮, 姚克俭. 全钒液流电池电解液分布的数值模拟[J]. 化工进展, 2013, 32(2): 313-314.
XU Bo, QI Liang, YAO Ke-jian. Investigation and simulation on electrolyte distribution for all-vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2013, 32(2): 313-314.
[11] ROE S, MENICTAS C, SKYLLAS-KAZACOS M. A high energy density vanadium redox flow battery with 3 M vanadium electrolyte[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2016, 163(1): A5023-A5028.
[12] WU X W, LIU J, XIANG X J, et al. Electrolytes for vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2014, 86(5): 661-669.
[13] MOUSA A, SKYLLAS-KAZACOS M. Effect of additives on the low-temperature stability of vanadium redox flow battery negative half-cell electrolyte[J]. Chem Electro Chem, 2015, 2: 1742-1751.
[14] VIJAYAKUMAR M, LI L Y, GRAFF G, et al. Towards understanding the poor thermal stability of V5+ electrolyte solution in vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196: 3669-3672.
[15] CUNHA A, MARTINS J, RODRIGUES N, et al. Vanadium redox flow batteries: A technology review[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2015, 39: 889-918.
[16] DING C, NI X, LI X, et al. Effects of phosphate additives on the stability of positive electrolytes for vanadium flow batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 164: 307-314.
[17] YEON S, SO J, YUN J, et al. Effect of phosphate additive for thermal stability in a vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage, 2017, 14: 041007.
[18] CHU Y Q, LIU C Z, REN H M, et al. Electrochemical performance of VO2+/VO2+ redox couple in the H2SO4-CH3SO3H solutions[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2016, 11: 1987-1996.
[19] HE Z X, HE Y Y, CHEN C, et al. Study of the electrochemical performance of VO2+/VO2+ redox couple in sulfamic acid for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Ionics, 2014, 20: 949-955.
[20] WANG G, CHEN J W, WANG X Q, et al. Influence of several additives on stability and electrochemical behavior of V(Ⅴ) electrolyte for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2013, 709: 31-38.
[21] HWANG J, KIM B, MOON J, et al. A highly efficient and stable organic additive for the positive electrolyte in vanadium redox flow batteries: Taurine biomolecules containing —NH2 and —SO3H functional groups[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6: 4695-4705.
[22] LI S, HUANG K L, LIU S Q, et al. Effect of organic additives on positive electrolyte for vanadium redox battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56: 5483-5487.
[23] WANG G, CHEN J W, XU Y D, et al. Study on stabilities and electrochemical behavior of V(Ⅴ) electrolyte with acid additives for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2014, 4:73-81.
[24] LIANG X X, PENG S, LEI Y, et al. Effect of l-glutamic acid on the positive electrolyte for all-vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 95: 80-86.
[25] HE Z X, SHI L, SHEN J X, et al. Effects of nitrogen doping on the electrochemical performance of graphite felts for vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2015, 39: 709-716.
[26] SHAO Y Y, WANG X Q, ENGELHARD M, et al. Nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon for energy storage in vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195: 4375-4379.
[27] NGUYEN T D, WHITEHEAD A, SCHERER G G, et al. The oxidation of organic additives in the positive vanadium electrolyte and its effect on the performance of vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 334: 94-103.
[28] LI L Y, KIM S, WANG W, et al. A stable vanadium redox-flow battery with high energy density for large-scale energy storage[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2011, 1(3): 394-400.
Performance optimization of electrolyte based on sulfate-chloride mixed acid for vanadium redox flow battery
YANG Ya-dong1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ZHANG Yi-min1, 3, 4, 5, 6, TANG Li2, LIU Tao1, 3, 4, 5, HUANG Jing1, 3, 4, 5, YANG Xiao2
(1. College of Resource and Environment Engineering, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Vanadium and Titanium Resources Comprehensive Utilization, Pangang Group Research Institute Co., Ltd., Panzhihua 617000, China;
3. State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Mineral Metallurgical Resources Utilization and Pollution Control, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, China;
4. Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center of High Efficient Utilization for Vanadium Resources, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, China;
5. Hubei Provincial Engineering Technology Research Center of High Efficient Cleaning Utilization for Shale Vanadium Resource, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430081, China;
6. College of Resource and Environment Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China)
Abstract: In order to improve the energy density and broad temperature adaptability of vanadium redox flow battery, the stability and electrochemical performance of electrolyte based on sulfate-chloride mixed acid electrolyte were optimized systematically. The static stability tests of vanadium ions and chloride ions show that the electrolyte of 2.4 mol/L vanadium concentration can keep stable for 10 d and the volatilization of hydrogen chloride can be effectively avoided when chloride ion concentration is 6.0-6.4 mol/L and sulfate concentration is 2.0-3.0 mol/L. The CV and EIS tests of electrolyte after stability optimization indicate that the electrolyte with 2.2 mol/L vanadium concentration, 2.75 mol/L sulfate concentration and 5.8 mol/L chloride ion concentration presents the best electrochemical performance. The charge-discharge tests of optimized electrolyte indicate that the VRFB with optimized electrolyte composition can be operated successfully at the temperature of -20-50 ℃ and the current density of 40-80 mA/cm2, and the energy efficiency can reach 75%.
Keywords: vanadium redox flow battery; electrolyte; stability; electrochemical performance
Foundation item: Project(51774216) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects (2017ACA185, 2017AAA034) supported by the Hubei Technical Innovation Special Project, China
Received date: 2019-10-25; Accepted date: 2021-04-20
Corresponding author: ZHANG Yi-min; Tel: +86-13907158287; E-mail: zym126135@126.com
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金面上项目(51774216);湖北省技术创新专项重大项目(2017ACA185,2017AAA034)
收稿日期:2019-10-25;修订日期:2021-04-20
通信作者:张一敏,教授,博士;电话:13907158287;E-mail:zym126135@126.com