文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-11-2363-06
铜合金层错能的热力学计算
侯利民1,侯利锋1,卫 欢1,卫英慧1, 2
(1. 太原理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,太原 030034;
2. 山西工程技术学院,阳泉 045000)
摘 要:层错能是金属材料重要的本征参数,对金属材料变形机制和力学性能有着重要的影响。特别是在强烈塑性变形过程中,层错能的变化对金属变形机制和晶粒细化机制有着决定性作用。层错能的测定或计算方法有很多种,热力学法能够方便快捷地计算出层错能的值,可以直观地判断温度、成分等对合金层错能的影响。采用热力学方法计算纯Cu及Cu-Ti、Cu-Zn合金的层错能,计算结果表明:在室温条件下,Cu-Ti和Cu-Zn合金的层错能都随溶质元素含量的增加而降低,两种合金中添加相同含量的溶质元素,溶质元素Ti对合金层错能的影响更大;两种合金偏聚自由能随溶质元素含量的增加而升高。
关键词: 铜合金;层错能;热力学
中图分类号:TG430.4020 文献标志码:A
随着工业发展的需求,人们采用多种方法来强化金属材料,其中利用严重塑性变形方法制备的纳米晶金属材料由于具有极高的强度而受到材料学界的广泛关注。目前研究的重点已从材料的制备和结构表征逐渐深入到显微组织的调整和新变形机制的探索。层错能作为材料重要的本征参数对其变形机制和力学性能有着重要的影响[1],特别是在强烈塑性变形中,层错能的大小对金属晶粒细化机制有着重要的作用[2-5]。研究发现,随着层错能的降低,材料的变形方式由位错为主转变为孪生为主,同时随着层错能的降低,材料的加工硬化速率会提高。因此,确定合金层错能大小,特别是不同合金元素及其含量对层错能的影响,对预测合金的变形机制及性能,超细晶材料组织与性能的控制优化具有重要意义[6-8]。层错能的测定方法如下[9-10]:加工硬化法、临界切应力法和低温蠕变等,实验工作量大,测量数值分散,结果可靠性低;第一性原理法[11-12]模型设计要求精,计算软件要求高,计算量大。而热力学法计算得到的层错能是某一特定温度的函数,方便快捷,并能直接得到温度、成分等因素对合金层错能的影响,计算结果和实验结果基本一致[13-15]。目前采用热力学模型计算层错能主要应用于面心立方[16-18]和六方系[19]合金。Cu合金作为面心立方结构的金属,具有较好的塑性变形能力。建立可靠的层错能热力学计算[20-22]模型可达到控制其塑性变形行为,调整显微组织的目的。
基于此,本文作者采用层错能的热力学计算模型,以Cu-Ti和Cu-Zn合金为例,分析Ti、Zn含量对Cu层错能的影响,以期为后续研究Cu合金变形机理提供理论支持。
1 热力学模型
1.1 FCC结构层错能
在面心立方结构中,a/6<112>不全位错的滑移面为{111}原子密排面,形成的层错破坏了密排面的正常堆垛顺序,相当于在FCC结构中形成了由两层HCP组成的结构[23]。对于纯金属,可以认为层错能γSF是具有两层HCP结构γ原子与具有两层HCP结构ε原子的吉布斯自由能差[16],即
 (1)
(1)
式中:V代表金属摩尔体积; 为吉布斯自由能差。对合金材料而言,其FCC结构与HCP结构的吉布斯自由能之差并不严格等于层错能,这是因为元素在层错区的浓度与合金的平均成分不同,使得在层错区和基体的浓度有着明显的不同。因此,合金的层错能[17]可表示为
为吉布斯自由能差。对合金材料而言,其FCC结构与HCP结构的吉布斯自由能之差并不严格等于层错能,这是因为元素在层错区的浓度与合金的平均成分不同,使得在层错区和基体的浓度有着明显的不同。因此,合金的层错能[17]可表示为
 (2)
(2)
式中:N0是阿伏伽德罗常数; 表示单位面积的FCC相和HCP相之间的吉布斯自由能差;
表示单位面积的FCC相和HCP相之间的吉布斯自由能差; 指由于偏聚等原因使合金元素在层错区和基体区中浓度不同而引起的能量变化;
指由于偏聚等原因使合金元素在层错区和基体区中浓度不同而引起的能量变化; 为磁畴转化对层错能的贡献。本研究中铜合金中不存在磁畴的变化,所以其层错能可由式(3)表示:
为磁畴转化对层错能的贡献。本研究中铜合金中不存在磁畴的变化,所以其层错能可由式(3)表示:
 (3)
(3)
1.2  的计算
的计算
 是指全部由置换原子组成体系的自由能,对于Cu-M二元合金体系,
是指全部由置换原子组成体系的自由能,对于Cu-M二元合金体系, 可表示为
可表示为
 (4)
(4)
式中: ,
, 分别表示溶剂元素Cu和溶质元素M发生γ→ε相变时的吉布斯自由能差,
分别表示溶剂元素Cu和溶质元素M发生γ→ε相变时的吉布斯自由能差, 为混合超额自由能,x表示合金元素的摩尔分数。MIEDEMA等[24]总结了过渡金属、非过渡金属和惰性金属之间形成固溶体时形成热的经验值规律,其中混合生成焓ΔHmix的半经验表达式为
为混合超额自由能,x表示合金元素的摩尔分数。MIEDEMA等[24]总结了过渡金属、非过渡金属和惰性金属之间形成固溶体时形成热的经验值规律,其中混合生成焓ΔHmix的半经验表达式为
 (4-1)
(4-1)
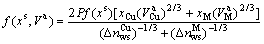 (4-2)
(4-2)
 (4-3)
(4-3)
 (4-4)
(4-4)
 (4-5)
(4-5)
 (4-6)
(4-6)
 (4-7)
(4-7)
 ,
, (4-8)
(4-8)
 ,
, (4-9)
(4-9)
式中: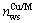 为合金元素的Wigner-Seitz原子胞边界的电子密度平均值;
为合金元素的Wigner-Seitz原子胞边界的电子密度平均值; 代表电负性;
代表电负性;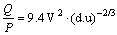 ;
; 为过渡金属与非过渡金属形成合金时的修正系数,所以对于讨论的3种元素而言,
为过渡金属与非过渡金属形成合金时的修正系数,所以对于讨论的3种元素而言, 、O=0、α=0.04[25];
、O=0、α=0.04[25]; 为浓度函数,
为浓度函数, 为原子Cu被M的包围程度,
为原子Cu被M的包围程度, 代表原子M被Cu包围的程度;
代表原子M被Cu包围的程度; 和
和 分别表示合金元素的摩尔分数和摩尔体积,
分别表示合金元素的摩尔分数和摩尔体积, 和
和 指合金中的表面摩尔分数和表面摩尔体积。
指合金中的表面摩尔分数和表面摩尔体积。
根据热力学关系,可知Cu-M二元合金中混合超额自由能: 和混合超额熵
和混合超额熵 及混合超额焓
及混合超额焓 之间的关系为:
之间的关系为:
 (5)
(5)
而超额熵与焓又有以下关系:
 (6)
(6)
式中: 和
和 分别为Cu和M元素的熔点。
分别为Cu和M元素的熔点。
1.3  的计算
的计算
理论上,偏聚自由能 主要包括3部分[17],即
主要包括3部分[17],即
 (7)
(7)
式中: 指铃木偏聚所导致的化学自由能变化;
指铃木偏聚所导致的化学自由能变化; 表示由于基体和层错区合金元素浓度不同产生的表面自由能;
表示由于基体和层错区合金元素浓度不同产生的表面自由能; 为由于原子尺寸不同所引起的弹性自由能。由于Ti和Zn元素在Cu基体中主要形成置换固溶体,YAKUBTSOV等[25]认为溶质原子以置换原子形式存在对表面自由能的影响很小;同时Ti和Zn元素与Cu元素原子半径相差不大,晶格畸变产生的自由能忽略不计,所以本研究只讨论铃木偏聚所产生的自由能。根据平衡条件[11]可得:
为由于原子尺寸不同所引起的弹性自由能。由于Ti和Zn元素在Cu基体中主要形成置换固溶体,YAKUBTSOV等[25]认为溶质原子以置换原子形式存在对表面自由能的影响很小;同时Ti和Zn元素与Cu元素原子半径相差不大,晶格畸变产生的自由能忽略不计,所以本研究只讨论铃木偏聚所产生的自由能。根据平衡条件[11]可得:
 (8)
(8)
式中: 表示
表示 相(基体相)的自由能,xb表示合金元素在基体的摩尔分数;
相(基体相)的自由能,xb表示合金元素在基体的摩尔分数; 指
指 相(层错相)的自由能,xs表示合金元素在层错区的摩尔分数。为了方便计算,把
相(层错相)的自由能,xs表示合金元素在层错区的摩尔分数。为了方便计算,把 相和
相和 相作为规则溶液处理,YAKUBTSOV等[25]推导了合金元素在层错区的浓度,如式(9)所示:
相作为规则溶液处理,YAKUBTSOV等[25]推导了合金元素在层错区的浓度,如式(9)所示:
 (9)
(9)
由式(9)可得,溶质发生偏聚所引起的自由能[26]的变化为
 (10)
(10)
表1 Cu及Ti和Zn元素的计算参数[24, 27]
Table 1 Calculation parameters of Cu, Ti and Zn[24, 27]

式中:参数R表示摩尔气体常数;xs-M和xb-M分别表示组元M在层错区和基体区的摩尔分数。
2 计算结果与讨论
2.1 自由能的计算
根据上述计算模型,应用计算机软件编程进行计算,计算所用参数见表1。根据式(4)计算Cu-Ti与Cu-Zn合金在室温(298K)下,不同溶质含量下的自由能的变化,计算结果如图1所示。从图1可以看出,随着溶质元素含量的增加Cu-Zn 和Cu-Ti合金由置换原子组成的体系自由能逐渐减小:随Ti含量从0增加到10%(摩尔分数),Cu-Ti合金体系自由能从567.7 J下降到了-227.4 J;Cu-Zn合金体系自由能随Zn含量从0增加到30%从628.9 J减小到了-269.7 J。两种合金的体系自由能随溶质元素含量的变化呈线性关系,其中Cu-Ti合金体系斜率较大,Cu-Zn合金体系斜率较小。对本研究中合金体系而言,体系自由能均随着合金元素含量增大而降低,然而随着合金元素含量的增加,溶质元素偏聚增大,由此引起能量变化对层错能的影响不能忽略。
2.2 元素偏聚引起的能量变化

图1 自由能随溶质含量的变化趋势
Fig. 1 Value of free energy change with solute content

图2 偏聚自由能随溶质元素含量的变化趋势
Fig. 2 Segregation free energy changes with solute content
图2所示为偏聚自由能随溶质元素添加含量的变化趋势,从图2上可以看出,Cu-Ti和Cu-Zn合金的偏聚自由能都是随着溶质含量的增加而增大的,前者由82.3 J增大到了531.4 J,后者从30.1 J上升到了518.2 J。这说明随着溶质元素的增加,两种合金的偏聚自由能对层错能的影响逐渐加大,结合图1的结果可以得出,随着溶质元素含量的加大,合金层错能中偏聚自由能的作用大大增加。
2.3 层错能
结合前面两部分的结果,综合考虑体系自由能和偏聚自由能对层错能的影响,Cu-Ti和Cu-Zn合金的层错能随溶质元素含量的变化如图3所示。从图3中可以看出,随着溶质元素含量的增加,合金的层错能逐渐减小:其中Cu-Ti合金层错能随Ti含量(0~10%)的增加从20.82 mJ/m2降到9.75 mJ/m2,Cu-Zn合金层错能则随Zn含量(0~30%)的增加从21.13 mJ/m2降到7.97 mJ/m2;两种溶质元素的添加均使得合金的层错能有所减小,且添加相同含量的Ti对合金层错能的影响更大,这是因为与Zn相比Ti的化合价较高,电子浓度较高。
图4所示为文献[28-29]中Cu基合金的层错能随溶质含量的变化曲线,表明Cu合金层错能显著按电子浓度规则降低,P、Ge、Al等高价溶质元素对Cu合金影响显著,Zn影响程度中等,而Mn则影响较小。

图3 层错能随溶质含量的变化趋势
Fig. 3 Stacking faule energy change with solute content

图4 Cu基合金的层错能随溶质含量的变化曲线[28]
Fig. 4 Variation of stacking fault energy of Cu based alloys with change of solute content[28]
然而溶质Ti、P和Al一样,属于高价溶质元素,会导致铜合金金层错能急剧下降,这个规律与本研究的计算结果一致。表2列出了Cu及Cu-Zn合金的计算值与实验值的对比,本研究中计算结果与CARTER等[30]的结果相近。CARTER等采用TEM节点法得到Cu-10%Zn和Cu-30%Zn(摩尔分数)的SFE分别为22和7 mJ/m2,而本研究中采用热力学方法计算得到的SFE分别为19.42和7.96 mJ/m2,结果说明本研究中计算模型的可靠性。本研究中计算结果与文献[31-32]结果相差较大,文献[31-32]中也是采用TEM节点法,与文献[30]的区别在于二者所用TEM像明暗场不同,明暗场的变换就产生了误差。其次依赖于实验,实验条件的改变势必会影响SFE值的准确性;而本研究中所采用热力学法在原理上与文献中不同,参数的选取依赖于实验,这必将造成两者结果存在一定的误差。此外,本研究计算基于理想状态下进行,忽略了晶格畸变和基体和层错区合金元素浓度不同所引起的自由能变化,这也会导致合金层错能值略小。
表2 Cu及Cu-Zn合金层错能计算值与实验值对比(mJ/m2)
Table 2 Comparison between stacking fault energy calculation value and experimental value of Cu and Cu-Zn alloy (mJ/m2)

3 结论
1) 利用层错能计算模型分别研究了Cu-Ti和Cu-Zn合金的层错能随溶质元素含量增加的变化,与实验数据进行对照,结果表明Cu-Zn合金的计算值和实验值基本一致。
2) 在室温条件下,Cu-Ti和Cu-Zn合金的层错能都随溶质元素的增加而降低,且高价溶质元素Ti对Cu合金层错能的影响更大。
3) 随溶质元素含量的增加,溶质元素偏聚自由能对层错能的影响增大。
REFERENCES
[1] HIRTH J P, LOTHE J. Theory of dislocations[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1968.
[2] YE Y X, FENG Y Y, LIAN Z C, HUA Y Q. Plastic deformation mechanism of polycrystalline copper foil shocked with femtosecond laser[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 309: 240-249.
[3] EL-DANAF E A, AL-MUTLAQ A, SOLIMAN M S. Role of stacking fault energy on the deformation characteristics of copper alloys processed by plane strain compression[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 5289(25/26): 7579-7588.
[4] GONG Y L, WEN C E, LI Y C, WU X X, CHENG L P, HAN X C, ZHU X K. Simultaneously enhanced strength and ductility of Cu-xGe alloys through manipulating the stacking fault energy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 569: 144-149.
[5] CAI Bao-zhuang, TAO Jing-mei, WANG Wei, YANG Xin-cheng, GONG Yu-lan, CHENG Lian-ping, ZHU Xin-kun. The effect of stacking fault energy on equilibrium grain size and tensile properties of ultrafine-grained Cu-Al-Zn alloys processed by rolling[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 610: 224-230.
[6] PETROV Y N, YAKUBYSOV I A. Thermodynamic calculation of stacking fault energy for multicomponent alloys with FCC lattice based on iron[J]. Physics of Metals and Metallography, 1986, 62: 34-38.
[7] 张福州. 广义层错能的第一性原理计算及定域性分析[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2008.
ZHANG Fu-zhou. Generalized stacking fault energy calculated from first principles and analysis of local approximation[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2008.
[8] CHETTY N, WEINERT M. Stacking faults in magnesium[J]. Physical Review B, 1997, 56(17): 10844.
[9] 冯 端, 王业宁. 金属物理[M],北京: 科学出版社, 1964.
FENG Duan, WANG Ye-ning. Metal physics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1964.
[10] 何 刚, 赵恒北, 戎咏华, 敦正洪, 陈世朴, 徐祖耀. 层错几率峰位移测定法及在Fe-Mn-Si合金中的应用[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 1999, 33(7): 765-768.
HE Gang, ZHAO Heng-bei, RONG Yong-hua, DONG Zheng-hong, CHEN Shi-pu, XU Zhu-yao. Peak shift method on stacking fault probability determination and its application on Fe-Mn-Si alloys[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 1999, 33(7): 765-768.
[11] ABBASI A, DICK A, HICKEL T, NEUGEBAUER J. First-principles investigation of the effect of carbon on the stacking fault energy of Fe-C alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(8): 3041-3048.
[12] WEN Yu-feng, SUN Jian, HUANG Jian. First-principles study of stacking fault energies in Ni3Al intermetallic alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(3): 661-664.
[13] HENDRICKSON A A. Solute segregation to stacking faults[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1962, 10(9): 900-907.
[14] DORN J E. Thermodynamics of stackine faults in binary alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1963, 11(3): 218-230.
[15] MIODOWNIK A P. The calculation of stacking fault energies in Fe-Ni-Cr alloys[J]. Calphad, 1978, 2(3): 207-226.
[16] 万见峰, 陈世朴, 徐祖耀. Fe-30Mn-6Si-xN形状记忆合金层错能的热力学计算[J]. 金属学报, 2000, 36(7): 679-684.
WAN Jian-feng, CHEN Shi-pu, XU Zu-yao. Thermodynamical calculation of the stacking fault energy in Fe-30Mn-6Si-xN shape memory alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2000, 36(7): 679-684.
[17] ERICSSON T. On the suzuki effect and spinodal decomposition[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1966, 14(9): 1073-1084.
[18] 于兴福, 田素贵, 杜洪强, 王明罡, 孟凡来. 元素W,Co对Ni-Al合金层错能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(12): 2148-2151.
YU Xing-fu, TIAN Su-gui, DU Hong-qiang, WANG Ming-gang, MENG Fan-lai. Influence of elements W, Co on the stacking fault energy of Ni-Al alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(12): 2148-2151.
[19] 冯中学, 张喜燕, 潘复生. 溶质元素及其偏聚对六方系金属层错能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41(10): 1765-1769.
FENG Zhong-xue, ZHANG Xi-yan, PAN Fu-sheng. Influence of solute and solute segregation on the stacking fault energy in HCP metals[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(10): 1765-1769.
[20] 王翠萍, 刘兴军, 马云庆, 大沼郁雄, 贝沼亮介, 石田清仁. Cu-Ni-Sn三元系相平衡的热力学计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(11): 1848-1853.
WANG Cui-ping, LIU Xing-jun, MA Yun-qing, OHNUMA I, KAINUMA R, ISHIDA K. Thermodynamic calculation of phase equilibria in Cu-Ni-Sn ternary system[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15 (11): 1848-1853.
[21] 刘兴军, 王翠萍, 甘世溪, 大沼郁雄, 贝沼亮介, 石田清仁. 高性能铜合金热力学数据库的开发及其在材料设计中的应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(10): 2511-2522.
LIU Xing-jun, WANG Cui-ping, GAN Shi-xi, OHNUMA I, KAINUMA R, ISHIDA K. Development of thermodynamic database for copper base alloy systems and its application in material design[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(10): 2511-2522.
[22] 慕思国, 汤玉琼, 郭富安, 唐谟堂, 彭长宏. Cu-Cr-Zr系合金非真空熔炼过程的热力学分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(8): 1330-1335.
MU Si-guo, TANG Yu-qiong, GUO Fuan, TANG Mo-tang, PENG Chang-hong. Thermodynamic analysis for non-vacuum melting of Cu-Cr-Zr alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(8): 1330-1335.
[23] 于兴福, 田素贵. 杨景红. W、Co对Ni合金层错能影响的热力学计算[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2004, 3(4): 294-297.
YU Xing-fu, TIAN Su-gui, YANG Jing-hong. Thermodynamic calculation on the influence of W and Co on the stacking fault energy of Ni alloys[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2004, 3(4): 294-297.
[24] MIEDEMA A R, CHATEL P F, BOER F R. Chemical bonding and fermi level pinning at metal-semiconductor interfaces[J]. Physica, 1980, 100: 1-15.
[25] YAKUBTSOV I A, ARIAPOUR A, PEROVIC D D. Effect of nitrogen on stacking fault energy of f.c.c. iron-based alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47(4): 1271-1279.
[26] ISHIDA K. Calculation of lattice defect images for scanning electron microscopy[J]. Direct Physica Status Solidi A(Applied Research), 1976, 36(2): 717-728.
[27] DINSDAL A T. Sgte data for pure elements[J]. CALPHAD, 1991, 15(4): 317-435.
[28] ENGLER O. Deformation and texture of copper-manganese alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2000, 48: 4827-4840.
[29] GALLADHER P C J. The influence of alloying, temperature and related effects on the stacking fault energy[J]. Metallurgical Transaction, 1970, 1: 2429-2462.
[30] CARTER C B, RAY I L F. On the stacking-fault energies of copper alloys[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 1977, 35: 189-200.
[31] LORETTO M H, CLAREBROUGH L M, SEGALL R L. Stacking-fault tetrahedra in deformed face-centred cubic metals[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 1965, 11: 459-465.
[32] HOWIE A, SWANN P R. Direct measurements of stacking-fault energies from observations of dislocation nodes[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 1961, 6: 1215-1226.
[33] 杨 鹏. 层错能对超细晶铜和铜锌合金力学性能和微观结构的影响[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2010.
YANG Peng. Effect of stacking-fault energy on the mechanical properties and microstructure of ultrafine-grain Cu and Cu-Zn alloys[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Technology, 2010.
[34] MA X L, ZHOU H, NARAYAN J, ZHU Y T. Stacking-fault energy effect on zero-strain deformation twinning in nanocrystalline Cu-Zn alloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 109: 89-93.
Thermodynamic calculation of stacking fault energy of copper alloy
HOU Li-min1, HOU Li-feng1, WEI Huan1, WEI Ying-hui1, 2
(1. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China;
2. Shanxi Institute of Technology, Yangquan 045000, China)
Abstract: Stacking fault energy (SFE) is an intrinsic parameter of metallic material, which has a significant impact on the plastic deformation mechanism and mechanical property. Especially for severe plastic deformation, the SFE can change the deformation and grain refinement mechanism of metal. There are many measurements or methods for calculating the value of SFE. Thermodynamic method, as one of the widely adopted way, can visually detect the effect of the temperature and alloying elements on the SFE. The thermodynamic method was used to estimate the SFE value of Cu, Cu-Ti and Cu-Zn alloys. The results show that at room temperature, the SFE values of Cu-Ti and Cu-Zn alloys decrease with the concentration of alloying elements increasing. When the same solute element content of two kinds of alloys is added, the solute Ti has more influence on the stacking fault energy of alloy. The segregation free energy for Cu-Zn and Cu-Ti alloy would be raised with the increasing of solute elements.
Key words: Cu alloy; stacking fault energy; thermodynamic
Foundation item: Project(51374151) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2015-10-12; Accepted date: 2016-01-28
Corresponding author: HOU Li-feng; Tel: +86-3516018685; E-mail: houlifeng78@126.com
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51374151)
收稿日期:2015-10-12;修订日期:2016-01-28
通信作者:侯利锋,博士,副教授;电话:0351-6018685,E-mail:houlifeng78@126.com