NH4+-Mg2+-PO43--H+-H2O体系的固液平衡热力学
姜 科,周康根,彭佳乐
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:对NH4+-Mg2+-PO43--H+-H2O体系中固相MgNH4PO4,Mg3(PO4)2,MgHPO4及Mg(OH)2与液相间的热力学平衡关系进行计算,绘制溶液总镁与总磷摩尔比为1?1时该体系的lgcMg—pH图、lgcN—lgcMg图和lgcN—pH图,确定体系中各种固相稳定存在的pH值范围。结果表明,溶液中的氨氮浓度和pH值是影响固相稳定存在的重要因素,MgNH4PO4的稳定区随氨氮浓度的降低而变小并最终消失,当pH=8.5且MgNH4PO4与Mg3(PO4)2共存时,溶液中的氨氮平衡浓度最低。
关键词:磷酸铵镁;氨氮;废水;热力学
中图分类号:X131.2 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)05-1178-05
Thermodynamics of solid-liquid equilibrium in NH4+-Mg2+-PO43--H+-H2O system
JIANG Ke, ZHOU Kang-gen, PENG Jia-le
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The thermodynamics of equilibrium was calculated between solid phases MgNH4PO4, Mg3(PO4)2, MgHPO4, Mg(OH)2 and liquid phase in NH4+-Mg2+-PO43--H+-H2O system. The lgcMg—pH, lgcN—lgcMg and lgcN—pH diagrams when the molar ratio n(Mg)/n(P) was equal to 1?1 in liquid phases were drawn, and the pH range when solid phases existed stably in the system was determined. The results show that the ammonia-nitrogen concentration and pH are very important factors which influence the stable zone of solid phases. The stable zone of MgNH4PO4 reduces and finally disappears with the decrease of ammonia-nitrogen concentration. The lowest ammonia-nitrogen concentration in equilibrium is found at pH=8.5 when MgNH4PO4 and Mg3(PO4)2 coexist with liquid phase.
Key words: magnesium ammonium phosphate; ammonia-nitrogen; wastewater; thermodynamics
随着社会经济的发展和人们生活水平的提高,水环境污染也日趋严重。其中,氨氮作为一种主要的水体污染物,一旦其含量超标,会引起水环境质量迅速恶化,给自来水厂处理带来困难,毒害水中的鱼类等水生动物,严重危害人类健康。为此,人们采用多种方法如生物法、折点加氯法、吹脱法、磷酸铵镁化学沉淀法等对水中的氨氮进行处理[1]。其中,磷酸铵镁化学沉淀法通过向氨氮废水中投加镁盐和磷酸盐,使废水中的氨氮转化为缓释肥料中的营养元素(主要成分为MgNH4PO4,Magnesium ammonium phosphate,简称MAP)。MAP沉淀法具有简单、快速、高效等优点[2]。迄今已有大量关于MAP沉淀法的实验研究报道,包括城市生活污水中N与P的回收、垃渗滤液、焦化废水、冶金废水中氨氮的处理等[3-9]。与此同时,得出MAP的沉淀-溶解平衡的热力学分析结果。如Ohlinger等[10]考虑了离子强度对离子活度的影响,各种形态的氨氮、镁和磷盐的分布,得出MAP的沉淀溶解-平衡常数为10-13.26;Ronteltap等[11]对尿素体系中MAP沉淀的性质进行了热力学研究,考察了高离子强度对MAP的溶度积的影响;Mijangosa等[12]假定Mg-NH3-H3PO4体系物质总浓度为1 mol/L,Mg的总浓度为0.10 mol/L,运用MINEQL+软件对体系进行模拟分析,结果显示在pH=8~10时,MAP容易生成,但是,磷酸镁的产生对MAP有较大影响,随着反应的进行,体系pH值降低,阻碍了MAP的产生;Micha?owski等[13]对碳酸盐体系中MAP的性质进行了研究,研究表明,当n(Mg)?n(N)?n(P)=1?1?1时,体系中的平衡固相是磷酸镁,即使生成MAP也会向更稳定的磷酸镁转化;只有当n(Mg)?n(N)?n(P)=1.0?1.6?1.0时,MAP才是平衡固相;Vesna Babic?-Ivancˇic?等[14]对MgCl2-NH4H2PO4-NaOH-H2O体系中MAP转化为磷酸氢镁的过程进行了动力学分析,得出在反应60 min后,体系中以MAP沉淀为主,磷酸氢镁只有在初始Mg2+浓度高于氮、磷浓度时才存在。MAP的沉淀-溶解平衡不是单纯的MAP与NH4+,Mg2+和PO43-之间的平衡,还涉及Mg3(PO4)2,MgHPO4和Mg(OH)2等多种固相与液相间的平衡。目前,热力学分析主要关注的是MAP的沉淀-溶解平衡,尚无有关全面描述NH4+-Mg2+-PO43--H+-H2O体系中各种沉淀与液相间的相平衡关系的文献报道。在此,本文作者通过NH4+-Mg2+-PO43--H+-H2O体系的lgcMg—pH,lgcMg—lgcN图与lgcN—pH图的建立,考察体系中各种固相与液相的平衡关系,为MAP法处理氨氮废水的实验过程提供了一定的理论依据。
1 体系的热力学分析
1.1 热力学数据和模型的建立
在NH4+-Mg2+-PO43--H+-H2O体系中,除了Mg2+,PO43-,NH4+,H+及MgNH4PO4(s)外,还可能存在固相MgHPO4(s),Mg3(PO4)2(s),Mg(OH)2(s)和溶解态物质H3PO4(aq),H2PO4-,HPO42-,MgPO4+,MgHPO4(aq),MgH2PO4+,MgOH+,NH3?H2O(aq)等,这些物质之间的溶解平衡或电离平衡关系如表1所示。
假设体系中游离Mg2+,NH43--和NH+4浓度的负对数依次为x,y和z,由式(1)~(4)的沉淀-溶解平衡关系可得如下方程。

表1 NH4+-Mg2+- PO43--H+-H2O体系中的热力学平衡数据(25 ℃)
Table 1 Thermodynamic data in NH4+-Mg2+- PO43--H+-H2O system (25 ℃)

由式(5)~(12)的电离平衡关系依次可得:

设总氮、总磷、总镁浓度分别为cMg,cP和cN,则:
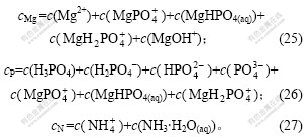
1.2 热力学计算过程
根据相律,当温度与压力恒定时,自由度F、相数P与独立组分数C之间的关系为F=C-P。本体系的独立组分数C=5。当只考虑1种固相与溶液的平衡时,相数P=2,因此,F=3。为了能在平面图上描述体系的相平衡关系,讨论以下3种自由度为1时固相与溶液的平衡关系:
a. 溶液中Mg,P的总摩尔比n(Mg)?n(P)=1?1,且氨氮浓度一定(F=3-2=1)。
在氨氮浓度确定的条件下,由式(17)~(27)可以得出溶液中的c(Mg2+),c(PO43-)与pH值之间及c(NH4+)与pH值之间的关系,再根据式(13)~(16),可以求出不同pH值时各沉淀与溶液共存时的c(Mg2+),c(PO43-)和c(NH4+),从而得lgcMg—pH关系图。
b. 溶液中Mg和P的总摩尔比n(Mg)?n(P)=1?1,且pH值一定(F=3-2=1)。
在pH值确定的条件下,由式(17)~(27)可以得出溶液中的c(Mg2+)和c(PO43-)之间及c(NH4+)和cN之间的关系,再根据式(13)~(16),可以求出不同cN时各沉淀与溶液共存时的c(Mg2+),c(PO43-)和c(NH4+),从而得lgcMg—lgcN关系图。
c. 溶液中Mg与P的总摩尔比n(Mg)?n(P)=1?1,且有2固相与溶液平衡(F=4-3=1)。
在体系中两固相(含MAP)与液相共存时,根据式(13)~(16),可以分别得出MgHPO4,Mg3(PO4)2,Mg(OH)2与MAP共存时c(Mg2+),c(PO43-),c(NH4+)和pH值之间的关系,再结合式(17)~(27),可以求出不同pH值条件下各沉淀与溶液共存时的c(Mg2+),c(PO43-)和c(NH4+),从而得lgcN—pH关系图。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 不同氨氮浓度下的lgcMg—pH关系
不同氨氮浓度下体系的lgcMg—pH的关系如图1所示。由图1可知,在溶液中不存在氨氮,且pH<6.43时,溶液中稳定存在的固相是MgHPO4;当6.43<pH<11.26时,Mg3(PO4)2是稳定存在的;当pH>11.26时,Mg(OH)2更容易生成。这说明在实验室制备MgHPO4,Mg3(PO4)2和Mg(OH)2固体时,需要将pH值分别控制在适宜的范围内。图1中的虚线表示了溶液中存在氨氮,是MAP与溶液的固液共存线,其中,①④⑤⑥围成的区域表示cN=1.0 mol/L时MAP的稳定区,③⑤围成的区域表示cN=0.01 mol/L时MAP的稳定区。由此可见,随着氨氮浓度的降低,MAP的稳定区变小,并最终消失。因此,要采用MAP法处理氨氮废水,必须控制合适pH值,并保持cMg和cN在一定范围内,使MAP在溶液中稳定存在。
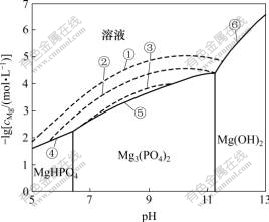
①、②、③分别表示cN=1, 0.1, 0.01 mol/L时MAP与溶液的平衡;④、⑤、⑥分别表示MgHPO4, Mg3(PO4)2, Mg(OH)2与溶液的平衡
图1 n(Mg)?n(P)=1?1不同氨氮浓度下的lgcMg—pH关系
Fig.1 lgcMg—pH diagram at n(Mg)?n(P)=1?1 and different NH3-N concentrations
2.2 不同pH值条件下的lgcMg—lgcN关系
pH=6.0, 8.5, 10.0时的lgcMg—lgcN关系如图2~4所示。由图2可知,当pH=6.0且氨氮平衡浓度为39.8 mmol/L时,溶液中共存的固相为MAP和MgHPO4;当氨氮平衡浓度大于39.8 mmol/L时,MAP与溶液共存;当氨氮平衡浓度小于39.8 mmol/L时,MgHPO4与溶液共存。这说明当pH=6.0时,氨氮浓度只有高于39.8 mmol/L,溶液中才能产生MAP沉淀。
由图3可知,当pH=8.5且氨氮平衡浓度为4.6 mmol/L时,溶液中共存的固相为MAP和Mg3(PO4)2;当氨氮浓度低于4.6 mmol/L时,溶液中难以生成MAP沉淀。由图4可知,当pH=11.0且氨氮浓度为1.16 mol/L时,溶液中共存的固相为MAP和Mg(OH)2;当氨氮浓度低于1.16 mol/L时,溶液中稳定存在的固相是Mg(OH)2。由此可见,溶液的pH值对溶液中氨氮平衡浓度有重要影响。

图2 n(Mg)?n(P)=1?1,pH=6.0时的lgcMg—lgcN关系
Fig.2 lgcMg—lgcN at n(Mg)?n(P)=1?1 and pH=6.0

图3 n(Mg)?n(P)=1?1,pH=8.5时的lgcMg—lgcN关系
Fig.3 lgcMg—lgcN at n(Mg)?n(P)=1?1 and pH=8.5

图4 n(Mg)?n(P)=1?1,pH=11.0时的lgcMg—lgcN关系
Fig.4 lgcMg—lgcN at n(Mg)?n(P)=1?1 and pH=11.0
2.3 两固相共存时pH值对氨氮平衡浓度的影响
不同pH值条件下2种固相与溶液共存时的氨氮平衡浓度随pH值的变化关系如图5所示。
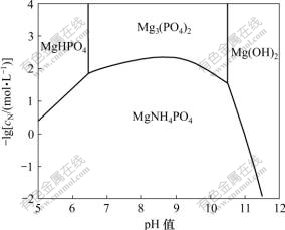
图5 两种固相与溶液共存时的lgcN—pH关系
Fig.5 lgcN—pH when two solid phases coexist in solution
从图5和计算结果可以看出,当pH=6.42时,体系中MgHPO4,Mg3(PO4)2,MAP与溶液共存,氨氮平衡浓度为15.0 mmol/L;当pH=10.60时,体系中Mg(OH)2,Mg3(PO4)2,MAP与溶液共存,氨氮平衡浓度为68.3 mmol/L。
当pH<6.42时,溶液中共存的固相是MAP和MgHPO4;当pH值为6.42~10.60时,溶液中共存的固相是Mg3(PO4)2和MAP;当pH>10.60时,溶液中共存的固相是Mg(OH)2和MAP。氨氮浓度最低出现在MAP和Mg3(PO4)2共存线上,其中,当pH=8.50时氨氮平衡浓度最低,为4.6 mmol/L;当pH值为8.00~9.50时,氨氮平衡浓度均在7.0 mmol/L以下;当pH>11.00时,氨氮平衡浓度达到1 mol/L以上。
由此可见,用MAP法处理氨氮废水时,pH值是影响氨氮去除效率最主要的因素,pH值在8.00~9.50之间且MAP和Mg3(PO4)2 2种固相与溶液共存时,最有利于降低溶液中的氨氮浓度。当pH值过低,共存固相为MAP与MgHPO4,或pH值过高,共存固相为MAP与Mg(OH)2时,溶液中的平衡氨氮浓度都较高。
另外,随着pH值升高,溶液中与MAP共存的固相经历了MgHPO4—Mg3(PO4)2—Mg(OH)2的变化,造成溶液中的剩余磷含量随着呈先降后升的趋势。
3 结 论
a. MAP的稳定区随氨氮浓度的降低而变小,当氨氮浓度低于4.6 mmol/L时,MAP稳定区消失,MAP不能稳定存在,说明MAP法更适用于处理高浓度氨氮废水,处理后的氨氮浓度不能低于MAP与液相平衡时的氨氮浓度。
b. 当pH<6.42时,溶液中MAP和MgHPO4两固相共存;当pH值为6.42~10.60时,MAP和Mg3(PO4)2两固相共存;当pH>10.60时,MAP和Mg(OH)2两固相共存。
c. 在给定pH值条件下,当MAP与另一固相Mg(OH)2,MgHPO4或Mg3(PO4)2共存时,溶液中的平衡氨氮浓度最低。体系中的氨氮平衡浓度随pH值的变化呈先降低后升高的趋势,在MAP和Mg3(PO4)2两固相共存且pH=8.5时,氨氮平衡浓度最低。
参考文献:
[1] 黄 骏, 陈建中. 氨氮废水处理技术研究进展[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2002, 3(1): 65-68.
HUANG Jun, CHEN Jian-zhong. Recent advances on the treatment technologies of ammonia-nitrogen wastewater[J]. Techniques and Equipment for Environment Pollution Control, 2002, 3(1): 65-68.
[2] 张书军, 冯晓西, 乌锡康, 等. 磷酸铵镁沉淀法脱氨机理、应用及沉淀剂循环[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2006, 7(7): 128-132.
ZHANG Shu-jun, FENG Xiao-xi, WU Xi-kang, et al. A review on ammonia removal from wastewater by precipitation as magnesium-ammonium-phosphate: Mechanism, application and precipitant recycle[J]. Techniques and Equipment For Environment Pollution Control, 2006, 7(7): 128-132.
[3] 贾玉鹤, 李 晶, 刘洪波, 等. 磷酸铵镁沉淀法去除垃圾渗滤液中氨氮的实验研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2007, 1(8): 229-231.
JIA Yu-he, LI Jing, LIU Hong-bo, et al. A new method for removing NH3-N in landfill leachate-MAP precipitation [J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2007, 1(8): 229-231.
[4] 刘大鹏, 王继徽, 刘晓澜, 等. MAP法处理焦化废水中氨氮的pH值影响[J]. 工业水处理, 2004, 24(1): 44-47.
LIU Da-peng, WANG Ji-hui, LIU Xiao-lan, et al. pH effect on the treatment of ammonia-nitrogen from coke plant wastewater by MAP process[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2004, 24(1): 44-47.
[5] 史世庄, 王香平, 乔国强, 等. 化学沉淀法脱除焦化废水中的氨氮[J]. 武汉科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 27(1): 28-30.
SHI Shi-zhuang, WANG Xiang-ping, QIAO Guo-qiang, et al. Removal of ammoniacal nitrogen from coking wastewater by chemical precipitation[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2004, 27(1): 28-30.
[6] 王力平, 李义科, 庞 宏, 等. 稀土冶炼氨氮废水氨氮去除实验研究[J]. 给水排水, 2004, 30(4): 50-52.
Wang Li-ping, Li Yi-ke, Pang Hong, et al. Research on ammonia nitrogen removal from rare earth refining wastewater[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2004, 30(4): 50-52.
[7] 霍守亮, 席北斗, 刘鸿亮, 等. 磷酸铵镁沉淀法去除与回收废水中氮磷的应用研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2007, 26(3): 371-376.
Huo Shou-liang, Xi Bei-dou, Liu Hong-liang, et al. Removal and recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater by struvite crystallization[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2007, 26(3): 371-376.
[8] Uludag-demirer S, Demirer G N, Chen S. Ammonia removal from anaerobically digested dairy manure by struvite precipitation[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2005, 40(12): 3667- 3674.
[9] Jaffer Y, Clark T A, Pearce P, et al. Potential phosphorus recovery by struvite formation[J]. Water research, 2002, 36(7): 1834-1842.
[10] Ohlinger K N, Young T M, Schroeder E D. Predicting struvite formation in digestion[J]. Water Research, 1998, 32(12): 3607-3614.
[11] Ronteltap M, Maurer M, Gujer W. Struvite precipitation thermodynamics in source-separated urine[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(5): 977-984.
[12] Mijangosa F, Kamel M, Lesmesa G, et al. Synthesis of struvite by ion exchange isothermal supersaturation technique[J]. Reactive & Functional Polymers, 2004, 60: 151-161.
[13] Micha?owski T, Pietrzyk A. A thermodynamic study of struvite+ water system[J]. Talanta, 2006, 68(3): 594-601.
[14] Babic?-ivancˇic? V, Kontrec J, Brecˇevic? L, et al. Kinetics of struvite to newberyite transformation in the precipitation system MgCl2-NH4H2PO4-NaOH-H2O[J]. Water Research, 2006, 40(18): 3447-3455.
[15] Musvoto E V, Wentzel M C, Ekama G A. Integrated chemical-physical progresses modeling-ⅡSimulating aeration treatment of anaerobic digester supernatants[J]. Water Research, 2000, 34(6): 1868-1880.
[16] Udert K M, Larsen T A, Gujer W. Estimating the precipitation potential in urine-collecting systems[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(11): 2667-2677.
收稿日期:2008-12-05;修回日期:2009-04-08
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50674100)
通信作者:周康根(1963-),男,湖南涟源人,教授,博士生导师,从事冶金环境工程及废水处理研究;电话:13873189654;E-mail: zhoukg63@mail.csu.edu.cn