
Effect of melt convection on primary dendrite arm spacing in directionally solidified Pb-26%Bi hypo-peritectic alloys
HU Xiao-wu, LI Shuang-ming, GAO Si-feng, LIU Lin, FU Heng-zhi
State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, Northwestern Polytechnical University,Xi’an 710072, China
Received 7 December 2009; accepted 15 April 2010
Abstract: Primary dendrite arm spacing (PDAS) of α phase in directionally solidified Pb-26%Bi (mass fraction) hypo-peritectic alloys was measured by considering the effect of melt convection in cylindrical samples with different diameters. The experimental results show the measured PDAS increases with increasing diameter of the sample. At the growth velocity of 5 μm/s, its value changes from 161.5 μm for the sample with 1.8 mm in diameter to 240.4 μm for the sample with 7 mm in diameter. The strong melt convection in large diameter samples causes a high bulk alloy composition and a high concentration gradient in peritectic β phase, resulting in a larger PDAS. Simultaneously, the high concentration gradient could effectively promote the peritectic transformation, enhancing the dissolution of the thin α dendrite.
Key words: Pb-26%Bi; hypo-peritectic alloy; primary dendrite arm spacing; melt convection; directional solidification
1 Introduction
Peritectic solidification has attracted more attention in experimental and theoretical studies[1], since many technologically important materials are peritectic, such as Sn-Cd[2-3], Sn-Sb[4], Pb-Bi[5-6], Zn-Cu[7-8], Zn-Ag[9], high temperature intermetallic Ti-Al[10] and Ni-Al[11], superconducting materials YBCO[12], magnetic materials Nd-Fe-B[13], and structural materials Fe-Ni[14-15] and Fe-Cr-Ni[16].
In solidification of these alloys, dendrite structure is the commonly encountered pattern. The microstructural scales involving the primary dendrite arm spacing (PDAS) and the secondary dendritic arm spacing (SDAS) have been carried out in directional solidification of various peritectic alloys including Pb-Bi[17], Zn-Cu[17] and Nd-Fe-B[18]. Most of the experimental results are correlated with the processing conditions based on the diffusive mechanism without consideration of melt convection.
The effect of melt convection on phase selection in peritectic alloys has been reported [2, 5]. It is found that convection effects can lead the formation of significantly different microstructures from those predicted by the diffusive growth models. The oscillating tree-like structure instead of discrete band structure was observed in the present of melt convection. Recently, BISWAS et al[19] studied the effect of melt convection on the SDAS of NdFeB alloys using the forced crucible rotation technique, and found that the SDAS values decreased with reducing melt convection. Although there are many investigations focusing on the microstructure evolution in peritectic systems under the consideration of the melt convection effect, little research has been conducted on the effect of melt convection on the PDAS in peritectic systems. The reason of the increase of the PDAS under melt convection is not well understood.
In this study, the effect of melt convection on the PDAS in directionally solidified Pb-26%Bi (mass fraction) hypo-peritectic alloys was performed. Two kinds of alumina tubes with different inner diameters of 1.8 mm and 7 mm were used to investigate the effect of melt convection on directionally solidified micro- structures. The reason for the increase of the PDAS in Pb-26%Bi hypo-peritectic alloy under convective conditions was investigated.
2 Experimental
Pb-26%Bi alloy was prepared from 99.95% pure lead and 99.99% pure bismuth. The alloy was melted in a resistance furnace under an argon atmosphere, and molten alloy was poured into a graphite mould. The samples of different diameters were cut from the as-cast ingot. A vertical Bridgman furnace described in detail elsewhere[20] was used to produce directionally solidified rods of the Pb-26%Bi alloy. The samples were placed into a graphite cylinder of the furnace. After heating to stabilization at 375 °C for 30 min, the samples were withdrawn into a water cooled cylinder containing liquid Ga-In-Sn metal at a preset velocity (from 5 to 250 μm/s). The length of the transition zone, L, which equals 4Dl/(k0v), where Dl, k0 and v are the diffusion coefficient in liquid phase (1.3×10-5 cm2/s), partial coefficient (0.579) and growth velocity, respectively. For the growth velocity of 5 μm/s, L is approximate 1.8 mm, and as the growth velocity increases, the L will decrease. In this work, all samples were solidified to 5 cm, which was long enough to ensure a constant primary spacing distribution. The temperature measurements were carried out by using a NiCr-NiSi thermocouple. The calculated temperature gradient around the solid-liquid interface was about 20 K/mm.
In order to study the effect of melt convection on the PDAS in directionally solidified Pb-26%Bi hypo-peritectic alloys, a device similar to that introduced by KOHLER et al[21] was used. Due to the melt convection intensity proportional to the cubic power of the characteristic sample size, a thin alumina capillary (outer diameter (dO) of 3 mm, inner diameter (dI) of 1.8 mm) was inserted into a larger one (dO of 8 mm, dI of 7 mm), as shown in Fig.1. In this situation, for each

Fig.1 Setup used to solidify Pb-26%Bi samples: (a) Illustration of alumina crucible (dO of 8 mm, dI of 7 mm) separated into two regions by an alumina capillary (dO 3 mm, dI 1.8 mm); (b) Crucible and capillary tube (thicknesses of outer and inner crucible are 0.5 and 0.6 mm, respectively)
experimental run, a Pb-Bi cylinder with 1.8 mm in diameter was solidified together with a tube of 3 mm/7 mm of dI/dO. In addition, the sample with 7 mm in diameter was solidified separately under the same growth conditions.
The quenched specimens were transversely sectioned, as shown in Fig.2. The A-A, B-B and C-C sections are at the same height, that is to say that the solidification fractions of all considered samples are the same. Then, the sections were ground, polished and etched with the reagent of 100 mL distilled water (H2O), 10 mL nitric acid (HNO3) and 4 g ammonium molybdate ((NH4)6MO7O24·4H2O). An Olympus TG-3 optical microscope was employed to photograph these specimens. The concentrations in dendrite and interdendrite were measured by SEM-EDS. The values of the PDAS (λ1) were obtained on the transverse sections.
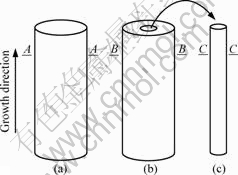
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of directionally solidified samples and transverse sections (A-A, B-B and C-C): (a) d=7 mm; (b) dI/dO=3 mm/7 mm; (c) d=1.8 mm
3 Results and discussion
Fig.3 shows the solidified microstructures in both tube with 3 mm/7 mm of dI/dO and cylinder of 1.8 mm-diameter at various growth velocities. The microstructures consist of dendrites of primary α phase embedded in a matrix of peritectic β phase. The higher magnification microstructures of tubes with 3 mm/7 mm of dI/dO are shown in Figs.3(a1)-(d1), and Figs.3(a2)-(d2), corresponding to the microstructures solidified in cylinders with 1.8 mm in diameter at different growth velocities. In comparison, Fig.4 gives the solidified microstructures of samples with 7 mm in diameter at various growth velocities.
The average experimental values of PDAS (λ1) measured as a function of the growth velocity (v) are shown in Fig.5, where triangles present the experimental results of the PDAS of α phase in 7 mm-diameter samples. Besides, the squares present the measured results in tube with 3 mm/7 mm in dI/dO, and circles

Fig.3 Transverse microstructures of tube both 3 mm/7 mm of dI/dO diameter and cylinder with 1.8 mm in diameter for a series of Pb-26%Bi samples: (a) v=5 μm/s; (b) v=50 μm/s; (c) v=100 μm/s; (d) v=250 μm/s

Fig.4 Transverse microstructures of sample with 7.0 mm in diameter: (a) v=5 μm/s, λ1=240.4 μm; (b) v=50 μm/s, λ1=143.2 μm; (c) v=100 μm/s, λ1=92.8 μm; (d) v=250 μm/s, λ1=63.7 μm
correspond to the results in 1.8 mm-diameter cylinder, respectively. The relationships between λ1 and v for samples with different diameters were obtained using a linear regression method as follows:
λ1=441.34v-0.33 for d=7 mm (1)
λ1=325.73v-0.31 for dI/dO=3 mm/7 mm (2)
λ1=258.86v-0.27 for d=1.8 mm (3)
From Fig.5, it is clear that the PDAS becomes large with increasing the sample diameter. The value increases from 161.5 μm for 1.8 mm-diameter cylinder to 240.4 μm for 7 mm-diameter sample at v=5 μm/s. It is also indicated that the differences in all samples with different

Fig.5 Measured primary dendrite arm spacing (λ1) of primary α-phase of sample with different diameters as function of v
diameters are small at high growth velocity, which results from small deviation in melt convection at high growth velocity. In addition, it is noted that the exponent of velocity decreases with decreasing the tube diameter, and it is 0.27 for the smallest diameter used in this study. This is close to the exponent of 0.25 predicted by HUNT[22] for diffusive growth, that is to say that experimental condition for smaller-diameter sample would be close to diffusive growth condition. By considering the DS experiments carried out under the same conditions for the samples with different diameters, the influence of processing conditions on the increase of the PDAS of primary α-phase is the same, and the changes of PDAS depend on the variation in melt convection.
For a given system, the intensity of melt convection can be characterized by a solute Rayleigh number (Ra), which can be written as follows[5]:
 (4)
(4)
where g is the acceleration due to gravity; βs is the solute expansion coefficient; w0 is the alloy mass fraction; d is the diameter of sample; αL is the thermal diffusivity of the liquid; and v is the kinematics viscosity. In Eq.(4), the Rayleigh number is proportional to d3, thus the melt convection will be reduced as the sample diameter decreases.
In the case of the Pb-26%Bi peritectic alloy, the mass fraction of solute (Bi) is less than that of solvent (Pb). As the crystals of the primary dendrite (Pb) come from the solid-liquid interface, the solute (Bi) in the melt surrounding the primary dendrite increases and the dense profile in the interdendritic melt promotes natural convection.
The increase in PDAS with increasing sample diameter may be contributed by two factors. One is the macrosegregation resulting from melt convection and the another is the influence of melt convection on peritectic transformation.
According to the boundary layer model proposed by KARMA et al[23], it is well known that the macrosegregation will increase along the sample with increasing the melt convection during the directional solidification. For a given solidification fraction, the macrosegregation in larger-diameter sample is heavier, subsequently, and the bulk alloy composition in liquid will be higher. Fig.6 presents the measured compositions of transverse sections A-A, B-B and C-C in Fig.2 at various growth velocities. It indicates that the composition increases with increasing sample diameter. Especially, the deviation in composition between large- diameter sample and small-diameter sample is higher at lower growth velocity due to the significant melt convection.

Fig.6 Measured Bi mass fractions of samples at different growth velocities
McCARTNEY and HUNT[24] investigated the directional solidification of Al-Mg-Si alloys, and found that the relationship between primary spacing (λ) and liquid temperature gradient (GL), the growth velocity (v) and the bulk alloy composition (w∞) was  . It has been observed that the primary spacing is proportional to
. It has been observed that the primary spacing is proportional to 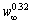 . TRIVEDI and SOMBOONSUK[25] reported a detailed study of the variation in primary dendrite spacing in a directionally solidified succinonitrile-acetone solution, and found that the primary spacing increased with the increase of acetone concentration. In the present experiment, the primary dendrite arm spacing increases with increasing sample diameter because of the increased bulk alloy composition resulted from melt convection.
. TRIVEDI and SOMBOONSUK[25] reported a detailed study of the variation in primary dendrite spacing in a directionally solidified succinonitrile-acetone solution, and found that the primary spacing increased with the increase of acetone concentration. In the present experiment, the primary dendrite arm spacing increases with increasing sample diameter because of the increased bulk alloy composition resulted from melt convection.
Due to differing from single phase alloys, the PDAS in peritectic systems may be influenced by the peritectic reaction and transformation. The peritectic reaction takes place through the solute diffusion in the liquid, the reaction rate will be fast and the time for reaction is short, thus the peritectic reaction could be ignored. The peritectic transformation is the major growth mechanism in Pb-Bi peritectic system and controlled by the solid diffusion mechanism.
In large-diameter samples, the melt convection is stronger, causing the solute boundary layer reduce and the formation of a steep solute gradient at the interface. The increased solute diffusion is in favor of the peritectic transformation in the large-diameter samples. These results alter the PDAS value in directionally solidified Pb-26%Bi alloys with different diameter samples.
Following the analysis developed by WAGNER[26], the solute flux from β envelope to α phase during peritectic transformation is given as follows:
 (5)
(5)
where  ,
, 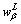 ,
, 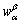 and
and 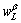 are shown in Fig.7;
are shown in Fig.7; 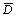 is the interdiffusion coefficient in the β phase; Δx is the thickness of β envelope; and t is transformation time. In Eq.(5), the expression of
is the interdiffusion coefficient in the β phase; Δx is the thickness of β envelope; and t is transformation time. In Eq.(5), the expression of  is calculated as
is calculated as
 (6)
(6)
Besides, the left side of Eq.(5) can be written as follows[26]:
 (7)
(7)
where  is the average interdiffusion coefficient in the β phase. Substituting Eq.(7) into Eq.(5) yields:
is the average interdiffusion coefficient in the β phase. Substituting Eq.(7) into Eq.(5) yields:
 (8)
(8)
where the parameter A expresses:
 (9)
(9)

Fig.7 Hypothetical peritectic phase diagram showing distance used phases, compositions and temperatures
It can be seen from Eq.(9) that the parameter A keeps constant for a given alloy system. The rate of peritectic transformation in Eq.(8) depends on the concentration gradient 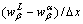 through the peritectic β envelope. Fig.8 shows the concentration profiles of α dendrite and interdendritic β envelope measured at v=50 μm/s. It is clearly found that the slope of line for tube with 3 mm/7 mm in dI/dO is larger than that in 1.8 mm-diameter cylinder. Consequently, the concentration gradient through the β envelope in the large-diameter sample becomes steep, leading to a higher rate of peritectic transformation from α to β and dissolution of the thin α dendrite.
through the peritectic β envelope. Fig.8 shows the concentration profiles of α dendrite and interdendritic β envelope measured at v=50 μm/s. It is clearly found that the slope of line for tube with 3 mm/7 mm in dI/dO is larger than that in 1.8 mm-diameter cylinder. Consequently, the concentration gradient through the β envelope in the large-diameter sample becomes steep, leading to a higher rate of peritectic transformation from α to β and dissolution of the thin α dendrite.
Fig.9 illustrates schematically the dissolution of thin α dendrites. In Figs.9(a) and (b), only dendrite Ⅱ disappears in the sample with small diameter, where the melt convection is weak. In the larger-diameter sample, the melt convection is so strong that dendrites Ⅰ and Ⅱ in Fig.9(c) are both dissolved, as shown in Fig.9(d), due to the high rate of peritectic reaction and transformation. As a result, the PDAS becomes large with increasing diameter of the sample, which is in agreement with the experimental observation, as shown in Fig.3.
Accordingly, the volume fraction of α dendrite will be lower in large-diameter sample than that in small- diameter sample resulting from dissolution of thin α
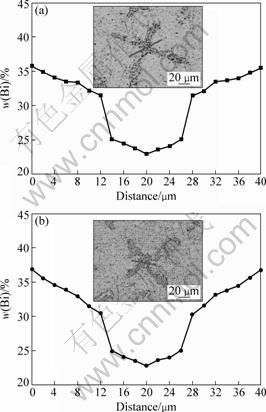
Fig.8 Distribution of Bi mass fraction in dendrite stem and inter-dendritic region at v=50 μm/s: (a) d=1.8 mm; (b) dI/dO=3 mm/7 mm (Inserts showing micrographs of samples)

Fig.9 Schematic diagram of dissolution of thin α dendrites in samples with small or large diameter: (a), (b) Small-diameter sample with weak melt convection; (c), (d) Large-diameter sample with strong melt convection
dendrite. As illustrated in Fig.10, a reduction of the α dendrite volume fraction is observed with increasing sample diameter. The tendency is consistent with the dissolution of thin α dendrite in larger-diameter sample.
Generally, there could be two factors governing the PDAS in samples with different diameters for peritectic solidification. One is the macrosegregation, which tends to increasing the PDAS with increasing sample diameter. The other is the influence of melt convection on peritectic transformation, resulting in increase of PDAS with increase in melt convection. The combined effect of these two factors leads the PDAS of primary α phase to
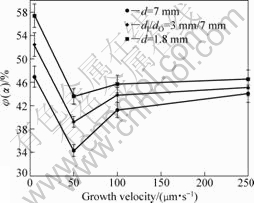
Fig.10 α dendrite volume fraction vs growth velocity
increase with enhancing melt convection due to increasing sample diameter.
4 Conclusions
1) The effect of melt convection on the PDAS of primary α phase during directional solidification of Pb-26%Bi hypo-peritectic alloy was investigated experimentally with samples with different diameters. The measured PDAS increases with increasing diameter of sample.
2) For the large-diameter sample, the strong melt convection gives rises to the enhancement of the solute diffusion and the reduction of the solute boundary layer which favors the peritectic transformation, and results in thin α dendrites dissolution and increase in the PDAS of primary α phase in Pb-26%Bi hypo-peritectic alloy.
3) In the large-diameter sample, the macrosegregation leads to a higher bulk alloy composition, which would cause λ1 to increase. Thus, an increase in PDAS should be observed with increasing sample diameter.
References
[1] KERR H W, KURZ W. Solidification of peritectic alloys [J]. Inter Mater Rev, 1996, 41(4): 129-164.
[2] TRIVEDI R, PARK J S. Dynamics of microstructure formation in the two-phase region of peritectic systems [J]. J Crystal Growth, 2002, 235: 572-588.
[3] TRIVEDI R, SHIN J H. Modelling of microstructure evolution in peritectic systems [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 413-414: 288-295.
[4] HU Xiao-wu, LI Shuang-ming, LIU Lin, FU Heng-zhi. Microstructure evolution of directionally solidified Sn-16%Sb hyperperitectic alloy [J]. China Foundry, 2008, 5: 167-171.
[5] LIU S, TRIVEDI R. Effect of thermosolutal convection on microstructure formation in the Pb-Bi peritectic system [J]. Metall Trans A, 2006, 37: 3293-3304.
[6] LOGRASSO T A, FUH B C, TRIVEDI R. Phase selection during directional solidification of peritectic alloys [J]. Metall Trans A, 2005, 36: 1287-1300.
[7] MA D, LI Y, NG S C, JONES H. Unidirectional solidification of Zn-rich Zn-Cu peritectic alloys-Ⅱ. Microstructural length scales [J]. Acta Mater, 2000, 48: 1741-1751.
[8] SU Yun-peng, WANG Meng, LIN Xin, HUANG Wei-dong. Researches on lamellar structures in the unidirectional solidification Zn-2wt.%Cu peritectic alloy [J]. Mater Lett, 2004, 58: 2670-2674.
[9] XU W, MA D, FENG Y P, LI Y. Observation of lamellar structure in a Zn-rich Zn-6.3at.%Ag hyper-peritectic alloy processed by rapid solidification [J]. Scripta Mater, 2001, 44: 631-636.
[10] SU Yan-qing, LIU Chang, LI Xin-zhong, GUO Jing-jie, LI Bang-sheng, JIA Jun, FU Heng-zhi. Microstructure selection during the directionally peritectic solidification of Ti-Al binary system [J]. Intermetallics, 2005, 13: 267-274.
[11] LEE J H, VERHOEVEN J D. Peritectic formation in the Ni-Al system [J]. J Crystal Growth, 1994, 144: 353-366.
[12] RAO Qun-li, FAN Xiao-lan, SHU Da, WU C C. In-situ XRD study on the peritectic reaction of YBCO thin film on MgO substrate [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2008, 461: L29-L33.
[13] ZHONG Hong, LI Shuang-ming, LV Hai-yan, LIU Lin, ZOU Guang-rong, FU Heng-zhi. Microstructure evolution of peritectic Nd14Fe79B7 alloy during directional solidification [J]. J Crystal Growth, 2008, 310: 3366-3371.
[14] SU Yan-qing, GUO Jing-jie, LI Xin-zhong, LI Shuang-ming, ZHONG Hong, LIU Lin, FU Heng-zhi. Peritectic reaction and its influences on the microstructures evolution during directional solidification of Fe-Ni alloys [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2008, 461: 121-127.
[15] LUO Liang-shun, SU Yan-qing, LI Xin-zhong, GUO Jing-jie, YANG H M, FU Heng-zhi. Producing well aligned in situ composites in peritectic systems by directional solidification [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92: 061903-1-3.
[16] FU J W, YANG Y S, GUO J J, MA J C, TONG W H. Formation of a two-phase microstructure in Fe-Cr-Ni alloy during directional solidification [J]. J Crystal Growth, 2008, 311: 132-136.
[17] MA D, XU W, NG S C, LI Y. On secondary dendrite arm coarsening in peritectic solidification [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2005, 390: 52-62.
[18] ZHONG Hong, LI Shuang-ming, LIU Lin, LV Hai-yan, ZOU Guang-rong, FU Heng-zhi. Secondary dendrite arm coarsening and peritectic reaction in NdFeB alloys [J]. J Crystal Growth, 2008, 311: 420-424.
[19] BISWAS K, HERMANN R, WENDROCK H, PRIEDE J, GERBETH G, BUECHNER B. Effect of melt convection on the secondary dendritic arm spacing in peritectic Nd-Fe-B alloy [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2009, 480: 295-298.
[20] LI Shuang-ming, JIANG Bin-lun, MA Bo-le, FU Heng-zhi. Halo formation in directional solidification of Ni-Ni3Nb hypereutectic alloy [J]. J Crystal Growth, 2007, 299: 178-183.
[21] KOHLER F, GERMOND L, WAGNIERE J D, RAPPAZ M. Peritectic solidification of Cu-Sn alloys: Microstructural competition at low speed [J]. Acta Mater, 2009, 57: 56-68.
[22] HUNT J D. Solidification and casting of metals [M]. London: The Metals Society, 1979.
[23] KARMA A, RAPPEL W-J, FUH B C, TRIVEDI R. Model of banding in diffusive and convective regimes during directional solidification of peritectic systems [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 1998, 29: 1457-1470.
[24] McCARTNEY D G, HUNT J D. Measurements of cell and primary dendrite arm spacings in directionally solidified aluminium alloys [J]. Acta Metall, 1981, 29: 1851-1863.
[25] TRIVEDI R, SOMBOONSUK K. Constrained dendritic growth and spacing [J]. Mater Sci Eng, 1984, 65: 65-74.
[26] WAGNER C. The evaluation of data obtained with diffusion couples of binary single-phase and multiphase systems [J]. Acta Metall, 1969, 17: 99-107.
熔体对流对Pb-26%Bi亚包晶合金定向凝固初生相的一次枝晶间距的影响
胡小武,李双明,高思峰,刘 林,傅恒志
西北工业大学 凝固技术国家重点实验室,西安 710072
摘 要:测量不同直径管中Pb-26%Bi(质量分数)亚包晶合金定向凝固试样的初生α相的一次枝晶间距,考察熔体对流对初生α相一次枝晶间距的影响。结果表明:一次枝晶间距随着试样直径的增大而增大。在凝固速度5 μm/s,直径1.8 mm的试样中的初生α相的一次枝晶间距为161.5 μm,而在直径为7 mm的试样中则增大到240.4 μm。大直径试样中的熔体强对流将促进有效溶质扩散,加快包晶反应和包晶转变导致细小的α枝晶溶解,从而使得初生α相的一次枝晶间距增大。
关键词:Pb-26%Bi;亚包晶合金;一次枝晶间距;熔体对对流;定向凝固
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Project(50395100) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(NCET-07-0692) supported by the New Century Talents Program of the Ministry of Education, China; Project(34-TP-2009) supported by Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, China
Corresponding author: LI Shuang-ming; Tel: +86-29-88493264; Fax: +86-29-88492227; E-mail: lsm@nwpu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60679-1