J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. (2011) 18: 1321-1325
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-011-0840-1
Effect of TiO2 addition on zirconia-mullite composites fabricated by in-situ controlled crystallization of Si-Al-Zr-O amorphous bulk
LIANG Shu-quan(梁叔全), LIU Rong(刘荣), TAN Xiao-ping(谭小平), GUAN Di-kai(官迪凯)
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
? Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2011
Abstract: Zirconia-mullite composite ceramics were fabricated by in-situ controlled crystallization of Si-Al-Zr-O amorphous bulk. The effects of TiO2 addition on the fabrication of zirconia-mullite composites were investigated. The ultra-fine zirconia-mullite composite ceramics were prepared from the amorphous bulk treated at 980 °C for nucleation and 1 140 °C for crystallization. The phase transformation of the ceramics was examined using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffractometry (XRD). The microstructural features of the samples were evaluated with scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDX) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The mechanical properties were also determined using Vickers indentation. The results show that the TiO2 additives with mass fraction of 1%-7% reduce the formation temperature of t-ZrO2 and mullite. When the mass fraction of TiO2 additives is less than 5%, the phases do not change, and most of TiO2 dissolves in ZrO2. When the mass fraction of TiO2 additives is over 5%, the excessive TiO2 forms a new phase, ZrTiO4. Meanwhile, the results also show that TiO2 additives have a great impact on the microstructure and mechanical properties of zirconia-mullite composites. As the TiO2 content increases from 1% to 7% (mass fraction), the grain size and the Vickers hardness of zirconia-mullite composites increase. The composite with 3% (mass fraction) TiO2 additives attains relatively higher fracture toughness.
Key words: TiO2; ZrO2; mullite; comoposites
1 Introduction
Zirconia-mullite composites are important structural ceramic materials. These composites have better corrosion resistance, larger strength and toughness than mullite. Zirconia-mullite composites are promising candidates for application requiring high strength, toughness, wear resistance and thermal-shock resistance [1-4]. Different processing routes to prepare zirconia-mullite composites have been reported [5-8]. Also different effective additives have been reported to improve the mechanical properties of zirconia-mullite ceramics [9-13], such as SiC and Nb2O5. As known, TiO2 is one of the most effective additives to improve sintering behavior in zirconia-mullite composites. However, the studies on producing zirconia ceramics prepared by in-situ controlled crystallization of Si-Al-Zr-O amorphous bulk with TiO2 additives are rare.
In previous works [13-14], ultra-fine zirconia- mullite composites were prepared by in-situ controlled crystallization of Si-Al-Zr-O amporphous bulk. Higher densification can be obtained using this technology, which is hard to be achieved by nano-sized powder sintering. Therefore, this work primarily focuses on the effects of TiO2 additive on the phase transition, microstructure and mechanical properties of zirconia- mullite ceramics prepared by in-situ controlled cryllization.
2 Experimental
2.1 Preparation of samples
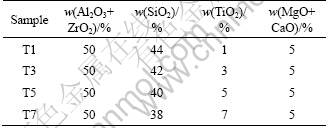
The composition of the raw materials was given in Table 1. The raw materials were mixed and homogenized by conventional ball milling with zirconia balls for 4 h. Then 20 g mixed powder was put into an Al2O3 crucible and heated in air at 1 620-1 700 °C for 2-4 h in an electric furnace. The homogeneous flux was thereafter poured into a stainless mold and cooled with air to produce amorphous bulks. Afterward, the as-prepared amorphous bulks were first treated at 980 °C for nucleation, and then treated at 1 140 °C for crystallization to obtain nano-composite zirconia-toughened mullite ceramics. According to the different titania mass fraction, samples were nominated as T1 (1%), T3 (3%), T5 (5%) and T7 (7%), respectively.
2.2 Characterization of samples
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC, Model 409PC, NETZSCH, German) was carried out in argon within a temperature range between 1 00 °C and 1 300 °C with a heating rate of 10 °C/min. Ultra-fine α-Al2O3 powder was served as the reference substance. Non- crystalline samples were crushed and ground in agate mortar, and then 75 μm (200 mesh) sieve was used for screening.
Table 1 Composition of TiO2-containing ceramics
X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD, D/max2000, Japan) was performed with a graphite monochromatic Cu Kα radiator operating at 30 kV and 40 mA. X-ray diffraction patterns were acquired in a 5°-80° (2θ) range, with a step size of 0.02° (2θ) and a counting time of 10 s.
The microstructure of samples was observed using ?eld-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, Sirion 200s, USA) operating at 30 kV. Samples were ?rst etched with diluted HF solutions for 3 min, and subsequently washed with distilled water. Tecnai G2 20S-TWIN transmission electron microscope (TEM) was also used to examine the crystallization status.
Fracture toughness (KIC) of the ceramics was measured using a Vikers hardness tester and the following formula [15] with a Vickers indentor. The load is 98 N and the holding time is 15 s.
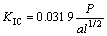 (1)
(1)
where P is the indentation force (N), c is the crack length (m), a is the half length of the diagonal (m), l=c-a, as described in Fig.1.
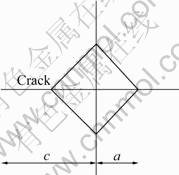
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of fracture toughness measurement
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Phase formation during heating process
Figure 2 shows the DSC results of samples T1, T3, T5 and T7. In Fig.2, two peaks were observed. The first exothermic peak appeared at around 900-1 050 °C. The second exothermic peak originated at around 1 140- 1 200 °C. Based on the former research results [14], the ?rst exothermic peak corresponded to the crystallization of t-ZrO2 and mullite from the amorphous. The second peak was associated with the further precipitation of mullite and the formation of cristobalite. With the increase of TiO2 additives (1%-5%, mass fraction), the temperature of the first exothermic peak decreased significantly (Fig.2). When w(TiO2) was more than 5%, the temperature change was not obvious. It was shown that the TiO2 additives with mass fraction of 1%-7% reduced the formation temperature of t-ZrO2 and mullite, while it had little effect on the precipitation of other phases.
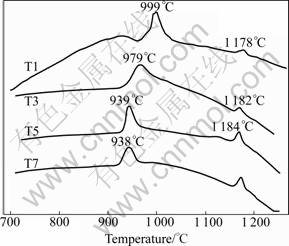
Fig.2 DSC results of a series of composites with increasing TiO2 content
Figure 3 displays the XRD patterns of T1 samples treated at different temperatures. t-ZrO2 and mullite were precipitated initially when heat treated at 980 °C, which was similar to the reports by SCH?LLER [16] and COMER [17]. The main phases were t-ZrO2, mullite and SiO2, which were consistent with the sample without TiO2 additives [14].

Fig.3 XRD patterns of T1 samples treated at different temperatures: (a) Amorphous; (b) 980 °C; (c) 980 °C/1 140 °C
Figure 4 illustrates the X-ray diffraction patterns of samples with different TiO2 additives. The samples were firstly treated at 980 °C for nucleation, and then treated at 1 140 °C for crystallization. According to the XRD patterns, three main crystalline phases, ZrO2, mullite and cristobalite, were detected in all samples, which were the same as the undoped samples [14]. TiO2 additives did not affect the precipitation of the main crystal phases. With the TiO2 additives increasing, a small amount of cordierite and ZrTiO4 phase were formed, while the cristobalite phase decreased. This may be due to the new cordierite phase generated by the reaction between SiO2 and MgO, or due to more mullite precipitated.
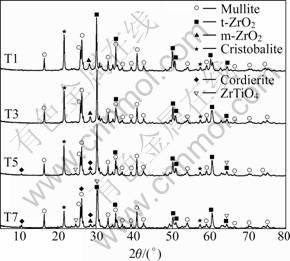
Fig.4 XRD patterns of composites with increasing TiO2 content
3.2 Microstructure characterization of TiO2- containing composites
Figure 5 shows the TEM image of T7 sample, and Fig.6 shows EDS analysis diagrams of A, B and C particles indicated in Fig.5. EDS analysis of A point showed that this region was basically composed of Zr, Ti and O, and the proportion of Zr was approximately equal to Ti. Combined with the XRD analysis, it could be inferred that A particle was ZrTiO4. B particle also consisted of three elements, but the proportion of Zr was almost six times higher than Ti. Hence, it could be inferred that most of TiO2 were dissolved into ZrO2 grains. C particle was mainly composed of Al, Si, O, and a small amount of Ti. Combined with the XRD analysis, it could be inferred that a small amount of TiO2 was dissolved in mullite grains.

Fig.5 Typical TEM image of T7
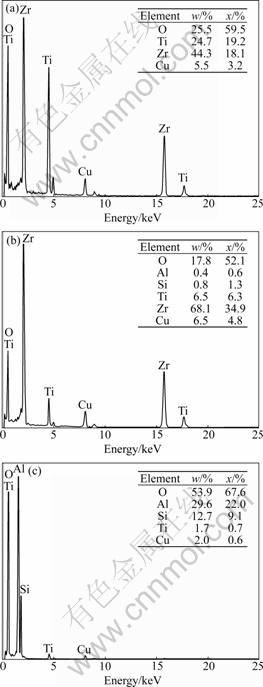
Fig.6 EDS analysis diagrams of ZrTiO4 phase (a), ZrO2 phase (b) and mullite phase (c)
Figures 7 (a)-(d) display the SEM micrographs of the polished and etched surfaces of zirconia-mullite composites with 1%, 3%, 5% and 7% (mass fraction) TiO2. The samples were firstly treated at 980 °C for nucleation, and then treated at 1 140 °C for crystallization. It could be seen from Fig.7 that the grain morphology appeared to be a mixture of near-spherical and lath-like. With more TiO2 additives, grains tended to increase obviously. According to the TEM observation and EDS analysis, lath-like particles were supposed to be mullite and near-spherical particles were ZrO2 phase, which indicated that, in varying degrees, TiO2 additives promoted the growth of mullite and ZrO2 grains. The similar behavior has been reported by HONG and MESSING [18-19].
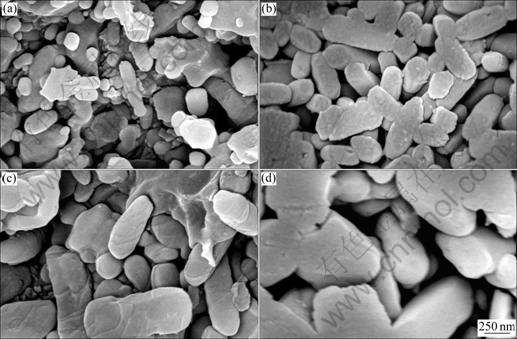
Fig.7 Typical SEM micrographs of samples T1 (a), T3 (b), T5 (c) and T7 (d)
3.3 Mechanical properties
The Vickers hardness and fracture toughness of the composites are shown in Fig.8. The hardness increased with the content of TiO2 increasing. The reason for this was that TiO2 reduced the formation temperature of t-ZrO2 and mullite, and more t-ZrO2 and mullite phase were precipitated with the TiO2 content increasing. While the fracture toughness exhibited a slight increase firstly and then decreased when the mass fraction of TiO2 additives was more than 3%. The reasons were as follows: When TiO2 additives were less than 3%, the main phase grains became more and more complete and the grain size increased. However, when the content of TiO2 was more than 3%, some new phases, like ZrTiO4 phase and cordierite phase, were started to precipitate, which were much different with the matrix and generated high stress concentration. The stress concentration accelerated the crack growth, which decreased the fracture toughness of composites.

Fig.8 Mechanical properties of T1, T3, T5 and T7
4 Conclusions
1) When the mass fraction of TiO2 additives is less than 5%, most of TiO2 particles are dissolved into ZrO2, and a small amount of TiO2 is dissolved into mullite grains; when the mass fraction of TiO2 additives is more than 5%, the excessive TiO2 form a new phase, ZrTiO4. Meanwhile, with TiO2 additives increasing, a small amount of cordierite phase is also formed, while cristobalite phase decreases.
2) The TiO2 additives with mass fraction of 1%-7% reduce the formation temperature of t-ZrO2 and mullite, and promote the growth of mullite and ZrO2 grains.
3) With the increasing content of TiO2, the hardness increases, but the fracture toughness exhibits a slight increase at first when the mass fraction of TiO2 is less than 5% and then decreases.
References
[1] SCHINEIDER H, SCHREUER J, HILDMANN B. Structure and properties of mullite—A review [J]. Am Ceram Soc, 2008, 28(2): 329-344.
[2] MEDVEDOVSKI E. Alumina-mullite ceramics for structural applications [J]. Ceramics International, 2006, 32(4): 369-375.
[3] LAN F T, LI K Z, LI H J, FU Q G. A cordierite mullite anti-oxidation coating for carbon composite [J]. Carbon, 2007, 45(13): 2692-2716.
[4] ZHANG H Y, MALJKOVIC N, MITCHELL B S. Structure and interfacial properties of nanocrystalline alumina/mullite composites [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 326(2): 317-323.
[5] GARRIDO L B, AGLIETTI E F. Reaction-sintered mullite-zirconia composites by colloidal processing of alumina-zircon-CeO2 mixtures [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 369(1/2): 250-257.
[6] GARRIDO L B, AGLIETTI E F, MARTORELLO L, CAMERUCCI M A, CAVALIERI A L. Hardness and fracture toughness of mullite–zirconia composites obtained by slip casting [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 419(1/2): 290-296.
[7] ANANTHAKUMAR S, JAYASANKAR M, WARRIER K G K. Microstructural, mechanical and thermal characterization of sol-gel derived aluminium titanate-mullite ceramic composites [J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(11): 2965-2973.
[8] KHOR K A, YU L G, LI Y. Spark plasma reaction sintering of ZrO2-mullite composites from plasma spheroidized zircon/alumina powers [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, 339(1/2): 286-296.
[9] EBADZADEH T, GHASEMI E. Effect of TiO2 addition on the stability of t-ZrO2 in mullite-ZrO2 composites prepared from various starting materials [J]. Ceram int, 2002, 28(4): 447-450.
[10] HONG J S, HUANG X X, GUO J K, LI B S, GUI L H. Strengthening and toughening of mullite ceramics by SiC particles and Y-TZP [J]. J Inorg Mater, 1990, 5(4): 340-345.
[11] WANG J, KOU H M, L X J, PAN Y B, GUO J K. Reinforcement of mullite matrix with multi-walled carbon nanotubes [J]. Ceram int, 2007, 33(5): 719-722.
[12] JIN X H, GAO L, KAN Y M, CHEN Y R, YUAN Q M. Influence of Nb2O5 on the mechanical performances and toughening mechanism of ZrO2 in ZTM-Al2O3 [J]. J Inorg Mater, 2000, 15(6): 1009-1014.
[13] HUANG Y F, XIE G S, XIAO H N. The influence of CeO2 in ZTM ceramics prepared by in-situ sintering [J]. Ceramics, 2006(6): 9-11. (in Chinese)
[14] LIANG S Q, LI SQ, TAN X P. Crystallization behavior of Si-Al-Zr-O amorphous bulk with higher zirconium [J]. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2005, 15(8): 1189-1194. (in Chinese)
[15] PONTON C B, RAWLINGS R D. Mechanical properties of siliceramic glass-ceramics [J]. Mater Sci Tech, 1989, 5(9): 865-872.
[16] SCHULLER K H. Reaction between mullite and glassy phase in porcelains [J]. Br Ceram Soc, 1964, 63(2): 103-117.
[17] COMER J J. Electron microscopy studies of mullite development in ?red kaolinites [J]. Am Ceram Soc, 1960, 43(7): 378-384.
[18] HONG S H, MESSING G L. Mullite transformation kinetics in P2O5-, TiO2- and B2O3-doped aluminosilicate gels [J]. Am Ceram Soc, 1997, 80(6): 1551-1559.
[19] HONG S H, MESSING G L. Anisotropic grain growth in diphasic-gel-derived titania-doped mullite [J]. Am Ceram Soc, 1998, 81(5): 1269-1277.
(Edited by HE Yun-bin)
Foundation item: Project(50721003) supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China for Creative Research Group
Received date: 2010-09-13; Accepted date: 2011-03-01
Corresponding author: LIANG Shu-quan, Professor, PhD; Tel: +86-731-88876691; E-mail: sqliang@mail.csu.edu.cn