DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.10.022
无线传感器网络中基于稀疏投影的数据收集方案
李鹏1, 2,王建新1
(1. 中南大学 信息科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 湖南中医药大学 管理与信息工程学院,湖南 长沙,410208)
摘要:考虑到现有的基于压缩感知的数据收集方法大多采用密集投影来收集节点的数据,导致数据传输代价过高、节点能耗过快缩短了网络生命周期,提出一种基于稀疏投影的数据收集方案(DGSP)。其步骤为:首先,设计一种基于最小化传输开销的稀疏投影矩阵用于节点数据采样,并利用亚高斯分布的尾部有界性证明其RIP性质;然后,以网络负载均衡和网络生命周期最大化为目标来构建数据收集树,并将树中节点的下一跳选择问题建模成半匹配问题;最后,提出改进的Hungarian算法在多项式时间内解决它。仿真结果表明:相比于目前典型的CDG,EDCA和MTT方案而言,DGSP的数据重构误差、能耗和延时等更低。
关键词:无线传感器网络;数据收集;压缩感知;稀疏投影;半匹配;能耗
中图分类号: TP393 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)10-3445-09
Data gathering scheme based on sparse projection in wireless sensor networks
LI Peng1, 2, WANG Jianxin1
(1. School of Information Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Management and Information Engineering, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China)
Abstract: Considering that the existing data gathering schemes based on compressive sensing usually use the dense projection to achieve the sensor readings, which results in the higher transmission cost and the larger energy consumption, and thus shortens the lifetime of network, a data gathering scheme based on the sparse projection (DGSP) was proposed. The procedures were as follows. Firstly, the sparse projection matrix based on the minimization of the transmission overhead was designed for the sampling at the nodes, and the nature of its RIP was proved by the sub-Gaussian distribution tail roundedness. A data gathering tree was then constructed based on the load balancing of network and the maximum lifetime of network, and the next hop selection problem of the nodes was modeled into the semi-matching problem. An improved Hungarian algorithm was finally proposed to solve it in the polynomial time. The simulation results show that, compared with the CDG, EDCA and MTT schemes, the data reconstruction error, energy consumption and delay of DGSP are lower.
Key words: wireless sensor networks; data gathering; compressive sensing; sparse projection; semi-matching; energy consumption
无线传感器网络(wireless sensor networks, WSN)是近年来国内外广泛关注的研究热点[1-2]。无线传感器网络在工作过程中,节点会不断地感知和采集周边物理环境的数据,并将通过无线天线将数据以多跳的方式发送给远方的Sink节点(或称为基站)进行处理,即进行数据收集[3]。由于节点只有有限的能量以及有限的存储、计算和通信能力,如何有效地解决网络负载失衡、数据收集延时较大等问题,以使网络能长时间地工作并满足数据收集的应用需求,是目前数据收集中面临的主要问题[4-5]。压缩感知[6] (compressive sensing, CS)也被称为压缩采样或稀疏采样,是一种利用稀疏的或可压缩的信号进行信号重建的技术。基于压缩感知的数据收集方法能够节省传统采样方式前期所需的存储空间和计算资源,而将上述资源用于后期的恢复算法中,因此,将压缩感知技术应用到数据收集中具有重要意义。CHENG等[7]提出一种基于矩阵完成技术的数据收集方案EDCA。该方案首先随机地选择部分节点来进行数据采样和编码并将其结果直接传到Sink,然后Sink基于核范数优化技术进行数据的重构。XIE等[8]提出一种基于最小化传输次数的数据收集方案MTT。该方法认为用于进行压缩采样的投影矩阵中经常包含很多零值,为了节省传输开销,只需要选择节点中的那些投影向量为非零值(即自身有数据需要传输)的轮次来建立路由路径,实现数据收集,并构建一颗具有最小化总传输次数的数据收集树,通过一种启发式算法予以解决。然而,该方案假定数据每次传输开销为1,这与真实应用场景不相符,方案的局限性较大。CHUN 等[9]基于压缩感知技术研究了在数据收集过程中对传感器节点进行投影操作时,如何在节点的单位能量消耗下最大化信息增益,并提出了3种启发式算法予以解决。刘卉等[10]提出一种基于投影矢量的双组播树高效路由数据收集,该算法将贝叶斯压缩感知理论与传感器路由相结合,解决了现有算法不能满足传感器对能耗敏感的问题。SAEED等[11]提出利用人工智能技术来建立数据融合树以最大化基于压缩感知进行数据融合带来的优点,进而延长传感器网络的生命周期,降低传输延时。LUO等[12]提出了CDG方案用于大规模无线传感器网络中的数据收集,首先设计了1种分块的投影矩阵来采集节点数据,然后Sink节点基于最短路径树来收集各个节点得到的投影值,节省了传输开销,取得了较高的数据重构精度。然而,总体来说,以上基于压缩感知的数据收集方法采用密集投影矩阵进行节点数据的采样,没有考虑如何将投影矩阵设计与无线传感器网络特性相结合以节省网络能耗,从而导致数据收集的能耗较高,缩短了网络的生命周期。为此,本文作者提出一种基于稀疏投影的数据收集方案(DGSP)。结合无线传感器网络的传输特性,分析投影操作与数据稀疏程度的关系,设计一种基于最小化传输开销的稀疏投影矩阵,并利用亚高斯分布的尾部有界性证明其RIP性质,然后以网络负载均衡和网络生命周期最大化为目标构建数据收集树,并将树中节点的下一跳选择问题建模成半匹配问题,最后提出改进的Hungarian算法在多项式时间内解决此问题。
1 问题建模
1.1 网络模型
设N个传感器节点随机地分布在1个面积为N×N的正方形区域内。整个传感器网络组成1个连通的无向图G(V,E)(其中,V为传感器节点集合,V={V1,V2,…,VN},|V|=N+1;E为图G中边的集合,若2个传感器节点Vi和Vj相互处于对方的通信半径内,则(Vi,Vj)∈E)。为了使算法具有可扩展性,节点不需要知道自己的位置信息,只要求节点知道自己的邻居信息,这可以很容易地通过相互交换1个“Hello”消息来实现[13]。此外,网络具有如下性质。
1) 网络是连通的静态网络,传感器节点和Sink部署后不再移动,Sink位于网络的中心,节点的传输半径相等。
2) 节点的初始能量是异构的,而且不能补充,网络中节点采用的能量消耗模型如下:
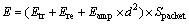 (1)
(1)
其中:Etr和Ere分别为发送数据和接收数据消耗的能量;Eamp为多路衰减模型的功率放大系数;d为源节点到目标节点的距离;Spacket为数据包的大小。所有节点使用相同的发射功率和接收功率。
1.2 相关定义
为了描述方便,现给出本文中用到的相关定义。
定义1:RIP(restricted isometry property)性质[6]。对于任意的信号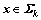 (
(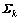 表示k稀疏向量集合),若存在常数
表示k稀疏向量集合),若存在常数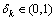 ,则有下面的不等式成立:
,则有下面的不等式成立:
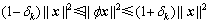 (2)
(2)
称矩阵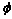 满足k阶RIP性质。
满足k阶RIP性质。
定义2:亚高斯分布[14]。给定任意的随机变量θ,若存在1个常数c>0,使得对于任意的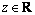 ,有下面不等式成立:
,有下面不等式成立:
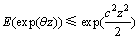 (3)
(3)
则称该随机变量θ服从亚高斯分布。
定义3:节点的生命周期(轮)。任一节点vi在1颗树T中存活的轮数为
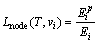 (4)
(4)
式中: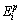 为节点vi当前的初始能量;Ei为节点vi在1轮数据收集中消耗的能量。
为节点vi当前的初始能量;Ei为节点vi在1轮数据收集中消耗的能量。
定义4:树的生命周期(轮)。指树T中第1个节点vi死亡时,该节点已经进行数据收集的轮数:
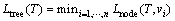 (5)
(5)
定义5:二分图匹配。给定1个二分图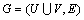 ,其中
,其中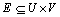 。若在图G中存在1个边集
。若在图G中存在1个边集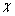 (
( ),使得
),使得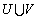 中的每个节点至多是
中的每个节点至多是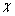 中1条边的端点,即U中的每个节点至多与V中的1个节点匹配,反之亦然,则称
中1条边的端点,即U中的每个节点至多与V中的1个节点匹配,反之亦然,则称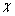 属于二分图匹配。
属于二分图匹配。
定义6:半匹配[15]。给定1个二分图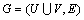 ,其中
,其中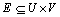 。若在图G中存在1个边集
。若在图G中存在1个边集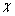 (
( ),使得U中的每个节点仅仅是
),使得U中的每个节点仅仅是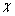 中1条边的端点,则称
中1条边的端点,则称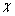 属于半匹配。
属于半匹配。
1.3 问题描述
无线传感器网络一般部署在比较危险或人类很难进入的区域,传感器节点往往是无法替换的,因此,希望网络能工作尽可能长时间。已有研究表明[16],基于压缩感知的数据收集方法能实现网络负载均衡,降低数据传输开销,进而延长网络生命周期。依据1.1节中的网络模型,基于压缩感知进行数据收集的基本过程为:设所有节点的原始数据表示为N×1的列向量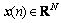 。由于网络数据的时空相关性,x在
。由于网络数据的时空相关性,x在
某一变换基Ψ上可被稀疏表示为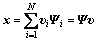 ,然后采用1个与Ψ不相关的测量矩阵
,然后采用1个与Ψ不相关的测量矩阵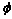
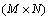 对x进行测量,得到
对x进行测量,得到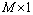 的测量值
的测量值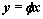 ,最后,当Sink节点收到M个测量值y后,通过求解l1范数最小化问题就能精确地重构出x,如图1所示。
,最后,当Sink节点收到M个测量值y后,通过求解l1范数最小化问题就能精确地重构出x,如图1所示。
综上所述,本文研究的问题是:如何设计一种基于传输开销最小化的稀疏投影矩阵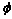 来收集各个节点的数据,并结合
来收集各个节点的数据,并结合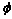 的设计来建立1颗优化的数据收集树T,从而实现数据收集的高精确度与网络生命周期的最大化。
的设计来建立1颗优化的数据收集树T,从而实现数据收集的高精确度与网络生命周期的最大化。
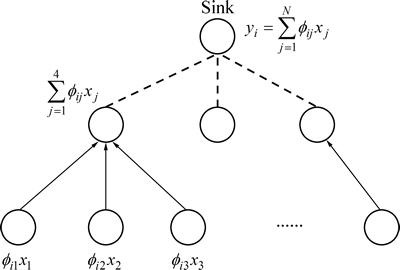
图1 基于压缩感知的数据收集
Fig. 1 Data gathering based on compressive sensing
2 稀疏投影矩阵设计
2.1 主要思路
在无线传感器网络中,目前大多数基于压缩感知的数据收集方法都采用密集投影矩阵,如随机高斯矩阵、以随机±1为原始构成的Rademacher矩阵等,这些矩阵与大多数固定正交基构成的矩阵不相关,因此,很容易满足RIP性质,成为目前投影矩阵的首选。然而,事实上,在无线传感器网络中,由于节点采集到的大量数据是稀疏的,节点之间的数据具有相关性,因此,密集投影并不是必需的,它会带来巨大的计算开销和传输开销,浪费了节点的能量[17]。为此,本文设计一种基于最小化传输开销的投影矩阵,该矩阵在满足RIP性质的前提下,能够使网络传输的能量开销最小。
稀疏投影矩阵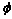 的设计原则为:不只是要满足RIP原则,还需结合无线传感器网络的特性来尽可能地降低网络通信开销。依据该原则,网络中用于节点数据采样的稀疏投影矩阵为
的设计原则为:不只是要满足RIP原则,还需结合无线传感器网络的特性来尽可能地降低网络通信开销。依据该原则,网络中用于节点数据采样的稀疏投影矩阵为
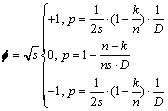 (6)
(6)
根据式(6),每个传感器节点得到的投影向量只包含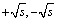 和0。式(6)中,0表示在该次投影处理中该节点自身没有数据需要传输,p为概率;
和0。式(6)中,0表示在该次投影处理中该节点自身没有数据需要传输,p为概率;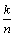 为节点上的数据稀疏程度,数据的稀疏程度越高(即
为节点上的数据稀疏程度,数据的稀疏程度越高(即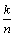 越小),则为了保证数据重构的精度,就要求投影矩阵中的非零值越多。另外,投影矩阵的稀疏程度还与节点本身的度D有关,节点的度越大,表明节点在其通信范围内拥有更多的邻居。依据空间相关性可知,这样的节点在1轮数据收集中可以尽量少地参与投影操作,因为它的数据可以由邻居节点的相关数据来表示。总的来说,对于1个
越小),则为了保证数据重构的精度,就要求投影矩阵中的非零值越多。另外,投影矩阵的稀疏程度还与节点本身的度D有关,节点的度越大,表明节点在其通信范围内拥有更多的邻居。依据空间相关性可知,这样的节点在1轮数据收集中可以尽量少地参与投影操作,因为它的数据可以由邻居节点的相关数据来表示。总的来说,对于1个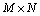 的稀疏投影矩阵
的稀疏投影矩阵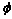 ,设s表示
,设s表示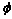 的稀疏程度,s越小、节点感知得到的数据的稀疏程度
的稀疏程度,s越小、节点感知得到的数据的稀疏程度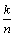 越高或者节点的度D越小,则
越高或者节点的度D越小,则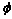 越密集,数据传输的通信代价越大,反之亦然。
越密集,数据传输的通信代价越大,反之亦然。
2.2 RIP性质证明
据压缩感知理论,以远少于Nyquist—Shanon的要求对原始数据进行采样之所以还能够实现数据精确重构的关键在于投影矩阵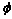 满足一定阶数的RIP性质。投影矩阵满足RIP性质的验证较困难,对于N采样的K稀疏信号需要验证
满足一定阶数的RIP性质。投影矩阵满足RIP性质的验证较困难,对于N采样的K稀疏信号需要验证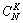 个矩阵。为了解决该问题,本文根据文献[18]和亚高斯分布的尾部有界性定理,给出验证RIP性质的方法。
个矩阵。为了解决该问题,本文根据文献[18]和亚高斯分布的尾部有界性定理,给出验证RIP性质的方法。
引理1:给定任意正整数M,N和0<δK<1,若存在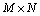 阶随机矩阵
阶随机矩阵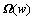 的概率分布满足如下不等式:
的概率分布满足如下不等式:

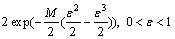 (7)
(7)
则存在常数c0>0和c1>0,使得对给定的δK和任意的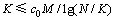 ,以超过
,以超过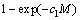 的概率使式(2)成立。
的概率使式(2)成立。
根据文献[14],本文设计的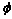 严格服从亚高斯分布,要验证
严格服从亚高斯分布,要验证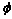 具有RIP性质,即要证明引理1成立。为此,下面首先给出亚高斯分布的尾部有界性定理:设
具有RIP性质,即要证明引理1成立。为此,下面首先给出亚高斯分布的尾部有界性定理:设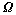 是1个
是1个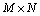 阶随机矩阵,
阶随机矩阵,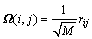 ,对任意的向量
,对任意的向量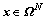 ,有如下引理。
,有如下引理。
引理2[14]:设rij为服从亚高斯投影分布且具有单位方差的随机变量,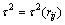 ,则对任意的
,则对任意的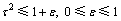 ,有
,有
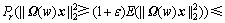
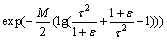 (8)
(8)
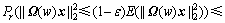
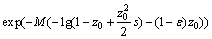 (9)
(9)
其中: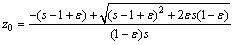 。
。
证明:下面证明式(7)的正确性。为了便于描述,设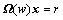 ,
,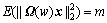 ,矩阵
,矩阵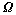 的第i行为
的第i行为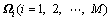 ,
,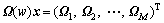 ,
,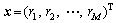 。由稀疏投影分布的零均值和单位方差可知:
。由稀疏投影分布的零均值和单位方差可知: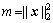 。
。
对于任意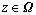 ,易证明
,易证明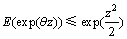 ,即
,即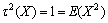 ,此时式(9)的左边可写为
,此时式(9)的左边可写为
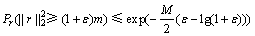 (10)
(10)
依据泰勒级数展开式,有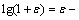
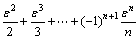 ,从而式(10)可重写为
,从而式(10)可重写为
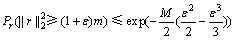 (11)
(11)
又由 的独立同分布性,有
的独立同分布性,有
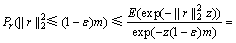
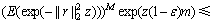
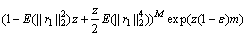 (12)
(12)
容易计算 ,且有
,且有
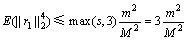 (13)
(13)
则
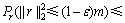
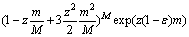 (14)
(14)
显然,当z取由式(9)定义的z0时,式(14)的右边达到最小,即

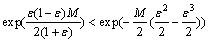 (15)
(15)
式(7)成立。证毕。
3 数据收集树
将设计的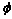 与网络能耗结合考虑,构造1颗基于稀疏投影的数据收集树,以实现网络负载均衡和网络生命周期最大化。
与网络能耗结合考虑,构造1颗基于稀疏投影的数据收集树,以实现网络负载均衡和网络生命周期最大化。
3.1 能耗分析
下面通过1个例子分析数据收集树的构造与网络生命周期的关系。数据收集树的能耗分析结果如图2所示,其中,实线表示存在通信链路,虚线表示不存在通信链路。假设传感器节点1,2,3和4的初始能量分别为2,6,4和3 J,每个节点1次传输数据和接收数据的能耗为1(见图2(a))。从图2(b)可以看到:在每轮的数据收集中,节点2从节点3和4接收数据,然后加上自身的数据向Sink转发,消耗的能量为3 J,其他节点消耗的能量为1,因此,网络的生命周期为2轮。而从图2(c)可以看到:在每轮的数据收集中,节点2每轮消耗的能量为2,其他节点为1,因此,网络的生命周期为1。可见:为节点选择最优的下一跳来实现节点数据的转发,对于节省能量、延长网络生命周期具有重要意义。
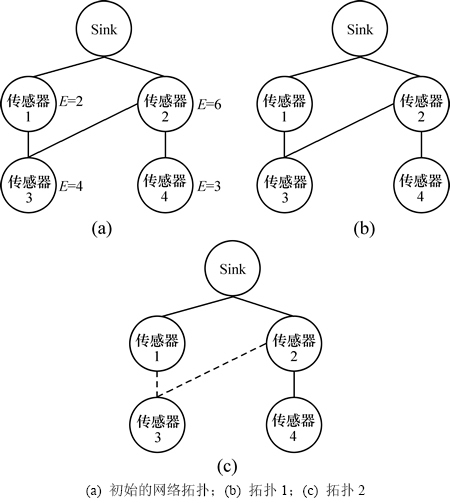
图2 数据收集树的能耗分析
Fig. 2 Energy consumption analysis of data gathering trees
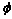 对于数据收集树构造过程中的下一跳节点选择具有重要影响,依据
对于数据收集树构造过程中的下一跳节点选择具有重要影响,依据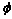 的设计,任意节点vi在1轮数据收集过程中的某次投影处理的能量消耗如下。
的设计,任意节点vi在1轮数据收集过程中的某次投影处理的能量消耗如下。
1) 若节点vi是叶子节点,且 ,则Ei=0。
,则Ei=0。
2) 若节点vi是叶子节点,且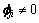 ,节点vi的父亲节点为vj,则
,节点vi的父亲节点为vj,则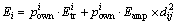 。
。
3) 若节点vi不是叶子节点,且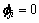 ,节点vi有μ个孩子节点,则
,节点vi有μ个孩子节点,则
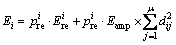
4) 若节点vi不是叶子节点,且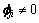 ,节点vi有μ个孩子节点,则
,节点vi有μ个孩子节点,则
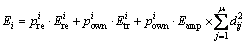
其中: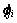 为节点vi在一轮数据收集过程中的第j次投影操作;
为节点vi在一轮数据收集过程中的第j次投影操作;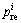 为节点i接收到的数据包大小;
为节点i接收到的数据包大小;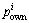 为节点i自身的数据包大小;
为节点i自身的数据包大小;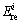 为节点i接收来自孩子节点集合1 bit数据消耗的能量总和;
为节点i接收来自孩子节点集合1 bit数据消耗的能量总和;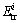 为节点i发送1 bit数据消耗的能量。由于大规模无线传感器网络中节点感知的数据具有一定的相关性,因此,并不需要在每次处理中都对节点的数据进行采集。本文设计的
为节点i发送1 bit数据消耗的能量。由于大规模无线传感器网络中节点感知的数据具有一定的相关性,因此,并不需要在每次处理中都对节点的数据进行采集。本文设计的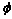 的优点在于既能减小节点能耗,又能降低传输的数据量。
的优点在于既能减小节点能耗,又能降低传输的数据量。
3.2 基于稀疏投影的数据收集(DGSP)
依据上述的能耗分析和设计的稀疏投影矩阵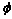 ,以实现网络负载均衡和网络生命周期最大化为目标,本文构建1颗基于稀疏投影的数据收集树,其主要步骤如下。
,以实现网络负载均衡和网络生命周期最大化为目标,本文构建1颗基于稀疏投影的数据收集树,其主要步骤如下。
算法1:基于稀疏投影的数据收集。
输入:无向连通图G(V,E),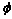 和节点的能量。
和节点的能量。
输出:数据收集树。
步骤1 初始时,图G仅包含Sink节点,从Sink节点出发将通信半径内的所有1跳邻居加入。
步骤2 从1跳邻居出发将其通信半径内的所有节点加入,迭代地执行,直到网络中的所有节点都加入到图G中,形成全连通图。
步骤3 从Sink节点出发,对图G进行广度优先遍历,得到节点访问序列: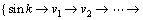
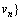 ,存入堆栈
,存入堆栈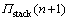 中。
中。
步骤4 从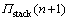 中依次取元素(即从距离Sink节点的跳数最大的节点i出发),寻找最优化传输的下一跳节点。
中依次取元素(即从距离Sink节点的跳数最大的节点i出发),寻找最优化传输的下一跳节点。
1) 若存在跳数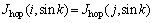 ,且节点i和j共有唯一的父节点,则比较i和j的剩余能量;若
,且节点i和j共有唯一的父节点,则比较i和j的剩余能量;若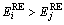 ,则删除节点j与其父节点之间的边。
,则删除节点j与其父节点之间的边。
2) 若存在跳数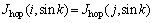 ,且节点i和j的父节点有多个父节点,根据定义6可知,该问题可以转化为经典的半匹配问题。
,且节点i和j的父节点有多个父节点,根据定义6可知,该问题可以转化为经典的半匹配问题。
3) 若不存在跳数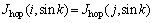 ,且节点i有多个父节点,则从父节点中选择剩余能量最多、所属的投影列向量值为0的节点作为节点i的下一跳,删除节点i与其他父节点之间的边。
,且节点i有多个父节点,则从父节点中选择剩余能量最多、所属的投影列向量值为0的节点作为节点i的下一跳,删除节点i与其他父节点之间的边。
步骤5 迭代执行步骤(4),直到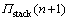 为空,当步骤(4)终止时,则得到所需的数据收集树。
为空,当步骤(4)终止时,则得到所需的数据收集树。
根据图1所示的数据收集模型,设传感器节点的原始数据可表示为向量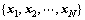 ,依据设计的投影矩阵
,依据设计的投影矩阵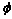 ,各个传感器节点的原始数据首先可被压缩采样表示为:
,各个传感器节点的原始数据首先可被压缩采样表示为: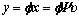 ,然后各个传感器节点将其被压缩采样后的数据沿着算法1中的数据收集树上传至Sink,Sink则依据已知的
,然后各个传感器节点将其被压缩采样后的数据沿着算法1中的数据收集树上传至Sink,Sink则依据已知的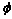 和y,采用OMP算法求解l1范数最小化问题,即可以实现对各个节点上原始数据的精确重构。
和y,采用OMP算法求解l1范数最小化问题,即可以实现对各个节点上原始数据的精确重构。
3.3 半匹配问题
如算法1中步骤4所示,当节点i和j的父节点有多个父节点时,它们的下一跳选择问题即为半匹配问题,它是二分图匹配问题的1种特例,Hungarian 算法[19]是目前求解这问题的最典型手段。然而,将Hungarian算法直接用于无线传感器网络中节点的下一跳选择时,由于算法本身的时间复杂度较高、迭代过程繁杂,会导致节点能量消耗过快。为了实现数据收集树的负载均衡和延长网络生命周期,本文提出改进的Hungarian算法用于求解节点的下一跳选择问题。
算法2:半匹配求解算法。
输入:二分图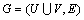 。
。
输出:半匹配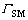 。
。
步骤1:初始时,设置队列Q={ }。
步骤2:For 每个根节点 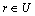 。
。
从r开始执行宽度优先搜索,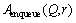
Let 
//S是宽度优先搜索中首先被访问的节点集合
Let 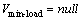
// 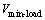 是节点集合V中具有最小负载的节点
是节点集合V中具有最小负载的节点
步骤3:While Q非空。
Let 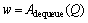
If 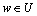 Then
Then
Let 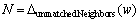
Else
Let 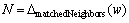
// 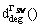 是
是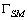 中节点的度
中节点的度
If 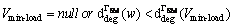 Then
Then
Let 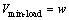
End
End
For each 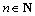
Let 
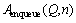
End
Let 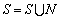
End
// 沿着从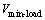 到r的路径切换边
到r的路径切换边
步骤4:Let 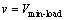
Let 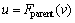 //
// 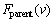 是节点v的父亲节点
是节点v的父亲节点
添加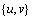 到
到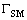
While 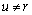
Let 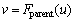
从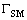 中移除
中移除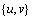
Let 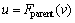
添加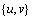 到
到 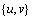
End
End
在算法2中,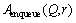 是将r加入到队列Q中;
是将r加入到队列Q中;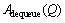 是从队列Q中移除的元素集合;
是从队列Q中移除的元素集合;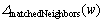 是返回与节点w匹配的所有邻居节点集合;
是返回与节点w匹配的所有邻居节点集合;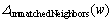 是返回与节点w不匹配的所有邻居节点集合。算法2执行
是返回与节点w不匹配的所有邻居节点集合。算法2执行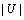 次迭代,每次迭代最多需要花费
次迭代,每次迭代最多需要花费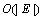 时间来建立可供选择的搜索树和最多花费
时间来建立可供选择的搜索树和最多花费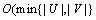 时间沿着可供选择的路径来切换不同的边参与匹配操作,因此,算法2的时间复杂度为
时间沿着可供选择的路径来切换不同的边参与匹配操作,因此,算法2的时间复杂度为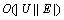 。
。
4 仿真实验
为了验证不同方案的性能,以Matlab2012为工具,采用CitySee系统[20]测得的温度进行一系列仿真实验,考察方案DGSP在不同噪声环境下进行数据收集的精确性和能量有效性,并与目前较典型的CDG[12],EDCA[7]和MTT[8]这3种方案进行对比分析。测试所使用的软硬件环境如下:Inter(R) Core(M) i3-3240 CPU 3.40 GHz, 500 G硬盘,4.0 GB内存,Microsoft Windows 7 Professional。
在本文仿真中,设在高斯噪声所涉及的无线传感器网络中总共有N = 1 000节点。1 000个传感器节点被随机分布在区域为50 m×50 m的监测区域内;节点间的同步通过物理层和数据链路层来实现,其中,数据链路层采用IEEE802.15.4标准中的CSMA/CA机制来进行空闲侦听和冲突避免,物理层则采用2.4 GHz频段,其数据传输率为250 kb/s。实验参数设置为:每个节点的初始能量为50 J;节点接收和发送单位数据的能耗都为50×10-6 J/bit;节点上收发电路的能耗为50×10-6 J/bit;节点成功发送1位数据通过1 m距离的能耗为100×10-9 J/bit/m2;节点上计算能耗为5×10-6 J/bit;每个数据包的长度为1 024 bit;每个控制包的长度为64 bit。数据重构算法采用OMP算法。
不同方案的衡量指标包括能耗、延时和重构误差等。其中,数据重构误差采用信噪比CSNR和相对误差CRE来衡量:
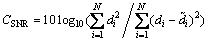 (16)
(16)
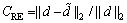 (17)
(17)
图3所示为DGSP与其他3种方案的数据重构误差比较结果。从图3可以看到:随着投影矩阵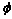 的测量次数增加,4种方案的数据重构误差都降低,但当测量次数小于400次时,DGSP的重构误差要稍比其他3种方案的高。这是由于DGSP依据设计的稀疏投影矩阵来进行节点的数据采样,当测量次数较少时,这种采样方式可能会导致部分节点的数据没有被有效地收集,影响了数据重构性能;而随着投影矩阵测量次数的增加,DGSP的性能优势越来越明显。这主要是因为DGSP充分考虑了相邻节点上数据的相关性,当测量次数达到一定次数时,采用稀疏投影矩阵进行节点数据采样可以克服由于受到网络初始拓扑结构的影响以及测量矩阵稀疏化所导致的数据丢失现象。因此,当测量次数大于400次时,DGSP的重构误差要远比其他3种方案的低。
的测量次数增加,4种方案的数据重构误差都降低,但当测量次数小于400次时,DGSP的重构误差要稍比其他3种方案的高。这是由于DGSP依据设计的稀疏投影矩阵来进行节点的数据采样,当测量次数较少时,这种采样方式可能会导致部分节点的数据没有被有效地收集,影响了数据重构性能;而随着投影矩阵测量次数的增加,DGSP的性能优势越来越明显。这主要是因为DGSP充分考虑了相邻节点上数据的相关性,当测量次数达到一定次数时,采用稀疏投影矩阵进行节点数据采样可以克服由于受到网络初始拓扑结构的影响以及测量矩阵稀疏化所导致的数据丢失现象。因此,当测量次数大于400次时,DGSP的重构误差要远比其他3种方案的低。
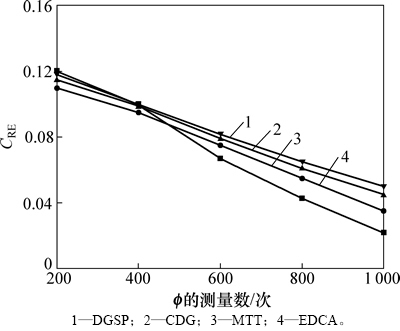
图3 不同方案的重构误差比较
Fig. 3 Comparison of reconstruction error of different schemes
图4所示为DGSP与其他3种方案的数据收集能耗比较结果。从图4可以看到:随着CSNR增大,不同方案的能耗都增大,在相同的CSNR条件下,EDCA的能量开销最大,而DGSP的能量开销最小;当CSNR从10 dB增加到50 dB时,相比于CDG,MTT和EDCA这3种方案,DGSP的能耗分别降低约23.34%,35.25%和44.94%。这主要是因为DGSP通过设计的稀疏投影矩阵进行节点数据采样,减少了节点的传输开销;另外,通过对节点的下一跳选择问题进行优化,实现了负载均衡,从而节省了节点能量。
图5所示为DGSP与其他3种方案的网络生命周期比较结果。从图5可以看到:随着投影矩阵的测量次数增加(意味着4种方案需要采样并传输的数据量增加),网络的传输开销增加导致网络生命周期缩短。但总体来说,DGSP的网络生命周期始终要优于其他3种方案,其中,EDCA的网络生命周期最短。这是因为MTT以最小化数据传输次数为目标,通过求解0-1线性规划问题来构建数据收集树,相比于采用矩阵完成技术的EDCA,MTT的传输开销更小,能耗更低。CDG则利用了感知数据的内部相关性进行数据编码,设计了一种半稀疏化的投影矩阵来进行压缩采样,能实现负载均衡,在降低全局通信开销的同时并没有引入复杂的计算开销和传输控制开销,因此,取得了比EDCA和MTT更好的结果。而DGSP在CDG的基础上进一步对投影矩阵和数据传输路径进行了优化,因此,DGSP的网络生命周期最长。
图6所示为DGSP与其他3种方案的数据收集延时比较结果。从图6可以看到:随着CSNR增大,4种方案的延时都增大,但总的来说,MTT的延时最低,DGSP的延时要略比CDG的低,EDCA的延时最高。这是由于EDCA采用密集投影进行节点的数据采样,并且为了得到较高的CSNR,EDCA需要进行多次矩阵运算,增加了计算开销。而CDG和DGSP则都对数据传输路径进行了优化,降低了各个节点的数据传输跳数,取得了比EDCA更好的延时性能。MTT延时最低的主要原因是它假设每次数据传输开销为1,以最小化数据传输次数为目标,从Sink出发,MTT迭代地找到1条具有最小的传输代价增加值的边加入到最终的数据收集树中。该方法虽然延时最低,但对于数据传输开销的假设过于苛刻,而DGSP是更真实的网络模型,取得了与MTT相近的延时性能,因此,本文认为DGSP是高效的,相比于MTT而言,更加适用于真实的无线传感器网络应用环境。
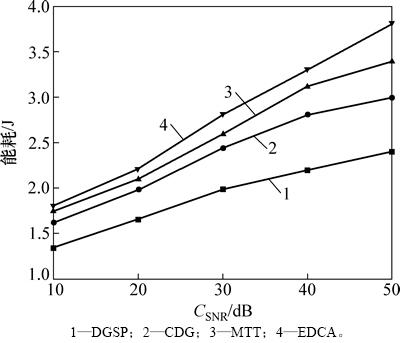
图4 不同方案的能耗比较
Fig. 4 Comparison of energy consumption of different schemes
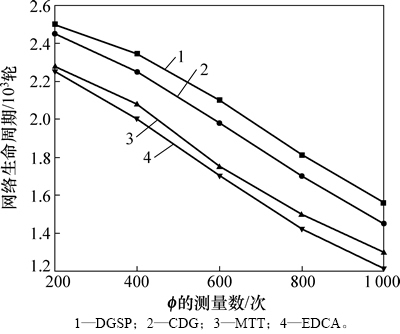
图5 不同方案的网络生命周期比较
Fig. 5 Comparison of network lifetime of different schemes
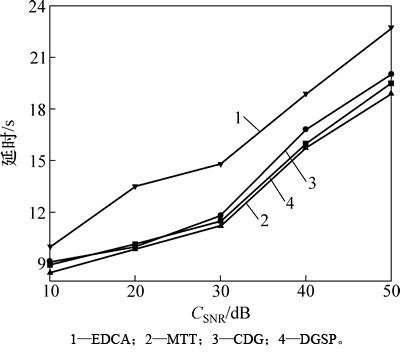
图6 不同方案的延时比较
Fig. 6 Comparison of delay of different schemes
5 结论
1) 设计了一种基于最小化传输开销的投影矩阵用于数据采样。相比于密集投影矩阵而言,该矩阵在满足RIP原则的前提下,利用了各个节点间感知数据的相关性来对矩阵进行稀疏化,在保证数据收集质量的同时,显著降低了网络通信开销。
2) 将采样后的数据传输问题建模成半匹配问题,并提出一种半匹配问题求解算法为节点选择最优的下一跳,用于数据传输,最后以实现网络负载均衡和网络生命周期最大化为目标构建了1颗数据收集树。
3) 采用CitySee系统测得的温度进行仿真实验,结果表明,本文方法在降低数据重构误差和延时、节约能耗和延长网络生命周期等方面要优于目前较典型的CDG,EDCA和MTT等方案。
参考文献:
[1] GUO Shuo, GU Yu, JIANG Bo, et al. Opportunistic flooding in low-duty-cycle wireless sensor networks with unreliable links[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2014, 63(11): 2787-2802.
[2] 崔莉, 鞠海玲, 苗勇, 等. 无线传感器网络研究进展[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2015, 42(1): 163-174.
CUI Li, JU Hailing, MIAO Yong, et al. Overview of wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2015, 42(1): 163-174.
[3] ZHAO Miao, LI Ji, YANG Yuanyuan. A framework of joint mobile energy replenishment and data gathering in wireless rechargeable sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2014, 13(12): 2689-2705.
[4] MA Junchao, LOU Wei, LI Xiangyang. Contiguous link scheduling for data aggregation in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 25(7): 1691-1701.
[5] 徐建波, 李仁发. 无线传感器网络中一种新型的混合型数据收集协议[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2015, 45(2): 254-260.
XU Jianbo, LI Renfa. A Novel framework for miscellaneous data gathering in wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2015, 45(2): 254-260。
[6] KRAHMER F, WARD R. Stable and robust sampling strategies for compressive imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(2): 612-622.
[7] CHENG Jie, JIANG Hongbo, MA Xiaoqiang, et al. Efficient data collection with sampling in WSNs: making use of matrix completion techniques[C]//Proceedings of the Global Communications Conference(GLOBECOM). Miami, Florida, USA: IEEE Press, 2010: 1-5.
[8] XIE Ruitao, JIA Xiaohua. Minimun transmission data gathering trees for compressive sensing in wireless sensor networks[C]//Proceedings of the Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM). Houston, Texas, USA: IEEE Press, 2011: 1-5.
[9] CHUN T C, RAJIB R, HU Wen. Energy efficient information collection in wireless sensor networks using adaptive compressive sensing[C]//The 34th IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks(LCN). Zürich, Switzerland: IEEE Press, 2009: 443-450.
[10] 刘卉, 李泽军. 基于投影矢量的双组播树高效路由数据收集[J]. 传感技术学报, 2013, 26(4): 570-576.
LIU Hui, LI Zejun. High-efficiency routing data collection of dual multicast tree based on the projection vector[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2013, 26(4): 570-576.
[11] SAEED M, JAMSHID S, MIR M P. A novel intelligent energy-efficient delay-aware routing in WSN, based on compressive sensing[C]//The 5th IEEE International Symposium on Telecommunications(IST). Tehran, Iran: IEEE Press, 2010: 415-420.
[12] LUO Chong, WU Feng, SUN Jun, et al. Efficient measurement generation and pervasive sparsity for compressive data gathering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2010, 9(12): 3728-3738.
[13] 胡升泽, 包卫东, 王博, 等. 无线传感器网络基于多元簇首的分簇数据收集算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(2): 403-408.
HU Shengze, BAO Weidong, WANG Bo, et al. Clustering data gathering algorithm based on multiple cluster heads for wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2014, 36(2): 403-408.
[14] 方红, 章权兵, 韦穗. 基于亚高斯随机投影的图像重建方法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2008, 45(8): 1402-1407.
FANG Hong, ZHANG Quanbing, WEI Sui. A method of image reconstruction based on sub-Gaussian random projection[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2008, 45(8): 1402-1407.
[15] HARVEY N J A, LADNER R E,  L, et al. Semi-matchings for bipartite graphs and load balancing[J]. Algorithms & Data Structures, 2013, 59(1): 294-306.
L, et al. Semi-matchings for bipartite graphs and load balancing[J]. Algorithms & Data Structures, 2013, 59(1): 294-306.
[16] ZHENG Haifeng, YANG Feng, TIAN Xiaohua, et al. Data gathering with compressive sensing in wireless sensor networks:a random walk based approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel & Distributed Systems, 2015, 26(1): 35-44.
[17] CAIONE C, BRUNELLI D, BENINI L. Distributed compressive sampling for lifetime optimization in dense wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2012, 8(1): 30-40.
[18] WANG W, GAROFALAKIS M, RAMCHANDRAN K. Distributed sparse random projections for refinable approximation[C]//ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN). Louis, Missouri, USA: ACM Press, 2007: 331-339.
[19] ALLEN W J, RIZZO R C. Implementation of the Hungarian algorithm to account for Ligand symmetry and similarity in structure-based design[J]. Journal of Chemical Information & Modeling, 2014, 54(2): 518-529.
[20] MAO Xufei, XIN Miao, HE Yuan, et al. CitySee: Urban CO2 monitoring with sensors[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM). Orlando, FL, USA: IEEE Press, 2012: 1611-1619.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2015-11-20;修回日期:2016-01-22
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(61472449,61173169,61402542)(Projects(61472449, 61173169, 61402542) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:李鹏,博士研究生,从事无线传感器网络及压缩感知技术研究;E-mail:lpchs617@csu.edu.cn