Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 3186-3192
Microstructure and mechanical properties of isothermal multi-axial forging formed AZ61 Mg alloy
Xiang-sheng XIA1, Ming CHEN2, yong-jin LU3, Fu-you FAN2, Chun-hua ZHU2, Jing HUANG1, Tian-quan DENG1, Shi-feng ZHU1
1. Southwest Technique and Engineering Institute, Chongqing 400039, China;
2. Research Development Center of Changsha Electromechanical Products, Changsha 410100, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Material Processing and Die and Mould Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
Received 11 December 2012; accepted 30 January 2013
Abstract: Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ61 Mg alloy during isothermal multi-axial forging (MAF) were studied. The mechanisms of grain refinement and relationship between the microstructures and mechanical properties were discussed. The results show that the average grain size decreases with increasing the number of MAF passes. The grains are significantly refined at the lst and 2nd MAF passes, and gradually refined at higher MAF passes. The initial grain size of 148 μm decreases to about 14 μm after 6 MAF passes. The grain refinement occurs mainly by continuous dynamic recrystallization. With increasing the MAF passes, both the tensile strength and the elongation to failure of the alloy are significantly enhanced.
Key words: Mg alloy; multi-axial forging; microstructure; mechanical properties
1 Introduction
Mg alloys, well known as lightweight high-strength material, are very attractive in applications for the automotive, railway and aerospace industries [1-5]. However, due to their hexagonal close-packed (HCP) structure and low stacking fault energy, they generally present limited ductility and strength at ambient temperature [6-9]. An effective tactic to minimize these disadvantages is to develop Mg alloys with fine-grained microstructures [10-13].
Several SPD processes such as equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE), accumulative roll bonding (ARB) and torsion under high pressure (HPT), multi-axial forging (MAF), have been proposed for fine-grained materials producing [14-19]. Among these SPD techniques, MAF is a more versatile technique because it can be scaled relatively easily to produce large bulk samples and the process is readily amenable to simplification [20,21]. YANG et al [22,23] reported that MAF under decreasing temperature conditions can accelerate the evolution of fine-grained structures in AZ31 Mg alloy. GUO et al [24] reported that a main mechanism of grain refinement in as-cast AZ80 Mg alloy can be directly associated with grain splitting due to formation of microbands. Such microbands intersect each other during hot MAF, resulting in continuous subdivision of coarse grains into misoriented fine domains. To the most our knowledge, most investigations of MAF have concentrated on using this procedure to process aluminum alloys, ferroalloys and titanium alloys [25-29]. However, little research has been conducted on this issue in Mg alloys.
The present investigation was initiated to evaluate the effect of isothermal MAF on microstructure and tensile properties of AZ61 Mg alloy. The mechanisms of grain refinement and the relationship between microstructures and mechanical properties were also discussed.
2 Experimental
The alloy used in the present study was AZ61 Mg alloy. Rectangular samples with dimensions of 80 mm×80 mm×160 mm were cut from the as-cast AZ61 Mg alloy ingot. The MAF was carried out at the isothermal temperature of 350 °C and pressing speed of 4 mm/s, and the MAF die was preheated to 350 °C before deformation. The schematic diagram of multi-axial forging is shown in Fig. 1. The dimensional ratios of the samples were kept at 1:1:2 during MAF, while the loading direction was turned by 90° from pass to pass. Oil lubricant was used as lubricant during MAF. The MAF die configuration imposed the equivalent strain εe of 0.693 on samples during each pass according to the following equation [21]: εe=|ln(h0/h)|, where h0 and h are the initial and final height of samples, respectively. After deformation the samples were water quenched immediately.
Vickers micro-hardness was measured on the plane perpendicular to the axis of the final forging for the MAF-processed alloy. For each measurement, a load of 1.96 N was applied for 15 s. Seven measurements were taken on each sample at randomly selected points and then averaged to give the Vickers microhardness. Tensile samples having dimensions of 1.5 mm × 5.5 mm in cross-section and 10 mm in gauge length were cut perpendicular to the final forging axis of the MAF. Tensile testing was carried out at room temperature at a constant displacement rate equivalent to an initial strain rate of 1×10-4 s-1. The microstructures were observed using Olympus metallographic microscope (OM). Samples for microscopic examination were carried out in the central part of specimens parallel to the final forging axis. After mechanical polishing, samples were etched for 3 s using a solution of 100 mL ethanol, 6 g picric acid, 5 mL acetic acid and 10 mL water. The mean grain sizes were calculated using the linear intercept method.
3 Results
3.1 Microstructural evolution during MAF
The microstructure of the as-cast AZ61 Mg alloy is shown in Fig. 2. The as-cast sample exhibits a microstructure consisting of α-Mg matrix and intermetallic network phase β-Mgl7Al12, which is produced by divorced eutectic phase. Most of the β-Mgl7Al12 distributes along the grain boundaries, and some appears as particles and exists inside the grains. The average grain size of matrix is about 148 μm.
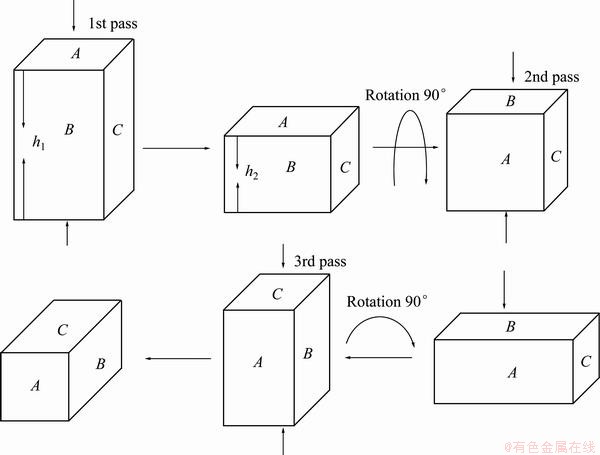
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of multi-axial forging

Fig. 2 Optical microstructure of as-cast AZ61 Mg alloy
Figure 3 shows the microstructures of MAF processed AZ61 Mg alloy with different MAF passes during the isothermal temperature processing. It can be seen from Fig. 3 that significant dynamic recrystallization takes place during MAF process. After 1 pass of MAF processing, coarse grains are elongated vertical to compression direction, a limited number of new small grains nucleate at the original grain boundaries due to dynamic recrystallization (DRX), especially at the grain boundary triple junctions, and the reason is that the stress concentration at triple junctions is higher than other place. The original coarse grains and DRX fine grains can be clearly recognized, which is called the necklace dynamic recrystallization (necklace structure) as shown in Fig. 3(a). The microstructure is rather heterogeneous and typically incompletely recrystallized. With increasing the number of MAF passes, as shown in Fig. 3(b), the volume fraction of the fine recrystallized grains is increased. It also can be seen that in some grains the original grain boundary shows no evidence of DRX. This highlights that there is an inhomogeneity in the DRX process. With further increasing the number of MAF passes, more fine grains nucleate at the boundaries of the newly formed fine grains. In this way, recrystallized fine grains are formed and broaden as dynamic recrystallisation proceeds. Eventually, recrystallized fine grains replace the original coarse grains. After 6 passes of MAF processing, a homogeneous equiaxed grain structure with an average grain size of approximately 14 μm is achieved, and the volume fraction of the fine recrystallized grains comes to 95%.
3.2 Mechanical properties
Figure 4 shows the yield strength, ultimate tensile strength and elongation to failure of the samples before and after different MAF passes. It can be observed that the yield strength, ultimate tensile strength and elongation to failure of MAF processed AZ61 Mg alloy are gradually improved with increasing the MAF passes, which indicates that MAF process might be useful to enhance the mechanical properties of AZ61 Mg alloy. The yield strength, ultimate tensile strength and elongation to failure of AZ61 Mg alloy after 6 passes reach 286.6 MPa, 183.0 MPa and 16.1%, which are 1.4 times, 2.8 times and 1.8 times of the as-cast AZ61 Mg alloy, respectively.
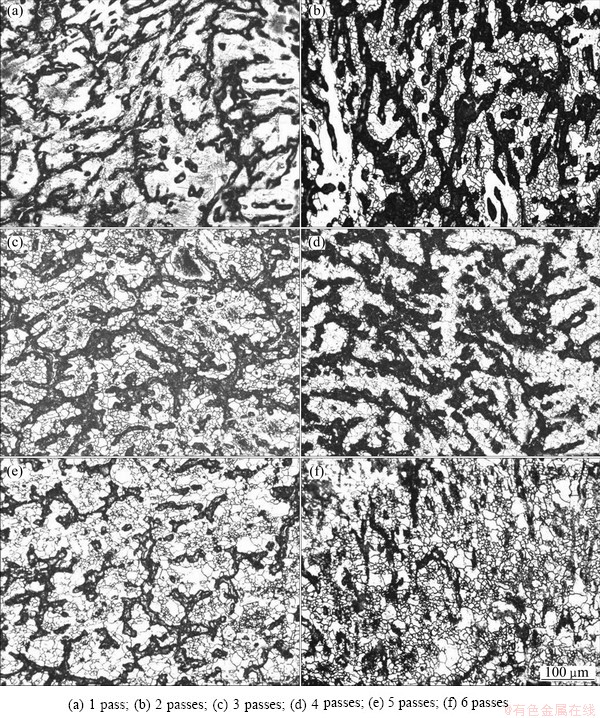
Fig. 3 Optical microstructures of MAF processed AZ61 Mg alloy with different passes
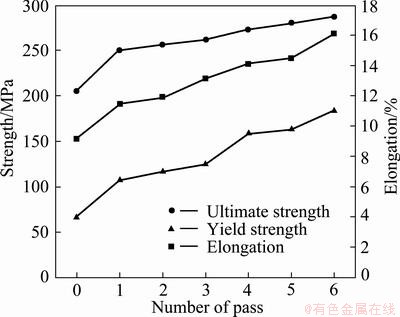
Fig. 4 Mechanical properties of AZ61 Mg alloy after MAF
Figure 5 shows the change of Vickers hardness at room temperature of MAF processed AZ61 Mg alloys with different passes. It is obvious that the hardness increases rapidly with a low number of MAF passes and then more slowly with a high number of MAF passes.
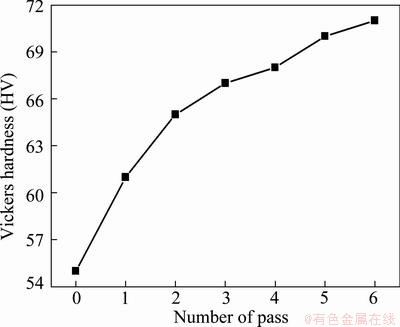
Fig. 5 Change of Vickers hardness at room temperature of MAF processed AZ61 Mg alloy with each pass
4 Discussion
4.1 Grain refinement during MAF
Figure 6 shows the grain size of the AZ61 Mg alloy during MAF. The results indicate that the grain size is influenced by MAF passes, which could be divided into two stages. In the first stage, the grain size obviously decreases with increasing the number of MAF passes. For instance, as the MAF pass increases from 0 to 2, the grain size of alloy decreases from 148 to 54 μm. In the second stage, at higher MAF passes, the grain size of AZ61 Mg alloy is slightly improved with the increase of MAF passes. In the present study, the change of grain size during MAF process could be attributed to the following aspects. On one hand, the discovery of a bimodal distribution of grain size after one pass and the nucleation of fine grains at original grain boundaries indicate that the dynamic recrystallisation occurs (Fig. 3). Dynamic recrystallization process is classified into either continuous or discontinuous one. In general, continuous recrystallization is considered a recovery process where a progressive increase in boundary misorientation and the conversion of low angle boundaries into the high angle boundaries may be realized [30]. In the present study, the dynamic recrystallization can be attributed to continuous recrystallization, it is well known that continuous DRX is one of the most important DRX mechanisms in Mg and Mg alloy. At the early stage of deformation, new strain-free grains nucleate at the original grain boundaries (Fig. 3(a)). With increasing the number of MAF passes, dislocations can also accumulate at the newly formed DRX grain boundaries then some substructures followed by DRX grains occur, finally new small grains form on the surface of the first necklace layer [31], and the initial grain size of 148 μm decreases to about 14 μm after 6 MAF passes. However, it can be seen from Fig. 3(b) that the dynamic recrystallization does not take place in some grains. This is because that the only minority of grains which possess advantageous orientation deform preferentially during the recrystallization process. The density of the dislocations will improve enormously owing to deformation asynchronism of the grains, resulting in the nonuniform distribution of deformation, and with increasing the number of MAF passes, the grains which possess disadvantageous orientation have the advantageous orientation for deformation due to the change of the loading direction. The uniform distribution of deformation can be obtained. On the other hand, high migration of grain boundary at high processing temperature can lead to rapid grain growth. However, the time is too short to allow obviously grain growth.
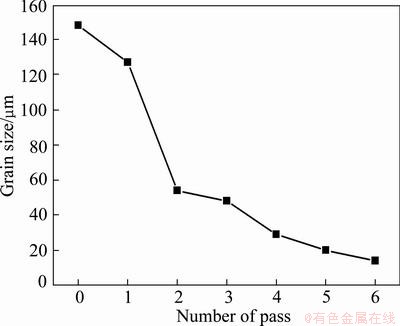
Fig. 6 Grain size of AZ61 alloy after different MAF passes
The grain refinement is profoundly affected by variables such as deformation temperature, strain rate, and cumulative strains (number of MAF passes). Significant grain refinement could be achieved when the Zener-Hollomon parameter (Z=exp[Q/RT)] is high, i.e. using high strain rates or low temperatures [32,33]. The temperature selected for deformation has a significant effect on the grain refinement. MIURA et al [34] reported that the grains are refined by mechanical twinning and kinking in addition to grain refinement by dynamic recrystallization (DRX) at higher temperatures. However, the grain refinement at lower temperatures would be induced by mechanism of low temperature continuous dynamic recrystallization. In the present study, as discussed above, dynamic recrystallization is the main mechanism for grain refinement. The cumulative strains (number of MAF passes) also have important effects on grain refinement. GUO et al [24] reported that there is a critical strain when the total strain exceeds the critical strain; the grain size is almost keeping constant during the deformation. It is difficult to get more grain refinement further. It is evident from Fig. 6 that the reduction of the grain size appears not to be saturated. Therefore, it is expected that further grain refinement of AZ61 Mg alloy should be possible from prolonged MAF passes.
Compared with the as-cast AZ61 Mg alloy, the amount of Mgl7Al12 is obviously reduced during MAF process. AZ61 Mg alloy is located in the α-Mg single-phase region at processing temperature. REN et al [35] suggested that the second phases is gradually dissolved in the α-Mg matrix when the alloy is isothermally treated or thermomechanically processed at 300 °C. But as we known, the dissolution of Mgl7Al12 during isothermal treatment needs a long holding time. In the present study, the Mgl7Al12 is obviously reduced during MAF process in a short time. This could be attributed to the formation of high-density dislocations and vacancies during MAF process, which provides a high diffusion path of Al atoms.
4.2 Effect of microstructure on mechanical properties
Grain refinement has great potential to improve both strength and ductility of Mg alloys [36,37]. The yield strength of the alloy varies with the grain size and the relationship follows the Hall-Petch equation of σy=σ0+κd-1/2, where σy is the yield strength, σ0 and κ are material constants, and d is the mean grain size. The value of κ is dependent on the number of slip systems [38]. The micromechanism could be understood in terms of pile-up of dislocations in the vicinity of the grain boundary. In addition, the texture resulting from the SPD processes at high temperature has an obvious effect on the mechanical properties due to the restricted number of slip systems available in the HCP lattice of magnesium. KIM et al [39] studied the texture development and its effect on mechanical properties of AZ61 Mg alloy fabricated by equal channel angular pressing. They observed that the yield strength did not fit the standard Hall-Petch relationship due to the texture modification during ECAP, and the texture softening appreciably overwhelms the strengthening due to grain refinement. Figure 7 shows the relationships between yield strength or room-temperature hardness and grain size. It can be seen that the results fit on a line described by the Hall-Petch relation. This indicates that the texture is no significant changes with the change of MAF passes and no obviously effect on the mechanical properties and the increase of mechanical properties is mainly induced by grain refinement.
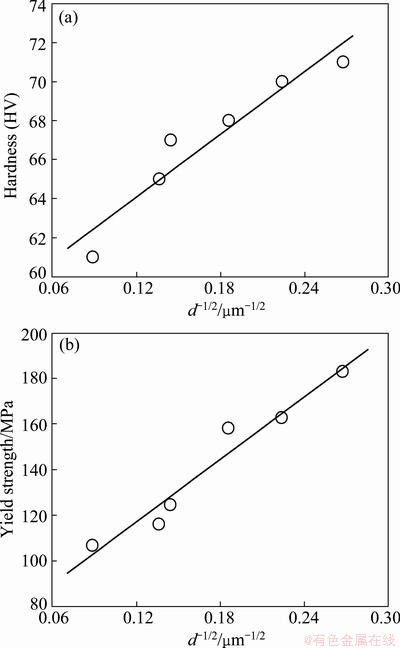
Fig. 7 Hall-Petch relation of hardness (a) and yield strength (b) in MAF formed AZ61 Mg alloy
5 Conclusions
1) Microstructure of AZ61 Mg alloy during isothermal multi-axial forging was studied. The average grain size decreases with increasing the number of MAF passes; the grains are significantly refined at the lst and 2nd MAF passes, and gradually refined at higher MAF passes. The initial grain size of 148 μm decreases to about 14 μm after 6 MAF passes.
2) The yield strength, ultimate tensile strength and elongation to failure of MAF processed AZ61 Mg alloy are gradually improved with increasing the MAF passes. The yield strength, ultimate tensile strength and elongation to failure of AZ61 Mg alloy after 6 passes reach 286.6 MPa, 183.0 MPa and 16.1%, which are 1.4 times, 2.8 times and 1.8 times of the as-cast AZ61 Mg alloy, respectively.
3) The relationships between yield strength or room-temperature hardness and grain size fit the standard Hall-Petch relationship. The texture is no obvious effect on the mechanical properties and the increase of mechanical properties is mainly induced by grain refinement.
References
[1] CHEN Qiang, LUO Shou-jing, ZHAO Zu-de. Microstructural evolution of previously deformed AZ91D Mg alloy during partial remelting [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 477: 726-731.
[2] LUO A A. Recent Mg alloy development for elevated temperature applications [J]. International Materials Reviews, 2004, 49: 13-30.
[3] CHEN Qiang, ZHAO Zu-de, ZHAO Zhi-xiang, HU Chuan-kai, SHU Da-yu. Microstructure development and thixoextrusion of Mg alloy prepared by repetitive upsetting-extrusion [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509: 7303-7315.
[4] ZHAO Zu-de, CHEN Qiang, WANG Yan-bin, SHU Da-yu. Microstructures and mechanical properties of AZ91D alloys with Y addition [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 515: 152-161.
[5] LUO Shou-jing, CHEN Qiang, ZHAO Zu-de. An investigation of microstructure evolution of RAP processed ZK60 magnesium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 501: 146-152.
[6] WANG Qing-feng, LI Han, LI Shu-bo, WANG Zhao-hui, DU Wen-bo. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of extruded Mg-12Zn-1.5Er alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21: 874-879.
[7] CHEN Qiang, YUAN Bao-guo, ZHAO Gao-zhan, SHU Da-yu, HU Chuan-kai, ZHAO Zu-de, ZHAO Zhi-xiang. Microstructural evolution during reheating and tensile mechanical properties of thixoforged AZ91D-RE magnesium alloy prepared by squeeze casting–solid extrusion [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 537: 25-38.
[8] ZHAO Zu-de, CHEN Qiang, KANG Feng, SHU Da-yu. Microstructural evolution and tensile mechanical properties of thixoformed AZ91D Mg alloy with the addition of yttrium [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 482: 455-467.
[9] MA Ming-long, ZHANG Kui, LI Xing-gang, LI Yong-jun, ZHANG Kang. Hot deformation behavior of rare earth magnesium alloy without pre-homogenization treatment [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(S1): s132-s139.
[10] CHEN Qiang, LIN Jun, SHU Da-yu, HU Chuan-kai, ZHAO Zu-de, KANG Feng, HUANG Shu-hai, YUAN Bao-guo. Microstructure development, mechanical properties and formability of Mg-Zn-Y-Zr magnesium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 554: 129-141.
[11] ZHAO Zu-de, CHEN Qiang, CHAO Hong-ying, HU Chuan-kai, HUANG Shu-hai. Influence of equal channel angular extrusion processing parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Al-Y-Zn alloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32: 575-583.
[12] GAO Lei, CHEN Rong-shi, HAN En-hou. Enhancement of ductility in high strength Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21: 863-868.
[13] ZHAO Zu-de, CHEN Qiang, TANG Ze-jun, WANG Yan-bin, NING Hai-qing. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of Al2O3sf/AZ91D magnesium matrix composites fabricated by squeeze casting [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2010, 45: 3419-3425.
[14] CHEN Qiang, ZHAO Zhi-xiang, SHU Da-yu, ZHAO Zu-de. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91D magnesium alloy prepared by compound extrusion [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 3930-3934.
[15] ZHAO Zu-de, CHEN Qiang, WANG Yan-bin, SHU Da-yu. Microstructural evolution of an ECAE-formed ZK60-RE Mg alloy in the semi-solid state [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 506: 8-15.
[16] HEBESBERGER T,  H P, VORHAUER A, WETSCHER F, PIPPAN R. StructureofCu deformedbyhigh pressure torsion [J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53: 393-402.
H P, VORHAUER A, WETSCHER F, PIPPAN R. StructureofCu deformedbyhigh pressure torsion [J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53: 393-402.
[17] ZHAO Zu-de, CHEN Qiang, WANG Yan-bin, SHU Da-yu. Microstructural evolution of an ECAE-formed ZK60-RE magnesium alloy in the semi-solid state [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 506: 8-15.
[18] LUO Shou-jing, CHEN Qiang, ZHAO Zu-de. Effects of processing parameters on the microstructure of ECAE-formed AZ91D Mg alloy in the semi-solid state [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 477: 602-607.
[19] ZHAO Zu-de, CHEN Qiang, TANG Ze-jun, HU Chuan-kai. Microstructural evolution and tensile mechanical properties of AM60B magnesium alloy prepared by the SIMA route [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 497: 402-411.
[20] ZHAO Zu-de, CHEN Qiang, HU Chuan-kai, SHU Da-yu. Microstructure and mechanical properties of SPD-processed an as-cast AZ91D+Y magnesium alloy by equal channel angular extrusion and multi-axial forging [J]. Materials and Design, 2009, 30: 4557-4561.
[21] CHEN Qiang, SHU Da-yu, HU Chuan-kai, ZHAO Zu-de, YUAN Bao-guo. Grain refinement in an as-cast AZ61 magnesium alloy processed by multi-axial forging under the multitemperature processing procedure [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 541: 98-104.
[22] YANG Xu-yue, SUN Zheng-yan, XING Jie, MIURA H, SAKAI T. Grain size and texture changes of Mg alloy AZ31 during multi-directional forging [J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(S1): s200-s204.
[23] MIURA H, YU G, YANG X, SAKAI T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ61 Mg alloy prepared by multi directional forging [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 1294-1298.
[24] GUO Q, YAN H G, CHEN Z H, ZHANG H. Grain refinement in as-cast AZ80 Mg alloy under large strain deformation [J]. Materials Characterization, 2007, 58: 162-167.
[25] SITDIKOV O, SAKAI T, GOLOBORODKO A, MIURA H. Grain fragmentation in a coarse-grained 7475 Al alloy during hot deformation [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 51: 175-179.
[26] RINGEVAL S, PIOT D, DESRAYAUD C, DRIVER J H. Texture and microtexture development in an Al-3Mg-Sc(Zr) alloy deformed by triaxial forging [J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54: 3095-3105.
[27] NAKAO Y, MIURA H. Nano-grain evolution in austenitic stainless steel during multi-directional forging [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 1310-1317.
[28] HAN Bao-jun, XU Zhou. Microstructural evolution of Fe-32%Ni alloy during large strain multi-axial forging [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 447: 119-124.
[29] YU S, MIRONOV, SALISHCHEV G A, MYSHLYAEV M M, PIPPAN R. Evolution of misorientation distribution during warm‘abc’ forging of commercial-purity titanium [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 418: 257-267.
[30] HUMPHREYS F J, HATHERLY M. Recrystalization and related annealing phenomena [M]. Oxford: Pergramon Press, 1996.
[31] XIA Xiang-sheng, ZHANG Kui, LI Xing-gang, MA Ming-long, LI Yong-jun. Microstructure and texture of coarse-grained Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr alloy after hot compression [J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 44: 521-527.
[32] WATANABE H, TSUTSUI H, MUKAI T, ISHIKAWA K, OKANDA Y, KOHZU M, HIGASHI K. Grain size control of commercial wrought Mg-Ag-Zn alloys utilizing dynamic recrystallization [J]. Materials Transactions, 2001, 42: 1200-1205.
[33] CHEN Qiang, SHU Da-yu, ZHAO Zu-de, ZHAO Zhi-xiang, WANG Yan-bin, YUAN Bao-guo. Microstructure development and tensile mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-RE-Zr magnesium alloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2012, 40: 488-496.
[34] MIURA H, YANG X, SAKAI T. Evolution of ultra-fine grains in AZ31 and AZ61 Mg alloys during multidirectional forging and their properties [J]. Materials Transactions, 2008, 49: 1015-1020.
[35] REN Yu-ping, QIN Gao-wu, PEI Wen-li, LI Song, GUO Yun, ZHAO Hong-da. Phase equilibria of Mg-rich corner in Mg-Zn-A1 ternary system at 300 °C [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 241-245.
[36] ZHAO Zu-de, CHEN Qiang, CHAO Hong-ying, HUANG Shu-hai. Microstructural evolution and tensile mechanical properties of thixoforged ZK60-Y magnesium alloys produced by two different routes [J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31: 1906-1916.
[37] YING Tao, HUANG Jian-ping, ZHENG Ming-yi, WU Kun. Influence of secondary extrusion on microstructures and mechanical properties of ZK60 Mg alloy processed by extrusion and ECAP [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 1896-1901.
[38] ZHANG Ding-fei, SHI Guo-liang, ZHAO Xia-bing, QI Fu-gang. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of Mg-x%Zn-1%Mn (x=4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) wrought magnesium alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21: 15-25.
[39] KIM W J, HONG S I, KIM Y S, MIN S H, JEONG H T, LEE J D. Texture development and its effect on mechanical properties of an AZ61 Mg alloy fabricated by equal channel angular pressing [J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51: 3293-3307.
等温多向锻造AZ61镁合金的组织演化与力学性能
夏祥生1,陈 明2,卢永进3,樊富友2,朱春华2,黄 静1,邓天泉1,朱世凤1
1. 西南技术工程研究所,重庆 400039;
2. 长沙机电产品研究开发中心,长沙 410100;
3. 华中科技大学 材料成形与模具技术国家重点实验室,武汉 430074
摘 要:研究AZ61镁合金在等温锻造过程中的显微组织及力学性能变化,讨论晶粒细化机理及显微组织与力学性能的关系。结果表明:合金的平均晶粒尺寸随着多向锻造道次的增加而减小,在初始的1、2道次变形过程中,晶粒急剧细化,随着变形道次的增加,晶粒细化能力减弱,经过6道次变形后,晶粒尺寸由初始的148 μm 细化到14 μm。晶粒细化主要是由于合金在锻造过程中发生了连续动态再结晶。随着变形道次的增加,合金的抗拉强度、屈服强度和伸长率逐渐增加。
关键词:镁合金;多向锻造;显微组织;力学性能
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Corresponding author: Xiang-sheng XIA; Tel: +86-23-68792232; E-mail: xiaxiangsheng1@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62851-4