DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.07.046
机车车辆二系弹簧载荷分配优化的改进遗传算法
韩锟,潘迪夫,韩洪飞
(中南大学 交通运输工程学院,湖南 长沙,410075)
摘要:为解决现有轨道机车车辆二系弹簧载荷优化调整算法在加垫控制性能上的欠缺,避免冗余计算,在构建轨道机车车辆二系支承结构几何模型和二系弹簧载荷分布调整优化模型基础上,提出一种改进遗传算法。该算法针对标准遗传算法求解时存在的加垫位置过多、加垫总量过大的问题,结合二系弹簧载荷增减载系数矩阵的特点,引入加垫位置约束条件改进个体编码方式;针对标准遗传算法在迭代后期存在无为冗余计算的问题,引入车体无张力状态判别条件改进算法优化准则,对提出的改进遗传算法进行实验验证。研究结果表明:所提出的算法因为引入加垫位置约束条件和无张力状态判别条件,在减小搜索可行域的同时有效避免了冗余计算,在获得相同求解精度时,求解效率和加垫控制特性均优于未改进的遗传算法,效率提高35.50%,加垫总量减少28.44%。
关键词:机车二系弹簧载荷;调簧;遗传算法
中图分类号:U260.72;TP18 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)07-2521-07
An improved genetic algorithm for secondary spring load equalization of railway vehicles
HAN Kun, PAN Difu, HAN Hongfei
(School of Traffic &Transportation Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China)
Abstract: In order to solve the problem of excessive shim quantity generated by standard genetic algorithm (SGA) and to avoid redundant computation, an improved genetic algorithm (IGA) for secondary spring load equalization of railway vehicles was presented based on the simplified geometry model and optimization model of secondary suspension system. Aimed at the excessive shim quantity generated by SGA, a location constraint-based coding strategy derived from load increase coefficient matrix for secondary suspension system was applied. Aimed at the low efficiency of SGA, the criterion of tension free position of the car-body was introduced to modify the optimization rule. Calculative examples were made by using IGA. The results show that IGA algorithm can reduce the feasible region without redundant computation due to the introduction of the location constraint and the optimality criterion. Compared with the SGA algorithm, IGA algorithm can achieve higher efficiency and better shim quantity control ability with the same accuracy, and the solving efficiency is increased by 35.50% while the total shim quantity is reduced by 28.44%.
Key words: locomotive secondary spring load; spring regulation; genetic algorithm
轨道机车车辆静态轮轴载荷分布不均匀,将在列车运行时的轮轨接触过程中产生一系列不利影响,轻则导致机车黏着牵引力下降[1]、车轮踏面和轨面波浪形磨损[2]、轮轨冲击加大[3]、车轮空转打滑[4],重则引发车轮踏面剥离甚至车轴断裂事故,大大增加列车倾覆脱轨风险[5]。为此,许多国际和国家标准(如BS EN 14363: 2006[6]和GB/T 3317-2006[7]等)均明确规定了轮轴重分配允许偏差。目前,国内外普遍采用调簧方法(即选择性的在部分支承弹簧处加调整垫)调整静态轮轴载荷分布,将其分配偏差控制在允许范围内。轨道机车车辆采用两系耦合的超静定弹性支承结构,在任一支承位置加垫将引起所有支承弹簧载荷重新分 布[8],故确定调整垫片的位置和数量属于复杂的多变量优化问题。对该问题的求解,现有方法可分为两大类:一类是偏差补偿法[9-10],其基本思想是将载荷初始分布与理想分布之差作为需加垫补偿的附加载荷,建立经验公式或数学模型得到加垫量与加垫引起附加载荷间的关系,据此求解加垫量。该方法的不足在于理想载荷分布难以确定,加垫调整效果难以保证。另一类是搜索算法,包括传统的非线性规划算法(如基于梯度的迭代算法[11]、基于罚函数法的SUMT算法[12]等)和基于进化算法及其他群体策略的智能优化方法。传统非线性规划算法对寻优初始条件依赖较大,且容易陷入局部最优解,而潘迪夫等[13-15]提出的智能优化方法虽显著提高了算法的鲁棒性和全局搜索能力,但仍存在以下不足:1) 算法存在冗余迭代,因试图消除理论上无法消除的载荷偏差而进行大量无效计算;2) 算法求出的优化解加垫位置过多、加垫总量过大,影响调簧过程的实效性及行车安全性。潘迪夫等[16-17]分别构建多目标遗传算法和两级免疫优化算法,在一定程度上解决了加垫总量过大的问题,但算法设计较复杂,且依然存在冗余迭代问题。为此,本文作者以机车车辆二系悬挂结构为研究对象,引入加垫位置约束条件和车体无张力状态判别条件,提出一种改进遗传算法求解二系弹簧最优加垫量,以避免冗余运算,提高调簧效率,控制加垫总量。
1 轨道机车车辆二系支承结构几何模型
1.1 基本假设
机车车辆二系支承结构是由车体与多个支承弹簧构成的超静定空间弹性力学系统。为保证分析的可行性和结果的可靠性,进行以下基本假设:1) 车体为刚体;2) 忽略车体重心高度的影响;3) 只考虑二系弹簧的垂向载荷;4) 忽略车体倾斜造成的位移与转角;5) 假设各二系弹簧相对于车体底架几何中心对称分布,且各二系弹簧与车体之接触点共面,车体同侧的二系弹簧与车体之接触点共线;6) 假设各二系弹簧底部处于同一水平基准面上。
1.2 几何模型
依据假设,以C0-C0轴式机车(三轴转向架电传动机车)为例,可将其二系支承结构简化为图1所示的多点弹性冗余支承结构。

图1 C0-C0轴式机车二系支承结构简化模型
Fig. 1 Simplified geometry model of secondary suspension system of C0-C0 locomotive
图1中:坐标原点设在车体底架二系支承点构成矩形平面的几何中心;a,b,S1和S2为车体几何参数;ex和ey分别为车体重心在X轴和Y轴的偏移量;Fg为车体所受重力;Fi(i=1, 2, …, 12)分别为各二系弹簧对车体的支承力。
2 轨道机车车辆二系弹簧载荷分布调整的优化模型
2.1 目标函数
图1中,二系弹簧载的理想分布为各二系弹簧载荷都相等,即
 ; i=1, 2, …, 12 (1)
; i=1, 2, …, 12 (1)
但由于各种制造误差(如车体重心与其几何中心的偏差、各二系支承点处的高度和刚度误差等)存在,实际的二系弹簧载荷分布并非为式(1)所描述的理想状态。采用各二系弹簧载荷与平均载荷误差的平方和J:
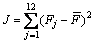 (2)
(2)
作为目标函数,J越小,载荷越趋近于均匀分布。式(2)中, 为二系弹簧载荷均值,
为二系弹簧载荷均值,
 (3)
(3)
2.2 决策变量
轨道机车车辆二系弹簧载荷的调整是通过选择性的在二系弹簧处加垫,改变支承点处的综合刚度从而改变二系弹簧载荷来实现,因此,选取12个二系支承点处的加垫量Δhi为决策变量(i=1, 2, …, 12)。
2.3 约束条件
2.3.1 等式约束
在图1所示的超静定弹性支承结构中,各二系支承点处的加垫量Δhi与二系弹簧载荷间存在等式约束关系[14]为
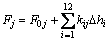 ; j=1, 2, …, 12 (4)
; j=1, 2, …, 12 (4)
式中:F0j为加垫前二系弹簧载荷;kij为二系弹簧增减载系数,是与车体几何参数和二系支承点刚度有关的常数。
2.3.2 不等式约束
为保证列车运行安全,二系支承点处的加垫量不允许过大,所以,Δhi应满足如下不等式约束:
0≤ ≤
≤ ; i=1, 2, …, 12 (5)
; i=1, 2, …, 12 (5)
式中:ΔHmax为二系支承点处的最大允许加垫量。可得轨道机车车辆二系弹簧载荷分布调整的优化模型为:

s.t. 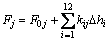
 , 0≤
, 0≤ ≤
≤ ;
;
i=1, 2, …, 12; j=1, 2, …, 12 (6)
3 轨道机车车辆二系弹簧载荷分布调整的改进遗传算法
3.1 优化模型现有求解方法存在的问题
对式(6)所示优化模型的求解,潘迪夫等[14]提出一种基于实数编码的遗传算法,将群体智能优化算法引入调簧领域,获得优于传统迭代算法的求解效果。但仍存在以下2个问题:1) 算法迭代过程中缺少对二系弹簧载荷分布是否已达最优的判断,大多以迭代次数达到预设值为优化准则,可能进行大量无效计算;2) 算法在解空间内进行随机搜索,没有利用任何关于二系弹簧载荷均匀性分配调整问题的先验知识,导致搜索效率低,且求解得到的加垫位置过多,加垫总量过大,不符合加垫量最少的实用性原则。
3.2 改进遗传算法
针对上述问题,本文从2方面对遗传算法进行改进:一是引入加垫位置约束,改进个体编码方式;二是引入车体无张力状态判断条件,改进算法优化准则。
3.2.1 个体编码方式的改进
以HXD1B型六轴大功率机车为例分析二系弹簧载荷加垫调整特点。该车型二系弹簧增减载系数矩阵K为
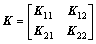 (7)
(7)
其中:

 ;
;
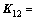
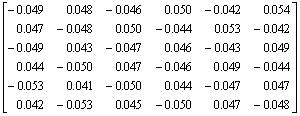 ;
;
 ;
;

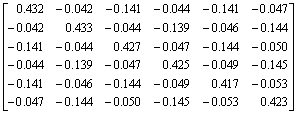 。
。
二系弹簧增减载系数矩阵K的元素kij表达了在第 i处二系弹簧下加单位厚度的垫片(1 mm)时第j处二系支承载荷的变化量(单位:kN)。观察矩阵K,可发现如下规律:矩阵K各列元素的和均为0,即
 ; j=1, 2, …, 12 (8)
; j=1, 2, …, 12 (8)
式(8)表明,在所有二系支承点同时添加相同厚度的垫片,不影响二系弹簧载荷分布。
矩阵K各奇数列元素之和以及偶数列元素之和均为0,即
 (9)
(9)
式中:j=1, 2, …, 12。
式(9)表明:在车体纵向同侧所有二系支承点同时添加相同厚度的垫片,不影响二系弹簧载荷分布。
由上述分析可知车体纵向两侧各6个二系支承点中至少各有1个支承点处的加垫量为0 mm。此规律可作为先验知识,对式(6)中的决策变量进行约束,即hi(i=1, …, 12)中至少有2个为0 mm,可分别选取车体纵向两侧二系弹簧载荷最大位置处的加垫量为0 mm。故决策变量的个数由12个减少到10个。对这10个独立的决策变量进行实数编码,如图2所示。

图2 个体编码
Fig. 2 Individuals’ code
3.2.2 算法优化准则的改进
若将同转向架同侧的一组二系弹簧等效为1个弹簧,则轨道机车车辆二系支承结构可简化为如图3所示的4点支承结构。

图3 轨道机车车辆二系支承结构简化模型
Fig. 3 Simplified geometry model of secondary suspension system of railway vehicles
图3中:FL1和FR1分别为一、二位转向架左侧二系弹簧对车体的支承力;FL2和FR2分别为一、二位转向架右侧二系弹簧对车体的支承力。
德国标准DIN25045中给出了关于轨道车辆车体无张力状态(tension free position)的定义[18]:若重心偏差是影响车体二系支承载荷分布偏差的唯一因素,即除重心偏差外没有其他因素影响车体二系载荷分布,则认为达到了无张力状态。PAN等[17]也指出,在车体无张力状态下,车体对角位置支承点载荷之和相等,即
 (10)
(10)
由无张力状态的定义可知,该状态是二系弹簧载荷分布的理想状态,故可将其作为目标状态,在算法迭代搜索过程中实时判断该状态是否达到,以此作为算法终止条件之一,以避免无为冗余迭代,提高算法效率。基于上述思想,引入式(10),与最大遗传代数Gmax共同构成优化准则来终止算法。在迭代过程中只要满足其中1个终止条件,即达到无张力状态或遗传代数达到Gmax,均终止算法。考虑到实际应用中存在测量误差和逼近误差, 以式(10)所示的等式作为终止条件可能导致算法陷入死循环,故采用下式作为实际判据:
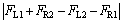 ≤
≤ (11)
(11)
式中:δ为判别阈值,为很小的正数。
3.2.3 改进遗传算法基本操作及流程
除编码方式和优化准则进行改进外,本文算法(以下简称IGA算法)进行遗传操作时,采用轮盘赌和“最优个体保存策略”相结合的选择操作,确保算法以概率1在有限步内收敛到全局最优解[19];采用自适应交叉和变异概率进行交叉和变异操作[20],以改善算法性能。IGA算法基本流程如图4所示。
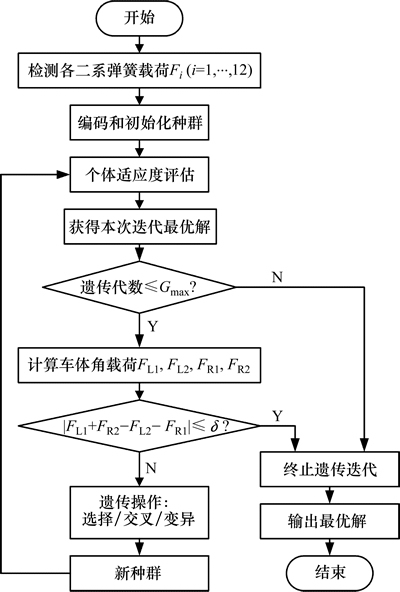
图4 IGA机车二系调簧算法流程图
Fig. 4 Locomotive secondary spring load adjustment flow of IGA
4 结果与分析
4.1 应用结果
运用IGA算法对国产HXD1B型电力机车车体实车参数进行仿真实验。该车型具有12点二系支承结构,实测得到202号车体调整前初始二系载荷分布情况见表1。
表1 HXD1B型机车202号车体初始二系载荷分布
Table 1 Unadjusted secondary spring load distribution of body No.202 of HXD1B locomotive

IGA算法参数选取如下:最大遗传代数Gmax=200;判别阈值δ=0.1 kN;种群规模N=50;交叉概率上下限pc1=0.9,pc2=0.6;变异概率上下限pm1=0.1,pm2=0.001;最大允许加垫值Hmax=7 mm。调整结果见表2。
对比表1、表2可知:经IGA算法调整后二系载荷均方差由调整前的0.91减小至0.41,减小了56%;最大载荷偏差由调整前的3.14 kN减小至0.95 kN,减小了69.75%;对角载荷之和的差由调整前的5.28 kN减小至0.10 kN,可判定车体已达无张力状态,极大地优化了机车二系载荷分布。
4.2 算法性能比较
为进一步验证IGA算法在时间效率、加垫总量控制方面的优越性及鲁棒性,将其与传统的迭代算法及文献[14]中提出的遗传算法调整结果进行比较。3种算法迭代过程中二系载荷分布方差收敛曲线如图5所示。由图5可知:传统迭代算法基于梯度下降寻优,属于局部优化算法,寻优精度和效率较GA和IGA算法差;IGA和GA算法具备全局优化能力,寻优精度和效率明显比迭代算法的高,前者寻优精度略比后者的高,但效率较后者大幅度提高。
表2 HXD1B型机车202号车体二系弹簧载荷调整结果
Table 2 Adjusted results of body No.202 of HXD1B locomotive

多次实验统计得到3种算法的载荷优化特性、加垫控制特性及求解效率特性,见表3。

图5 3种算法迭代收敛曲线
Fig. 5 Convergence curves of three algorithms
表3 3种算法性能比较
Table 3 Performance comparison of three algorithms
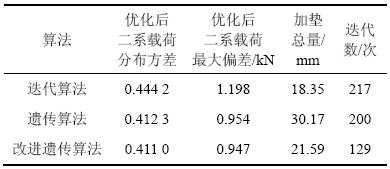
由表3可见:从优化后平均载荷方差和最大偏差2项指标来看,IGA算法和GA算法寻优结果接近,两者均优于传统迭代算法,寻优精度分别提高7.47%和7.18%。
在加垫性能方面,与GA算法相比,IGA算法由于引入最大初始载荷处不加垫的约束,加垫控制特性优于前者,加垫总量减少了28.44%。在求解效率上,一方面,IGA算法因为车体无张力状态判据的引入避免了搜索过程的盲目性导致的冗余迭代;另一方面,由于加垫位置约束条件的引入极大减少了搜索空间中可行解的范围。这使得IGA算法的效率明显比GA算法的高,迭代次数仅为后者的64.5%。
5 结论
1) 针对轨道机车车辆二系支承结构的特点,构建二系弹簧载荷分布调整的优化模型,设计了一种基于改进遗传算法的二系弹簧载荷均匀性分配调整方法(IGA算法);引入加垫位置约束条件改进个体编码方式,引入四支承点下车体无张力状态判别条件改进算法优化准则。IGA算法对不同车型的二系调簧问题具有普遍适用性,在多次实验中,均能稳健一致地收敛,算法稳定性高,鲁棒性好。
2) 利用二系弹簧载荷加垫调整增减载系数矩阵K的特点,引入加垫位置约束条件,有效减少了解空间内可行解的数量,获得了良好的加垫控制性能,加垫总量较未改进算法减少28.44%。
3) 引入车体无张力状态判别条件,改进算法优化准则,避免了迭代搜索过程因盲目性而导致的冗余计算,效率较未改进的遗传算法提高35.5%。
4) 本文提出的IGA算法具有鲁棒性强、加垫控制性能优越且求解效率高等特点,极大提高了轨道机车车辆二系弹簧载荷分配优化调整的可靠性和实用性。
参考文献:
[1] 顾树全. 对DF5型机车轴重调整过程的分析及新设想[J]. 内燃机车, 2003(11): 4-7.
GU Shuquan. Analysis of the axle load adjustment process for DF5 locomotive[J]. Diesel Locomotives, 2003(11): 4-7.
[2] 郭海英, 周勇, 耿海路. 机车车体称重调簧新工艺研究[J]. 机械管理开发, 2007(4): 60-63.
GUO Haiying, ZHOU Yong, GENG Hailu. Study on spring adjustment new technology for locomotive body weighing[J]. Mechanical Management and Development, 2007(4): 60-63.
[3] 李子春. 轨道结构垂向载荷传递与路基附加动应力特性的研究[D]. 北京: 铁道部科学研究院, 2000: 1-6.
LI Zichun. Study on the vertical land transmission through the track structure and the characteristics of subgrade dynamic stresses[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Railway Science, 2000: 1-6.
[4] 张正楠. 调整机车轮重的分析和计算[J]. 内燃机车, 1990(10): 26-31.
ZHANG Zhengnan. Analysis and computation of the locomotive wheel load[J]. Diesel Locomotives, 1990(10): 26-31.
[5] DIMITROV E, NENOV N, RUZHEKOV T. Electronic system for measuring railway vehicle wheel load in motion[C]// 33rd International Spring Seminar on Electronics Technology (ISSE). Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE, 2010: 370-373.
[6] BS EN 14363: 2005, Railway applications—testing for the acceptance of running characteristics of railway vehicles—testing of running behavior and stationary tests[S].
[7] GB/T 3317—2006, 电力机车通用技术条件[S].
GB/T 3317—2006, General technical specification for electric locomotive[S].
[8] CURTIS D L, SKRZYPEZYK W G, THOMAS T J. Method of adjusting the distribution of locomotive axle loads: United States, 4793047[P]. 1988-12-27.
[9] БЕЛОБАЕВ Г Я. ТЭМ3型内燃机车弹簧吊挂装置的调整[J]. 国外内燃机车, 1988(5): 50-52.
BELOBAEV G Y. Adjustment of the spring suspension mechanism of ТЭМ3-type diesel locomotive[J]. Foreign Diesel Locomotive, 1988(5): 50-52.
[10] 韩为民, 马睿, 朱善君, 等. 机车称重调簧算法的研究与应用[J]. 内燃机车, 2008(1): 19-22.
HAN Weimin, MA Rui, ZHU Shanjun, et al. Study and application of locomotive weighing and spring adjusting algorithm[J]. Diesel Locomotives, 2008(1): 19-22.
[11] 潘迪夫, 韩锟, 曾亚波, 等. 车体称重调簧试验装置及其应用[J]. 电力机车与城轨车辆, 2003, 26(5): 37-39.
PAN Difu, HAN Kun, ZENG Yabo, et al. Locomotive secondary spring load test device and its application[J]. Electric Locomotives & Mass Transit Vehicles, 2003, 26(5): 37-39.
[12] 王超, 倪文波, 王雪梅, 等. 基于SUMT算法的机车转向架调簧技术研究[J]. 内燃机车, 2008(8): 1-5.
WANG Chao, NI Wenbo, WANG Xuemei, et al. Study of spring adjustment technology of locomotive bogie based on SUMT[J]. Diesel Locomotives, 2008(8): 1-5.
[13] 潘迪夫, 黎航, 韩锟. 基于遗传算法的机车二系支承载荷调整优化方法[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2005, 26(3): 83-87.
PAN Difu, LI Hang, HAN Kun. Optimization model of locomotive secondary spring load adjustment based on genetic algorithm[J]. China Railway Science, 2005, 26(3): 83-87.
[14] 韩锟, 潘迪夫. 基于混合算法的机车二系弹簧载荷调整优化方法[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2006, 27(2): 88-92.
HAN Kun, PAN Difu. Optimization model for adjustment of locomotive secondary spring load based on hybrid algorithm[J]. China Railway Science, 2006, 27(2): 88-92.
[15] 杨本磊, 潘迪夫. 基于人工鱼群算法的机车二系支承载荷调整优化方法[J]. 计算机与现代化, 2011(1): 53-54.
YANG Benlei, PAN Difu. Optimization model of locomotive secondary spring load adjustment based on artificial fish-swarm algorithm[J]. Computer and Modernization, 2011(1): 53-54.
[16] 潘迪夫, 朱亚男. 基于多目标遗传算法的机车二系支承载荷调整优化方法[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2011, 8(2): 76-80.
PAN Difu, ZHU Yanan. Optimization model for locomotive secondary spring load adjustment based on multi-objective genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2011, 8(2): 76-80.
[17] PAN Difu, WANG Mengge, ZHU Yanan, et al. An optimization algorithm for locomotive secondary spring load adjustment based on artificial immune[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(12): 3497-3503.
[18] DIN 25045—1998, Railway vehicles-measurement and calculation calculation of static loads on running gears from passenger coach vehicle bodies[S].
[19] 汪民乐. 遗传算法的收敛性研究[J]. 计算机技术与自动化, 2015, 34(1): 58-62.
WANG Minle. Research on convergence of genetic algorithm[J]. Computing Technology and Automation, 2015, 34(1): 58-62.
[20] SRINIVAS M, PATNAIK L M. Adaptive probabilities of crossover and mutation in genetic algorithms[J]. IEEE Trans on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 1994, 24(4): 656-667.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2015-06-12;修回日期:2015-08-24
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51305467);湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(12JJ4050) (Project (51305467) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (12JJ4050) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province)
通信作者:韩锟,博士,副教授,从事载运工具智能测控技术及性能优化研究;E-mail: hkun@csu.edu.cn