DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-37540
Al、Cr和Nb在Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面的元素效应
孙顺平1,王 斌1,顾 顺1,李小平1,雷卫宁1,江 勇2,易丹青2
(1. 江苏理工学院 江苏省先进材料设计与增材制造重点实验室,常州 213001;
2. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:运用第一性原理平面波赝势方法计算了Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面结构,并通过元素界面偏析能的计算确定了Al、Cr和Nb在Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的偏析位置,结合脱粘功和差分电荷密度揭示了Al、Cr和Nb对Mo/MoSi2界面结合强度的影响。结果表明:Si顶位型配位方式的界面能最小,最为稳定,在Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面结构中倾向于以Si顶位型配位方式结合,其界面分离面在近界面MoSi2(110)一侧的亚界面层。Nb对界面结合不利,Cr可适当提高界面结合强度,而Al对界面强度的影响取决于其界面覆盖度。究其原因是由于Nb在界面偏析形成的Nb—Si键相比于Mo—Si键有明显减弱,Cr形成的Cr—Si键略有增强,而Al的界面覆盖度对形成的Mo—Al键强弱影响较大。
关键词 Mo/MoSi2;界面能;脱粘功;第一性原理
文章编号:1004-0609(2020)-03-0489-10 中图分类号:TG146.4+1 文献标志码:A
难熔金属钼(Mo)熔点高,热膨胀系数小,弹性模量高,且具有良好的机械稳定性及优异的高温抗蠕变性能,在航天工程领域有着广泛的应用和发展前景,是固体燃料火箭发动机推进器和喷管的重要服役材料[1-3]。但Mo的高温抗氧化性能较差,在725 ℃时即出现氧化物挥发,发生“灾害性”氧化,目前改善Mo高温氧化性能的主要方法是在其表面制备高温抗氧化涂层实现防护。大量工程实践证明硅化物是难熔金属钼的可靠涂层防护材料。在硅化物涂层中,MoSi2的高温抗氧化能力非常优异[2-5],高温下发生氧化时在表面形成致密的非晶态SiO2,可阻挡氧向内部扩散,而且非晶态SiO2具有流动性,能够弥补氧化进程中出现的微裂纹从而使涂层有自愈能力,可有效保护钼基体不被氧化[5-6]。1958年美国Langley Aeronautical实验室首次采用化学气相沉积(CVD)方法在Mo基体上制备了MoSi2涂层。目前,钼基硅化物涂层体系已经成为保障和支撑航天工程及空间装备等尖端技术高端应用的关键战略材料。
合金化已成为提高钼基硅化物涂层体系使役性能的重要方法。在纯Mo中添加Nb、Zr、Hf和Re等元素可得到钼合金,能够有效改善Mo的低温脆性,提高其高温抗氧化性能,可以进一步增大Mo在航天工程等高温结构材料领域的应用[7-10]。同样的,在MoSi2中添加合金元素Al、Cr和Nb等可以改善硅化物涂层的低温韧性和高温强度。其中Al元素可以减少MoSi2的屈服强度,改善合金的低温塑性[11],提高室温断裂韧性(4~6 MPa·m1/2)[12]。Cr元素对MoSi2的断裂韧性影响不大,但能够增加其高温(高于1573 K)屈服强度[13]。而且,Al和Cr元素由于与氧元素有很强的亲和力,能够阻止和改善MoSi2的Pesting氧化[13]。Nb元素对提高低温塑性、断裂韧性和高温强度都极为有效[11],被认为是改善MoSi2力学性能最有潜力的合金元素[14]。目前,元素Al、Cr和Nb等已成为钼基硅化物涂层体系中的常见合金化元素。
Mo与硅化物之间的界面结构及形貌特征决定了 钼/硅化物涂层系统的结合强度与使役性能。但钼/硅化物涂层体系的界面结构相对复杂,而且合金元素Al、Cr和Nb等常会偏析于其界面处影响界面的结合强度[15],这增加了界面问题的复杂性。针对涂层体系的界面问题,实验研究开展困难,表征难度较大,对Al、Cr和Nb等合金元素在Mo/MoSi2的界面元素效应研究还较为缺乏,这限制了新型涂层体系的开发与应用。第一性原理计算方法[16-20]通过界面原子尺度建模可以弥补实验研究及界面表征工作的局限,是研究材料界面问题的先进设计方法和重要手段。Hong等[21]研究了Mo(001)/MoSi2(001)的界面特征,并对元素Nb、C、O、B和S的界面偏析效应进行了计算,指出Nb和S会减弱Mo/MoSi2的界面强度,而C、O和B对界面结合有利。
本文作者[22]前期研究了MoSi2低指数表面的结构稳定性,指出MoSi2(110)表面能最低,最为稳定,而Mo作为体心立方结构,Mo(111)表面为密排面,也是相对稳定的表面形式,因而对钼/硅化物涂层系统中Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面结构展开深入研究是极为必要的。本文基于第一性原理计算研究了Mo(111)/ MoSi2(110)的界面结构、结合强度及电子结构,并揭示了合金元素Al、Cr和Nb在Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面元素效应,为新型难熔金属硅化物涂层体系的成分设计与界面调控奠定科学基础。
1 计算方法
第一性原理计算采用VASP软件[23]进行。采用PBE形式[24]的投影缀加平面波赝势(PAW)[25]描述元素的交换关联势,将Mo-4p64d55s1、Si-3s23p2、Al-3s23p1、Cr-3d54s1和Nb-4s24p65s14d4作为价电子,其余内层电子作为芯电子。在界面计算中,建立三明治型(A-B-A)结构的Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)共格界面,界面结构中Mo(111)和MoSi2(110)均选用对称性表面,其中MoSi2(110)表面为符合化学计量比表面。为保证z轴方向原子层之间不发生相互作用,需在界面模型中添加真空层,真空层厚度为15 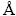 。K空间网格采用Monkhorst-Pack[26]方法划分,取值8×8×1,能量截断点为400 eV。体系总能量的收敛值为5.0×10-6 eV/atom,单个原子上的力低于0.1 eV/nm。
。K空间网格采用Monkhorst-Pack[26]方法划分,取值8×8×1,能量截断点为400 eV。体系总能量的收敛值为5.0×10-6 eV/atom,单个原子上的力低于0.1 eV/nm。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面能与脱粘功
由于界面结构中MoSi2(110)表面为符合化学计量比表面,表面终端不需要考虑,在Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)原子尺度建模时,只需确定Mo和MoSi2两相界面结合时的配位方式。在建立Mo(111)/ MoSi2(110)界面结构时,Mo(111)表面在MoSi2(110)表面8个可能的配位位置如图1所示。由于Mo(111)表面每层只有一个Mo原子,该原子位置即能代表Mo(111)的晶格位置。图1所示俯视图中以浅紫色圆圈表示Mo晶格的位置,而侧视图中以T、B和H表示这些位置具体的配位方式,分别为顶位、桥位和洞位。其中TMo和TSi为Mo顶位和Si顶位的配位方式,BMo、BSi、BMoSi1和BMoSi2为Mo桥位、Si桥位以及两种Mo-Si桥位的配位方式,而H1和H2为洞位的两种配位方式。
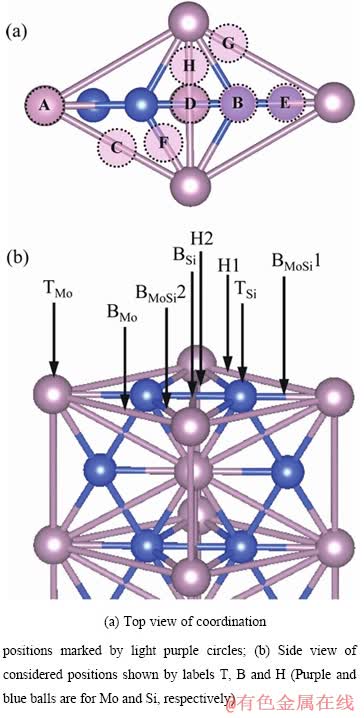
图1 不同配位方式Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面结构示意图
Fig. 1 Scheme of interface structures of Mo(111)/MoSi2(110) with different coordination types
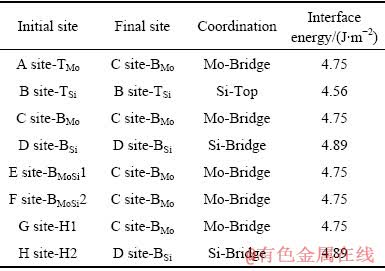
表1列出了Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的几何参数,包括Mo晶格的初始位置、弛豫后位置,以及配位方式。从表1中可以看出,只有三个配位位置是相对稳定的,Mo(111)表面的Mo原子配位在MoSi2(110)表面Si原子的顶位(B位置-Si顶位型),两个Mo原子之间的桥位(C位置-Mo桥位型),以及两个Si原子之间的桥位(D位置-Si桥位型),而其余5个位置都是不稳定的,因为在原子弛豫后Mo晶格分别移动到了上述的三个相对稳定的位置。
表1 Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的几何参数及界面能
Table 1 Geometric parameters and interface energies of Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)
为了研究Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面的稳定性,需要计算体系的界面能。根据表/界面能的定义[27-28],Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面能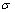 的计算公式如下
的计算公式如下
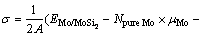
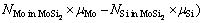 (1)
(1)
式中: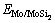 为Mo/MoSi2界面结构的总能;
为Mo/MoSi2界面结构的总能;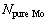 、
、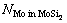 和
和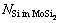 分别为界面结构中纯Mo部分的Mo原子数、MoSi2部分的Mo原子数和Si原子数;
分别为界面结构中纯Mo部分的Mo原子数、MoSi2部分的Mo原子数和Si原子数;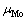 和
和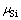 是界面结构中Mo元素和Si元素的化学势;A为界面面积,可由图1(a)所示俯视图通过晶格常数计算得出。
是界面结构中Mo元素和Si元素的化学势;A为界面面积,可由图1(a)所示俯视图通过晶格常数计算得出。
对于界面结构中的MoSi2而言,其在体相中的化学势应与其在界面中的化学势平衡,则有
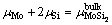 (2)
(2)
由于Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面中的MoSi2(110)表面为符合化学计量比的表面(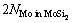 =
= 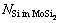 ),因而Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)体系的界面能与
),因而Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)体系的界面能与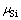 无关。结合公式(1)和(2),可得到其计算公式如下
无关。结合公式(1)和(2),可得到其计算公式如下
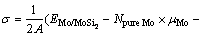
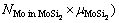 (3)
(3)
根据式(3)可以计算出Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面能,计算结果也列在表1中。从表1中可以看出,界面能与界面结构中两相的配位方式有关,两相的配位方式不同,界面能数值不同,但三种配位方式的界面能数值相差不大。Si桥位型配位方式界面能最大(4.89 J/m2),Mo桥位型配位方式界面能次之(4.75 J/m2),Si顶位型配位方式界面能最小(4.56 J/m2)。Si顶位型配位方式的界面能最小,表明该型配位方式最为稳定,在实际的Mo(111)/MoSi2(110) 界面结构中倾向于以Si顶位型配位方式结合。
Mo与硅化物之间的界面结构及特征决定了钼/硅化物涂层系统的结合强度。可通过界面系统总能的计算得到界面的脱粘功(Wsep),以此来评判界面的结合强度。Mo(111)/MoSi2(110) 界面的脱粘功Wsep计算公式如下
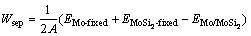 (4)
(4)
式中: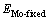 和
和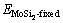 分别为界面结构沿分离面脱离后原子未驰豫情况下Mo部分及MoSi2部分的总能。
分别为界面结构沿分离面脱离后原子未驰豫情况下Mo部分及MoSi2部分的总能。
图2显示了Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面结构与脱粘功。图2中实线位置表示Mo(111)与MoSi2(110)的界面结合位置,而三种配位方式界面结构的俯视图也被显示在图中。在界面结合时,由于近界面的亚界面层中原子的电荷可能会往界面层积聚,而使亚界面层的结合作用减弱,因此近界面层的脱粘功也应被计算。图2中虚线位置显示了各个近界面层脱粘功的计算结果。通过比较各层脱粘功的大小得到界面结构的分离面,从而可确定界面实际的结合强度。
从图2中可以看出,Mo桥位型和Si桥位型配位方式的界面分离面在界面层,而Si顶位型配位方式的界面分离面在近界面MoSi2(110)一侧的亚界面层。三种不同配位方式的界面脱粘功相差不大,其中Mo桥位型配位方式脱粘功最大(3.80 J/m2),Si桥位型(3.67 J/m2)和Si顶位型(3.66 J/m2)配位方式脱粘功非常接近。脱粘功的计算结果表明Si顶位型配位方式的界面结合强度相对较弱。
2.2 Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面电荷密度
研究界面的电子结构可以分析界面原子电荷的得失情况,有助于进一步理解Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面结合特征。图3所示为Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面的差分电荷密度图。
从图3中的差分电荷密度图可以看出,Mo原子和Si原子之间存在着强共价键,这主要是由Mo-4d和Si-3p的轨道杂化所引起。从图3中也可以看出,Mo桥位型和Si桥位型配位方式的界面层,以及Si顶位型配位方式近界面MoSi2(110)一侧的亚界面层有明显的电荷减小,表明这些界面层及亚界面层结合强度较弱,易于在这些位置发生界面分离。该结论与上述脱粘功的计算结果一致。
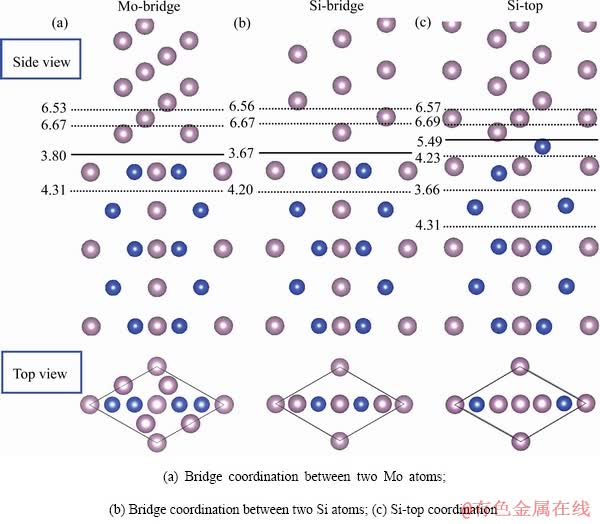
图2 Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面结构与脱粘功
Fig. 2 Interface structures and works of separation of Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)
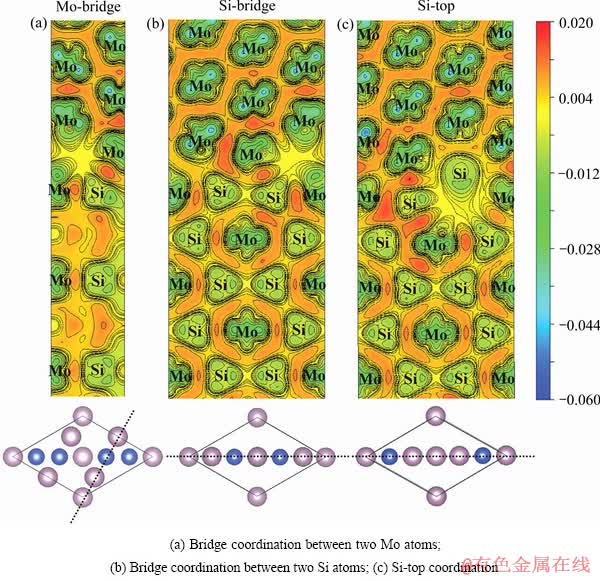
图3 Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面的差分电荷密度
Fig. 3 Deformation charge density of Mo(111)/MoSi2(110) interface(Unit: e/  3)
3)
2.3 Al、Cr和Nb在Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面元素效应
2.3.1 Al、Cr和Nb元素的界面偏析能与偏析路径
研究合金元素的界面效应,应先考虑合金元素在界面结构中可能占据的位置,如置换位置或间隙位置。之后,应判断其是倾向于界面处或在体相内,即评估合金元素是否有界面偏析的可能。由Langmuir- McLean公式[29-30],合金元素在Mo/MoSi2的界面偏析能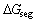 可通过式(5)计算
可通过式(5)计算
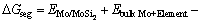
 (5)
(5)
式中: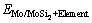 、
、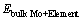 和
和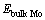 分别为合金元素掺杂在Mo/MoSi2界面结构中的总能、合金元素掺杂在Mo晶格中的总能和纯Mo晶格的总能。
分别为合金元素掺杂在Mo/MoSi2界面结构中的总能、合金元素掺杂在Mo晶格中的总能和纯Mo晶格的总能。
从式(5)的定义可以看出,界面偏析能为正值表示合金元素倾向偏析于界面处,而界面偏析能为负值则表示元素倾向存在于体相内。
由2.1部分界面能的计算结果得知,在实际的Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面结构中倾向于以Si顶位型配位方式结合,因此本工作仅考虑Si顶位型配位方式下合金元素对Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面元素效应。元素效应计算时在界面结构中分别掺杂一个或两个Al、Cr和Nb原子,界面覆盖度以MoSi2(110)表面的每层原子数为单位,则合金元素Al、Cr和Nb在Mo(111)/ MoSi2(110)的界面覆盖度为1/3 ML或2/3 ML。
表2列出了合金元素Al、Cr和Nb在Mo(111)/ MoSi2(110)的界面偏析能和偏析位置。表2中,合金元素的占位采用点缺陷记号方法,为了描述不同原子具体的偏析位置,定义若占据界面Mo一侧原子位置以下标1表示,占据界面MoSi2一侧原子位置则以下标2表示。从表2中可以看出,界面覆盖度为1/3 ML时,Al、Cr和Nb在Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面偏析能分别为1.06、1.39和0.40 eV,表明三种元素都存在界面偏析的可能。Yamazaki等[15]也提出Cr会偏析于C11b-MoSi2/C40-NbSi2双相硅化物的界面处。Al、Cr和Nb在Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面的偏析位置与这三种元素在MoSi2中的占位特征[31]一致,Al原子倾向占据Si原子位置,Cr和Nb倾向占据Mo原子位置。但是,由于界面结构相对复杂,三种原子的偏析位置各不相同,Al原子占据界面MoSi2一侧的Si原子位置(AlSi2),Cr原子占据界面Mo一侧的Mo原子位置(CrMo1),而Nb原子占据界面MoSi2一侧的Mo原子位置(NbMo2)。
表2 Al、Cr 和Nb在Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)的界面偏析能和偏析位置
Table 2 Segregation energies and segregation positions of Al, Cr and Nb at Mo(111)/MoSi2(110) interface
当合金元素在界面处的浓度继续提高,界面覆盖度为2/3 ML时,后期抵达界面的Al、Cr和Nb原子可能分别占据界面MoSi2一侧的Si原子位置(AlSi2),界面MoSi2一侧的Mo原子位置(CrMo2),和界面Mo一侧的Mo原子位置(NbMo1)。其中,Nb元素在Mo(111)/ MoSi2(110)的界面偏析能为正值,表明Nb仍存在继续界面偏析的可能,而Al和Cr界面偏析能为负值,表明Al和Cr原子界面偏析难以继续进行。但是,由于Al、Cr元素是MoSi2涂层中的主要合金化元素,在涂层的制备过程中难以排除其已存在于界面处的可能性,为谨慎起见,本工作中仍然计算了界面覆盖度为2/3 ML,Al和Cr原子对Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面结合的影响。
2.3.2 Al、Cr和Nb元素偏析对界面结合的影响
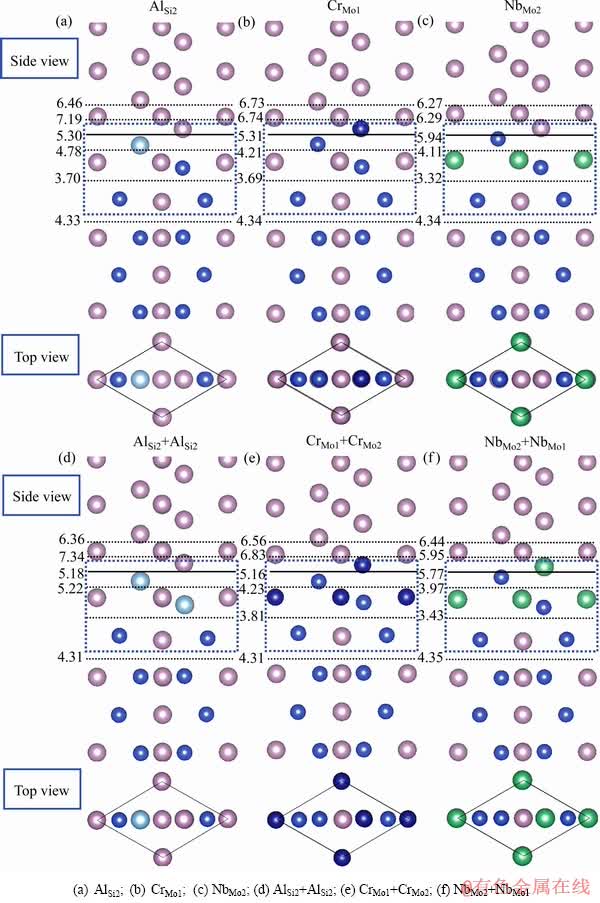
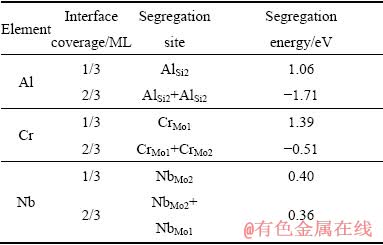
图4 Al、Cr 和Nb在Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面的偏析结构与脱粘功
Fig. 4 Segregation structures and works of separation of Al, Cr and Nb at Mo(111)/MoSi2(110) interface
在偏析能和偏析位置的研究基础上,可计算合金元素偏析于界面时界面系统的脱粘功(Wsep),并进一步结合相应的电荷密度分析合金元素偏析对界面结合的影响。图4显示了合金元素Al、Cr和Nb在Mo(111)/ MoSi2(110)界面的偏析结构与脱粘功。图4中实线位置表示Mo(111)与MoSi2(110)的界面结合位置,虚线位置表示各个近界面层的位置。为了更清晰地显示合金元素在界面中的偏析位置,图4也以俯视图的方式显示了近界面多个原子层(蓝色虚线框内)的结构特征。从图4可以看出,偏析Al、Cr和Nb元素的Mo(111)/ MoSi2(110)界面分离面均在近界面MoSi2(110)一侧的亚界面层,与纯净界面的分离面位置相同。与纯净界面的脱粘功相比,偏析三种元素的界面脱粘功相差不大。元素界面覆盖度为1/3 ML时,偏析Al和Cr的界面脱粘功略有增加,分别为3.70 J/m2和3.69 J/m2;而偏析Nb的界面脱粘功有一定程度的下降,为3.32 J/m2,约下降10%。元素界面覆盖度为2/3 ML时,含Al界面的脱粘功有一定程度的下降(3.53 J/m2);含Cr界面的脱粘功进一步增加(3.81 J/m2),继续偏析Nb的界面脱粘功略有回升,为3.43 J/m2,但仍低于纯净界面的脱粘功。脱粘功的计算结果表明Nb偏析于界面对界面结合不利,Cr元素可适当提高界面结合强度,而Al元素对界面强度的影响取决于Al的界面覆盖度。目前有关Al、Cr和Nb在Mo(111)/ MoSi2(110)界面元素效应的实验研究还未见报道。不过,Yamazaki等[15]指出Cr对C11b-MoSi2/C40-NbSi2双相硅化物的界面结合有利,而Hong等[21]通过计算研究发现Nb会减弱Mo(001)/MoSi2(001)的界面强度,本工作的计算结果与Hong等的观点一致。
图5 偏析Al、Cr和Nb的Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面的差分电荷密度
Fig. 5 Deformation charge densities of segregation structures of Al, Cr and Nb at Mo(111)/MoSi2(110) interface(Unit: e/ 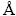 3)
3)
图5所示分别为偏析Al、Cr和Nb的Mo(111)/ MoSi2(110)界面的差分电荷密度图。从图5中可以看出,偏析Al、Cr和Nb界面的电荷密度与纯净界面的电荷密度特征非常接近,均在近界面MoSi2(110)一侧的亚界面层有明显的电荷减小,这表明这些亚界面层结合较弱。这一结论与脱粘功的计算结果一致。从图5也可以看出,Nb在界面偏析形成的Nb—Si键相比于Mo—Si键有明显减弱,Cr形成的Cr—Si键相比于Mo—Si键略有增强,而Al的界面覆盖度对形成的Mo—Al键强弱影响较大。这也解释了Nb偏析于界面对界面结合不利,Cr元素可适当提高界面结合强度,Al元素对界面强度的影响取决于Al的界面覆盖度。
3 结论
1) Si顶位型配位方式界面能最小、最为稳定,在Mo(111)/MoSi2(110)界面结构中倾向于以Si顶位型配位方式结合。
2) Mo桥位型和Si桥位型配位方式的界面分离面在界面层,而Si顶位型配位方式的界面分离面在近界面MoSi2(110)一侧的亚界面层。
3) Al、Cr和Nb三种元素都存在界面偏析的可能,但偏析位置各不相同,Al原子占据界面MoSi2一侧的Si原子位置(AlSi2),Cr原子占据界面Mo一侧的Mo原子位置(CrMo1),而Nb原子占据界面MoSi2一侧的Mo原子位置(NbMo2)。当合金元素在界面处浓度进一步提高时,继续偏析的Nb原子占据界面Mo一侧的Mo原子位置(NbMo1),而Al和Cr原子界面偏析难以继续进行。
4) Nb偏析于界面对界面结合不利,Cr元素可适当提高界面结合强度,而Al元素对界面强度的影响取决于Al的界面覆盖度,这是由于Nb在界面偏析形成的Nb—Si键相比于Mo—Si键有明显减弱,Cr形成的Cr—Si键相比于Mo—Si键略有增强,而Al的界面覆盖度对形成的Mo—Al键强弱影响较大。
REFERENCES
[1] 孙顺平, 顾 顺, 江 勇, 易丹青. 合金元素在Mo中的活度和溶解度[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(1): 115-121.
SUN Shun-ping, GU Shun, JIANG Yong, YI Dan-qing. Activity and solubility of alloying elements in Mo[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 29(1): 115-121.
[2] LI W, FAN J, FAN Y, XIAO L, CHENG H. MoSi2/ (Mo,Ti)Si2 dual-phase composite coating for oxidation protection of molybdenum alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 740: 711-718.
[3] ZHANG H A, HUANG Y, LIN J, CHEN Y, GU S. Growth kinetics and microstructure evolution of intermediate phases in MoSi2-Si3N4-WSi2/Mo diffusion couples[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering & Performance, 2016, 26(2): 1-6.
[4] 李 恒, 郝安林, 王雅雷, 熊 翔, 陈招科, 孙 威, 韩欣欣. 放电等离子烧结MoSi2陶瓷的微观结构与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(11): 2296-2302.
LI Heng, HAO An-lin, WANG Ya-lei, XIONG Xiang, CHEN Zhao-ke, SUN Wei, HAN Xin-xin. Microstructure and mechanical properties of MoSi2prepared by spark plasma sintering[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(11): 2296-2302.
[5] SUN J, FU Q, GUO L, LIU Y, HUO C, LI H. Effect of filler on the oxidation protective ability of MoSi2 coating for Mo substrate by halide activated pack cementation[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 92: 602-609.
[6] Jiang Y, Gong Q, Cai Z, Shao Y, Zhuang D, Liang J. Fabrication of CrSi2/MoSi2/SiC-Mo2C gradient compositecoatingonMosubstrate and the stabilizing effect of Cr on the coating’s anti-oxidation properties[J]. Surface andCoatingsTechnology, 2015,282: 188-199.
[7] Majumdar S. A study on microstructure development and oxidation phenomenon of arc consolidated Mo-Nb-Si-(Y) alloys[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials,2019, 78: 76-84.
[8] Chaudhuri A, Behera A N, Sarkar A, Kapoor R, Ray R K, Suwas S. Hot deformation behaviour of Mo-TZM and understanding the restoration processes involved[J]. Acta Materialia, 2019, 164: 153-164.
[9] Bolbut V, Bogomol I, Loboda P, Krüger M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a directionally solidified Mo-12Hf-24B alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018, 735: 2324-2330.
[10] Zhang Y, Wang T, Jiang S, Zhang B, Wang Y, Feng J. Effect of rhenium content on microstructures and mechanical properties of electron beam welded TZM alloy joints[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2018, 32: 337-343.
[11] Dasgupta T, Umarji A M. Improved dustility and oxidation resistance in Nb and Al co-substituted MoSi2[J]. Intermetallics, 2008, 16(6): 739-744.
[12] Mitra R, Rao V V R, Rao A V. Effect of small aluminum additions on microstructure and mechanical properties of molybdenum di-silicide[J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7(2): 213-232.
[13] Xu J, di Wu J, Li Z, Munroe P,Xie Z H. Mechanical properties of Cr-alloyed MoSi2-based nanocomposite coatings with a hierarchical structure[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 565: 127-133.
[14] Sharif A A, Misra A, Mitchell T E. Deformation mechanisms of polycrystalline MoSi2 alloyed with 1 at.% Nb[J]. Materials Scienceand Engineering A, 2003, 358(1/2): 279-287.
[15] Yamazaki T, Koizumi Y, Yuge K, Chiba A, Hagihara K, Nakano T, Kishida K, Inui H. Mechanisms of lamellar structure formation and Cr interfacial segregation inC11b-MoSi2/C40-NbSi2dual phase silicide verified by a phase-field simulation incorporating elastic in homogeneity[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2015,108: 358-366.
[16] Zheng H,Tran R,Li X G,Radhakrishnan B,Ong S P. Role of Zr in strengthening MoSi2from density functional theory calculations[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018,145: 470-476.
[17] Sun S P, Li X P, Zhang Y, Wang H J, Yu Y, Jiang Y, Yi D Q. Prediction of the mechanical properties of MoSi2 doped with Cr, Nb and W from first-principles calculations[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 714: 459-466.
[18] 蓝国强, 江 勇, 江 亮. 微合金化元素Zr 对热障涂层关键界面的强化效应及机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(9): 1967-1975.
LAN Guo-qiang, JIANG Yong, JIANG Liang. Strengthening effects and mechanisms of micro-alloying Zr on key interface in thermal barrier coating systems[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(9): 1967-1975.
[19] Sun S P, Li X P, Wang H J, Jiang Y, Yi D Q. Prediction on anisotropic elasticity, sound velocity, and thermodynamic properties of MoSi2 under pressure[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 652: 106-115.
[20] LUO K, ZANG B, FU S, JIANG Y, YI D Q. Stress/strain aging mechanisms in Al alloys from first principles[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(7): 2130-2137.
[21] Hong T, Smith J R, Srolovitz D J. Impurity effects on adhesion: Nb, C, O, B, and S at a Mo/MoSi2 interface[J]. Physical Review B, 1993,47(20): 13615-13625.
[22] Sun S P, Li X P, Wang H J, Jiang Y, Yi D Q. Adsorption of oxygen atom on MoSi2 (110) surface[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 382: 239-248.
[23] Kresse G, Furthmuller J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set[J]. Physical Review B, 1996, 54(16): 11169-11186.
[24] Perdew J P, Burke K M, Emzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(18): 3865-3868.
[25] Kresse G, Joubert J. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method[J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59(3): 1758-1775.
[26] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations[J]. Physical Review B, 1976, 13(12): 5188-5192.
[27] Cao F, Zheng J,Jiang Y, Chen B, Wang Y, Hu T. Experimental and DFT characterization of eta’ nano-phase and its interfaces in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2019, 164: 207-219.
[28] Sun S P, Zhu J L, Gu S, Li X P, Lei W N, Jiang Y, Yi D Q, Chen G H. First principles investigation of the surface stability and equilibrium morphology of MoO3[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 467/468: 753-759.
[29] Dowben P A, Miller A. Surface segregation phenomena[M]. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press Inc, 1990.
[30] Zhang W, Smith J R, Wang X G, Evans A G. Influence of sulfur on the adhesion of the nickel/alumina interface[J]. Physical Review B, 2003, 67(24): 245414.
[31] Li X P, Sun S P, Yu Y, Wang H J, Jiang Y, Yi D Q. Composition and temperature dependences of site occupation for Al, Cr, W, and Nb in MoSi2[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2015, 24(12): 120502.
Element effect of Al, Cr, and Nb on Mo(111)/MoSi2(110) interface
SUN Shun-ping1, WANG Bin1, GU Shun1, LI Xiao-ping1, LEI Wei-ning1, JIANG Yong2, YI Dan-qing2
(1. Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Materials Design and Additive Manufacturing, Jiangsu University of Technology, Changzhou, 213001;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The interface structures of Mo(111)/MoSi2(110) were calculated by the first-principle plane wave pseudopotential method. The segregation positions of Al, Cr and Nb at Mo(111)/MoSi2(110) were determined by the segregation energies, and their effects on the interface strength were revealed by the works of separation and deformation charge density. The results show that the interface energy of the Si-top coordination is the smallest. The Mo(111)/MoSi2(110) structure prefers to Si Top coordination, and its separation surface is the sub-interface on the MoSi2 side. Nb is unfavorable to interface strength, Cr can improve interface strength, and the influence of Al on interface strength depends on its interface coverage. The reason is that Nb—Si bond induced by Nb is significantly weaker than Mo—Si bond, while Cr—Si bond induced by Cr are slightly stronger than Mo—Si bond. And the interface coverage of Al has a great influence on the strength of Mo—Al bonds.
Key words: Mo/MoSi2; interface energy; works of separation; first-principle calculation
Foundation item: Project(51401093) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects (17KJA430006, 15KJA430003) supported by the Key Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu University, China
Received date: 2019-03-22; Accepted date: 2019-09-02
Corresponding author: SUN Shun-ping; Tel: +86-519-86953280; E-mail: sunshunping@jsut.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51401093);江苏省高等学校自然科学研究重大项目(17KJA430006,15KJA430003)
收稿日期:2019-03-22;修订日期:2019-09-02
通信作者:孙顺平,副教授,博士;电话:0519-86953280;E-mail:sunshunping@jsut.edu.cn