低孔隙岩石中断裂带内部结构及与油气成藏
付晓飞1, 2,尚小钰1, 2,孟令东1, 2
(1. 东北石油大学 CNPC断裂控藏实验室,黑龙江 大庆,163318;
2. 东北石油大学 非常规油气成藏与开发省部共建国家重点实验室培育基地,黑龙江 大庆,163318)
摘要:通过大量的野外露头资料,研究低-非孔隙性岩石内断裂变形机制及形成断裂带内部结构,分析断裂对非常规油气富集的控制作用。研究结果表明:低-非孔隙性岩石内断裂变形机制为破裂作用、碎裂作用和碎裂流作用,分别形成初角砾岩、角砾岩和碎裂岩以及超碎裂岩,前3类断层岩渗透性相对较高,多为流体运移的通道。不同岩性地层内形成的断裂带结构有共性也有差异,共同特征是:伴随位移增加,断裂带逐渐从“一元”结构向“二元”结构发展,一旦大规模断层泥形成,变形集中在断层核上,破碎带宽度不再明显增加。不同的是演化模式的差异,碳酸盐岩压溶作用明显,伴随大量压溶缝形成和生长连接,最终演化成断裂。火山岩特别是凝灰岩中,开始发生断裂变形不形成破碎带,而是先形成断层核。超固结泥岩形成的断裂带开始渗透性增强,伴随断层泥产生,渗透率又会接近母岩。这种差异可能造成断层封闭模式演化及油气富集规律的差异。仅发育破碎带小规模断层、无内聚力的断层角砾岩、碎裂岩以及具有连续断层核的破碎带为典型的高渗透性断层,对非常规储层油气充注起到重要的作用。断层核渗透性决定断层封闭类型及油气富集模式,高渗透性断层核本身不具有封闭能力,主要靠岩性对接封闭,油气通常富集在区域性盖层之下且主要富集在断裂的下盘。低渗透断层核具有很强的封闭能力,油气在两盘均可以富集。破碎带由于大量裂缝发育,成为非常规油气富集的“甜点”区,有些致密气和页岩气富集区沿着断层呈条带状分布。
关键词:低-非孔隙性岩石;断裂变形;结构;非常规储层;油气运聚成藏
中图分类号:TE122.3 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)06-2428-11
Internal structure of fault zone and oil/gas reservior in low-porosity rock
FU Xiaofei1, 2, SHANG Xiaoyu1, 2, MENG Lingdong1, 2
(1. Laboratory of CNPC Fault Controlling Reservoir, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing 163318, China;
2. Unconventional Oil/Gas Accumulation and Development, Province and Ministry Build State Key Laboratory Breeding Base, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing 163318, China)
Abstract: Based on a lot of outcrop data, the fault deformation mechanism and fault zone internal structure of low-non porosity rocks were studied, and the control of fault on the unconventional oil and gas accumulation was analyzed. The results show that fault deformation mechanism of low-non porosity rocks are fracturing, cataclasis and cataclastic flow effect, which respectively forms the beginning of breccia, breccia, cataclasite, and ultra-cataclasite. The former three types are relatively high in fault rocks permeability, and are the channels of fluid migration. The fault zone structure formed in different lithostratigraphies has both similarity and difference. The common feature is that fault zone gradually develops from “one dimensional” structure to “two-component” structure with increased displacement. Once the large-scale fault gouge forms, the deformation concentrated on fault core and damage zone width doesn’t increased significantly. The difference is in development pattern. The pressure solution of carbonate rock is apparent, and accompanied by a lot of pressure solution seam formation and growth connection, ultimately evolves into the fault. The volcanic rock, especially tuff, doesn’t form damage zone at the beginning of fault deformation, but first forms fault core. The fault zone formed in overconsolidated mudstone. The permeability increases at first, and with the growth of fault gouge, the permeability becomes close to that of the parent rock again. This difference may cause the disparity in the evolution of fault sealing model and the rule of hydrocarbon enrichment. Only developed damage zone of the small-scale fault, non-cohesive fault breccia, cataclasite and damage zone with the continuous fault core are the features of high permeability fault, which plays an important role in oil and gas filling in the unconventional reservoir. The permeability of fault core determines fault sealing type and hydrocarbon accumulation pattern, and high-permeability fault core itself doesn’t have the sealing ability, and mainly depends on juxtaposition seal. Oil and gas usually accumulates under the regional cover mainly at the footwall of fault. Low permeability fault core has sealing ability well, and oil and gas can accumulate at both the hanging wall and the footwall. With the development of a lot of fractures, damage zone becomes the “sweets” area of unconventional oil and gas enriches, and some rich regions of tight gas and shale gas distributes have band along the fault.
Key words: low-non-porosity rock; fault deformation; structure; unconventional reservoir; oil/gas migration and accumulation
断裂变形机制及断裂带内部结构是断层封闭性和流体沿断裂运移规律研究的基础[1]。一般来说按着孔隙度大小可将岩石分为3类:一是高孔隙度(high porosity)岩石,Fisher等[2]认为孔隙度大于15%,为多种类型的砂岩;二是低孔隙度(low porosity)岩石,Fisher等[2]认为孔隙度小于15%,多为处于超固结成岩阶段的砾岩、砂岩和黏土岩;三是非孔隙性(non porosity)岩石,孔隙度普遍小于5%,包括碳酸盐岩、火山岩、变质岩、埋藏抬升后的硫酸盐岩和卤化物岩。高孔隙度砂岩在未固结—半固结成岩阶段,断裂变形机制为颗粒边界摩擦滑动引起颗粒旋转和滚动,即为颗粒流(granular/particulate flow)[3-4],导致颗粒重排,形成解聚带(disaggregation zone)[5-7]。在固结成岩阶段,断裂变形机制为碎裂作用(cataclasis),之后颗粒边界摩擦滑动引起颗粒旋转和滚动,即为碎裂流(cataclastic flow),形成碎裂变形带(cataclastic bands)[8-16]。低孔隙度或非孔隙度岩石断裂变形机制有别于高孔隙度砂岩,因此,本文作者以固结的火山岩、碳酸盐岩、致密的砂岩和高度固结的泥岩为研究对象,考虑影响断裂变形的多种因素,系统研究断裂变形机制和断裂带内部结构,以便为剖析断裂的通道和遮挡作用打下基础,也为研究断裂对火山岩、碳酸盐岩、低渗透砂岩和页岩中非常规油气富集的控制作用提供依据。
1 低孔隙性岩石中断裂变形机制及微构造类型
地壳主要由沉积岩、火山岩和变质岩三大类岩石组成,沉积岩包括2类:一是由母岩风化产物组成的沉积岩,包括碎屑岩(砾岩、砂岩、粉砂岩和黏土岩)和化学岩(碳酸盐岩、硫酸盐岩、卤化物岩和硅岩等)。成岩阶段达到中成岩阶段B亚期—晚成岩阶段时,碎屑岩一般变为低孔隙性岩石,岩石力学特征为脆性。Fisher等[2]认为当石英砂岩孔隙度低于15%,标准化围压小于0.25时,石英砂岩发生典型的脆性变形,据此认为孔隙度小于15%的石英砂岩为低孔隙度砂岩。化学岩多为非孔隙性岩石(non-porous rock),但并非所有岩石变形均表现为脆性,碳酸盐岩和硅岩总体为脆性岩石,硫酸盐岩和卤化物岩在浅埋藏阶段为脆性,深埋后整体为塑性岩石,宋岩等[17]认为库车凹陷膏泥岩和盐岩脆-塑性转换深度大约为3 km。火山岩在侵入和喷发阶段处于熔融状态,发生断裂变形通常不形成明显的断裂带结构[18],冷却后即为脆性的非岩石。大部分变质岩为脆性的非孔隙性岩石。对于低-非孔隙性岩石能否成为有效储层,重要的因素之一就是断裂变形导致大规模裂缝形成,同时,由于断裂变形形成特殊的断裂带内部结构,对油气运聚又有着重要的影响。
1.1 断裂变形机制
砂岩中断裂变形机制的转换起因于2种作用:一是成岩作用的增强,特别是石英压溶胶结作用导致砂岩孔隙度明显降低,Fisher等[2]认为当石英砂岩孔隙度低于15%,标准化围岩小于0.25时,石英砂岩中断裂变形由高孔隙度阶段的颗粒流和碎裂流向破裂为主的变形转变。二是抬升作用,埋藏固结成岩后抬升阶段发生断裂变形,由于应力松弛和压力释放[19-20],节理大量发育,展示了明显的脆性变形特征。影响断裂变形机制的因素既有内因(岩性、矿物成分、成岩阶段、孔隙度和渗透率),也有外因(温度、围压、超压和变形深度)[8, 19]。对低孔隙岩石而言,主要的影响因素为岩性、围压和变形深度、超压和温度。
1.1.1 岩性对变形机制的影响
低-非孔隙性岩石主要发生脆性变形,形成渗透性较高的断裂带。但随着泥质含量增加,塑性变形越来越明显,泥岩、泥灰岩、膏泥岩和盐岩发生塑性变形,产生泥岩涂抹。秦皇岛地区柳江盆地张赵庄背斜北翼的两条逆冲断层(图1),背斜核部为张夏组鲕粒灰岩,顶部发育厚度为1 m的泥灰岩,逆冲断层伴随背斜拱起而形成,断裂在鲕粒灰岩层发生典型的脆性变形,形成初角砾岩带,而在泥灰岩层产生明显的泥岩涂抹。
1.1.2 深度对变形机制的影响
非孔隙性岩石中发生断裂变形与低孔隙砂岩相似,在埋藏小于3 km时,断裂变形开始主要产生破裂作用(图2)[21],产生大量的粒间裂缝和粒内裂缝[19],形成无内聚力的断层角砾岩和断层泥,一般来说,这种断裂带具有“膨胀”特征,随着裂缝形成和张开,渗透率明显增大[2, 19]。随着裂缝越来越发育,当埋深超过3 km后,沿着裂缝发生摩擦滑动并伴随破碎的颗粒滚动,即为碎裂作用(Cataclasis),产生碎裂流(图2),变形结果形成断层泥、有内聚力的断层角砾岩和碎裂岩[19],断层泥带渗透率较低,而有内聚力的断层角砾岩带和碎裂岩带渗透率同围岩比,有时较高,有时较低,变高和变低的控制因素目前不清楚。埋藏固结成岩后抬升阶段发生断裂变形,由于应力松弛和压力释放[19-20],裂缝大量发育,断裂变形形成无内聚力的断层角砾岩和断层泥(图2),形成高渗透断裂带。
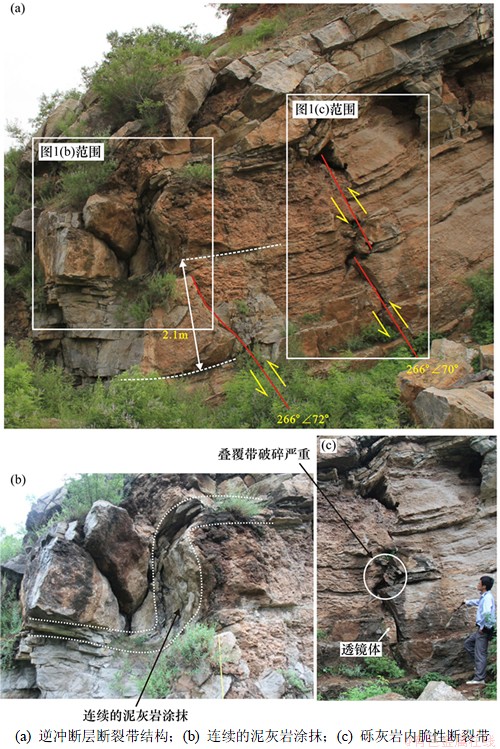

图1 秦皇岛柳江盆地秋子裕背斜西翼逆冲断层断裂带结构
Fig. 1 Thrust fault zone strcture at west edge of Qiuziyu Anticline, Liujiang Basin, Qinhuangdao
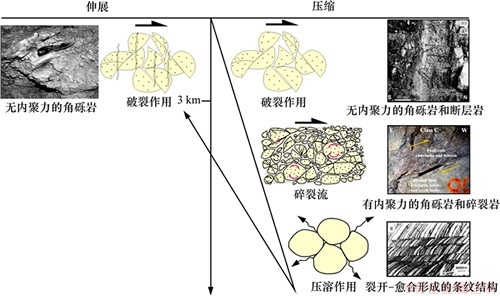
图2 低-非孔隙性岩石断裂变形机制及断层岩类型
Fig. 2 Deformation mechanism and fault rock type of low-non porosity rock
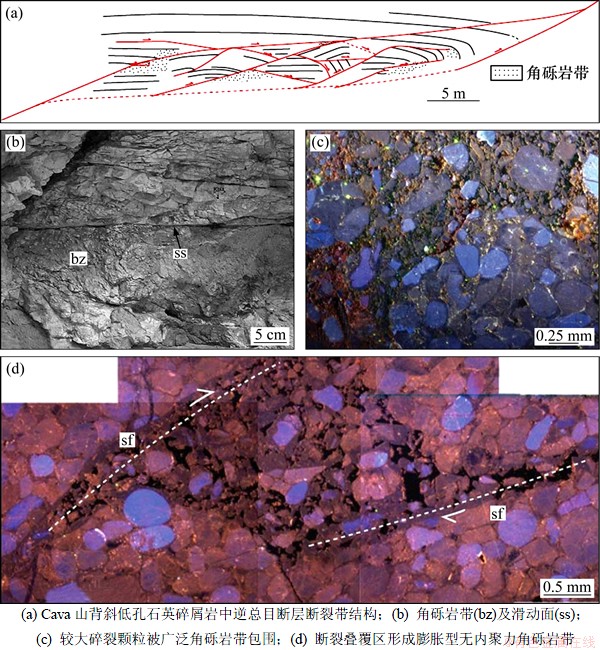
图3 阿巴拉契亚山脉中段前陆冲断带中发育在低孔隙石英砂岩中的逆冲断层断裂带结构[21]
Fig. 3 Fault structure of low porosity quartz sandstone developed thrust fault from foreland thrust zone in the middle of Appalachian Chain[21]
1.1.3 超压对变形机制影响
低孔隙岩石断裂变形机制主要为破裂作用,形成高渗透性断裂带,伴随超压流体注入,减小了围压的作用,即使变形深度很大依然形成膨胀型断层角砾岩带。阿巴拉契亚山脉中段Alleghanian前陆冲断带出露的、发育在低孔隙(孔隙度小于3%,经历最大埋深接近6 km)石英砂岩中的逆冲断层(断距约为30 m)[21]广泛发育破碎带,分布在逆冲断层叠覆转换带上(图3(a)),主要由相互交织断层网络、次级逆冲断层(为不连续的滑动面)组成,破碎带内常见节理发育带、交织小断层带(断距一般小于10 m)、断层岩带主要为无内聚力断层角砾岩(图3(b))。断层之间的叠覆带见有明显的膨胀角砾岩带(图3(c)),Cook等[21]认为与超压流体沿断裂运移有关。
1.1.4 温度对变形机制影响
对于致密的石英砂岩来说,在地温超过90 ℃时,断裂变形使碎裂带发生明显的石英压溶胶结[22],形成封闭性很强的碎裂带[8]。应力诱导的压溶作用在碳酸盐岩断裂变形中更为明显(图2)[23]。狭窄的裂缝形成后被结晶矿物充填即为裂开-封闭机理[23-32],压溶胶结作用是裂缝充填的主因,形成胶结的断裂带和裂缝,常与母岩构成条纹结构(图2)。
1.2 岩石变形形成的微构造特征
高孔隙性砂岩变形形成的微构造类型为变形带,从未固结—半固结、固结到超固结成岩阶段分别形成解聚带、碎裂带和压溶胶结的碎裂带,按着力学性质可分为膨胀带、剪切带和压缩带[19]。低-非孔隙性岩石变形受成岩阶段影响较小,岩石变形形成的微构造多为裂缝,按着力学性质分为张裂缝、剪裂缝和压溶缝。断裂带内裂缝展布规律符合里德尔剪切,将岩石切割破碎(图4),形成断层角砾岩(图4),进一步变形产生碎裂流作用,形成碎裂岩(图4),最终演变成断层泥。
2 断裂带内部结构特征
2.1 断裂带内部结构及物性结构
低-非孔隙性岩石内断裂带具有典型的二分结构:断层核和破碎带。断层核包括无内聚力角砾岩、有内聚力角砾岩和碎裂岩、断层泥、构造透镜体和滑动面。破碎带发育大量的裂缝,且随着离断层核距离增加,裂缝密度越来越小。对比不同分带的物性特征(图5),有内聚力角砾岩和碎裂岩孔隙度和渗透率比母岩的略低;无内聚力断层角砾岩孔隙度比母岩高2%~5%,渗透率高1~4个数量级;强烈破碎带孔隙度比母岩高5%~6%,渗透率高4~6个数量级;一般破碎带孔隙度比母岩高2%~6%,渗透率高1~6个数量级。变形深度超过3 km断裂即使形成有内聚力的碎裂岩和超碎裂岩,其孔隙度和渗透率也比母岩的略高[1, 33]。Holland等[34]研究表明:在脆性泥岩中发生断裂变形,不再产生典型的泥岩涂抹;相反,主要发生碎裂作用。开始产生小规模膝折、褶皱和破裂,高密度裂缝产生,导致岩石内聚力明显降低,但母岩的构造仍能清晰可见,被称为变形岩石(distorted rock)(图6),孔隙度明显增大,渗透率增加。进一步发生变形,断裂带内泥质大量增加,使断层岩内开启裂缝减小、内聚力增大,被称为转换类型断层岩(母岩向断层泥转换)(图6),孔隙度增大,但渗透率明显降低。变形最终形成断层泥(fault gouge),尽管孔隙度增大,但渗透率基本接近母岩的渗透率(图6)。
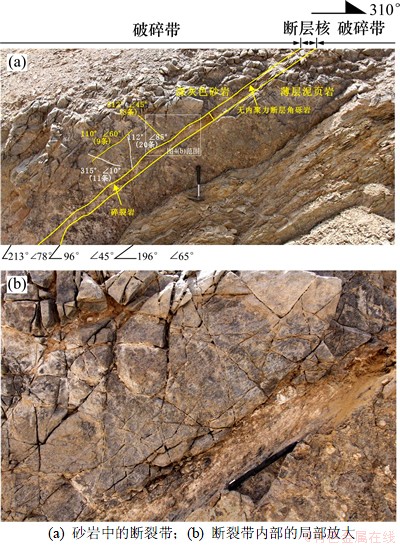

图4 塔里木盆地柯坪地区萤石矿剖面出露志留系砂岩中的断裂
Fig. 4 Silurian sandstone fault of fluorspar mineral section at Keping,Tarim Basin
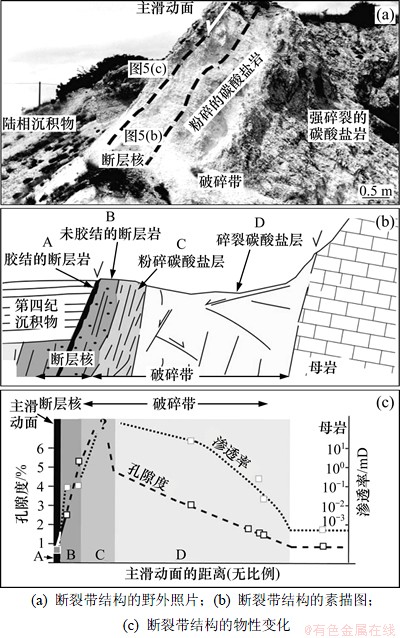
图5 意大利Funico盆地边界断层断裂带结构及物性变化
Fig. 5 Fault zone structure and physical property alternation of Italy Funico basin boundary fault

图6 脆性泥岩断裂带变形、渗透性及演化过程[34]
Fig. 6 Brittle mudstone fault zone deformation,permeability and evolutionary process[34]
2.2 断裂带内部结构形成演化过程
断层核和破碎带二元结构的形成首先源于破裂作用,开始先形成破碎带,伴随断距增加,断裂带从破碎带向“二元”结构发展。Micarelli等[35]的研究表明(图7):位移小于1 m的断层缺少断层核(图7(a)和(b));位移为1~5 m的断层有不连续的断层核(图7(a)和(c));大位移断层有由碎裂岩组成的连续的断层核(图7(a)和(d))。伴随断层核形成,变形集中在断层核上,破碎带宽度不再明显增加(图7(e))。发育成熟的断层形成断层核和破碎带二元结构,若变形发生在3 km以内,断层核可能主要为无内聚力的角砾岩和断层泥,无内聚力角砾岩为高渗透;若变形发生在3 km以外,断层核主要为碎裂岩,物性相对较高,碎裂作用进一步增强,形成超碎裂岩,物性逐渐降低。伴随变形程度不断增加,角砾岩和碎裂岩逐渐向断层泥演化。
Gray等[36]研究美国内华达丝兰山脉熔接凝灰岩断裂带结构发现,断裂随着位移增加,逐渐从单一断层核向“二元”结构方向发展(图8),断层核由角砾岩向碎裂岩和断层泥方向发展(图8)。
3 断裂带结构对非常规储层中油气富集的控制作用
3.1 高渗透断层核和破碎带为油气运移提供了通道条件
从低-非孔隙性岩石断裂带内部结构形成过程看,油气垂向运移通道有4种类型:一是规模较小的无断层核的断层(图7(b)),主要发育破碎带,大量裂缝相互交织组成油气垂向运移通道;二是在埋藏小于3 km内特别是抬升期断裂变形形成的有连续断层核的断层[37],断层核为无内聚力角砾岩,为高渗透性运移通道;三是在埋深大于3 km断裂变形形成的有连续断层核断层,断裂变形伴随高压流体注入,形成无内聚力角砾岩带(图3),也为油气垂向运移的通道;四是埋深大于3 km断裂变形形成破碎程度不高的碎裂岩带[33],比超碎裂岩带和母岩具有更高的孔渗性,为流体垂向运移的通道。在低-非孔隙性岩石内形成的这四类断裂,为油气充注的通道。
3.2 断层核渗透性决定断层侧向封闭能力及油气分布模式
低-非孔隙性岩石内形成的断裂具有断层核和破碎带二元结构,破碎带中发育大量裂缝,不具有封闭能力,即使裂缝被胶结物充填,也和母岩具有相同的渗透性,起封闭作用的主要是断层核。断层核渗透性不同,断层封闭能力和封闭类型不同。若断层核为高渗透的角砾岩带或碎裂岩带,则断裂带本身不具有封闭能力,主要靠岩性对接封闭[18],油气紧邻区域性盖层分布,且主要分布在断裂的下盘。典型的是松辽盆地徐家围子断陷徐中断裂[18],该断裂为走滑断层,形成于营城组一段时期,为“裂隙式”火山喷发的通道,没形成明显的断裂带结构,在泉头组沉积晚期—青山口组沉积早期再活动,形成断层角砾岩带和破碎带,为天然气垂向运移的通道,断层角砾岩为高渗透性通道,不具有封闭能力,因此,主要靠岩性对接封闭,天然气富集在区域性盖层之下,且主要分布在断裂下盘,由于走滑作用的“丝带效应”,天然气沿徐中断裂呈“正弦曲线”形态分布[18]。

图7 西西里岛Hyblean高原碳酸盐岩内断裂演化模式[35]
Fig. 7 Development pattern of Sicilian Island Hybleam highland carbonate rock fault[35]
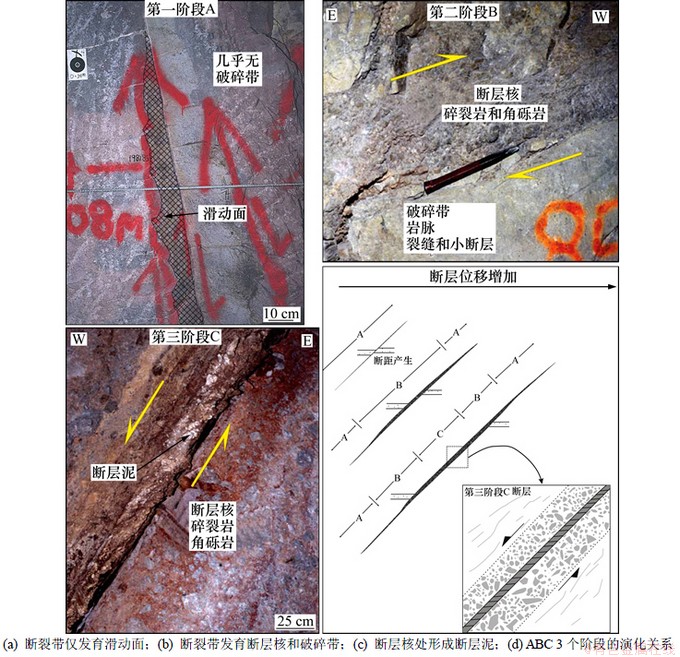
图8 Yucca山脉火山凝灰岩中3个级别(断距逐渐增大)正断层断裂带结构[36]
Fig. 8 Fault zone structure of three levels (throw increases gradually) normal fault in Yucca chain volcanic tuff[36]
对于高渗透的断层核形成早期通常不起到分割油气作用,但伴随着胶结作用发生,断层封闭能力越来越强。由于胶结作用总是发生在特定性质断层内,因此,一个区块总会出现一些断层分割油气,一些断层不封闭的特征。代表性实例为海拉尔盆地苏德尔特浅变质潜山,断裂变形发生在南屯组沉积时期,在基岩中形成断层角砾岩充填(图9),不具有封闭能力,油气整体向苏德尔特潜山充注。同时,规模较大断层活动导致深部流体注入,胶结作用发生(图9),断层封闭,特别是以规模较大的断层封闭最强,导致出现大断层分割油气,而小断层两侧油水界面相似的特征。
若断层核为低渗透的断层泥带或超碎裂岩带时,由于断裂带本身具有很强的封闭能力,能够在断层下盘、上盘或两盘封闭住一定的烃柱高度,由于断层泥多为磨蚀作用形成,很难用SGR去预测[38],因此,定量预测烃柱高度很难。
3.3 低-非孔隙性岩石与顶部区域性盖层断裂带结构差异造成输导和封闭耦合
低-非孔隙性岩石主要发生脆性变形,形成渗透性较高的断裂带;相反,顶部的区域性盖层(泥岩、泥灰岩、膏泥岩和盐岩)则发生塑性变形,产生泥岩涂抹,其连续性取决于盖层厚度与断距之间关系(SSF为泥岩厚度与断距的比值),一般认为SSF大于5时[39-45],规模较大断层形成的泥岩涂抹失去连续性。只要泥岩涂抹保持连续性,断层垂向就是封闭的。
3.4 破碎带明显改造储层形成非常规油气富集的“甜点”区
低—非孔隙性岩石中破碎带发育,Kim等[46]将破碎带分为围岩破碎带(wall damage zone)、连接破碎带(linkage damage zone)和端部破碎带(tip damage zone)。
连接型破碎带为叠覆断层相互作用,在转换带位置形成的破碎带,Soliva等[47]认为,当断层位移大于叠覆区离距时,转换带开始产生大量次级破裂,形成破碎带,其宽度与断层位移呈正相关关系。破碎带由于应力集中,次级破裂发育,不仅有效改善储层,同时激发流体运移,成为非常规储层中油气的富集区域。端部破碎带,又称过程带(process zone),由于端点应力集中,微破裂发育而形成的扩容区[48-49]。由于断裂端点地震不可识别的特征,过程带总是孤立地出现在断层端点附近。围岩破碎带裂缝的密度随着距离断层核距离增加而逐渐减小[1],当裂缝密度与区域裂缝密度接近时,标志着破碎带结束。Barnett页岩中发育大量与断层相关裂缝[50],若不被胶结,则将成为页岩气富集的“甜点区”。

图9 海拉尔盆地苏德尔特潜山胶结的断层角砾岩带
Fig. 9 Cemented fault breccia zone in Suderte buried hill of Hailaer Basin
4 结论
(1) 在低-非孔隙性岩石内断裂变形机制为破裂作用、碎裂作用和碎裂流作用,分别形成初角砾岩、角砾岩和碎裂岩以及超碎裂岩。前3类断层岩渗透性较高,多为流体运移的通道。
(2) 不同岩性地层内形成的断裂带结构有共性也有差异,共同特征是,伴随位移增加,断裂带逐渐从“一元”结构向“二元”结构发展,一旦大规模断层泥形成,变形集中在断层核上,破碎带宽度不再明显增加。不同的是演化模式的差异,碳酸盐岩压溶作用明显,伴随大量压溶缝形成和生长连接,最终演化成断裂。火山岩特别是凝灰岩中,开始发生断裂变形不形成破碎带,而是先形成断层核。超固结泥岩形成的断裂带开始渗透性增强,伴随断层泥产生,渗透率又会接近母岩。这种差异可能造成断层封闭模式演化及油气富集规律的差异。
(3) 仅发育破碎带小规模断层、无内聚力的断层角砾岩、碎裂岩以及具有连续断层核的破碎带为典型的高渗透性断层,对非常规储层油气充注起到重要的作用。
(4) 断层核渗透性决定断层封闭类型及油气富集模式,高渗透性断层核本身不具有封闭能力,主要靠岩性对接封闭,油气通常富集在区域性盖层之下且主要富集在断裂的下盘。低渗透断层核具有很强的封闭能力,油气在两盘均可以富集。
(5) 破碎带由于大量裂缝发育,成为非常规油气富集的“甜点”区,有些致密气和页岩气富集区沿着断层呈条带状分布。
参考文献:
[1] 付晓飞, 许鹏, 魏长柱, 等. 张性断裂带内部结构特征及与油气运移和保存[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(2): 1-13.
FU Xiaofei, XU Peng, WEI Changzhu, et al. Internal structure of normal fault and hydrocarbon migration and conversation[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(2): 1-13.
[2] Fisher Q J, Casey M, Harris S D, et al. Fluild flow properties of faults in sandstone: The importance of temperature history[J]. Geology, 2003, 31: 965-968.
[3] Twiss R J, Moores E M. Structural geology[M]. Freeman, San Francisco: CA, 1992: 100-145.
[4] Rawling G C, Goodwin L B. Cataclasis and particulate flow in faulted, poorly lithified sediments[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2003, 25: 317-331.
[5] Mandl G, DeJong L N J, Maltha A. Shear zones in granular material[J]. Rock Mechanics, 1977, 9: 95-144.
[6] Du Bernard X, Eichhubl P, Aydin A. Dilation bands: A new form of localized failure in granular media[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2002, 29(24): 2176-2179.
[7] Bense V F, van den Berg E H, van Balen R T. Deformation mechanisms and hydraulic properties of fault zones in unconsolidated sediments,the Roer Valley Rift System, The Netherlands[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2003, 11: 319-332.
[8] Fisher Q J, Knipe R J. The permeability of faults within siliciclastic petroleum reservoir of the North sea and Norwegian continental shelf[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2001, 18: 1063-1081.
[9] Aydin A, Johnson A M. Development of faults as zones of deformation bands and as slip surfaces in sandstones[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1978, 116: 931-942.
[10] Aydin A, Johnson A M. Analysis of faulting in porous sandstones[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1983, 5: 19-31.
[11] Beach A, Welborn A I, Brockbank P J, et al. Reservoir damage around faults: Outcrop examples from the Suez rift[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 1999, 5: 109-116.
[12] Du Bernard X, Labaume P, Darcel C, et al. Cataclastic slip band distribution in normal fault damage zones, Nubian sandstones,Suez rift[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107: 21-41.
[13] Wibberley C A J, Petit J P, Rives T. Mechanics of cataclastic ‘deformation band’ faulting in high-porosity sandstone, Provence[J]. Sciences, 2000, 331: 419-425.
[14] Underhill J R, Woodcock N H. Faulting mechanisms in high-porosity sandstones: New Red Sandstone, Arran, Scotland[C]//Jones M E, Preston R M F. Deformation of Sediments and Sedimentary. London: Geological Society, Special Publications, 1987: 91-105.
[15] Beach A, Brown J L, Welbon A I, et al. Characteristics of fault zones in sandstones from NW England: application to fault transmissibility[C]//Meadows N S, Trueblood S P, Hardman M, et al. Petroleum Geology of the Irish Sea and Adjacent Areas. London: Geological Society, Special Publications, 1997: 315-324.
[16] Knott S D. Fault seal analysis in the North Sea[J]. AAPG, 1993, 77: 778-792.
[17] 宋岩, 赵孟军, 李本亮, 等. 我国中西部前陆盆地油气地质特征及勘探战略[J]. 中国工程科学, 2010, 12(5): 39-45.
SONG Yan, ZHAO Mengjun, LI Benliang, et al. Oil and gas geological characteristics and exploration strategy in foreland basins, central and western China[J]. China Engineering Science, 2010, 12(5): 39-45.
[18] 付晓飞, 沙威, 于丹, 等. 松辽盆地徐家围子断陷火山岩内断层侧向封闭性及与天然气成藏[J]. 地质论评, 2010, 56(1): 60-70.
FU Xiaofei, SHA Wei, YU Dan, et al. Lateral sealing of faults and gas reservoir formation in volcanic rocks in Xujiaweizi fault depression[J]. Geological Review, 2010, 56(1): 60-70.
[19] Fossen H. Structural geology[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2010: 119-185.
[20] Fossen H, Schultz R A, Shipton Z K, et al. Deformation bands in sandstone: A review[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164: 755-769.
[21] Cook J E, Dunne W M, Onasch C M. Development of a dilatant damage zone along a thrust relay in a low-porosity quartz arenite[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2006, 28: 776-792.
[22] Walderhaug O. Kinetic modeling of quartz cementation and porosity loss in deeply buried sandstone reservoirs[J]. AAPG, 1996, 80(5): 731-745.
[23] Gaviglio P. Crack-seal mechanism in a limestone: A factor of deformation in strike-slip faulting[J]. Tectonophysics, 1986, 131: 247-255.
[24] Ramsay J G. Abstract, Tectonic studies group meeting[R]. London: Geology Society, 1977: 73-75.
[25] Ramsay J G. The crack-seal mechanism of rock deformation[J]. Nature, 1980, 284(13): 135-139.
[26] Labaume P, Berty C, Laurent P. Syn-diagenetic evolution of shear structures in superficial nappes: An example from the Northern Apennines(NW Italy)[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1991, 13: 385-398.
[27] Petit J P, Wibberley C A J, Ruiz G. ‘Crack-seal’slip: A new fault valve mechanism?[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1999, 21: 1199-1207.
[28] Blenkinsop T G. Deformation microstructures and mechanisms in minerals and rocks[M]. Kluwer: Kluwer Academic Publisher, 2000: 1-80.
[29] Alvarez W, Engelder T, Geiser P A. Classification of solution cleavage in pelagic limestones[J]. Geology, 1978, 6: 263-266.
[30] Salvini F, Billi A, Wise D U. Strike-slip fault-propagation cleavage in carbonate rocks: The Mattinata Fault zone, Southern Apennines, Italy[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1999, 21: 1731-1749.
[31] Graham B, Antonellini M, Aydin A. Formation and growth of normal faults in carbonates within a compressive environment[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(1): 11-14.
[32] Antonellini M, Aydin A. Effect of faulting on fluid flow in porous sandstones: Petrophysicial properties[J]. AAPG, 1994, 78: 355-377.
[33]  Y, Diraison M, Orellana N. Fault zone geometry of a mature active normal fault: A potential high permeability channel (Pirgaki fault, Corinth rift, Greece)[J]. Tectonophysics, 2006, 426: 61-76.
Y, Diraison M, Orellana N. Fault zone geometry of a mature active normal fault: A potential high permeability channel (Pirgaki fault, Corinth rift, Greece)[J]. Tectonophysics, 2006, 426: 61-76.
[34] Holland M, Urai J L, van der Zee W, et al. Fault gouge evolution in highly overconsolidated claystones[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2006, 28: 323-332.
[35] Micarelli L, Benedicto A C, Wibberley A J. Structural evolution and permeability of normal fault zones in highly porous carbonate rocks[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2006, 28: 1214-1227.
[36] Graya M B, Stamatakosb J A, Ferrillb D A, et al. Fault-zone deformation in welded tuffs at Yucca Mountain, Nevada, USA[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2005, 27: 1873-1891.
[37] Agosta F, Aydin A. Architecture and deformation mechanism of a basin-bounding normal fault in Mesozoic platform carbonates, central Italy[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2006, 28: 1445-1467.
[38] Bretan P, Yielding G, Jones H. Using Calibrate shale gouge ratio to estimate hydrocarbon column heights[J]. AAPG, 2003, 87(3): 397-413.
[39] Lindsay N G, Murphy F C, et al. Outcrop studies of shale smear on fault surface[J]. International Association of Sedimentologists Special Publication, 1993, 15: 113-123.
[40] Doughty P T. Clay smear seals and fault sealing potential of an exhumed growth fault, Rio Grande rift, New Mexico[J]. AAPG, 2003, 87(3): 427-444.
[41] Faerseth R B, Johnsen E, Sperrevik S. Methodology for risking fault seal capacity: Implications of fault zone architecture[J]. AAPG, 2007, 91(9): 1231-1246.
[42] Koledoye B A, Aydin A, May E. A new process-based methodology for analysis of shale smear along normal faults in the Niger Delta[J]. AAPG, 2003, 87(3): 445-663.
[43] Gibson R G. Fault-zone seals in siliciclastic strata of the Columbus Basin, Offshore Trinidad[J]. AAPG, 1994, 78(9): 1372-1385.
[44] Fristad T, Groth A, Yielding G, et al. Quantitative seal prediction: a case study from Oseberg Syd[C]//Moller-Pedersen P, Koestler A G. Hydrocarbon seals: Importance for exploration and production. Singapore: Norwegian Petroleum Society Special Publication, 1997: 107-124.
[45] Childs C, Manzocchi T, Walsh J J, et al. A geometric model of fault zone and fault rock thickness variations[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2007, 31: 117-127.
[46] Kim Y S, Peacock D C P, Sanderson D J. Fault damage zone[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2004, 26: 503-517.
[47] Soliva R, Benedicto A, Schultz R A, et al. Displacement and interaction of normal fault segments branched at depth: Implications for fault growth and potential earthquake rupture size[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2008, 30: 1288-1299.
[48] Cowie P A, Shipton Z K. Fault tip displacement gradients and process zone dimensions[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1998, 20: 983-997.
[49] Atkinson B K. Fracture mechanics of rock[M]. London: Academic Press, 1987: 477-525.
[50] Julia F W G, Reed R M, Holder Jon. Natural fractures in the Barnett shale and their importance for hydraulic fracture treatments[J]. AAPG, 2007, 91(4): 603-622.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2012-06-25;修回日期:2012-09-05
基金项目:教育部科学技术研究重点项目(212041);黑龙江省普通高等学校新世纪优秀人才培养计划项目(1251-NCET-015);中石油中青年创新基金资助项目(2012-5006-0107)
通信作者:付晓飞(1973-),男,内蒙古赤峰人,教授,从事断裂变形、封闭性及流体运移研究;电话:13936973951;E-mail:Fuxiaofei2008@sohu.com