文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-06-1167-08
振动频率对间接超声辅助铸造Al-24%Si合金的影响
赵龙志,李 洋,张 坚,赵明娟
(华东交通大学 机电工程学院 载运工具与装备教育部重点实验室,南昌 330013)
摘 要:采用间接超声振动辅助铸造法制备Al-24%Si合金(质量分数),利用金相显微镜、电子万能试验机、磨损试验机、扫描电镜和显微硬度计分别研究超声波频率对合金的显微组织、抗压强度、磨损性能和显微硬度的影响。结果表明:施加20.4 kHz的超声处理对合金中初晶硅和共晶硅的细化作用最佳,初晶硅平均尺寸为100 μm,共晶硅平均尺寸为40 μm;随着超声频率的增大,合金抗压强度先增大后减小,磨损率先减小后增大;磨损机制主要为磨粒磨损和粘着磨损;合金的显微硬度先增大后减小,与合金中硅相尺寸呈负相关关系。
关键词:Al-24%Si合金;显微组织;超声频率;抗压强度;磨损性能;显微硬度
中图分类号:TB331 文献标志码:A
过共晶铝硅合金密度低,热膨胀系数小并具有良好的力学性能,因此,被广泛应用于航空航天、汽车和电子行业,具有广阔的应用前景[1-3]。然而,普通铸造方法制备的过共晶铝硅合金中,初晶硅呈粗大的板条状,严重割裂基体,降低合金的力学性能,限制了其应用领域。因此,细化初晶硅具有重要的意义。
变质处理是细化初晶硅的常用方法,它主要是在合金熔体中添加变质剂,如赤磷和稀土。赤磷能够很好地细化初晶硅,使初晶硅的粒度变小,但是赤磷不能够细化共晶硅;稀土不仅能细化初晶硅,而且对共晶硅也有明显的细化作用,但稀土变质成本高,不利于工业化应用[4-6]。近年来,人们发现在凝固阶段的金属熔体中导入超声波振动,能够很明显地细化凝固组织,因此,超声振动细化晶粒得到了人们的青睐[7-8]。
超声波振动处理是利用超声波的空化、声流和热效应等作用于熔体,以期达到细化晶粒目的[9-12],超声波的加入方式通常有两种,一种是直接法[13],即将变幅杆直接插入熔体中进行超声波处理,另外一种是间接法[14],即对盛有熔体的坩埚进行处理。目前,人们对超声处理的研究热点多集中在直接法,该方法处理效果明显,但变幅杆必须承受600 ℃以上的高温,变幅杆易烧蚀,降低了其处理效果和使用寿命,间接法变幅杆工作温度低,处理效果稳定,易于操作且成本低廉。刘清梅等[14]通过在变幅杆外侧缠绕电流线圈,利用电流线圈产生的电磁力将坩埚吸附在变幅杆上,从侧部间接导入超声振动,发现间接法施加超声振动细化晶粒的方法可行。然而,在高硅铝合金凝固过程中施加磁场也能细化初晶硅[15],上述侧部间接导入超声振动的方法无法排除磁场在细化晶粒方面的作用。本文作者采用的间接法排除了磁场的干扰,从坩埚底部施加间接超声振动辅助铸造法制备了Al-24%Si合金,研究了振动频率对合金显微组织以及力学性能的影响。
1 实验
本实验中以工业用ZL102和高纯硅块(Si≥99.9%,质量分数)为原料,配制成Al-24%Si高硅铝合金,在800 ℃保温150 min。然后,将800 ℃下的高硅铝合金熔体倒入施加超声振动且温度可控的不锈钢坩埚中,实验装置图如图1所示。浇注前,先将不锈钢坩埚预热至450 ℃;浇注后,超声振动持续作用时间为7 min。所用超声波发生器为TJS-3000智能数控超声波发生器V6.0,功率为1000 W,变幅杆振幅为10 μm,依次选择加载的超声谐振频率为20.0、20.2、20.4、20.6和20.8 kHz。
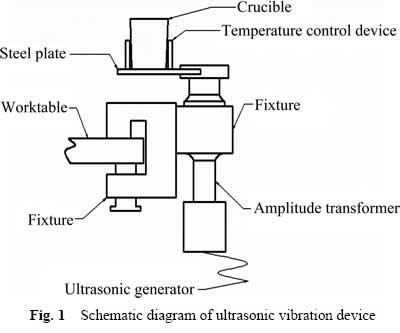
图1 超声振动装置示意图
制取底部直径60 mm和高度40 mm的圆柱体铸锭,采用线切割法从中间沿断面取样,分别切割10 mm×10 mm×25 mm的压缩试样和7 mm×7 mm×30 mm的磨损试样。采用蔡司AxioVert.A1型金相显微镜观察了铝硅合金的显微组织。Al-24%Si合金显微硬度测试在XHV-1000Z型显微硬度计上进行,试验选定载荷为5 N,加载时间为20 s,每个试样测取10个硬度值,然后取平均值作为该试样的硬度值。压缩性能在岛津AG-X型立式电子万能压缩试验机上进行,压缩速率为1 mm/min。利用M-2000型磨损试验机测试合金的磨损性能,主轴转速为180 r/min,载荷为300 N,超声波清洗,取试样磨损前后的质量差作为磨损量,质量用精确度为0.1 mg的MA110型电子分析天平测得。用磨损量除以试样的初始质量得到该试样的磨损率,用磨损率来衡量试样的磨损性能。采用JSM6360LA型扫描电子显微镜观察了试样的磨损形貌。
2 结果与分析
2.1 超声振动对铝硅合金的影响
2.1.1 超声振动对显微组织的影响
不同处理条件下Al-24%Si合金的显微组织如图2所示。其中图2(a)所示为未施加超声振动处理的铝硅合金,图2(b)所示为施加超声振动处理的铝硅合金。未施加超声振动的铝硅合金中,初晶硅呈现出粗大的板条状,长度在200~1600 μm之间(见图2(a))。由于在未经任何处理的铝硅合金中,初晶硅的析出不会受到阻碍,导致其持续析出至熔体凝固,最终表现为粗大的板条状。而施加超声振动后的铝硅合金中,初晶硅表现为小块状,尺寸约为150 μm(见图2(b))。在铝硅熔体凝固过程中施加超声振动,由于受超声振动的空化、声流、谐振等作用的影响,初晶硅不能持续析出长大,从而使硅相尺寸减小。硅相尺寸的减小,使得硅相对基体的割裂作用减弱,从而提高合金力学性能。
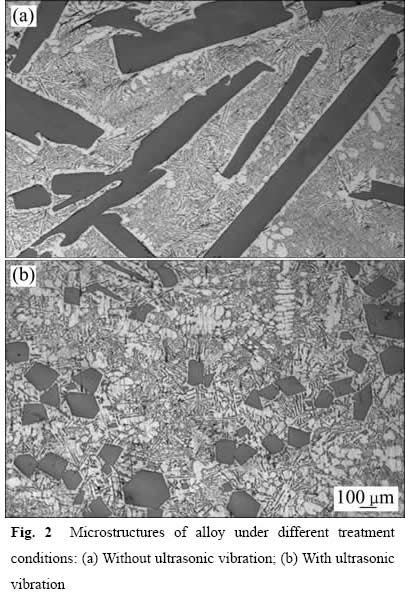
图2 不同处理条件下合金的显微组织
2.1.2 超声振动对力学性能的影响
图3所示为未施加和施加超声处理后的合金性能对比。图3中左侧柱状图依次为不施加超声处理的合金抗压强度、磨损率和硬度,右侧柱状图依次为经过20.4 kHz超声处理的合金抗压强度、磨损率和硬度。由图3可知,未经过超声处理的合金抗压强度、磨损率和硬度依次为239 MPa、0.0443和95 HV,经过20.4 kHz超声处理的合金抗压强度、磨损率和硬度依次为493 MPa、0.0261和128 HV。相对于未经超声处理的合金,经过20.4 kHz超声处理的合金的抗压强度和硬度明显提高,分别提高106%和34%,磨损率则降低41%。如前所述,不经过超声处理的铝硅合金中,初晶硅呈板条状,共晶硅为粗针状。经过20.4 kHz超声处理的合金中初晶硅和共晶硅分布表现为小块状和极细的针状。
铝硅合金中硅的含量以及硅相的平均尺寸是影响合金力学性能的直接因素,由于未经过超声处理和经过超声处理的合金中Si含量都是24%,所以硅相的尺寸是影响合金各项力学性能的唯一原因。铝硅合金细晶强化中,合金的强度与组织中硅相尺寸和数量的关系为[16]

式中: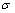 为铝硅合金的强度;f为合金中硅的体积分数;d为硅相的平均尺寸。显然,铝硅合金的强度与硅相的尺寸成反比。硅相的尺寸越大,铝硅合金的强度越差。所以超声处理够显著提高铝硅合金的抗压强度、磨损率和显微硬度,且细化后硅相平均尺寸越小合金力学性能越好。
为铝硅合金的强度;f为合金中硅的体积分数;d为硅相的平均尺寸。显然,铝硅合金的强度与硅相的尺寸成反比。硅相的尺寸越大,铝硅合金的强度越差。所以超声处理够显著提高铝硅合金的抗压强度、磨损率和显微硬度,且细化后硅相平均尺寸越小合金力学性能越好。
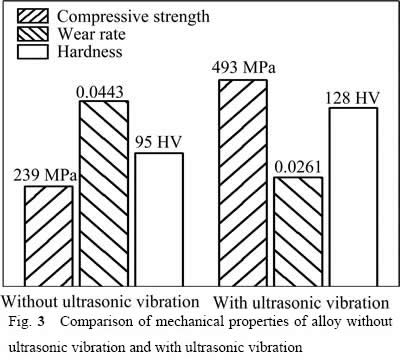
图3 未施加超声和施加超声后合金的性能对比
2.2 振动频率对合金显微组织的影响
图4所示为经过不同谐振频率的超声波处理后Al-24%Si合金的显微组织形貌。图中深灰色区域为初晶硅和共晶硅组织,浅白色区域为初生α(Al)组织。图4(a)和(b)所示分别为经过20.0 kHz超声处理后的合金显微组织形貌。由图4(a)可知,初晶硅主要呈长板条状、短棒状和大块状,平均尺寸为120 μm。共晶硅主要表现为细针状和粗针状,平均尺寸为70 μm(见图4(b))。图4(c)和(d)所示分别为经过20.2 kHz超声处理后的合金显微组织形貌。初晶硅主要呈现长板条状、短板条状和大块状,短棒状的初晶硅数量居多,平均尺寸为110 μm,且长板条状和大块状初晶硅组织都从中心开始发生断裂现象(见图4(c))。共晶硅表现为粗针状,平均尺寸为80 μm(见图4(d))。图4(e)和(f)所示分别为经过20.4 kHz超声处理后的合金显微组织形貌。经过20.4 kHz超声处理的合金中初晶硅表现为小块状,平均尺寸为100 μm,相对形状较为规律且分散性较好(见图4(e))。共晶硅呈现极细的针状,平均尺寸为40 μm(见图4(f))。图4(g)和(h)所示分别为经过20.6 kHz超声处理后的合金显微组织形貌。能够观察到初晶硅也呈小块状,平均尺寸为120 μm,初晶硅尺寸明显大于图4(e)中所示初晶硅尺寸,且初晶硅的分散性欠佳(见图4(g))。共晶硅表现为短小的粗针状,平均尺寸为40 μm(见图4(h))。图4(i)和(j)所示分别为经过20.8 kHz超声处理后的合金显微组织形貌。经过20.8 kHz超声处理后的合金,初晶硅表现为大块状,平均尺寸为160 μm,分散性不佳(见图4(i))。共晶硅表现为粗针状和极细的长针状,以粗针状居多,平均长度为60 μm(见图4(j))。对比5种条件下合金的显微组织可知,施加超声振动后,初晶硅和共晶硅都得到不同程度的细化。这是因为施加超声振动后,超声波的空化作用导致金属熔体中产生了大量的空化泡,空化泡在长大的过程中会从周围熔体吸收大量的热,产生局部过冷提高过冷度,促进晶粒细化。空化泡长大到一定程度会发生破裂,破裂时产生瞬间的高温和高压引发增殖形核效应即空化效应,使晶粒进一步得到细化。同时,超声波的声流作用使金属熔体内部产生剧烈的搅拌效应,导致枝晶在根部颈缩,最终熔断(见图4(a)和(c))。空化和声流共同作用,使得板条状的初晶硅破碎成为块状和短棒状的初晶硅,粗针状的共晶硅断裂成为细针状的共晶硅。但是,对比5种显微组织可见,相对于其他4种显微组织,超声频率为20.4 kHz的显微组织中,初晶硅及共晶硅均得到了良好细化,且分布较为均匀(见图4(e))。这是因为当施加超声振动的频率和金属熔体系统的固有频率相近或者成一定比值时,结晶体会在振动信号的激励下产生谐振效应[17]。铝硅合金熔体处于谐振状态时,初晶硅和共晶硅剧烈震荡,界面能级发生变化,最终导致相变驱动力减小,硅晶粒长大速度随之减小。同时,铝硅合金熔体内的谐振效应产生的机械力改变了初晶硅的搭接,使初晶硅重新熔入液相,增强了超声振动对铝硅合金组织的细化作用。
2.3 振动频率对力学性能的影响
2.3.1 振动频率对合金抗压强度的影响
图5所示为经过不同谐振频率超声处理后合金的抗压强度。随着超声频率的增加,合金的抗压强度先增加后减小。由图5可知,经过20.4 kHz的超声处理的合金抗压强度最高,为493 MPa。合金试样的抗压强度与合金的显微组织中硅相的尺寸有直接关系,含
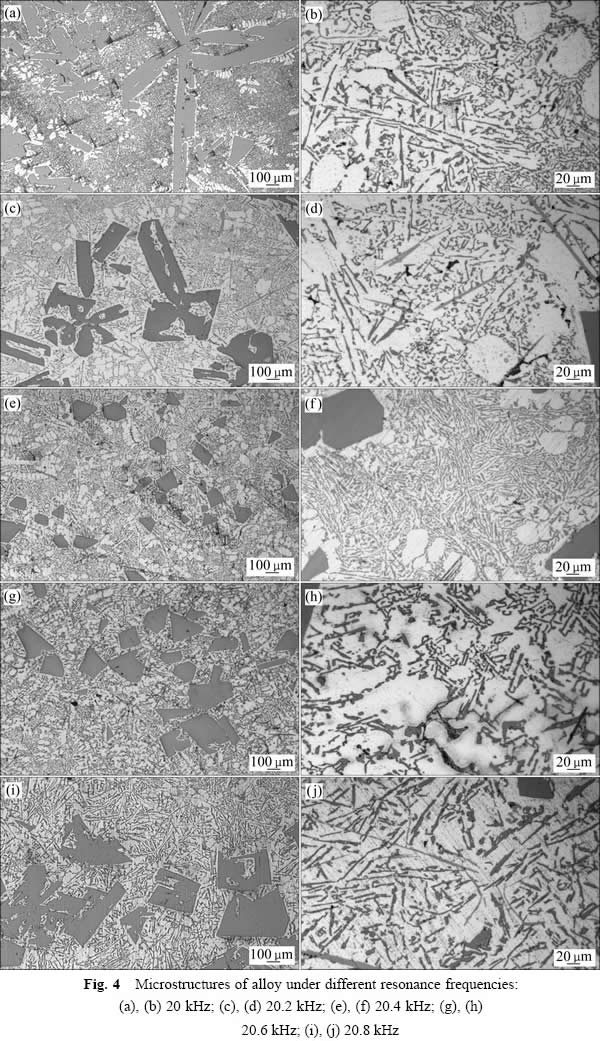
图4 不同谐振频率作用下合金的显微组织
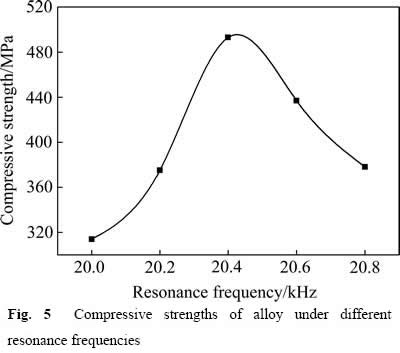
图5 不同谐振频率作用下合金的抗压强度
有板条状初晶硅的合金抗压强度明显低于含有块状初晶硅的合金,含有大块状初晶硅的合金抗压强度也明显低于含有小块状初晶硅的合金。由于空化和声流作用,经过不同谐振频率超声波处理的合金组织中板条状初晶硅数量明显下降,硅相主要为块状的初晶硅和细针状的共晶硅。而经过20.4 kHz超声处理的合金会额外受到谐振效应的作用,其中初晶硅呈极小的块状,板条状初晶硅完全消失,细化作用最佳。初晶硅和共晶硅得到充分细化后,当合金承受载荷时,组织变形均匀,塑性相对提高,抗压强度也相应提高。
2.3.2 振动频率对合金显微硬度的影响
图6所示为不同处理方式的Al-24%Si合金的显微硬度。经过显微硬度测试,分别得到经过谐振频率为20.0、20.2、20.4、20.6和20.8 kHz超声处理的合金的显微硬度。超声频率为20.4 kHz时,合金的硬度达到最高128 HV。结合图4中合金的显微组织可知,随着超声频率的增加,铝硅合金的显微硬度先增大后减小,且铝硅合金的显微硬度与合金显微组织中硅相尺寸总体上呈负相关关系。由于气孔、杂质等因素影响,合金的显微硬度不是严格遵循与硅相尺寸呈负相关关系。但总体而言,在误差允许范围内,硅相尺寸大的合金对应的显微硬度低,硅相尺寸小的合金对应的合金的显微硬度高。经过超声的作用,铝硅合金中初晶硅和共晶硅得到不同程度的细化。图4表明,超声处理不仅影响硅相的尺寸大小,同时也影响硅相在基体中的分散性。硅相得到充分细化的组织中,分散性最均匀。由于硅相的细化以及分散性的改善,初晶硅对基体的割裂作用减弱,合金的硬度得到提高。另一方面,超声的施加也能改善合金组织中缺陷分布的均匀性,从而使合金硬度得到明显提高。
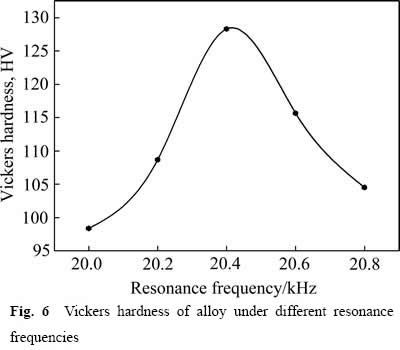
图6 不同谐振频率作用下合金的显微硬度

图7 不同谐振频率作用下合金的磨损率
2.3.3 振动频率对合金耐磨性的影响
图7所示为经过不同谐振频率超声处理后合金的磨损率。随着超声频率的增加,合金磨损率先减小后增大。施加20.4 kHz超声处理的合金磨损率最低,为0.0261。如前所述,在20.4 kHz超声作用下,铝硅合金熔体额外受到该谐振频率下特有的谐振效应影响,初晶硅和共晶硅受到的细化作用最为显著(见图4(e))。细化后小块状初晶硅和极细针状共晶硅与基体的结合良好。在往复摩擦力的作用下,相对于板条状及大块状初晶硅以及粗针状共晶硅而言,细化最佳的合金中硅相从基体上剥离的难度加剧,进而表现出低磨损率。所以细化作用良好的组织对应的合金磨损率也较低。
图8所示为合金磨损后的表面形貌。其中图8(a)和(b)所示分别为未施加超声的铝硅合金的磨损形貌,图8(c)和(d)所示分别为施加超声为20.4 kHz的铝硅合金的磨损形貌。相对于未施加超声的合金,施加超声
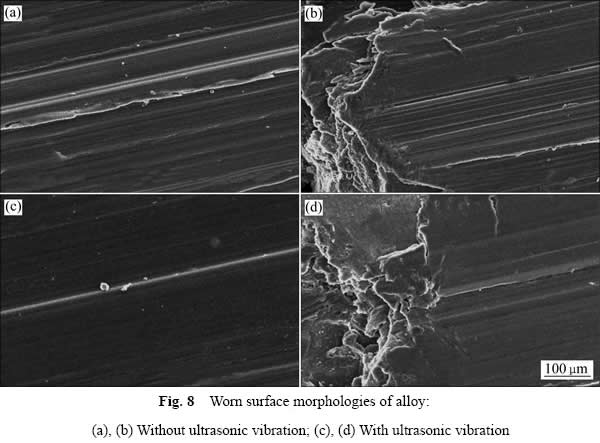

图8 合金磨损后的表面形貌
的合金磨损面较为光滑,犁沟较浅且数量相对较少(见图8(a)和(c))。所有合金的磨损形貌中都有犁沟和结疤出现,说明磨损机制为磨粒磨损和粘着磨损[18]。在磨损过程中,铝硅合金的磨损面有硬质硅颗粒脱落,硬质颗粒在载荷作用下与磨损面产生微切削作用,进而产生犁沟。细化初晶硅,能够让硅相和基体很好的结合,提高合金的耐磨性。同时,脱落的硅相颗粒数量和体积明显降低,所以超声处理后合金的犁沟相对较浅,且犁沟数量要明显少于未施加超声处理的铝硅合金。图8(c)和(d)所示分别为磨损结束阶段合金的表面磨损形貌,图中可见深浅以及数量不一的犁沟。此外,合金表面发生了明显的塑性变形,并出现疤状的结点。磨损过程中,合金试样与珩磨轮的实际接触面只占表观基础面中很小的一部分,磨损作用使合金表面接触点处于塑性状态。同时,磨损产生的高温在磨损面形成粘着结点,并最终形成疤状形貌。
3 结论
1) 超声振动处理Al-24%Si合金,最高能够使抗压强度提高106%,硬度提高34%,磨损率降低41%。
2) 超声频率为20.4 kHz时,超声对Al-24%Si合金中硅相的细化作用最显著。
3) 随着超声频率的增加,铝硅合金的抗压强度先增大后减小,磨损率先减小后增大,在20.4 kHz时分别达到最大值及最小值。
4) 随着超声振动频率的增加,铝硅合金的显微硬度先增大后减小。
REFERENCES
[1] 安建军, 严 彪, 程 光. 高性能高硅铝基合金研究展望[J]. 金属功能材料, 2009, 16(4): 50-52.
AN Jian-jun, YAN Biao, CHENG Guang. Development of high performance Al-Si alloy with high Si content[J]. Metallic Functional Materials, 2009, 16(4): 50-52.
[2] 禹胜林, 薛松柏, 尹邦跃, 黄 薇. Al-Si电子封装材料粉末冶金法致密性研究[J]. 材料工程, 2014(2): 45-50.
YU Sheng-lin, XUE Song-bai, YIN Bang-yue, HUANG Wei. Sintering densification of Al-Si composite by powder metallurgy method for electronic packaging[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2014(2): 45-50.
[3] 孙廷富, 杨 波, 翟 景, 郭安振, 郭 锋, 崔崇亮. 过共晶铝硅合金缸体/缸套工作面加工技术及应用[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2013, 36(5): 120-124.
SUN Ting-fu, YANG Bo, ZHAI Jing, GUO An-zhen, GUO Feng, CUI Chong-liang. Working face machining technique and application of hypereutectic silicon aluminium alloy engine cylinder/cylinder sleeve[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2013, 36(5): 120-124.
[4] 刘相法, 乔进国, 刘玉先, 李士同, 边秀房. Al-P中间合金对共晶和过共晶Al-Si合金的变质机制[J]. 金属学报, 2004, 40(5): 471-476.
LIU Xiang-fa, QIAO Jin-guo, LIU Yu-xian, LI Shi-tong, BIAN Xiu-fang. Modification performance of the Al-P master alloy for eutectic and hypereutectic Al-Si alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2004, 40(5): 471-476.
[5] XING P F, GAO B, ZHUANG Y X, LIU K H, TU G F. On the modification of hypereutectic Al-Si alloys using rare earth Er[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2005, 23(5): 327-333.
[6] CHEN C, LIU Z X, REN B, WANG M X, WENG Y G, LIU Z Y. Influences of complex modification of P and RE on microstructure and mechanical properties of hypereutectic Al-20Si alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(2): 301-306.
[7] ESKIN G I. Principles of ultrasonic treatment application for light alloys melts[J]. Advanced Performance Materials, 1997, 4(2): 223-232.
[8] PAN J, YOSHIDA M, SASAKI G, FUKUNAGA H, FUJIMURA H, MATSUURA M. Ultrasonic insert casting of aluminum alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2000, 43(2): 155-159.
[9] KHALIFA W, EL-HADAD S, TSUNEKAWA Y. Microstructure characteristics and tensile property of ultrasonic treated-thixocast A356 alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(10): 3173-3180.
[10] 谭伟民, 陆春华, 马立群, 沈晓冬, 许仲梓. 高能超声制备金属基复合材料的研究进展与展望[J]. 材料导报, 2006, 20(Z2): 258-260.
TAN Wei-min, LU Chun-hua, MA Li-qun, SHEN Xiao-dong, XU Zhong-zi. Research progress and prospect of metal matrix composites fabricated by high intensity ultrasonic[J]. Materials Review, 2006, 20(Z2): 258-260.
[11] ZHANG L H, JUN Y U, ZHANG X M. Effect of ultrasonic power and casting speed on solidification structure of 7050 aluminum alloy ingot in ultrasonic field[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2010, 17(3): 431-436.
[12] SUN Q J, LIN S B, YANG C L, ZHAO G Q. Penetration increase of AISI 304 using ultrasonic assisted tungsten inert gas welding[J]. Science & Technology of Welding & Joining, 2009, 14(8): 765-767.
[13] 闫 洪, 贺 儒, 李正华. 超声原位Mg2Si/AM60复合材料显微组织及力学性能的研究[J]. 功能材料, 2013, 44(22): 3338-3342.
YAN Hong, HE Ru, LI Zheng-hua. Research on microstructures and mechanical properties of in-situ Mg2Si/AM60 composites with ultrasonic treatment[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2013, 44(22): 3338-3342.
[14] 刘清梅, 龚永勇, 侯 旭, 戚飞鹏, 翟启杰. 侧部导入超声处理对共晶Al-Si合金凝固特性的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(2): 308-312.
LIU Qing-mei, GONG Yong-yong, HOU Xu, QI Fei-peng, ZHAI Qi-jie. Influence of side ultrasonic treatment on solidification characterization of Al-Si eutectic alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(2): 308-312.
[15] 冉新天, 任忠鸣, 邓 康, 李 喜, 李伟轩. Al-18%Si合金在梯度强磁场中凝固时初生硅的行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(1): 72-78.
RAN Xin-tian, REN Zhong-ming, DENG Kang, LI Xi, LI Wei-xuan. Behavior of primary Si of Al-18%Si alloy in high gradient magnetic field[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(1): 72-78.
[16] 甘卫平, 刘 泓, 杨伏良. 不同制备工艺对高硅铝合金组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2006, 20(3): 126-128.
GAN Wei-ping, LIU Hong, YANG Fu-liang. Microstructures and mechanical properties of high silicon aluminum alloy effected by different process[J]. Materials Review, 2006, 20(3): 126-128.
[17] 蒋日鹏, 李晓谦, 李开烨, 张 雪. 超声对铝合金凝固传热与组织形成的影响与作用机制[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(10): 3807-3813.
JIANG Ri-peng, LI Xiao-qian, LI Kai-ye, ZHANG Xue. Effect of ultrasonic on heat transfer and microstructure formation of aluminum alloy during solidification and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology) , 2012,43(10): 3807-3813.
[18] 温诗铸. 材料磨损研究的进展与思考[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2008, 28(1): 1-5.
WEN Shi-zhu. Research progress on wear of materials[J]. Tribology, 2008, 28(1): 1-5.
Influence of vibration frequency on indirect ultrasonic aided casting Al-24%Si alloy
ZHAO Long-zhi, LI Yang, ZHANG Jian, ZHAO Ming-juan
(Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education for Conveyance and Equipment,
Abstract: Al-24%Si alloy was prepared by indirect ultrasonic aided casting method. With metalloscope, vertical electronic universal testing machine, abrasion tester, scanning electron microscope and microhardness tester, the influences of ultrasonic frequency on the microstructure, compressive strength, wear performance and hardness of the alloy were investigated. The results show that 20.4 kHz ultrasonication has the best refining effect on the alloy primary silicon and eutectic silicon with average sizes are 100 and 40 μm, respectively. Along with the increase of ultrasonic frequency, the compressive strength increases first and then decreases, while the wear rate decreases first and then increases. Furthermore, the wear mechanism of the alloy is mainly represented as abrasive wear and adhesive wear. Additionally, the alloy microhardness increases first and then decreases along with the increase of ultrasonic frequency, and has a negative correlation with grain size of silicon in the alloy.
Key words: Al-24%Si alloy; microstructure; ultrasonic frequency; compressive strength; wear property; microhardness
Foundation item: Project(51165008) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects (20142BDH80004, 20132BBE5006) supported by Provincial Science and Technology Department of Jiangxi, China; Project(KJLD14040) supported by Provincial Education Department of Jiangxi, China
Received date: 2015-09-28; Accepted date: 2016-01-17
Corresponding author: ZHAO Long-zhi; Tel: +86-791-87046157; E-mail: zhaolongzhi@163.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51165008);江西省科技厅资助项目(20142BDH80004,20132BBE5006);江西省教育厅科研资助项目(KJLD14040)
收稿日期:2015-09-28;修订日期:2016-01-17
通信作者:赵龙志,教授,博士;电话:0791-87046157;E-mail: zhaolongzhi@163.com