铝合金应力/应变时效机制的第一性原理研究
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2014年第7期
论文作者:罗康 臧冰 傅上 江勇 易丹青
文章页码:2130 - 2137
关键词:应力时效;极限固溶度;界面能;第一性原理
Key words:stress aging; solubility limit; interface energy; first-principles
摘 要:基于第一性原理计算方法探讨了铝合金应力/应变时效的可能机制,综合评估了时效温度和外加应力/应变对Al-Sc合金中Al3Sc固溶边界和Al-Cu合金中Al/θ''''''''界面能的潜在影响。计算结果表明:在传统时效过程中引入外加拉应力/应变,声子态密度在高态区有红移现象,可以明显降低溶解熵;同时,导致相图中固溶线上移,表明外加拉应力/应变可降低Al3Sc在Al-Sc合金中的极限固溶度,从而增加析出相的最大可能体积分数。外加应力/应变对Al-Cu合金中不同取向的Al/θ''''''''界面形成能有不同程度的影响,这种差别可以通过泊松效应进一步放大,从而影响到Al-Cu合金中析出相的择优取向。这2种机制在应力/应变时效中均可能发挥重要作用。
Abstract: First-principles based calculations were carried out to explore the possible mechanisms of stress/strain aging in Al alloys. Potential effects of temperature and external stress/strain were evaluated on the solvus boundary of Al3Sc in Al-Sc alloy, and the interface energy of Al/θ'''''''' in Al-Cu alloys. Results show that applying tensile strain/stress during conventional aging can significantly decrease the solubility entropy, by red-shifting the phonon DOS at high states. The resulted solvus boundary would shift up on the phase diagram, suggesting a reduced solubility limit and an increased maximum possible precipitation volume of Al3Sc in Al-Sc alloy.Moreover, the applied strain/stress has different impacts on the formation energies of different orientated Al/θ'''''''' interfaces in Al-Cu alloys, which can be further exaggerated by the Poisson effect, and eventually affect the preferential precipitation orientation in Al-Cu alloy. Both mechanisms are expected to play important roles during stress/strain aging.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2130-2137
Kang LUO1, Bing ZANG1, Shang FU1, Yong JIANG1, 2, Dan-qing YI1, 2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Lab of Nonferrous Materials of Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 17 October 2013; accepted 8 April 2014
Abstract: First-principles based calculations were carried out to explore the possible mechanisms of stress/strain aging in Al alloys. Potential effects of temperature and external stress/strain were evaluated on the solvus boundary of Al3Sc in Al-Sc alloy, and the interface energy of Al/θ'' in Al-Cu alloys. Results show that applying tensile strain/stress during conventional aging can significantly decrease the solubility entropy, by red-shifting the phonon DOS at high states. The resulted solvus boundary would shift up on the phase diagram, suggesting a reduced solubility limit and an increased maximum possible precipitation volume of Al3Sc in Al-Sc alloy. Moreover, the applied strain/stress has different impacts on the formation energies of different orientated Al/θ'' interfaces in Al-Cu alloys, which can be further exaggerated by the Poisson effect, and eventually affect the preferential precipitation orientation in Al-Cu alloy. Both mechanisms are expected to play important roles during stress/strain aging.
Key words: stress aging; solubility limit; interface energy; first-principles
1 Introduction
Precipitation hardening, also called age hardening, is a most widely used heat treatment technique aimed to increase the yield strength of malleable alloys. It relies on changes in solid solubility with temperature to produce fine size second-phase precipitates, to impede the movement of dislocations or grain boundaries during plastic deformation. The yield strength of the alloy is thus largely dictated by the number density and spatial distribution of the precipitates. It has been noticed [1-3] that, applying stresses/strains during the aging process, namely stress/strain aging, can impose a great effect on the habit planes, density and size of second-phases in the alloys, and hence the effectiveness of age hardening. NAKADA and LESLIE [4] first proposed that the commensuration strain due to the lattice misfit of coherent precipitates might be largely compensated by the applied stress/strain, and thus the nucleation and perhaps the growth of the precipitates can be enhanced. Based on an interface diffusion model, other researchers [5,6] demonstrated that for Al-Cu alloys, stress/strain aging may play a more effective role in the nucleation than the growth stage. HOSFORD and AGRAWAL [7] further improved the model by considering the stress-biased diffusion of solute atoms. All these mechanism models were focused on the nucleation and growth of the precipitates. We still lack the knowledge of whether and how an external stress/strain impacts the solvus boundary, namely, whether and how the maximum possible volume fraction of the precipitate phase vary differently with temperature when subjected to stress/ strain. On the other hand, interface structure and composition of a precipitate phase are critical in determining its nucleation and growth behaviors, and as well its interaction with dislocations. Thus, interface energy under stress/strain also needs a thorough investigation.
In this work, we plan to develop a density functional theory (DFT) based strategy to investigate the impact of temperature and external stress/strain on both the solvus boundary (i.e., solubility limit) and the interface energetics of the second phase precipitates in alloys. This strategy will be demonstrated for L12-Al3Sc in an Al-Sc alloy and the θ'' interface in an Al-Cu alloy. Based on the obtained results, the possible mechanisms of stress/strain aging in Al alloys are discussed. This approach would enable us to eventually achieve the energetics- and interface-level understanding of stress/strain aging effects.
2 Calculation methods
All calculations were performed using the semi-commercial DFT code VASP [8]. The plane-wave basis sets were generated with valence configurations of Al 3s23p1, Cu 3d104s1 and Sc 3p64s23d1. The electron-ion interaction was described by the projector augmented wave method within the frozen-core approximation [9]. The exchange-correlation functions used the generalized gradient approximation [10]. For hcp-Sc calculations in a 2×2×2 16-atom orthorhombic superlattice, an adequately high energy cutoff of 300 eV and a 15×15×9 Monkhorst–Pack (MP) k-mesh for Brillouin-zone integrations were used. Calculations on the precipitate phase L12-Al3Sc used a 2×2×2 32-atom fcc superlattice and a 9×9×9 MP k-mesh. The calculations for a dilute Al-Sc solid solution (Al31Sc) used a 2×2×2 fcc Al superlattice and a 9×9×9 MP k-mesh. The coherent Al/θ'' interface was modeled using an Al/θ''/Al sandwich configuration with an 18×18×1 MP k-mesh. All structures were fully relaxed until the total force on each ion converged to to within 0.01 eV/ 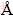 . Phonon calculations employed the direct supercell approach within the quasiharmonic approximation [11]. Force constants were calculated within the density-functional perturbation theory [12], using a stringent ionic force criterion of 10-7 eV/
. Phonon calculations employed the direct supercell approach within the quasiharmonic approximation [11]. Force constants were calculated within the density-functional perturbation theory [12], using a stringent ionic force criterion of 10-7 eV/ 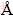 . The phonon modes were calculated from the force constant matrix using PHONOPY [13].
. The phonon modes were calculated from the force constant matrix using PHONOPY [13].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Solvus boundary under stress/strain
The orientation relationship of L12-Al3Sc in the matrix is {001}[001]Al3Sc//{001} [001]Al [14]. Following the experimental practices, we apply a series of uniaxial tensile strains to the matrix (along Al[001]), to assess the maximum possible stress/strain effect on the solvus boundary of L12-Al3Sc in Al-Sc alloys. In the isotropic elastic regime, the tensile stress along [001] inevitably leads to a compression in both the [010] and [100] directions (Poisson effect). Consequently, the cubic lattices may distort to an orthorhombic structure with a>b=c. The solubility, x0, can be expressed as [15]
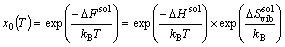 (1)
(1)
where kB is the Boltzmann constant. The solubility enthalpy, 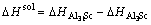 is defined as the difference between the formation enthalpies of Al31Sc and L12-Al3Sc, and
is defined as the difference between the formation enthalpies of Al31Sc and L12-Al3Sc, and
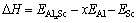 (2)
(2)
where 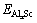 represents the total energy of Al31Sc or L12-Al3Sc, and EAl (or ESc) is the elemental energy at its pure state. With Eq. (2), the solubility enthalpy,
represents the total energy of Al31Sc or L12-Al3Sc, and EAl (or ESc) is the elemental energy at its pure state. With Eq. (2), the solubility enthalpy, 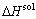 , can be rewritten as
, can be rewritten as
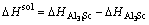
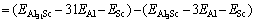
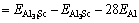 (3)
(3)
and similarly,
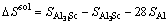 (4)
(4)
The vibrational entropies can be further evaluated from the obtained phonon DOS as
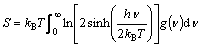 (5)
(5)
where h is Planck’s constant, υ is the frequency, and g(υ) is the phonon DOS.
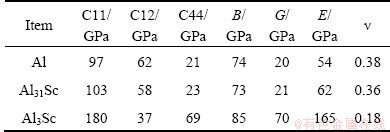
Table 1 compares the calculated elastic properties of Al, the dilute solid solution Al31Sc, and the compound L12-Al3Sc. Note that the elastic properties of Al and Al31Sc are quite close. L12-Al3Sc has much higher shear and elastic modulus, and a very low Poisson ratio. Note, the elastic modulus of L12-Al3Sc is about three times higher than that of Al or Al31Sc, and thus, upon the same tensile stress, the stretching of L12-Al3Sc should be about one third of the matrix.
Table 1 Calculated bulk elastic properties
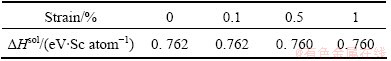
Vibration calculations are then performed on all the distorted (orthorhombic) structures. Here, we only consider the strains below 1%, to ensure the matrix to maintmain elastity. For the reason mentioned above, only one third of the applied strains will be imposed on L12-Al3Sc. Also, according to Eqs. (3) and (4), Sc does not really contribute to solubility enthalpy and entropy, and hence will be ignored in such calculations. The computed solubility enthalpies are listed in Table 2. Note that ΔHsol does not change obviously with the strains, and thus strain effect on phonon vibrations can be important. Figure 1 compares the calculated phonon DOS under strains for the three systems. A left-shift is evident in both of the two high states, particularly for Al and Al3Sc.
Table 2 ΔHsol of Al3Sc in Al under strains
Low frequency phonon modes give a large contribution to vibrational entropy. Thus, the increase in vibrational entropy of Al and Al3Sc due to the strain effect should be more significant than that of Al31Sc. This is clearly seen in Fig. 2.
Figure 2(a)-(c) plots the calculated vibrational entropy changes with temperature for the three systems. Note that the entropies increase rapidly with the increasing strain, before reaching a plateau at ~600 K. The entropy changes of Al and Al3Sc are more sensitive to strain than Al31Sc, especially at low strains. According to Eqs. (1)-(4), the different responses of vibrational entropies of Al3Sc, Al, and Al31Sc to strain will govern the accurate position of the solvus boundary of Al31Sc in Al. The resulted solubility entropies and solubility free energies (ΔFsol) are plotted in Figs. 2(d) and (e), respectively. Note that the applied strains increase the solubility entropy at all the temperatures of interest. ΔFsol always decreases with temperature, while at a fixed temperature, the increasing trend of ΔFsol with strain is pronounced. Recall that -ΔFsol measures the driving force of nucleation. Through Eq. (1), ΔFsol further dictates the maximum possible solubility of Al3Sc in Al. Thus, the increase of ΔFsol with strain indicates that applying strain/stress would not only promote the nucleation, but also reduce the solubility of Al3Sc in Al. Eventually, the solvus boundaries of Al3Sc can be plotted as shown in Fig. 2(f). The solvus boundary curve shifts up on the phase diagram under strains, resulting in a decrease in solubility limits and hence an increase of the maximum possible precipitation amount of Al3Sc in Al. This is expected to provide a larger strengthening effect than conventional aging, which we believe, is one major mechanism of stress/strain aging.
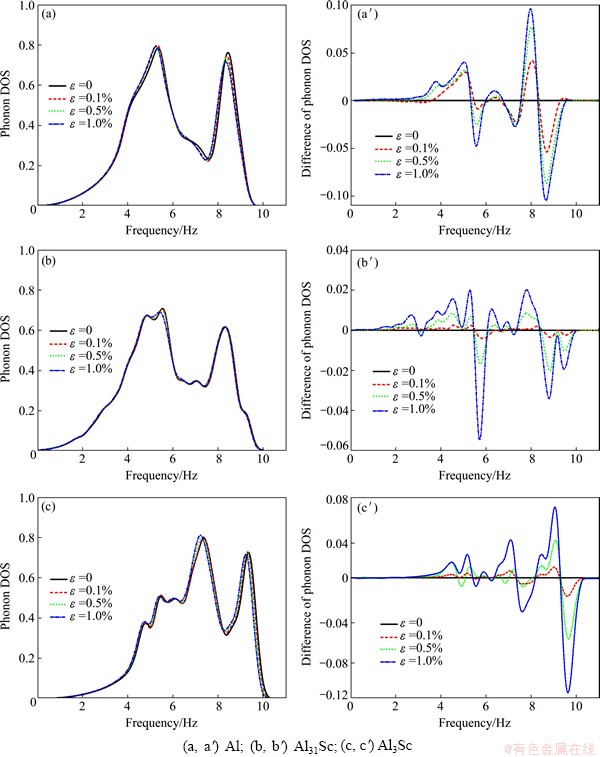
Fig. 1 Calculated phonon DOS (a, b, c) and differential phonon DOS (a′, b′, c′) under applied strains
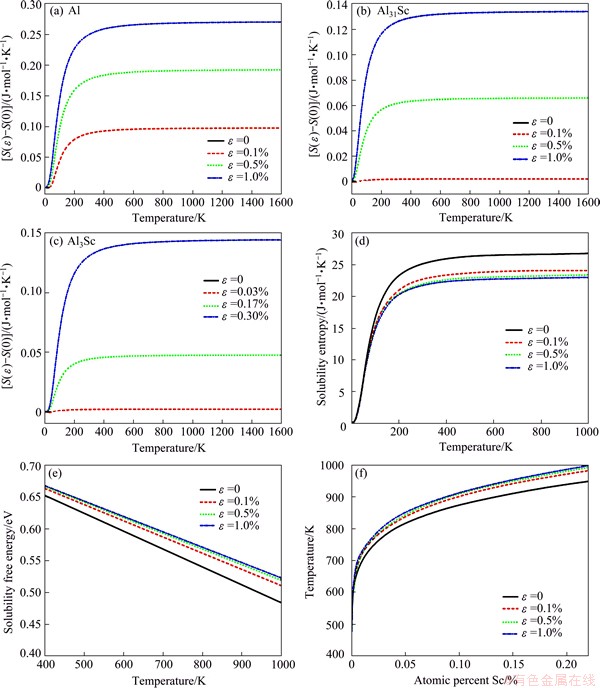
Fig. 2 Entropy difference (a, b, c) due to uniaxial external strains and ΔS sol (d), ΔF sol (e), and solvus boundaries (f) of Al3Sc in Al under applied strains
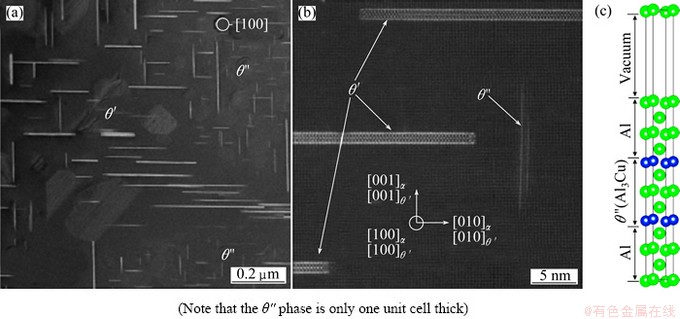
Fig. 3 HAADF-STEM images of coherent, metastable precipitates (θ'' and θ') (a, b) in an Al-1.7%Cu alloy [23] and sandwich model of Al/θ'' interface (c)
3.2 Interface energy and precipitation orientation under stress/strain
It is known that θ'' phase and Al matrix have a completely coherent relationship of (001)[001]θ''// {001}[001]Al [16]. Figure 3 shows the recently obtained high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) images of metastable precipitates (θ'' and θ') in an α-phase Al-Cu alloy [17]. It is noticed that θ'' forms as ultra-thin platelets on the three equivalent {001}α planes of the aluminium matrix. The thickness of the θ'' precipitate is no more than a few atomic layers, namely, it is only one unit cell thick (c=7.68 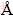 ).
).
We extend the defect model in Refs. [18,19] to express the interface energy under strain (ε) as
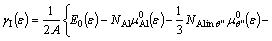
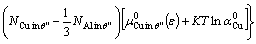 (6)
(6)
where A is the interface area, E0 is the total energy of the interface, μi and Ni are the chemical potential and the atom number of each species, i, respectively. The superscript “0” refers to the pure bulk state. αCu, the activity of Cu in Al, is related to the activity coefficient, γCu, as
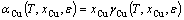 (7)
(7)
At dilute concentrations (xCu <10%), γCu can be approximated as [16]
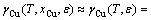
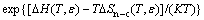 (8)
(8)
where ΔH and ΔSn-c are, respectively, the enthalpy and the non-configurational entropy differences due to the formation of the dilute solid solution. A detailed description of DFT computation of ΔH and ΔSn-c can be found in Ref. [20].
To calculate the strained interface energies, we considered two different directions of loads, i.e., either vertical (along [001]) or parallel (along [100]) to an Al{001}[001]// θ''(001)[001] interface. It is believed that nano-sized θ'' deforms well compatibly with the matrix in its early elastic regime. We hence applied a series of strains, ranging from 0 up to 2%, uniformly to the supercell. Following one our previous practice [21], the upper and lower Al blocks in the supercell were displaced rigidly, leaving the two interfacial rows of Al atoms permitted to relax, as well as all atoms in θ'', until the net force on each diminishes below the threshold. The resulted interface energies under strains were then calculated, and are plotted in Fig. 4. It is noted that, different strain signs and directions have small but different impacts on interface energy.
Figure 5 replots the calculated Al/θ'' interface energies under strains for T=298, 398, and 498 K. Obviously, temperature and strain have opposite effects on interface energy. The interface energy always increases with temperature. Thus, the stability of the interface would decline with temperature. In contrast, the external strain always increases the interface stability, no matter whether the load is compressive or tensile, along the vertical or parallel direction, so as to promote the θ'' precipitation. More interestingly, we note that, under a same degree of compressive strain, the formation energy of a parallel oriented interface is slightly higher that of a vertical interface, while under a same degree of tensile strain, the formation energy of a vertically oriented interface would become slightly higher. These results can be further correlated to the “stress/strain-orienting effect” [3] that is often observed in stress/strain aging experiments.
Figure 6 shows schematically the stress-orienting effect. During normal aging (i.e., under zero stress/strain, Fig. 6(b)), θ'' forms in three equivalent crystallographic orientations, the [010], [001], and [100], as manifested in Fig. 3. A compressive stress/stain (e.g., along [001] in Fig. 6(a)) would reduce the interface energy of the vertically-oriented θ'' slightly more than its parallel counterpart, so that the [010] oriented θ'' would be more favored. If a tensile stress/stain is applied along the same direction (Fig. 6(c)), it would reduce the interface energy of the parallelly-oriented θ'' slightly more, so as to favor the [001] oriented θ''. The [100] orientation is completely equivalent to the [010], and shall respond in exactly the same way as the [010]. Undoubtedly, such orientation selectivity would be further exaggerated by the Poisson effect. As the matrix is compressed along the [001] in Fig. 6(a), the preferable [010] orientation would be further favored by the induced stretching in the transverse direction of [010]. The induced amount of stretching can be estimated by the Poisson ratio of the matrix. Consequently, the stress/strain-induced orientation effect observed in stress/strain aging [3] can be well reproduced by our theoretical calculations. The different influence of applied strain/stress on the formation energies of the different orientated Al/θ'' interfaces shall thus be regarded as one major mechanism for the stress/strain-orienting effect.
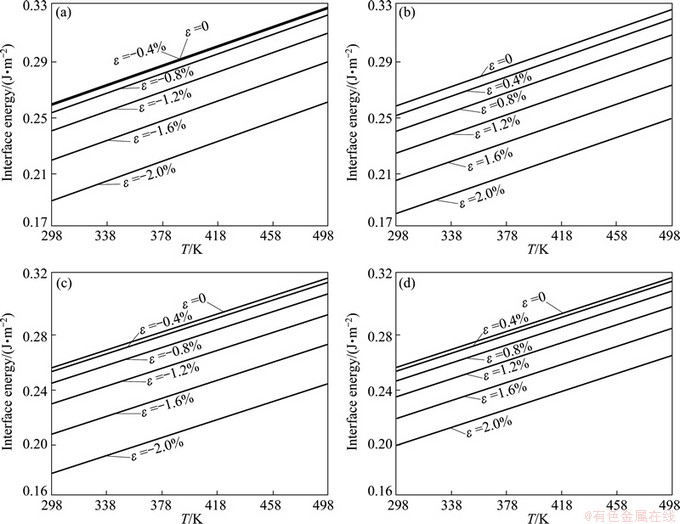
Fig. 4 Calculated interface energies of Al(001)/θ''(001) under compressive (a, c) and tensile (b, d) strains over temperature range of interest (from T=298 to 498 K)
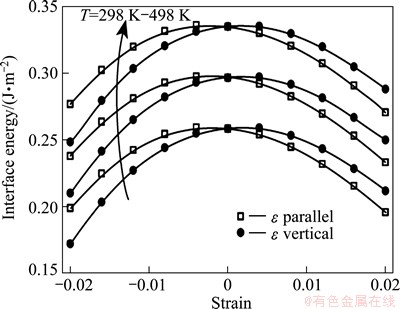
Fig. 5 Replot of calculated interface energies of Al(001)/θ''(001) under externally imposed strains along [001] and [100] for T=298, 398, and 498 K (from down to up), respectively
To validate our proposed mechanisms, we further performed TEM analyses on stress-aged Al-5%Cu alloys (under T=453 K for 6 h) under different load conditions, zero and 50 MPa (ε=~0.1%). Figure 7 shows the obtained bright-field TEM images and diffraction patterns using FEI Tecnai G2 20 transmission electron microscope (operated at 200 kV). It is clearly revealed that only a ~0.1% tensile strain could increase significantly the volume fraction of Al2Cu (θ'') precipitates in Al, consistent well with our predictions in Fig. 2(f). Meanwhile, the parallelly-oriented θ'' was also strongly favored when the matrix was under such a small stretching (ε=~0.1%), as seen in Fig. 7(b). Our calculations in Fig. 5 can predict well qualitatively this stress-orienting trend, but seriously overestimate the magnitude of the required stress/strain.
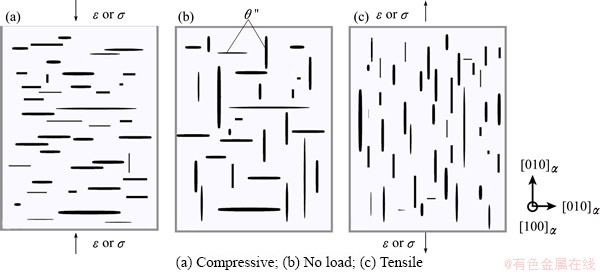
Fig. 6 Schematic diagrams for describing theoretically predicted “stress/strain-orienting effect”—preferential precipitation orientation of θ'' changes with different load conditions
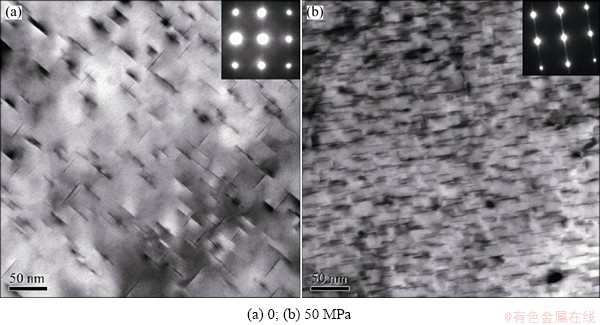
Fig. 7 Bright-field TEM images and diffraction patterns of Al-5%Cu alloys under load conditions
4 Conclusions
1) The solubility free energies would decrease with strains, and the solvus boundary curve shifts up on the phase diagram. This indicates that applying strain/stress during aging not only promotes the nucleation, but also reduces the solubility of Al3Sc in Al (in the way of decreasing solubility entropy). As a result, an increasing precipitation amount of Al3Sc in Al could be expected. This shall be regarded as one major mechanism of stress/strain aging that accounts for its enhanced precipitation strengthening effect.
2) The interface energy always increases with temperature, but decreases with strain at a given temperature. The strain effect is slightly larger under a parallel tensile or a vertical compressive strain, than under a parallel compressive or a vertical tensile strain of same magnitude. This can be regarded as one major mechanism for the stain/stress-orienting effect observed in stress/strain aging.
3) Compared with experimental observations, our interface energy calculations can predict well qualitatively the stress-orienting trend in Al-5%Cu, but might seriously overestimate the magnitude of the required stress/strain.
References
[1] ZHU A W, STARKE E A Jr. Stress aging of Al-xCu alloy: Experiments [J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49(12): 2285-2295.
[2] XIA Q K, LIU Z Y, LI Y T. Microstructure and properties of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy exposed at 200 °C with and without stress [J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(4): 1806-1814.
[3] CAO Su-fang, PAN Qing-lin, LIU Xiao-yan, LU Zhi-lun, HE Yun-bin, LI Wen-bin. Effect of external stress on aging precipitation behavior of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(8): 1513-1519. (in Chinese)
[4] NAKADA Y, LESLIE W C. Stress-orienting of Fe16N2 precipitates in a Fe-N alloy [J]. TransactionsoftheAmericanSocietyforMetals, 1967, 60: 223-238.
[5] SANKARAN R. Discussion of effect of stress during aging on the precipitation of theta prime phase in Al-4%Cu [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1976, 7(5): 770-771.
[6] LI D Y, CHEN L Q. Computer simulation of stress-oriented nucleation and growth of θ′ precipitates in Al-Cu alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46(8): 2573-2585.
[7] HOSFORD W F, AGRAWAL S P. Authors’ reply [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1976, 7(5): 771-772.
[8] KRESSE G,  J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set [J]. Physical Review B, 1996, 54(16): 11169-11186.
J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set [J]. Physical Review B, 1996, 54(16): 11169-11186.
[9] KRESSE G, JOUBERT D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method [J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59(3): 1758-1775.
[10] WU Z G, COHEN R E. More accurate generalized gradient approximation for solids [J]. Physical Review B, 2006, 73(23): 235116.
[11] JIANG Y, SMITH J R, EVANS A G. Temperature dependence of the activity of Al in dilute Ni(Al) solid solutions [J]. Physical Review B, 2006, 74(22): 224110.
[12] GIANNOZZI P, GIRONCOLI S D, PAVONE P, BARONI S. Ab initio calculation of phonon dispersions in semiconductors [J]. Physical Review B, 1991, 43(9): 7231-7242.
[13] TOGO A, OBA F, TANAKA I. First-principles calculations of the ferroelastic transition between rutile-type and CaCl2-type SiO2 at high pressures [J]. Physical Review B, 2008, 78(13): 134106.
[14] MAO Z, CHEN W, SEIDMAN D N, WOLVERTON C. First- principles study of the nucleation and stability of ordered precipitates in ternary Al-Sc-Li alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(8), 3012-3023.
[15] FONTAINE D D. Cluster approach to order-disorder transformations in alloys [J]. Solid State Physics, 1994, 47: 33-176.
[16] GEROLD V. On the structures of Guinier-preston zones in Al-Cu alloys introductory paper [J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1988, 22(7): 927-932.
[17] BOURGEOIS L, DWYER C, WEYLAND M, NIE J F. MUDDLE B C. Structure and energetics of the coherent interface between the θ' precipitate phase and aluminium in Al-Cu [J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(18): 7043–7050.
[18] ZHANG W, SMITH J R, EVANS A G. The connection between ab initio calculations and interface adhesion measurements on metal/oxide systems: Ni/Al2O3 and Cu/Al2O3 [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(15): 3803-3816.
[19] LUO K, JIANG Y, YI D Q, ZANG B. Energetics response to precipitates interface Al/θ' under strain aging [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(10): 2785-2791. (in Chinese)
[20] JIANG Y, SMITH J R, EVANS A G. Temperature dependence of the activity of Al in dilute Ni(Al) solid solutions [J]. Physical Review B, 2006, 74(22): 224110.
[21] JIANG Y, WEI Y, SMITH J R, HUTCHINSON J W, EVANS A G. First principle based predictions of the toughness of a metal/oxide interface [J]. International Journal of Materials Research, 2010, 101(1): 8-15.
罗 康 1,臧 冰 1,傅 上1,江 勇 1,2,易丹青 1,2
1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 教育部有色金属材料科学与工程重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:基于第一性原理计算方法探讨了铝合金应力/应变时效的可能机制,综合评估了时效温度和外加应力/应变对Al-Sc合金中Al3Sc固溶边界和Al-Cu合金中Al/θ''界面能的潜在影响。计算结果表明:在传统时效过程中引入外加拉应力/应变,声子态密度在高态区有红移现象,可以明显降低溶解熵;同时,导致相图中固溶线上移,表明外加拉应力/应变可降低Al3Sc在Al-Sc合金中的极限固溶度,从而增加析出相的最大可能体积分数。外加应力/应变对Al-Cu合金中不同取向的Al/θ''界面形成能有不同程度的影响,这种差别可以通过泊松效应进一步放大,从而影响到Al-Cu合金中析出相的择优取向。这2种机制在应力/应变时效中均可能发挥重要作用。
关键词:应力时效;极限固溶度;界面能;第一性原理
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (51171211) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2014CB644001-2) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: Yong JIANG; Tel: +86-731-88836320; Fax: +86-731-88830263; E-mail: yjiang@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63323-9

