Numerical analysis of aerated heap bioleaching with variable irrigation and aeration combinations
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2020年第5期
论文作者:黄明清 吴爱祥
文章页码:1432 - 1442
Key words:forced aeration; irrigation-to-aeration ratio; oxygen concentration; temperature distribution; copper leaching rate
Abstract: Forced aeration is an effective way to accelerate the heap bioleaching process. To reveal the effects of different irrigation and aeration combinations on bioleaching performance of copper sulfides, numerical simulations with COMSOL were carried out. Results showed the oxygen concentration is the highest at the bottom with forced aeration, the airflow transports spherically from the aeration pipeline to the slope, and the horizontal diffusion distance is further than vertical value. When the irrigation-to-aeration ratio is higher, the average heap temperatures are mainly decided by aeration rates; otherwise, temperature distributions are the equilibrium of mineral reaction heat, the livixiant driven heat and the airflow driven heat. When the aeration rate is higher than 0.90 m3/(m2·h), oxygen concentration is no longer a limiting factor for mineral dissolution. Additionally, on the premise of sufficient oxygen supply, Cu recovery rate is higher at the bottom with low irrigation rate; while it is higher at upper regions with high irrigation rate. The numerical analysis uncovered some insights into the dynamics and thermodynamics rules in bioleaching of copper sulfides with forced aeration.
Cite this article as: HUANG Ming-qing, WU Ai-xiang. Numerical analysis of aerated heap bioleaching with variable irrigation and aeration combinations [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(5): 1432-1442. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4379-x.

J. Cent. South Univ. (2020) 27: 1432-1442
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4379-x
HUANG Ming-qing(黄明清)1, WU Ai-xiang(吴爱祥)2
1. College of Zijin Mining, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350108, China;
2. School of Civil and Resource Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing,Beijing 100083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020
Abstract: Forced aeration is an effective way to accelerate the heap bioleaching process. To reveal the effects of different irrigation and aeration combinations on bioleaching performance of copper sulfides, numerical simulations with COMSOL were carried out. Results showed the oxygen concentration is the highest at the bottom with forced aeration, the airflow transports spherically from the aeration pipeline to the slope, and the horizontal diffusion distance is further than vertical value. When the irrigation-to-aeration ratio is higher, the average heap temperatures are mainly decided by aeration rates; otherwise, temperature distributions are the equilibrium of mineral reaction heat, the livixiant driven heat and the airflow driven heat. When the aeration rate is higher than 0.90 m3/(m2·h), oxygen concentration is no longer a limiting factor for mineral dissolution. Additionally, on the premise of sufficient oxygen supply, Cu recovery rate is higher at the bottom with low irrigation rate; while it is higher at upper regions with high irrigation rate. The numerical analysis uncovered some insights into the dynamics and thermodynamics rules in bioleaching of copper sulfides with forced aeration.
Key words: forced aeration; irrigation-to-aeration ratio; oxygen concentration; temperature distribution; copper leaching rate
Cite this article as: HUANG Ming-qing, WU Ai-xiang. Numerical analysis of aerated heap bioleaching with variable irrigation and aeration combinations [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(5): 1432-1442. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4379-x.
1 Introduction
Heap bioleaching is an increasingly widespread commercial technology to treat low grade copper sulfide ores due to it’s advantageous in operational simplicity, low cost and eco-friendly technical process [1-3]. Microbial leaching is a complex coupled system with many influential factors, such as gas, solution, solids, microorganism and heat. Oxygen is a fundamental element for aerobic microorganism activity and propagation, and it’s usually provided by the gas that flows through the heap. Oxygen presents as an electron acceptor in the oxidation of ferrous iron to ferric iron, where microorganisms get the energy for growth. In this process, the generated Fe3+ acts as the oxidant in the mineral biochemical dissolution. Additionally, the airflow not only carries the heat through the heap, but also promotes the mineral dissolution to release more reaction heat. HECTOR [4] found that the oxygen consumption was as much as 0.25 t for 1 t leached copper at Quebrada Blanca mine. Therefore, the lack of airflow or oxygen could result in a bioleaching retard or even suspension. Forced aeration is presently the most economic and convenient way to supply the oxygen into the heap. In this way, oxygen is sprayed across the heap continually through ventilation pipelines that were installed beneath the heap. However, due to the opposite flow direction of leaching solution and aerated gas, the supply of oxygen becomes difficult or invalid, or leads to massive power wastes. BRIERLEY [5] pointed out that the necessity of aeration and aeration rate is one of critical technical questions in biohydrometallurgy.
Thus, a proper combination of irrigation rate and aeration rate becomes a key issue to accelerate the bioleaching process. SIDBORN et al [6] derived an oxygen consumption formulation based on the two-dimensional dynamic model of copper sulphides. BOUFFARD [7] found that the aeration rate should not be reduced during the whole bioleaching period, and any adjustment either in aeration rate or spray rate could lead to significant variations of mineral oxidation rates. LI et al [8] investigated the bioleaching evolutions with different spray intensities and aeration rates and found that metal recovery rate is the highest when the spray-to-aeration ratio is 2/3. Likewise, LEAHY et al [9] found that low airflow rate tended to restrain the copper leaching, while this restrain disappeared when the aeration rate was higher than 10-4 m/s. LEAHY’s another work showed that 10-3 m/s was the best aeration rate, with which Cu leaching rate was higher at the middle height than at the bottommost and topmost sections [10].
The aforementioned findings showed that heap bioleaching performance was highly depended on irrigation rate, aeration rate and their combinations. Using numerical simulations with software COMSOL, this work aims to uncover some insights into the dynamics and thermodynamics rules in bioleaching of copper sulfide ores with variable aeration rates and irrigation-to-aeration ratios.
2 Numerical simulations
2.1 Description of model
A two-dimensional model is cut out from the trapezoid cross section along the heap strike, and the model follows the assumptions of 1) the heap bottom is rectangular and any cross section perpendicular to the heap strike is an isosceles trapezoid with homogeneous leaching performance. 2) The porosity, permeability coefficient and moisture content are constant parameters; the livixiant flow through the heap with a constant rate, and the capillary action is ignored. 3) Chalcocite and pyrite dominate the minerals of the copper sulfides, copper grade uniformly distributes the heap and other metal sulfide is mainly pyrite. Fe2+ concentrations are sufficient. The leaching is controlled by oxygen concentration and temperatures. 4) The ambient temperature is in a local thermodynamic equilibrium with the livixiant and the heap. 5) The overall microorganism to adsorptive quantity ratio is a constant.
The heap height is 20 m, the slope angle is 40°, and the upper and bottom widths are 32.3 m and 80 m, respectively (Figure 1(a)). The Cu grade is 0.62%, heap density is 1600 kg/m3, and heap porosity is 30%. One ventilation pipeline is installed in the middle of heap bottom along the strike. Due to the symmetric distribution of model sections along the axis of the heap, physical mechanical properties and simulation results are considered the same at both sides. Hence, the numerical simulation is analyzed with focus on one side. The meshing of the analyzed model is shown in Figure 1(b).
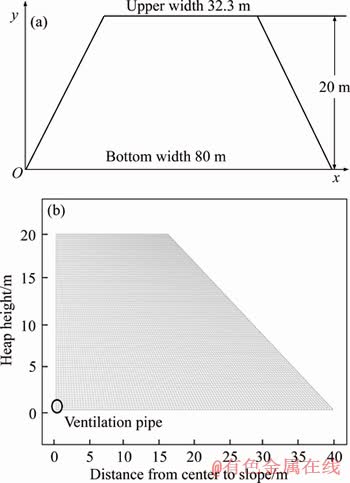
Figure 1 Two-dimensional geometric model of heap (a) and its mesh generation (b)
The boundary conditions imposed on the mathematical model are as the same as those described by LEAHY et al [10]. Additionally, the parameters used in the numerical analysis are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Main parameters of heap bioleaching model

2.2 Model formulation
1) Cu leaching equation
According to the basic assumption, Cu leaching rate α can be stated by Michaelis-Menton equation when soluble oxygen is the limiting factor for mineral dissolution:
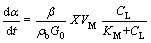 (1)
(1)
where α is Cu recovery rate, %; β is the stoichiometric coefficient, i.e. O2 consumption per unit mass during Cu leaching, kg Cu/kg O2; ρb is the heap density, kg/m3; G0 is the Cu grade, %; X is the microorganism concentration, number/m3; VM is the maximum microorganism growth rate, kg O2/(number·s); CL is the dissolved oxygen concentration, kg/m3; KM is the Michel constant when the growth rate is the half of VM. Additionally,
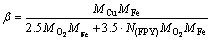 (2)
(2)
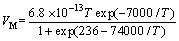 (3)
(3)
where MCu, MFe and MO2 are the molar mass of the chalcocite, pyrite and oxygen, respectively, kg/mol; N(FPY) is the leached pyrite amount per leached chalcocite, mol pyrite/mol Cu2S; T is the gas and livixiant temperature when the heap reaches thermodynamic equilibrium, K.
2) Gas seepage equation
Since low aeration rates are usually used, the gas seepage is assumed to follow the Darcy law. Hence, according to the gas equation of continuity, equation of motion and gas state equation, the gas seepage equation can be derived as:
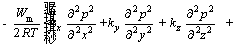
 (4)
(4)
where Wm is the average gas molecular mass of the heap, g/mol; R is gas constant, J/(mol·K); T is the thermodynamic temperature, K; kx, ky, kz are common permeability coefficients along the x, y and z directions, respectively; p is the absolute gas pressure of the heap porosity, Pa; ng is the gas content, %; m is the gas quantity flowing through a unit heap volume per unit time, kg/(m3·s).
3) Oxygen equilibrium equation
The oxygen flow is described by the convection and molecular diffusion equations:
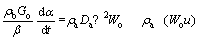 (5)
(5)
where Da is the diffusion coefficient, m2/s; Wo is the oxygen concentration in the air, %; μ is air viscosity, kg/(m·s).
4) Heat equilibrium equation
The heap temperature during bioleaching can be described by the heat equilibrium equation with a steady-state condition, as showed by:
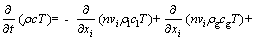
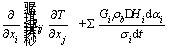 (6)
(6)
where T is the ambient temperature, K; n is the overall porosity of the heap, %; vi and vj are velocities, m/s; ρlcl and ρgcg are thermal capacities of the unit solution volume and unit gas volume, respectively, J/(kg·K); λij is the heat dispersion tensor; xi is the spatial step length; Gi is the gas velocity of the component i, m/s; αi is the recovery rate of the component i, %;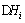 is the reactive enthalpy change of the component i, kJ/mol; σi is the overall stoichiometric coefficient of the oxygen.
is the reactive enthalpy change of the component i, kJ/mol; σi is the overall stoichiometric coefficient of the oxygen.
2.3 Simulation scheme
The general-purpose simulation software COMSOL Multiphysics (Version 3.5a) is introduced to simulate the heap bioleaching performance [11]. The numerical simulation is processed in two groups. The irrigation rate in Group 1 is 0.018 m3/(m2·h), and the variables of aeration rates are 0, 0.09, 0.36, 0.90 and 1.80 m3/(m2·h), respectively. The irrigation rate in Group 2 is 0.036 m3/(m2·h), while the irrigation- to-aeration ratios are 1:2.5, 1:10, 1:25, 1:50, respectively. In a 300-d simulated bioleaching, the gas flow rate, oxygen concentration, heap temperature and Cu recovery rate throughout the heap are to be numerically analyzed.
3 Numerical results and discussion
3.1 Bioleaching with variable aeration rates
1) Distributions of oxygen concentration and airflow velocity
In Group 1, comparisons of distributions of oxygen concentration and gas flow velocity throughout the heap are analyzed with and without aeration (Figure 2). Under atmospheric conditions, the atmospheric oxygen permeates into the heap via the slope and bottom. The infiltrated airflow from the slope firstly migrates horizontally into the heap, and then it is imposed by a vertical component force due to the higher temperature. Therefore, the migrating direction of gas flow is gradually transformed from horizontal to vertical, and eventually becomes a complete vertical airflow near the heap surface.
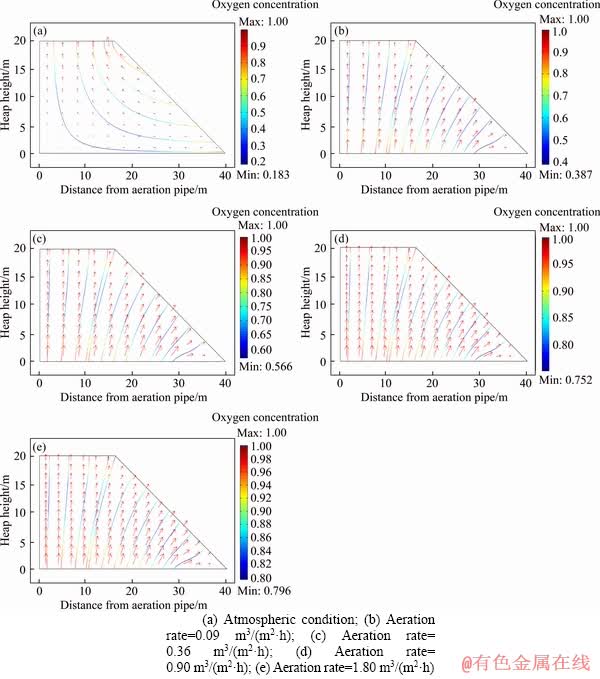
Figure 2 Distributions of oxygen concentration and airflow velocity with variable aeration rates:
However, the airflow rate decreases dramatically as the infiltrating distance increases. When the infiltrating distance is 4-6 m from the heap slope, the oxygen concentration decreases to less than 50% than ambient value. The oxygen concentration even decreases to only 20% of the ambient concentration when the airflow transport distance is more than 20 m. Considering that in situ heap width is far more than 20 m, and the required dissoluble oxygen concentration for microorganism is 10-25 mmol/L, the O2 supplied by natural diffusion fails to meet the microbial demands.
When the forced aeration is introduced, the airflow diffuses to the slope and the surface from the aeration pipeline. With increasing aeration rates, the low-oxygen concentration areas decrease and the minimum O2 concentration increases. Moreover, an increase in the aeration rate results in a wider airflow radius and a higher O2 concentration at the same location. These results indicate that the aeration pipeline must not be installed too sparsely or too densely, so as to keep a uniform O2 distribution and avoid low-oxygen concentration areas.
2) Distributions of temperatures
When the ambient temperature is 25 °C, the heap exhibits different temperature profiles depending on the aeration rates (Figure 3). Under atmospheric condition or the aeration rate of 0.09 m3/(m2·h), the temperature peaks at the heap bottom and gradually decreases as height increases. When the aeration rate is higher than 0.90 m3/(m2·h), the high-temperature areas (>50 °C) and the maximum temperature (61.1-65.4 °C) gradually contract. Acidophilic mesophilic and moderately thermophilic bacteria are the most widely used microorganisms in heap leaching, and their favorable growth temperature ranges are the 25-45 °C, 45-50 °C, respectively. Hence, temperature areas that are beneficial to microorganism growth and mineral dissolution tend to enlarge.
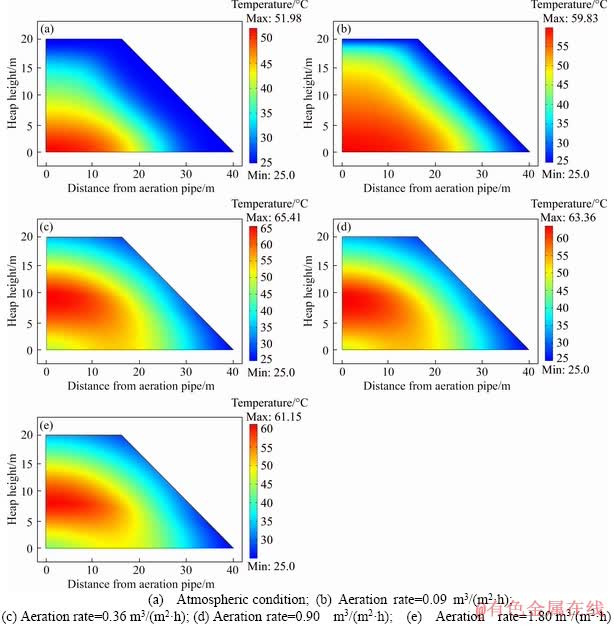
Figure 3 Distributions of temperatures with variable aeration rates:
When the external heat factor is steady, the heat balance is mainly influenced by convective heat transfer, heat conduction and mineral dissolution heat. Under atmospheric conditions, the heap permeability usually becomes terrible in late bioleach stages, and thus the mineral reaction heat is restrained at the bottom. In addition, the heat is carried downwards by the solution flow, which promotes the heat at the bottom to become higher than other regions.
When the forced aeration rate increases, the O2 concentration improves and no longer is a limiting factor for mineral dissolution. Hence, the mineral dissolution rate accelerates and the released heat quickly gathers within the heap. A micro airflow also forms from the bottom and carries the heat upwards to the middle and upper sections. Generally, aeration is beneficial to a more homogeneous temperature distribution, expanding the favorable temperature areas for microbial growth and community succession.
3) Distributions of copper recovery rates
After leaching for 300 d, the Cu leaching rates throughout the heap show a same trend with or without aeration (Figure 4). Centered at the aeration pipeline, the Cu leaching rate elliptically varies outward from the bottom. In two-dimensional models, points with the same Cu leaching rate are connected to form a continuous elliptical line. Areas with higher Cu leaching rate (>60%) gradually expand and lower ones (<20%) gradually contract with increasing aeration rates. Interestingly, Cu leaching rate is the highest at the heap surface and slope, and is the lowest at the bottom when the aeration rate is less than 0.36 m3/(m2·h); while it is the highest at the middle and lower sections, and decreases at the bottom, surface and slope when the aeration rate is higher than 0.90 m3/(m2·h).
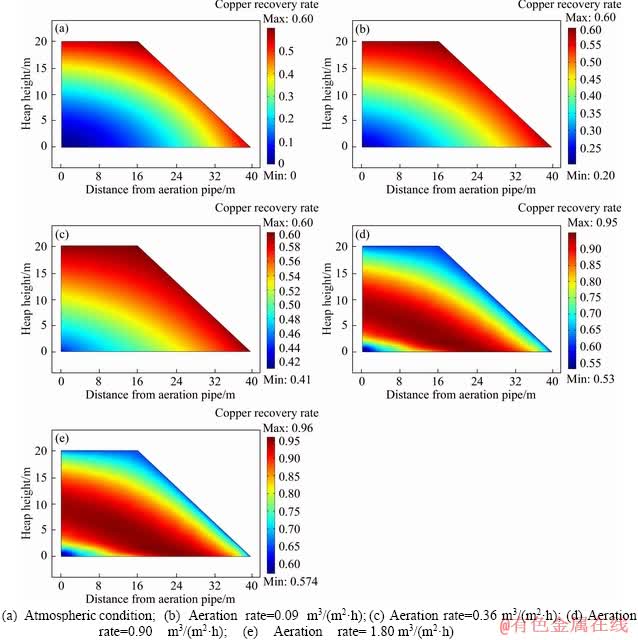
Figure 4 Distributions of copper recovery rates with variable aeration rates:
It is obvious that distributions of Cu leaching rate and oxygen concentration are in a correlative similarity. Under atmospheric conditions, O2 concentration at the surface and slope is higher than other sections; therefore, the Cu leaching rate is higher. When the aeration is implemented, the airflow near the airline or slope is advantageous, which leads to higher Cu leaching rates at these sections. However, the enhanced effect of aeration vanishes when the ventilation rate is higher than 0.90 m3/(m2·h), indicating that O2 concentration is sufficient in this range. DONATI et al [12] also found that the copper leaching rate no longer increased when the O2 concentration reached a critical value.
3.2 Bioleaching with variable irrigation-to- aeration ratios
1) Distributions of oxygen concentration and gas flow velocity
A bottom-up gas flow formed in the heap after ventilation, and the flow rate dramatically decreased with increasing heap heights (Figure 5). When the irrigation-to-aeration ratio (Ql/Qg) is less than 1:10, the horizontal component of airflow velocity is greater than the vertical component at the same height. When Ql/Qg>1:25, the airflow gradually turns from the vertical diffusion to globular diffusion. Oxygen concentrations at the heap bottom, slope and surface are nearly equal to the ambient values; while the low oxygen concentration areas distribute at the central heaps. However, the low oxygen concentration areas gradually reduce with the improvement of aeration rates.
2) Distribution of temperatures
When the irrigation rate remains at 0.036 m3/(m2·h), the average temperature of the heap increases with increasing aeration rate when Ql/Qg<1:10. When Ql/Qg>1:25, however, the average temperature in the same section of the heap increases firstly and then decreases (Figure 6).
In the condition of low irrigation rate, the aeration rate is the predominant factor that influences the heap temperature. When the irrigation rate increases, the dissolution between mineral and leaching solution becomes sufficient, thus releases abundant heat and further promotes the heap temperature. However, the resistance of airflow also increases due to the opposite permeate directions; therefore, the temperature distribution is decided by Ql/Qg. The variation of Ql/Qg always commences with variations of mineral dissolution rate and reaction heat. Considering that the solution drives the heat towards the heap bottom, while the gas flow drives the heat towards the upper areas, the heat equilibrium is codetermined by these three factors.
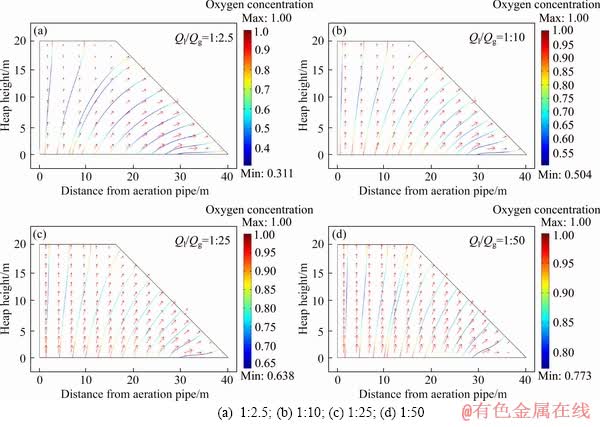
Figure 5 Distributions of oxygen concentration and gas flow velocity with irrigation-to-aeration ratio:

Figure 6 Distributions of temperature with irrigation-to-aeration ratio:
3) Copper recovery rates
At the height of 0, 5, 10 and 15 m from the bottom up, Cu recovery rate at different horizontal distances from the ventilation pipe is shown in Figure 7. When Ql/Qg is 1:2.5, Cu recovery rate near the slope is distinctly higher than that at the central areas. On the contrary, Cu recovery rate from the heap center to the slope increases firstly and then decreases at the bottom when Ql/Qg is 1:10, while Cu leaching rate gradually decreases from the aeration pipeline to the slope when leaching locations are higher than 5 m. Likewise, when Ql/Qg is 1:25 and 1:50, the Cu leaching rates at different heights and sections exhibit similar phenomenon, i.e. increase firstly and then decrease towards the slope when height is less than 5 m, and gradually decreases outwards from the center when heights are 10 m and 15 m.
The comparison of Figures 5 and 7 shows that Cu recovery rate has a close relation with gas permeating distance. The aeration rate, however, is the predominant factor to decide the gas diffusion ability. Under ambient conditions, oxygen is mainly provided by the gas permeated from heap slope, which is limited by ambient factors. When the aeration is introduced, the oxygen supply within the heap mainly depends on the aeration rate. The gas diffusion ability escalates compared to the natural conditions when the Ql/Qg is in the range of 1:2.5 to 1:50; yet the horizontal and vertical diffusion distances are limited to 25 m and 15 m, respectively. Additionally, higher irrigation-to-aeration ratio leads to a larger area with high Cu extraction rate (>60%).
3.3 Comparison of copper recovery rates with different irrigation rates
In this work, irrigation rates are set as 0.018 and 0.036 m3/(m2·h) in two groups, and both cases indicate that copper recovery rate increases no more when the aeration rate is higher than 0.90 m3/(m2·h). It suggests the aeration rate in this range meets the oxygen requirements for the mineral dissolution. When the aeration rate is 0.90 m3/(m2·h), the irrigation-to-aeration ratios Ql/Qg are 1:50 and 1:25, respectively. Further analysis is proceeded with respect to the relations between leaching location from the aeration pipeline and Cu leaching rates at different heights (Figure 8).
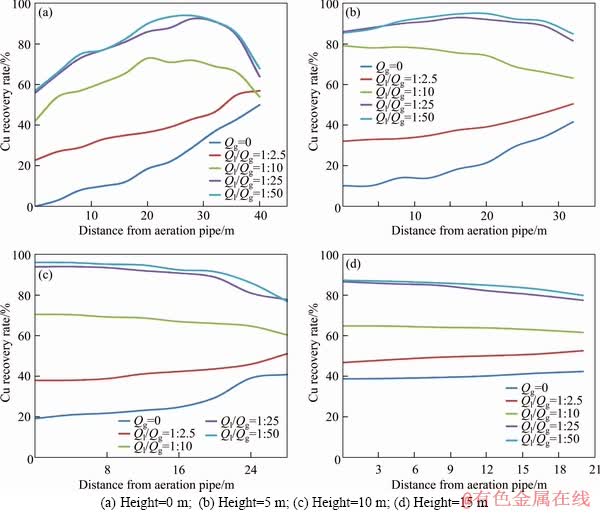
Figure 7 Cu recovery rates at different horizontal distances from aeration pipeline at variable heights:
If the aeration rates in two groups are the same and meet the requirements of oxygen demand, Cu leaching rate is relatively higher at the height less than 5 m above the bottom when the irrigation rate is 0.018 m3/(m2·h); while Cu leaching rate is higher at 10 m above the bottom when the irrigation rate increases to 0.036 m3/(m2·h). These observations are in agreement with temperature distributions by using two spray intensities. When the irrigation rate is higher, the heat is carried downwards by solution, and the temperatures at lower levels increase in a range that is detrimental for microbial growth. However, temperatures at middle and higher levels keep in a favorable range due to the coupling effect of aeration and reaction heat, and thus it enhances the leaching process.
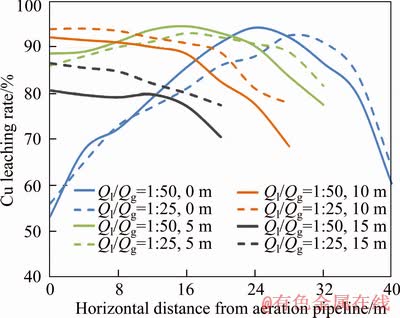
Figure 8 Relations of Cu leaching rates and horizontal distances from aeration pipeline (Solid line:Ql=0.018 m3/(m2·h); Dotted line: Ql=0.036 m3/(m2·h))
4 Conclusions
1) The oxygen concentrations at heap surface and slope are much higher than other regions under atmospheric conditions; infiltrated airflow transports horizontally firstly and gradually transforms to vertical flow. Oxygen concentration is the highest at the bottom when the forced aeration is introduced; the airflow transports spherically outwards from the aeration pipeline, and the horizontal diffusion distance is further than vertical distance. The middle-height sections are susceptible to low-oxygen concentrations, and the specific locations and areas depended on aeration rates.
2) Temperatures are the highest at the bottom when low aeration rates are implemented; temperatures gradually decrease as the height increases. The high-temperature areas constrict when high aeration rates are introduced; the areas beneficial to microbial growth expand accordingly. When Ql/Qg is higher, the average heap temperatures are mainly decided by aeration rates; otherwise, the distributions of heap temperatures are the equilibrium of mineral reaction heat, the heat driven downwards by the livixiant and the heat driven upwards by the airflow.
3) Cu leaching rates are higher at the heap surface and slope with low aeration rates and an increase in aeration rate results in a lager high- leaching rate area. When the aeration rate is higher than 0.90 m3/(m2·h), the oxygen concentration is no longer a limiting factor for microbial growth and mineral dissolution.
4) When Ql/Qg is lower, Cu leaching rates at the same height gradually increase from the center to the slope. When Ql/Qg is higher, Cu leaching rates at the bottom increase firstly and then decrease towards the slope; while they gradually decrease from the aeration pipeline outwards when the height >10 m. On the premise of sufficient oxygen supply, Cu recovery rate is higher at the bottom with low irrigation rate; while it becomes higher at upper regions once high irrigation rate is introduced.
References
[1] BRIERLEY J A, BRIERLEY C L. Present and future commercial applications of biohydrometallurgy [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59(2, 3): 233-239.
[2] YIN Sheng-hua, CHEN Wei, CHEN Xun, WANG Lei-ming. Bacterial-mediated recovery of copper from low-grade copper sulphide using acid-processed rice straw [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 288: 1-8.
[3] WANG Jun, ZHAO Hong-bo, QIN Wen-qin, QIU Guan-zhou. Bioleaching of complex polymetallic sulfide ores by mixed culture [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(7): 2633-2637.
[4] HECTOR M L. Copper bioleaching behaviour in an aerated heap [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2001, 62: 257-269.
[5] BRIERLEY C L. Biohydrometallurgical prospects [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 104(3, 4): 324-328.
[6] SIDBORN M, CASAS J, MARTI'NEZ J, MORENO L. Two-dimensional dynamic model of a copper sulphide ore bed [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71: 67-74.
[7] BOUFFARD S C. Application of the HeapSim model to the heap bioleaching of the Pueblo Viejo ore deposit [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 94(3, 4): 116-123.
[8] LI Hong-xu, LI An, WU Ai-xiang, QIU Guan-zhou. Effect of irrigation rate and air flow rate on temperature distribution of secondary copper sulfide during bio-heap leaching process [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(7): 1424-1432. (in Chinese)
[9] LEAHY M J, DAVIDSON M R, SCHWARZ M P. A column bioleaching model for chalcocite: An investigation of oxygen limitation and bacterial inoculation on leaching [C]// Bac-Min 2004 Conference. Bendigo, Australia, 2004.
[10] LEAHY M J, SCHWARZ M P, DAVIDSON M R. An air sparging CFD model for heap bioleaching of copper-sulphide [C]// The Third International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries. Melbourne, Australia, 2003.
[11] COMSOL A B, BURLINGTON M A. COMSOL multiphysics user’s guide (Version 3.5a) [M]. Stockholm, Sweden: COMSOL Inc., 2008.
[12] DONATI E R, SAND W. Microbial processing of metal sulfides [M]. Netherland: Springer Verlag, 2007.
(Edited by YANG Hua)
中文导读
不同喷淋速率与通风强度组合下强制通风生物堆浸数值模拟
摘要:强制通风是强化生物堆浸的有效措施。为了揭示不同喷淋速率与通风强度组合对硫化铜矿生物浸出的影响,利用COMSOL进行了数值模拟。结果表明,通风后堆底氧气浓度最高,气流以通风管道为中心向边坡作球形扩散,且水平扩散距离大于竖直距离。当喷淋速度-通风强度比较高时,堆场平均温度主要由通风强度控制;较低时则是矿物反应热、溶浸液携带热量及气流携带热量三者的平衡结果。当通风强度高于0.90 m3/(m2·h)时,氧气不再成为矿物溶解的限制性因素。此外,若氧气供应充足,低喷淋速率时堆底Cu回收率较高,而高喷淋速率时矿堆中上部Cu回收率较高。数值模拟揭示了硫化铜矿生物堆浸过程中一些动力学及热力学规律。
关键词:强制通风;喷淋速率-通风强度比;氧气浓度;温度分布;铜浸出速率
Foundation item: Projects(51804079, 51804121) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2019J05039) supported by Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, China; Project(2019T034) supported by Fuzhou University Testing Fund of Precious Apparatus, China
Received date: 2019-06-27; Accepted date: 2020-04-07
Corresponding author: HUANG Ming-qing, PhD, Senior Engineer; Tel: +86-591-22866516; E-mail: seango@126.com; ORCID: 0000- 0001-9449-1987

