DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39798
Ni、Si元素对Cu-Fe合金显微组织和力学性能的影响
岳世鹏,接金川,曲建平,李廷举
(大连理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,大连 116024)
摘 要:利用光学显微镜、电子探针分析、透射电子显微镜、X射线衍射仪及拉伸实验等技术研究Ni、Si元素对Cu-20Fe(质量分数,%)合金的组织及力学性能的影响。结果表明:添加Ni和Si元素导致Cu-20Fe合金中α-Fe枝晶发生明显的粗化行为。此外,由于合金元素的添加使得γ-Fe和富铜析出相之间的界面能减小,从而使得富铜析出相的形貌发生显著变化,即由近球形转变为立方形。相比于未添加合金元素的二元合金而言,添加合金元素之后,多组元合金的强度和塑性均得到提高。多组元合金的屈服强度和伸长率分别为304 MPa和16%。通过理论计算和实验验证,确定合金的主要强化机制为固溶强化和析出强化。
关键词:显微组织;形貌转变;界面能;强化机制
文章编号:1004-0609(2021)-06-1485-09 中图分类号:TF11.31 文献标志码:A
引文格式:岳世鹏,接金川,曲建平, 等. Ni、Si元素对Cu-Fe合金显微组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(6): 1485-1493. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39798
YUE Shi-peng, JIE Jin-chuan, QU Jian-ping, et al. Effect of Ni and Si on microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-Fe alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(6): 1485-1493. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39798
近几十年来,由于形变铜基原位复合材料同时具备较高的强度和较好的导电性,因此受到研究人员的广泛关注[1-5]。其主要应用在高速铁路接触线、电接触器和引线框架以及作为高强磁场中脉冲磁体导体材料。截至目前为止,制备比较成熟及应用比较广泛的铜基原位复合材料主要包括Cu-Ag系、Cu-Nb系和Cu-Fe系[6-8]。其中,Cu-Ag系和Cu-Nb系相较Cu-Fe系而言存在致命的缺点,即Ag、Nb等均属于贵金属,其成本较高;而且Nb的熔点较高。这均限制了该类材料在工业条件下的大规模制备。相反,对于Cu-Fe系而言,其具有以下两个优势:1) Fe在地壳中的储量较为丰富,因此其价格较为便宜;2) Fe的熔点较低,制备工艺比较简单。但是Cu-Fe系也存在较为显著的缺陷,即虽然在室温下Cu与Fe之间的相互固溶度是极小的,但是高温下Fe在Cu的中固溶度相对较高,且低温下其析出动力学相对比较缓慢。因此,相较于Cu-Ag系和Cu-Nb系原位复合材料而言,Cu-Fe系的电导率显著降低。众所周知,材料的性能主要取决于其成分和组织,所以近年来为了优化Cu-Fe系的强度和电导率主要采取了变形-中间热处理结合以及微合金化两种策略。SONG等[9-10]研究了第三组元Cr、Ag、Co对形变Cu-Fe原位复合材料组织和性能的影响,结果表明,Ag原子细化富铁枝晶同时又强化了铜基体,而Cr、Co等原子则强化了富铁枝晶,且相较于Cr、Co等元素,Ag元素能同时提高Cu-Fe系原位复合材料的强度和电导率。高海燕[11]进一步通过第一性原理计算研究了Ag原子对Cu-Fe合金电导率的影响,结果表明Fe原子与Ag原子在铜基体中存在竞争性溶解。谢志雄[12]研究了Ag元素对Cu/Fe界面润湿角的影响,结果表明随着Ag元素含量的增加Cu/Fe间的界面润湿角显著减小,充分地解释了Ag元素对Fe枝晶的细化效果。
综上所述,之前的研究大多数仅仅把焦点放在如何提高材料的力学和电学性能上面,而关于合金化对铜基体和富铁枝晶内部析出相形貌的的影响研究却鲜见报道。因此,本研究拟通过向Cu-Fe合金中加入Ni、Si元素来调控铜铁合金的组织和力学性能。所选的元素基于以下两个方面的考量:1) 已有的研究表明,铜基原位复合材料的强度可以由混合定律描述,即复合材料的强度取决于铜基体和纤维增强相的强度及其体积分数。大多数研究人员仅仅是关注纤维增强相的种类及其体积分数对复合材料强度的影响,很少有研究这关注相同体积分数下铜基体的强度对复合材料强度的影响。2) 所选的Ni、Si元素可以在低温时效时大量析出,因此,对材料的电导率不会带来太大的影响。
1 实验
实验用的Cu80Fe20和Cu75Fe20Ni4Si1(质量分数,%)采用电解铜板(99.95%)、工业纯铁(99.7%)、电解镍板(99.95%)以及冶金级硅(99.7%)按照名义成分配好后置于氮化硼坩埚内部,采用真空感应熔炼设备在高纯氩气保护氛围下进行熔炼,待铁板熔化后将熔体温度快速升高至(1900±20) K并保温5 min,然后将合金液浇铸到尺寸为直径45 mm×150 mm的圆形石墨坩埚中,待合金锭完全冷却后取出。
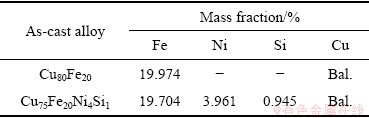
从铸锭底部相同高度的横截面中心部位取样首先利用XRF-1800型X射线荧光光谱分析仪进行化学成分分析,其结果如表1所示。然后再经过研磨、抛光后,采用由5 g三氯化铁、5 mL盐酸和95 mL无水乙醇配制的腐蚀液进行化学腐蚀。采用奥林巴斯GX51型光学显微镜和JEOL JEM-2100F型透射电镜分析式样的显微组织和成分。采用EPMA-1600型电子探针对其进行元素分析。采用EMPYREAN1600型X射线衍射仪对不同合金的相组成进行分析,其扫描角度为20°~100°,扫描速率为4 (°)/min。室温拉伸实验在MTS-CMT 5205型电子万能试验机上进行,拉伸速率为0.5 mm/min。每组试样取3个平行的实验值最后取其平均值。
表1 两组样品的名义成分和测量成分
Table 1 Nominal and measured chemical compositions of both samples
2 结果与讨论
2.1 显微组织
不同成分Cu-Fe合金的显微组织如图1所示。由图1可以看出,两组样品显微组织均由暗灰色的α-Fe枝晶和亮白色的铜基体组成。当未添加合金元素时,二元合金的显微组织呈细小的胞状晶,而随着Ni、Si元素的加入,多元合金的枝晶臂发生了明显的粗化,呈发达的树枝状,并且α-Fe枝晶的体积分数由原来的26.85%下降至25.19%。这与HEE等[13]报道的向Cu-10Fe合金中单独添加Si元素能够细化α-Fe枝晶的结果是相反的。另外,根据EDS结果可以看出随着合金元素的加入,铜基体中Fe的含量出现明显的升高。因此,可以推断出在Ni、Si两种合金元素的综合作用下可以改变高温下γ-Fe与剩余液相的界面能,从而抑制高温下γ-Fe枝晶形核使得析出的γ-Fe枝晶的数量减少,因而转变成发达的树枝晶。
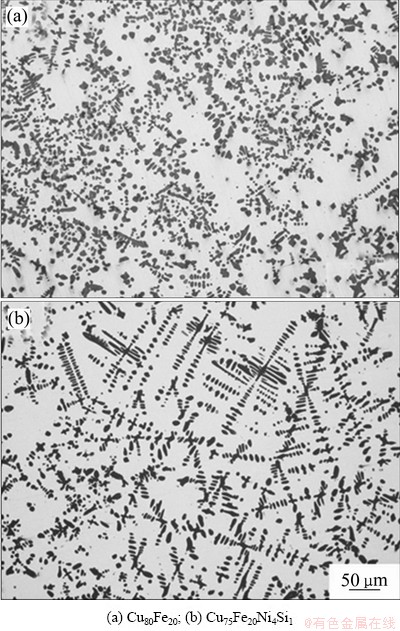
图1 不同成分Cu-Fe合金的铸态显微组织
Fig. 1 Solidification macrostructures of as-cast Cu-Fe alloy with different compositions
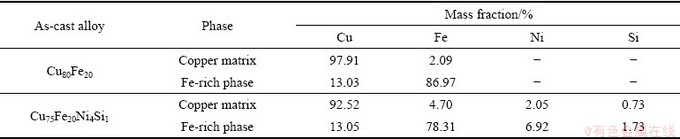
图2所示为多元合金的元素面分布图。由图2可以看出,相较于铜基体而言,Ni和Si元素在α-Fe枝晶中的含量更高,这主要是由Ni和Si元素与Fe元素的亲和力较大所造成的。也就是说相较于Cu而言,Fe与Ni、Si元素的混合焓较负。此外Ni、Si元素主要偏聚在α-Fe和铜基体的界面处。铜基体和α-Fe枝晶的化学成分见表2。
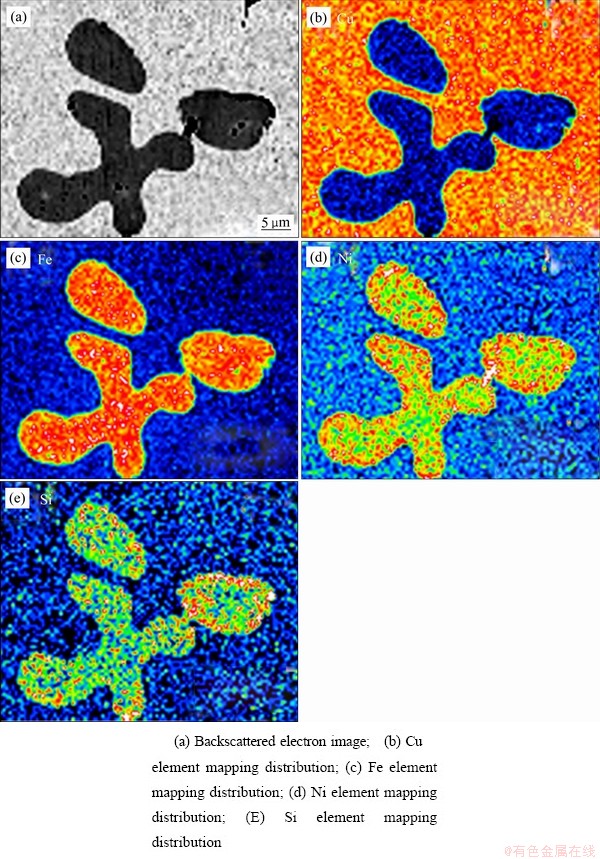
图2 多元合金的EPMA分析
Fig. 2 EPMA analysis of multicomponent alloy
表2 铜基体和α-Fe的化学成分
Table 2 Chemical composition of copper matrix and α-Fe
2.2 X射线衍射分析
图3所示为不同成分合金的XRD谱。由图3可见,添加Ni、Si元素前后,两组合金的衍射花样并无显著差别,表明其相组成并未发生变化,即Ni和Si的加入并没有在二元合金中引入新的金属间化合物,而是主要以固溶的形式存在于α-Fe枝晶和铜基体中,这与之前的EPMA元素分析是相符的。此外,由其衍射花样可以看出,两组合金均由α-Fe和ε-Cu组成。为了进一步说明Ni、Si元素在α-Fe枝晶和铜基体具有优先溶解性,根据X射线衍射花样计算出的不同成分的合金的α-Fe枝晶和铜基体的晶面间距,其结果如表3所示。通过对比表3中的数据可以发现,随着Ni、Si元素的加入,α-Fe枝晶的晶面间距增大,而铜基体的晶面间距减小。结果表明:向Cu-Fe二元合金中添加Ni、Si元素时,会优先固溶在α-Fe枝晶中。
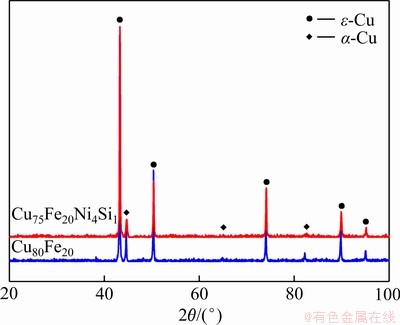
图3 不同成分合金的XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of alloys with different compositions
2.3 α-Fe中富铜析出相形貌演变
根据铜铁二元合金相图可知,高温下铜在γ-Fe中的固溶度较大,而室温下其溶解度几乎为0。因此,当合金凝固后在后续的降温过程中会在α-Fe中形成高密度弥散分布的纳米级富铜析出相。虽然Ni、Si合金元素的添加对Cu-Fe二元合金的组织没有产生较为明显的变化,但是α-Fe中的析出相的形貌却发生了显著的改变。图4所示为二元合金中初生α-Fe枝晶TEM明场像,其中右上角的插图为析出相的选区电子衍射斑点。从图4可以看出,析出相为晶体结构为无序的FCC,晶格常数为0.3615富铜析出相。其形貌为近球形,平均尺寸约为(53±2) nm。另外,通过对比发现富铜析出相的尺寸要远远大于含铜钢在500 ℃时效500 h时的析出相尺寸[14]。因此,可以推断出该富铜析出相的形核与长大要先于降温过程中γ-Fe向α-Fe的晶型转变,即富铜析出相是在铸锭冷却过程中从γ-Fe枝晶而并非α-Fe枝晶中析出的。图4所示高径角环形暗场像及其元素分布图和EDS进一步表明析出相中贫Fe富Cu。
图5所示为多元合金中初生α-Fe枝晶TEM明场像,其中右上角的插图为析出相的选区电子衍射斑点。同样地,由其衍射斑点和元素面分布图及EDS结果表明析出相为富铜相。但是通过仔细对比图4和图5可以发现,富铜析出相的形貌发生了显著的改变,即由二元合金中的近球形转变成多元合金中的立方体形,且其枝晶尺寸发生了明显粗化,约为(85±5) nm。这说明析出相的类型与合金成分无关,改变原始合金的成分仅仅对析出相的形貌产生了影响。
众所周知,富铜析出相的平衡形貌将取决于形成新相所引起的最小自由能变△G,而由于基体γ-Fe与富铜析出相之间存在晶格常数的差异以及新相在析出过程中会形成新的相界面。因此,从理论上来讲最小自由能变包括两部分即弹性畸变能和化学交互作用能(俗称界面能)。根据上述实验结果,假设富铜析出相的形状为完美的球形和立方形,那么总的自由能变则可以表示为[15]
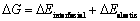 (1)
(1)
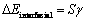 (2)
(2)
式中:△Einterfacial为界面能;S为富铜析出相的表面积;γ为富铜析出相与γ-Fe基体之间的界面能密度,其值为0.14 J/m2;△Eelastic为由晶格失配所引起的弹性畸变能,根据线弹性理论其值可以表示为[15]
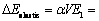
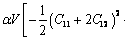
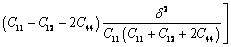 (3)
(3)
式中: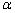 为与析出相形状相关的常数,对于球形和立方形析出相其值分别为0.709和0.558[15];E1为弹性畸变能密度;V为弹性畸变能体积;C11、C12和C44为γ-Fe基体的弹性常数,其值分别为C11=181、C12=153、C44=53[16];△为由γ-Fe基体和富铜析出相之间的晶格差异所引起的晶格失配应变,其值为0.0069[16]。
为与析出相形状相关的常数,对于球形和立方形析出相其值分别为0.709和0.558[15];E1为弹性畸变能密度;V为弹性畸变能体积;C11、C12和C44为γ-Fe基体的弹性常数,其值分别为C11=181、C12=153、C44=53[16];△为由γ-Fe基体和富铜析出相之间的晶格差异所引起的晶格失配应变,其值为0.0069[16]。
表3 两组样品的α-Fe和铜基体晶面间距
Table 3 Interplanar distance of copper matrix and α-Fe dendrite for both samples
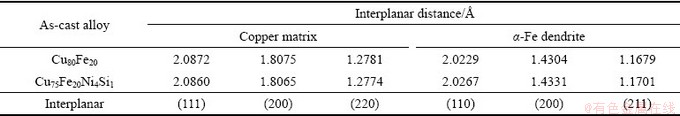
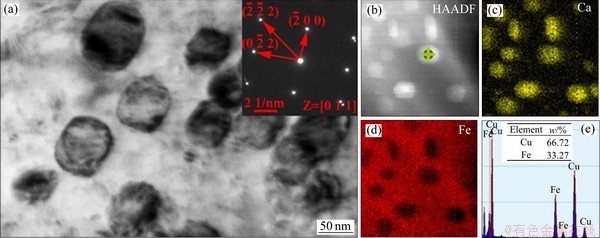
图4 二元合金中α-Fe枝晶中的TEM明场像及元素面分布图和EDS谱
Fig. 4 TEM bright field image(a), HAADF(b) of α-Fe and corresponding element mapping distribution of Cu(c), Fe(d) and EDS patterns(e) in as-cast binary alloy
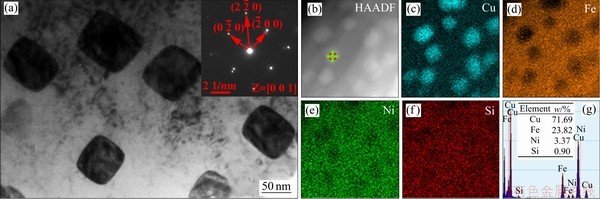
图5 多元合金中α-Fe枝晶中明场像及其元素面分布图和EDS谱
Fig. 5 TEM bright field image(a), HAADF(b) of FCC Cu particles and corresponding element mapping distribution of Cu(c), Fe(d), Ni(e), Si(f) and EDS patterns(g) in as-cast multi-constituent alloy
为了便于计算,假设球形析出相的体积V=(2a)3,那么其半径r=(4π/3)-1/3(2a),表面积S=4a2(36π)1/3。结合式(1)、(2)和(3),球形析出相的总自由能变△Gsp和相同体积的立方形析出相的总自由能变△Gcu可以通过式(4)和(5)表示[15]:
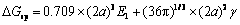 (4)
(4)
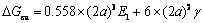 (5)
(5)
因此,球形析出相和立方形析出相的所引起的自由能变的差值可以表示为[15]
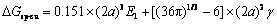 (6)
(6)
基于上述分析,可以发现当△Gsp-cu<0时,析出相的将由球形转变成立方形,这意味着存在一个临界的析出相形貌转变尺寸。当△Gsp-cu=0时,可以通过方程(6)计算出析出相形貌转变的临界尺寸,并表示为[15]
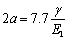 (7)
(7)
图6所示为二元合金的球形析出相与立方形析出相自由能差值与析出相尺寸之间的函数关系图。由图6可以看出,在二元合金中当富Cu析出相的尺寸达到一定值后,其形貌也存在由近球形向立方形的转变。经结算可知,其临界尺寸2a=111 nm。计算结果表明当0<2a<111 nm时,析出相的形貌为球形在热力学上是稳定的,其对应的球形析出相的最大半径rmax=69 nm。在本研究中,根据TEM结果测得的铸态二元合金α-Fe枝晶中的析出相的平均直径为(53±2) nm,其值远小于通过热力学计算的临界转变半径。因此,α-Fe基体中析出富铜析出相呈球形。对于多元合金而言,根据之前的XRD结果分析可知,由Ni、Si元素固溶所引起的γ-Fe晶格常数变化可以忽略不计。因此,两组样品的弹性畸变能密度可以认为是相同的。然而,WANG等[17]研究表明向三元合金Fe-Cu-Mn合金中每加入1%的Ni其富铜析出相与α-Fe之间的界面能密度γ下降1.9%。虽然关于Si元素对于Cu/Fe界面能密度的影响却鲜有报道,但是SHU等[18]研究表明,在Cu/Fe相界面形成一层无序、纤薄的MnNiSi层将会使其界面能下降50%。基于以上分析并结合EPMA元素面分布图,可以推断出,Ni、Si元素的加入改变了γ-Fe与富铜析出相之间的界面能。因此改变了多元合金中析出相形貌转变的临界参数,进而在相同的铸造条件下,使得铸态多元合金α-Fe枝晶中的富铜析出相呈现立方形。

图6 二元合金△Gsp-cu随参数2a的函数关系
Fig. 6 △Gsp-cu of binary alloy as function of parameter 2a
2.4 力学性能
室温下不同成分的两组样品的工程应力应变曲线如图7所示。另外,样品的屈服强度(σ0.2)、抗拉强度(σUTS)以及断后伸长率见表4。由表4可知多元合金的抗拉强度和屈服强度分别为436 MPa和304 MPa,相比于二元合金分别提高37%和46%。另外,添加合金元素之后断后伸长率由原来的二元合金的11%提高到16%。结果表明,Ni、Si元素的添加同时提高了二元合金的强度和塑性。然而,众所周知的是,强度和塑性本身是相互矛盾的,即强度升高往往伴随着塑性的降低。
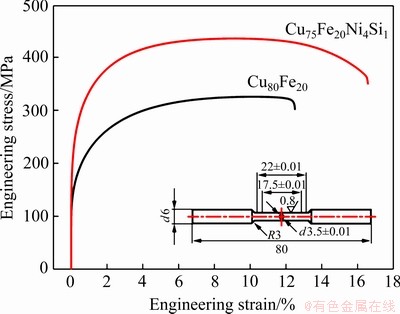
图7 室温下不同成分合金的工程应力-应变曲线
Fig. 7 Engineering stress-strain curves of alloys with different compositions at room temperature
表4 两组样品的抗拉强度、屈服强度以及伸长率
Table 4 Ultimate tensile strength, yield strength and total elongation of both sample

为了进一步分析Ni、Si元素对二元Cu-Fe合金的强化作用,根据现有的强化模型对各个强化机制给二元合金所带来的强度贡献做了简单的计算。对于包含有塑性较好的两相铸态甚至是低变形态的Cu-Fe二元合金而言,其整体的屈服强度满足混合定律,其计算公式如下[19]:
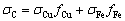 (8)
(8)
式中:σC、σCu和σFe分别为复合材料的屈服强度、铜基体的屈服强度和富铁相的屈服强度;fCu和fFe分别为铜基体和富铁相的体积分数。
根据之前的XRD结果和TEM相貌分析可知,由于铜基体中的富铁析出相的体积分数较小,因此,铜基体的强度贡献主要来自于溶质元素固溶所导致铜基体晶格畸变从而产生相应的应变场进而对位错滑移产生相应的阻力,这种强化方式称为固溶强化。而在富铁枝晶中,可以观察到高密度纳米级的富铜析出相,因而除了溶质原子固溶所带来的固溶强化之外,还存在另一种重要的强化机制,即析出强化机制。其中析出强化机制根据析出相是否可变形分为位错切过机制和位错绕过机制,后者又被称为奥罗万强化机制。在本研究中,富铁枝晶中的富铜析出相的尺寸均在几十个纳米左右,因此在计算其所带来的强度贡献时,将采用奥罗万强化机制进行计算。研究结果表明,在极其稀释的铜基固溶体中(平均溶质溶度≤2%,摩尔分数),溶质原子可以作为独立的点缺陷,固溶强化所带来的强度贡献满足Labusch’s理论,其计算公式如下[20]:
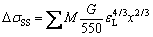 (9)
(9)
式中:M为泰勒因子,对于无织构的多晶材料,其值取3;G为铜基体的剪切模量,其值取45.5 GPa;x为铜基体中溶质原子的平均摩尔浓度;εL为Labusch参数,其计算公式如下[20]:
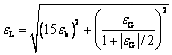 (10)
(10)
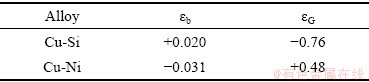
式中:εb和εG分别为相应的尺寸失配参数和模量失配参数,其数值见表5[21]。
表5 铜合金中失配参数
Table 5 Misfit parameters for copper alloys
根据之前的EMPA成分分析可知,Ni、Si元素在铜基体的固溶度较低,因此可以采用上述公式进行计算。而相对于Fe元素,尽管在室温下铜铁之间的相互固溶度均是极小的,但是由于其在高温下在铜基体的固溶度较高,而低温下其析出动力学又相对比较缓慢,同时铸锭的冷却是一个变温过程而且冷却时间较短,所以大多数固溶在铜基体中的Fe原子来不及析出而保留在铜基体中。因此其对铜基体带来的强度贡献并不满足上述计算公式。高海 燕[11]的研究结果表明,在铜铁二元合金的铸态组织中,铜基体中除了含有较高含量的Fe原子亦有少量纳米级的富铁析出相,并指明Fe原子对铜基体的固溶强化的强度贡献可由式(11)进行计算:
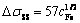 (11)
(11)
相对于铜基体,对于溶质元素对富铁枝晶的强度贡献,本研究将参考钢中合金元素对钢的强化进行计算,根据雍启龙等[22]研究结果,其溶质元素对富铁枝晶的固溶强化贡献将采用式(12)对其进行计算:
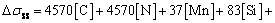
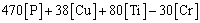 (12)
(12)
式中:[X]为溶质原子的平均质量分数。
由以上分析可以,在两组样品的富铁枝晶中存在高密度的纳米级析出相,其强化机制遵循奥罗万强化机制,其计算公式如下[23]:
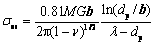 (13)
(13)
 (14)
(14)
式中:M为泰勒因子,其值取3;G为富铁枝晶的剪切模量,其值取83 GPa;b为伯氏矢量,其值取0.246;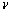 为泊松比,其值取0.293;dp为富铜析出相的平均尺寸;λ为富铜析出相之间的平均间距;
为泊松比,其值取0.293;dp为富铜析出相的平均尺寸;λ为富铜析出相之间的平均间距;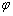 为富铜析出相之间的体积分数,其中dp、λ和
为富铜析出相之间的体积分数,其中dp、λ和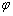 具有TEM明场像统计得出。
具有TEM明场像统计得出。
综合上述分析,不同成分下的合金的整体屈服强度可以通过式(15)进行计算:
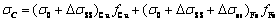 (15)
(15)
式中:σ0为铜和铁的本征晶格流变应力,其值分别为52 MPa和48 MPa。
将所有参数代入式(9)~(14)进行计算,二元合金和多元合金的屈服强度分别为243 MPa和315 MPa。经过与实验测得屈服强度相比,虽然在数值上存在一定的误差,但是整体符合较好,结果表明,不同成分下的合金的强化机制主要为固溶强化和析出强化控制。
3 结论
1) 本研究中Ni、Si元素的添加并未改变原始二元合金的显微组织和相组成,不同成分下的合金均由α-Fe枝晶和铜基体组成。但是α-Fe枝晶中的富铜析出相的形貌由近球形转变成立方形,这主要是由于Ni、Si元素的加入使得Cu/Fe界面能密度降低,进而改变了多元合金中的析出相形貌转变的临界尺寸。
2) 相较于二元合金,其强度和塑性同时得到了提高,这主要归因于Ni、Si元素的加入引起的晶粒细化以及固溶强化。
REFERENCES
[1] BEVK J, HARBISON J P, BELL J L. Anomalous increase in strength of in situ formed Cu-Nb multifilamentary composites[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1978, 49(12): 6031-6038.
[2] FUNKENBUSCH P D, COURTNEY T H, KUBISCH D G. Fabricability of and microstructural development in cold worked metal matrix composites[J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1984, 18(10): 1099-1104.
[3] FUNKENBUSCH P D, COURTNEY T H. Microstructural strengthening in cold worked in situ Cu-14.8Vol.% Fe composites[J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1981, 15(12): 1349-1354.
[4] SPITZIG W A, PELTON A R, LAABS F C. Characterization of the strength and microstructure of heavily cold worked Cu-Nb composites[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1987, 35(10): 2427-2442.
[5] SNOECK E, LECOUTURIER F, THILLY L, et al. Microstructural studies of in situ produced filamentary Cu/Nb wires[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1998, 38(11): 1643-1648.
[6] HONG S I, HILL M A. Microstructural stability and mechanical response of Cu-Ag microcomposite wires[J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46(12): 4111-4122.
[7] DENG Li-ping, HAN Ke, WANG Bing-shu, et al. Thermal stability of Cu-Nb microcomposite wires[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 101: 181-188.
[8] VERHOEVEN J D, CHUEH S C, GIBSON E D. Strength and conductivity of in situ Cu-Fe alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1989, 24(5): 1748-1752.
[9] SONG J. Heavily drawn Cu-Fe-Ag and Cu-Fe-Cr microcomposites[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 113(1): 610-616.
[10] SONG J S, HONG S I. Strength and electrical conductivity of Cu-9Fe-1.2Co filamentary microcomposite wires[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2000, 311(2): 265-269.
[11] 高海燕. 高强高导形变Cu-Fe-Ag原位复合材料制备技术基础[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2007.
GAO Hai-yan. Study on high strength and high conductivity deformation processed Cu-Fe-Ag in situ composites[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2007.
[12] 谢志雄. 多元合金化Cu-Fe原位复合材料的组织和性能研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2012.
XIE Zhi-xiong. Study on microstructure and properties of multi-element alloyed Cu-Fe deformation processed in situ composites[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2012.
[13] HEE R J, Kim J T, HONG S H, et al. Effect of silicon on microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-Fe alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 707(15): 184-188.
[14] WEN Y R, LI Y P, HIRATA A, et al, Microstructure characterization of Cu-rich nanoprecipitates in a Fe-2.5Cu-1.5Mn-4.0Ni-1.0Al multicomponent ferritic alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(6): 2133-2147.
[15] KHACHATURYAN A G, SEMENOVSKAYA S V, MORRIS JR J W. Theoretical analysis of strain-induced shape changes in cubic precipitates during coarsening[J]. Acta Metallurgica,1988, 36(6): 1563-1572.
[16] CHEN K X, KORZGAVYI P A, DEMANGE G, et al. Morphological instability of iron-rich precipitates in Cu-Fe-Co alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 163: 55–67.
[17] WANG Y, YIN J, HOU Huai-yu, et al. Ab initio based modeling of interfacial segregation at Cu-rich precipitates in Fe-Cu-Ni alloys[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B (Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms), 2019, 456: 32–36.
[18] SHU Shi-peng, WELLS P B, NATHAN A, et al. Thermodynamics and kinetics of core-shell versus appendage co-precipitation morphologies: An example in the Fe-Cu-Mn-Ni-Si system[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 157: 298–306.
[19] 湛永钟. 铜基复合材料及其制备技术[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2015: 159.
ZHANG Yong-zhong. Copper matrix composites and its preparation technology[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology press, 2015: 159.
[20] HART E W. Theory of dispersion hardening in metals[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1972, 20(2): 275–289.
[21] NAGARJUNA S, SRINIVAS M, BALASUBRAMANIAN K, et al. On the variation of mechanical properties with solute content in Cu-Ti alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 259(1): 34-42.
[22] 雍启龙. 钢铁材料中的第二相[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006: 83.
YONG Qi-long. Secondary phases in steels[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006: 83.
[23] LEI Qian, LI Zhou, ZHU An-yin, et al. The transformation behavior of Cu-8.0Ni-1.8Si-0.6Sn-0.15Mg alloy during isothermal heat treatment[J]. Materials Characterization, 2011, 62(9): 904-911.
Effect of Ni and Si on microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-Fe alloy
YUE Shi-peng, JIE Jin-chuan, QU Jian-ping, LI Ting-ju
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China)
Abstract: The effects of Ni and Si elements on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-20Fe (mass fraction, %) alloy were studied by optical microscope, electron probe analysis, transmission electron microscope, X-ray diffractometer and tensile experiment. The results show that the addition of Ni and Si elements leads to obvious coarsening behavior of the α-Fe dendrites in the Cu-20Fe alloy. In addition, due to the addition of alloying elements, the interface energy between γ-Fe and the copper-rich precipitation phase is reduced, so that the morphology of the copper-rich precipitation phase has undergone a significant change, that is, it changes from a nearly spherical shape to a cube. Compared with the binary alloy without adding alloying elements, the strength and plasticity of the multi-component alloy are improved after the addition of alloying elements. The yield strength and elongation of the multi-component alloy are 304MPa and 16%, respectively. Through theoretical calculation and experimental verification, it is determined that the main strengthening mechanism of the alloy is solid solution strengthening and precipitation strengthening.
Key words: microstructure; morphology transformation; interface energy; strengthening mechanism
Foundation item: Projects(2018YFE030610) supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China; Projects(2018B10030) supported by the Ningbo Major Science and Technology, China
Received date: 2021-10-10; Accepted date: 2021-12-03
Corresponding author: JIE Jin-chuan; Tel: +86-15941130325; E-mail: jiejc@dlut.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家重点研发计划资助项目(2018YFE0306103);宁波市重大科技专项(2018B10030)
收稿日期:2021-10-10;修订日期:2021-12-03
通信作者:接金川,副教授,博士;电话:15941130325;E-mail:jiejc@dlut.edu.cn