黄铜矿在氨水-氯化铵溶液中的界面反应
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2018年第3期
论文作者:华晓鸣 郑永飞 许茜 鲁雄刚 程红伟 邹星礼 宋秋实 宁志强
文章页码:556 - 566
关键词:黄铜矿;界面反应;氨;钝化层;氧化机理
Key words:chalcopyrite; interfacial reaction; ammonia; passivation layer; oxidation mechanisms
摘 要:对黄铜矿在氨水-氯化铵溶液中的反应界面进行研究。利用X射线光电子能谱分析(XPS)技术对黄铜矿反应界面进行表征。研究发现, 覆盖在黄铜矿基底之上的反应界面钝化层由表层的铁氧化物以及被其覆盖的硫化铜组成。黄铜矿结构中的铁离子存在优先溶解现象,形成钝化层中的硫化铜或CuFe1-xS2。当表层铁氧化物层逐渐自发剥离后,硫化铜层成为新的钝化层。由硫化铜层表面S2-、 、 、S0和 等组分含量推算硫化铜的组成。提出黄铜矿在不同pH和氧化电位条件下的氧化和钝化机理。最后,建立黄铜矿界面三步反应模型,剖析钝化层的形成及转化机理。
Abstract: The interfacial reactions of chalcopyrite in ammonia–ammonium chloride solution were investigated. The chalcopyrite surface was examined by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) techniques. It was found that interfacial passivation layers of chalcopyrite were formed from an iron oxide layer on top of a copper sulfide layer overlaying the bulk chalcopyrite, whereas CuFe1-xS2 or copper sulfides were formed via the preferential dissolution of Fe. The copper sulfide layer formed a new passivation layer, whereas the iron oxide layer peeled off spontaneously and partially from the chalcopyrite surface. The state of the copper sulfide layer was discussed after being deduced from the appearance of S2-, , , S0 and . A mechanism for the oxidation and passivation of chalcopyrite under different pH values and redox potentials was proposed. Accordingly, a model of the interfacial reaction on the chalcopyrite surface was constructed using a three-step reaction pathway, which demonstrated the formation and transformation of passivation layers under the present experimental conditions.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 556-566
Xiao-ming HUA1, Yong-fei ZHENG2, Qian XU2, Xiong-gang LU2, Hong-wei CHENG2, Xing-li ZOU2, Qiu-shi SONG1, Zhi-qiang NING1
1. School of Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110004, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Advanced Special Steel, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Advanced Ferrometallurgy, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China
Received 20 November 2016; accepted 23 May 2017
Abstract: The interfacial reactions of chalcopyrite in ammonia–ammonium chloride solution were investigated. The chalcopyrite surface was examined by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) techniques. It was found that interfacial passivation layers of chalcopyrite were formed from an iron oxide layer on top of a copper sulfide layer overlaying the bulk chalcopyrite, whereas CuFe1-xS2 or copper sulfides were formed via the preferential dissolution of Fe. The copper sulfide layer formed a new passivation layer, whereas the iron oxide layer peeled off spontaneously and partially from the chalcopyrite surface. The state of the copper sulfide layer was discussed after being deduced from the appearance of S2-, 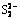 ,
, 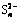 , S0 and
, S0 and  . A mechanism for the oxidation and passivation of chalcopyrite under different pH values and redox potentials was proposed. Accordingly, a model of the interfacial reaction on the chalcopyrite surface was constructed using a three-step reaction pathway, which demonstrated the formation and transformation of passivation layers under the present experimental conditions.
. A mechanism for the oxidation and passivation of chalcopyrite under different pH values and redox potentials was proposed. Accordingly, a model of the interfacial reaction on the chalcopyrite surface was constructed using a three-step reaction pathway, which demonstrated the formation and transformation of passivation layers under the present experimental conditions.
Key words: chalcopyrite; interfacial reaction; ammonia; passivation layer; oxidation mechanisms
1 Introduction
Chalcopyrite is the most refractory and abundant source of copper [1]. Oxidation of chalcopyrite is an important research topic in environmental geochemistry, since it is one of the main copper minerals and significant accessory minerals in many igneous and sedimentary rocks [2,3]. A decline in copper grades has occurred in recent times, which is a future challenge to the copper industry [4]. An efficient hydrometallurgical process has thus far not been widely applied to the industry; neither has significant research been conducted for gaining a deeper understanding of the reaction mechanisms of low-grade and/or complex ores. However, hydrometallurgy provides numerous advantages for mineral processing. For example, a hydrometallurgical refining pathway enables selective dissolution and precipitation of elements in a desired form at a preferred stage of the process [5]. To ensure further industrial applications of chalcopyrite, a full understanding of the mechanism of its leaching process is necessary.
In a previous study on interfacial reactions, Fe hydroxide/oxyhydroxide was detected in the first few atomic layers when fresh chalcopyrite was exposed to water [6]. Iron was leached out of the chalcopyrite structure, preferentially forming a layer of a metal-deficient phase [7]. An intermediate phase of Cun-1Fen-1S2n was considered to be the product [8]. The products Cu5FeS4 and Cu2S were formed between the outer iron oxide layer and bulk chalcopyrite [9]. Furthermore, a passivation film of CuS2 was formed on the surface at a low potential in alkaline solution by atmospheric and electrochemical methods [10]. Sulfur remained unoxidized as CuS2, with Fe(OH)3 and Fe2O3, forming a film that retarded the oxidation. Furthermore, ferrous-promoted chalcopyrite leaching was assumed to be due to the formation of intermediate CuS2, which is more amenable to oxidation than chalcopyrite. It was proposed that some copper was leached into the solution, forming an altered layer of Cu0.8S2 in air-saturated ammonia solution [9]. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) observations revealed that in addition to Cu-rich sulfides and iron hydroxides, a CuSn layer approximately 1 μm in thickness existed on a polished chalcopyrite surface [11].
A previously developed model [12] predicted that the formation of Cu2S and chalcopyrite leaching occurred when the redox potential of the solution was below a critical potential, due to the function of the ferrous and cupric ion concentrations. CuS2 first converted to CuS, after which it formed a group of secondary covellite phases with stoichiometries between Cu1.6S and Cu1.1S [13]. CuS and CuS2 appeared to be the two main Cu sulfides, owning to iron depletion from the subsurface area [14]. In another study, the absolute energies of calculated and experimental Cu L-edge spectra were closely aligned for both Cu/Fe sulfides and CuS2, but not for Cu2S and CuS. Moreover, a solid product with a stoichiometry of Cu0.75S2 was formed after Fe2+ and Cu2+ were dissolved from the chalcopyrite structure at a mass ratio of 4:1 [15]. The thickness of the formed layer was about 3 nm, and it was composed of CuS and other S compounds.
Other analytical studies of oxidized or leached chalcopyrite suggest that a formed S0 layer may also act as a diffusion barrier to the transport of ions and electrons in the absence of either bacteria or electrochemical inducement, thereby dismissing the possibility of 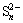 formation and claiming that only the sulfur species S2-,
formation and claiming that only the sulfur species S2-, 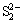 , S0 and
, S0 and 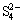 were detectable on the leached CuFeS2 surface [16]. Evidence of the formation of a copper-rich sulfide with a composition of either Cu5FeS4 or Cu2S was found [17]. When the chalcopyrite surface was exposed to air, Cu and S components could not be examined because of the formation of an Fe oxide layer having a thickness of between 20 and 40 nm.
were detectable on the leached CuFeS2 surface [16]. Evidence of the formation of a copper-rich sulfide with a composition of either Cu5FeS4 or Cu2S was found [17]. When the chalcopyrite surface was exposed to air, Cu and S components could not be examined because of the formation of an Fe oxide layer having a thickness of between 20 and 40 nm.
The passivation layer and intermediate compounds vary with the physicochemical conditions, so does the dissolution process [18]. As a result, there is no real consensus from the results of previous studies regarding the intermediary products during the oxidation process of chalcopyrite. This paper presents optical microscopy (OM) images, XPS investigation results, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the leaching- product layer of chalcopyrite, which demonstrate the occurrence of a mild interfacial reaction in ammonia– ammonium chloride solution. The aim of this study is to provide a deeper understanding of alkaline leaching theory in terms of the formation of layers and the interfacial reactions on the chalcopyrite surface, especially the complex Cu sulfide under-layer, and to provide a model of the interfacial reaction by using a three-step reaction pathway.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and methods
The raw ore was extracted from a mine in Sinkiang, China. The composition determined by X-ray fluorescence (XRF, Shimadzu, XRF-1800) spectrometry analysis was as follows: 3.6524% Cu, 2.5450% Ni, 39.5300% Fe, 26.1787% S, 6.2071% Si, and 2.3080% Mg (mass fraction). No concentrate was used in the XRF or X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku, D/Max-2550) analyses. Samples for OM measurements were chosen carefully so as to be devoid of gangue, and those for leaching experiments were carefully selected such that the chalcopyrite content was at least 80% (mass fraction). To focus on the mechanism of the leaching process of one phase, samples with high purity of chalcopyrite were selected because this would ensure reduced interference from other ores during the leaching experiments. All samples were mounted in epoxy resin and polished with 2.5 μm diamond abrasive and finally dispersed in deionized water. The mounted and polished samples were rinsed with deionized water/ethanol and dried after being leached in ammonia–ammonium chloride solution (1 mol/L NH3·H2O with 2 mol/L NH4Cl) at 25 °C.
2.2 Characterization
The interfacial reaction surface of the leached sample was observed by OM (Leica, DM4000M). The surface of each sample was rinsed with deionized water/ethanol and dried after being leached for the scheduled time (0-100 h). The leaching layer was examined by SEM (JEOL, JSM-6700F) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS, Oxford INCA EDS system), which were used to distinguish the different mineral phases and to analyze the surface changes. The surface of the sample was coated with platinum before the measurements. An XPS measurement (Fisher Scientific, ESCALAB) was performed on the interfacial reaction surface of chalcopyrite on the cubic sample by adopting a monochromatic Al Kα X-ray source. All core-level spectra were referenced to the C 1s neutral carbon peak at 284.8 eV. The spot size was 400-600 μm, which almost entirely covered the area of the chalcopyrite surface.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Mineral composition
The crude ore belonged to a low-grade copper-nickel mineral whose chemical analysis data are discussed in Section 2. According to the XRD pattern of the ore shown in Fig. 1, chalcopyrite, pentlandite, and pyrrhotite were the main sulfidic mineral phases associated with magnetite and other gangue.
Figure 2(a) shows an optical microscope photograph of the surface of the polished cubic ore that was carefully chosen so as to be devoid of gangue. The photograph was composed of several images, owing to the limitations of the microscope. Figure 2(b) shows a computer-generated image of the area shown in Fig. 2(a), which is depicted as an electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) image; here, different colors represent different minerals as given in the elemental maps. The purpose of the computer-generated image was to distinctly describe different mineral phases. For instance, the blue area shows the mapping image of Ni, which represents pentlandite, the only nickel ore containing Fe, S, and Ni. The green area shows the mapping image of Cu, which represents chalcopyrite, the only copper ore which contains Fe, S, and Cu. The yellow area shows the mapping image of O, which represents magnetite, the only oxidized ore containing Fe and O. The gray area represents pyrrhotite, which contains only Fe and S. Moreover, the mineral phase in Fig. 2(a) could be identified by XRD analysis, EBSD elemental analysis, and the description obtained by microphysiography [19]. Chalcopyrite (yellow phase), pentlandite (white phase), pyrrhotite (gray phase), and magnetite (blue phase) were products of crystallization differentiation that possessed brecciated structures. An interfacial reaction experiment was performed after analysis of the mineral composition and phase.
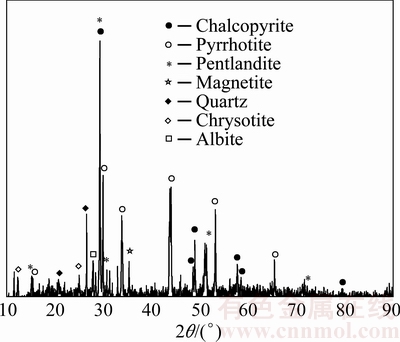
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of raw ore
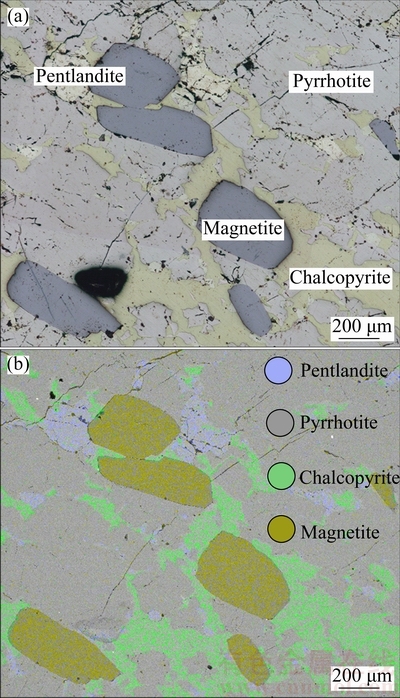

Fig. 2 OM image assembled from several separate images (a) and computer-generated image depicted as electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) image, where different colors represent different minerals as given in elemental map (b)
3.2 Mineral interfacial reaction
Figure 3 shows an optical microscope photograph of the interfacial reaction with leaching time from 0 to 100 h and acid-treated at 25 °C. With respect to the interfacial leaching experiment, the process of layer formation might be determined according to the optical changes. Then, the mechanism of mineral leaching was identified by surface characterization. The mineral phase could be identified clearly before leaching, where chalcopyrite (yellow phase) and pyrrhotite (gray phase) were identified (Fig. 3(a)). The primary research target in this work was the interfacial reaction on the chalcopyrite surface.
CuFeS2+NH3+H2O+O2→[Cu(NH3)4]SO4+(NH4)2SO4+Fe2O3·nH2O (1)
CuFeS2+O2+OH-→CuSn+Fe2O3·nH2O+S+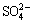 (2)
(2)
Equation (1) [20] indicates that in the presence of NH3·H2O and O2 (thus leading to the requirement of an appropriate redox potential (φh) and pH, which will be discussed later), chalcopyrite was oxidized on the surface with the formation of 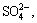 FeOOH/Fe2O3·nH2O/ Fe(OH)3 [21], or even S [22] or CuSn [23]. In contrast, Eq. (2) indicates the incomplete oxidation of chalcopyrite or, in all probability, the intermediate process of the industrial leaching method. The oxidation of elemental S was complex, and it involved more than just a change from
FeOOH/Fe2O3·nH2O/ Fe(OH)3 [21], or even S [22] or CuSn [23]. In contrast, Eq. (2) indicates the incomplete oxidation of chalcopyrite or, in all probability, the intermediate process of the industrial leaching method. The oxidation of elemental S was complex, and it involved more than just a change from 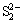 to S8 or
to S8 or 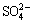 ; intermediate oxidation of thiosulfate anions and polythionate occurred during the process [20]. In reality, the process of the interfacial reaction on chalcopyrite is more complex than that has previously been considered. Therefore, the research processes described in Eqs. (1) and (2) should be taken into consideration.
; intermediate oxidation of thiosulfate anions and polythionate occurred during the process [20]. In reality, the process of the interfacial reaction on chalcopyrite is more complex than that has previously been considered. Therefore, the research processes described in Eqs. (1) and (2) should be taken into consideration.
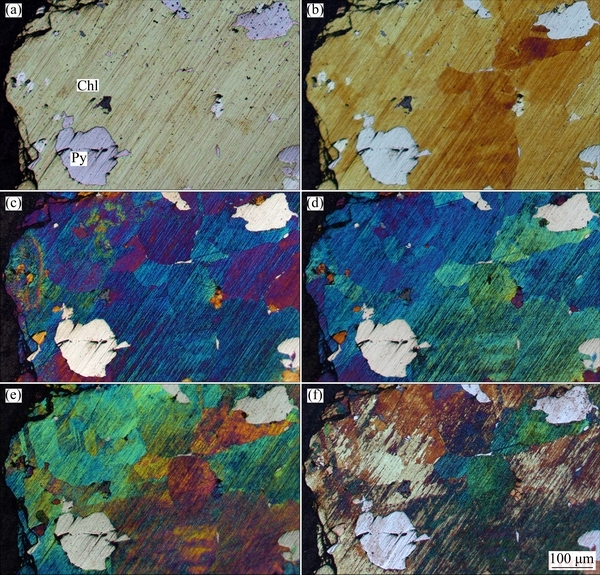
Fig. 3 OM images of interfacial reaction at leaching time 0 h (a), 5 h (b), 20 h (c), 50 h (d), 100 h (e), and acid-treated (f) in 1 mol/L NH3·H2O and 2 mol/L NH4Cl at 25 °C (Chl: Chalcopyrite, Py: Pyrrhotite)
It was visually clear from Fig. 3(b) that the chalcopyrite surface became redder over time, which suggests the presence of layers (Fe oxides) on the mineral surface. The image shows that in the active redox region, Fe was selectively leached out prior to Cu, as reported previously [24], and a FeOOH layer in alkaline solution formed. With increasing time, the layer on chalcopyrite gradually changed in color to blue without any residual red layer, and the Fe-deficient Cu polysulfide layer under the Fe oxide layer became fully visible after 20 h (Fig. 3(c)). Different reaction speeds on the chalcopyrite surface could have been due to different surface conditions after polishing. Furthermore, the absence of green and red surface layers suggested a new interfacial change in the unstable ferrihydrite layer and the Fe-deficient Cu polysulfide layer (Figs. 3(d) and (e)), though other characterization methods would be required to fully understand the interfacial process. The sample surface was treated with diluted hydrochloric acid to deeply excavate the layers, as shown in Fig. 3(f). A hierarchical structure might be present on the interfacial surface; Cu might remain on the surface, with the formation of Cu5FeS4, CuS, or Cu2S [6,25], whereas the oxidized environment might not oxidize chalcopyrite sufficiently.
As shown in Figs. 4(a)–(c), the sample was treated with diluted hydrochloric acid for 1 min after leaching for 100 h to initiate dissolution on the top layer, in order to take advantage of OM and XPS analyses. The acid treatment dissolved the top Fe-sufficient layer and exposed the Cu polysulfide layer, which could then be characterized by XPS analysis. In comparison, the leaching condition could not prevent the interfacial surface layers from peeling off; instead, it exposed the under-layers to the solution, perhaps because of the over-exfoliation of the surface layer (Figs. 4(d) and (e)). Debris could be observed on the surface in the enlarged image (Fig. 4(f)). It was concluded that the yellow, fresh surface was not chalcopyrite, since no further visual interfacial reaction occurred.
Figure 5 shows Fe 2p and O 1s XPS spectra obtained from the layers of the chalcopyrite surface in the sample shown in Fig. 3(e); neither Cu nor S was detected. Although the two areas showed different colors on the interfacial reaction surface (blue/cyan and red), they showed almost the same intensity peak position and shape, suggesting that the same layer was present on top of the interfacial surface and it had almost the same state. The photoelectron peaks at 712.10 and 724.70 eV corresponded to the binding energies of Fe 2p3/2 and Fe 2p1/2, respectively. Two typical satellite peaks (Sat) were also observed in Fig. 5(a). These satellite peaks resulted from charge transfer screening, which, in turn, can be solely attributed to the presence of Fe3+ ions [26]. Fe 2p spectra were dominated by iron oxide/hydroxide products, including Fe(OH)3 and FeOOH, between 711 and 712 eV [27]. Ferrihydrite [28] had similar photoelectron peaks. However, the binding energy of Fe 2p3/2 in this research was 712.10 eV, resulting in a chemical shift of more than 1 eV. This shift might suggest a change in the chemical environment of the elements, indicating the formation of a new chemical bond between Fe3+ and other substances [29]. It could be suggested that the presence of 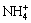 and Cl- caused the formation of chelate.
and Cl- caused the formation of chelate.
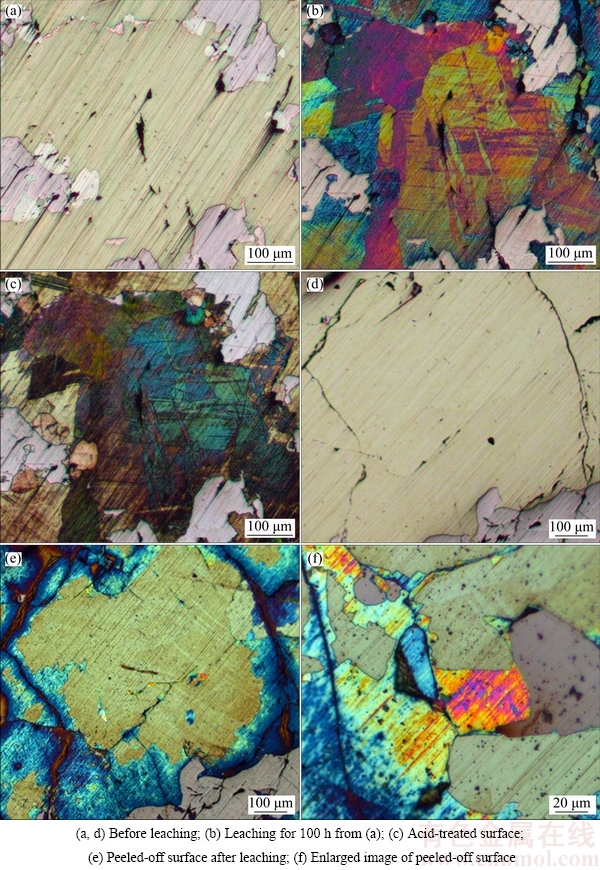
Fig. 4 OM images of chalcopyrite surface at 25 °C
The O 1s photoelectron peaks could be decomposed into four peaks, at 530.01, 531, 531.79, and 532.7 eV, corresponding to O2-, —OH, absorbed water, and attached water, respectively. The existence of the —OH group suggested that the oxidized iron was in the state of FeOOH. Furthermore, the —OH/O2- and O/Fe ratios were 1.14 and 1.77, respectively, which conformed to the stoichiometry of Fe–O–OH, as reported previously [30]. Furthermore, the difference in the fractions of Fe3+, O2-, —OH, and H2O did not have contradictory effects on the surface layers during several experiments. This led to the conclusion of the existence of ferrihydrite which was the reason for these ratios being indeterminate. Most importantly, unstable ferrihydrite could transform to goethite or hematite under different conditions [28], whereas detectable ferrihydrite was the initial product during the hydrolysis of Fe. The phenomenon of different colors of FeOOH is discussed later.
Figure 6 shows Fe 2p, O 1s, Cu 2p, and S 2p XPS spectra of the leaching layers on the chalcopyrite surface treated with diluted hydrochloric acid for 1 min (A) and on the peeling-off surface (P), whose positions are as shown in Figs. 4(c) and (e), respectively. The spectra of A and P were extremely similar, with just a slight difference in the elemental ratios.
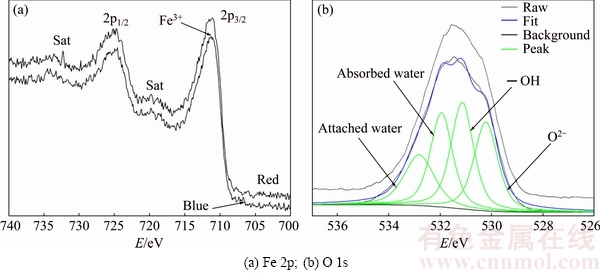
Fig. 5 XPS spectra of chalcopyrite surface after leaching at 25 °C (red and blue/cyan areas on surface shown in Fig. 3(e))
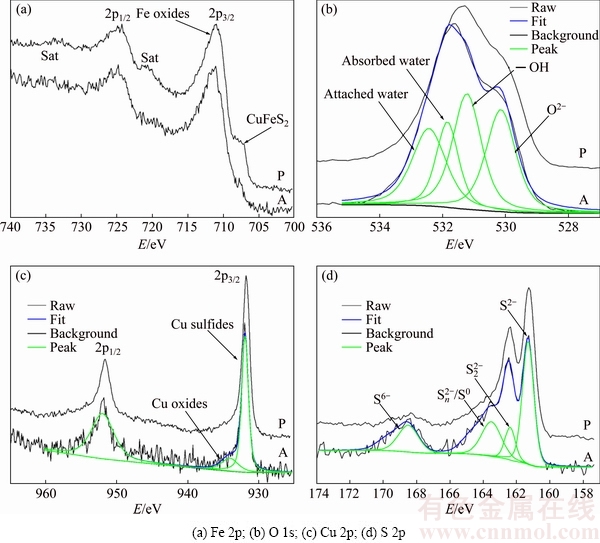
Fig. 6 XPS spectra on interfacial surface of acid-treating (A) and peeling-off (P) surfaces
The Fe 2p photoelectron peaks for A and P were almost the same (Fig. 6(a)), indicating the dissolution of Fe and the formation of FeOOH. Nonetheless, a feeble peak at 707.8 eV, representing the binding energy of Fe in the state of CuFeS2, could be attributed to the exposure of chalcopyrite. The O 1s photoelectron peaks for A and P could be decomposed into four peaks, in accordance with the spectra shown in Fig. 5. Meanwhile, O2-/Fe3+ or —OH/Fe3+ ratios ranging from 1 to 2 in several experiments revealed the existence of FeOOH.
Cu 2p3/2 photoelectron peaks were clearly observed in the survey spectra, as shown in Fig. 6(c). The peak at 932.05 eV could be ascribed to the absence of Cu(II) from covellite (CuS) [31] or other Cu(II)-sulfide species, which was a result of Fe dissolution. In addition, Cu2S did not exist according to a previous study [18]. Else, Cu oxides might be present in the CuSn layer owing to the occurrence of slight oxidation, which was observed in the Cu 2p spectra for greater clarity.
The S 2p photoelectron peaks could be decomposed into 4 peaks at 161.32, 162.40, 163.52, and 168.5 eV and assigned to S2-, 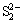 ,
, 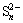 , S0 and
, S0 and 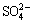 , respectively. Synthesis of model polysulfides and their subsequent examination by XPS indicated that polysulfides did not play a role in inhibiting chalcopyrite dissolution, leading to the conclusion that dissolution occurred via the oxidation of the disulfide phase. The S2-:
, respectively. Synthesis of model polysulfides and their subsequent examination by XPS indicated that polysulfides did not play a role in inhibiting chalcopyrite dissolution, leading to the conclusion that dissolution occurred via the oxidation of the disulfide phase. The S2-: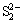 :
: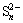 /S0:
/S0: 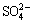 mass ratio was 2.60:0.63:1.26:1, indicating the distribution state of elemental S [32]. It was thought that CuS2* was the metastable phase [16], which might account for the complicated changes in S. It was proposed that chalcopyrite firstly oxidized to Fe hydroxyl oxide, CuS2, and S; then, CuS2 oxidized to CuS and CuSn; subsequently, CuSn oxidized further to Cu oxide species. From the survey, it was concluded that the products of A and P were FeOOH, Cu-S species, S0, and
mass ratio was 2.60:0.63:1.26:1, indicating the distribution state of elemental S [32]. It was thought that CuS2* was the metastable phase [16], which might account for the complicated changes in S. It was proposed that chalcopyrite firstly oxidized to Fe hydroxyl oxide, CuS2, and S; then, CuS2 oxidized to CuS and CuSn; subsequently, CuSn oxidized further to Cu oxide species. From the survey, it was concluded that the products of A and P were FeOOH, Cu-S species, S0, and 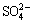 , which is in good agreement with the XPS results and the conclusion drawn from the metastable phase.
, which is in good agreement with the XPS results and the conclusion drawn from the metastable phase.
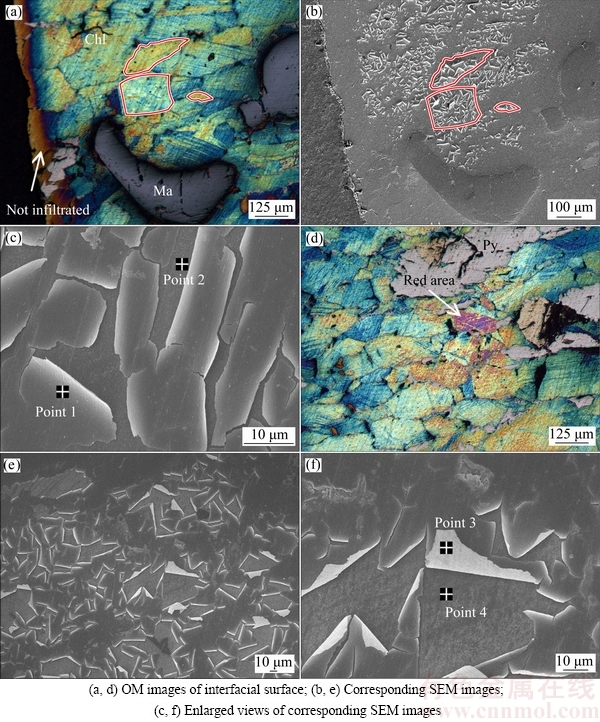
Fig. 7 OM images of chalcopyrite surface subjected to SEM analysis after leaching in ammonia–ammonium chloride solution at 35 °C (Chl: Chalcopyrite; Ma: Magnetite; Py: Pyrrhotite)
Figures 7(a) and (d) show optical microscope photographs of the mineral interfacial surface after leaching in ammonia–ammonium chloride solution at 35 °C. The increase in the reaction temperature to 35 °C led to the same phenomenon as that observed at 25 °C but the interfacial reaction was faster, completing in just 2.5 h. Figures 7(a) and (b) reveal that most of the interfacial surfaces were cyan in color, with a small quantity of magnetite (dark blue phase) and pyrrhotite (gray phase). Figure 7(b) illustrates that the surface of the cyan area in the FeOOH layer was exfoliated, whereas the surface of the dark blue area was flat. Interestingly, the exfoliated area in Fig. 7(b) was distributed in accordance with the crystal boundaries in Fig. 7(a), which are marked as red loops. In the enlarged SEM image (Fig. 7(c)) obtained by EDS analysis, 19.77% O (mole fraction) was detected at Point 1, whereas no O was detected at Point 2. The result of composition of the top FeOOH layer was the same as that observed by XPS analysis. Stronger exfoliation occurred in the red area (Fig. 7(e)) than in the cyan area; moreover, the brim of the FeOOH layer underwent crimping, which seemed to cause further exfoliation (Fig. 7(f)). Further, 37.75% O (mole fraction) was detected at Point 3, but no O was detected at Point 4. Undoubtedly, the interfacial reaction layers consisted primarily of FeOOH as the top layer and CuSn as the under-layer. S0 was distributed in the under-layer, which underwent slight oxidation. The color change on the surface might be related to the composition of the exfoliated surface.
3.3 Leaching mechanism and model of chalcopyrite
Most researchers believe that the formal oxidation state of CuFeS2 is a Cu+Fe3+(S2-)2 valence state, and not Cu2+Fe2+(S2-)2 [18]. However, in chalcopyrite, there is a considerable degree of covalent bonding between S and Fe and between S and Cu. In the leaching experiment, the effect of a number of oxidants such as O2, Fe3+, H2O2, and 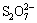 was examined. However, a model of the leaching process under different values of the factors of pH and φh was not applied. Furthermore, there is general agreement in the literature that chalcopyrite leaching is significantly affected by the solution redox potential having an optimum range, suggesting the participation of leaching steps that involve both oxidation and reduction [6]. Solution pH is another typical factor that affects not only the range of φh but also the formation of a passivation layer. The leaching process under different pH and φh can be summarized in Table 1.
was examined. However, a model of the leaching process under different values of the factors of pH and φh was not applied. Furthermore, there is general agreement in the literature that chalcopyrite leaching is significantly affected by the solution redox potential having an optimum range, suggesting the participation of leaching steps that involve both oxidation and reduction [6]. Solution pH is another typical factor that affects not only the range of φh but also the formation of a passivation layer. The leaching process under different pH and φh can be summarized in Table 1.
Table 1 Leaching process under different pH and potentials
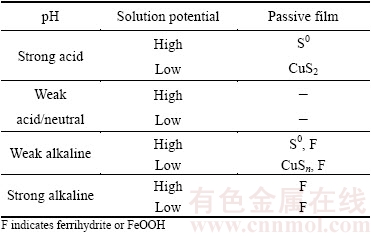
In acidic/neutral solution, Eq. (3) is independent of the electrolyte pH. Here, CuFe1-xS2 and CuS2* indicate metastable phases on the chalcopyrite surface. When the pH increases, the surface state of chalcopyrite that is expressed in Eq. (3) may not be affected, whereas φh will not change. Conversely, the reactions in Eqs. (4) and (5) are dependent on the pH of the electrolyte. When the pH increases, the concentration of H+ decreases, whereas φh of the reactions in Eqs. (4) and (5) decreases according to the Nernst equation. Loss of electrons from CuFeS2 and CuS2 is easier, and the reaction occurs more readily as well. Hence, the formation of a layer on chalcopyrite is difficult in weak acidic or neutral solution. More importantly, the reactions in Eqs. (4) and (5) will be suppressed in low-pH solution that produces different passive films. The oxidants control the potential of the solution, which possibly creates a high- or low-potential environment. In high-potential solutions, S2- oxidizes more readily to S0. Otherwise, S2- does not oxidize easily, and a passive film of CuSn is formed.
CuFeS2→CuFe1-xS2/CuS2*+Fe3++e (3)
CuS2*+H2O→Cu2++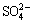 +H++e (4)
+H++e (4)
CuFeS2+H2O→Cu2++Fe3++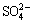 +H++e (5)
+H++e (5)
CuFeS2+OH-→CuS2*+FeOx(OH)y+zH2O+e (6)
In alkaline solution, the reaction changes to that in Eq. (6). Here, FeOx(OH)y represents iron oxides, iron hydroxides, or a mixture of the two. Similar to the acidic condition, under the alkaline condition, the concentration of H+ decreases as the pH increases, and φh of the reaction of Eq. (6) decreases according to the Nernst equation. Loss of electrons from CuFeS2 is easier, and the reaction occurs more readily as well. Undoubtedly, the formation of a layer on chalcopyrite is difficult in strong alkaline solution. In addition, the reaction in Eq. (6) would be suppressed in weak alkaline solution that produces different passive films. Similar to the case above, the oxidants control the potential of the solution, thereby determining the potential environment. In high-potential solution, S2- more readily oxidizes to S0. However, S2- is not oxidized easily, and a passive film of CuSn will be formed. In addition, ferrihydrite or FeOOH will appear in the alkaline solution. Moreover, the S0 layer may appear in high-potential solution, and the CuSn layer may appear in low-potential solution. However, S0 or CuSn passive films are less evident in weakly acidic or strongly alkaline electrolytes.
Figure 8 shows a model of the interfacial reaction of the chalcopyrite surface in ammonia–ammonium chloride solution. Fe is leached out preferentially as a result of the incomplete structure of CuFe1-xS2, and this intermediate sulfide decomposes to Cu sulfides, which alternatively exist in the form of Cu sulfides that could impede further leaching [11]. Thermodynamically, iron has a much greater affinity for oxygen than copper. The charge of Fe3+ is three times that of Cu2+/Cu+ but Fe3+ has a smaller ionic radius from a kinetic point of view. Therefore, Fe3+ ions migrate more rapidly to the interface under the present experimental conditions. The formation of Cu sulfides occurs only when the redox potential of the solution is lower than a critical potential [12], which is a function of the concentration of the oxidizing agent. The under-layer is composed of Cu(II), S2-, 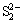 , and
, and 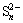 , as well as crystalline S0 and FeOOH particles. The appearance of S2- in this period may be explained by the occurrence of a reduction step to form a lower oxidation state S species and shorter chain
, as well as crystalline S0 and FeOOH particles. The appearance of S2- in this period may be explained by the occurrence of a reduction step to form a lower oxidation state S species and shorter chain 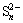 . In alkaline solution, unstable ferrihydrite forms firstly, and then it transforms to FeOOH·nH2O, which causes the formation of the passivation film. Consequently, the exfoliation that occurs on the top FeOOH layer is attributed to the weak combination of oxides and sulfides in ammonia solution.
. In alkaline solution, unstable ferrihydrite forms firstly, and then it transforms to FeOOH·nH2O, which causes the formation of the passivation film. Consequently, the exfoliation that occurs on the top FeOOH layer is attributed to the weak combination of oxides and sulfides in ammonia solution.
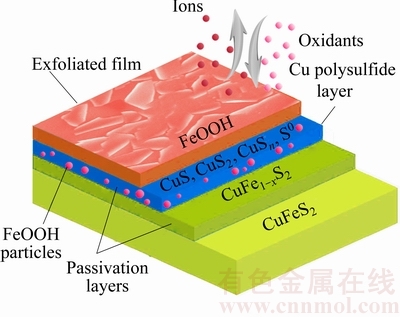
Fig. 8 Model of interfacial reaction surface of chalcopyrite surface
Based on these results, a model of the interfacial reaction on the chalcopyrite surface was constructed using a three-step reaction pathway. The first step involves the release of Fe3+ from the chalcopyrite surface, which preferentially forms thin layers of unstable ferrihydrite/FeOOH and CuFe1-xS2. The same reaction occurs in the second step, involving deeper layers in the chalcopyrite structure. Meanwhile, FeOOH becomes the first layer and Cu—S becomes the under-layer. This subsequent step does not result in the release of cations to the solution, and an oxidation-retarding film containing Cu—S together with FeOOH is formed; however, it does result in the re-formation of a middle layer of short-chain polysulfides. In this step, the oxidation process is controlled by solid-state mass transport [10], which means that the Fe3+ ions are transported from the bulk chalcopyrite through the passivation film to the solid/electrolyte interface. Certainly, the polymerization of S does not result in the release of Fe from the solid, but it does enable an oxidation reaction to proceed, thereby resulting in the formation of crystalline S0. In other words, S2- and other short-chain polysulfides may reconstruct to form crystalline elemental sulfur (S0) upon further oxidation. In the third step, the FeOOH layer is partially exfoliated, because more oxidants can come into contact with the under-layer. A small quantity of Cu polysulfides are oxidized to Cu oxides, and the Cu sulfide film is not removed, thus resulting in the formation of a passivation film.
4 Conclusions
1) Optical microscopy analysis demonstrated the interfacial reaction behavior of the chalcopyrite surface under weak alkaline conditions. Fe was selectively leached out prior to Cu, causing the formation of a flat passivation layer of FeOOH. Meanwhile, the Fe-deficient Cu polysulfide layer under the FeOOH layer became visible after 50 h. SEM analysis showed that the FeOOH layer could partially peel off and automatically form the Cu-rich sulfide layer. XPS analysis suggested that the interfacial layers consisted mainly of FeOOH as the top layer and CuS, CuS2, CuSn, S0, and FeOOH particles in the under-layers.
2) The following is a summary of the mechanisms of the oxidation and the passivation of chalcopyrite under different values of pH and φh. In a strongly acidic electrolyte, the passivation layer consists of S0 (high φh) or CuSn (low φh). In a neutral electrolyte, the passivation effect is less evident. In a weakly alkaline electrolyte, the passivation layer consists of S0 with FeOOH (high φh) and CuSn with FeOOH (low φh). By contrast, in a strongly alkaline electrolyte, only FeOOH is present in the passivation layer.
3) A model of the interfacial reaction on the chalcopyrite surface was constructed. The first oxidation step involves the release of Fe3+, which preferentially forms Fe oxides and CuFe1-xS2. In the next step, more Fe3+ ions in chalcopyrite move to the solid/electrolyte interface, forming the FeOOH top layer; this is followed by the formation of an oxidation-retarding film composed of Cu sulfides (CuS, CuS2, CuSn), S0, and FeOOH particles. The final step may result in the re-formation of the middle layer containing S2- and other short-chain polysulfides after the exfoliation of the top layer.
References
[1] PENG Tang-jian, ZHOU Dan, LIU Xue-duan, YU Run-lan, JIANG Tao, GU Guo-hua, CHEN Miao, QIU Guan-zhou, ZENG Wei-min. Enrichment of ferric iron on mineral surface during bioleaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(2): 544-550.
[2] GHAHREMANINEZHAD A, DIXON D G, ASSELIN E. Electrochemical and XPS analysis of chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) dissolution in sulfuric acid solution [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 87: 97-112.
[3] FANTAUZZI M, ELSENER B, ATZEI D, RIGOLDI A, ROSSI A. Exploiting XPS for the identification of sulfides and polysulfides [J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(93): 75953-75963.
[4] WATLING H R. Chalcopyrite hydrometallurgy at atmospheric pressure: 1. Review of acidic sulfate, sulfate-chloride and sulfate- nitrate process options [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 140: 163-180.
[5] RUDNIK E,  D. Comparative studies on hydrometallurgical treatment of smelted low-grade electronic scraps for selective copper recovery [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(8): 2763-2771.
D. Comparative studies on hydrometallurgical treatment of smelted low-grade electronic scraps for selective copper recovery [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(8): 2763-2771.
[6] LI Y, KAWASHIMA N, LI J, CHANDRA A P, GERSON A R. A review of the structure, and fundamental mechanisms and kinetics of the leaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2013, 197: 1-32.
[7] WU Shi-fa, YANG Cong-ren, QIN Wen-qing, JIAO Fen, WANG Jun, ZHANG Yan-sheng. Sulfur composition on surface of chalcopyrite during its bioleaching at 50 °C [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(12): 4110-4118.
[8] ARCE E M,  I. A comparative study of electrochemical behavior of chalcopyrite, chalcocite and bornite in sulfuric acid solution [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2002, 67(1-4): 17-28.
I. A comparative study of electrochemical behavior of chalcopyrite, chalcocite and bornite in sulfuric acid solution [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2002, 67(1-4): 17-28.
[9] GRIONI M, GOEDKOOP J B, SCHOORL R, GROOT F M F, FUGGLE J C,  F, KOCH E E, ROSSI G, ESTECA J M, KARNATAK R C. Studies of copper valence states with Cu L3 X-ray-absorption spectroscopy [J]. Physical Review B, 1989, 39(3): 1541-1545.
F, KOCH E E, ROSSI G, ESTECA J M, KARNATAK R C. Studies of copper valence states with Cu L3 X-ray-absorption spectroscopy [J]. Physical Review B, 1989, 39(3): 1541-1545.
[10] YIN Q, VAUGHAN D J, ENGLAND K E R, KELSALL G H, BRANDON N P. Surface oxidation of chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) in alkaline solutions [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2000, 147(8): 2945-2951.
[11] HACKL R P, DREISINGER D B, PETERS E, KING J A. Passivation of chalcopyrite during oxidative leaching in sulfate media [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1995, 39(1): 25-48.
[12] HIROYOSHI N, MIKI H, HIRAJIMA T, TSUNEKAWA M. A model for ferrous-promoted chalcopyrite leaching [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 57(1): 31-38.
[13] WATLING H R, SHIERS D W, LI J, CHAPMAN N M, DOUGLAS G B. Effect of water quality on the leaching of a low-grade copper sulfide ore [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 58: 39-51.
[14] PRATESI G, CIPRIANI C. Selective depth analyses of the alteration products of bornite, chalcopyrite and pyrite performed by XPS, AES and RBS [J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2000, 12(2): 397-409.
[15] BIEGLER T, HORNE M D. The electrochemistry of surface oxidation of chalcopyrite [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1985, 132(6): 1363-1369.
[16] HARMER S L, THOMAS J E, FORNASIERO D, GERSON A R. The evolution of surface layers formed during chalcopyrite leaching [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(17): 4392-4402.
[17] URBANO G,  REYES J L, LARIOS R, CRUZ R. Electrochemical and spectroscopic study of interfacial interactions between chalcopyrite and typical flotation process reagents [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2016, 23(2): 127-136.
REYES J L, LARIOS R, CRUZ R. Electrochemical and spectroscopic study of interfacial interactions between chalcopyrite and typical flotation process reagents [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2016, 23(2): 127-136.
[18] ZHAO Hong-bo, WANG Jun, QIN Wen-qing, HU Ming-hao, ZHU Shan, QIU Guan-zhou. Electrochemical dissolution process of chalcopyrite in the presence of mesophilic microorganisms [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 71: 159-169.
[19] SHANG Jun. Mineragraphy [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007: 86-110. (in Chinese)
[20] YANG Xian-wan, QIU Ding-fan. Hydrometaillurgy [M]. Beijng: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2011: 231–234. (in Chinese)
[21] SASAKI K, TAKATSUGI K, ISHIKURA K, HIRAJIMA T. Spectroscopic study on oxidative dissolution of chalcopyrite, enargite and tennantite at different pH values [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 100(3-4): 144-151.
[22]  M, LIIPO J, AROMAA J. Dissolution of copper and iron from sulfide concentrates in cupric chloride solution [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2012, 102: 13-18.
M, LIIPO J, AROMAA J. Dissolution of copper and iron from sulfide concentrates in cupric chloride solution [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2012, 102: 13-18.
[23] ZHAO Hong-bo, HU Ming-hao, LI Yi-ni, ZHU Shan, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou, WANG Jun. Comparison of electrochemical dissolution of chalcopyrite and bornite in acid culture medium [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(1): 303-313.
[24] HOLLIDAY R I, RICHMOND W R. An electrochemical study of the oxidation of chalcopyrite in acidic solution [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1990, 288(1-2): 83–98.
[25] BUCKLEY A N, WOODS R. An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of the oxidation of chalcopyrite [J]. Australian Journal of Chemistry, 1984, 37(12): 2403-2413.
[26] LI Li-li, CHU Ying, LIU Yang, DONG Li-hong. Template-free synthesis and photocatalytic properties of novel Fe2O3 hollow spheres [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111(5): 2123-2127.
[27] KALEGOWDA Y, CHAN Y L, WEI D H, HARMER S L. X-PEEM, XPS and ToF-SIMS characterisation of xanthate induced chalcopyrite flotation: Effect of pulp potential [J]. Surface Science, 2015, 635: 70-77.
[28] BARIK R, JENA B K, DASH A, MOHAPATRA M. In situ synthesis of flowery-shaped α-FeOOH/Fe2O3 nanoparticles and their phase dependent supercapacitive behavior [J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(36): 18827-18834.
[29] MEI Le-fu, LIAO Li-bing, WANG Zi-se, XU Chun-chun. Interactions between phosphoric/tannic acid and different forms of FeOOH [J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2015, 2015: 1-10.
[30] LI Xiao-qin, ZHANG Wei-xian. Sequestration of metal cations with zero-valent iron nanoparticles a study with high resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HR-XPS) [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111(19): 6939–6946.
[31] GOH S W, BUCKLEY A N, LAMB R N, ROSENBERG R A, MORAN D. The oxidation states of copper and iron in mineral sulfides, and the oxides formed on initial exposure of chalcopyrite and bornite to air [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(9): 2210-2228.
[32] MIKHLIN Y, TOMASHEVICH Y, TAUSON V, VYALIKH D, MOLODTSOV S, SZARGAN R. A comparative X-ray absorption near-edge structure study of bornite, Cu5FeS4, and chalcopyrite, CuFeS2 [J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 2005, 142(1): 83-88.
华晓鸣1,郑永飞2,许 茜2,鲁雄刚2,程红伟2,邹星礼2,宋秋实1,宁志强1
1. 东北大学 冶金学院,沈阳110004;
2. 上海大学 省部共建高品质特殊钢冶金与制备国家重点实验室,
上海市钢铁冶金新技术开发应用重点实验室,材料科学与工程学院,上海 200072
摘 要:对黄铜矿在氨水-氯化铵溶液中的反应界面进行研究。利用X射线光电子能谱分析(XPS)技术对黄铜矿反应界面进行表征。研究发现, 覆盖在黄铜矿基底之上的反应界面钝化层由表层的铁氧化物以及被其覆盖的硫化铜组成。黄铜矿结构中的铁离子存在优先溶解现象,形成钝化层中的硫化铜或CuFe1-xS2。当表层铁氧化物层逐渐自发剥离后,硫化铜层成为新的钝化层。由硫化铜层表面S2-、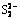 、
、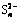 、S0和
、S0和 等组分含量推算硫化铜的组成。提出黄铜矿在不同pH和氧化电位条件下的氧化和钝化机理。最后,建立黄铜矿界面三步反应模型,剖析钝化层的形成及转化机理。
等组分含量推算硫化铜的组成。提出黄铜矿在不同pH和氧化电位条件下的氧化和钝化机理。最后,建立黄铜矿界面三步反应模型,剖析钝化层的形成及转化机理。
关键词:黄铜矿;界面反应;氨;钝化层;氧化机理
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (2014CB643405) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: Qian XU; Tel: +86-21-66136568; E-mail: qianxu@shu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64688-6

