


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 2357-2363
Effect of cooling condition on microstructure of semi-solid AZ91 slurry produced via ultrasonic vibration process
ZHANG Liang1, WU Guo-hua1, WANG Shao-hua2, DING Wen-jiang1
1. National Engineering Research Center of Light Alloy Net Forming, Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai 200240, China;
2. Science and Technology on Space Physics Laboratory, Beijing 100076, China
Received 9 July 2012; accepted 6 August 2012
Abstract: The effects of cooling conditions on the microstructure of semi-solid AZ91 slurry produced via ultrasonic vibration process were investigated. AZ91 melts were subjected to ultrasonic vibration in different temperature ranges under different cooling rates. The results show that fine and spherical α-Mg particles are obtained under ultrasonic vibration at the nucleation stage, which is mainly attributed to the cavitation and acoustic streaming induced by the ultrasonic vibration. The reduction of lower limit of ultrasonic vibration temperature between the liquidus and solidus increases the solid volume fraction and average particle size. Increasing cooling rate increases the solid volume fraction and reduces the average shape factor of particles. The appropriate temperature range for ultrasonic vibration is from 605 ℃ to 595 ℃ or 590 ℃, and the suitable cooling rate is 2-3 ℃/min.
Key words: AZ91 alloy; semi-solid; ultrasonic vibration; microstructure; cooling condition
1 Introduction
The semi-solid metal (SSM) processing, including thixoforming and rheocasting, is an effective net-shape forming process which combines the elements of both casting and forging, showing many advantages over the conventional process [1-3]. In recent years, more and more researches have been focused on rheocasting because of its low cost and high productivity [4,5]. Rheocasting involves stirring the solidifying alloy to prepare non-dendritic semi-solid slurry, then shaping the slurry directly. The transportation and storage of semi-solid slurry are the major difficulties during rheocasting, so the control of cooling conditions is very important during the preparation of semi-solid slurry.
A number of processes have been developed to prepare semi-solid slurry. Alternatively, the ultrasonic vibration is a simple and effective process to produce semi-solid metal slurry [6]. During the ultrasonic vibration process, an ultrasound field is imposed to the solidifying melt resulting in grain refinement, increased homogeneity, reduced microsegregation as well as degassing [7-9]. Currently, the ultrasonic vibration process is mainly used in producing the semi-solid slurry of aluminum alloys. L? et al [10,11] prepared semi-solid aluminum alloy slurry with direct and indirect ultrasonic vibration process. Their results indicated that good semi-solid slurry of aluminum alloy could be obtained in a short time by applying ultrasonic vibration near its liquidus temperature, and a considerable improvement in the mechanical properties was achieved after rheocasting. There are not as many published researches on ultrasonic treatment of magnesium alloys as on aluminium alloys. LIU et al [12] and GAO et al [13] studied the effect of ultrasonic power on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91 magnesium alloy. These investigations showed that ultrasonic treatment resulted in formation of fine non-dendritic grains in the solidified microstructures, and the tensile and compressive strengths as well as the fracture strains of the castings were improved by ultrasonic treatment. ZHANG et al [14,15] investigated the effects of ultrasonic treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-9.0%Al binary and AZ80 magnesium alloys and reported the effects of ultrasonic treatment on the size and morphology of Mg17Al12 phase. They showed that Mg17Al12 phase in the entire cross section of the castings was significantly refined and also lost its continuity along the grain boundaries. LAN et al [16] used ultrasonic treatment for dispersion of nano-sized SiC particles in molten AZ91D magnesium alloy to produce metal matrix nanocomposites. They showed a nearly uniform distribution and good dispersion of SiC nano-particles within the matrix. Most researches on ultrasonic treatment of magnesium alloys were focused on grain refinement, and studies on the semi-solid slurry preparation of magnesium alloy via ultrasonic vibration process were limited.
In this work, semi-solid slurry of AZ91 magnesium alloy was prepared by ultrasonic vibration process and the effects of cooling conditions on the microstructure of semi-solid AZ91 slurry were investigated.
2 Experimental
A commercial ingot of the AZ91D alloy with a measured composition of Mg-8.45Al-0.56Zn-0.19Mn was used as the principal alloy. In each experiment, about 1.2 kg of the alloy was melted in an electrical resistance furnace under a protective gas of CO2+SF6. When the melt temperature was stabilized at 680 ℃, the crucible with melt was transferred to another furnace for ultrasonic treatment. This furnace was pre-heated to different temperatures below 580 ℃ in order to get different cooling rates. The schematic of ultrasonic vibration device is shown in Fig. 1. It consists of an ultrasonic generator and transducer with a maximum power of 2.0 kW and fixed frequency of about 20 kHz, a ultrasonic horn and a moveable platform. In each experiment, as soon as the melt temperature decreased from 680 to 660 ℃, the ultrasonic vibration device was lowered and 7 cm of the tip of its horn which had been pre-heated to 660 ℃ was immersed into the melt.
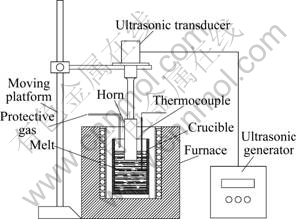
Fig. 1 Schematic of ultrasonic vibration device used in this study
Several experiments were conducted to study the effects of cooling conditions on the microstructure of semi-solid AZ91 slurry. Because the liquidus and solidus temperatures of the alloy used in this study are about 598 ℃ and 431 ℃ (determined by the cooling curve in Fig. 2), respectively, different temperature ranges of the melt were chosen to carry out the ultrasonic vibration. They were from 605 ℃ to 595 ℃, from 605 ℃ to 590 ℃ and from 605 ℃ to 585 ℃, respectively. After being vibrated with different cooling rates (1.56, 2.82 and 8.04 ℃/min) in different temperature ranges, some slurries were extracted out by a steel tube with an inner diameter of 10 mm and quenched in water immediately.
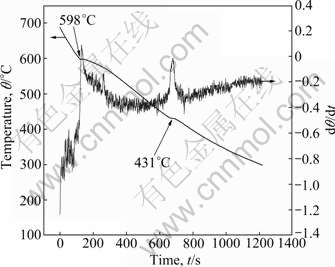
Fig. 2 Cooling curve of AZ91 alloy with its first derivative curve
Specimens for the metallographic examination were cut from the quenched rods, then polished and etched by 4% (volume fraction) nitric acid ethanol solution. The microstructures were examined using an optical microscope and micrographs of the samples were analyzed by a quantitative metallographic analysis software, including the solid volume fraction, the average size and shape factor of solid particles. At least five representative areas with the total surface of 80 mm2 in each sample were studied through metallographic evaluations. The solid volume fraction was calculated by the ratio of all particles area in the total area of the photomicrograph. For the shape of solid particle is irregular, the average diameter measured in one particle was defined as the size of that particle. The shape factor (SF) was defined as SF=4πA/P2, where A and P are the area and the perimeter of the primary particles, respectively. SF varies from 0 to 1, and when the value of SF is close to 1, the sectional shape of the particle approaches a circle. More than 100 particles in each sample were measured in order to obtain the average size and shape factor of solid particles.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of ultrasonic vibration on microstructure of AZ91 slurry
Figure 3 shows the microstructures of semi-solid AZ91 slurry quenched at 585 ℃ without and with ultrasonic vibration. As seen, microstructure of the alloy in semi-solid state consists of primary α-Mg particles which distribute in a liquid matrix. The liquid matrix forms due to the solidification of the remaining liquid in the semisolid slurry during water quenching. It is clear that the size and morphology of primary α-Mg particles are influenced significantly by ultrasonic vibration. Without ultrasonic vibration (see Fig. 3(a)), the α-Mg particles in the slurry show a coarse dendrite shape. After ultrasonic vibration from 605 ℃ to 585 ℃ (see Fig. 3(b)), the α-Mg particles become fine, spherical and uniformly dispersed in the matrix.
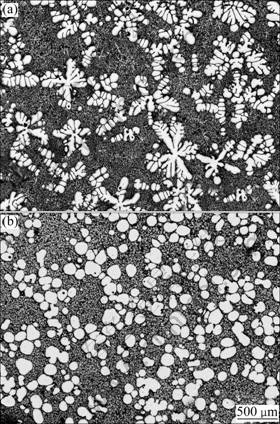
Fig. 3 Comparison of quenched microstructures of AZ91 slurry: (a) Quenched at 585 ℃ without ultrasonic vibration; (b) Quenched at 585 ℃ with ultrasonic vibration from 605 ℃ to 585 ℃
The refinement and spheroidization of the primary α-Mg particles could be mainly attributed to the cavitation and acoustic streaming induced by ultrasonic vibration. Cavitation caused by ultrasonic vibration will enhance heterogeneous nucleation. Cavitation refers to the phenomenon of growth and collapse of micro- bubbles under an ultrasonic field. During the growth period, the micro-bubbles expand and the melt evaporates inside the bubbles. The evaporation and expansion decrease the temperature of the micro-bubbles; therefore, undercooling happens around the micro- bubbles surfaces and makes these bubbles be the sources of nuclei [6,17]. In addition, cavitation cleans the surface of solid impurity particles that are poorly wetted by the melt, thereby enhancing heterogeneous nucleation [18].
In the presence of acoustic streaming, temperature and solute are distributed uniformly throughout the bulk melt, and solute concentration at the solidification front is removed, so that the nuclei almost have the same growth velocity in all directions and the dendritic growth of the nuclei is restricted [11]. Furthermore, the mechanical pressure caused by the acoustic streaming may fragment the dendrite arms or disintegrate the agglomerated inoculation surfaces [18]. Therefore, the dendritic growth of primary α-Mg is limited.
3.2 Effect of ultrasonic vibration temperature range on microstructure of semi-solid AZ91 slurry
Figure 4 shows the quenched microstructures of the semi-solid slurry treated by ultrasonic vibration in different temperature ranges under the cooling rate of 1.56 ℃/min. It has been reported that the microstructures with fine uniform grains are achieved under ultrasonic vibration at the nucleation stage [19]. The liquidus temperature of the alloy used in this study is about 598 ℃, measured by the cooling curve in Fig. 2. Therefore, the initial temperature of ultrasonic vibration was selected at 605 ℃. And the temperature range of ultrasonic vibration is from 605 ℃ to 595 ℃, from 605 ℃ to 590 ℃ or from 605 ℃ to 585 ℃. Figure 5 shows the influence of ultrasonic vibration temperature range on the solid volume fraction, average size and shape factor of the particles. As seen, the solid volume fraction and average size of the particles both increase with the reduction of lower limit of ultrasonic vibration temperature. When the temperature is lower than 590 ℃, the solid volume fraction increases to 20% or even more. The increasing of solid volume fraction makes the intensity of convection in the slurry weaker, so it is difficult to separate the agglomeration particles if the temperature is much lower than the liquidus. The increasing of average particle size is mainly due to the extension of ultrasonic vibration time which makes the primary α-Mg particles grow large. The shape factors of particles in the three slurries are nearly the same, about 0.7, corresponding to a good spherical degree.
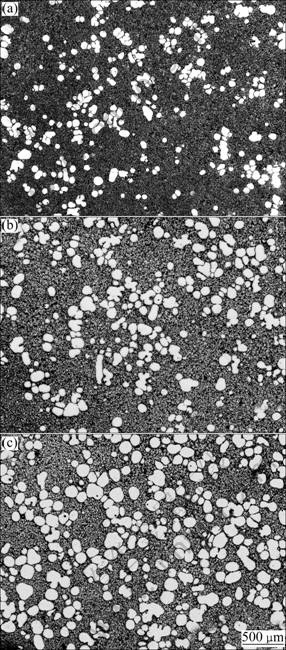
Fig. 4 Microstructures of semi-solid slurry treated by ultrasonic vibration in different temperature ranges: (a) 605-595 ℃; (b) 605-590 ℃; (c) 605-585 ℃
The ideal semi-solid slurry for rheological forming possesses an accurately specified volume fraction of fine and globular solid particles uniformly distributed in the liquid phase [20,21]. It is well accepted that the finer and rounder the particles are, the better the rheology of the semisolid slurry is [22]. In this study, the suitable ultrasonic vibration temperature for preparing semi-solid AZ91 slurry is from 605 ℃ to 595 ℃ or 590 ℃.
3.3 Effect of cooling rate on microstructure of semi-solid AZ91 slurry
In this study, the semi-solid AZ91 slurry was produced by ultrasonic vibration during solidification from the temperature above liquidus to a certain temperature between liquidus and solidus. So the cooling rate is an important parameter during the ultrasonic treatment. In the experiments, different cooling rates were obtained by controlling the temperature of the crucible around. Figure 6 shows the quenched microstructures and particle size analyses of the semi-solid slurry treated by ultrasonic vibration from 605 ℃ to 590 ℃ under different cooling rates (1.56, 2.82 and 8.04 ℃/min). Figure 7 shows the influence of cooling rate on the solid volume fraction and average shape factor of particles. It is clear that increasing cooling rate can increase the solid volume fraction of semi-solid slurry and reduce the average shape factor of particles. The frequency distribution of the particle size also changes a lot. When the cooling rate is low (1.56 ℃/min), the particle size is nonuniform, both large particles (larger than 120 μm) and small particles (smaller than 60 μm) are present in the slurry. When the cooling rate is high (8.04 ℃/min), the amount of large particles (larger than 120 μm) increases.
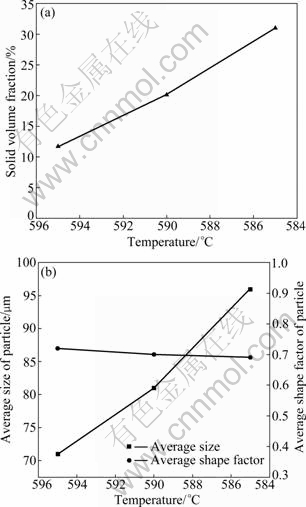
Fig. 5 Influence of ultrasonic vibration temperature on solid volume fraction, average size and shape factor of particles
These variations in rheological parameters are mainly caused by the changes of primary α-Mg particle nucleation and growth with the increasing cooling rate. First, the number of nuclei and particle growth rate increase with increasing cooling rate, which makes the solid volume fraction of AZ91 slurry increase. Second, the ultrasonic vibration time reduces with the increase of cooling rate which makes the average shape factor of particles decrease. As seen, when the cooling rate is high (8.04 ℃/min), the morphology of primary α-Mg particles are mainly rosette-like shape and a small quantity of spherical particles are observed occasionally. Finally, low cooling rate (1.56 ℃/min) extends the ultrasonic vibration time which makes some of the primary α-Mg particles grow larger, and high cooling rate (8.04 ℃/min) improves the particle growth rate which also makes the particles larger. In summary, the cooling rate during ultrasonic vibration could not be too high or too low, and the appropriate cooling rate in the experimental conditions of this study is 2-3 ℃/min.
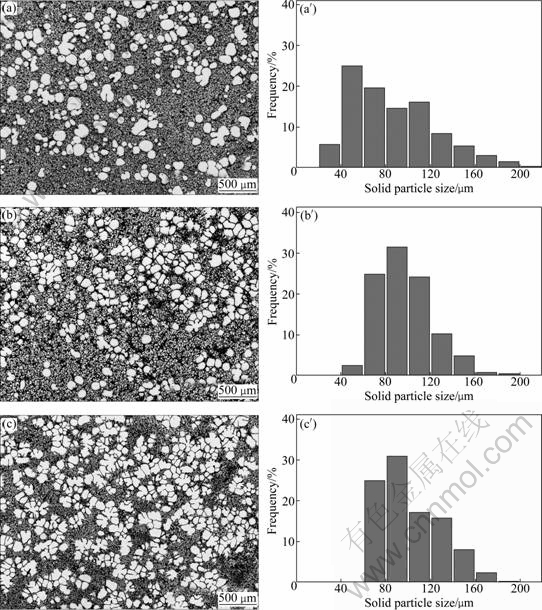
Fig. 6 Microstructures (a, b, c) and frequency distribution of particle size (a′, b′, c′) at different cooling rates: (a, a′) 1.56 ℃/min; (b, b′) 2.82 ℃/min; (c, c′) 8.04 ℃/min
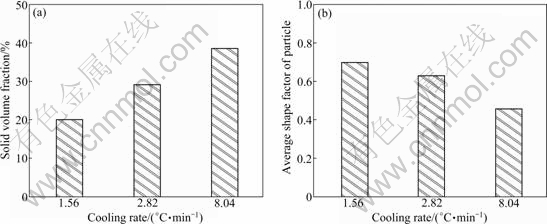
Fig. 7 Influence of cooling rate on solid volume fraction (a) and average shape factor (b) of particles
4 Conclusions
1) The ultrasonic vibration has a significant effect on the refinement and spheroidization of primary α-Mg particles during cooling and solidification process from the temperature above liquidus to the temperature between liquidus and solidus, which is mainly attributed to the cavitation and acoustic streaming induced by the ultrasonic vibration.
2) Under the same cooling rate and upper limit of ultrasonic vibration temperature, the reduction of lower limit of ultrasonic vibration temperature will increase the solid volume fraction of the slurry and average size of the particles. In this study, the suitable ultrasonic vibration temperature range for preparing semi-solid AZ91 slurry is from 605 ℃ to 595 ℃ or 590 ℃.
3) In the same ultrasonic vibration temperature range, a high cooling rate will increase the solid volume fraction of the slurry and reduce the average shape factor of particles. The appropriate cooling rate under the experimental conditions of this study is 2-3 ℃/min.
References
[1] FLEMINGS M C. Behavior of metal alloys in the semisolid state [J]. Metal Trans A, 1991, 22: 957-981.
[2] WANG J L, SU Y H, TSAO C Y A. Structural evolution of conventional cast dendritic and spray-cast non-dendritic structures during isothermal holding in the semi-solid state [J]. Scripta Mater, 1997, 37: 2003-2007.
[3] CZERWINSKI F, ZIELINSKA-LIPIEC A. The melting behaviour of extruded Mg-8%Al-2%Zn alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51: 3319-3332.
[4] WANNASIN J, CANYOOK R, BURAPA R, SIKONG L, FLEMINGS M C. Evaluation of solid fraction in a rheocast aluminum die casting alloy by a rapid quenching method [J]. Scripta Mater, 2008, 58: 1091-1094.
[5] WU S, XIE L, ZHAO J, NAKAE H. Formation of non-dendritic microstructure of semisolid aluminum alloy under vibration [J]. Scripta Mater, 2008, 58: 556-559.
[6] L? S L, WU S S, LIN C, HU Z Q, AN P. Preparation and rheocasting of semisolid slurry of 5083 Al alloy with indirect ultrasonic vibration process [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2011, 528: 8635-8640.
[7] ZHANG S, ZHAO Y, CHENG X, CHEN G, DAI Q. High-energy ultrasonic field effects on the microstructure and mechanical behaviors of A356 alloy [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2009, 470: 168-172.
[8] JIAN X, XU H, MEEK T T, HAN Q. Effect of power ultrasound on solidification of aluminum A356 alloy [J]. Mater Lett, 2005, 59: 190-193.
[9] DAS A, KOTADIA H R. Effect of high-intensity ultrasonic irradiation on the modification of solidification microstructure in a Si-rich hypoeutectic Al-Si alloy [J]. Mater Chem Phys, 2011, 125: 853-859.
[10] L? Shu-lin, WU Shu-sen, ZHU Ze-ming, AN Ping, MAO You-wu. Effect of semi-solid processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of 5052 aluminum alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(s): s758-s762.
[11] WU S S, L? S L, AN P, NAKAE H. Microstructure and property of rheocasting aluminum-alloy made with indirect ultrasonic vibration process [J]. Mater Lett, 2012, 73: 150-153.
[12] LIU X B, OSAWA Y, TAKAMORI S, MUKAI T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91 alloy produced with ultrasonic vibration [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 487: 120-123.
[13] GAO D M, LI Z J, HAN Q Y, ZHAI Q J. Effect of ultrasonic power on microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91 alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2009, 502: 2-5.
[14] ZHANG Z Q, LE Q C, CUI J Z. Influence of high-intensity ultrasonic treatment on the phase morphology of a Mg-9.0wt.%Al binary alloy [J]. Rare Met, 2009, 28: 86-90.
[15] ZHANG Zhi-qing, LE Qi-chi, CUI Jian-zhong. Effect of high-intensity ultrasonic field on process of semi-continuous casting for AZ80 magnesium alloy billets [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(s): s376-s381.
[16] LAN J, YANG Y, LI X C. Microstructure and microhardness of SiC nanoparticles reinforced magnesium composites fabricated by ultrasonic method [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 386: 284-290.
[17] ABRAMOV V, ABRAMOV O, BULGAKOV V, SOMMER F. Solidification of aluminium alloys under ultrasonic irradiation using water-cooled resonator [J]. Mater Lett, 1998, 37: 27-34.
[18] KHOSRO-AGHAYANI M, NIROUMAND B. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on microstructure and tensile strength of AZ91 magnesium alloy [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2011, 509: 114-122.
[19] LIU X B, OSAWA Y, TAKAMORI S, MUKAI T. Grain refinement of AZ91 alloy by introducing ultrasonic vibration during solidification [J]. Mater Lett, 2008, 62: 2872-2875.
[20] KLEINER S, BEFFORT O, UGGOWITZER P J. Microstructure evolution during reheating of an extruded Mg-Al-Zn alloy into the semisolid state [J]. Scripta Mater, 2004, 51: 405-410.
[21] FAN Z. Semisolid metal processing [J]. Int Mater Rev, 2002, 47: 49-85.
[22] TZIMAS E, ZAVALIANGOS A. A comparative characterization of near equiaxed microstructures as produced by spray casting, magnetohydrodynamic casting and the stress induced, melt activated process [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, 289: 217-227.
冷却条件对超声振动法制备AZ91半固态浆料组织的影响
张 亮1,吴国华1,王少华2,丁文江1
1. 上海交通大学 轻合金精密成型国家工程研究中心,上海 200240;
2. 空间物理重点实验室,北京100076
摘 要:利用超声振动法制备AZ91合金半固态浆料,在不同温度区间和冷却速率下对熔体进行超声处理,研究冷却条件对AZ91半固态浆料微观组织的影响。结果表明:在形核阶段,熔体在超声振动引发的空化和声流效应作用下,能够获得细小、近球状的初生α-Mg固相颗粒;在固液相线温度区间内,随着超声温度下限的降低,半固态浆料的固相率和固相颗粒的平均尺寸增加;在超声振动过程中,随着冷却速率的提高,半固态浆料的固相率增大,固相颗粒的平均形状因子降低。在本实验条件下,适宜的超声振动温度区间为605 ℃到595 ℃或590 ℃,合适的冷却速率为2~3 ℃/min。
关键词:AZ91合金;半固态;超声振动;微观组织;冷却条件
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project (2011M500772) supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China; Project (2007CB613701) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project (2009AA033501) supported by the National High-tech R&D Program of China
Corresponding author: WU Guo-hua; Tel: +86-21-54742630; Fax: +86-21-34202794; E-mail: ghwu@sjtu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61471-4