文章编号:1004-0609(2008)03-0444-05
K418高温合金和42CrMo合金钢的激光焊接
刘秀波1, 2,虞 钢1,庞 铭1,张振国2,范积伟2
(1. 中国科学院 力学研究所,北京 100080;
2. 中原工学院 材料与化学工程学院,郑州 450007)
摘 要:进行了K418高温合金和42CrMo钢的激光焊接实验,分别采用OM、SEM、XRD和EDS等手段分析了焊缝的金相组织和物相组成,评价了焊缝的显微硬度和拉伸强度。结果表明:焊缝主要由树枝状非平衡凝固的FeCrNiC (g)固溶体组成,此外,还有少量细小、弥散的Ni3Al (g ?)相、Laves 颗粒和少量MC碳化物分布在树枝晶间区域。由于主要强化相g ?在激光辐照后的部分溶解和随后快速凝固的抑制作用,焊缝的硬度虽分布较均匀但低于母材。由于没有获得穿透的焊接接头,焊接接头的强度约只有母材的88.5%,焊缝的断裂机制是塑性和脆性断裂的混合机制。由于在焊缝中存在一些Laves 颗粒,这促进了微裂纹和微孔的形成和扩展,降低了焊接接头的抗拉强度。
关键词:激光焊接;焊缝;组织;力学性能
中图分类号:TG 156;TN 249 文献标识码:A
Laser welding of superalloy K418 to 42CrMo steel
LIU Xiu-bo1, 2, YU Gang1, PANG Ming1, ZHANG Zhen-guo2, FAN Ji-wei2
(1. Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100080, China;
2. School of Materials and Chemical Engineering, Zhongyuan Institute of Technology, Zhengzhou 450007, China)
Abstract: The superalloy K418 and steel 42CrMo were welded laser. The microstructure of the weld was characterized by optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). The mechanical properties of the weld were evaluated by microhardness and tensile strength testing. The results show that the laser weld has non-equilibrium solidified microstructures consisting of FeCrNiC austenite solid solution, and little fine and dispersed Ni3Al (g ?) phase, Laves particles and little MC carbides distribute in the interdendritic regions. The average microhardness of the weld is relatively uniform and lower than that of the base metal because the main strengthening phase g ? partially dissolutes and solidifies quickly after laser. About 88.5% tensile strength of the base metal is achieved in the welded joint because the full penetration welding is gained, and the fracture mechanism is ductility and brittleness. The existence of some Laves particles in the weld also facilitates the initiation and propagation of the microcracks and microvoids and decreases the tensile strength of the welded joint.
Key words: laser welding; weld; microstructure; mechanical properties
发动机的一些关键部件对其寿命有很大影响,而这些关键部件通常是由铸态的K418镍基高温合金和调质状态的42CrMo合金钢焊接而成,二者的热物理性能和高温力学性能差异很大[1],属于典型的异种材料焊接。目前,对K418和42CrMo焊接的主要方法是电子束焊接和摩擦焊,但电子束焊接需要真空环境且产生有害的X射线,摩擦焊接头常发生低应力破坏和表面缺陷。上述部件的连接问题一直困扰着我国的涡轮增压器研制工作者[2-3]。
激光焊接具有功率密度高、焊接速度快、焊接深宽比大、工件热变形小、容易实现自动化且不需要真空环境及不产生X射线等特点,特别适合焊接特殊难焊的同种和异种金属材料[4-10]。近十几年来,在YAG激光加工技术中采用了光纤传输技术,使激光焊接技术获得了更为广泛的推广与应用[11]。
为了有效探索焊接上述两种材料的新途径,为最终提高发动机涡轮增压器转子的质量和整体寿命,本文作者在前期进行的K418和42CrMo异种金属平板激光焊接的基础上[12],开展了K418和42CrMo异种材料的涡轮盘和转轴实物零件的激光焊接实验,以期为有效地提高涡轮增压器转子的制造效率和可靠性乃至提高发动机的服役寿命提供参考。
1 实验方法
激光焊接实验在中国科学院力学研究所激光智能制造工艺力学实验室开发的成套设备上进行,额定输出功率为3 kW,光束模式为多模。聚集镜镜头焦距为200 mm,侧吹保护气为高纯氩气,侧吹角度为35?,侧吹方向和焊接方向相反。K418高温合金和42CrMo钢采用对接,连续激光焊接,中间不留间隙,焊前用丙酮反复清洗待焊零件。由于激光焊接对工作台的精度要求很高,实验中通过千分表调整工作台的水平和垂直精度,使其误差范围精确可控。焊接后,沿垂直于焊接方向切取待分析区域,按常规方法制备金相试样,利用X射线衍射分析仪分析焊接接头的物相组成,利用金相显微镜和扫描电镜结合能量谱仪观察分析焊接接头的微观组织和微区成分以及拉伸实验后的断口形貌,在材料实验机上对焊接接头进行拉伸实验。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 表面质量
K418高温合金和42CrMo钢激光焊接接头宏观形貌如图1所示。由图1可见,通过之前对上述两种材料的平板焊接工艺参数的摸索[8],已基本得到获得高质量接头的激光焊接工艺参数。对于5.5 mm厚的材料,激光输出功率为3 kW,转轴转速为8 mm/s,离焦量为-3 mm。

图1 K418高温合金和42CrMo钢激光焊接接头宏观形貌
Fig.1 Macromorphology of laser welded joint between K418 superalloy and 42CrMo alloy steel
2.2 焊缝的物相和微观组织结构分析
对焊缝进行X射线衍射物相分析表明,焊缝主要由g -FeCrNiC镍基固溶体、Ni3Al (g ?)和MC碳化物组成(见图2)。

图2 焊缝的X射线衍射物相分析结果
Fig.2 X-ray diffraction results of laser weld
对焊缝进行显微组织分析表明,由于激光固有的快速加热和快速冷却特点,在经过优化的工艺参数处理下,焊缝主要由树枝状非平衡凝固g-FeCrNiC镍基固溶体基体、少量颗粒状Ni3Al (g ?) 和MC碳化物组成(见图3)。整个焊缝微观组织细小均匀,根据Hall-Petch原理,这将有利于焊接接头的强度和塑性等力学性能。

图3 焊缝的微观组织结构
Fig.3 Typical microstructures of laser weld: (a) OM image; (b) SEM image
经过高倍显微镜的仔细观察(见图3(b)),在树枝状基体之间的区域分布一些不规则的颗粒,其化学成分经EDS检测为 Ni 37.926 9,Fe 27.939 3,Cr 8.753 2,Mo 6.060 3,Al 1.857 7,Nb 12.959 1,Ti 4.503 5 (质量分数,%),近似于(Fe, Cr, Ni)2(Ti+Nb+Mo)。综合考虑本研究的实验结果并参考JANAKI等[13-15]的结果与推理分析,初步分析认为这些不规则的颗粒为镍基高温合金凝固过程中的Laves相,Laves相的存在普遍认为对凝固组织的力学性能有一定的不利影响,因此,在激光焊接K418等镍基高温合金时,如何采取进一步的改进措施,优化工艺参数,如控制热输入/冷却速率以降低如Nb、Mo和Ti之类的重合金元素在凝固过程中的偏聚,减少Laves相的形成,从而达到最终获得优质焊接接头的目的,有待于继续研究。
2.3 显微硬度分析
对整个焊接接头进行显微硬度测试,结果如图4所示。由图4可看出,焊缝的硬度HV最低,约为220,K418侧热影响区(HAZ)的硬度约为400,然后快速下降至K418母材的硬度,约为380。在整个焊接接头中42CrMo侧热影响区(HAZ)的硬度最高,达450~650,然后逐渐下降至42CrMo母材的硬度,约250。对沿平行焊缝长度方向的硬度进行分析表明,除了个别硬度较高的点外,整个焊缝的硬度都在240左右波动,显示出较为均匀的组织分布。产生该现象的原因是镍基高温合金中的强化相Ni3(Al, Ti)g ?的部分溶解和随后的快速凝固抑制其生成,焊缝的硬度最低,K418侧热影响区和母材的硬度较高,显然与g ?的强化作用以及热影响区较为集中有关;42CrMo侧热影响区的硬度最高是激光焊接在此区域的自淬火效应,生成了马氏体,其热传导系数特别是在温度低于600 ℃的条件下较K418大的缘故[1] 。
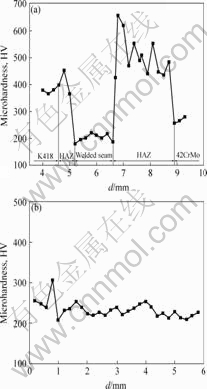
图4 焊缝的显微硬度分布
Fig.4 Microhardness distribution of laser weld along different directions: (a) Transverse direction; (b) Longitudinal direction
2.4 焊接接头的力学性能分析
焊接接头的力学性能测试结果表明,由于没有获得完全的穿透焊接接头,拉伸实验断口位于焊缝,经计算,焊接接头的拉伸强度为523 MPa,大约为42CrMo母材的88.5%。通过观察拉伸断口的微观形貌,在焊接熔合良好的区域,存在较多的不同形状和大小的韧窝,显示出该区域成分具有较好的韧性(见图5(a));而在部分熔合区域,存在一些撕裂棱和冰糖状断口(见图5(b)),预示为脆性断裂。而这种混合断裂特征经常发生于具有较高强度和良好塑性的材料。由图5(b)可看出,在焊缝断口韧窝坑内存在细小的Laves颗粒,预示着由应力集中引起的微孔和微裂纹起源于Laves相和基体界面,Laves相的存在也在一定程度上降低了焊接接头的强度和塑性。

图5 焊缝的断口形貌
Fig.5 SEM images of tensile fracture surfaces of laser weld: (a) Base alloy steel 42CrMo; (b) Partially melted region
3 结论
1) 采用激光对K418高温合金和42CrMo合金钢进行焊接,获得了表面平整、外观成形、质量良好且具有较高强度的焊接接头。
2) K418高温合金和42CrMo合金钢的激光焊接焊缝主要由树枝状非平衡凝固的g-FeCrNiC 固溶体、少量细小弥散的Ni3Al g ?相、Laves 颗粒以及分布在树枝晶之间的少量MC碳化物组成。
3) 由于主要强化相g ?在激光辐照后的部分溶解和随后快速凝固的抑制作用,焊缝的硬度虽分布较均匀,但低于母材的硬度。
4) 由于未形成穿透焊接接头,焊缝中存在一些Laves 颗粒,这将会促进微裂纹和微孔的形成和扩展,从而降低其抗拉强度,接头的强度约只为母材的88.5%,接头的断裂机制是塑性和脆性断裂的混合 机制。
REFERENCES
[1] 谭 真, 郭广文. 工程合金热物性[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1994.
TAN Zhen, GUO Guang-wen. Thermo-physical properties of engineering alloys[M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 1994.
[2] 杜随更, 傅 莉, 王晋伟, 曹 营. K418高温合金与42CrMo钢异种金属摩擦焊接头碳化物带形成机制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(2): 323-327.
DU Sui-geng, FU Li, WANG Jin-wei, CAO Ying. Forming mechanism of carbide band in friction welding joint of superalloy K418 and steel 42CrMo[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(2): 323-327.
[3] 杜随更, 傅 莉, 曹 营, 王晋伟. K418涡轮盘和42CrMo轴摩擦焊接头的强化[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2004, 22(1): 112-115.
DU Sui-geng, FU Li, CAO Ying, WANG Jin-wei. On strengthening the friction welding joint between K418 Turbo disk and 42CrMo shaft[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2004, 22(1): 112-115.
[4] 虞 钢, 虞和济. 集成化激光智能加工工程[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2002.
YU Gang, YU He-ji. Integrated laser intelligent processing engineering[M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 2002.
[5] MAI T A, SPOWAGE A C. Characterization of dissimilar joints in laser welding of steel-kovar, copper-steel and copper- aluminium[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 374: 224-233.
[6] RIBOLLA A, DAMOULIS G L, BATALHA G F. The use of Nd: YAG laser weld for large scale volume assembly of automotive body in white[J]. J Mater Process Technol, 2005, 164/165: 1120-1127.
[7] KUO T Y, LIN H C. Effects of pulse level of Nd: YAG laser on tensile properties and formability of laser weldments in automotive aluminium alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, A416: 281-289.
[8] 王红英, 李志军. AZ61镁合金激光焊接接头的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(8): 1388-1393.
WANG Hong-ying, LI Zhi-jun. Microstructure and properties of AZ61 magnesium alloy joints produced by laser welding method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(8): 1388-1393.
[9] IDOWU O A, OJO O A, CHATURVEDI M C. Effect of heat input on heat affected zone cracking in laser welded ATI Allvac 718Plus superalloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, A454/455: 389-397.
[10] WANG A H, XU H G, YANG P, ZHANG X L, XIE C S. Nd: YAG laser butt welding of a 12vol.% SiC particulate-reinforced magnesium alloy composite[J]. Mater Lett, 2007, 61: 4023-4026.
[11] 关振中. 激光加工工艺手册[M]. 北京: 中国计量出版社, 1998.
GUAN Zhen-zhong. Handbook of laser processing[M]. Beijing: China Measurement Press, 1998.
[12] 庞 铭, 虞 钢, 刘 兆, 郑彩云, 王立新, 宁伟健. K418 与42CrMo异种金属的激光穿透焊接[J]. 中国激光, 2006, 33(8): 1122-1126.
PANG Ming, YU Gang, LIU Zhao, ZHENG Cai-yun, WANG Li-xin, NING Wei-jian. Dissimilar metal of K418 and 42CrMo full penetration laser welding[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2006, 33(8): 1122-1126.
[13] JANAKI R G D, VENUGOPAL R A, PRASAD R K, REDDY G M, SARIN S J K. Microstructure and tensile properties of Inconel 718 pulsed Nd-YAG laser welds[J]. J Mater Process Technol, 2005, 167: 73-82.
[14] JANAKI R G D, VENUGOPAL R A, PRASAD R K, REDDY G M. Control of Laves phase in Incol 718 GTA welds with current pulsing[J]. Sci Technol Weld Joi, 2004, 9(5): 390-398.
[15] RADHAKRISHNA C, PRASAD R K. The formation and control of Laves phase in super-alloy 718 welds[J]. J Mater Sci, 1997, 32: 1977-1984.
基金项目:中国科学院重大仪器研制资助项目(Y2003004);中国博士后科学基金资助项目(20060400105)
收稿日期:2007-09-05;修订日期:2007-11-29
通讯作者:虞 钢,研究员,博士;电话:010-82544250;E-mail: gyu@imech.ac.cn
(编辑 李艳红)