DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.07.024
珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩元素地球化学组成及意义
焦鹏1,郭建华1,张向涛2,张琳婷1,王张虎1
(1. 中南大学 地球科学与信息物理学院,有色金属成矿预测教育部重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 中海石油(中国)有限公司深圳分公司,广东 深圳,510240)
摘要:在珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷,选择5口井19件珠江组泥岩样品,分析元素(包括常量、微量和稀土)地球化学组成,并在此基础上,结合区域地质背景,探讨地质意义,主要是该沉积时期的沉积环境、物源区性质、构造背景及物源区的风化特征。研究结果表明:研究区泥岩的Al2O3,K2O,MgO,SiO2与PAAS的质量分数相近,富集Na2O和CaO,贫MnO和P2O5。不相容元素Th质量分数较高,指示物源区供应的中酸性碎屑组分较多,高强场元素Sr的平均质量分数接近于后太古宙页岩(PAAS)质量分数平均值而远低于大陆上地壳(UCC)质量分数平均值; Ta的平均质量分数介于UCC和PAAS的之间, 而Hf的平均质量分数比UCC的低,比PAAS的高;w(∑LREE)/w(∑HREE)和[w(La)/w(Yb)]N均值分别为8.89和10.16,轻重稀土分异明显;陆丰凹陷早中新世属于潮湿气候下的海陆过渡沉积,总体处于弱氧化-还原、半咸水沉积环境,西北部和中部沉积水体较深,东北部次深,东南部较浅,而东北部和东南部的水体盐度要比西北部和中部的水体盐度高。珠江组源岩主要为来源于上地壳的长英质岩石,西北部源区的构造背景具有类似活动大陆边缘的特征,东北部源区的构造背景具有类似被动大陆边缘的特征,东南部源区的构造背景具有类似岛弧的特征,中部为东北部和西北部物源交汇区。利用指数CIA指数和ICV揭示出东沙隆起、华南沿海气候条件相似(温暖、湿润),其中西北部源区经历的化学风化作用最强,东南部次之,东北部最弱。
关键词:珠江口盆地;陆丰凹陷;珠江组;元素地球化学;沉积环境;物源分析;古气候
中图分类号:P595 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)07-2347-10
Element geochemistry of the Neogene Zhujiang formation mudstones in Lufeng depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin and its geological implication
JIAO Peng1, GUO Jianhua1, ZHANG Xiangtao2, ZHANG Linting1, WANG Zhanghu1
(1. Key Laboratory of Metallogenic Prediction of Nonferrous Metals, Ministry of Education,
School of Geosciences and Info-Physics, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Shengzhen Branch of CNOOC Ltd, Shenzhen 510240, China)
Abstract: According to regional geological background, the geological significance mainly including the sedimentary environment, provenance attribute, tectonic setting and weathering of provenance were investigated based on the geographical and chemical formation of elements including the major elements, trace elements and rare earth elements analysis of 5 wells with 19 Zhujiang mudstone samples collected from the Lufeng depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin. The results show that the mass fraction of Al2O3,K2O,MgO and SiO2 is similar to that of PAAS of the mudstone in the research areas, with the enriched Na2O and CaO, lacking of MnO and P2O5. The mass fraction of the incompatible elements The is higher and the acidic clastic components supplied in the indicating source area are more. The average mass fraction of the high field-strength element (HFSE) Sr is close to that of the post archean shale (PAAS),but is much lower than that of the upper continental crust(UCC).The average mass fraction of Ta is between that of UCC and PAAS, nevertheless, the average mass fraction of Hf is lower than that of UCC and higher than that of PAAS. The ratio of mass fraction of ∑LREE to ∑HREE (8.89) and that La to Yb (10.16) suggests a distinct difference between LREE and HREE. Lufeng depression is marine-continental transition depositional sediment which is formed in humid climate, and its paleo-environment is under weak oxidation-education and brackish half-salt water condition. The sedimentary water during Early Miocene in the northwest and central is relatively deep, while that in the northeast is less deep and that in southeast is comparatively shallow. The water salinity in the southeast and northeast is higher than that in the northwest and central part. The parental rocks of Zhujiang formation are mainly supracrustal felsic rocks, the tectonic background of active continental margin in northwest, the tectonic background of passive continental margin in northeast, the tectonic background of arc in southeast, and the provenance in central part is an intersectional area of the ones in northeast and northwest. Chemical index of alteration (CIA) and index chemical variation (ICV) reveal that the climatic conditions of the Dongsha Massif and coastal region of South China in early Miocene are similar (warm and humid),and the order of the chemical intensity of the source areas is in the northwest, southeast and northeast.
Key words: Pearl River Mouth Basin; Lufeng depression; Zhujiang formation; element geochemistry; sedimentary environments; provenance analysis; paleoclimate
元素地球化学作为近代地球化学的一个重要组成部分,近年来其理论不断丰富,应用也逐渐增多,尤其在判别沉积环境、分析沉积物物源及沉积背景等方面应用广泛[1-3]。区域资料揭示,陆丰凹陷珠江组岩性主要为泥岩夹细、粉砂岩,是一套海相三角洲—滨岸沉积,靠近东沙隆起区域有台地灰岩、生物礁等发育。古珠江口盆地沉积物特征总体反映出华南尤其广东及沿海源区的特征,但对于不同的凹陷来说,其供给物质的水流体系和物质来源不尽相同。在中新世,陆丰地区的物质来源主要是东北部的古韩江水流体系和西部的古珠江水流体系,某些区域还存在着混合沉积区,除此之外,东沙隆起的火山活动对研究区南部也有一定的影响[4]。本文以珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷珠江组为研究对象,通过分析珠江组泥岩的元素地球化学组成和某些特征元素的质量分数比值,研究珠江组时期陆丰凹陷的沉积环境,并探讨沉积物源区物质组成及构造背景等特征。
1 地质背景
珠江口盆地位于南海北部、华南大陆的南缘,呈NE走向,大致平行华南大陆岸线的陆架和陆坡区展布。图1所示为研究区位置图及取样井,陆丰凹陷隶属于北部坳陷带(珠一坳陷)东部的1个次级构造单元,西与惠州凹陷相邻,东与韩江凹陷相邻,南北分别与东沙隆起和北部断阶相接,主要经历了晚白垩世—早渐新世裂陷、晚渐新世—早中新世的裂后坳陷及中中新世晚期至今的块断活动3个演化阶段[4]。盆地以中生代岩浆岩为基底[5],充填地层具有先陆后海的沉积组合。下部为盆地裂陷期充填的神狐组、文昌组和恩平组陆相沉积,上部为裂后热沉降期充填的珠海组、珠江组、韩江组、粤海组及第四系海陆交互相及海相沉积。
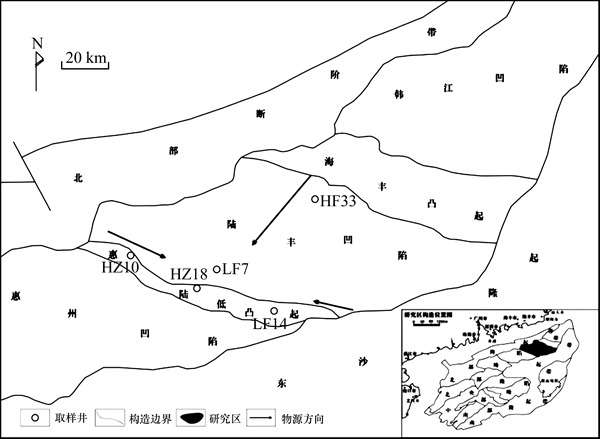
图1 研究区位置图及取样井
Fig. 1 Location map of study area and sampled well
2 样品与方法
研究主要选用陆丰凹陷HF33井(3个)、HZ10井(4个)、HZ18井(3个)、LF14井(3个)及LF7井(6个)合计19个珠江组泥岩样品,测试其元素质量分数,见图1。样品处理及测试由同济大学海洋地质国家重点实验室完成,常量元素质量分数采用电感耦合等离子光谱仪(IRIS advantage ICP,AES)、微量元素和稀土元素采用电感耦合等离子质谱仪(VGX7 ICP-MS)进行分析。
3 地球化学分析结果
3.1 常量元素特征
表1所示为陆丰凹陷新近系珠江组泥岩常微量元素质量分数及典型元素质量分数比值,图2所示为陆丰凹陷新近系珠江组泥岩常量元素的PAAS平均质量分数标准化蛛网图。从表1和图2可以看出:研究区珠江组泥岩样品中的Al2O3和SiO2质量分数普遍较高,其中西北部和东北部样品中SiO2质量分数最高,平均分别达到64.15%和64.87%。与澳大利亚后太古宙页岩(PAAS)[6]常量元素质量分数相比,区内样品中Al2O3,K2O,MgO和SiO2的质量分数与PAAS质量分数相近,具有富Na2O和CaO,贫MnO和P2O5的特点。
3.2 微量元素特征
表1中样品微量元素最显著的特点是东北部的微量元素总质量分数及Cr,Co,Sr, Zr和Ba等元素平均质量分数较低。区内珠江组泥岩样品微量元素中大离子亲石元素Ba除中部的平均质量分数近似于全球平均大陆上地壳成分(UCC)质量分数并略低于PAAS质量分数之外,其余地区的Ba质量分数都远比全球平均大陆上地壳成分[6] (UCC)和PAAS的低。通常,不相容元素Th富集于中酸性岩中,过渡族元素Cr和Co富集于基性和超基性岩石中,区内泥岩样品质量分数相对高的Th,Cr和Co丰度指示物源区供应的基性、超基性和中酸性碎屑组分较多。
表1 陆丰凹陷新近系珠江组泥岩常微量元素质量分数及典型元素质量分数比值
Table 1 Major and trace element mass fraction and its typical ratios of the Neogene Zhujiang formation mudstones in Lufeng depression
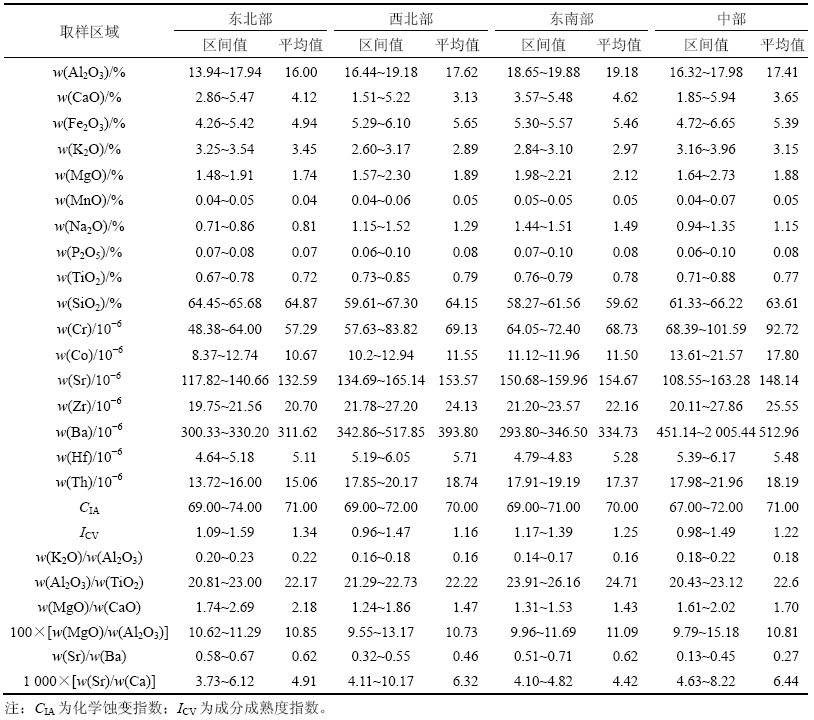
图2 陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩常量元素平均质量分数PAAS标准化蛛网图
Fig. 2 Spider plot of average major elements of mudstones from Zhujiang formation, Lufeng depression
3.3 稀土元素特征
表2所示为陆丰凹陷新近系珠江组泥岩稀土元素质量分数及典型元素质量分数的比值。从表2可见:各分区样品的稀土元素总质量分数平均值在171.41×10-6~210.86×10-6之间,接近PAAS的质量分数均值184.77×10-6,高于UCC[6]的质量分数均值148.14×10-6。4个区域中以中部w(∑LREE)最大,平均值为210.86×10-6;西北部w(∑LREE)次之,平均值为203.96×10-6;东南部w(∑LREE)又次之,平均值为190.32×10-6;东北部w(∑LREE)最小,平均值为171.41×10-6。各分区样品的w(∑LREE)/w(∑HREE)在8.72~9.00之间。
图3所示为陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩样品w(REE)分布模式(球粒陨石标准化)。从图3可以看出:经球粒陨石标准化后,表现为w(∑LREE)富集,w(∑HREE)分布平坦;分布曲线总体向右倾斜,La-Sm段曲线略陡,Dy-Lu曲线较平缓,w(Eu)表现为低谷,w(Eu)显著负异常,是典型沉积岩配分模式。指示轻重稀土元素分异度的[w(La)/w(Yb)]N区间为9.76~10.44,表明轻重稀土元素分异明显;指示轻稀土元素分异程度的[w(La)/w(Sm)]N都小于4,表明轻稀土元素之间分异中等;指示重稀土元素分异程度的[w(Gd)/w(Yb)]N一般大于2,表明重稀土元素的分异不太明显。区内样品δw(Eu)范围为0.62~0.68,铕(Eu)具有明显的亏损,铕(Eu)负异常的相对高点出现在中部,其余区域略低于PAAS的铕(Eu)异常(0.66);δw(Ce)范围为1.05~1.07,铈(Ce)中等亏损。
表2 陆丰凹陷新近系珠江组泥岩稀土元素质量分数及典型元素比值
Table 2 REE mass fraction and typical element ratios of the Neogene Zhujiang formation mudstones in Lufeng depression
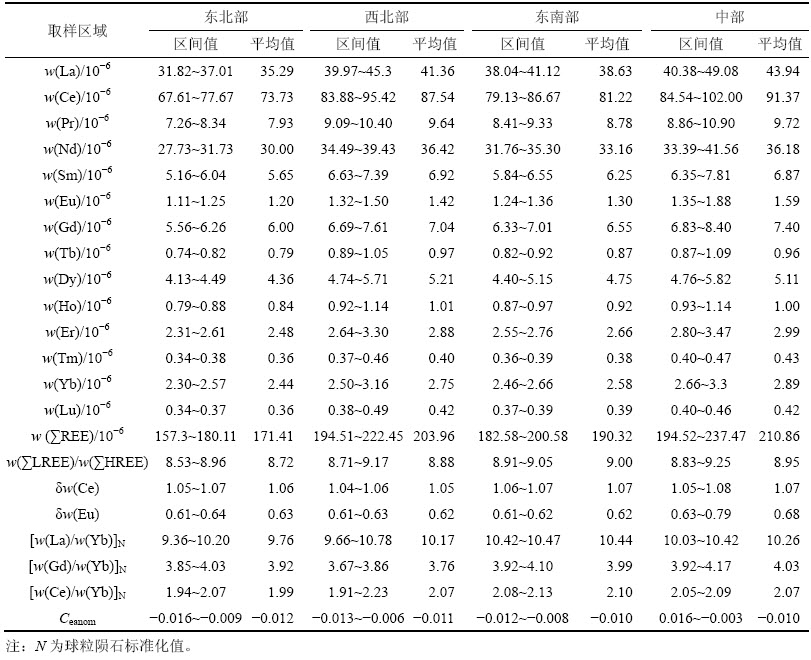
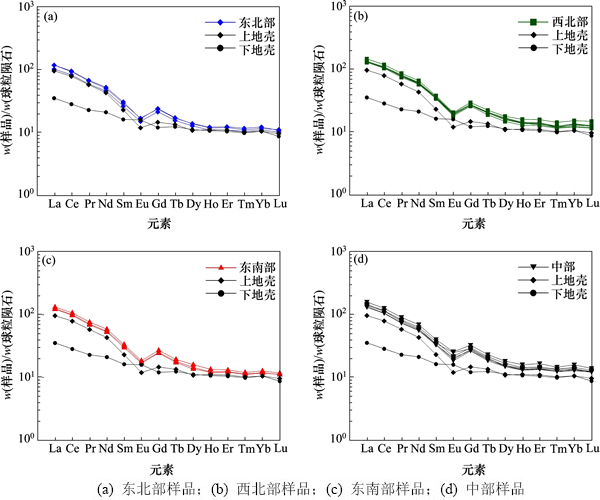
图3 陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩样品REE质量分数分布模式(球粒陨石标准化)
Fig. 3 REE mass fraction distribution patterns of mudstones from Zhujiang formation, Lufeng depression (chondrite-normalized)
4 沉积环境
4.1 古气候
w(Mg)/w(Ca)可以作为古气候变化的良好指示剂[6-7]。在利用w(Mg)/w(Ca)判断古气候条件时,需考虑钾盐、钠盐是否参与沉淀:参与时,w(Mg)/w(Ca)低值以及K+和Na+的质量分数高值指示干热气候;不参与时,w(Mg)/w(Ca)高值指示干热气候。研究区样品中K2O和Na2O平均质量分数分别为2.89%~3.45%和0.81~1.49%,可见K+和Na+质量分数较高,说明它们参与沉淀,因此,潮湿气候对应高w(Mg)/w(Ca),干燥气候对应低w(Mg)/w(Ca)。表1中陆丰凹陷珠江组各分区样品w(MgO)/w(CaO)整体较高,各分区平均值为1.43~2.18,其中东北部w(MgO)/w(CaO)较高,但差异不大,说明研究区早中新世时期整体为相对潮湿的气候条件,这也与古生物研究的结论相符。珠江组中出现海相沟鞭藻类化石以及热带、亚热带植物孢粉从种类和数量上占优势,都反映了当时珠江口盆地整体为滨海浅水至海湾潮间带的沉积环境,古气候为潮湿的热带—亚热带气候环境[8]。
4.2 氧化还原性
稀土元素中Ce异常对水体氧化-还原性具有指示意义,ELDERFIELD等[9]提出用Ceanom表示Ce的异常:当Ceanom>-0.1时,表现为Ce富集,为缺氧条件;当Ceanom<-0.1时,表现为Ce亏损,为氧化条件[9]。表2所示为陆丰凹陷新近系珠江组泥岩稀土元素质量分数及典型元素质量分数的比值。从表2可见:东北部、西北部、东南部、中部泥岩样品的Ceanom指数区间为分别为-0.016~-0.009(均值为-0.012),-0.013~ -0.006(均值为-0.011),-0.012~-0.008(均值为-0.010)和-0.016~-0.003(均值为-0.010),各分区Ceanom均大于-0.100,说明研究区在早中新世处于弱氧化-还原环境。
4.3 古水深和离岸距离
元素Sr在沉积相分析中效果明显[10-11],因为随着沉积环境水体加深,w(Sr)和1 000×[w(Sr)/w(Ca)]显著变大,因而可以利用Sr的质量分数和1 000× [w(Sr)/w(Ca)]判断水深,进而划分沉积相。如表2所示,东北部、西北部、东南部和中部泥岩样品的1 000× [w(Sr)/w(Ca)]分别为0.04~0.06(平均值为0.05),0.04~ 0.10(平均值为0.06),0.04~0.05(平均值为0.04)和0.04~ 0.08(平均值为0.06),说明研究区西北部和中部水体较深,东北部水体深度次之,东南部水体相对最浅。
4.4 古盐度
100×[w(MgO)/w(Al2O3)]常用于反映沉积环境中含盐度,其值与水体的盐度呈正相关[12]。从表1可以发现:区内珠江组泥岩样品100×[w(MgO)/w(Al2O3)]普遍在10左右,说明研究区珠江组沉积时期以陆海过渡沉积环境为主。
w(Sr)/w(Ba)与古盐度呈明显的正相关关系[7],其值增大,反映古盐度增加。从表2可见:区内东北部和东南部w(Sr)/w(Ba)较高,西北部和中部的较低,说明珠江组沉积时期东北部和东南部水体盐度要比西北部和中部的水体盐度高。这可能是东北部和东南部离东沙隆起更近,受到碳酸盐岩影响所致。
5 物源属性
5.1 源区物质组成
COX等[13]研究认为:泥质岩中碱性长石的质量分数与w(K2O)/w(Al2O3)相关。表1中,除东北部外,其余珠江组泥岩样品w(K2O)/w(Al2O3)平均值都小于0.2,说明母岩中碱性长石质量分数较低。GIRTY等[14]发现w(Al2O3)/w(TiO2)对于判断沉积物物源效果明显。表1中西北部、东北部、东南部、中部泥岩样品的w(Al2O3)/w(TiO2)平均值分别为22.22,22.17,24.71和22.60,说明珠江组泥岩最可能来源于安山质和流纹质(或者花岗闪长质和英云闪长质)。
FLOYD等[15]总结了判断源岩成分的w(Hf)- w(La)/w(Th)图解,GU等[16]则归纳出判别源岩成分的w(Co)/w(Th)-w(La)/w(Sc)图解。图4所示为陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩源岩属性综合判别图。从图4(a)可见:各分区珠江组泥岩样品都落在长英质物源区内。从图4(b)可见:西北部、东南部及东北部珠江组泥岩样品投点多落在长英质火山岩附近,说明源岩以长英质火山岩为主;中部泥岩样品主要分布在长英质火山岩附近,但有2个泥岩样品分别落在安山质岩石和长英质火山岩以及花岗岩和长英质火山岩之间,说明有安山质岩石和花岗岩混入。
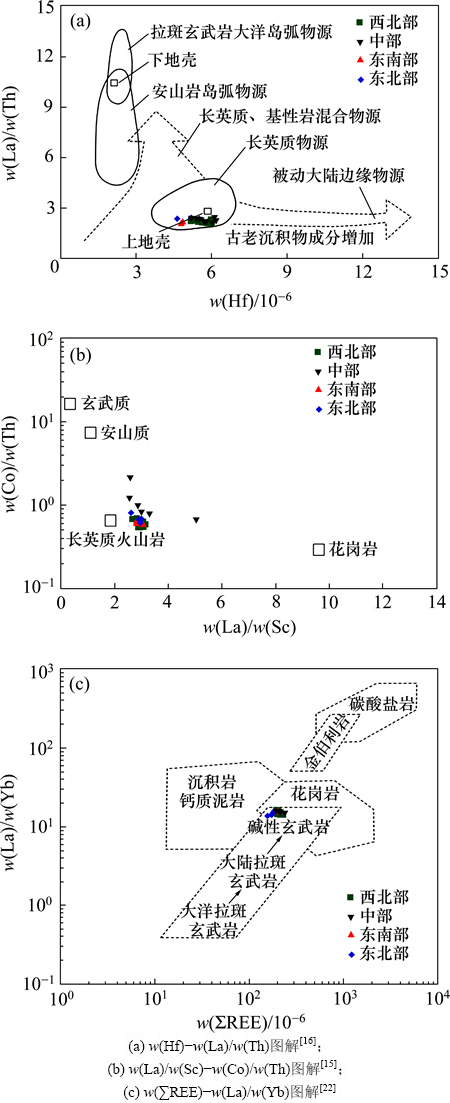
图4 陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩源岩属性综合判别图
Fig. 4 Comprehensive discrimination of sedimentary provenance of Zhujiang Formation mudstones, Lufeng depression
稀土元素的特征参数和配分曲线也是指示沉积物物源的重要指标[17-19],比较常用的参数有δw(Eu),w(∑LREE)/w(∑HREE)等。图3 所示为陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩样品w(∑REE)分布模式(球粒陨石标准化),图4(c)所示为陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩w(∑REE)-w(La)/w(Yb)源岩判别图解,各分区样品与上地壳稀土元素分布模式相似程度高。图4(c)中所有分区的泥岩样品的投点分布区域,也反映了沉积岩源岩的中酸性长英质属性。
5.2 构造背景判别
前人总结出的通过碎屑岩地球化学组分特征判别构造背景的一系列图解同样适用于细碎屑岩(粉砂岩、泥岩等)的研究,因为细碎屑岩通常与碎屑岩相伴生,具有相同的物源和沉积背景,地球化学特征相似。ROSER等[18]提出的常量元素w(K2O)/w(Na2O)-w(SiO2)构造背景判别图解已经得到广泛应用,并且取得了很好的效果。图5所示为陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩常量元素构造背景判别图,图中西北部样品投点反映在活动大陆边缘背景,东北部样品投点反映被动大陆边缘背景;东南部样品投点于活动大陆边缘和岛弧区域内,说明可能受到东沙物源的影响;中部样品则被动大陆边缘和活动边缘区域内都有分布,反映了研究区中部具有混合物源的特点。
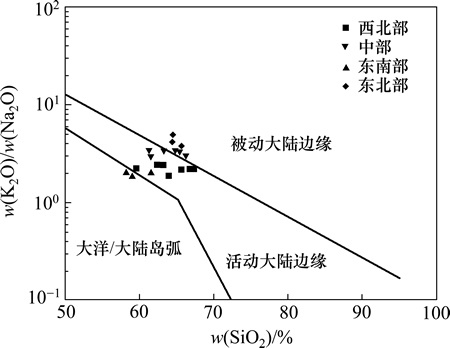
图5 陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩常量元素构造背景判别图
Fig. 5 Discrimination of tectonic setting by major elements of Zhujiang Formation mudstones, Lufeng depression
与常量元素相比,陆源碎屑中的微量元素相对稳定,更适用于研究沉积物源区属性。参照BAHTIA等[20]判别的图解,可得出陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩微量元素构造背景判别图,见图6。图6中西北部样品投点反映大陆边缘和大洋岛弧背景,说明西北部主要受到古珠江物源影响;东北部样品投点反映大陆边缘背景,说明东北部主要受到古韩江物源影响;东南部样品投点主要反映大洋岛弧背景,说明东沙隆起物源对研究区东南部影响较大;中部样品则在大洋岛弧和大陆边缘区域内都有分布,反映了研究区中部具有混合物源的特点。
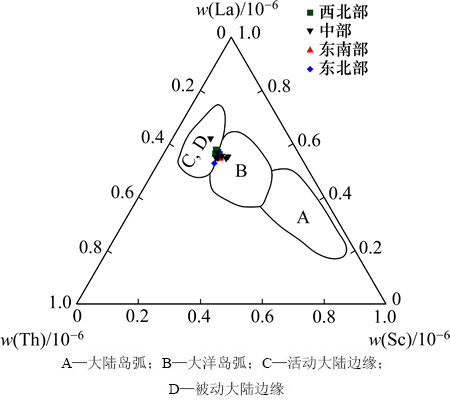
图6 陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩微量元素构造背景判别图
Fig. 6 Discrimination of tectonic setting by trace elements of Zhujiang Formation mudstones, Lufeng depression
将研究区泥岩w(∑REE)及特征值除以1.2可以得到同期沉积的杂砂岩的w(∑REE)及特征值,即校正后∑REE的质量分数。这是因为在相同构造背景下,泥岩中w(∑REE)要比杂砂岩高20%左右[21]。表3所示为研究区泥岩w(∑REE)特征值。表3列出了研究区各分区泥岩校正后的w(∑REE)及其特征值,通过与BHATIA[22]总结出的4种构造背景w(∑REE)及其特征值比较可以看出,研究区各分区珠江组泥岩样品的w(La),w(Ce),w(La)/w(Yb),[w(La)/w(Yb)]N,w(∑REE)和δw(Eu)与之对比吻合度不高,但总体来看,东南部具有大陆岛弧的特征,西北部具有活动大陆边缘的特征,与常量元素和微量元素构造背景判别结果基本 一致。
在渐新世末期,广东大陆仍以上升为主,渐新世以后只有极少数盆地有沉积,珠江口盆地受渐新世开始的海底扩张影响,构造活动强烈。在32~23.8 Ma,珠江口盆地沉积物特征总体反映出华南尤其是广东及沿海源区的特征,之后发生的“白云运动”对珠江口盆地的沉积充填影响重大[23]。自早中新世开始,古韩江三角洲物源的影响范围就到达研究区中部LF7井区,并对东南部LF14井区造成一定影响。自早中新世末—中中新世开始,随着古韩江三角洲物源的退缩及古珠江三角洲物源的扩大,LF7井区受到两者沉积物的共同影响,其中古珠江三角洲物源最远可能到达LF14井区[4]。研究区南部的东沙隆起是自古近纪以来的继承性隆起,物源整体提供能力逐步减弱,在晚渐新世,局部以三角洲形式向四周提供碎屑物质,直到16.5 Ma之后其几乎完全淹没于水下,提供物源的能力完全丧失[24]。
表3 研究区泥岩稀土元素特征值与不同构造背景稀土元素特征值对比
Table 3 The correlation of REE characteristic parameters of mudstones in study area and the ones in different tectonic setting

5.3 源区古风化程度和古气候特征
源区的化学风化程度可以用化学蚀变指数CIA来反映:当CIA为50~65时,表明寒冷、干燥,起低风化作用;当CIA为62~85时,表明温暖、湿润,起中等风化作用;当CIA为85~100时,表明炎热、潮湿,起强烈风化作用。需注意的是:CIA也与母岩类型有关,若母岩中碳酸盐岩组分质量分数高,则其值也较低[25]。表1中陆丰凹陷珠江组泥岩样品的CIA在69~74之间,西北部CIA较低,可能与珠江口盆地物源区转变有关[26],但各个物源区的平均值都达到70,反映各个物源区经历的化学风化作用中等,可能处于温暖、湿润的气候条件。
ICV指数常用来判定细碎屑岩的成分成熟度,判定过程需充分考虑硅酸盐矿物和黏土矿物的影响[25]。东北部、西北部、东南部、中部的珠江组泥岩样品ICV平均值分别为1.34,1.16,1.25和1.22,反映西北部物源区成分成熟度较高,化学风化作用较强,东南部次之,东北部物源区成分成熟度较低,化学风化作用较弱。
6 结论
1) 研究区早中新世属于干燥气候下的海陆过渡沉积,总体处于弱氧化-还原条件、半咸水环境,沉积水体西北部和中部较深,东北部次深,东南部相对较浅,而东北部和东南部的水体盐度要比西北部和中部的水体的盐度高。
2) 根据常量元素、微量元素和稀土元素组合及典型比值特征,推测出珠江组沉积期物源区岩石以来自于上地壳的中酸性长英质岩为主,受壳内分异作用影响明显。
3) 利用泥岩元素地球化学特征区分研究区珠江组物源区构造背景效果明显。西北部物源区表现为活动大陆边缘,东北部物源区表现为被动大陆边缘,东南部物源区表现为岛弧,中部为东北部和西北部物源交汇区。
4) 利用指数CIA和ICV揭示出东沙隆起、华南沿海在早中新世均处于温暖、湿润的气候条件,其中西北部物源区化学风化作用最强,东南部次之,东北部最弱。
参考文献:
[1] 王嘹亮, 沈艳杰, 程日辉, 等. 北黄海盆地中—上侏罗统火山岩岩石地球化学特征及构造背景[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(1): 149-155.
WANG Liaoliang, SHENG Yanjie, CHENG Rihui, et al. Geochemistry and tectonic background of Middle—Upper Jurassic volcanic rocks in the North Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(1): 223-232.
[2] 李明龙, 郑德顺, 戴光忠, 等. 豫西济源盆地侏罗系泥质岩地球化学特征及其环境和物源示踪[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(2): 228-238.
LI Minglong, ZHENG Deshun, DAI Guangzhong, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the Jurassic argillaceous rocks of the Jiyuan Basin,Western Henan and the implications for environments and provenances[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(2): 228-238.
[3] 操应长, 王艳忠, 徐涛玉, 等. 特征元素比值在沉积物物源分析中的应用: 以东营凹陷王58井区沙四上亚段研究为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(2): 230-238.
CAO Yingchang, WANG Yanzhong, XU Taoyu, et al. Application of the ratio of characteristic elements in provenance analysis: a case study from the upper part of the fourth member of the Shahejie Fm in the W58 area, Dongying depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(2): 230-238.
[4] 张向涛, 陈亮, 佘清华, 等. 南海北部古韩江物源的演化特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(4): 41-48.
ZHANG Xiangtao, CHEN Liang, SHE Qinghua, et al. Provenance evolution of the Paleo—Hanjiang River in the North South China sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(4): 41-48.
[5] 王家林, 张新兵, 吴健生, 等. 珠江口盆地基底结构的综合地球物理研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2002, 21(2): 13-22.
WANG Jialin, ZHANG Xinbing, WU Jiansheng, et al. Integrated geophysical researches on base texture of Zhujiang River Mouth Basin[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2002, 21(2): 13-22.
[6] TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The continental crust: its composition and evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1985: 117-140.
[7] 经雅丽, 张克信, 林启祥, 等. 浙江长兴煤山下三叠统和龙山组、南陵湖组沉积地球化学特征与古环境意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2005, 24(1): 35-40.
JING Yali, ZHANG Kexin, LIN Qixiang, et al. Sedimentary geochemistry characteristics and paleoenvironmental meaning of Helongshan Formation and Nanlinghu formation in Meishan, Changxing County, Zhejiang Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2005, 24(1): 35-40.
[8] 范时清, 廖健雄. 中国南海新生代古环境的变迁[J]. 广西科学院学报, 2005, 21(1): 51-55.
FAN Shiqing, LIAO Kinhung. Changes of Cenozoic paleo- environment in Northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 2005, 21(1): 51-55.
[9] ELDERFIELD H, PAGETT M. REE in ichthyoliths: variations with redox conditions and depositional environment[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 1986, 49(86): 175-197.
[10] 汪凯明, 罗顺社. 燕山地区中元古界高于庄组和杨庄组地球化学特征及环境意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2009, 28(4): 356-364.
WANG Kaiming, LUO Shunshe. Geochemical characteristics and environmental significance of Gaoyuzhuang and Yangzhuang formations in Yanshan region[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2009, 28(4): 356-364.
[11] VEIZER J, DEMOVIC R. Strontium as a tool for facies analysis[J]. Sedimentary Petrology, 1974, 44(1): 93-115.
[12] 杨振宇, 沈渭洲, 郑连弟. 广西来宾蓬莱滩二叠纪瓜德鲁普统—乐平统界线剖面元素和同位素地球化学研究及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(1): 1-15.
YANG Zhenyu, SHEN Weizhou, ZHENG Liandi. Elements and isotopic geochemistry of Guadalupian—Lopingian boundary profile at the Penglaitan section of Laibin, Guangxi Province, and its geological implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(1): 1-15.
[13] COX R, LOWE D R, CULLERS R L. The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States[J]. Geochemical et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(14): 2919-2940.
[14] GIRTY G H, RIDGE D L, KNAACK C, et al. Provenance and depositional setting of Paleozoic chert and argillite, Sierra Nevada, California[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1996, 66(1): 107-118.
[15] FLOYD P A, LEVERIDGE B E. Tectonic environment of Devonian Gramscatho basin, South Cornwall: Framework mode and geochemical evidence from turbidities sandstones[J]. Geological Society of London Journal, 1987, 144(4): 531-542.
[16] GU X X, LIU J M, ZHENG M H, et al. Provenance and tectonic setting of the Proterozoic turbidites in Hunan, South China: Geochemical evidence[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2002, 72(3): 393-407.
[17] 李双建, 王清晨. 库车坳陷第三系泥岩地球化学特征及其对构造背景和物源属性的指示[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2006, 25(3): 221-229.
LI Shuangjian, WANG Qingchen. Geochemical characteristics of tertiary mudstones in Kuqa depression and their implications to tectonic setting and provenance attribute[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2006, 25(3): 221-229.
[18] ROSER B P, KORSCH R J. Determination of tectonic setting of sandstone-mudstone suites using SiO2 content and K2O/Na2O ratio[J]. Journal of Geology, 1986, 94(5): 635-650.
[19] 余烨, 张昌民, 李少华, 等. 惠州凹陷珠江组泥岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(1): 40-49.
YU Ye, ZHANG Changmin, LI Shaohua, et al. Geochemistry characteristics and geological significance of mudstones from Zhujiang Formation of Huizhou depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Science and Technology), 2014, 38(1): 41-49.
[20] BHATIA M R, CROOK K W. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basin[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1981, 92(2): 181-193.
[21] 许中杰, 程日辉, 王嘹亮, 等. 广东惠来地区早—中侏罗世桥源组海平面相对升降及构造背景的元素地球化学证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(4): 966-982.
XU Zhongjie, CHENG Rihui, WANG Liaoliang, et al. Relative change of sea-level and element geochemistry evidence of tectonic setting during early or middle Jurassic in Qiaoyuan formation of Huilai Area in Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(4): 966-982.
[22] BHATIA M R. Rare earth elements geochemistry of Australian Paleozoic greywackes and mudrocks: provenance and tectonic control[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1985, 45(1/2): 97-113.
[23] 庞雄, 陈长民, 邵磊, 等. 白云运动: 南海北部渐新统—中新统重大地质事件及其意义[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(2): 145-150.
PANG Xiong, CHEN Changmin, SHAO Lei, et al. Baiyun Movement: a great tectonic event on the Oligocene—Miocene boundary in the northern South China sea and its implications[J]. Geological Review, 2007, 53(2): 145-150.
[24] 李小平, 施和生, 杜家元, 等. 珠海组—珠江组时期东沙隆起物源提供能力探讨[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(4): 654-662.
LI Xiaoping, SHI Hesheng, DU Jiayuan, et al. Capability of Dongsha Massif as provenance during Zhujiang—Zhuhai Formations[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(4): 654-662.
[25] NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature, 1982, 299: 715-717.
[26] 邵磊, 庞雄, 乔培军, 等. 珠江口盆地的沉积充填与珠江的形成演变[J]. 沉积学报, 2008, 26(2): 179-184.
SHAO Lei, PANG Xiong, QIAO Peijun, et al. Sedimentary filling of the Pearl Mouth Basin and its response to the evolution of the Pearl River[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2008, 26(2): 179-184.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2015-07-13;修回日期:2015-09-09
基金项目(Foundation item):国家科技重大专项(2011ZX05023-001) (Project(2011ZX05023-001) supported by the National Major Science and Technology)
通信作者:郭建华,教授,博士生导师,从事沉积学与层序地层学研究;E-mail: gjh796@mail.csu.edu.cn