铜离子和钙离子对羧甲基纤维素在绿泥石表面吸附的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第1期
论文作者:冯其明 冯博 卢毅屏
文章页码:237 - 242
关键词:绿泥石;羧甲基纤维素;铜离子;钙离子;吸附
Key words:chlorite; carboxymethyl cellulose; copper ions; calcium ions; adsorption
摘 要:通过浮选实验、吸附量测试、ζ电位测试和共沉淀实验,研究铜离子和钙离子对羧甲基纤维素(CMC)抑制绿泥石浮选的影响。结果表明,CMC分子和绿泥石表面存在的静电排斥作用阻碍CMC在绿泥石表面的吸附,铜离子和钙离子的存在增加CMC在绿泥石表面的吸附量。两种离子增加CMC吸附量的作用机理存在不同。在pH 9的条件下,钙离子不能吸附在绿泥石表面,但能与荷负电的CMC分子反应,减弱CMC与绿泥石表面的静电排斥作用,从而增加CMC的吸附量;铜离子能吸附在绿泥石表面为CMC的吸附提供质点,吸附在绿泥石表面和CMC分子上的铜离子降低二者的电位,减弱静电排斥作用,从而增加CMC在绿泥石表面的吸附量。
Abstract: The effects of copper ions and calcium ions on the depression of chlorite using CMC (carboxymethyl cellulose) as a depressant were studied through flotation tests, adsorption measurements, ζ potential tests and co-precipitation experiments. The results show that the electrostatic repulsion between the CMC molecules and the chlorite surfaces hinders the approach of the CMC to the chlorite while the presence of copper ions and calcium ions enhances the adsorption density of CMC. The action mechanisms of these two types of ions are different. Calcium ions can not adsorb onto the mineral surfaces, but they can interact with the CMC molecules, thus reducing the charge of the CMC and enhancing adsorption density. Copper ions can adsorb onto the mineral surfaces, which facilitates the CMC adsorption through acid/base interaction. The enhanced adsorption density is also attributed to the decreased electrostatic repulsion between the CMC and mineral surfaces as copper ions reduce the surface charge of both the mineral surfaces and the CMC molecules.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 237-242
Qi-ming FENG, Bo FENG, Yi-ping LU
School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 21 November 2011; accepted 21 February 2012
Abstract: The effects of copper ions and calcium ions on the depression of chlorite using CMC (carboxymethyl cellulose) as a depressant were studied through flotation tests, adsorption measurements, ζ potential tests and co-precipitation experiments. The results show that the electrostatic repulsion between the CMC molecules and the chlorite surfaces hinders the approach of the CMC to the chlorite while the presence of copper ions and calcium ions enhances the adsorption density of CMC. The action mechanisms of these two types of ions are different. Calcium ions can not adsorb onto the mineral surfaces, but they can interact with the CMC molecules, thus reducing the charge of the CMC and enhancing adsorption density. Copper ions can adsorb onto the mineral surfaces, which facilitates the CMC adsorption through acid/base interaction. The enhanced adsorption density is also attributed to the decreased electrostatic repulsion between the CMC and mineral surfaces as copper ions reduce the surface charge of both the mineral surfaces and the CMC molecules.
Key words: chlorite; carboxymethyl cellulose; copper ions; calcium ions; adsorption
1 Introduction
Chlorite is a magnesium rich phyllosilicate mineral that occurs as a gangue component of many metal sulfide ore deposits around the world. Chlorite may report to flotation concentrates, thus reducing the concentrate grade [1]. Since chlorite is a magnesium silicate mineral, large quantity of chlorite in flotation concentrates can cause problems during smelting [2]. The depression of chlorite in oxide and sulphide flotation can be achieved using reagents typically used for the depression of silicate minerals, such as Na2SiO3, CMC and fluorocompounds [3]. CMC is a commonly used silicate depressant and has been used in separating sulphide minerals from gangues containing chlorite [4].
Carboxymethyl cellulose, or more correct sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, is the sodium salt of a carboxymethyl ether of cellulose. CMC has carboxyl substituent groups along the cellulose chain, which render the polymer significantly anionic [5,6]. In order for CMC to exert its depression effect it must first adsorb on the surface of the mineral. The mechanisms of adsorption of CMC onto minerals have been widely studied, with hydrophobic bonding considered to be the primary adsorption mechanism [7-9]. LIU et al [10] proposed a different mechanism that the adsorption of polysaccharide molecules results from the acid/base interactions between the polysaccharide and the metal hydroxyl complexes present on the mineral surface. As CMC is an anionic polymer, many studies have demonstrated that the adsorption density of CMC onto mineral is strongly dependent on the ionic strength of the solution [11-16]. This phenomenon is chiefly attributed to two factors: the thinning of electrical double layers around both the mineral surface and the CMC macromolecules, thus reducing the electrostatic repulsion, as well as the increased degree of coiling of a CMC macromolecule in the presence of a high concentration of electrolyte. The latter was confirmed by the intrinsic viscosity measurements of polymer solutions at varying levels of supporting electrolyte [17]. However, different ions have different effects on the adsorption of CMC on minerals, and the action mechanisms of metal cations affecting the interaction between CMC and chlorite have not been systematically explained.
In the present work, the influence of two types of cations on the adsorption of CMC on chlorite is systematically studied. Moreover, the mechanisms of the effect of ions on CMC adsorption are also discussed for providing a reference for further study.
2 Experimental
2.1 Samples and reagents
The chlorite used for all experiments was obtained from Haicheng, Liaoning Province, China. Mineralogical and X-ray powder diffraction data confirmed that the chlorite sample was of high purity with trace amounts of talc (Fig. 1). The sample was dry ground and screened through 150, 75 and 37 μm series sieves. All the different size fractions were collected and kept separately for various studies.
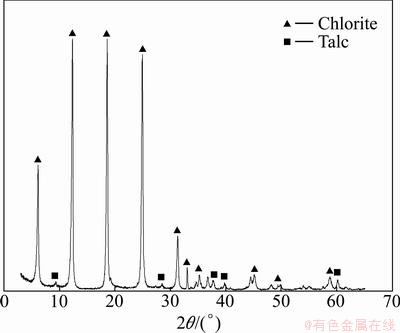
Fig. 1 XRD of chlorite
The samples of CMC used in the study were obtained from Tianjin Kermil Chemical Reagents Development Centre, Tianjin, China. The relative molecular mass of CMC is 700000 and DS (degree of substituent) is 0.9. The CMC solution was prepared by dispersing a known mass of sample in cold distilled water and then dissolving it in boiling distilled water. The solutions were prepared fresh each day.
Potassium nitrate was used to maintain the ionic strength and hydrochloric acid and potassium hydroxide were used as the pH modifiers. All the reagents used in this study were of analytical grade. Deionized double distilled water was used for all tests.
2.2 Experiments
2.2.1 Adsorption studies
For the adsorption tests, 1 g of chlorite powder was taken and made up to 40 mL after addition of desired concentration of CMC solution in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. The suspensions were then agitated for 0.5 h using a magnetic stirrer. The suspensions were then centrifuged and the supernatants were pipetted out for determination of CMC concentration by the method suggested by DUBOIS et al [18].
2.2.2 Flotation tests
Single mineral flotation tests were carried out in a microflotation cell. The mineral suspension was prepared by adding 2.0 g of minerals to 40 mL of solution. The pH of the mineral suspension was adjusted to a desired value by adding KOH or HCL stock solution. The prepared CMC solution was added at a desired concentration and conditioned for 5 min. Flotation was allowed for a total of 4 min. The floated and unfloated particles were collected, filtered and dried. The flotation recovery was calculated based on the solid mass distributions between the two products.
2.2.3 Zeta potential measurements
Small amount of chlorite was added to desired amount of 10-3 mol/L KNO3 solution and ultrasonicated for 3 min, magnetically stirred for 10 min and the pH was adjusted using HCl or KOH. Finally, the ions solution was added and left for conditioning for 10 min. The zeta potential was then measured using a zeta plus potential meter.
2.2.4 Co-precipitation tests
Co-precipitation tests were carried out between CMC and copper/calcium ions in aqueous solution to elucidate the interaction in the solution. A known amount of cupric chloride/calcium chloride solution was mixed with CMC solution. The pH was adjusted by adding KOH solution. The suspensions were then agitated for 0.5 h using a magnetic stirrer. After equilibration, the solution was centrifuged at 5000 r/min for 10 min. The supernatant was then analyzed for total copper/ calcium ions by ICP (inductive coupled plasma emission spectrometer) tests.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of ions on adsorption of CMC on chlorite
Flotation tests were carried out at pH 9 under various ionic concentrations to establish the effects that the types of ions had to the flotation response of chlorite in the presence of CMC depressant. Figure 2 indicates that the higher the ionic concentration is, the more effective the depression of chlorite by CMC irrespective of the types of ions is. However, it is clear that calcium ions are far less effective in promoting depression than copper ions. Full depression of chlorite is reached at a lower copper ions concentration than calcium ions.
In order for depressants to exert their depression they must first adsorb on the surface of the mineral to render them hydrophilic. Therefore, the adsorption of polymers onto the mineral surface is an important factor affecting the flotation response. A series of adsorption studies were carried out to probe the effect of ion types on the adsorption density of the CMC. The results are presented in Fig. 3. It is readily evident that the adsorption density of CMC reduces with the increase of pH from 3 to 9 since CMC is more negatively charged at pH 9 than at pH 3 and the surface charge of chlorite does change negative from pH 3 to 9. It can be concluded that the electrostatic repulsion plays an important role in this system. The adsorption density of CMC onto chlorite increases with the addition of copper ions and calcium ions at pH 9. With the same concentration, a greater adsorption density of CMC on chlorite is obtained with copper ions than with calcium ions. These results complement the microflotation data and illustrate that copper ions and calcium ions have different effects on the adsorption of CMC onto chlorite surfaces.
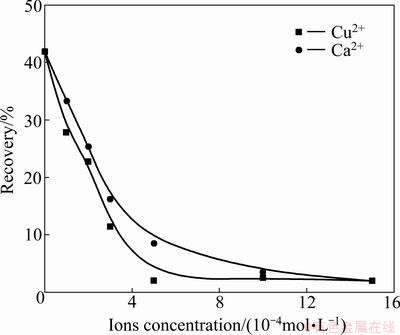
Fig. 2 Effect of ionic concentration on depression of CMC with flotation conditions of pH=9.0, c(PAX)=1×10-4 mol/L and c(MIBC)=1×10-4 mol/L
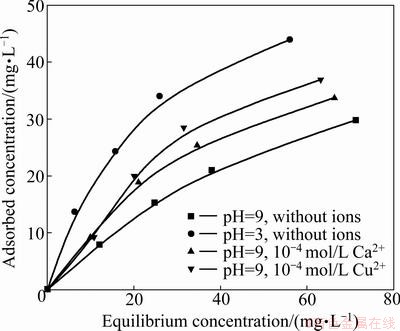
Fig. 3 Effect of ions on adsorption density of CMC onto chlorite
3.2 Mechanisms of ions affecting CMC adsorption density
The results from the microflotation and adsorption experiments above suggest that there is a difference in the adsorption amount of CMC on the mineral surfaces in the presence of copper ions as opposed to calcium ions. In order to investigate the reason why copper ions and calcium ions have different effects on the adsorption amount of CMC, the interactions of ions with chlorite surfaces and with CMC molecules were evaluated.
3.2.1 Adsorption of ions onto chlorite surface
Adsorption amounts of ions in the absence of CMC were measured at pH 9 by ICP. The results are presented in Fig. 4. It can be seen that the adsorption of calcium ions onto chlorite surfaces at pH 9 is negligible. With the increasing calcium initial concentration, the adsorption concentration never changes. From Fig. 5, we can see that at pH 9, only a tiny fraction of calcium ions exist in the form of hydroxyl complexes and the adsorption of divalent calcium ions onto the mineral surfaces is thermodynamically unfavourable [19].
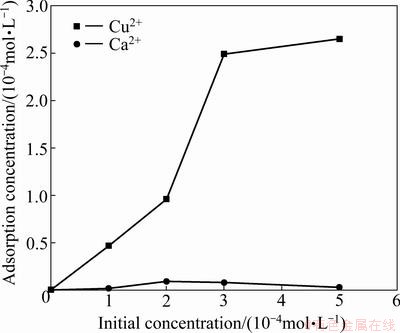
Fig. 4 Adsorption amount of ions on chlorite in the absence of CMC at pH 9
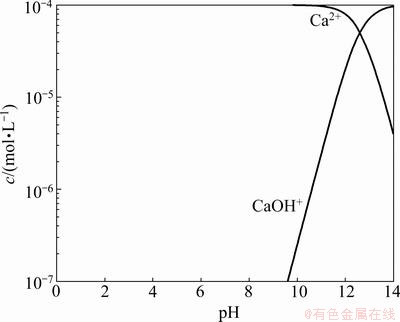
Fig. 5 Species distribution diagram for Ca2+ at 1×10-4 mol/L
Different from the calcium ions, Fig. 4 shows that the copper ions significantly adsorb onto the surfaces of chlorite at pH 9. Many researchers found the adsorption of ions increases with the increasing amount of hydroxyl complexes [20,21]. Figure 6 shows that most of the copper ions exist in the form of hydroxyl complexes at pH 9, so the adsorption of copper ions is mainly in the form of hydroxyl complexes. The adsorption of hydroxyl species on the surfaces of chlorite increases the overall number of metal hydroxide sites on the mineral surfaces. This may cause an increase in the amount of CMC adsorption through the acid/base interactions (i.e. hydrogen bonding, or some form of chemical interactions).
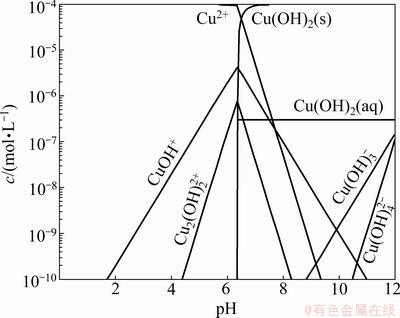
Fig. 6 Species distribution diagram for Cu2+ at 1×10-4 mol/L
The zeta potentials of chlorite particles as a function of pH in the absence and presence of ions are shown in Fig. 7. It can be seen from the zeta potential curve without metal ions that the chlorite has a point-of-zero charge (PZC) of pH 4.5. The zeta potential of chlorite becomes increasingly negative as the pH increases above 4.5. In the presence of 1×10-4 mol/L copper ions, positive shifts in zeta potential of the chlorite are observed in a wide pH range. This apparently arises from the presence of the metal species in the system. Different from the effect of copper ions, the addition of calcium ions has a negligible effect on the zeta potential of chlorite. The results confirm that the copper ions adsorbed on the chlorite surfaces at pH 9 while the calcium ions did not. Positive shifts in the zeta potential of the chlorite caused by the addition of copper ions will reduce the electrostatic repulsion between CMC and chlorite mineral surfaces, thus increasing adsorption density of CMC.
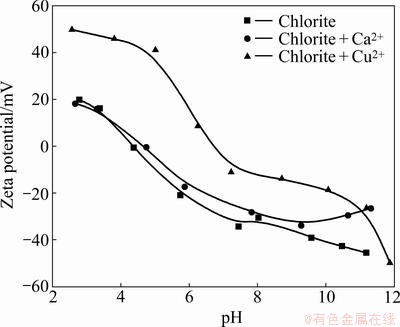
Fig. 7 Zeta potential of chlorite as function of pH in absence and presence of ions
3.2.2 Interaction between ions and CMC molecules
The calcium ions can not adsorb on the chlorite surfaces at pH 9. However, the adsorption of calcium ions on the chlorite surfaces increases dramatically when CMC is present in solution. From Fig. 8, we can see that 3×10-5 mol/L calcium ions adsorb onto the chlorite surfaces when 1×10-4 mol/L calcium ions are added into the solution. Since the adsorption of calcium ions direct onto the surfaces is unfavourable, the ions must be brought in touch with the chlorite by catching a ride on the CMC macromolecules [22]. The adsorbed amount of copper ions also increases from 4.67×10-5 mol/L to 8×10-5 mol/L in the presence of CMC, illustrating that the copper ions also interact with the CMC molecules.
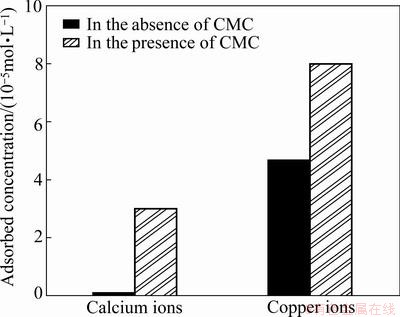
Fig. 8 Adsorbed amount of ions on chlorite in absence and presence of CMC at pH 9
The carboxylic acid groups on the CMC macromolecules are known to react with calcium ions [23]. The results of the co-precipitation tests conducted by interacting CMC with copper ions and calcium ions are given in Table 1. It is apparent from the results that the total concentration of copper species in the solution decreases significantly from 1×10-2 mol/L to 0.065×10-2 mol/L and that of calcium ions decreases from 1×10-2 mol/L to 0.461×10-2 mol/L with the addition of CMC. These studies prove that both the copper and calcium ions interact with CMC in the bulk solution and an increase in the adsorption amount of calcium ions and copper ions onto the chlorite surface in the presence of CMC molecules is caused by the chemical reaction which takes place in the solution between the ions and the CMC molecules.
The interaction between the copper and calcium ions and the CMC macromolecules in the bulk solution makes the CMC less negatively, so the electrostatic repulsion between the chlorite and the CMC molecules decreased and the adsorption density of CMC increased on the chlorite surface.
Table 1 Co-precipitation test results of ions and CMC macromolecules at pH 9

4 Conclusions
1) At pH 9, both CMC macromolecules and chlorite surfaces are negatively charged, and the electrostatic repulsion between the CMC molecules and the chlorite surfaces hinders the adsorption of the CMC molecules onto the chlorite surfaces. Both the copper ions and the calcium ions enhance the adsorption density of CMC. CMC adsorbs more densely onto the surfaces of chlorite in the presence of copper ions than in the presence of calcium ions at the same ionic concentration.
2) Only a tiny fraction of calcium ions exist in the form of hydroxyl complexes at pH 9 and the adsorption of divalent calcium ions onto the mineral surface is thermodynamically unfavourable. However, copper ions can adsorb onto the surface of chlorite in the form of hydroxyl complexes at pH 9. Both types of ions can interact with the negatively charged sites on the CMC molecules.
3) The increase of the adsorption density of CMC is due to the adsorbed ions on chlorite surface providing the adsorption sites for CMC, and the interaction between the ions and the CMC macromolecules also increases the adsorption density by decreasing the electrostatic repulsion between the CMC and the chlorite surface.
References
[1] FORNASIERO D, RALSTON J. Cu(II) and Ni(II) activation in the flotation of quartz, serpentine and chlorite [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2005, 76(1-2): 75-81.
[2] ZHANG Xiu-pin, DAI Hui-xin. Research on magnesium reduction of a nickel ore beneficiation [J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2006, 35(3): 12-17. (in Chinese)
[3] ZHENG Gui-shan, LIU Li-jun, LIU Jiong-tian, WANG Yong-tian, CAO Yi-jun. Study of chlorite flotation and its influencing factors [J]. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 2009, 1(1): 830-837
[4] SILVESTER E J, BRUCKARDAND W J, WOODCOCK J T. Surface and chemical properties of chlorite in relation to its flotation and depression [J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2011, 120(2): 65-70.
[5] JENKINS P, RALSTON J. The adsorption of a polysaccharide at the talc aqueous solution interface [J]. Colloids and Surfaces, 1998, 139(1): 27-40.
[6] MACKENZIE J, SALMAN T. Guar based reagents [J]. Engineering and Mining Journal, 1980, 10: 80-87.
[7] STEENBERG E, HARRIS P J. Adsorption of carboxymethyl cellulose, guar gum and starch onto talc, sulphides, oxides and salt type minerals [J]. South African Journal of Chemistry, 1984, 37: 85-90.
[8] MORRIS G E, FORNASIERO D, RALSTON J. Polymer depressants at the talc–water interface: Adsorption isotherm, microflotation and electrokinetic studies [J]. International Journal of Minerals Processing, 2002, 67: 211-227.
[9] WANG J, SOMASUNDARN P. Adsorption and conformation of carboxymethylcellulose at solid-liquid interfaces using spectroscopic, AFM and allied techniques [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2005, 291(1): 75-83.
[10] LIU Q, ZHANG Y, LASKOWSKI J S. The adsorption of polysaccharides onto mineral surfaces: An acid/base interaction [J]. International Journal of Minerals Processing, 2000, 60: 229-254.
[11] CAWOOD S R, HARRIS P J, BRADSHAW D J. A simple method for establishing whether the adsorption of polysaccharides on talc is a reversible process [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18(1): 1060-1063.
[12] BEAUSSART A, VASILEV A M, BEATTIE D A. Evolution of carboxymethyl cellulose layer morphology on hydrophobic mineral surfaces: Variation of polymer concentration and ionic strength [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 346 (2): 303-310.
[13] BICAK O, EKMEKCI Z, BRADSHAW D J, HARRIS P J. Adsorption of guar gum and CMC on pyrite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20(10): 996-1002.
[14] SHORTRIDGE P G, HARRIS P J, BRADSHAW D J, KOOPAL L K. The effect of chemical composition and molecula weight of polysaccharide depressants on the flotation of talc [J]. International Journal of Minerals Processing, 2000, 59(3): 215-224.
[15] KHRAASHEH M, HOLLAND C, CREANY C, HARRIS P, PAROLIS L. Effect of molecular weight and concentration on the adsorption of CMC onto talc at different ionic strengths [J]. International Journal of Minerals Processing, 2005, 75(3-4): 197-206.
[16] PAROLIS L A, MERWE V D, GROENMEYER G V, HARRIS P. The influence of metal cations on the behaviour of carboxymethyl celluloses as talc depressants [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A, 2008, 317: 109-115.
[17] PAWLIK M, LASKOWSKI J S, ANSARI A. Effect of carboxymethylcellulose and ionic strength on the stability of mineral suspensions in a potash ore flotation system [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2003, 260(2): 251-258.
[18] DUBOIS M., GILES K A, HAMILTON J K, REBERS P A, SMITH F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1956, 28(3): 350-356.
[19] AHMED S M, CLEAVE A B. Adsorption and flotation studies with quartz: Part I. Adsorption of calcium, hydrogen and hydroxyl ions on quartz [J]. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1965, 43: 23-65.
[20] JAMES R O, HEALY T W. Adsorption of hydrolyzable metal ions at the oxide–water interface: III. A thermodynamic model of adsorption [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1972, 40(1): 65-81.
[21] JAMES R O. HEALY T W. Adsorption of hydrolyzable metal ions at the oxide–water Interface: I. Co(II) adsorption on SiO2 and TiO2 as model systems [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1972, 40(1): 42-52.
[22] BURDUKOVA E, VAN LEERDAM G C, PRINS F E, SMEINK R G, BRADSHAW D G, LASKOWSKI J S. Effect of calcium ions on the adsorption of CMC onto the basal planes of New York talc–A ToF-SIMS study [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2008, 21: 1020-1025.
[23] FIXMAN M P. Polyelectrolytes: A fuzzy sphere model [J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1964, 41: 3772-3778.
冯其明,冯 博,卢毅屏
中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:通过浮选实验、吸附量测试、ζ电位测试和共沉淀实验,研究铜离子和钙离子对羧甲基纤维素(CMC)抑制绿泥石浮选的影响。结果表明,CMC分子和绿泥石表面存在的静电排斥作用阻碍CMC在绿泥石表面的吸附,铜离子和钙离子的存在增加CMC在绿泥石表面的吸附量。两种离子增加CMC吸附量的作用机理存在不同。在pH 9的条件下,钙离子不能吸附在绿泥石表面,但能与荷负电的CMC分子反应,减弱CMC与绿泥石表面的静电排斥作用,从而增加CMC的吸附量;铜离子能吸附在绿泥石表面为CMC的吸附提供质点,吸附在绿泥石表面和CMC分子上的铜离子降低二者的电位,减弱静电排斥作用,从而增加CMC在绿泥石表面的吸附量。
关键词:绿泥石;羧甲基纤维素;铜离子;钙离子;吸附
(Edited by Hua YANG)
Foundation item: Project (51174229) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Qi-ming FENG; Tel/Fax: +86-731-88836817; E-mail: feng_309@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62451-6

