
Electrochemical corrosion properties of Zr- and Ti-based bulk metallic glasses
KOU Hong-chao1, LI Yong1, ZHANG Tie-bang1, LI Jian2, LI Jin-shan1
1. State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, Northwestern Polytechnical University,Xi’an 710072, China;
2. Wuhan Research Institute of Materials Protection, Wuhan 430030, China
Received 18 June 2010; accepted 18 November 2010
Abstract: The corrosion behaviors of Ti-based and Zr-based amorphous alloys and their corresponding crystallized alloys were studied by electrochemical methods. It is found that the corrosion potentials of Zr-based amorphous alloy and its corresponding crystalline counterpart are both lower than those of the Ti-based amorphous alloy in the 1 mol/L H2SO4 solution. In the 3.5% NaCl solution,Zr-based crystallized alloy exhibits the lowest corrosion potential among the experimental samples. No passivation is observed in the corrosion process for the Zr-based crystalline alloy. However, Zr- and Ti-based amorphous alloys both exhibit passivation characteristics. EIS measurements indicate the amorphous alloys exhibit better corrosion resistance than the crystallized one in the NaCl solution. Surface analysis shows that both amorphous alloys in the NaCl solution are eroded by pitting corrosion. In the H2SO4 solution, all the alloys display similar behaviors and their surfaces can mostly keep intact except for some cracks on the corroded surface at local region.
Key words: bulk metallic glasses; pitting corrosion; corrosion resistance; passivation
1 Introduction
Bulk metallic glasses (BMGs) have attracted increasing attention in the past decade due to their excellent properties which are not achievable for the conventional crystalline materials[1-2]. The excellent corrosion resistance, high wear resistance, biocompatibility, low elastic modulus and high fracture toughness make the BMGs promising candidates for functional and structural materials[3-4]. Many amorphous alloys have been found to exhibit high corrosion resistance in rigorous conditions such as concentrated hydrochloric and phosphoric acids, where most conventional crystalline metallic materials suffer serious corrosion[5-6]. It has been shown that the high corrosion resistance of amorphous alloys is related to their high chemical homogeneity and reactivity[1, 7]. The lack of dislocation, grain boundary, vacancy and other crystalline defects, which always act as initiation sites of corrosion, results in the formation of uniform protective surface films[8]. Among these alloys, Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Be system bulk amorphous alloys have attracted special attention in the past few years because of their high glass forming ability (Rc=1 K/s), excellent mechanical and engineering properties[9-10].
Some corrosion studies have been reported on the BMGs. For instance, a few investigations have been reported on Zr-based amorphous alloys in different corrosive media[11-13]. The results indicate that Zr-based amorphous alloys are usually prone to pitting in chloride solutions and exhibit a higher corrosion resistance than stainless steel, but the corrosion resistance of BMGs is not as good as that of stainless steel in HCl solution[11-12]. The previous studies almost focused on the corrosion behaviors of the amorphous alloys, which and compared with the conventional steel. And it has been shown the various aqueous solutions and element composition also play an important role on corrosion behavior in addition to their homogeneous structure because the tendency of a metal to passivate depends on alloy composition and solution chemistry. This is the reason that the BMGs are not always superior to be crystalline alloys in their corrosion. Therefore, further study is needed for the regularity of corrosion resistance about amorphous alloys.
In this work, the corrosion behaviors of the bulk amorphous Ti40Zr25Ni8Cu9Be18 alloy, the bulk amorphous Zr41.25Ti13.75Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 alloy and its crystalline counterpart were investigated. The effects of composition and structural variation on electrochemical response of the alloys in different corrosive solutions were established through comparing their corrosion behaviors with each other.
2 Experimental
The two kinds of master alloy ingots used in the experiment were prepared by arc melting a mixture of pure Zr, Ti, Ni, Cu and Be in a Ti-gettered argon atmosphere. The purities of all the components were greater than 99.6% (mass fraction). The ingots were re-melted four times to ensure the homogeneity. The amorphous plates with the dimensions of 30 mm× 20 mm×3 mm were produced by injection casting into a water cooled copper mould in an argon atmosphere. An amorphous plate was annealed in vacuum at 773 K for 5 min to obtain the fully crystallized sample. The structures of the amorphous sample and the crystallized one were investigated by X-ray diffractometry (XRD, PHILIPS X’ Pert MPD) with Co Kα radiation. Each plate was cut into a piece with the dimensions of 15 mm× 15 mm×3 mm for electrochemical experiment. All the experimental samples were mechanically polished down to 1 200 abrasive papers, cleaned by sonicleaning with absolute ethanol for 10 min, and then, immediately dried before the electrochemical tests. After connecting the samples to the wires and setting aside an area of 1 cm× 1 cm for the effective electrochemical reaction, the remaining area was sealed with paraffin wax.
The electrolytes used were 3.5% NaCl and 1 mol/L H2SO4, which were prepared from reagent grade chemical and distilled water. The electrochemical experiment was performed on a PARSTAT 2273 advanced electrochemical system with PowerSuite software (Princeton Applied Research, Oak Ridge, TN). Electrochemical measurements were conducted in a typical three-electrode cell consisted of the corrosion sample (working electrode), a platinum-foil counter electrode and a saturated calomel reference electrode. The salt bridge was agar and saturated solution of KCl. All potentials cited in the research will be referred to the saturated calomel electrode (SCE)[14]. Three electrodes constituted the polarization loop and the circuit potential measurements. There was a polarization current through the polarization loop, and its control and measurement were carried out in this circuit. The potentials related to the reference electrode potential was measured or controlled by measuring potential or using controlling instrument in the circuit of potential measurements, where there was almost no current. By using the three-electrode system the current and potential of the working electrode could be simultaneously measured, and so the polarization curve of a single electrode was obtained. The temperature for testing was (30±1) °C. The corrosion sample was allowed to stabilize in the electrolyte until the open-circuit potential changed a little about for a time period of 30 min. The point where open-circuit potential occurred was considered to be the open-circuit corrosion potential. The scanning range was from -5 V to 1.5 V at a scan rate of 1 mV/s. The frequency for testing AC impedance was 100 kHz-10 mHz and the AC voltage amplitude was 10 mV.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure characteristic
X-ray diffractometry was employed to investigate the structural characteristics of the experimental samples. Fig.1(a) shows that the as-cast Zr41.25Ti13.75Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 and Ti40Zr25Ni8Cu9Be18 amorphous alloys consist of a single glassy phase, as evidenced by a main halo peak without distinct crystalline peaks in their X-ray diffraction patterns. XRD pattern of the crystalline counterpart is shown in Fig.1(b). There are all crystalline peaks instead of the amorphous halo which are identified as ZrBe2, Zr2Cu, Zr7Cu10 crystalline phases and a few unknown phases presented in this system. It is obvious that the annealed Zr41.25Ti13.75Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 alloy mainly adopts in crystalline state.
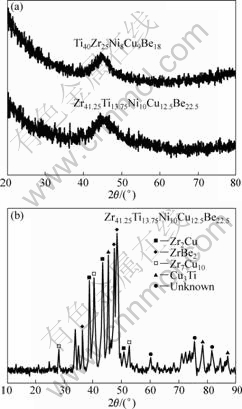
Fig.1 XRD patterns of amorphous alloys (a) and crystallized Zr41.25Ti13.75Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 alloy (b)
3.2 Potentiodynamic polarization
The corrosion behavior of the samples was examined with the help of potentiodynamic polarization measurements. Figs.2(a) and (b) show the polarization curves including anodic and cathodic polarization for the alloys in 3.5% NaCl and 1 mol/L H2SO4 solutions respectively in a water bath at 303 K. It can be seen from Fig.2 (a) that the corrosion potential of Zr-based, Ti-based amorphous alloys and the corresponding Zr-based crystalline counterpart are -0.194 V, -0.304 V and -0.385 V, respectively, in the 3.5% NaCl solution. Zr-based glassy alloy possesses the highest corrosion potential among the experimental samples, indicating the excellent corrosion resistance from the view of corrosion thermodynamics. For the Zr-based amorphous alloy, the passivation is observed at the beginning of anodic polarization. The passive film generated in the passivating process is destroyed slowly with the increase of potential. In the case of the Ti-based amorphous alloy, the processing of polarization is similar to that of the Zr-based, and there is only once for passivation. This is attributed to the increase of Zr element with low standard electrode potential (-1.53 V), resulting in a further decrease in the anodic passive current density and higher chemical stability. The passivation behavior with a significantly low current density indicates that highly
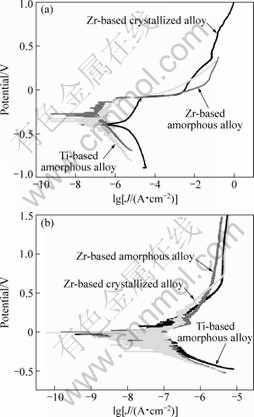
Fig.2 Polarization curves of amorphous aollys and crystallized alloys in 3.5% NaCl solution (a) and in 1 mol/L H2SO4 solution (b)
protective and uniform surface films have been formed on the surface of the BMGs exposed to the 3.5% NaCl solution. By contrast, there is no passivation in the procedure of anodic polarization for the Zr-based crystalline alloy, and corrosion rate accelerated suddenly with the increase of potential. The fully crystallized sample exhibits bad corrosion resistance in the 3.5% NaCl solution, the structural and chemical homogenization is thought to be responsible for the better corrosion resistance of the amorphous alloys compared with the crystalline counterpart in 3.5% NaCl solution. It can be seen from Fig.2(b) the corrosion potential of Zr-based, Ti-based amorphous alloys and the corresponding Zr-based crystalline counterpart are -0.025 V, 0.024 V and -0.009 V, respectively, in the 1 mol/L H2SO4 solution. The Zr-based amorphous alloy and crystalline one have similar polarization curves. They spontaneous passivated with a similar corrosion potential, but no passivation is observed in the anodic polarizing process for the Ti-based amorphous alloy. This could be explained by chemical composition, but not the structure as mentioned in the NaCl solution. For example, Zr element with low standard electrode potential plays a significant role in the electrochemical behavior for the three alloys in the 1 mol/L H2SO4 solution.
3.3 Electrochemical impedance spectra
Fig.3 shows the electrochemical impedance spectra
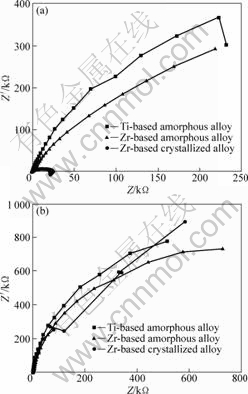
Fig.3 EIS of amorphous and crystallized alloys at open circuit potential in 3.5% NaCl solution (a) and in 1 mol/L H2SO4 solution (b)
(EIS) of samples in the NaCl and H2SO4 solutions, respectively. The Nyquist plots of the tested alloys present only one capacitive loop. Only the capacitive loop among several equivalent circuit models have been employed to fit the impedance data for the alloy system. The fitting model can be represented by the equivalent circuit composed of one parallel arrangement in series with the ohmic resistance and the result is shown in Fig.4, where the CPE is constant phase element instead of pure capacities, taking account of the deviations of the system from the ideal state due to surface heterogeneities; Rs is solution resistance; Rt is the electrochemical transfer resistance. The mathematical expression of impedance for the CPE can be signified as follows: Z=Y0-1w-n[cos(nπ/2)-jsin(nπ/2)], in which Z is the impedance of CPE; j is the imaginary part of unit; w is angular frequency; Y0 is a constant; and n is an index (0≤n≤1)[15-16]. In the low-frequency area, the increases of the impedance and the electrochemical transfer resistance result in better corrosion resistance. The charge transfer resistance becomes smaller with the
decrease of curvature radius for alloy capacitance arc, indicating the worse corrosion resistance. From the aforementioned analysis, the amorphous alloys present higher corrosion resistance compared with the crystalline counterpart in the NaCl solution but no significant difference is observed in the H2SO4 solution. The result from electrochemical impedance spectra is consistent with that obtained by polarization curves.
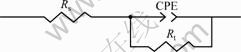
Fig.4 Equivalent circuit for amorphous alloys and crystallized alloy
3.4 Surface analysis
The observations of SEM and automated 3D non-contact surface analysis were performed after potentiodynamic polarization. The micrographs are shown in Fig.5 and Fig.6, respectively. From Fig.5, it can be seen that pitting has occurred in the amorphous alloys
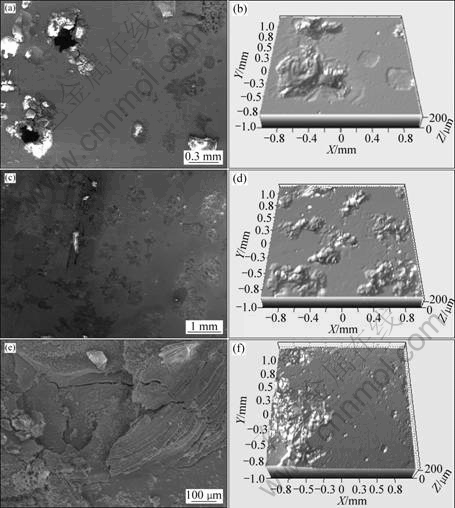
Fig.5 Micrographs of corrosion surface for alloys in NaCl solution: (a), (b) Ti40Zr25Ni8Cu9Be18 amorphous alloy; (c), (d) Zr41.25Ti13.75Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 amorphous alloy; (e), (f) Zr41.25Ti13.75Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 crystallized alloy
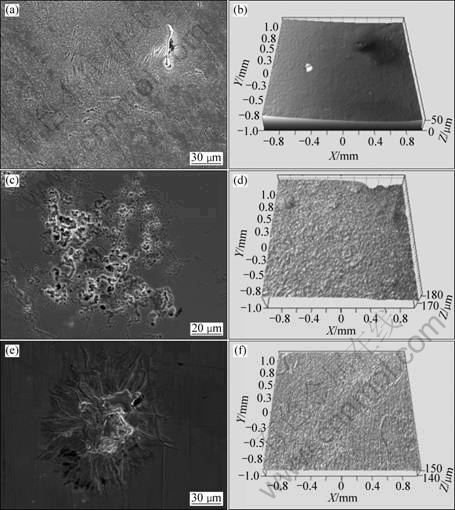

Fig.6 Micrographs of corrosion surface for alloys in H2SO4 solution: (a), (b) Ti40Zr25Ni8Cu9Be18 amorphous alloy; (c), (d) Zr41.25Ti13.75Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 amorphous alloy; (e), (f) Zr41.25Ti13.75Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 crystallized alloy
owing to breakdown of passive film in the NaCl solution, and the inhomogeneous distributed pits on the surface of the Zr-based bulk metallic glass are relatively smaller than those of the Ti-based one, which is agreement with potentiodynamic polarization result as discussed earlier. The corroded surface morphologies of the amorphous samples are different from those of crystallized samples. The fully crystallized sample shows less corrosion resistance as compared with the BMGs, which have been seriously corroded in the form of stripping and crack. The main reason for such active behavior lies in chemically inhomogeneous and crystalline defects. Fig.6 shows that all the alloys display similar behaviors, and they present some cracks on the corroded surface at local region and their surface can mostly keep intact. The morphology observations of the corroded sample confirm the potentiodynamic polarization results.
4 Conclusions
1) In the NaCl solution, the amorphous alloys both exhibit spontaneously passivated behavior and preserve better corrosion resistance than the corresponding crystallized ones. There is surface pitting only on the samples of BMGs, and it is different from the crystallized alloy where general corrosion takes place.
2) In the H2SO4 solution, all the samples exhibit similar behaviors in the processing of potentiodynamic polarization. The transformation of the relative amount of element content does not significantly affect the corrosion resistance of Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Be system bulk amorphous alloys.
References
[1] INOUE A. Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2000, 48(1): 279-306.
[2] ZHANG Xiao-li, WANG Jin-xiang, SUN Yu-xin, LIU Jia-cong. Application and research development of bulk amorphous alloys [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2007, 7(24): 6383-6390. (in Chinese)
[3] SALIMON A I, ASHBY M F, BR?CHET Y, GREER A L. Bulk metallic glasses: What are they good for? [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 375-377: 385-388.
[4] L?FFLER J F. Bulk metallic glasses [J]. Intermetallics, 2003, 11(6): 529-540.
[5] NIE X P, YANG X H, JIANG J Z. Ti microalloying effect on corrosion resistance and thermal stability of CuZr-based bulk metallic glasses [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 481(2): 498-502.
[6] MONDAL K, MURTY B S, CHATTERJEE U K. Electrochemical behavior of multicomponent amorphous and nanocrystalline Zr-based alloys in different environments [J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(8): 2212-2225.
[7] PANG S J, ZHANG T, ASAMI K, INOUE A. Bulk glassy Fe-Cr-Mo-C-B alloys with high corrosion resistance [J]. Corrosion Science, 2002, 44(8): 1847-1856.
[8] HABAZAKI H, UKAI H, IZUMIYA K, HASHIMOTO K. Corrosion behaviour of amorphous Ni-Cr-Nb-P-B bulk alloys in 6 M HCl solution [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 318(2): 77-86.
[9] LU J, RAVICHANDRAN G, JOHNSON W L. Deformation behavior of the Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 bulk metallic glass over a wide range of strain-rates and temperatures [J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(12): 3429-3443.
[10] TSAU C H, WU C C, WU S S. The thermal stability and mechanical behaviors of Zr-Cu-Ni-Ti-Be bulk metallic glasses [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 182: 257-261.
[11] POURGASHTI M H, MARZBANRAD E, AHMADI E. Corrosion behavior of Zr41.2Ti13.8Ni10Cu12.5Be22.5 bulk metallic glass in various aqueous solutions [J]. Materials & Design, 2010, 31(5): 2676-2679.
[12] CHIEH T C, CHU J, LIU C T, WU J K. Corrosion of Zr52.5Cu17.9Ni14.6Al10Ti5 bulk metallic glasses in aqueous solutions [J]. Materials Letters, 2003, 57(20): 3022-3025.
[13] MONDAL K, MURTY B S, CHATTERJEE U K. Electrochemical behaviour of amorphous and nanoquasicrystalline Zr-Pd and Zr-Pt alloys in different environments [J]. Corrosion Science, 2005, 47(11): 2619-2635.
[14] MORRISON M L, BUCHANAN R A, PEKER A, LIAW P K, HORTON J A. Electrochemical behavior of a Ti-based bulk metallic glass [J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2007, 353: 2115-2124.
[15] MENG Q G, ZHANG S G, LI J G. Corrosion and oxidation behavior of Pr-based bulk metallic glasses [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 452(2): 273-278.
[16] WANG Cheng, ZHANG Qing-sheng, JIANG Feng, ZHANG Hai-feng, HU Zhuang-lin. Corrosion behavior of Mg65Y10Cu25 amorphous alloy in 3.5 %NaCl solution [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(5): 1016-1020. (in Chinese)
Zr基和Ti基块体非晶合金的电化学腐蚀性能
寇宏超1,李 勇1,张铁邦1,李 健2,李金山1
1. 西北工业大学 凝固技术国家重点实验室,西安 710072;
2. 武汉材料保护研究所,武汉 430030
摘 要:用电化学方法研究Ti基和Zr基非晶合金及与非晶成分相同的Zr基晶态合金在1 mol/L H2SO4和3.5% NaCl溶液中的腐蚀行为。极化曲线测试结果表明:在H2SO4溶液中,Zr基非晶和晶态合金自腐蚀电位比Ti基非晶合金的低;在NaCl溶液中,Zr基晶态合金的自腐蚀电位最低,而且在腐蚀过程中没有发生钝化,然而非晶合金都表现出钝化特性。交流阻抗测试结果表明:在NaCl溶液中非晶合金比晶态合金表现出更好的耐腐蚀性能,但是在H2SO4溶液中并没看到它们之间有明显的区别。表面形貌分析表明:在NaCl溶液中,这2种非晶合金都发生点蚀,而在H2SO4溶液中所有试验合金都表现出类似的特征,试样表面基本保持平整,只是在腐蚀表面的局部区域有一些裂纹出现。
关键词:块体非晶合金;点蚀;耐腐蚀性;钝化
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Project (2007CB607603) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project (B08040) supported by the “111” Project, China
Corresponding author: ZHANG Tie-bang; Tel: +86-29-88491764; E-mail: tiebangzhang@nwpu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60750-4