Microstructures of rapidly solidified Al-In immiscible alloy
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2001年第1期
论文作者:刘源 郭景杰 苏彦庆 丁宏生 贾均
文章页码:84 - 89
Key words:Al-In immiscible alloy; rapid solidification; microstructure
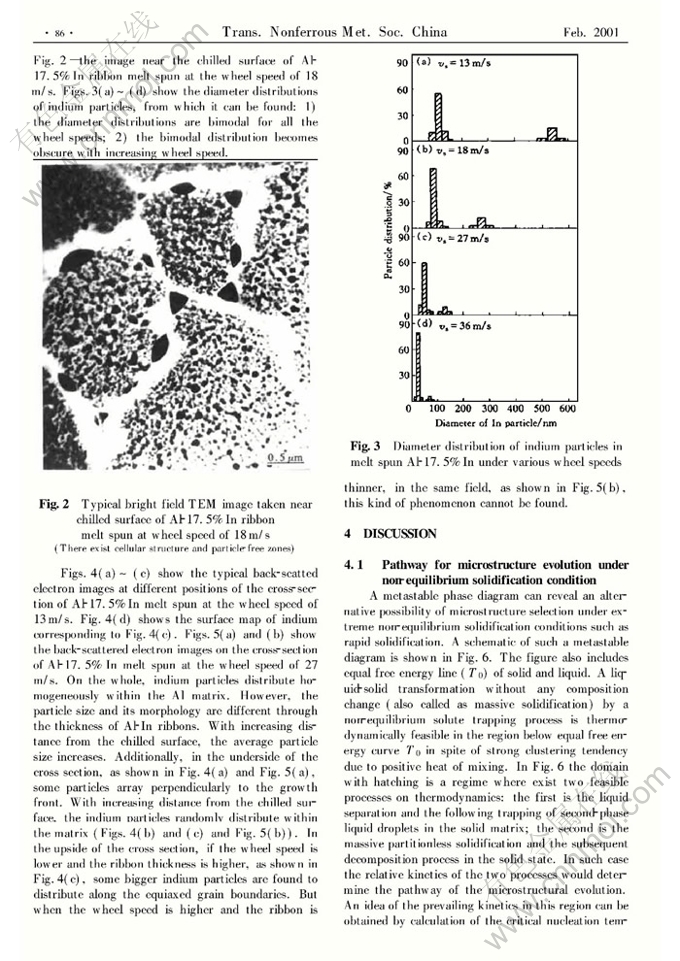
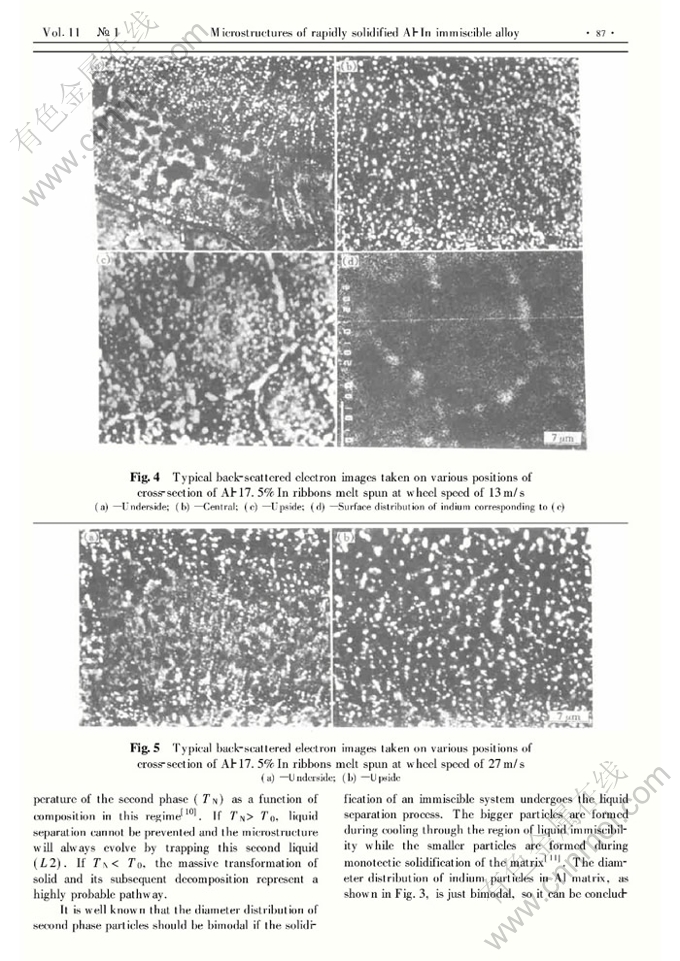
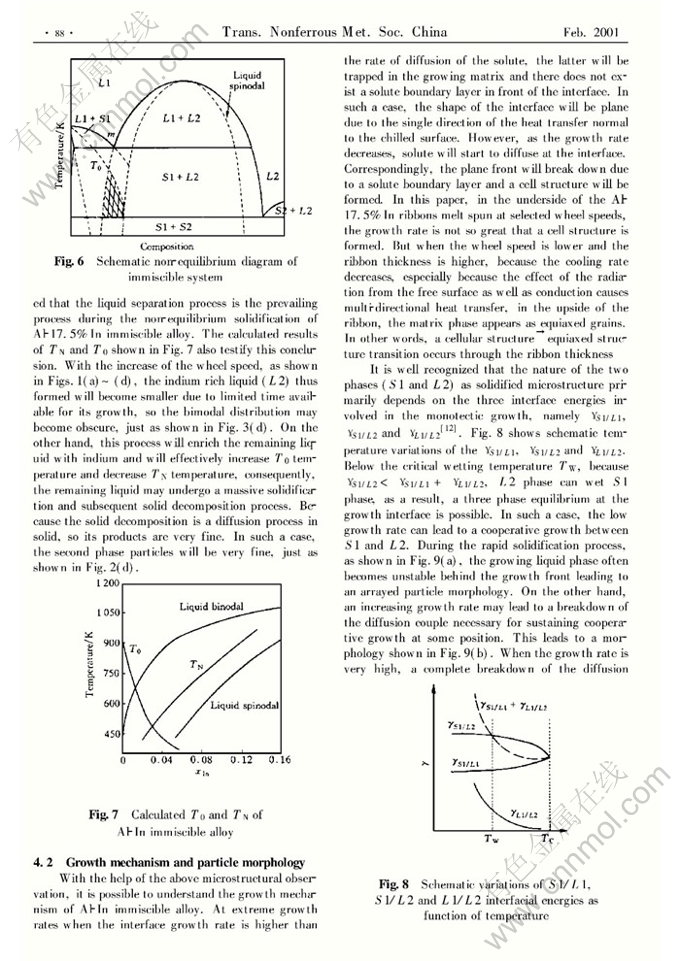
Abstract: The microstructural evolution and growth mechanism of the melt spun Al-In monotectic alloy were studied. During the rapid solidification of Al-17.5%In, a cellular structure→equiaxed structure transition occurs through the ribbon thickness. The as-solidified microstructures are characterized by a homogeneous distribution of nanometer sized indium particles embedded within the matrix. However, with increasing distance from the chilled surface, the average particle size increases. In the underside of the ribbon, some particle arrays are perpendicular to the growth front. Next, all of the indium particles distribute randomly within the matrix. In the upside of the ribbon, some bigger indium particles distribute along the equiaxed grain boundaries. The diameter distributions of indium particles within Al matrix are bimodal. Compared with the massive partitionless solidification, the liquid separation process is the prevailing process during the nonequilibrium solidification. The cooling rate, the interface energies (γS1/L1,γS1/L2 and γL1/L2) and the growth mechanism all have effects on the microstructure.