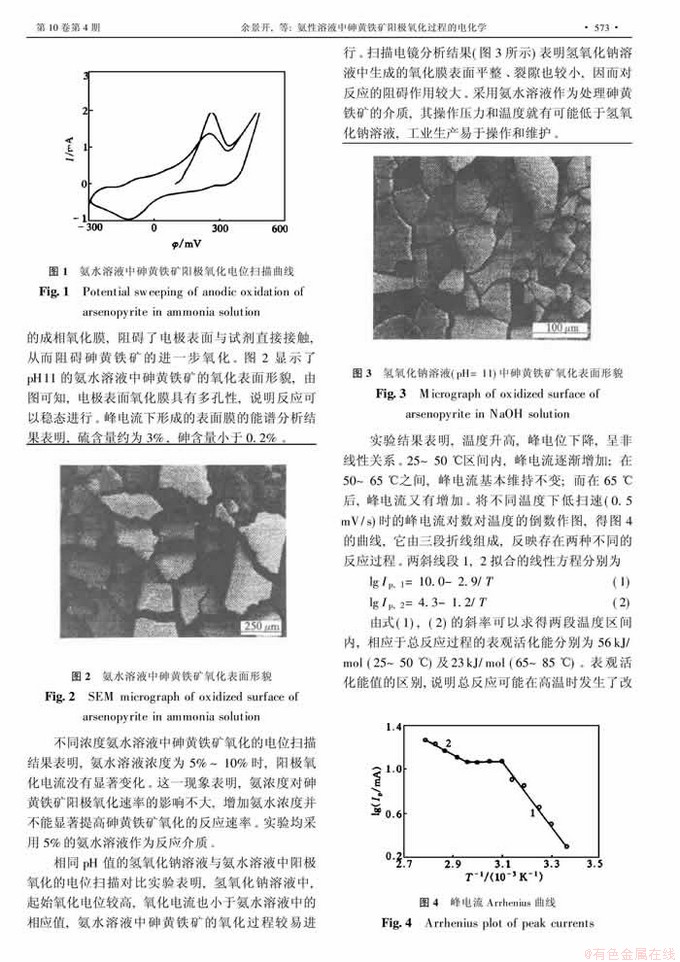
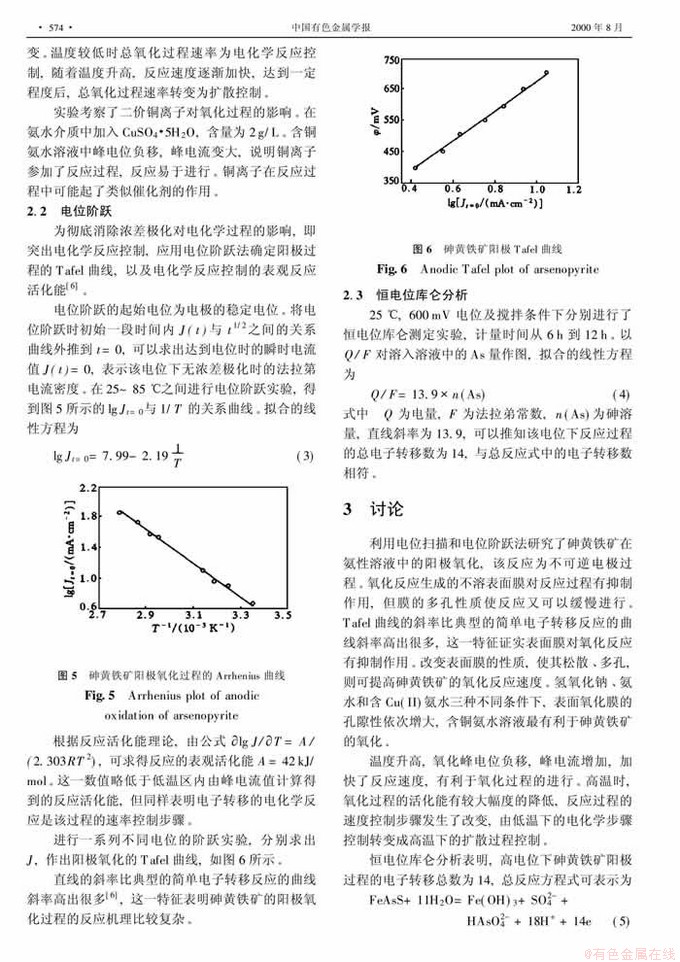
氨性溶液中砷黄铁矿阳极氧化过程的电化学
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2000年第4期
论文作者:余景开 方兆珩
文章页码:572 - 575
关键词:砷黄铁矿; 阳极氧化; 氨溶液; 电化学
Key words:arsenopyrite; anodic process; ammonia solution
摘 要:通过电化学研究, 考察了氨溶液中砷黄铁矿的阳极氧化反应。 实验表明氧化生成的表面膜对反应有抑制作用,该膜具有多孔性, 可使反应继续进行。 低温时, 阳极氧化过程由电化学反应控制; 高温时, 反应受扩散过程控制。 氨浓度对氧化过程的反应速率没有显著影响, 溶液中Cu2+ 能降低氧化峰电位, 改变氧化表面膜的形态, 使膜的孔隙增大, 反应速度加快。 砷黄铁矿的阳极氧化总反应为FeAsS+11H2O=Fe(OH)3 + SO42-+ HAsO42- +18H + +14e。
Abstract: Anodic process of arsenopyrite in ammonia solutions was studied by electrochemical methods. The process is an irreversible reaction with formation of a ferric oxidized film and slowed down by the film. The process rate is controlledby the electrochemical reaction on the electrode surface in the low temperaturerange, or alternatively by the diffusion process through the film in the highertemperature range. The concentration of ammonia has no remarkable effect on theprocess, and cupric ion in solutions makes the anodic peak potential shift negatively and the surface film porous, resulting in oxidation process to be accelerated. The overall reaction can be expressed as FeAsS+11H2O=Fe(OH)3 + SO42- + HAsO42- + 18H+ +14e