DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.06.09
钠离子电池正极材料VO2(B)纳米带阵列的可控合成与电化学性能
秦牡兰,刘万民,张志成,徐星星
(湖南工程学院 化学化工学院,湘潭 411104)
摘 要:以V2O5作为钒源,乙二醇作为结构导向剂和还原剂,在不使用模板的情况下,通过水热法制备VO2(B)纳米带阵列结构。利用X射线衍射仪(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和透射电子显微镜(TEM)对合成产物的晶体结构和形貌进行表征,研究乙二醇的含量和水热反应时间对产物结构和形貌的影响。作为钠离子电池正极材料,研究水热反应时间和充放电电压范围对VO2(B)电化学性能的影响。结果表明:当乙二醇含量为10 mL时,在180 ℃水热反应6 h所合成的VO2(B)纳米带阵列在1.5~4 V的电压范围内具有更好的电化学性能。
关键词:钠离子电池;正极材料;VO2(B);纳米带阵列;水热法
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-06-1151-08 中图分类号:TM912 文献标志码:A
锂离子电池因其能量密度和功率密度高、循环寿命长、自放电小和环境友好等优点,已被广泛应用于便携式电子器件中,并正向电动汽车和储能领域拓展[1-5]。但地球上锂的储量十分有限,锂的大量开发利用必将导致锂资源短缺和锂价格上涨,从而限制锂离子电池的进一步大规模发展。
钠与锂为同主族元素,两者具有相似的物理化学性质,且钠元素在地球上储量丰富,价格低廉,所以钠离子电池是一种更适合于大规模储能的新型储能电池[6-7]。然而钠离子比锂离子具有更大的尺寸,使得钠离子在电极材料中的脱嵌更加困难,因此,寻找具有合适的钠离子脱嵌结构的电极材料对钠离子电池的发展与应用非常关键[8-10]。
钒氧化物由于其理论容量大、储量丰富和价格低廉等优点而被认为是非常有前景的锂离子电池正极材料[11-13],然而,钒氧化物用作钠离子电池正极材料仍存在诸多问题[14-15]。钒氧化物的电子导电率和离子导电率较低,脱嵌钠离子过程中结构不稳定,导致其可逆容量低、倍率性能差[16-17]。钒氧化物尺寸纳米化,不仅可以缩短钠离子扩散和电子传输的距离,还可以增大电解液与电极材料的接触面积,降低极化,提高材料的利用效率,从而有效地改善其电化学性能[18-21]。
亚稳相VO2(B)作为一种典型的钒氧化物,由于其层状结构可快速地脱嵌锂离子而受到广泛关注[22-25],近年来,具有纳米结构的VO2(B)主要被研究用作锂离子电池正极材料[26-28]。WANG等[29]将制备的VO2(B)纳米片作为钠离子电池正极材料时获得了良好的高倍率循环性能,VO2(B)纳米片以1000 mA/g充放电时循环50次后仍具有70 mA·h/g的放电比容量,但在小电流密度下的循环性能还有待进一步提高。本文作者在不使用模板的情况下,以乙二醇作为结构导向剂和还原剂,通过简便的水热法制备了VO2(B)纳米带阵列,对其结构和形貌进行表征,并对其作为钠离子电池正极材料的电化学性能进行测试和分析,研究了水热反应时间和充放电电压范围对其电化学性能的影响。
1 实验
1.1 材料制备
将0.5 g V2O5粉末分散在20 mL去离子水中,搅拌5 min得到悬浮液,然后加入10 mL 乙二醇,将悬浮液倒入50 mL聚四氟乙烯内胆中,在180 ℃水热反应6 h,然后自然冷却至室温,将得到的产物过滤,分别用去离子水和无水乙醇洗涤几次,在空气中50 ℃干燥12 h后得到深蓝色产物。
1.2 材料的结构和形貌表征
通过X射线衍射(XRD, Rigaku D/max2500)对合成产物的晶体结构进行检测;采用场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM, FEI Sirion200)和透射电子显微镜(FETEM, JEOL JEM-2100F)对合成产物的结构和形貌进行表征。
1.3 材料的电化学性能测试
通过组装扣式电池对合成产物进行电化学性能检测。将活性物质VO2(B)、导电剂乙炔黑和粘连剂聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)以质量比7:2:1分散在N-甲基吡咯烷酮(NMP)溶剂中制得浆料,然后将浆料涂覆在铝箔上,在120 ℃真空干燥10 h,冲孔后得到正极片。在充满高纯氩气的手套箱中(Mikrouna, MKSS1-1305-0838),使用金属钠片作为负极,Whatman 玻璃纤维作为隔膜,溶于碳酸乙烯酯(EC)和碳酸二甲酯(DMC)(体积比为1:1)溶剂中的1 mol/L NaClO4作为电解液,组装CR2025型扣式电池。采用蓝电测试系统(Land CT2001A,武汉)通过充放电性能测试研究水热反应时间和充放电电压范围对合成产物电化学性能的影响。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 结构和形貌分析
水热反应过程中溶剂总体积设定为30 mL,研究乙二醇的含量对产物结构和形貌的影响。当乙二醇的含量分别为10、15、20和30 mL时,在180 ℃反应12 h所合成产物的XRD谱如图1所示。当乙二醇的含量分别为10和15 mL时,合成产物的所有衍射峰都能指数化为亚稳态单斜VO2(B)(空间群为C2/m),晶格参数为a=11.989 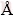 ,b=3.693
,b=3.693 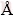 ,c=6.399
,c=6.399 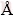 ,这与报道的标准值相吻合(PDF卡片号:31—1438,a=12.030
,这与报道的标准值相吻合(PDF卡片号:31—1438,a=12.030 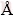 ,b=3.693
,b=3.693 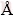 ,c=6.420
,c=6.420 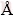 )[30];当乙二醇的含量提高到20 mL时,衍射峰的强度大大减弱,说明合成产物的结晶度大幅度降低;当乙二醇的含量达到30 mL时,没有观察到衍射峰,说明没有得到晶体相。XRD检测结果说明,乙二醇含量较低时,更有利于得到高纯度的VO2(B)相。
)[30];当乙二醇的含量提高到20 mL时,衍射峰的强度大大减弱,说明合成产物的结晶度大幅度降低;当乙二醇的含量达到30 mL时,没有观察到衍射峰,说明没有得到晶体相。XRD检测结果说明,乙二醇含量较低时,更有利于得到高纯度的VO2(B)相。
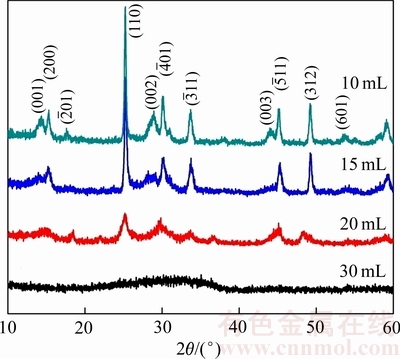
图1 以不同含量的乙二醇作为溶剂所合成产物的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of synthesized products with different contents of ethylene glycol as solvent
图2所示为以不同含量的乙二醇作为溶剂、在 180 ℃反应12 h所合成产物的SEM像。由图2(a)和(b)可看出,当乙二醇的含量分别为10和15 mL时,均能得到纳米带阵列结构,但随着乙二醇含量的增加,纳米带之间出现粘接现象;当乙二醇的含量提高到20 mL时,没有出现明显的纳米带结构,而是纳米带粘接在一起形成的块体结构;当乙二醇的含量达到30 mL时,得到的是不均匀的微米球结构。
上述实验结果说明,乙二醇含量对产物结构和形貌的影响显著。在反应体系中,乙二醇同时具有结构导向剂和还原剂的作用[31]。当乙二醇的含量比较少时,层状结构的V2O5和具有极性结构的乙二醇发生作用,被还原成VO2(B),并在脱水过程中发生取向生长,自组装成VO2(B)纳米带阵列结构。当乙二醇的含量增加时,乙二醇的结构导向作用减弱,主要起还原剂的作用。当使用纯的乙二醇作为溶剂时,在高温高压作用下,V2O5颗粒与乙二醇发生反应生成非晶态的钒化合物。因此,通过控制乙二醇的含量可实现产物的可控制备。
图3所示为乙二醇加入量为10 mL时通过不同水热反应时间所合成产物的XRD谱。由图3可知,水热反应时间分别为2、6和12 h时,所合成产物的衍射峰都与VO2(B)的特征峰相一致,且在水热反应时间为2 h所合成的产物中没有检测到不纯相,说明高纯度的VO2(B)能在2 h 内快速合成。随着水热反应时间的延长,衍射峰变得更尖锐,说明产物的结晶度更好。
图4所示为乙二醇加入量为10 mL时通过不同水热反应时间所合成产物的SEM像。当水热反应时间分别为2、6和12 h时,合成的产物均为纳米带阵列,这说明能比较容易地合成VO2(B)纳米材料,并且其形貌能得到很好的控制。纳米带阵列结构能缩短钠离子扩散和电子传输的距离,有利于电解液渗透从而增加电极材料和电解液的接触面积,并使材料能更好地承受钠离子脱嵌过程中造成的体积变化[32],因而有望表现出较好的电化学性能。
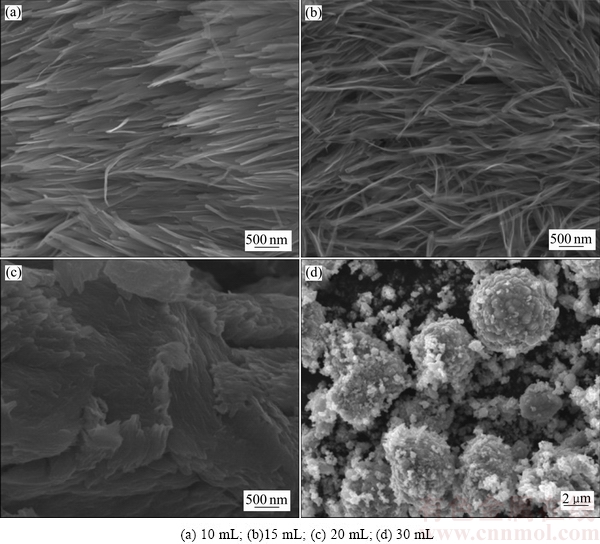
图2 以不同含量的乙二醇作为溶剂所合成产物的SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of synthesized products with different contents of ethylene glycol as solvent
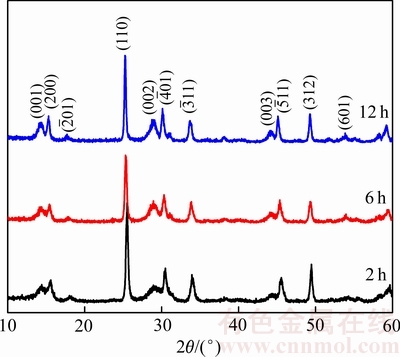
图3 不同反应时间所合成产物的XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of synthesized products with different reaction time
图5所示为乙二醇加入量为10 mL时在180 ℃水热反应6 h所合成产物的TEM像,由图5可知,产物由纳米带组成,纳米带的厚度约为10 nm,宽度约为50 nm,长度约为2 μm。HRTEM像(见图5(b))中清晰的晶格条纹说明纳米带具有很好的结晶度,观察到的0.308和0.352 nm的晶面间距分别与VO2(B)中相邻的(002)和(110)晶面的晶面间距相一致。单根VO2(B)纳米带沿着与(110)晶面呈104.5°的[110]方向生长,其(002)晶面与电解液相接触,从而有利于钠离子的扩散[26]。
2.2 电化学性能分析
通过充放电测试研究了乙二醇加入量为10 mL时,水热反应时间对VO2(B)作为钠离子电池正极材料的电化学性能的影响。由图6可知,在1.5~3.5 V的电压范围内以20 mA/g充放电时,在180 ℃水热反应6 h所合成的VO2(B)具有180 mA·h/g的初始放电比容量,循环60次后,放电比容量降低为65 mA·h/g;水热反应时间分别为2和12 h时所合成的VO2(B)分别具有162和173 mA·h/g的初始放电比容量,循环60次后,其比容量分别降低为57和55 mA·h/g;水热反应时间为6 h时,所合成的材料具有更高的放电比容量和更
好的循环性能。从XRD谱(见图3)和SEM像(见图4)中可以看出,相比于通过水热反应2 h所合成的VO2(B),通过水热反应6 h所合成的VO2(B)具有更好的结晶度和更规整的形貌;而相比于水热反应时间为12 h的产物,水热反应时间为6 h时所合成的纳米带的厚度更薄、长度更长,为钠离子和电子提供了更短的扩散距离和更好的传输路径[32]。
乙二醇加入量为10 mL时在180 ℃水热反应6 h所合成产物在不同充放电电压范围内的循环性能如图7所示。图7(a)所示为VO2(B)在不同电压范围内的首次充放电曲线。放电曲线中,在2.16 V有一个明显的放电电压平台,在其他电压范围内有宽幅的电压平台,对应于钠离子在VO2(B)电极材料中的嵌入过程,其反应式为:VO2+xNa++xe→NaxVO2;在充电曲线中,没有观察到明显的电压平台,这说明钠离子在VO2(B)电极材料中的脱嵌是一个多步相变过程[33]。VO2(B)在3.5~4.0 V有一个宽幅的充电电压平台,说明有更多的钠离子脱出。VO2(B)在1.5~4.0 V的初始放电比容量为214 mA·h/g,初始充电比容量为215 mA·h/g,要大于在1.5~3.5 V的初始放电比容量(180 mA·h/g)和初始充电比容量(140 mA·h/g)。图7(b)所示为VO2(B)在不同电压范围内以20 mA/g充放电时的循环性能。VO2(B)在1.5~4.0 V电压范围内第2次放电比容量为177 mA·h/g,从第2次循环到第60次后的容量保持率为47%;在1.5~3.5 V,第2次放电比容量为160 mA·h/g,从第2次循环到第60次后的容量保持率为40%。因此,VO2(B)在1.5~4.0 V具有更高的放电比容量和更好的循环性能。这说明VO2(B)在1.5~4.0 V电压范围内具有更好的钠离子可逆脱嵌性能。
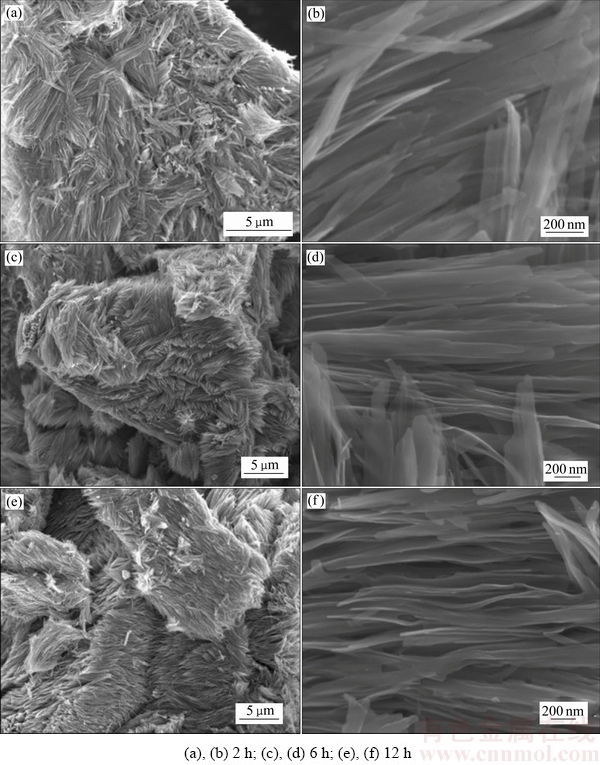
图4 不同反应时间所合成产物的SEM像
Fig. 4 SEM images of synthesized products with different reaction time
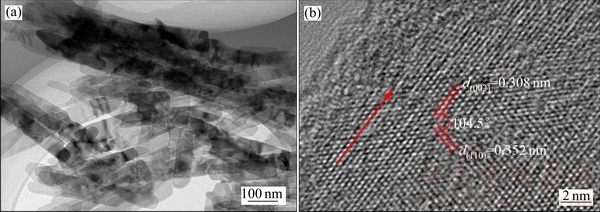
图5 VO2(B)的TEM和HRTEM像
Fig. 5 TEM (a) and HRTEM (b) images of VO2(B)
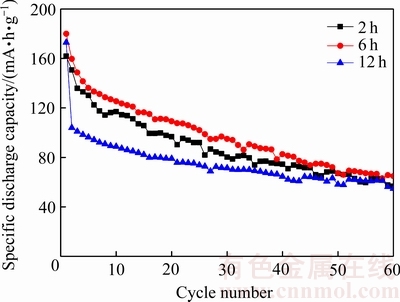
图6 不同反应时间所合成产物的循环性能
Fig. 6 Cycling performance of synthesized products with different reaction time
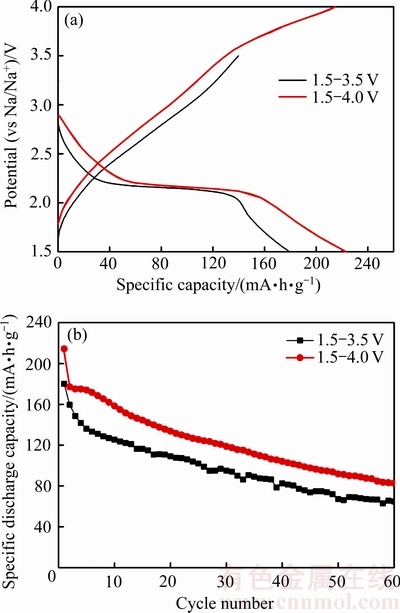
图7 VO2(B)在不同充放电电压范围内的初始充放电曲线和循环性能
Fig. 7 Galvanostatic charge/discharge curves (a) and cycling performance (b) of VO2(B) in different voltage ranges
通过充放电测试进一步研究了VO2(B)在不同电流密度下的循环性能,如图8所示。图8(a)所示为VO2(B)在不同电流密度下的初始放电曲线。以20、50和100 mA/g充放电时分别获得了214、170和159 mA·h/g 的初始放电比容量。图8(b)所示为VO2(B)在不同电流密度下的循环性能。VO2(B)在第1次和第2次充放电之间有明显的不可逆容量,这可能是由于固体电解质膜(SEI)的形成、电解液的分解以及电极材料的极化造成的[34]。VO2(B)以50 mA/g充放电时第2次放电比容量为127 mA·h/g,从第2次循环到第100次后的容量保持率达到56%。当分别以20和100 mA/g充放电时,从第2次循环到第100次后的容量保持率仅分别为33%和38%。因此,VO2(B)以较大的电流密度(如50 mA/g)充放电时具有更好的循环性能。这可能是由于VO2(B)电极材料以较小的电流密度(如20 mA/g)放电到1.5 V时,材料中能嵌入更多的钠离子,而在随后的充电过程中钠离子不能全部脱出来,从而表现出较差的循环性能[29]。
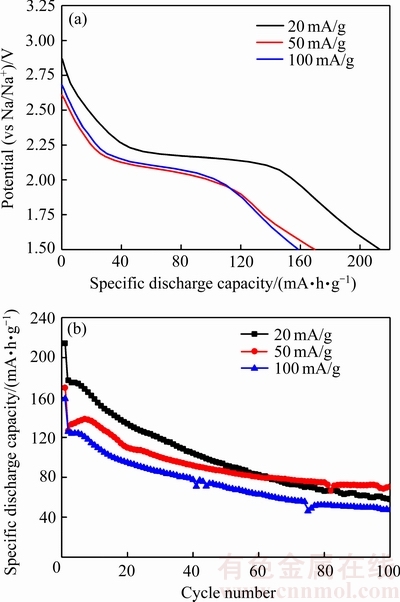
图8 VO2(B)在不同电流密度下的初始放电曲线和循环性能
Fig. 8 Galvanostatic discharge curves (a) and cycling performance (b) of VO2(B) at different current densities
3 结论
1) 以乙二醇作为结构导向剂和还原剂,通过水热法合成了亚稳相VO2(B)超薄纳米带阵列。乙二醇的含量对产物的结构和形貌影响显著,当乙二醇含量为10 mL时,在180 ℃水热反应时间6 h可制备由厚度约为10 nm、宽度约为50 nm、长度约为2 μm的纳米带组成的纳米阵列结构。
2) 作为钠离子电池正极材料,VO2(B)在1.5~4.0 V电压范围内具有更高的放电比容量和更好的循环性能。以20mA/g充放电时,具有214 mA·h/g 的初始放电比容量,以50 mA/g充放电时,循环100次后,容量保持率达到56%。
REFERENCES
[1] Scrosati B, Garche J. Lithium batteries: Status, prospects and future[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(9): 2419-2430.
[2] Manthiram A. Materials challenges and opportunities of lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2011, 2: 176-184.
[3] Jeong G, Kim Y U, Kim H, Kim Y J, Sohn H J. Prospective materials and applications for Li secondary batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(6): 1986.
[4] Etacheri V, Marom R, Elazari R, Salitra G, Aurbach D. Challenges in the development of advanced Li-ion batteries: A review[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(9): 3243.
[5] Karden E, Ploumen S, Fricke B, Miller T, Snyder K. Energy storage devices for future hybrid electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 168(1): 2-11.
[6] Yang Ting-zhou, Niu xiao-ying, Qian Tao, Shen xiao-wei, Zhou jing-qiu, Xu na, Yan cheng-lin. Half and full sodium-ion batteries based on maize with high-loading density and long-cycle life[J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(34): 15497-15504.
[7] Jiang yu, Zhang hao-chuan, Yang hai, Qi zhen-yu, Yu yan. Na3V2(PO4)3@nitrogen,sulfur-codoped 3D porous carbon enabling ultra-long cycle life sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(18): 6048-6055.
[8] 方永进, 陈重学, 艾新平, 杨汉西, 曹余良. 钠离子电池正极材料研究进展[J]. 物理化学学报, 2017, 33(1): 211-241.
FANG Yong-jin, CHEN Zhong-xue, AI Xin-ping, YANG Han-xi, CAO Yu-liang. Recent developments in cathode materials for Na ion batteries[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2017, 33(1): 211-241.
[9] 杨绍斌, 董 伟, 沈 丁, 李思南, 王中将, 张佳民, 孙 闻, 张 琴. 钠离子电池负极材料的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(5): 1054-1064.
YANG Shao-bin, DONG Wei, SHEN Ding, LI Si-nan, WANG Zhong-jiang, ZHANG Jia-min, SUN Wen, ZHANG Qin. Research progress of anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(5): 1054-1064.
[10] Slater M D, Kim D, Lee E, Johnson C S. Sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(8): 947-958.
[11] Cheng Fang-yi, Chen jun. Transition metal vanadium oxides and vanadate materials for lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(27): 9841.
[12] 梁叔全, 潘安强, 刘 军, 钟 杰, 陈 涛, 周 江. 锂离子电池纳米钒基正极材料的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(10): 2448-2464.
LIANG Shu-quan, PAN An-qiang, LIU Jun, ZHONG Jie, CHEN Tao, ZHOU Jiang. Research developments of V-based nanomaterials as cathodes for lithium batteries[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(10): 2448-2464.
[13] WANGYuan-hong, LIUHeng, ZHUDing, GUOZai-ping, LIUHua-kun, DOUShi-xue. Preparation and electrochemical performance of hollow spherical polypyrrole/V2O5 composite[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(6): 1303-1308.
[14] An xin-xin, Yang hu-lin, Wang ya-ping, Tang yan, Liang shu-quan, Pan an-qiang, Cao guo-zhong. Hydrothermal synthesis of coherent porous V2O3/carbon nanocomposites for high-performance lithium- and sodium-ion batteries[J]. Science China Materials, 2017, 60(8): 717-727.
[15] 魏湫龙, 蒋周阳, 谭双双, 李启东, 麦立强. 钒氧化物纳米材料在钠离子电池中的应用[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2016, 44(5): 693-706.
WEI Qiu-long, JIANG Zhou-yang, TAN Shuang-shuang, LI Qi-dong, MAI Li-qiang. Vanadium oxide nanomaterials for sodium-ion battery[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2016, 44(5): 693-706.
[16] Uchaker E, Zheng Y Z, Li S, Candelaria S L, Hu S, Cao G Z. Better than crystalline: Amorphous vanadium oxide for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(43): 18208-18214.
[17] 李秀娟, 曹云鹤, 华 康, 王 畅, 徐卫林, 方 东. 钒氧基电极材料特点及其改性方法[J]. 化学进展, 2017, 29(10): 1260-1272.
LI Xiu-juan, CAO Yun-he, HUA Kang, WANG Chang, XU Wei-lin, FANG Dong. Characterization and modification method of oxovanadium-based electrode materials[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2017, 29(10): 1260-1272.
[18] Wang ying, Cao guo-zhong. Developments in nanostructured cathode materials for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2008, 20(12): 2251-2269.
[19] Chou S L, Wang J Z, Sun J Z, Wexler D, Forsyth M, Liu H K, MacFarlane D R, Dou S X. High capacity, safety, and enhanced cyclability of lithium metal battery using a V2O5 nanomaterials cathode and room temperature ionic liquid electrolyte[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(22): 7044-7051.
[20] Wang Y, Takahashi K, Lee K H, Cao G Z. Nanostructured vanadium oxide electrodes for enhanced lithium-ion intercalation[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2006, 16(9): 1133-1144.
[21] Wang ying, Cao guo-zhong. Synthesis and enhanced intercalation properties of nanostructured vanadium oxides[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2006, 18(12): 2787-2804.
[22] Liu jun-feng, Li qiu-hong, Wang tai-hong, Yu da-peng, Li da-tong. Metastable vanadium dioxide nanobelts: Hydrothermal synthesis, electrical transport, and magnetic properties[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2004, 43(38): 5048-5052.
[23] Armstrong G, Canales J, Armstrong A R, Bruce P G. The synthesis and lithium intercalation electrochemistry of VO2(B) ultra-thin nanowires[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 178(2): 723-728.
[24] Chen zhan-jun, Gao shao-kang, Jiang li-long, Wei ming-deng, Wei le-mei. Crystalline VO2(B) nanorods with a rectangular cross-section[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 121(1/2): 254-258.
[25] Subba Reddy C V, Walker E H, Wicker S A, Williams Q L, Kalluru R R. Synthesis of VO2(B) nanorods for Li battery application[J]. Current Applied Physics, 2009, 9(6): 1195-1198.
[26] Balogun M S, Luo Y, Lyu F, Wang F, Yang H, Li H, Liang C, Huang M, Huang Y, Tong Y. Carbon quantum dot surface-engineered VO2 interwoven nanowires: A flexible cathode material for lithium and sodium ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(15): 9733-9744.
[27] Mai li-qiang, Wei qiu-long, An qin-you, Tian Xiao-cong, Zhao yun-long, Xu xu, Xu lin, Chang liang, Zhang qing-jie. Nanoscroll buffered hybrid nanostructural VO2(B) cathodes for high-rate and long-life lithium storage[J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(21): 2969-2973.
[28] Zhang lei, Zhao kang-ning, Xu wang-wang, Meng jia-shen, He liang, An qin-you, Xu xu, Luo yan-zhu, Zhao ting-wei, Mai li-qiang. Mesoporous VO2 nanowires with excellent cycling stability and enhanced rate capability for lithium batteries[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(63): 33332-33337.
[29] Wang wei, Jiang bo, Hu li-wen, Lin zhe-shuai, Hou jun-gang, Jiao shu-qiang. Single crystalline VO2 nanosheets: A cathode material for sodium-ion batteries with high rate cycling performance[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 250: 181-187.
[30] Chen wen, Peng jun-feng, Mai li-qiang, Yu hua, Qi yan-yuan. Synthesis and characterization of novel vanadium dioxide nanorods[J]. Solid State Communications, 2004, 132(8): 513-516.
[31] ZHANG Hui, LI Shen-zhong, MA Xiang-xiang, YANG De-ren. Controllable growth of dendrite-like CuO nanostructures by ethylene glycol assisted hydrothermal process[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43(5): 1291-1296.
[32] Jiang jian, Li yuan-yuan, Liu jin-ping, Huang xin-tang, Yuan chang-zhou, Lou xiong-wen. Recent advances in metal oxide-based electrode architecture design for electrochemical energy storage[J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(38): 5166-5180.
[33] Chao dong-liang, Zhu chang-rong, Xia xin-hui, Liu ji-lei, Zhang xiao, Wang jin, Liang pei, Lin jian-yi, Zhang Hua, Shen ze-xiang, Fan hong-jin. Graphene quantum dots coated VO2 arrays for highly durable electrodes for Li and Na ion batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(1): 565-573.
[34] Ren G, Hoque M N F, Pan X, Warzywoda J, Fan Z. Vertically aligned VO2(B) nanobelt forest and its three-dimensional structure on oriented graphene for energy storage[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(20): 10787-10794.
Controllable synthesis and electrochemical performance of VO2(B) nanobelt arrays as cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries
QIN Mu-lan, LIU Wan-min, ZHANG Zhi-cheng, XU Xing-xing
(School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Engineering, Xiangtan 411104, China)
Abstract: VO2(B) nanobelt arrays were synthesized by hydrothermal method with V2O5 as vanadium source and ethylene glycol as structure-directing agent and reductant, without using template. The crystal structure and morphology of synthesized VO2(B) were characterized by X-ray diffractometry (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The influences of ethylene glycol content and reaction time on structure and morphology of synthesized product were studied. As cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries, the effects of reaction time and charge-discharge voltage range on the electrochemical performance of synthesized VO2(B) were further researched. The results show that VO2(B) nanobelt arrays synthesized at 180 ℃ for 6 h using 10 mL ethylene glycol have better electrochemical performance in the voltage range of 1.5-4 V.
Key words: sodium-ion battery; cathode material; VO2(B); nanobelt array; hydrothermal method
Foundation item: Projects(17C0400, 15B054) supported by the Scientific Research Fund of the Education Department of Hunan Province, China; Project(2017JJ2060) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China
Received date: 2018-01-02; Accepted date: 2018-04-23
Corresponding author: QIN Mu-lan; Tel: +86-15274946795; E-mail: qinmulan@126.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:湖南省教育厅资助科研项目(17C0400,15B054);湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(2017JJ2060)
收稿日期:2018-01-02;修订日期:2018-04-23
通信作者:秦牡兰,讲师,博士;电话:15274946795;E-mail: qinmulan@126.com