文章编号:1004-0609(2015)-11-3209-07
稀土电解槽流场的数值模拟
刘 钊,李宗安,张小伟,庞思明,陈德宏,王志强
(北京有色金属研究 总院稀土材料国家工程研究中心 有研稀土新材料股份有限公司,北京 100088)
摘 要:采用雷诺应力模型(RSM)对上插式阴极结构稀土熔盐电解槽内部流场进行模拟研究,得到电解槽内部含气率和流场分布规律。计算结果表明:电解产生的气体主要集中在阳极内表面附近,且在电解槽上端靠近阳极处,含气率达到最大值;阳极内表面附近的最大上升流速为0.9 m/s;电解槽底部大部分区域电解质的流动速度均小于0.01 m/s,基本上属于流动死区;在底吹气体搅拌模型下,电解槽底部出现逆时针涡流,该区域电解质的流动速度较未通气体时的相比增加10倍以上,这能够在一定程度上改善电解槽底部的流动性,减轻底部“结瘤”现象。
关键字:稀土电解槽;雷诺应力模型;流场;气体搅拌;数值模拟
中图分类号:TF845 文献标志码:A
Numerical simulation of flow field in rare earth electrolysis cell
LIU Zhao, LI Zong-an, ZHANG Xiao-wei, PANG Si-ming, CHEN De-hong, WANG Zhi-qiang
(Grirem Advanced Materials Co., Ltd., National Engineering Research Center for Rare Earth Materials,
General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals, Beijing 100088, China)
Abstract: The flow field of the plug-in cathode structure rare earth electrolysis cell was numerically simulated based on Reynolds stress model (RSM). And the distribution rules of gas fraction and velocity field were obtained. The results show that, the anode gas generated by electrolysis mainly concentrates in the vicinity of the inner surface of the anode, and the gas fraction reaches the maximum value at the upper of the electrolysis cell near the anode. The velocity of the upside near the inner surface of the anode is 0.9 m/s. The bottom velocity of the electrolyte is less than 0.01 m/s, which basically belongs to stagnant zones. Compared with the way of without gas stirring at the bottom of the electrolysis cell, there is a anticlockwise eddy current, and the bottom velocity of the electrolyte increases by more than 10 times, which can improve liquidity at a certain degree, and reduce the “nodulation” at the bottom of the cell.
Key wards: rare earth electrolysis cell; Reynolds stress model; flow field; gas stirring; numerical simulation
目前,制备单一稀土金属及合金的主要方法是熔盐电解法[1-3]。在电解过程中,尤其是对电解质而言,其运动同时受电磁力、阳极气体、自身重力和黏性力的交互作用,运动行为非常复杂[4],不仅决定了稀土氧化物原料的传质以及电解质的传热过程,还对电解生产的稳定性、槽体寿命、电流效率以及能耗均有着重要影响。因此,研究稀土熔盐电解过程中的电解质运动行为显得尤为重要。
由于电解过程的高温和电解质的高腐蚀性,使得对于稀土电解槽流场的研究比较困难,因此,采用计算机模拟对电解槽内部流场进行研究是目前常用的研究方法。刘宇新等[5]采用CFD软件对表面化学反应自动生成气体的流场进行了数值模拟,得出了电解槽的熔体整体流场分布图及在不同位置气体浓度分布曲线图;董云芳等[6]利用CFD软件对60 kA底部阴极稀土电解槽进行研究,得到了不同极距下阳极表面气体的运动速度和阴阳极之间气体的分布情况;刘中兴等[7]针对60 kA底部阴极稀土电解槽内部流场,对比分析了不同阳极倾角下电解槽内部气液两相流动情况,得出了最佳倾斜角度。但是,底部阴极稀土电解槽目前还处于研究开发阶段,并未得到工业化应用,所以,目前工业化生产所用的稀土电解槽还是以上插式阴极结构电解槽为主;龚志军等[8]研究气泡运动对钠制电解槽内部熔盐流场的影响,得到了在平行于阳极方向和垂直于阳极方向上阳极气体对电解质所产生的作用。
在实际采用熔盐电解法生产稀土金属及其合金的过程中,电解槽底部边缘很容易产生“结瘤”现象,该现象发生的主要原因是稀土氧化物在电解质体系中的溶解度比较低,未参与反应的稀土氧化物到达电解槽底部就会形成“结瘤”,这不仅降低了电流效率,还影响了产品质量和槽体寿命[9]。本文作者针对实际生产中的这种现象,通过模拟查找发生“结瘤”现象的具体原因,并采取措施在一定程度上缓解了该现象的发生,进而提高产品质量和生产效率。
通常对于流场的研究所采用的湍流模型都是以Boussinesq假设为基础的标准k-ε模型,它是一个完全发展的湍流模型,对于计算包括浮力流在内的一些复杂湍流都存在一定的问题[10-11]。而雷诺应力模型(RSM)是从雷诺应力出发,能够体现流体的各向异性特点,而且考虑了历史效应对流体所产生的影响,保证了模拟结果的准确性,能够模拟大多数复杂的湍流情况[12-13]。因此,本文作者采用雷诺应力模型,通过对单独阳极气体作用下的稀土电解槽流场进行模拟研究,查找其内部存在的问题,并采取一定的手段对电解质的流动性进行改进。
1 数学模型的建立
本文作者针对目前常用的上插阴极稀土熔盐电解槽进行研究,其槽型结构为圆形电解槽,最大工作电流为6 kA。在实际电解过程中,电解质的运动比较复杂,为了简化模型,对电解槽流场进行如下假设:1) 电解过程中,视电解质为等温流体,忽略热量传递引起的热对流;2) 将电解质看作是黏性、不可压缩湍流;3) 忽略电磁力的影响,认为阳极气体是电解质运动的主要驱动力[14];4) 假设阳极气体为球体,在运动过程中无变形、聚集,且气泡之间无相互作用。
本模拟中选用欧拉气液两相流模型,把电解质作为连续相处理,把气泡作为离散相处理。
1.1 控制方程
电解槽内的气液两相流遵循以下控制方程[15]:
连续性方程,
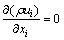 (1)
(1)
动量方程,
 (2)
(2)
式中:ρ为流体密度,kg/m3;ui、uj分别为在i和j方向上的速度分量,m/s;xi、xj分别为在i和j方向上的坐标值,m;p为时均压力,Pa;μ为分子黏度,Pa·s, 为雷诺应力。
为雷诺应力。
雷诺应力输运方程为


 (3)
(3)
式中:xk为位置坐标;Uk为平均速度,m/s;Cs为常数;k为湍动能;ε为湍流耗散率;δij为应力产生项;Gij为浮力产生项。
湍动能(k)及其耗散率(ε)方程如下:
k方程,

 (4)
(4)
式中:t为时间,s;μl为脉动速度分量,m/s;δk为应力;φk为由平均速度梯度引起的湍动能k的产生项。
ε方程,

 (5)
(5)
式中:cε1为1.44;cε1为1.92;f2为液相率。
1.2 模拟区域及网格划分
考虑到上插式阴极结构圆形电解槽的对称性,选取电解槽纵截面的一半作为研究区域,建立了二维轴对称气液两相流模型,其结构示意图如图1所示。模拟区域包括电解质和电解质上部槽体内的部分空气,其中电解质高度为490 mm,空气区域高度为70 mm。

图1 二维轴对称气液两相流模型模拟区域结构示意图
Fig. 1 Simulating regional structure diagram of two-dimensional axisymmetric gas liquid two phase flow model
1.3 边界条件及计算方法
定义阳极内表面为气体的速度入口,阳极气体以球形气泡的形式从阳极内表面产生并释放出去,其平均当量直径为2.64 mm[16],单位时间单位面积上的气体产生速率可以按式(6)进行计算[17]:
 (6)
(6)
式中:q为气体产生速率,m3/(s·m2);J为阳极电流密度,A/m2;R为摩尔气体常数,8.314 J/(mol·K);T为电解质温度,K;F为法拉第常数,取值为96485 C/mol;p为大气压力,101325 Pa。
依据式(6),计算得到的气体产生速率为0.02 m3/(s·m2)。
图1中空气区域的上表面定义为压力出口边界条件,所有壁面采用无滑移边界条件。
本模拟中采用FLUENT进行求解,湍流模型采用雷诺应力模型,近壁面采用标准壁面函数法进行处理,控制方程离散采用QUICK格式,速度-压力耦合采用SIMPLE算法[18]。
2 模拟结果与分析
2.1 原始模型下的流场模拟结果
图2所示为电解槽内含气率分布图。从图2可以看出,气体主要集中在阳极内表面附近,而在电解槽底部区域,基本无气体存在。这是由于电解过程中气体主要在阳极内表面产生,当电解达到稳定状态后,阳极内表面会形成一个动态的气泡层,随着电解的进行,气泡沿阳极内表面上浮并从电解质上表面逸出。

图2 电解槽内含气率的分布
Fig. 2 Distribution of gas volume fraction in electrolysis cell
图3所示为电解槽不同高度截面内含气率的径向分布。从图3可以看出,由于高度为0.10 m的截面位于阳极下表面,所以该截面不含气体;随着高度的增加,气泡覆盖范围越宽,气泡浓度也随之增大,在电解质上表面且靠近阳极区域达到最大值;沿着径向远离阳极内表面,气泡浓度逐渐降低。这主要是由电解过程中阳极气体的产生区域所决定的。

图3 不同高度横截面内含气率的径向分布
Fig. 3 Radical distribution of gas volume fraction in cross section with different heights
图4所示为上插式阴极结构圆形电解槽内部流场。由图4(a)可以看出,靠近阳极内表面一侧的电解质在阳极气体浮力的驱动下形成上升流,并向电解质的自由液面流动,到达自由液面之后流向阴极,继而在重力作用下在阴极表面形成下降流,因此,在阴阳极之间形成“涡流”,其窝心位置为(0.11 m,0.45 m)。由图4(b)可以看出,阳极内表面附近的上升流在距离自由液面30 mm、阳极内表面5 mm处速度达到最大值,为0.9 m/s;而阴极表面的向下降流区域,电解质的流动速度较小,均小于0.2 m/s;在电解槽底部区域(y为0~0.11 m),电解质的流动速度非常小,最大速度仅为0.015 m/s,大部分区域电解质的速度都小于0.01 m/s,这部分电解质基本不参与运动,属于流动死区。

图4 上插式阴极结构圆形电解槽内部流场
Fig. 4 Flow field of plug-in cathode structure in circular eletrolysis cell
由于稀土氧化物在氟化物熔盐体系中的溶解度比较低,一般仅为2%~4%[10],并且容易形成高熔点(>1300 ℃)、高密度(>6.0 g/cm3)、在电解质中溶解度小的稀土氟氧化物。与此同时,未反应的稀土氧化物就会沉降到电解槽底部,长时间后就会在电解槽底部堆积,形成“结瘤”,不仅会影响产品质量,还因其电导率小、导电差,致使槽电压显著升高,增加能耗,严重时甚至造成电解不能顺利进行。
通过上述研究发现,电解槽底部电解质流动性相对较差,是导致“结瘤”现象发生的最直接原因,这对提高产品质量、生产效率和槽体寿命是极其不利的,所以必须采取一定措施对电解槽底部流场进行改善。本模型中采取的措施就是通过底部侧吹CO气体的方式,改善电解槽底部电解质的流动性。一方面,底部侧吹CO气体能够对电解槽底部电解质直接进行气体搅拌,增强该处电解质的流动性;另一方面,CO气体能够与电极反应中产生的O2反应,从而一定程度上减缓石墨阳极的氧化消耗,增加阳极的使用寿命。
2.2 底吹气体模型下的流场模拟结果
底吹气体模型示意图如图5所示。图5(a)所示为底吹气体的电解槽结构示意图,外加气体直接沿着石墨槽体内壁通入到电解槽底部。图5(b)所示为电解槽底部吹气示意图。

图5 底部吹气模型流场示意图
Fig. 5 Schematic diagrams of flow field by bottom blowing gas model
图6所示为底部吹气模型下CO气体流量为4.71 L/min时所得电解槽的含气率分布。从图6可以看出,进入电解槽底部的CO气体主要沿着阳极内表面逸出电解槽,与图4(a)相比,气体在阴阳极之间的覆盖区域明显增加。

图6 底部吹气模型下电解槽的含气率分布图
Fig. 6 Distribution of gas volume fraction in electrolysis cell by bottom blowing gas model
图7所示分别为底吹气体模型下的上插式阴极结构圆形电解槽内部电解质的流线图及其速度等高线图。从图7(a)可以看出,在阴阳极之间所形成的“涡流”,其窝心位置变为(0.085 m,0.37 m),与图4(a)相比,略向阴极偏移,这主要是由于在阴阳极之间区域,气体的覆盖区域有所增加,致使阳极内表面附近的上升流更加剧烈,从而使得窝心偏向阴极附近。由于电解槽底部CO气体的推动作用,使得在电解槽底部出现了明显的涡流,其窝心位置为(0.115 m,0.08 m)。从图7(b)看出,阳极内表面附近的上升流在距离自由液面90 mm、阳极内表面25 mm处速度达到最大值,为1 m/s;阴极表面附近的下降流区域,其电解质的速度有所增加,均大于0.2 m/s。该区域电解质的速度较之前未通CO气体相比,提高了10倍以上,电解槽底部电解质的运动明显增加,因此,该区域未反应的稀土氧化物就会被重新带到阴阳极之间参与氧化还原反应,从而一定程度上缓解底部“结瘤”现象的发生,提高电流效率。
但是,底吹CO气体的流量必须维持在一定的范围之内。原因是电解产生的稀土金属从阴极表面向电解槽底部金属接收器滴落的过程中,如果电解槽底部的涡流较强,电解产生的金属容易被带到阳极参与二次反应,这样就会导致稀土金属的氧化损失,反而降低电流效率。因此,底吹气体模型的吹气流量应该根据实际生产控制在一定的速度范围之内。

图7 底吹气体模型下电解槽内部电解质的流线图和速度等效线图
Fig. 7 Flow field electrolyte in electrolysis cell by bottom blowing gas model
3 结论
1) 电解过程中产生的气体主要集中在阳极内表面附近,其含气率在电解槽上部靠近阳极处达到最大。
2) 阳极内表面附近的上升流在距离自由液面30 mm、距离阳极表面5 mm处速度达到最大值,为0.9 m/s;而阴极表面的下降流区域,电解质的流动速度较小,均小于0.2 m/s;电解槽底部大部分区域电解质的速度都小于0.01 m/s,这部分电解质基本不参与运动,属于流动死区。
3) 底吹气体模型下,在电解槽底部出现了明显的涡流,使得该区域电解质的流动速度与未进行底吹气体搅拌时的相比增加了10倍以上,这对改善电解槽底部的流动死区十分有利。但是,气体流量应该在不影响金属收集的前提下控制在一定的范围之内。
REFERENCES
[1] 陈宇昕. 氟化物体系电解稀土氧化物制备稀土金属研究[J]. 稀土, 2014, 35(2): 99-106.
CHEN Yu-xin. Research progress of preparation of rare earth metals by electrolysis in fluoride salt system[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2014, 35(2): 99-106.
[2] 庞思明, 颜世宏, 李宗安, 陈德宏, 徐立海, 赵 斌. 我国熔盐电解法制备稀土金属及其合金工艺进展[J]. 稀有金属, 2011, 35(3): 440-447.
PANG Si-ming, YAN Shi-hong, LI Zong-an, CHEN De-hong, XU Li-hai, ZHAO Bin. Development on molten salt electrolytic methods and technology for preparing rare earth metals and alloys in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2011, 35(3): 440-447.
[3] 郭 探, 王世栋, 叶秀深, 李 权, 刘海宁, 郭 敏, 吴志坚. 熔盐电解法制备稀土合金研究进展[J]. 中国科学(化学), 2012, 42(9): 1328-1333.
GUO Tan, WANG Shi-dong, YE Xiu-shen, LI Quan, LIU Hai-ning, GUO Min, WU Zhi-jian. Research progress in the preparation of rare earth alloys by molten salt electrolysis method[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2012, 42(9): 1328-1333.
[4] 李 劼, 张翮辉, 张红亮, 徐宇杰, 杨 帅, 赖延清. 大型铝电解槽电解质流场涡结构的数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(7): 2082-2088.
LI Jie, ZHANG He-hui, ZHANG Hong-liang, XU Yu-jie, YANG Shuai, LAI Yan-qing. Numerical simulation on vortical structures of electrolyte flow field in large aluminium reduction cells[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(7): 2082-2088.
[5] 刘宇新, 刘中兴, 杨立军. 稀土电解槽气液两相流动数值模拟[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2011, 10: 27-30.
LIU Yu-xin, LIU Zhong-xing, YANG Li-jun. Numerical simulation of gas-liquid two phase flow in rare earth electrolysis cell[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2011, 10: 27-30.
[6] 董云芳, 刘中兴, 伍永福, 徐立勇, 何金辉. 60 kA底部阴极稀土电解槽极距的模拟优化[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2013(10): 32-35.
DONG Yun-fang, LIU Zhong-xing, WU Yong-fu, XU Li-yong, HE Jin-hui. Simulation and optimization of polar distance in 60 kA bottom-cathode rare earth electrolyze[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2013(10): 32-35.
[7] 刘中兴, 董云芳, 伍永福, 何金辉, 徐立勇. 60kA底部阴极稀土电解槽阳极倾角对流场影响的数值模拟[J]. 稀土, 2013, 34(4): 21-24.
LIU Zhong-xing, DONG Yun-fang, WU Yong-fu, HE Jin-hui, XU Li-yong. Numerical simulation of effect of anode inclination on the flow of the molten salt in 60 kA bottom-cathode rare earth electrolytic cell[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2013, 34(4): 21-24.
[8] 龚志军, 伍永福, 刘中兴, 吴文斐. 阳极气泡运动对制钠电解槽内熔盐流场的影响[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2014(10): 24-26.
GONG Zhi-jun, WU Yong-fu, LIU Zhong-xing, WU Wen-fei. Effect of anode bubble movement on molten salt flow field in sodium electrolytic cell[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2014(10): 24-26.
[9] 陈德宏, 颜世宏, 李宗安, 赵 斌, 王志强, 庞思明. 熔盐电解钕中金属的溶解和泥渣的形成探讨[J]. 稀有金属, 2011, 32(4): 482-484.
CHEN De-hong, YAN Shi-hong, LI Zong-an, ZHAO Bin, WANG Zhi-qiang, PANG Si-ming. Solution of neodymium and formation of slime during the neodymium electrolysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2011, 32(4): 482-484.
[10] BLAZEK J. Computational fluid dynamics: principles and applications[M]. Kidlington: Elsevier Science Ltd, 2001: 233.
[11] 张小伟, 金小礼, 王 寅, 邓 康, 任忠鸣. 连铸板坯滑动水口三维流场湍流计算模型比较[J]. 过程工程学报, 2010, 10(6): 1041-1047.
ZHANG Xiao-wei, JIN Xiao-li, WANG Yan, DENG Kang, RENG Zhong-ming. Comparison of turbulent models on 3-D flow in the SEN of slab continuous casting controlled by slide gate[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2010, 10(6): 1041-1047.
[12] TUCKER H J. The distortion of turbulence by irrational strain[R]. McGill University Mechanical Engineering Department, 1970.
[13] LEE M J, REYNOLDS W C. Numerical experiments on the structure of homogeneous turbulence[R]. Stanford University, 1985.
[14] ZHOU Nai-jun, XIA Xiao-xia, BAO Sheng-chong. Effect of electromagnetic force and anode gas[J]. J Cent South Univ Technol, 2006, 13(5): 496-500.
[15] 翁键松, 刘根凡, 麦浚宇. 径向喷射规整旋流器内部流场研究[J]. 流体机械, 2014, 42(4): 11-16.
WENG Jian-song, LIU Gen-fan, MAI Jun-yu. Study on the flow field in radial jet cyclone[J]. Fluid Machinery, 2014, 42(4): 11-16.
[16] 刘奎仁, 陈建设, 魏绪钧, 郑天仓, 谢丽英, 孔向明. NdF3-LiF-Nd2O3体系表面张力的研究[J]. 稀土, 2000, 21(6): 37-39.
LIU Kui-ren, CHEN Jian-she, WEI Xu-jun, ZHENG Tian-cang, XIE Li-ying, KONG Xiang-min. A study on the surface tension of NdF3-LiF-Nd2O3 system[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2000, 21(6): 37-39.
[17] SOLHEIM A, JOHANSEM S T, ROLSETH S, THONSTAD J. Gas driven flow in Hall-Heroult cell[J]. Journal of Metals, 1988, 11(40): 57-63.
[18] 詹水清, 李 茂, 周孑民, 周益文, 杨建红. 铝电解槽熔体内氧化铝浓度分布的数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(10): 2658-2666.
ZHAN Shui-qing, LI Mao, ZHOU Jie-min, ZHOU Yi-wen, YANG Jian-hong. Numerical simulation of alumina concentration distribution in melts of aluminum reduction cells[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(10): 2658-2666.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2011AA03A409)
收稿日期:2015-03-13;修订日期:2015-09-13
通信作者:李宗安,教授级高工;电话:010-82241180;传真:010-89583401;邮箱:zonganli@126.com