文章编号:1004-0609(2009)05-0943-06
石煤提钒低温硫酸化焙烧矿物分解工艺
刘万里,王学文,王明玉,胡 健,张力萍
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:针对石煤提钒常压硫酸浸出能耗高、作业周期长的缺陷,提出石煤低温硫酸化焙烧矿物分解新工艺。以贵州凯里石煤为原料,对石煤低温硫酸化焙烧的时间、焙烧温度、硫酸加入量以及焙砂水浸工艺参数进行研究。结果表明:先对石煤进行低温硫酸化焙烧处理,再将焙砂按液固比1.2 mL/g加水于100 ℃下搅拌浸出2 h,钒的浸出率可达78.2%;而在相同酸矿比和固液比的条件下,采用常压直接酸浸石煤时,在100 ℃下搅拌浸出48 h后,钒的浸出率只有67.8%。石煤通过低温硫酸化焙烧可有效强化矿物分解过程,缩短提钒作业周期,提高酸的利用率及钒的浸出率。
关键词:钒;石煤;矿物分解;硫酸化焙烧
中图分类号:TF 841.3 文献标识码:A
Mineral decomposition process of vanadium recovery from
stone coal by low temperature sulphating roasting
LIU Wan-li, WANG Xue-wen, WANG Ming-yu, HU Jian, ZHANG Li-ping
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The new mineral decomposition process of vanadium recovery from stone coal by low temperature sulphating roasting was proposed, which overcomes the shortages of high energy consumption and long working cycle existing in stone coal decomposition with sulfuric acid solution under normal atmosphere. Using the stone coal obtained from Kaili of Guizhou Province, China, as raw material, the process parameters, such as roasting time, roasting temperature, sulfuric acid addition volume and the leaching with water for the calcine, were investigated. The results show that when the stone coal is firstly treated by low temperature sulphating roasting, then the obtained calcine is leached in water with liquid-to-solid ratio of 1.2 mL/g at 100 ℃ for 2 h, the leaching rate of vanadium is 78.2%. However, when the stone coal is leached with the same sulfuric acid addition and the same liquid-to-solid ratio under normal atmosphere at 100 ℃ for 48 h, the leaching rate of vanadium is only 67.8%. The process of low temperature sulphating roasting can effectively enhance the mineral decomposition of stone coal, which shortens the working cycle of vanadium recovery from stone coal and increases the utilization ratio of sulfuric acid and vanadium leaching rate.
Key words: vanadium; stone coal; mineral decomposition; sulphating roasting
钒是一种稀有金属,广泛用于冶金、化工等行 业[1-4]。钒钛磁铁矿和石煤是钒冶炼的两种主要矿物原料。我国石煤的蕴藏量极为丰富,主要分布在湖南、湖北、浙江、江西、广东、广西、贵州、安徽、河南、陕西等省、自治区,已探明的石煤储量达618.8亿t,其中w(V2O5)≥0.5%的石煤中V2O5储量为7 707.5 万t [5]。近年来,随着钒市场行情的好转,以石煤为原料生产精钒的企业在不断增加,石煤提钒在国内精钒行业所占的比例愈来愈大[6-7]。
目前,石煤提钒矿物分解工艺主要有钠化焙烧—水浸[8-9]、钙化焙烧—酸浸[10]、石煤矿直接酸浸[11-12]等。石煤钠化焙烧—水浸提钒工艺具有工艺简单,加工成本低的优点,但焙烧过程环境污染严重,这一分解工艺在许多地方都被禁止使用。钙化焙烧—酸浸工艺,虽然焙烧烟气污染小,但浸出过程酸耗量大,且浸出液后续处理工艺比较复杂,生产成本高。石煤直接酸浸工艺的优点是作业环境好,当硫酸的加入量达到石煤质量的15%~20%,钒的浸出率可达60%~ 70%[13]。目前,许多石煤提钒的企业大多数都采用这一工艺,但石煤矿直接酸浸矿物分解速度慢,浸出时间长,一般需要36~48 h,酸的利用率只能达到70%左右。魏昶等[14]采用氧压酸浸的方法来加快分解石煤速度,提高浸出作业效率,但石煤氧压酸浸如何实现工业生产还有待进一步研究。
本文作者结合上述两种石煤酸浸工艺的优点,采用石煤提钒低温硫酸化焙烧-水浸的矿物分解工艺,对石煤焙烧和水浸工序进行系统研究。
1 实验
1.1 实验原料
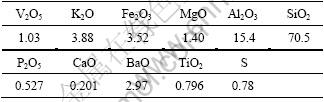
实验原料为贵州凯里石煤矿;实验所用的硫酸为分析纯98%的浓硫酸;实验所用的水为去离子水。表1列出了凯里石煤矿的化学成分,其中Al、Fe、Ba含量较高。图1所示为凯里石煤样品的XRD谱。由图1可知,凯里石煤中主要矿相有石英(SiO2)、钾云母(KAl2(Si3Al)O10(OH)2)和伊利石(K(Al, V)2(Si, Al)4- O10(OH)2)。
表1 石煤的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of stone coal (mass fraction, %)
1.2 实验原理
由图1可知,石煤样品中存在伊利石。在伊利石中钒是以类质同相的形式存在,即在伊利石晶格中部分Al3+被钒取代[13],这部分钒属于难溶出的钒,要提取伊利石中的钒首先必须破坏伊利石结构。酸浸可破坏伊利石结构,提取伊利石中的钒,即在一定酸度和温度下,让H+进入伊利石晶格中置换Al3+,使晶体结构发生变化,从而释放出钒。石煤中除V3+外,通常还有V4+。V4+也能被酸浸出[14]:


图1 石煤样品的XRD谱
Fig.1 XRD pattern of stone coal
上述化学反应的共同特点是生成物之一是可溶性的硫酸盐,另一种生成物则是水。由化学平衡原理可知,在反应体系内减小一种生成物的浓度可以提高反应物的转化率[15]。通过焙烧不仅可有效提高反应温度,增强硫酸在伊利石相中的渗透能力,强化石煤矿石分解过程,而且能大大加快反应产物水的挥发速度,促使反应向右进行,提高硫酸的转化率。然而,硫酸的沸点只有330 ℃[16],焙烧得到的硫酸氧钒在高温下不稳定,为了防止硫酸挥发及硫酸氧钒分解,石煤硫酸化焙烧宜控制在硫酸沸点以下进行,即低温硫酸化焙烧。石煤低温硫酸化焙烧既能有效地避免硫酸的挥发及硫酸氧钒的分解,又可最大限度地提高硫酸的利用率及钒的分解率。
1.3 分析方法
石煤提钒矿物分解实验分为焙烧和浸出两部分,每部分又包含单因素条件实验和综合条件实验。焙烧实验规模为每次100 g,考察因素有焙烧时间、焙烧温度及硫酸用量;浸出实验规模为每次50 g,考察因素有时间、温度及液固比,并在最佳单因素条件下进行石煤低温硫酸化焙烧-水浸工艺与石煤常压直接酸浸工艺的对比实验。
称取粒径小于0.106 mm的石煤矿粉100 g放在陶瓷钵内,加入一定量的浓硫酸拌匀,放进马弗炉在预定温度下焙烧一段时间;待焙砂冷却至室温,按一定液固比将水注入平底烧瓶内,在恒温磁力搅拌器上加热到指定温度后,再将焙砂加入到其中,至规定浸出时间,料浆抽滤,滤渣烘干称量,然后用硫酸亚铁铵法测定滤液和滤渣中钒的含量。
2 结果及讨论
2.1 石煤低温硫酸化焙烧
2.1.1 焙烧温度对钒浸出率的影响
图2所示为焙烧温度对钒浸出率的影响。实验过程为:100 g石煤矿粉加入20 mL浓硫酸拌匀后,放进马弗炉在预定温度下焙烧2 h,焙砂按液固比1.2 mL/g加水于100 ℃下浸出2 h。从图2可以看出,焙烧温度对钒的浸出率影响很大,温度较低时,钒的浸出率随焙烧温度的升高而增大,到250 ℃左右钒的浸出率最大,达到81.2%,之后钒的浸出率随焙烧温度的升高而下降。这是因为在100~250 ℃,硫酸在石煤中的渗透能力随温度的升高而增强,因此,在一定的焙烧时间内硫酸与石煤中Al、K、V等之间的化学反应进行得更彻底;当焙烧温度升至250 ℃之后,硫酸的蒸气压随温度升高显著增大,硫酸大量挥发,造成硫酸的有效利用率降低,进而导致钒的浸出率下降。此外,由V2O5催化氧化SO2的反应可以看出[16],当焙烧温度达到450 ℃之后,造成钒的浸出率进一步下降的另一原因可能是硫酸氧钒的分解:


图2 焙烧温度对钒浸出率的影响
Fig.2 Effect of roasting temperature on vanadium leaching rate
2.1.2 焙烧时间对钒浸出率的影响
图3所示为焙烧时间对钒浸出率的影响。实验过程为:100 g石煤矿粉加入20 mL浓硫酸拌匀后,在马弗炉内250 ℃焙烧预定时间,焙砂按液固比1.2 mL/g加水于100 ℃下浸出2 h。由图3可知,低温硫酸化焙烧可有效强化石煤分解过程,在250 ℃下,焙烧0.5 h,钒的浸出率超过70%;焙烧0.5~2.0 h,钒的浸出率随焙烧时间的延长而升高,250 ℃下焙烧2 h,钒的浸出率为78.2%;之后随着焙烧时间的延长,钒的浸出率略有下降。这表明焙烧时间达到2 h后,硫酸氧钒的形成速度小于其分解速度。因此,石煤在250 ℃下硫酸化焙烧,焙烧2 h较为适宜。

图3 焙烧时间对钒浸出率的影响
Fig.3 Effect of roasting time on vanadium leaching rate
2.1.3 硫酸用量对钒浸出率的影响
图4所示为硫酸用量对钒浸出率的影响。实验过程为:100 g石煤矿粉加入一定量的浓硫酸拌匀后,在马弗炉内250 ℃下焙烧2 h,焙砂按液固比1.2 mL/g加水于100 ℃下浸出2 h。从图4可以看出,钒的浸出率随硫酸用量的增加而增大;硫酸用量为20 mL时,钒的浸出率接近79%;硫酸用量增至30 mL时,钒的浸出率上升至93.5%。由于钒的浸出率与石煤中伊利石的解离程度有关,硫酸用量增加,伊利石中V、Al和K与硫酸的反应进行得越彻底。由表1可以算出,100 g石煤中的Al、Fe、K、V 恰好需要约30 mL浓硫酸与之反应。实验发现,虽然在一定范围内增加硫酸用量可以提高钒的浸出率,但硫酸用量增加到20 mL之后,不仅浸出液中游离酸浓度随硫酸用量增加而增大,而且浸出液中杂质浓度随硫酸用量的增加而急剧升高,给浸出液的后续处理带来困难。因此,100 g石煤矿粉中加入20 mL浓硫酸(相当于100 g石煤加入36 g硫酸)比较合适。必须指出,石煤提钒矿物分解,酸的用量与矿石的组成和结构有关,不同石煤有不同的酸矿比。

图4 硫酸用量对钒浸出率的影响
Fig.4 Effect of sulfuric acid volume on vanadium leaching rate
2.2 焙砂水浸提钒
2.2.1 浸出温度对钒浸出率的影响
图5所示为浸水温度对钒浸出率的影响。实验过程为:最佳焙烧条件下(250 g石煤矿粉加50 mL浓硫酸拌匀后,在马弗炉内250 ℃下焙烧2 h,冷却后焙砂分成5等份)得到的焙砂按液固比1.2 mL/g加水,在预定温度下浸出2 h。由图5可知,钒的浸出率在30~ 70 ℃之间随浸出温度的升高迅速增大,70~90 ℃之间浸出率增大得比较慢,浸出温度上升到90~100 ℃浸出率的增大速度又明显加快。这可能是石煤中的Al和K经硫酸焙烧后,在水浸时形成了明矾KAl(SO402?12H2O,明矾溶解度的变化[17]对钒的浸出率产生了影响。在30~70 ℃之间,明矾的溶解度随溶液温度的升高而增大,焙砂中铝的溶出率升高,从而带动钒的浸出率升高;当温度上升到70~90 ℃,由于明矾在溶液中接近饱和,阻碍了焙砂中铝的溶出,钒的浸出率随温度升高增幅变缓;当浸出温度上升到90~100 ℃,明矾的溶解度随温度升高进一步增大,加速焙砂中的铝的溶出,进而带动钒的浸出率继续上升。实验过程发现,浸出结束,趁热(~90 ℃)过滤,滤液冷却后有大量KAl(SO4)2?12H2O晶体析出。常压下,焙砂浸出液的沸点接近110 ℃,考虑到实际作业的可行性及经济性,浸出温度控制在90~100 ℃较为适宜。

图5 浸出温度对钒浸出率的影响
Fig.5 Effect of leaching temperature on vanadium leaching rate
2.2.2 液固比对钒浸出率的影响
图6所示为液固比对钒浸出率的影响。实验过程为:最佳焙烧条件下得到的焙砂按一定液固比加水,在100 ℃下浸出2 h。由图6可以看出,液固比在0.8~1.2 mL/g之间时,钒的浸出率随着液固比的增大迅速增大,因为温度一定,焙烧形成的硫酸盐在浸出液中的溶解度不变,液固比增大,浸出液体积增大,硫酸盐在浸出液中的溶解量增大,钒的浸出率随之提高;当液固比增大到1.2 mL/g后,钒的浸出率随液固比的增大而迅速减小,这是因为随着液固比的增大浸出液中游离酸浓度下降,导致焙砂中铝的溶出困难,钒的浸出率随之降低。由此看出,焙砂浸出的液固比应首选1.2 mL/g。

图6 液固比对钒浸出率的影响
Fig.6 Effect of liquid-to-solid ratio on vanadium leaching rate
2.2.3 浸出时间对钒浸出率的影响
图7所示为浸出时间对钒浸出率的影响。实验过程为:最佳焙烧条件下得到的焙砂按液固比1.2 mL/g加水,在100 ℃下浸出一定时间。从图7可以看出,在0.5~2.0 h内,钒浸出率随浸出时间的延长而迅速增大,2 h之后继续延长浸出时间,钒浸出率变化非常缓慢。由此看出,焙砂按液固比1.2 mL/g加水于100 ℃下搅拌浸出2 h后,焙砂中V的溶出已接近平衡。

图7 浸出时间对钒浸出率的影响
Fig.7 Effect of leaching time on leaching rate of vanadium
2.3 综合及对比实验
先将250 g石煤矿粉加入50 mL浓硫酸拌匀后,在马弗炉内250 ℃下焙烧2 h,然后将得到的焙砂(298.75 g)分成3等份,在浸出最佳条件下,进行3次综合条件实验。实验结果为:钒的液计浸出率分别为78.26%,78.31%和78.19%,平均为78.25%;渣计浸出率分别为76.75%,76.47%和76.34%,平均为76.52%。浸出过程中钒的平衡如表2所列。由表2 可以看出,钒的平衡情况较好,平衡率可达到98.27%,而产生正偏差的原因是溶液分析钒含量偏高。
表2 石煤在浸出过程中钒的平衡
Table 2 Balance of vanadium in stone coal leaching process
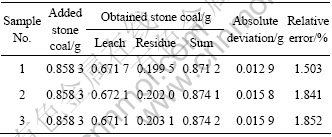
表3所列为表2中样品浸出渣的化学成分。对表1和表3进行分析,通过V的浸出率可以得出渣率,再通过渣率计算出Al与K的浸出率:

表3 浸出渣的化学成分
Table 3 Composition of leaching residue (mass fraction, %)

可得V的浸出率与Al和K的浸出率比较接近,这表明即使采用低温硫酸化焙烧,石煤中的V也不能优先被浸出。
为了突显低温硫酸化焙烧—水浸石煤矿物分解工艺的优点,特进行了石煤常压直接酸浸的对比实验。图8所示为2 500 g石煤矿粉搅拌加入由500 mL浓硫酸与水配成的3 000 mL稀硫酸中,100 ℃下常压浸出的实验结果。由图8可以看出,凯里石煤常压直接酸浸,搅拌浸出24 h,钒的浸出率不到67%;浸出48 h,钒的浸出率也只有67.8%。由此看出,在酸矿比和液固比相同的条件下,石煤经低温硫酸化焙烧-水浸工艺处理时,其钒浸出率比石煤经常压直接酸浸工艺处理时的提高了10%,作业时间缩短了40多小时。

图8 石煤常压硫酸浸出结果
Fig.8 Leaching results of stone coal with sulfuric acid under normal atmosphere
3 结论
1) 石煤经低温硫酸化焙烧可有效强化矿物分解过程,加速石煤中以类质同相形式存在于伊利石晶相中钒的分解,缩短作业时间,提高酸的利用率及钒的浸出率。石煤低温硫酸化焙烧-水浸工艺具有适用性强、分解效率高、操作简便等优点。
2) 贵州凯里石煤采用低温硫酸化焙烧-水浸工艺分解提钒时,其最佳工艺流程为:在粒径小于0.106 mm的100 g石煤中加入20 mL浓硫酸,拌匀后250 ℃下焙烧2 h,得到的焙砂按液固比1.2 mL/g,100 ℃下搅拌浸出2 h,钒的浸出率可达78.2%以上。
REFERENCES
[1] 廖世明, 柏谈论. 国外钒冶金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1985: 1-19.
LIAO Shi-ming, BO Tan-lun. The metallurgy of overseas vanadium[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1985: 1-19.
[2] 宾智勇. 石煤提钒研究进展和五氧化二钒的市场状况[J]. 湖南有色金属, 2006, 22(1): 16-20.
BIN Zhi-yong. Progress of the research on extraction of vanadium pentoxide from stone coal and the market of the V2O5[J]. Hunan Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 22(1): 16-20.
[3] LAN Y Z, LIU J. Review of vanadium processing in China[J]. Engineer Sciences, 2005, 3(3): 58-62.
[4] MOSKALYK R R, ALFANTAZI A M. Processing of vanadium: A review[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2003, 16(9): 793-805.
[5] 冯其明, 何东升, 张国范, 欧乐明, 卢毅屏. 石煤提钒过程中钒氧化和转化对钒浸出的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(8): 1348-1352.
FENG Qi-ming, HE Dong-sheng, ZHANG Guo-fan, OU Le-ming, LU Yi-ping. Effect of vanadium oxidation and conversion on vanadium leaching in extraction process of vanadium from stone coal[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(8): 1348-1352.
[6] 漆明鉴. 从石煤中提钒现状及前景[J]. 湿法冶金, 1999, 72(4): 1-10.
QI Ming-jian. The status and prospects of vanadium leaching from stone coal[J]. Hydrometallurgy of China, 1999, 72(4): 1-10.
[7] WANG M Y, XIANG X Y, ZHANG L P, XIAO L S. Effect of vanadium occurrence state on the choice of extracting vanadium technology from stone coal[J]. Rare Metals, 2008, 27(2): 112-115.
[8] 常 娜, 顾兆林, 李 云. 石煤提钒浸出工艺研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2006, 38(7): 57-59.
CHANG Na, GU Zhao-lin, LI Yun. Study on leaching vanadium from stone coal[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2006, 38(7): 57-59.
[9] 傅 立, 苏 鹏. 复合焙烧添加剂从石煤中提取钒的研究[J]. 广西民族学院学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 12(2): 105-107.
FU Li, SU Peng. Research on extraction of vanadium from rock coal used composite additives baked[J]. Journal of Guangxi University for Nationalities: Natural Science Edition, 2006, 12(2): 105-107.
[10] 郑祥明, 田学达, 张小云, 石 华, 邓益强. 湿法提取石煤中钒的新工艺研究[J]. 湘潭大学自然科学学报, 2003, 25(1): 43-45.
ZHENG Xiang-ming, TIAN Xue-da, ZHANG Xiao-yun, SHI Hua, DENG Yi-qiang. Extraction of vanadium pentoxide from stone coal with a wet chemical separation method[J]. Natural Science Journal of Xiangtan University, 2003, 25(1): 43-45.
[11] LI H R, FENG Y L, LIANG J L, LUO X B, DU Z W. Vanadium recovery from clay vanadium mineral using an acid leaching method[J]. Rare Metals, 2008, 27(2): 116-120.
[12] HE D S, FENG Q M, ZHANG G F, OU L M, LU Y P. An environmentally-friendly technology of vanadium extraction from stone coal[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20(12): 1184-1186.
[13] 鲁兆伶. 用酸法从石煤中提取五氧化二钒的试验研究与工业实践[J]. 湿法冶金, 2002, 21(4): 175-183.
LU Zhao-ling. Investigation and industrial practice on extraction of V2O5 from stone coal containing vanadium by acid process[J]. Hydrometallurgy of China, 2002, 21(4): 175-183.
[14] 魏 昶, 李存兄, 樊 刚, 李旻廷, 邓志敢. 石煤湿法强化提钒新工艺[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(S1): 80-83.
WEI Chang, LI Cun-xiong, FAN Gang, LI Min-ting, DENG Zhi-gan. New process of vanadium extraction black shale by strengthening hydrometallurgy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(S1): 80-83.
[15] 胡 英. 物理化学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2001: 239.
HU Ying. Physical chemistry[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2001: 239.
[16] 大连理工大学无机化学教研室. 无机化学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2001: 468.
The Staff Room of Inorganic Chemistry, Da lian University of Technology. Inorganic chemistry[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2001: 468.
[17] 梁英教, 车荫昌, 刘小霞, 李乃军. 无机物热力学数据手册[M]. 沈阳: 东北大学出版社, 1993: 564.
LIANG Yin-jiao, CHE Yin-chang, LIU Xiao-xia, LI Nai-jun. Inorganic matter thermodynamic data handbook[M]. Shenyang: Northeast University Press, 1993: 564.
基金项目:贵州省发改委资助项目(贵州省铜仁地区钒资源开发与利用规划2007GH001)
收稿日期:2008-08-21;修订日期:2008-12-30
通讯作者:王学文,副教授,博士;电话:0731-8830247;E-mail: wxwcsu@163.com
(编辑 李向群)