液态时效条件下Zn元素的添加对共晶Sn-58Bi焊料力学性能的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2015年第4期
论文作者:马东亮 吴 萍
文章页码:1225 - 1233
Key words:Zn; Sn-Bi solder; liquid-state aging; reflow soldering; creep
摘 要:对液态时效条件下Sn-58Bi-xZn (x=0, 0.7) 焊料样品的力学性能(包括拉伸强度和蠕变性能)以及相关的界面反应进行研究。结果表明,在Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn焊料样品中,Bi的粗化现象和Cu-Sn界面金属间化合物的生长都得到了有效抑制。通过掺杂0.7% Zn,回流焊接后焊条样品的极限拉伸强度比共晶Sn-58Bi的极限拉伸强度提高了6.05%,液态时效后的极限拉伸强度则提升了5.50%。对于焊点样品,掺杂0.7%Zn后的极限拉伸强度相比Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu在回流焊接后提升21.51%,而在液态时效后则提升29.27%。焊点强度的增加是由于Zn的掺杂导致Bi晶粒细化,使得断裂面从Cu和界面金属间化合物界面处转移到了界面金属间化合物和焊料界面处。纳米压痕的结果显示,通过向共晶Sn-58Bi焊料中掺杂0.7% Zn,焊料的抗蠕变性在回流焊接和液态时效后都有较大幅度的提升。
Abstract: Interfacial reaction, tensile strength and creep resistance of Sn-58Bi-xZn (x=0, 0.7, mass fraction, %) solder samples during liquid-state aging were investigated. The coarsening of Bi and the growth of Cu-Sn intermetallic compounds (IMCs) in Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn solder sample were both effectively suppressed. With the addition of 0.7% Zn, ultimate tensile strengths (UTSs) of the Sn-58Bi solder slabs were respectively increased by 6.05% and 5.50% after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging, and those of the Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu solder joints were also increased by 21.51% and 29.27%, respectively. The increase in strengthening effect of Cu/Sn-58Bi-xZn/Cu solder joints could be attributed to the fracture surface which was changed from the Cu/IMC interface to the IMC/solder interface due to the finer Bi grain. Nanoindentation results revealed that the creep behavior of Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn solder was significantly improved compared with that of the eutectic Sn-58Bi solder after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 1225-1233
Dong-liang MA1,2, Ping WU1,2
1. Department of Applied Physics, Institute of Advanced Materials Physics, Faculty of Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China;
2. Tianjin Key Laboratory of Low Dimensional Materials Physics and Preparing Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
Received 26 May 2014; accepted 20 October 2014
Abstract: Interfacial reaction, tensile strength and creep resistance of Sn-58Bi-xZn (x=0, 0.7, mass fraction, %) solder samples during liquid-state aging were investigated. The coarsening of Bi and the growth of Cu-Sn intermetallic compounds (IMCs) in Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn solder sample were both effectively suppressed. With the addition of 0.7% Zn, ultimate tensile strengths (UTSs) of the Sn-58Bi solder slabs were respectively increased by 6.05% and 5.50% after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging, and those of the Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu solder joints were also increased by 21.51% and 29.27%, respectively. The increase in strengthening effect of Cu/Sn-58Bi-xZn/Cu solder joints could be attributed to the fracture surface which was changed from the Cu/IMC interface to the IMC/solder interface due to the finer Bi grain. Nanoindentation results revealed that the creep behavior of Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn solder was significantly improved compared with that of the eutectic Sn-58Bi solder after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging.
Key words: Zn; Sn-Bi solder; liquid-state aging; reflow soldering; creep
1 Introduction
Low temperature soldering can reduce the thermal damage which is caused by thermal expansion mismatch among various materials in an electronic package. Eutectic Sn-58Bi solder is a promising low temperature Pb-free solder due to its lower melting temperature (139 °C). It can exhibit noticeable higher ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and shear strength [1,2], and show a slower creep rate and lower rupture strain [3-5] by doping with proper elements. Specifically, the bending strength and ductility of the eutectic Sn-58Bi solder have been greatly enhanced by 0.03% multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) addition [6,7].
In addition, Zn is known to be one of the inexpensive metals for solder alloys, and has been paid much attention on the study of the electronic packaging. Due to the higher activity, it is usually the first to react with the substrate metals [8,9]. Sn-Ag [10-12] or Sn-Ag-Cu [13-15] high temperature Pb-free solder with the addition of Zn has attracted considerable attention. When the Zn content is about 0.7%, it can slow the growth of IMCs, inhibiting both the formation of Kirkendall voids and the growth of whiskers on the surface of solder alloy. However, researches in the field of low temperature Pb-free solder with the addition of Zn are few. Therefore, in the research of low temperature Pb-free solder, understanding of effect of Zn is needed during the study of 0.7% Zn addition.
The purpose of this work is to investigate the mechanical properties of Sn-58Bi-xZn low temperature solder after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging reactions. Liquid-state aging of the solder alloys is an important factor to affect its mechanical properties, so microstructure transformation and growth of IMC layers have been observed. Moreover, the tensile strength and creep resistance are very important criteria for the low temperature candidate Pb-free solders. Thus, the tensile strength of Sn-58Bi-xZn solder slabs after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging as well as Cu/Sn-58Bi- xZn/Cu solder joints have also been investigated, and the creep behavior of Sn-58Bi-xZn rectangular solders are obtained by the nanoindentation method.
2 Experimental
2.1 Material processing
Two different compositions of Sn-58Bi-xZn (x=0 and 0.7) solders were prepared from commercial solder alloys Sn-58Bi with different Zn (99.9% purity) addition. The Sn-58Bi powder was mixed with Zn powder for 8 h in a ball mill. The mixture was then uniaxially compacted and sintered at 100 °C for 2 h in an inert argon atmosphere. Lastly, the billets were melted to solder ingots in an induction melting furnace under vacuum. The solder ingots were mechanically machined into rectangular solders with dimensions of 2.5 mm× 2.0 mm×1.0 mm for interfacial reaction study as well as nanoindentation tests. Cu plates (99.9% purity) with dimensions of 10.0 mm×5.0 mm×0.5 mm were used as the substrates. For tensile tests, the dimensions of a solder slab were 50.0 mm×5.0 mm×1.8 mm, and a Cu line/solder ball/Cu line solder joint was composed of a 400 μm diameter solder ball and two 450 μm diameter Cu wires. The fabrication process of the solder joint has been described elsewhere [16]. Before each experiment, the Cu substrate surface and two connecting ends of Cu wires were ground with 2000 grit SiC coated paper, and then were sequentially degreased in acetone, cleaned by deionized water, dipped in 3% HCl solution, and rinsed by deionized water again.
2.2 Interfacial reaction and DSC analysis
The Sn-58Bi and Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn rectangular solders were laid on the bare Cu substrates with soldering flux. After soldering at 200 °C for 60 s, the samples were then put into a tubular furnace for liquid-state aging for 60 min at a temperature of 180 °C in low vacuum condition. All the cross-sectioned samples were embedded in epoxy resin. The morphology of the Cu/solder interface was observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, XL30ESEM) with a backscattered electron (BSE) imaging mode, and the chemical compositions of IMCs were identified with energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX, Nanosem 430).
The melting property of the solder alloys was monitored by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC, Perkin Elmer Diamond). For DSC analysis, approximately 8 mg solder alloy was placed into an aluminum crucible and it was scanned from 25 °C to 170 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C /min under a nitrogen gas flow.
2.3 Tensile and nanoindentation tests
After reflow soldering at 200 °C for 60 s, Sn-58Bi-xZn (x=0 and 0.7%) solder slaps and joints were put into a tubular furnace for liquid-state aging 60 min at 180 °C in low vacuum condition. Tensile tests were then carried out at room temperature using an automated servohydraulic testing machine (MTS 810) at a constant tensile speed of 1 mm/min on solder slabs and 0.2 mm/min on solder joints, respectively. The fracture surface was observed using a metallographic microscope.
Before nanoindentation tests, all the as-soldered and aged rectangular solder samples were ground with 320, 800 and 2000 grade abrasive sandpapers in sequence, and was then polished using 1.0 μm Al2O3 suspension to produce a smooth surface. Nanoindentation tests were performed at room temperature using an MTS Nano Indenter XP system. The samples were all tested in a load-control method with a maximum load of 20 mN and holding time of 54 s at maximum load to investigate the creep resistance of them.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Interfacial reactions of Cu/Sn-58Bi-xZn
Figure 1 shows the SEM-BSE images of the interfaces between Sn-58Bi-xZn (x=0 and 0.7) rectangular solders and Cu substrates before and after liquid-state aging at 180 °C for 60 min. These Sn-58Bi-xZn solders contained an obvious dual coexistence structure, consisting of a Sn-rich phase (the gray area) and a Bi-rich phase (the white area). Moreover, with further increase in Zn content, needle-shaped black Zn-rich phases will be found in the solder matrix [17]. For Sn-58Bi sample, after soldering at 200 °C for 60 s, a Cu6Sn5 IMC layer formed at the Cu/Sn-58Bi interface firstly. After liquid-state aging at 180 °C for 60 min, a Cu3Sn IMC layer then formed at the Cu/Cu6Sn5 interface. For Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn sample, a CuZn and Cu6(Sn,Zn)5 IMC layer formed at the Cu/Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn interface during the soldering and the whole aging process. Additionally, Bi segregation (black rings) could also be observed at the Cu/Cu3Sn and Cu6(Sn,Zn)5/CuZn interface, respectively. The presence of Bi at the interface would result in more atoms being activated. As a result, the liquid-state aging reaction at the interface was accelerated when enough Bi segregated there.
The total thickness of the IMC layers at the Cu/solder interface during liquid-state aging at 180 °C for different time is shown in Fig. 2. This was determined by dividing the total area of the reaction layer to the horizontal length of the selected area. The thickness change of the different IMC layers at the Cu/Sn-58Bi-xZn interface followed a parabolic law when the aging time was further prolonged. The results demonstrated that the growth of IMC was mainly controlled by the diffusion mechanism.
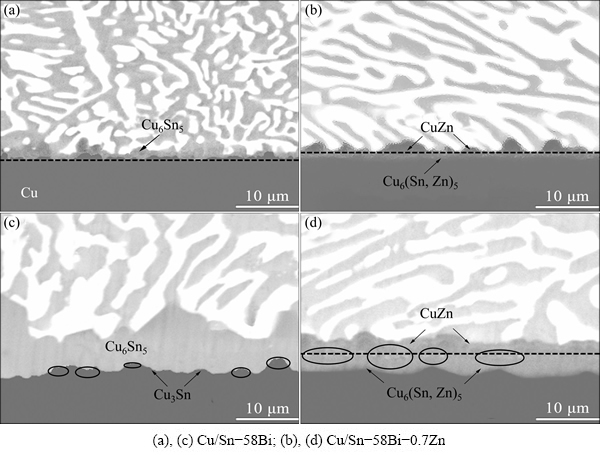
Fig. 1 SEM-BSE images of interfaces between rectangular solders and Cu substrates before and after liquid-state aging at 180 °C for 60 min
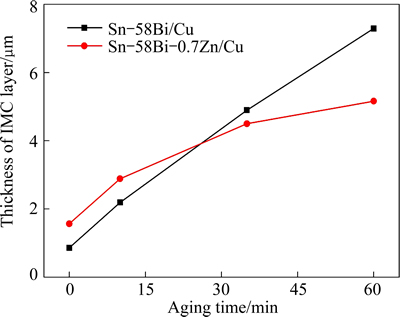
Fig. 2 Total thickness of IMC layers versus liquid-state aging time
Another noticeable phenomenon of the microstructural evolution was the finer Bi-rich phase in the Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn solder matrix during liquid-state aging. The Bi-rich phase evolution was captured by Image-Pro Plus software. First of all, the selected measurement items were used to quantify the Bi-rich phase. Before counting and measuring objects, the count/size analyzer should be configured. The red outlines of the Bi-rich phase in the same area size of Sn-58Bi and Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn solder matrix are captured after liquid-state aging for 60 min as shown in Figs. 3(a) and (b), respectively. Under such conditions, the area of the Bi-rich phase was calculated to be 1336 and 480 μm2 in Sn-58Bi and Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn solder matrixes, respectively. The results showed that the growth and coarsening of Bi were effectively suppressed with the Zn addition to the solder matrix.
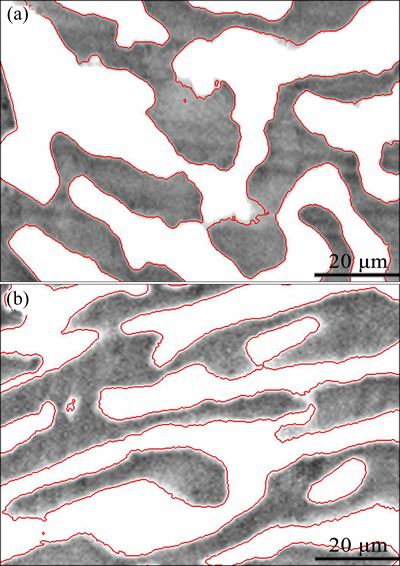
Fig. 3 Bi-rich phase distribution after liquid-state aging for 60 min outlined by Image-Pro Plus software in Sn-58Bi (a) and Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn (b) solder matrixes
The fundamental thermal properties of Sn-58Bi- xZn solder alloys were analyzed by DSC as shown in Fig. 4. The temperature of the onset point in the heating curve represented the solidus temperature, while the peak point represented the liquidus temperature. The results indicated that the solidus temperature of Sn-58Bi-xZn solder alloys slightly decreased with the Zn content increasing. Thus, the change of melting temperature was negligible during practical manufacturing process.
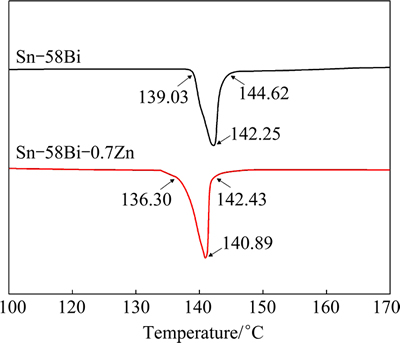
Fig. 4 DSC curves of Sn–58Bi–xZn (x=0 and 0.7) solders
The reduction in solidus temperature of solders can probably be attributed to the increase in the surface instability with higher surface free energy which is induced by the addition of Zn [18-20]. Generally, the systematic free energy of grain is composed of volume free energy and surface energy, and lower free energy could make grain formation more stable. The volume free energy is regarded as driving force for the grain formation when metallic atoms nucleate as crystal nucleus from liquid to solid state. Meanwhile, the surface energy with more surface area is to provide the retarding force. At the stage of grain growth, the decrease of volume free energy difference is much slower than the increase of surface energy. This is because further grain growth is inhibited and the grain size is also refined by the addition of Zn. Therefore, the interfacial and grain boundary surface energy are not completely consumed. As a result, the slight reduction in solidus temperature of solders was observed in the present work with higher free energy.
3.2 Tensile properties of solder slabs and solder joints
Tensile tests were performed in order to evaluate the influences of Zn metal on the tensile properties of Sn-58Bi-xZn solder slabs and Cu/Sn-58Bi-xZn/Cu solder joints. Figures 5(a) and (b) show the stress- displacement curves of the solder slabs after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging. It could be seen that the Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn and Sn-58Bi-0.3Zn solder slabs had higher UTS than that of the pure Sn-58Bi sample. However, the ductility of them was found to be worse. The curves of UTS vs content of Zn of the solder slabs are shown in Fig. 6(a). These Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn solder slabs had the highest UTS of 63.96 and 65.85 MPa after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging, respectively, which was 6.05% and 5.50% higher than that of the Sn-58Bi sample.
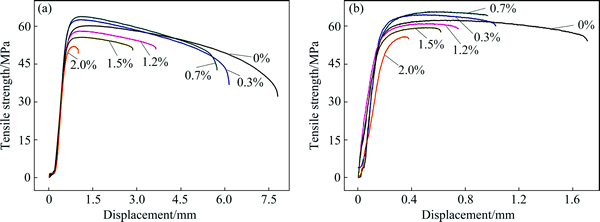
Fig. 5 Tensile stress-displacement curves of Sn-58Bi-xZn solder slabs after reflow soldering (a) and after liquid-state aging (b)
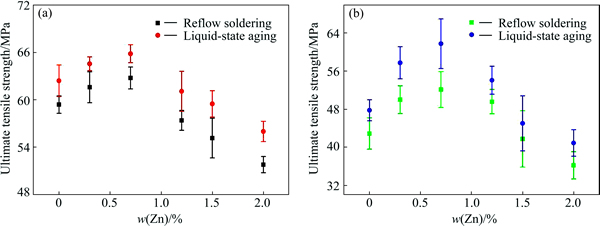
Fig. 6 UTS of Sn-58Bi-xZn solder slabs (a) and Cu/Sn-58Bi-xZn/Cu solder joints (d) after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging
The results could be understood from the microstructure and dislocation movement of the solder slabs. During the entire process of the solder ingots formation, the dispersed Bi-rich phase obstructed the motion of dislocations. These dislocations then bypassed the Bi-rich phase, leaving a dislocation loop surrounding each grain. The bypassing stress is usually called the Orowan stress [15]. Hence, the fracture resistance of solder slab was drastically weakened by the Orowan stress. With the addition of 0.7% Zn to the Sn-58Bi solder matrix, the growth and coarsening of Bi was significantly suppressed as shown in Fig. 3(b), the Orowan stress was then reduced. However, the addition of excess Zn also led to the formation of needle-shaped Zn-rich phase, which in turn hindered effective bonding between the Sn-rich phase and the Bi-rich phase. This was because the Zn element had higher affinity for oxygen than most metals, and the formed superfluous Zn oxides would degrade the integrity and mechanical properties of the solder. In addition, after liquid-state aging, the Sn-58Bi-xZn solder slabs had higher UTS and lower ductility than eutectic Sn-58Bi solder slabs. This could be explained by the fact that the Bi-rich phase in the Sn-58Bi solder slabs was obviously coarsened during the aging process. And the Sn-rich phase had good plasticity whereas the Bi-rich phase had much less plasticity, which resulted in brittle fracture of massive Bi-rich phases.
All the UTSs of Cu/Sn-58Bi-xZn/Cu solder joints after liquid-state aging are higher than those after reflow soldering, which can be seen from Fig. 6(b). Unlike the fracture mechanism of Sn-58Bi solder slab, the UTS of Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu solder joint was ascribed to the weakening of Cu/IMC interface which became the preferred fracture. The representative fracture surface of Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu solder joint is shown in Figs. 7(a) and (b). The embrittlement of the Cu/IMC interface was due to Bi segregation. From the kinetic point of view, the Bi segregation at the reactive Cu/Cu-Sn IMC interface was different from the grain boundary segregation. In the case of grain boundary segregation, solute uniformly dissolved in the solvent, and the grain boundary was considered relatively immobile. The typical traveling distance for solute atom segregated to the boundaries is about αd, where α is the ratio of the solute concentration in the grain boundary to that in the bulk, and d is the thickness of the grain boundary [21]. However, in the case of Cu/solder reactive interface, the reaction fronts were advanced deeply into the solder and substrate as Sn and Cu continued to react. For Bi to reach Cu/IMC interface, the Bi diffusion rate had at least to be fast enough to catch up with the moving Cu/IMC interface.
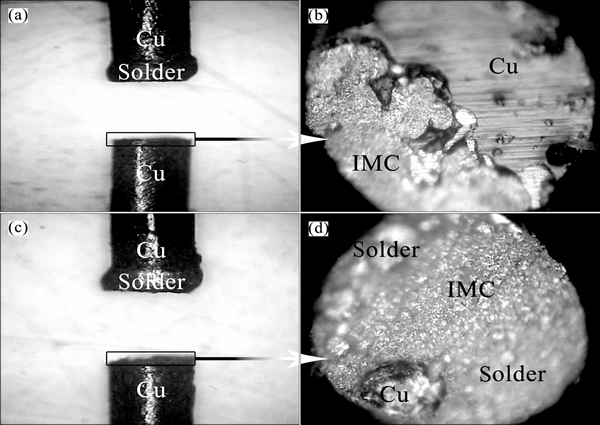
Fig. 7 Optical images of fractured Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu solder joint (a) and magnified cross section (b), fractured Cu/Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn/Cu solder joint (c) and magnified cross section (d)
During the liquid-state aging, Cu diffused through IMC to the solder matrix to react with Sn while Sn moved through the IMC to the substrate to react with Cu. As the former process did not affect the position of the Cu/IMC interface, the latter moved the interface away from the Bi source. For Bi particles segregated to the Cu/IMC interface, they must move faster than Sn through Cu-Sn IMC. Otherwise, Bi particles would never reach the Cu/IMC interface even though the interface might be a lower energy position. When the Bi segregation was found at the Cu/Cu3Sn interface (Fig. 1(c)), it is indicated that the Bi diffusion caught up with the moving Cu/IMC interface after aging. As the Cu6Sn5 transformed to Cu3Sn, the Bi particles segregated at the Cu/Cu3Sn interface because of the lattice distortion. At the same time, Bi particles acted as a barrier to Cu diffusion. During liquid-state aging, Cu atoms had to diffuse around Bi particles, creating Cu vacancies between Bi particles and Cu substrate. These vacancies then condensed to form voids. And the voids appeared accompanied by the segregated Bi particles around the Cu/Cu3Sn interface. Finally, the embrittlement of Bi and stress concentration caused by voids resulted in the reduction of tensile strength and reliability deterioration of solder joints.
Another interesting phenomenon was that the UTS of Cu/Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn/Cu solder joint was increased by 21.51% and 29.27% compared to that of Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu solder joint after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging, respectively. With the addition of 0.7% Zn to the eutectic Sn-58Bi solder, two layers of CuZn and Cu6(Sn,Zn)5 were produced between the Cu substrate and solder. The CuZn layer retarded the diffusion of both Cu and Sn, leading to a decreased consumption rate of the Cu in contact with the molten Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn solder during liquid-state aging. Through further examination, it could be found that the Zn gradually migrated to the surfaces of the molten solder to form ZnO and the previously formed CuZn IMC grains were transformed into Cu6(Sn,Zn)5. The diffusion of Bi particles were obviously restrained at the Cu/Cu-Sn IMC interface, and the Bi segregation was only found at the Cu6(Sn,Zn)5/CuZn interface during liquid-state aging as shown in Fig. 1(d). As mentioned above, Bi segregation accelerated the formation of voids at the Cu6(Sn,Zn)5/ CuZn interface. The voids would isolate the Cu6(Sn,Zn)5/ CuZn interface and then slightly decreased the interfacial bonding strength of the Cu/Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn/Cu solder joint. Thus, the fracture occurred at the IMC/solder interface as shown in Figs. 7(c) and (d). Moreover, the addition of excess Zn could lead to the formation of needle-shaped Zn-rich phase, Zn oxides and the thicker IMC layers, which would also degrade the mechanical properties of the solder joints.
3.3 Analysis of nanoindentation creep at room temperature
The load-penetration depth curves of Sn-58Bi and Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn rectangular solders after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging are respectively shown in Figs. 8(a) and (b). The changes of penetration depth at the maximum load of 20 mN are also shown in Figs. 9(a) and (b). The mechanical response in Fig. 8(a) and Fig. 9(a) came from a number of Bi and Sn-rich phase eutectic microstructures. Both as-soldered and aged samples exhibited typical indentation behavior of metallic materials with significant permanent deformation and insignificant elastic recovery, as revealed by the bulging behavior at the initial part of unloading curve. The bulging behavior appeared under the effect of creep, indicating that the creep of Sn-58Bi sample by nanoindentation test could not be avoided like β-Sn on SAC solder alloy [22]. The elastic part of the Sn-58Bi sample loading curves after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging were the same. However, the weaker plasticity was shown by the aged Sn-58Bi sample with flow stresses compared to that of the as-soldered one. The plastic deformation in Sn-58Bi sample by nanoindentation should start first in Sn-rich phase because Sn was softer than Bi. Further deformation would require dislocation movement to bypass Bi-rich phase. After liquid-state aging, Sn-rich phase was further coarsening, and allowed dislocation slip to pass through the phase boundary, resulting in a lower resistance to plastic deformation. The penetration depth of Sn-58Bi sample obtained an additional 239 nm displacements during the constant period at maximum load in as-soldered sample, and about 250 nm penetration depths were produced in aged sample during the prolonged holding of the indentation load at the peak value. This implied that the liquid-state aging accelerated creep deformation in the Sn-58Bi sample.
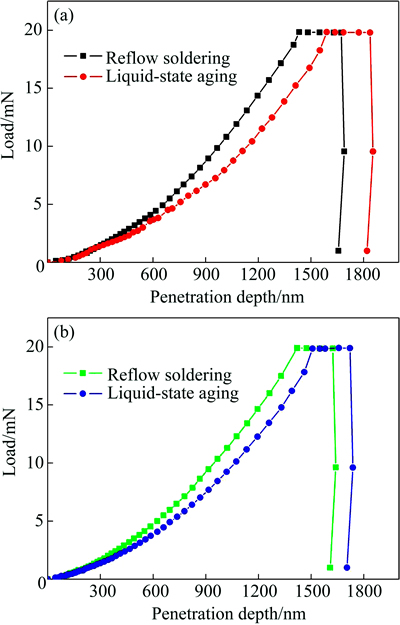
Fig. 8 Load-depth curves of Sn-58Bi (a) and Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn (b) rectangular solders after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging

Fig. 9 Changes of penetration depth at maximum load of 20 mN with holding time of 54 s for Sn-58Bi (a) and Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn (b) rectangular solders after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging
The mechanical response of Sn-rich, Bi-rich and Zn phase was shown in Fig. 8(b) and Fig. 9(b). After the indentation reached a depth of 1420 nm in the initial loading, holding at the maximum load acquired 203 nm penetration depths in the as-soldered Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn sample. For the aged one, a bigger creep displacement of 213 nm was achieved. Therefore, the creep deformation in the Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn sample was also accelerated during the aging. An interesting phenomenon was that the creep penetration depth of Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn sample was decreased compared to that of Sn-58Bi sample after liquid-state aging. This was because the addition of Zn could serve as heterogeneous nucleation points in eutectic Sn-58Bi solder, and then the coarsening of Bi-rich phases were restrained (Fig. 3(b)). The brittleness of solder matrix was thus decreased. Finally, the hardness of the Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn sample was lower than that of Sn-58Bi sample. However, the addition of excess Zn could lead to the formation of Zn oxides and voids, which would then greatly degrade the mechanical properties of the solder sample. Thus, the Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn sample appeared to be more creep resistant than the Sn-58Bi sample with reduced creep deformation and rate.
In Fig. 10, the indentation steady state creep strain rate ((1/h)·(dh/dt)) is plotted against the shear modulus compensated stress (σ/G) on a double logarithmic scale for Sn-58Bi and Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn rectangular solders using a power law creep equation [23,24], where h is the instantaneous displacement of the indenter, t is the creep time, σ is the stress amplitude corresponding to steady state conditions and G is the temperature dependent intrinsic shear modulus. The stress exponent (n) can be obtained by the slopes from Fig. 10. In the investigation, the n values were 2.90 and 4.76 for Sn-58Bi sample after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging, and were 3.04 and 5.66 for Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn sample. This indicated that the predominant creep mechanism of them might be climb-assisted dislocation slip [25-27]. The coarsening of Bi-rich phase in solder matrix could serve as obstacle for Sn-58Bi samples. Dislocations glided under the stresses bypassing these obstacles, leaving a dislocation loop surrounding each grain, and then resulted in creep deformation. However, for Sn-58Bi-xZn samples, the addition of Zn to Sn-58Bi solder suppressed the coarsening of Bi-rich phase, leading to higher creep resistance.
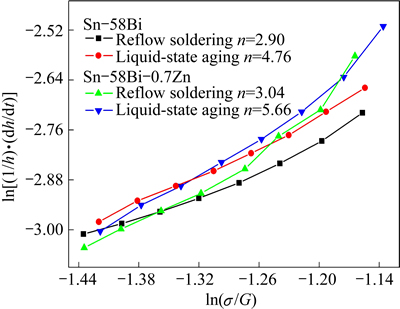
Fig. 10 Stress exponent values from nanoindentation tests for Sn-58Bi and Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn rectangular solders after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging
4 Conclusions
1) The coarsening of Bi and the growth of Cu-Sn IMCs were significantly suppressed during liquid-state aging by the addition of 0.7% Zn. The melting temperature of eutectic Sn-58Bi solder was found to be slightly decreased with the Zn content increasing, indicating the viable soldering application during practical manufacturing process.
2) Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn solder slab showed the highest UTS of 63.96 and 65.85 MPa after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging, respectively. The UTS degraded with further increment in the Zn addition. The UTS characterizations of Sn-58Bi-xZn solder slabs could be attributed to the combination of the following factors: 1) Bi-rich phases refined by Zn; 2) dislocation movement by the Orowan mechanism; 3) needle-shaped Zn-rich phase and superfluous Zn oxides formation.
3) The Bi segregation was suppressed at the Cu/IMC interface by Zn addition, and then the fracture surface of Cu/Sn-58Bi-xZn/Cu solder joint was changed from the Cu/IMC interface to the IMC/solder interface.
4) The creep behavior of the Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn solder was improved significantly as compared to that of the Sn-58Bi solder after reflow soldering and liquid-state aging.
References
[1] LI J F, MANNAN S H, CLODE M P, WHALLEY D C, HUTT D A. Interfacial reactions between molten Sn–Bi–X solders and Cu substrates for liquid solder interconnects [J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(11): 2907-2922.
[2] DONG Wen-xing, SHI Yao-wu, XIA Zhi-dong, LEI Yong-ping, Guo Fu. Effects of trace amounts of rare earth additions on microstructure and properties of Sn-Bi-based solder alloy [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2008, 37(7): 982-991.
[3] HE Peng,  Xiao-chun, ZHANG Bin-bin, MA Xin, QIAN Yi-yu. Effect of alloy element on microstructure and impact toughness of Sn-57Bi lead-free solders [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2010, 10: 13-17, 31. (in Chinese)
Xiao-chun, ZHANG Bin-bin, MA Xin, QIAN Yi-yu. Effect of alloy element on microstructure and impact toughness of Sn-57Bi lead-free solders [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2010, 10: 13-17, 31. (in Chinese)
[4]  Xiao-chun, HE Peng, ZHANG Bin-bin, MA Xin, QIAN Yi-yu. Effect of solidification mode on microstructure and properties of Sn-Bi solders [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2010, 10: 89-95. (in Chinese)
Xiao-chun, HE Peng, ZHANG Bin-bin, MA Xin, QIAN Yi-yu. Effect of solidification mode on microstructure and properties of Sn-Bi solders [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2010, 10: 89-95. (in Chinese)
[5] FUCHS C, SCHRECK T, KALOUDIS M. Interfacial reactions between Sn-57Bi-1Ag solder and electroless Ni-P/immersion Au under solid-state aging [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47(9): 4036-4041.
[6] HE Peng,  Xiao-chun, LIN Tie-song, LI Hai-xin, AN Jing, MA Xin, FENG Ji-cai, ZHANG Yan, LI Qi, QIAN Yi-yu. Improvement of mechanical properties of Sn-58Bi alloy with multi-walled carbon nanotubes [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(S3): s692-s696.
Xiao-chun, LIN Tie-song, LI Hai-xin, AN Jing, MA Xin, FENG Ji-cai, ZHANG Yan, LI Qi, QIAN Yi-yu. Improvement of mechanical properties of Sn-58Bi alloy with multi-walled carbon nanotubes [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(S3): s692-s696.
[7]  Xiao-chun, LIN Tie-song, WANG Jun, AN Jing, HE Peng. Morphology characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in Sn-58Bi/CNTs composites [J]. Materials Transactions, 2013, 54(7): 1228-1231.
Xiao-chun, LIN Tie-song, WANG Jun, AN Jing, HE Peng. Morphology characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in Sn-58Bi/CNTs composites [J]. Materials Transactions, 2013, 54(7): 1228-1231.
[8] SUGANUMA K, NIIHARA K, SHOUTOKU T, NAKAMURA Y. Wetting and interface microstructure between Sn-Zn binary alloys and Cu [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 1998, 13(10): 2859-2865.
[9] SHOHJI I, NAKAMURA T, MORI F, FUJIUCHI S. Interface reaction and mechanical properties of lead-free Sn-Zn alloy/Cu joints [J]. Materials Transactions, 2002, 43(8): 1797-1801.
[10] JEE Y K, KO Y H, YU J. Effect of Zn on the intermetallics formation and reliability of Sn-3.5Ag solder on a Cu pad [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2007, 22(7): 1879-1887.
[11] YU Chun, LU Hao, LI Shi-ming. Effect of Zn addition on the formation and growth of intermetallic compound at Sn–3.5 wt% Ag/ Cu interface [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 460(1-2): 594-598.
[12] KOTADIA H R, MOKHTARI O, BOTTRILL M, CLODE M P, GREEN M A, MANNAN S H. Reactions of Sn-3.5Ag-based solders containing Zn and Al additions on Cu and Ni(P) substrates [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2010, 39(12): 2720-2731.
[13] LUO Zhong-bing, ZHAO Jie, GAO Yan-jun, WANG Lai. Revisiting mechanisms to inhibit Ag3Sn plates in Sn-Ag-Cu solders with 1wt.% Zn addition [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 500(1): 39-45.
[14] SONG H Y, ZHU Q S, WANG Z G, SHANG J K, LU M. Effects of Zn addition on microstructure and tensile properties of Sn–1Ag–0.5Cu alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(6): 1343-1350.
[15] HAMADA N, UESUGI T, TAKIGAWA Y, HIGASHI K. Effects of Zn addition and aging treatment on tensile properties of Sn-Ag-Cu alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 527: 226-232.
[16] CHEN C M, HUANG C C, LIAO C N, LIOU K M. Effects of copper doping on microstructural evolution in eutectic SnBi solder stripes under annealing and current stressing [J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2007, 36(7): 760-765.
[17] EL-DALY A A, SWILEM Y, MAKLED M H, EL-SHAARAWY M G, ABDRABOH A M. Thermal and mechanical properties of Sn-Zn-Bi lead-free solder alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 484: 134-142.
[18] LINDEMANN F A. The calculation of molecular vibration frequencies [J]. Physikalische Zeitschrift, 1910, 11: 609-612.
[19] COUCHMAN P R, RYAN C L. The Lindmann hypothesis and the size-dependence of melting temperature [J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 1978, 37(3): 369-373.
[20] ZIMAN J M. Principles of the theory of solids [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1972.
[21] HONDROS E D, SEAH M P. Segregation to interfaces [J]. International Metals Reviews, 1977, 22: 262-301.
[22] SUN Yong, LIANG Jin, XU Zhi-hui, WANG Guo-feng, LI Xiao-dong. Nanoindentation for measuring individual phase mechanical properties of lead free solder alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2008, 19(6): 514–521.
[23] LIU Y C, TEO J W R, TUNG S K, LAM K H. High-temperature creep and hardness of eutectic 80Au/20Sn solder [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 448(1-2): 340-343.
[24] KUMAR K M, KRIPESH V, SHEN L, ZENG K Y, TAY A A O. Nanoindentation study of Zn-based Pb free solders used in fine pitch interconnect applications [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 423(1-2): 57-63.
[25] LANGDON T G. Creep at low stresses: An evaluation of diffusion creep and Harper-Dorn creep as viable creep mechanisms [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33(2): 249-259.
[26] SHARMA G, RAMANUJAN R V, KUTTY T R G, TIWARI G P. Hot hardness and indentation creep studies of a Fe-28Al-3Cr-0.2C alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 278(1-2): 106-112.
[27] MAHMUDI R, GERANMAYEH A R, NOORI H, SHAHABI M. Impression creep of hypoeutectic Sn-Zn lead-free solder alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 491(1-2): 110-116.
马东亮1,2,吴 萍1,2
1. 天津大学 理学院 应用物理系,天津 300072;
2. 天津大学 天津市低维功能材料物理与制备技术重点实验室,天津300072
摘 要:对液态时效条件下Sn-58Bi-xZn (x=0, 0.7) 焊料样品的力学性能(包括拉伸强度和蠕变性能)以及相关的界面反应进行研究。结果表明,在Sn-58Bi-0.7Zn焊料样品中,Bi的粗化现象和Cu-Sn界面金属间化合物的生长都得到了有效抑制。通过掺杂0.7% Zn,回流焊接后焊条样品的极限拉伸强度比共晶Sn-58Bi的极限拉伸强度提高了6.05%,液态时效后的极限拉伸强度则提升了5.50%。对于焊点样品,掺杂0.7%Zn后的极限拉伸强度相比Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu在回流焊接后提升21.51%,而在液态时效后则提升29.27%。焊点强度的增加是由于Zn的掺杂导致Bi晶粒细化,使得断裂面从Cu和界面金属间化合物界面处转移到了界面金属间化合物和焊料界面处。纳米压痕的结果显示,通过向共晶Sn-58Bi焊料中掺杂0.7% Zn,焊料的抗蠕变性在回流焊接和液态时效后都有较大幅度的提升。
关键词:Zn;Sn-Bi焊料;掺杂液态时效;回流焊接;蠕变
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (51074112) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Ping WU; Tel: +86-22-27403488; Fax: +86-22-27406852; E-mail: pingwu@tju.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63719-0

