DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.04.035
生物沥青-木屑混合成型行为和成型燃料品质分析
李士伟1, 2,李辉2,李昌珠2,王国平1,肖志红2,张爱华2,刘汝宽2,3,梁润芬1
(1. 南华大学 化学化工学院,湖南 衡阳,421001;
2. 湖南省林业科学院 生物环境工程研究所,湖南 长沙,410004;
3. 中南大学 化学化工学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:针对生物质成型产业现存的成型能耗较高和产品质量不佳的问题,采用生物柴油生产工艺的副产物生物沥青作为添加剂,按不同配比分别与樟木屑和杉木屑混合,制备成型燃料。考察生物沥青掺加量对木屑的成型能耗(挤压和推动能耗)和木屑成型燃料性质(密度、吸水性和燃烧特性)的影响规律。研究结果表明:当物料中生物沥青掺加量由0提高至20%时,挤压能耗依次降低,而推动能耗在0~5%处降低较为显著。木屑成型燃料的密度随着生物沥青掺加量的提高呈现先升高后降低的趋势,并在5%处取得最大值。成型燃料的吸水能力随着生物沥青掺加量的提高而持续降低。添加生物沥青能够降低成型燃料的着火温度,并扩大有效燃烧温度区间,从而提高成型燃料燃烧的稳定性和持续性。
关键词:生物沥青;能耗;密度;燃烧特性
中图分类号:TK6;S216.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2017)04-1111-08
Co-pelletization of bio-asphalt and sawdust:densification behavior and qualities of pellet fuel
LI Shiwei1, 2, LI Hui2, LI Changzhu2, WANG Guoping1, XIAO Zhihong2,ZHANG Aihua2, LIU Rukuan2, 3, LIANG Runfen1
(1. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, China;
2. Institute of Biological and Environmental Engineering, Hunan Academy of Forestry, Changsha 410004, China;
3. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Bio-asphalt, obtained from the production of biodiesel via transesterification method, was applied as an additive to be mixed with camphor wood sawdust and Chinese fir sawdust with setting ratios, respectively. The blends were further compressed into pellets. The effect of bio-asphalt dosage on compression properties (compaction and extrusion energy consumption), and properties (density, moisture uptake and combustion characteristics) of pellets were investigated. The results show that the compaction energy consumption decreases with bio-asphalt dosage increasing from 0 to 20%, while a marked decrement of extrusion energy consumption is obtained in the range of 0-5%. The maximum densities of pellets are also obtained around bio-asphalt dosage of 5%. The moisture uptake of pellet decreases with the increment of bio-asphalt dosage, while the higher heating value of pellet is identified as an opposite trend. Furthermore, pellet fuel’s ignition temperature is reduced with the addition of bio-asphalt, which can improve the stability and continuity of pellet’s combustion.
Key words: bio-asphalt; energy consumption; density; characteristics of combustion
生物质成型燃料是一种环保清洁的能源。其优点包括燃烧效率高、灰分、硫和氮含量低、以及储运成本不高,适宜成为国内外城市(国内特大型城市除外)供热的清洁燃料之一。然而,成型能耗过高、设备磨损严重和成型燃料质量不佳是限制国内生物质成型技术规模化的主要瓶颈。其原因主要是国内生物质成型原料来源广泛,且种类繁多,而常规成型设备通常对原料的种类和尺寸有要求。因此使用来源不一且外形多样的原料将导致成型能耗过高、设备磨损严重和成型燃料质量不佳等问题。同时,我国中南和南方地区普遍气候潮湿,全年相对湿度在80%以上。成型燃料生产和使用之间存在的时空差异,使得成型燃料长距离运输和跨季节储存日渐成为产业常态。成型燃料放置于高湿度环境中,构成成型燃料的生物质微粒的组织结构和亲水性官能团会因物理和化学吸附而吸水[1]。过高的成型燃料含水率会导致成型燃料燃烧性能降低,体积膨胀,强度降低,容易破碎,甚至发生粉化和霉变,导致仓储中爆炸或自燃事故的发生。因此,制备较高密度和高抗吸水性的成型燃料具有重要意义。为解决上述问题,国内外学者的研究主要集中在:1) 成型设备的研发与改进;2) 成型工艺及参数的优化;3) 使用物理或化学方法对生物质原料进行预处理,如蒸汽爆破[2]和水热炭化[3]。其中1)和3)的操作成本普遍较高,且部分仍处于理论研究阶段;2) 对不同原料的适应性差,其使用范围有一定的局限性。生物质混合成型技术为利用多种生物质原料之间的混合来制备成型燃料。该技术能够削弱成型原料之间的异质性,提高生物质成型效果,并具有操作简单,成本低廉,原料来源广泛的特点[4-5]。因而,混合成型有可能成为一种解决生物质成型技术瓶颈的有效途径。KONG等[6]研究了废纸纤维的掺入对木屑成型颗粒物理特性的影响,发现废纸纤维通过“固体桥接”作用可以强化木屑微粒之间的内嵌结合力,进而提高成型颗粒的塑性。JIANG等[7]研究了污泥与木屑混合成型的机理,发现不同种类成型燃料在强度方面所表现出的差异性的降低与污泥的加入有关。生物沥青是以地沟油为原料,生产生物柴油剩余的残渣,约占生物柴油产量的10%。其主要成分为脂类化合物和混合脂肪酸[8-9],通常被企业当作重油烧掉或丢弃,容易对环境产生不利影响。生物沥青的氮和硫含量低,与木质生物质相比具有较高的发热量。同时,少量油脂类物质的掺加有可能改善木屑成型燃料的成型能耗及燃料品质[10]。然而,目前尚没有生物沥青与木质生物质混合制备成型燃料的报道。基于以上分析,本文作者以南方常见经济木材樟木和杉木的粉碎样为成型原料,并选生物沥青为添加剂,制备成型燃料。重点研究生物沥青掺加量对木屑成型燃料的成型能耗、密度、吸水性及燃烧特性的影响,有望为生物质成型技术的优化和生物沥青的资源化利用提供一定的参考。
1 试验
1.1 原料与设备
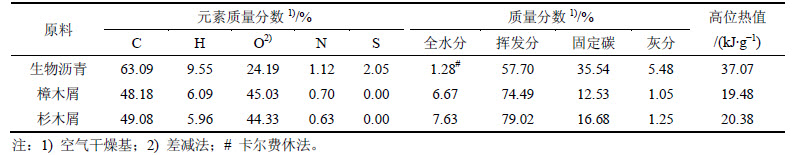
樟木和杉木取自长沙市郊的家具加工厂。经微型粉碎机粉碎后,取粒径为0.45~0.80mm的木屑于40℃干燥48h,并置于干燥器中备用。生物沥青取自长沙市近郊一家生物柴油生产企业。3种原料的元素分析、工业分析和高位热值见表1。
试验设备包括单颗粒燃料成型试验机(由济南恒瑞金试验机有限公司KLC-10型万能试验机改装);鼓风干燥箱;数显游标卡尺;分析天平(精度为0.1mg);恒湿恒温箱(高天试验设备有限公司,GT-TH-S-150Z);热重分析仪(岛津,DTG-60);电子扫描显微镜(日立,TM3000);氧弹式量热仪(长沙三德实业有限公司,SDACM 5000)。
1.2 成型燃料的制备
生物沥青以不同的质量分数(0,5%,10%,15%和20%)分别与樟木屑和杉木屑混合。调节混合物料的含水率为10%后密封在4℃冰箱内放置48h。打开温度控制器,使夹套内壁温度升至设定成型温度(150℃),保持30min。待内壁温度稳定后在压制槽底部放入不锈钢垫片,称取(0.8±0.002)g混合样品装入有垫片的夹套中,采用程序控制压杆,最大压力为4.5kN,设定停留时间30s。成型结束后取出不锈钢底板,系统控制压杆开始下行,将制成的成型燃料推出压制槽,冷却后备用。CW代表樟木成型燃料,CF代表杉木成型燃料,(5%)CW代表生物沥青以5%的质量分数与樟木屑混合所制备的成型燃料,其他编号命名方式一样。
表1 原料的元素分析和工业分析
Table 1 Ultimate and proximate analysis of materials
1.3 成型能耗计算
挤压能耗表示成型过程中压杆所做的功。推动能耗表示成型燃料成型后,压杆在对成型燃料施力到开始推动成型燃料的过程中所做的功。由压力-位移曲线图可计算出成型燃料挤压能耗及推动能耗,计算公式如下[11]:
 (1)
(1)
式中:W为挤压能耗或推动能耗,J/g;Fi为压力,N;Si为位移,m;m为成型燃料质量,g。
1.4 成型燃料物理性质
1.4.1 密度
出模初期成型燃料的密度计算公式如下:
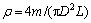 (2)
(2)
式中:ρ为密度,kg/m3;m为质量,kg;D为直径,m;L为长度,m。
1.4.2 吸水性
成型燃料于105℃下干燥24h后,放入温度为30℃,相对湿度为90%的恒湿恒温箱内,前320min每隔20min取出称质量。结束后将成型燃料继续放置于恒湿恒温箱内,48h后再次称量。成型燃料在t时刻的吸水率为
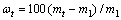 (3)
(3)
式中:ωt为t时刻吸水率,%;mt为t时刻质量,g;m1为成型燃料于105℃下干燥24h后的质量,g。
本文将成型燃料吸水48h后的吸水率视为实际平衡吸水率。KARADAG等[12]认为吸水树脂吸水率ωt与对应的时间t有如下关系:
 (4)
(4)
为确定该吸水模型对成型燃料的适用性,假设t为0时,成型燃料吸水率ωt为0,整理式(4)得:
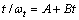 ;
;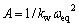 ;
;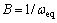 (5)
(5)
式中:kw为吸水速率常数;ωeq为理想状况下,成型燃料吸水饱和时的平衡吸水率。
由式(5)可知t/ωt与t呈线性关系。采用式(5)对成型燃料在0~320min内的吸水率数据进行拟合,并得到成型燃料吸水48h后的理论和实际平衡吸水率ωet。
1.5 成型燃料燃烧特性
1.5.1 热分析
测试样品为生物沥青及生物沥青掺加量分别为0,5%和20%的成型燃料,样品量为8~10mg。气氛为空气,流速为150mL/min。升温程序如下:1) 在30~105℃温度区间,升温速率为10℃/min,停留时间为10min;2) 在105~830℃温度区间,升温速率为15℃/min,停留时间为2min。
样品的综合燃烧特性指数S(min-2·℃-3)由下式计算[13]:
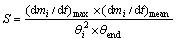 (6)
(6)
式中:θi为着火温度,采用切线法确定[14],℃;θend为样品燃烧后期燃烧速率为0.05%/min对应的温度,℃;(dmi/dt)max为最大燃烧速率,%/min;(dmi/dt)mean为从着火至燃尽阶段的平均燃烧速率,%/min。
1.5.2 高位热值
依据GB/T 30727—2014“固体生物质燃料发热量测定方法”,采用氧弹式量热仪测定高位热值,试验重复3次,结果取平均值。
2 结果与分析
2.1 成型能耗
在成型燃料生产的整个工序中,压缩成型阶段耗能最多,主要用于使物料发生形变和克服摩擦力做功,此阶段能耗是衡量成型工艺合理性和经济性的重要指标之一。根据工业级成型机的成型特点,作者使用单颗粒成型机将成型燃料的成型能耗分为2部分来研究,即挤压能耗和推动能耗。其中挤压能耗为成型机的压杆克服物料微粒之间的摩擦所产生的能耗和使物料发生形变的能耗。推动能耗为成型机的压杆克服成型燃料与夹套内壁之间的摩擦所产生的能耗。影响2种能耗的因素各不相同,但两者的降低均有助于降低生产能耗和成型核心部件的磨损,进而提高成型机的使用寿命。
图1(a)所示为2种木屑中掺加生物沥青后,成型燃料挤压能耗的变化趋势图。随着生物沥青掺加量的增加,樟木和杉木2种成型燃料的挤压能耗均呈现持续降低的现象,当生物沥青掺加量由0提高至20%时,两者的挤压能耗分别降低高达44.16%和43.51%。在本文所采用的试验条件下,成型燃料挤压能耗的降低与木屑流动性的提高以及木屑中木质素软化温度的降低有关。木屑中掺入生物沥青,可在一定程度上降低木屑及相互搭接的“分枝”之间的摩擦。木屑流动性得到提高,对成型设备提供较少的能量便可实现压缩成型。其次,通过对木屑的润湿作用,生物沥青中有机小分子插入到木质素大分子之间,能够削弱大分子间的作用力,降低木质素的玻璃态转变温度(Tg)[15-17]。木质素在增强木质细胞的机械强度方面起着重要的作用,因此,木质素软化温度的降低可以有效减小木屑被挤压时发生形变所需要的能耗。
生物沥青掺加量相同时,杉木屑成型时的挤压能耗比樟木屑的高。这与2种木屑理化性质的不同有关。木质素的Tg与相对分子质量成正比,与阔叶材(樟木)相比,针叶材(杉木)木质素平均相对分子质量较高[18],因此,杉木屑木质素的Tg比樟木屑的高。同时,与樟木屑相比,杉木屑表面更为粗糙,“分枝”也较多,如图2所示。较高的表面粗糙度和木质素Tg使得杉木屑受压缩时,需要消耗更多的能量来克服摩擦和产生形变。
组成木屑的纤维素分子具有黏弹性,使得物料经挤压阶段成型后因具有不完全塑性而向四周发生一定程度的膨胀,并挤压模具内壁。当成型燃料被压杆推出模具时,产生推动能耗。如图1(b)所示,为生物沥青掺加量对成型燃料推动能耗的影响。生物沥青掺加量由0提高至5%,樟木和杉木成型燃料的推动能耗分别降低高达73.13%和38.74%。推动能耗主要与成型燃料的塑性及成型燃料与夹具内壁之间的动摩擦因数有关。同时,成型燃料的塑性与其密度成正相关[19]。生物沥青掺加量由5%提高至20%,成型燃料的推动能耗变化不明显,而塑性持续降低。说明生物沥青的掺加降低了成型燃料与夹具内壁之间的动摩擦因数。在挤压阶段,可观察到生物沥青从夹具内渗出的现象,渗出的生物沥青能够在成型燃料和夹具内壁之间形成“液膜”降低摩擦因数。因此,生物沥青的掺加降低了推动能耗,是由成型燃料塑性的提高和摩擦因数的降低共同作用的结果。

图1 生物沥青掺加量对成型能耗的影响
Fig. 1 Effect of bio-asphalt dosage on energy consumption
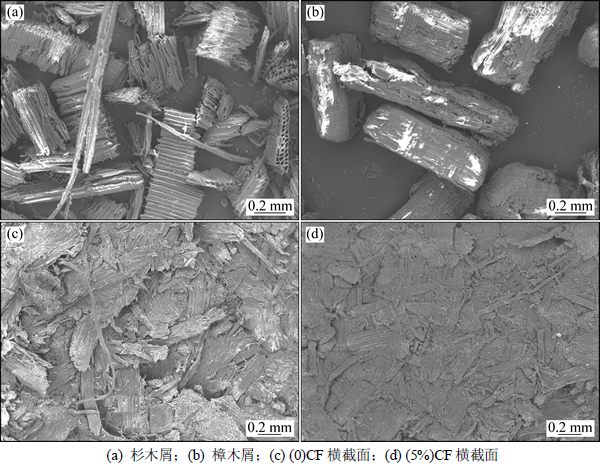
图2 木屑原料及成型燃料横截面扫描电镜图
Fig. 2 SEM images of sawdust materials and cross-section of pellet fuel
2.2 成型燃料物理性质
2.2.1 成型燃料密度
图3所示为樟木和杉木成型燃料密度随生物沥青掺加量的变化趋势。所制备的成型燃料密度均高于1000kg/m3。与纯木屑成型燃料相比,掺加生物沥青后成型燃料密度升高。由2.1可知:这是因为生物沥青的掺加,降低了木屑的软化温度,提高了木屑的流动性,木屑易于填充入成型燃料内部较小的空隙中[20]。对比图2(c)和2(d)可以看出:含5%生物沥青的成型燃料内部间隙较少,微粒之间结合紧密。随着生物沥青掺加量的提高,樟木和杉木成型燃料的密度先升高后降低,两者的密度最高分别达到了1130kg/m3和1150kg/m3。生物沥青的掺加量进一步提高(大于5%)时,成型燃料密度降低,这可能是由于过多的生物沥青在成型原料间形成“液膜”,阻碍氢键和“固体搭桥”作用的形成,减弱了木屑之间的结合力[21],同时也对成型燃料的塑性产生不利影响。
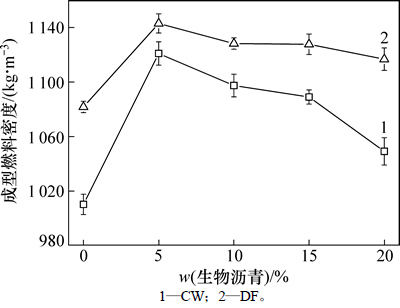
图3 生物沥青掺加量对成型燃料密度的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of bio-asphalt dosage on pellet fuel density
2.2.2 成型燃料吸水性
图4所示为生物沥青含量不同的成型燃料在温度为30℃,相对湿度为90%环境中的吸水曲线图。不同成型燃料的吸水率随时间的延长具有相似的变化趋势,即吸水率不断增加,但增长幅度逐渐放缓。其次,成型燃料在吸水性测试的220min内吸水迅速,220min后,吸水率增长缓慢并逐渐趋于平衡。例如樟木成型燃料吸水时间由220min延长至320min,吸水率仅提高1.4%~3.5%。纯木屑成型燃料吸水为木屑的组织结构及亲水性官能团对水分子的物理吸附和缓慢水合共同作用的结果。吸水前期(0~220min),物理吸附处于主导地位,吸水率的增长表现为短时间内的快速增加;吸水后期(220~2880min),与物理吸附相比,木屑中亲水性官能团与水分子间缓慢的水合作用贡献较大而使吸水率逐渐趋于平衡[12, 22]。
表2所示为生物沥青含量不同的成型燃料吸水动力学参数。由表2可以看出:线性拟合的相关度非常高。通过拟合方程计算得到的成型燃料吸水48h后的理论平衡吸水率ωet与实际值ωer比较接近,且两者随生物沥青掺加量的增加呈现相同的降低趋势。生物沥青的掺加对成型燃料吸水能力有显著的影响。随着生物沥青掺加量由0提高至20%,樟木成型燃料平衡吸水率ωer由13.7%降低至11.9%,杉木成型燃料平衡吸水率由13.2%降低至12.1%。掺加生物沥青后,成型燃料在吸水前期的吸水速率明显降低,说明生物沥青削弱了成型燃料对水分的物理吸附能力。其原因是生物沥青吸附在木屑的表面及填充于内部的孔隙中后,在一定程度上能够抑制水分在木屑组织结构间的扩散。

图4 生物沥青掺加量不同的成型燃料吸水曲线
Fig. 4 Moisture absorption curves of pellet fuel with different amount of bio-asphalt
表2 生物沥青掺加量不同的成型燃料吸水动力学参数
Table 2 Moisture absorbing kinetics parameters of pellet fuel with different amount of bio-asphalt

樟木和杉木成型燃料吸水速率常数kw的变化不具有明显的规律性,但含生物沥青的成型燃料的kw普遍要高于纯木屑成型燃料的。因此,kw的升高与成型燃料表面亲水性官能团的减少有关。从LAM等[2]以及KARADAG等[12]的研究中可以得到类似的结论。
2.3 成型燃料燃烧特性
图5(a)和5(b)所示分别为生物沥青含量不同的成型燃料的TG曲线和DTG曲线。图5中仅列出了生物沥青质量分数分别为0,5%和20%的樟木和杉木成型燃料的热分析曲线。成型燃料的燃烧过程均可以划分为脱水、挥发分析出及燃烧、焦炭的燃烧和燃尽4个阶段[12, 23]。综合上述成型燃料的燃烧特性参数(表3),可知生物沥青掺加量对成型燃料的燃烧特性有显著影响。随着生物沥青掺加量的升高,成型燃料在脱水阶段的质量损失率β1降低。说明生物沥青提高了成型燃料的疏水性,降低了其在储放阶段的吸水率。这有助于改善燃料在燃烧器内使用时的点火特性和低位热值。着火温度θi为衡量燃料着火性能的一个重要指标。θi越低,燃料着火性能越好。与纯木屑成型燃料相比,含生物沥青的成型燃料θi较低。这与挥发分析出阶段,生物沥青中小分子有机物的挥发和部分组分分解所产生的可燃性气体的释放有关[24]。
综合燃烧特性指数S普遍用于衡量成型燃料的综合燃烧特性,S越大表明成型燃料综合燃烧性能越好。由表3可知:樟木和杉木成型燃料的S均随生物沥青掺加量的升高而降低。但生物沥青掺加量为5%时,对成型燃料S影响较小,例如樟木成型燃料S仅降低3.5%;生物沥青掺加量提高至20%时,成型燃料S降低较为显著,例如杉木成型燃料S降低高达65.2%。掺入生物沥青后,成型燃料最大燃烧速率的降低和燃尽温度的升高是S降低的主要原因。
在含生物沥青的成型燃料的挥发分析出及燃烧阶段,吸附在木屑表面和填充入木屑内部孔隙的生物沥青,通过分子间吸引力和液膜的阻碍作用,降低了纤维素热解所产生的挥发分与周围氧气的结合速率,此阶段的最大燃烧速率因此大幅度下降。此外,与纯木屑成型燃料相比,含生物沥青的成型燃料的最大燃烧速率不仅降低,而且出现在焦炭燃烧阶段。这是因为在焦炭燃烧阶段,生物沥青具有最大的燃烧速率,生物沥青大量分解燃烧的同时也增加了焦炭与氧气接触的表面积,生物沥青与焦炭燃烧的叠加作用提高了此阶段的最大燃烧速率。但当生物沥青掺加量过高时,生物沥青会在焦炭燃烧阶段发生剧烈的重聚合结焦现象[25],降低焦炭与氧气的接触面积,进而对此阶段的燃烧速率产生不利影响。生物沥青灰分含量高于木屑,两者混合燃烧,较高的灰分含量会阻隔碳成分燃尽[14],因此成型燃料的燃尽温度随生物沥青掺加量的提高而升高。
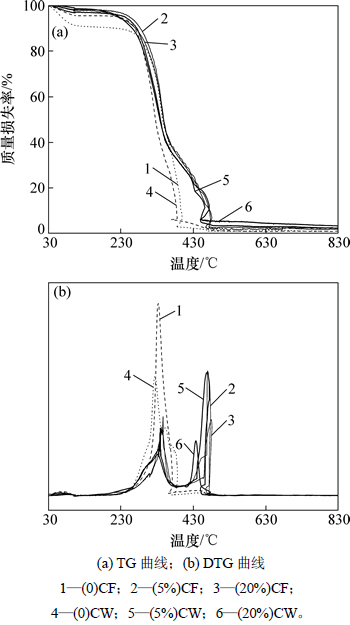
图5 生物沥青掺加量不同的成型燃料热分析曲线
Fig. 5 Thermal analysis curves of pellet fuel with different amount of bio-asphalt
表3 生物沥青掺加量不同的成型燃料燃烧特性参数
Table 3 Characteristic combustion parameters for pellet fuel with different amount of bio-asphalt
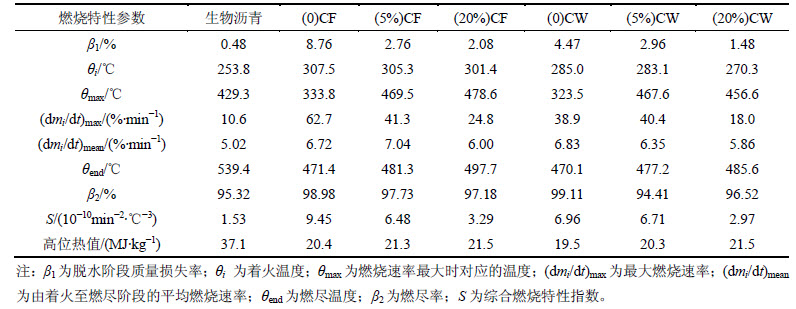
然而,生物沥青掺加量由0提高至20%,成型燃料从着火点至燃尽点的平均燃烧速率变化较小,且从着火点至燃尽点的有效燃烧温度区间依次增大。说明掺入生物沥青后,成型燃料燃烧的可持续性和稳定性得到增强。同时,生物沥青的掺入能够显著提高成型燃料的热值。当生物沥青掺加量由0提高至20%时,樟木成型燃料的高位热值提高9.29%,杉木成型燃料的高位热值提高5.39%。
3 结论
1) 在樟木屑和杉木屑中分别掺入生物沥青,通过提高木屑的流动性和降低木屑中木质素的玻璃态转变温度,降低了2种木屑在压缩成型过程中的挤压能耗。其中木屑表面结构和玻璃态转变温度的差异是造成生物沥青-杉木屑混合成型的挤压能耗高于生物沥青-樟木屑混合成型的挤压能耗的主要原因。
2) 适量生物沥青的掺入能够降低成型燃料的推动能耗,提高其密度。然而,掺加过多的生物沥青会在成型微粒间形成“液膜”,阻碍氢键和“固体搭桥”作用的形成,降低成型燃料的塑性和密度。
3) 吸水模型对吸水数据线性拟合的相关度很高。吸附在木屑微粒表面和填充于木屑内部孔隙中的生物沥青,能够降低成型燃料对水分子的物理吸附能力和亲水性官能团的水合作用,提高成型燃料的疏水性。
4) 综合混合成型燃料的燃烧特性和高位热值,生物沥青掺加量以5%为最佳,所制备的成型燃料的综合燃烧特性指数和高位热值较高,同时具有优异的燃烧可持续性、密度大、能耗低的优点。
参考文献:
[1] CHEN Yingquan, LIU Biao, YANG Haiping, et al. Evolution of functional groups and pore structure during cotton and corn stalks torrefaction and its correlation with hydrophobicity[J]. Fuel, 2014, 137: 41-49.
[2] LAM P S, LAM P Y, SOKHANSANJ S, et al. Steam explosion of oil palm residues for the production of durable pellets[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 141: 160-166.
[3] LIU Zhengang, QUEK A, KENT HOEKMAN S, et al. Production of solid biochar fuel from waste biomass by hydrothermal carbonization[J]. Fuel, 2013, 103: 943-949.
[4] MIRANDA T, ARRANZ J I, MONTERO I, et al. Characterization and combustion of olive pomace and forest residue pellets[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2012, 103: 91-96.
[5] LESTANDER T A, FINELL M, SAMUELSSON R, et al. Industrial scale biofuel pellet production from blends of unbarked softwood and hardwood stems: the effects of raw material composition and moisture content on pellet quality[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2012, 95: 73-77.
[6] KONG Lingjun, TIAN Shuanghong, HE Chun, et al. Effect of waste wrapping paper fiber as a “solid bridge’’ on physical characteristics of biomass pellets made from wood sawdust[J]. Applied Energy, 2012, 98: 33-39.
[7] JIANG Longbo, LIANG Jie, YUAN Xingzhong, et al. Co-pelletization of sewage sludge and biomass: the density and hardness of pellet[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 166: 435-443.
[8] 张佳运, 郭易木, 童天志, 等. 生物柴油残渣对老化沥青物理性能的影响[J]. 石油沥青, 2014, 28(4): 11-15.
ZHANG Jiayun, GUO Yimu, TONG Tianzhi, et al. Effect of biodiesel residue on physical properties of aging asphalt[J]. Petroleum Asphalt, 2014, 28(4): 11-15.
[9] 王晓辉, 司南, 叶爱英, 等. 植物油脚的综合利用[J]. 现代化工, 2007, 26(11): 21-24.
WANG Xiaohui, SI Nan, YE Aiying, et al. Comprehensive utilization of vegetable oil residue[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2007, 26(11): 21-24.
[10] LU Donghui, TABIL L G, WANG Decheng, et al. Experimental trials to make wheat straw pellets with wood residue and binders[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2014, 69: 287-296.
[11] LI Hui, LIU Xinhua, LEGROS R, et al. Pelletization of torrefied sawdust and properties of torrefied pellets[J]. Applied Energy, 2012, 93: 680-685.
[12]  B, SARAYDIN D, et al. Dynamic swelling behavior of γ-radiation induced polyelectrolyte poly (AAm-co-CA) hydrogels in urea solutions[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2005, 301(1): 102-111.
B, SARAYDIN D, et al. Dynamic swelling behavior of γ-radiation induced polyelectrolyte poly (AAm-co-CA) hydrogels in urea solutions[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2005, 301(1): 102-111.
[13] LIU Xiang, CHEN Meiqian, YU Dong, et al. Analysis of influence factors on co-combustion characteristics of bituminous coal with herbal biomass[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2012, 28(21): 200-207.
[14] 刘标, 陈应泉, 孟海波, 等. 棉秆和油菜秆热解焦炭的燃烧与吸附特性[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(10): 193-200.
LIU Biao, CHEN Yingquan, MENG Haibo, et al. Burning and adsorption characteristics of char obtained from pyrolysis of cotton stalk and rapeseed straw[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2014, 30(10): 193-200.
[15]  C, et al. Effect of glycerol on water sorption of bovine gelatin films in the glassy state[J]. Procedia Food Science, 2011, 1: 267-274.
C, et al. Effect of glycerol on water sorption of bovine gelatin films in the glassy state[J]. Procedia Food Science, 2011, 1: 267-274.
[16] STELTE W, CLEMONS C, HOLM J K, et al. Fuel pellets from wheat straw: the effect of lignin glass transition and surface waxes on pelletizing properties[J]. Bioenergy Research, 2012, 5(2): 450-458.
[17] KELLEY S S, RIALS T G, GLASSER W G. Relaxation behaviour of the amorphous components of wood[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1987, 22(2): 617-624.
[18] 郑秋阄, 范晶晶, 许凯, 等. 木质素结构在聚丙烯中抗氧化作用的影响[J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2013, 32(6): 8-11.
ZHENG Qiujiu, FAN Jingjing, XU Kai, et al. Effect of lignin structure on antioxidation in polypropylene[J]. Research and Exploration in Laboratory, 2013, 32(6): 8-11.
[19] CARONE M T, PANTALEO A, PELLERANO A. Influence of process parameters and biomass characteristics on the durability of pellets from the pruning residues of Olea europaea L[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2011, 35(1): 402-410.
[20] YUAN Xingzhong, LI Hui, ZENG Guangming, et al. Sub- and supercritical liquefaction of rice straw in the presence of ethanol water and 2-propanol-water mixture[J]. Energy, 2007, 32(11): 2081-2088.
[21] LIU Zhengang, Quek A, Balasubramanian R. Preparation and characterization of fuel pellets from woody biomass, agro-residues and their corresponding hydrochars[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 113: 1315-1322.
[22] 郝宏蒙, 杨海平, 刘汝杰, 等. 烘培对典型农业秸秆吸水性能的影响[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33(8): 90-94.
HAO Hongmeng, YANG Haiping, LIU Rujie, et al. Influence of torrefaction on typical agricultural straw hydrophilic property[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(8): 90-94.
[23] IDRIS S S, RAHMAN N A, ISMAIL L K. Combustion characteristics of Malaysian oil palm biomass, sub-bituminous coal and their respective blends via thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 123: 581-591.
[24] 王勇, 邹献武, 秦特夫. 生物质醇解重质油燃烧动力学研究[J]. 林产化学与工业, 2012, 32(1): 35-38.
WANG Yong, ZOU Xianwu, QIN Tefu. Combustion kinetics analysis of fuel oil derived from biomass liquefaction with 1-octanol[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products, 2012, 32(1): 35-38.
[25] 王贤华, 陈汉平, 张谋, 等. 生物油燃烧特性及动力学研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 36(4): 92-94.
WANG Xianhua, CHEN Hanping, ZHANG Mou, et al. Combustion characteristics of bio-oil and its kinetic analysis[J]. Huazhong University of Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(4): 92-94.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2016-04-28;修回日期:2016-06-22
基金项目(Foundation item):湖南省科技厅科技计划重点资助项目(2014WK2030);国家自然科学基金资助项目(21407046);中国科学院可再生能源重点实验室资助项目(Y407K91001);湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(13JJ4118) (Project (2014WK2030) supported by Key Project of Science and Technology Program of Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department; Project (21407046) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (Y407K91001) supported by Key Laboratory of Renewable Energy, Chinese Academy of Sciences; Project (13JJ4118) supported by Hunan Province Natural Science Foundation)
通信作者:李辉,博士,副研究员,从事生物质成型燃料制备研究; E-mail:lihuiluoyang@163.com