NH4+对不锈钢表面析氢和锰沉积反应的催化性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第11期
论文作者:杨凡 蒋良兴 于枭影 刘芳洋 赖延清 李劼
文章页码:2430 - 2439
关键词:硫酸铵;锰电沉积;析氢;不锈钢阴极
Key words:ammonium sulfate; manganese electrodeposition; hydrogen evolution; stainless steel cathode
摘 要:采用线性扫描伏安(LSV)、电化学阻抗谱(EIS)、恒电位极化、计时电流、扫描电镜(SEM)和X射线衍射(XRD)等方法,研究在不同电位区间硫酸铵浓度对不锈钢表面析氢和锰沉积反应的影响。结果表明,NH4+的放电反应可以加速整个阴极析氢反应动力学,NH4+的放电反应速率随硫酸铵浓度和过电位的增加而增加。锰在不锈钢表面的电结晶服从三维连续成核机理,晶核生长受扩散控制。增加过电位能加快形核速率,但使形核密度降低。在低电位区间,吸附于不锈钢表面的Mn2+优先放电;在中等电位区间,增加硫酸铵浓度能提高电流效率并生成更多块状晶体;在高电位区间,增加硫酸铵浓度会抑制形核过程,该条件下得到的晶体以柱状形态为主,且晶格中的氢含量更高。
Abstract: The effects of (NH4)2SO4 concentration (c((NH4)2SO4)) on hydrogen evolution and Mn electrodeposition on stainless steel (SS) in different potential ranges were investigated by linear sweep voltammetry (LSV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), potentiostatic polarization, chronoamperometry, scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques. The results show that the NH4+ discharge reaction (NDR) intensifies the overall hydrogen evolution kinetics, and the NDR is catalyzed by increasing c((NH4)2SO4) and over-potential. The electro-crystallization of Mn on SS follows a three-dimensional progressive nucleation and diffusion-limited growth mechanism. Increasing the over-potential could accelerate the nucleation rate and also cause the decline of the nucleation density. The absorbed Mn2+ preferably discharges at low over-potential. Increasing c((NH4)2SO4) at medium over-potential could improve the current efficiency and produce more block-like grains. The nucleation process is suppressed by increasing c((NH4)2SO4) at high over-potential, at which the formation of columnar grains with higher hydrogen contents becomes prevailing.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 2430-2439
Fan YANG, Liang-xing JIANG, Xiao-ying YU, Fang-yang LIU, Yan-qing LAI, Jie LI
School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 19 February 2019; accepted 18 September 2019
Abstract: The effects of (NH4)2SO4 concentration (c((NH4)2SO4)) on hydrogen evolution and Mn electrodeposition on stainless steel (SS) in different potential ranges were investigated by linear sweep voltammetry (LSV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), potentiostatic polarization, chronoamperometry, scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques. The results show that the NH4+ discharge reaction (NDR) intensifies the overall hydrogen evolution kinetics, and the NDR is catalyzed by increasing c((NH4)2SO4) and over-potential. The electro-crystallization of Mn on SS follows a three-dimensional progressive nucleation and diffusion-limited growth mechanism. Increasing the over-potential could accelerate the nucleation rate and also cause the decline of the nucleation density. The absorbed Mn2+ preferably discharges at low over-potential. Increasing c((NH4)2SO4) at medium over-potential could improve the current efficiency and produce more block-like grains. The nucleation process is suppressed by increasing c((NH4)2SO4) at high over-potential, at which the formation of columnar grains with higher hydrogen contents becomes prevailing.
Key words: ammonium sulfate; manganese electrodeposition; hydrogen evolution; stainless steel cathode
1 Introduction
Electrowinning (EW) is preferably used for extracting high-purity manganese (Mn) from aqueous solution [1,2]. Efforts have been undertaken to improve the current efficiency (CE) by accelerating the Mn elcectrodeposition reaction (MEDR) [3] or inhibiting the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) [4]. In electro- metallurgy of Mn, proper concentration of (NH4)2SO4 is needed in electrolyte to produce the Mn coating with good coverage and high CE [5]. However, recent studies have shown that excessive (NH4)2SO4 will result in a lower-than-desired CE, since the HER is intensified by increasing the (NH4)2SO4 concentration (c((NH4)2SO4)) [6]. The overall HER can be promoted through the discharge of NH4+ which produces extra hydrogen intermediates (Hads) on electrode surface through Eq. (1) [7]:
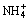 +e=Hads+NH3↑ (1)
+e=Hads+NH3↑ (1)
The 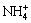 discharge reaction (NDR) is sensitive to substrate material. Industrially, Mn is always electro- deposited on stainless steel (SS) that presents suitable adhesion to coating, low electrical resistance, good flexibility and chemical inertness in catholyte [2]. However,
discharge reaction (NDR) is sensitive to substrate material. Industrially, Mn is always electro- deposited on stainless steel (SS) that presents suitable adhesion to coating, low electrical resistance, good flexibility and chemical inertness in catholyte [2]. However, 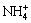 preferably absorbs and discharges on its surface [8,9]. As is known, SS contains varying levels of nickel (Ni) that is an electronegative alloying element [10,11]. Introducing Ni to the Fe matrix allows the charges to transfer from base metal to the alloying element and then enrich at the Ni sites [12]. The NDR could thus be expected to be more extensive on SS. The hydrogen evolution over-potential (ηHER) on SS decreases substantially in MnSO4-(NH4)2SO4-H2O solution, even lower than that on Mn. Therefore, the HER is recognized as the major competitive side reaction before the substrate has been covered with a thin layer, and the HER is responsible for the reduction of CE at initial stage of electrodeposition [13]. Meanwhile, the morphology, chemical compositions, and structure of the deposits are also affected by the NDR [6].
preferably absorbs and discharges on its surface [8,9]. As is known, SS contains varying levels of nickel (Ni) that is an electronegative alloying element [10,11]. Introducing Ni to the Fe matrix allows the charges to transfer from base metal to the alloying element and then enrich at the Ni sites [12]. The NDR could thus be expected to be more extensive on SS. The hydrogen evolution over-potential (ηHER) on SS decreases substantially in MnSO4-(NH4)2SO4-H2O solution, even lower than that on Mn. Therefore, the HER is recognized as the major competitive side reaction before the substrate has been covered with a thin layer, and the HER is responsible for the reduction of CE at initial stage of electrodeposition [13]. Meanwhile, the morphology, chemical compositions, and structure of the deposits are also affected by the NDR [6].
On the other hand, plenty of hydrogen bubbles catalyzed by NDR may cause an extra convection within the diffusion layer and enhance the mass transport of metal ions [14]. It is generally accepted that the species around cathode is dominated by the ammonium- manganese complexes ([Mn(H2O)6-n(NH3)n]2+) because Mn2+ ions can coordinate with NH3 to form the complexes in neutral solution [1,15]. Subsequently, Mn will be deposited through Eq. (2) [15] and the MEDR is controlled by the diffusion of these complexes to cathode surface [16]. The enhancement of mass transport of the complexes is essential to obtain a higher CE. Moreover, (NH4)2SO4 is a good conductive agent, thus a low cell voltage can be realized by increasing c((NH4)2SO4) [5].
[Mn(H2O)6-n(NH3)n]2++2e=Mn+(6-n)H2O+nNH3↑ (2)
Through above descriptions, the effects of 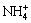 on Mn electrodeposition process are complicated. Generally, (NH4)2SO4 is the most important additive, which varies from 100 to 160 g/L in electrolyte. However, there has been short of comprehensive study referring to this compound, and its optimized concentration remains controversial. Extensive work has been performed on Mn deposition kinetics [17,18]; whereas the average CE reported by many researches is less than 80% [19]. The Mn nuclei formation and growth behaviors are sensitive to the HER occurring on substrate, and the initial layer directly determines the properties and quality of Mn coating [20]. Therefore, it is significant to study the effects of NH4+ on Mn electro- deposition on substrate, which conduces to improve the CE and provide theoretical guidance in selecting an appropriate concentration of (NH4)2SO4.
on Mn electrodeposition process are complicated. Generally, (NH4)2SO4 is the most important additive, which varies from 100 to 160 g/L in electrolyte. However, there has been short of comprehensive study referring to this compound, and its optimized concentration remains controversial. Extensive work has been performed on Mn deposition kinetics [17,18]; whereas the average CE reported by many researches is less than 80% [19]. The Mn nuclei formation and growth behaviors are sensitive to the HER occurring on substrate, and the initial layer directly determines the properties and quality of Mn coating [20]. Therefore, it is significant to study the effects of NH4+ on Mn electro- deposition on substrate, which conduces to improve the CE and provide theoretical guidance in selecting an appropriate concentration of (NH4)2SO4.
In electrometallurgy of Mn, the current contributing to the nucleation and growth of Mn on foreign substrate can hardly be determined individually since the HER occurs in parallel with MEDR. For that, a series of linear scan voltammetry (LSV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were performed to study the influence of (NH4)2SO4 on HER kinetics on SS electrode. Methods such as the potential step electrodeposition and chronoamperometry (CA) were used to screen the partial hydrogen evolution current from the overall current. The aim of this work is to reveal the complex role of (NH4)2SO4 during electrochemical extraction of Mn from aqueous system and clarify the nucleation and growth mechanisms of Mn on SS at initial stage of electro-crystallization.
2 Experimental
The electrolyte was prepared by dissolving MnSO4·H2O and (NH4)2SO4 into DI water (18.2 MΩ). The electrolyte contained 30 g/L Mn2+ with various concentrations of (NH4)2SO4. Ammonia and sulfuric acid were used to adjust the pH of the electrolyte (pH=7).
All electrochemical measurements were conducted on an electrochemical workstation (PARSTAT 2273, UK) with a three-electrode system. The SS (304 type) was used as working electrode (area of 100 mm2). Before each experiment, the working electrodes were ground with Al2O3 sand paper gradually from 400-grit to 2000-grit and then cleaned in acetone and DI water in an ultrasound cleaner. The graphite plate (area of 400 mm2) and Hg/Hg2Cl2/saturated KCl electrode were used as the counter electrode and reference electrode, respectively. All potentials in this work were reported versus the reference electrode. The gap between working electrode and counter electrode was 30 mm. The LSV experiments were swept from -0.7 to -1.7 V with a scan rate of 5 mV/s. The EIS measurements were performed at potentials ranging from -0.85 to -1.35 V, with frequency range from 0.1 Hz to 100 kHz, and the amplitude of the AC signal was 10 mV. The impedance data were fitted to an electrical equivalent circuit (EEC) using the Zsimpwin software. The CA measurements were carried out by stepping the potential from open circuit potential to different potentials.
In detail of the potential step electrodeposition, each experiment includes two stages of potentiostatic polarization. The first stage was performed at φ1 (ranging from -1.54 to -1.80 V with a certain interval) for 60 s, and then switched to more positive potential for the same period, at which the charge transfer associated reaction was only the dissolution of Mn. The quantities of electric charge (Q) were recorded by the electrochemical workstation. The deposits formed in Stage 1 dissolved completely in Stage 2. The Q1 included both the Mn deposition and hydrogen evolution, and the Q2 only contained the quantities of Mn deposited in Stage 1. Therefore, the partial current density for Mn electro- deposition (JMn) could be calculated by the Coulomb law (JMn= Q2/
Q2/ t), and the current efficiency for Mn deposition could be calculated by Q2/Q1. To minimize the IR-drop, the reference electrode was connected with the working electrode through a Luggin capillary.
t), and the current efficiency for Mn deposition could be calculated by Q2/Q1. To minimize the IR-drop, the reference electrode was connected with the working electrode through a Luggin capillary.
All experiments were performed at 308 K. Nitrogen gas was blown into electrolyte for 10 min prior to each experiment. The morphology was examined by the scanning electron microscopy with field effect (SEM-FEG, Nova NanoSEM230, CZE). The crystalline structure was investigated by X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Advance D8, SUI) with graphite monochromatized Cu Kα radiation (λ=1.5418  , 40 kV).
, 40 kV).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 HER catalyzed by (NH4)2SO4
LSV analyses were conducted at a potential of -0.7 to -1.7 V to ascertain the effects of c((NH4)2SO4) on the hydrogen evolution kinetics on SS. The onset hydrogen evolution potential on SS can be defined at around -0.9 V, and the curves undergo a gradual increase in the potential range from -0.80 to -1.50 V. The hydrogen evolution current is promoted by increasing c((NH4)2SO4). When the potential is swept to approximately -1.50 V, an apparent cathodic peak (C1) in Fig. 1(a) owning to the simultaneous NDR appears on the plots [2,7,8]. Following that, the slopes of the curves increase significantly with further increasing the potential to around -1.54 V, which can be attributed to the MEDR. The HER is considered as the dominant reaction before the Mn has been deposited at approximately -1.54 V [13]. The overall HER kinetics was characterized by the Tafel analysis. The ηHER on SS was determined by the Tafel equation (Eq. (3)), and the results are shown in Fig. 1(b).
ηHER=a+blg J (3)
where a is the intercept (mV), b is the Tafel slope (mV/dec) and J is the current density (A/cm2).
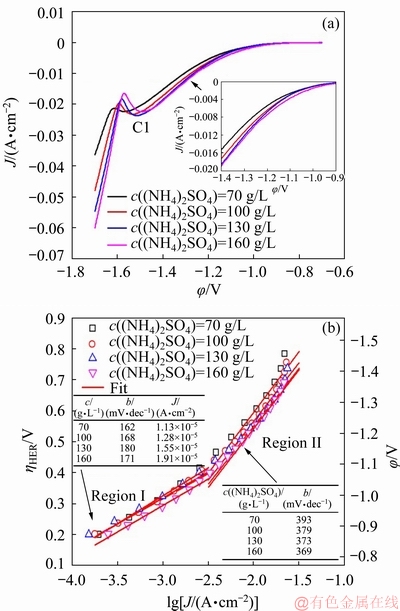
Fig. 1 LSV analyses performed in MnSO4-(NH4)2SO4-H2O solution (a) and corresponding Tafel plots for HER (b)
It is well-known that the HER occurs in neutral solution via the Volmer-Tafel pathway (Eqs. (4) and (5)) or the Volmer-Heyrovsky pathway (Eqs. (4) and (6)), both of which involve the adsorption and desorption of Hads on electrode surface [21]. Values of b can be used to evaluate the mechanistic pathways of the HER. If Eq. (4) is the rate-determining step, b can be expected to be around 118 mV/dec. When Eq. (4) occurs rapidly and is followed by a slower electro-desorption process (Eq. (6)), b is approximately 40 mV/dec.
H2O+e=Hads+OH- (b=118 mV/dec, T=298 K) (4)
2Hads=H2 (b=30 mV/dec, T=298 K) (5)
H2O+Hads+e=H2+OH- (b=39.3 mV/dec, T=298 K) (6)
In Fig. 1(b), each curve representing the dependence of ηHER versus lg J has two linear segments. At low over-potential, the Tafel slopes are closer to the theoretical value of the Volmer step, and the slopes increase to approximately 380 mV/dec in Region II. This change can be explained as follows: the species near the electrode are dominated by NH4+ at low over-potential. When increasing the over-potential to Region II, a small amount of Mn2+ may permeate into electric double-layer and absorb on electrode [22], which may decrease the coverage of Hads and result in a higher Tafel slope. In addition, the ability of a given electrode to catalyze the HER can be reflected by the exchange current density (J0) that increases monotonically from 1.13×105 to 1.91×105 A/cm2 with increasing c((NH4)2SO4) from 70 to 160 g/L, indicating the more efficient hydrogen evolution with the addition of (NH4)2SO4.
To further understand the mechanism of HER, EIS technique was adopted under different bias potentials that all locate in the corresponding regions in Fig. 1. The electrical equivalent circuit embedded in Fig. 2(b) was adopted to fit the EIS data. The Rs is the sum of the electrode resistance and solution resistance, Cdl is the double-layer capacitance, R1 represents the charge transfer resistance of the desorption of intermediates, R2 and C2 are the equivalent resistance and pseudo- capacitance associated with the adsorption of intermediates, respectively. CPEdl was used to replace C2 in the simulation, and the impedance of CPE(ZCPE) can be written as Eq. (7) [23].
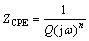 (7)
(7)
where Q is the double-layer capacitance (F/(cm2·s1-n)), ω is the angular frequency (s-1), and n represents the deviation from the ideal behavior.
Figure 2 shows the Nyquist plots for the HER. The spectra are mainly composed of a large capacitive arc that shrinks obviously as the increase of bias potential and c((NH4)2SO4). The fitting parameters are summarized in Table 1. The Rs, which is independent of the bias potentials, decreases gradually with the increase of c((NH4)2SO4). The R1 values are negligibly affected by the potentials and generally small in the potential region from -0.85 to -1.05 V. The R2 values are relatively large and present a well-defined exponential decrement with the increase of bias potential. However, the R2 decreases sharply, even approaching R1, as the bias potential is above -1.05 V. These phenomena suggested that the HER occurred in Region I is controlled by the charge transfer process, and the rate-determining step is the formation and adsorption of Hads [24]. The decline of R2 from 581 to 405 Ω/cm2 with increasing c((NH4)2SO4) from 70 to 160 g/L proves that the NDR is a secondary HER, and the overall HER is catalyzed by the addition of (NH4)2SO4.
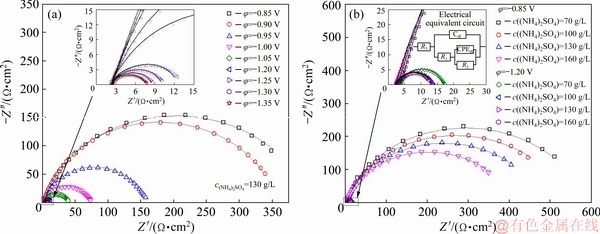
Fig. 2 Nyqusit plots obtained from MnSO4-(NH4)2SO4-H2O solution under different conditions
Table 1 Electrochemical data determined from EIS plots in Fig. 2

The Tafel behavior of the electrode can be analyzed by the experimental profile of φ vs lg R-1, and the Tafel slope could be calculated from the linear segment according to Eq. (8) [25]. Two linear segments are clearly observed, which presents a good correspondence to the LSV analyses.
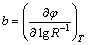 (8)
(8)
3.2 MEDR catalyzed by (NH4)2SO4
The potential step electrodeposition was employed to study the influence of c((NH4)2SO4) on Mn electro- deposition kinetics on SS. The Mn depsosition over-potential (ηMn) on SS was calculated by subtracting the electrode potential of Mn2+/Mn 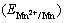 and the potential drop between working and reference electrodes from the applied potential. The
and the potential drop between working and reference electrodes from the applied potential. The 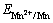 value was calculated by the Nernst equation (Eq. (9)) [26]. Based on the potential step plots, the Mn electrodepostion partial current (JMn) is plotted against ηMn in Fig. 3.
value was calculated by the Nernst equation (Eq. (9)) [26]. Based on the potential step plots, the Mn electrodepostion partial current (JMn) is plotted against ηMn in Fig. 3.
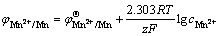 (9)
(9)
where 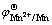 is the standard electrode potential of Mn2+/Mn, T is the thermodynamic temperature, R is the mole gas constant, F is the Faraday constant, z is the transfer electron number, and
is the standard electrode potential of Mn2+/Mn, T is the thermodynamic temperature, R is the mole gas constant, F is the Faraday constant, z is the transfer electron number, and 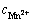 is Mn2+ concentration in bulk solution.
is Mn2+ concentration in bulk solution.
As depicted in Fig. 3, the plots have two linear segments in Region III (0.10-0.15 V) and Region IV (0.16-0.22 V). Previous studies demonstrated that the Tafel slope for Mn electrodeposition on metallic Mn has two linear regions in current density regions of 1×10-4 -1×10-3 and 1×10-2-1×10-1 A/cm2 [17,18]. In this work, the Tafel slope in Region III is about half of 2.303RT/(2F). The Tafel slope increases obviously in Region IV (approximately 210 mV/dec), and the limiting current density for MEDR is observed with further increasing the over-potential to Region V. The change of the Tafel slopes is indicative of the variation of the ions involved in MEDR. In Region III, the species in the neighborhood of SS are mainly composed of the 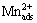 which has the lower activation energy to discharge. When the over-potential is above 0.15 V, plenty of Mn2+ ions crowd into electric double layer, hence, the deposits formed in Region IV are mainly from the discharge of Mn2+. In Region V, the NDR occurs inevitably [2], and the formation of ammonium-manganese complexes is prevailing. Due to the relative instability of these complexes in Region V [16], the species involved in MEDR may include Mn2+ and the complexes.
which has the lower activation energy to discharge. When the over-potential is above 0.15 V, plenty of Mn2+ ions crowd into electric double layer, hence, the deposits formed in Region IV are mainly from the discharge of Mn2+. In Region V, the NDR occurs inevitably [2], and the formation of ammonium-manganese complexes is prevailing. Due to the relative instability of these complexes in Region V [16], the species involved in MEDR may include Mn2+ and the complexes.
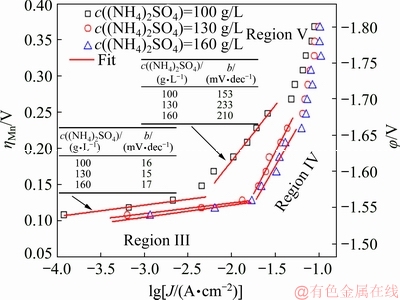
Fig. 3 Dependence of ηMn on lg JMn at different potentials
Figure 4 presents the current efficiency (CE) of Mn deposition at the potential step electrodeposition. The CE increases rapidly at low over-potential, and maintains at approximately 40% when the applied potential is more negative than -1.70 V. Increasing c((NH4)2SO4) can effectively increase the CE in potential range of from -1.55 to -1.70 V. However, with further increasing the over-potential, the CE starts to decline as the c((NH4)2SO4) is more than 130 g/L, indicating that the catalytic effect of (NH4)2SO4 on Mn deposition strongly depends on the cathodic potential.
The SEM images of the crystallites obtained by potentiostatic electrodeposition over a time span of 30 s are shown in Fig. 5. Two morphological patterns can be found at different potentials. Plenty of block-like grains are deposited at -1.65 V, and the perpendicularly oriented columnar grains with an arrow-shaped top are deposited at -1.75 and -1.85 V. The discontinuous grains are profound at high over-potential, and the submicron crystals grow continuously on the original crystallites (Fig. 5(b)). The grain coverage on SS shows down-trend with applying more negative potentials. The discharge of 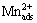 results in the boost of nucleation center on SS. However, this reaction is disturbed by increasing the over-potential and then more active sites for nucleation are substituted by the hydrogen evolution.
results in the boost of nucleation center on SS. However, this reaction is disturbed by increasing the over-potential and then more active sites for nucleation are substituted by the hydrogen evolution.
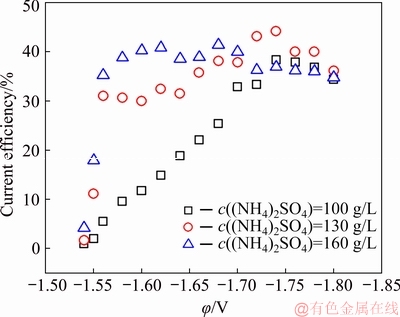
Fig. 4 Current efficiency obtained from potential step electrodeposition
The positive effects of NDR on Mn electrodeposition are observed in Region IV in Fig. 3, at which the coverage of the grains on SS increases obviously as the c((NH4)2SO4) increases from 100 to 160 g/L (Figs. 5(d, a, e)). The hydrogen evolution rates are promoted by the increase of c((NH4)2SO4), and the HER intensified by the NDR may accelerate the mass transport of metal ions to SS surface. Hence, increasing c((NH4)2SO4) in Region IV can decrease the ηMn and facilitate the electrodepostion process.
The negative effects of NDR can be noticed in Region V, at which the CE of Mn deposition decreases with increasing c((NH4)2SO4) higher than 130 g/L. When the limiting current for MEDR is reached, further increasing c((NH4)2SO4) may intensify the overall HER and interfere the nucleus formation. In addition, intensive hydrogen evolution can also affect the deposit composition. Figure 5(f) shows the XRD patterns of the Mn films obtained under different conditions. The crystalline structure of the fresh formed deposits can be indexed to gamma-Mn (γ-Mn) phase. The deposits obtained at 160 g/L (NH4)2SO4 exhibit a stronger (002) orientation, and this phenomenon shows a highly agreement with the results obtained by GONG et al who demonstrate that the more the hydrogen incorporates into Mn lattice, the stronger the diffraction peak will present in (002) orientation [16]. The deposits exposed in air for 30 d were completely transformed to alpha-Mn (α-Mn). The γ-Mn is a metastable phase that re-crystallizes to α-Mn at room temperature spontaneously. The transition kinetics is connected with the hydrogen contents in lattice [27]. The internal stress increases as more hydrogen atoms are embed into deposits, then the lattice shrinks and tensile stress arises. The NDR is profound at higher over-potential, and more Hads will then incorporate into deposits. After the hydrogen contents have exceeded the solubility limit, it would diffuse out from the lattice. Therefore, α-Mn is the only phase present after the aging process.
Fig. 5 SEM-FEG of deposits and XRD patterns of Mn films obtained under different conditions
3.3 Nucleation and growth
The CA measurements were performed to study the Mn electro-crystallization mechanism on SS. Figure 6 shows the variation of current density (J) with time (t) at different potentials. When the potential step is applied, a series of sharp spikes owning to a combination of double-layer charging and adsorption reaction are obvious at the very beginning [28]. Following closely, a nucleation peak referring to the formation and consequence growth of Mn nuclei can be observed. The transient-current density decreases gradually and reaches a constant value with prolonging time.
The transient-current density can be interpreted as follows:  discharges preferably and serves as the nucleation sites on the electrode. This reaction consumes plenty of
discharges preferably and serves as the nucleation sites on the electrode. This reaction consumes plenty of 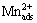 and creates a depletion zone in the vicinity of the electrode. After that, the reduction of Mn species in electric double-layer leads to the continuous decay of transient-current density. The transient current would remain stable when more Mn2+ ions diffuse from bulk solution to the depletion zone. It can be noted that the current density responses present the similar tendency in Fig. 6(b), and the equilibrium current density starts to decline after c((NH4)2SO4) increases to 160 g/L, suggesting that either the growth of the new phase or the HER is influenced by c((NH4)2SO4).
and creates a depletion zone in the vicinity of the electrode. After that, the reduction of Mn species in electric double-layer leads to the continuous decay of transient-current density. The transient current would remain stable when more Mn2+ ions diffuse from bulk solution to the depletion zone. It can be noted that the current density responses present the similar tendency in Fig. 6(b), and the equilibrium current density starts to decline after c((NH4)2SO4) increases to 160 g/L, suggesting that either the growth of the new phase or the HER is influenced by c((NH4)2SO4).
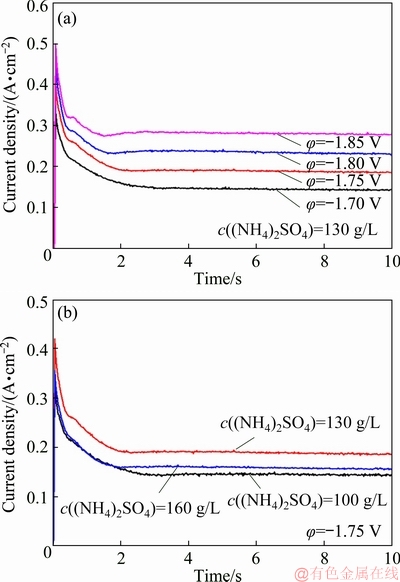
Fig. 6 CA analyses performed in MnSO4-(NH4)2SO4-H2O solution under different conditions
Many models have been utilized to reveal the mechanism of electrochemical nucleation and growth process of metal electrodeposition. Among these models, the widely used one to analyze the current density time transients that take into account the individual contribution of both HER and metallic ion electrodeposition is the model described by PALOMAR- PARDAVE et al [29]. In this model, the partial current density for hydrogen evolution (JHER) and Mn electrodeposition (JMEDR) are given by Eqs. (10) and (11), respectively. Additionally, to adequately model the transient-current densities, the capacitive current density (JDL) owning to the discharge of absorbed ions should be considered, and its algebraic expression is shown as Eq. (12) [30]. Therefore, the overall current density is expressed as Eq. (13).
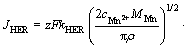
 (10)
(10)
where kHER is the rate constant of the HER (mol/(s·cm2)), MMn is the relative atomic mass of Mn, ρ is the density of the deposits (g/cm3), N0 is the number density of active sites for nucleation (cm-2), D is the diffusion coefficient of Mn2+ (cm2/s) and A is the nucleation rate per active site (s-1).
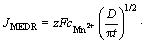
 (11)
(11)
 (12)
(12)
where kcap is the capacitive current density constant (A/cm2) and τcap is the capacitive charging time constant (s).
J=JDL+JHER+JMEDR (13)
Therein, six unknown parameters are presented in this model. These parameters were fitted to the experimental data by using the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm, and the results are summarized in Table 2. A high degree of fitting between the experimental data and the theoretical transient-current densities suggests the suitability of using this model to analyze the electro-crystallization process.
As shown in Table 2, the nucleation rate (A) increases monotonically as the applied potential becomes more negative, illustrating that the applied potential can serve as the initial driving force for the formation of nuclei on SS. Increasing the over-potential may shorten the incubation period and accelerate the electro- crystallization process. According to the atomistic theory of nucleation [31], it is possible to express the nucleation rate as follows:
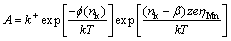 (14)
(14)
where β is the transition coefficient, f(nk) accounts for the nucleus-substrate interaction, k+ is the frequency factor, e is the Boltzmann constant, and nk is the number of atoms in the critical nucleus. Thereafter, the relationship between A and ηMn can be interpreted as Eq. (15). From the slopes by fitting the straight line of lg A/ηMn, the value of nk could be determined and tends to zero, which means that a simple Mn atom absorbed on SS forms a stable cluster that can grow irreversibly on SS [32]. The initial current of the capacitance charge attributing to the absorption of 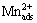 is evaluated by kcap that increases monotonically with increasing the over-potential. The rapid consumption of
is evaluated by kcap that increases monotonically with increasing the over-potential. The rapid consumption of 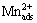 at more negative potentials gives rise to a shorter capacitive charging time. The intermediate discharging behavior presents a good agreement with the results reported by SIDES and HUANG [28].
at more negative potentials gives rise to a shorter capacitive charging time. The intermediate discharging behavior presents a good agreement with the results reported by SIDES and HUANG [28].
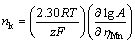 (15)
(15)
The hydrogen evolution rate (kHER) is catalyzed by applying more negative potentials. The gradual increase of kHER at high over-potential directly causes the shrink of the active sites for the nucleation. Besides, the diffusion coefficient D of metallic ions in each electrolyte does not significantly change with the potentials. The electrochemical kinetic parameters such as kHER, N0 and D are highly consistent with those reported by BOUDINAR et al who have studied the nucleation mechanism of Mn-Bi film from a sulfate- nitrate bath [33].
Table 2 Electrochemical parameters obtained from the best fit of current-transient analyses

Figure 7(a) presents the theoretical curves for the partial hydrogen evolution and Mn electrodeposition current density on SS. The JHER is provoked by applying more negative potentials, which displays a gradual increase at beginning and tends towards a constant value. This can explain the current density platform appearing in Fig. 6. After the JHER has been screened from the overall current density, the JMEDR exhibits a typical response for 3D nucleation and diffusion-controlled growth [28]. A nucleation peak is observed on plots, at which the transient-current density climbs its climax labeled Jmax with the corresponding time labeled tmax. The JHER increases significantly as the applied potential is negative than -1.80 V, while the Jmax attributed to Mn electrodeposition remains almost the same. When the limiting current density for MEDR reaches at -1.80 V, any further increase of potential would only accelerate the hydrogen evolution.
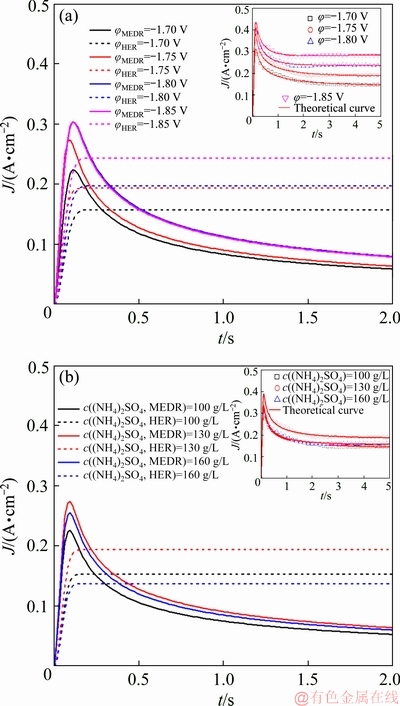
Fig. 7 Comparison between experimental transient-current and theoretical density of partial hydrogen evolution and Mn electrodeposition current density under different conditions
Figure 7(b) shows the transient-current densities obtained from different electrolytes. The stable JHER increases from 153 to 194 mA/cm2 with increasing c((NH4)2SO4) from 100 to 130 g/L, meanwhile, the Jmax increases from 226 to 274 mA/cm2. Herein, the positive effect of NDR on MEDR can be noticed by raising c((NH4)2SO4) to 130 g/L. However, the JHER presents the negative growth with further increasing c((NH4)2SO4) to 160 g/L. The changes of reaction interface and ions distribution may cause the discrepancy with Section 3.1. When the applied potential is more negative than -1.60 V, the reaction interface would switch from SS/electrolyte to Mn/electrolyte immediately. More ammonium- manganese complexes would crowd at the freshly formed crystallite surface as the c((NH4)2SO4) increases to 160 g/L. As a result, the JHER and Jmax decrease to 138 and 255 mA/cm2, respectively. In addition, the more the (NH4)2SO4 is added into electrolyte, the slower the nucleation rate is. The participation of ammonium-manganese complexes in MEDR would inhibit the nucleation process. As shown in Table 2, when the applied potential increases from -1.70 to -1.85 V, the increment of A obtained in Electrolyte III is obviously lower than that obtained in Electrolytes I and II. Therefore, with further increasing c((NH4)2SO4) to 160 g/L, the negative effect of NDR on MEDR will appear at high over-potentials.
Nucleation behavior is often characterized as either progressive or instantaneous behavior, SCHARIFKER and MOSTANY [34] suggested a dimensionless parameter, α, given by Eq. (16) to diagnose the nucleation behavior. Herein, two extreme situations are considered. A rapid nucleation rate on a small number of active sites makes α equal to zero, named instantaneous nucleation (IN). A slow nucleation rate on a large number of active sites makes α infinity, named progressive nucleation (PN). The α values calculated in all cases are beyond 1×108, which means that Mn nucleation exhibits a progressive behavior. Furthermore, the SCHARIFKER-HILLS three-dimensional (3D) theoretical model (SH model) was employed to verify the nucleation type, and the algebraic expressions relating to the IN and PN are shown in Eqs. (17) and (18), respectively. In order to make a better comparison between the predicted results and the experimental results, the J was substituted by the JMDER. As can be seen from the experimental non-dimensional plots (JMEDR/Jmax)2 versus (t/tmax)2 with the SH model, the plots fit very well with the theoretical curves for 3D progressive nucleation under all conditions. The Cottrell analysis was employed to verify the growth mechanism of Mn nuclei. The linear regions between JMDER and the t-1/2 illustrate that the growth process is believed to be under a diffusion control [35]. Hence, we can conclude that the electrodeposition of Mn on SS follows a 3D progressive nucleation and diffusion-limited growth mechanism. Enhancing mass transformation in some degree could effectively increase the CE at initial stage of electrodeposition.
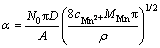 (16)
(16)
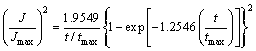 (17)
(17)
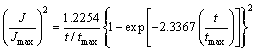 (18)
(18)
4 Conclusions
(1) The NDR is a secondary HER, which is provoked by applying more negative potentials. Increasing c((NH4)2SO4) produces extra Hads atoms and results in the decline of electrochemical impedance to the overall HER.
(2) The electrodeposition of Mn on SS follows a 3D progressive nucleation and diffusion-limited growth mechanism. Increasing the over-potential can accelerate the nucleation rate and also cause the decline of the nucleation density.
(3) The optimized c((NH4)2SO4) depends on the cathodic potential. The positive effect of NDR appears at potentials from -1.60 to -1.70 V, at which more block- like grains are produced by increasing c((NH4)2SO4). A lower c((NH4)2SO4) is recommended when the potential is more negative than -1.70 V. The nucleation rate is decreased by increasing c((NH4)2SO4), and the columnar grains with higher hydrogen contents will be produced when the NDR occurs intensively on SS.
References
[1] XUE Jian-rong, ZHONG Hong, WANG Shuai, LI Chuang-xin, WU Fang-fang. Influence of sodium silicate on manganese electrodeposition in sulfate solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 1126-1137.
[2] LU J M, DREISINGER D, GLüCK T. Manganese electro- deposition—A literature review [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2014, 141: 105-116.
[3] CHEN Xin, GUO Hua-jun, LUO Shu-liang, WANG Zhi-xing, LI Xin-hai. Effect of SnO2 intermediate layer on performance of Ti/SnO2/MnO2 electrode during electrolytic-manganese process [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 1417-1422.
[4] PADHY S K, TRIPATHY B C, ALFANTAZI A. Effect of sodium alkyl sulfates on electrodeposition of manganese metal from sulfate solutions in the presence of sodium metabisulphite [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2018, 177: 227-236.
[5] WEI P, HILEMAN O E, BATENI M R, DENG X H, PETRIC A. Manganese deposition without additives [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2007, 201: 7739-7745.
[6] FERNANDEZ-BARCIA M, HOFFMANN V, OSWALD S, GIEBELER L, WOLFF U, UHLEMANN M, GEBERT A. Electrodeposition of manganese layers from sustainable sulfate based electrolytes [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2018, 334: 261-268.
[7] RUDNIK E. Effect of gluconate ions on electroreduction phenomena during manganese deposition on glassy carbon in acidic chloride and sulfate solutions [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2015, 741: 20-31.
[8] KOZIN L F, MASHKOVA N V, MANILEVICH F D. Hydrogen overvoltage at manganese in ammonium-bromide-perchloric solution [J]. Protection of Metals and Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, 2009, 45: 25-30.
[9] YANG Fan, JIANG Liang-xing, YU Xiao-ying, YANG Jian, LIU Fang-yang, LV Xiao-jun, LAI Yan-qing, LI Jie. Hydrogen evolution behavior of aluminum cathode in comparison with stainless steel for electrowinning of manganese in sulfate solution [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2018, 179: 245-253.
[10] OLIVARES-RAMIREZ J M, CAMPOS-CORNELIO M L, URIBE GODINEZ J, BORJA-ARCO E, CASTELLANOS R H. Studies on the hydrogen evolution reaction on different stainless steels [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32: 3170-3173.
[11] XIE Li-shuai, LI Jin-shan, ZHANG Tie-bang, KOU Hong-chao. Role of milling time and Ni content on dehydrogenation behavior of MgH2/Ni composite [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 569-577.
[12] EZAKI H, MORINAGA M, WATANABE S. Hydrogen overpotential for transition metals and alloys, and its interpretation using an electronic model [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1993, 38: 557-564.
[13] XU Fu-yuan, DAN Zhi-gang, ZHAO Wei-nan, HAN Gui-mei, SUN Ze-hui, XIAO Ke, JIANG Lin-hua, DUAN Ning. Electrochemical analysis of manganese electrodeposition and hydrogen evolution from pure aqueous sulfate electrolytes with addition of SeO2 [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2015, 741: 149-156.
[14] DUNDALEK J, SNAJDR I, LIBANSKY O, VRANA J, POCEDIC J, MAZUR P, KOSEK J. Zinc electrodeposition from flowing alkaline zincate solutions: Role of hydrogen evolution reaction [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 372: 221-226.
[15] EBRAHIMIFAR H, ZANDRAHIMI M. Influence of electro- deposition parameters on the characteristics of Mn–Co coatings on Crofer 22 APU ferritic stainless steel [J]. Bulletin of Materials Science, 2017, 40: 1273-1283.
[16] GONG J, ZANGARI G. Electrodeposition and characterization of manganese coatings [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2002, 149: C209-C217.
[17] RADHAKRISHNAMURTHY P, REDDY A K N. The mechanism of manganese electrodeposition [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1974, 4: 317-321.
[18] HURLEN T, V 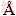 LAND T. Activation energy of the
LAND T. Activation energy of the 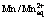 electrode [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1964, 9: 1087-1092.
electrode [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1964, 9: 1087-1092.
[19] FAN Xing, XI Su-yun, SUN Da-gui, LIU Zuo-hua, DU Jun, TAO Chang-yuan. Mn–Se interactions at the cathode interface during the electrolytic-manganese process [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 127-128: 24-29.
[20] BENFEDDA B, BENBRAHIM N, BOUDINAR S, KADRI A, CHAINET E, CHARLOT F, COINDEAU S, DAHMANE Y, HAMADOU L. Morphological, physicochemical and magnetic characterization of electrodeposited Mn-Bi and Mn-Bi/Bi thin films on Cu Substrate [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 208: 80-91.
[21] HONG Bo, YU Xiao-ying, JIANG Liang-xing, XUE Hai-tao, LIU Fang-yang, LI Jie, LIU Ye-xiang. Hydrogen evolution inhibition with diethylenetriamine modification of activated carbon for a lead-acid battery [J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4: 33574-33577.
[22] KOZIN L F, MASHKOVA N V, MANILEVICH F D. Kinetics and mechanism of the discharge-ionization of manganese in an ammonium chloride solution [J]. Protection of Metals, 2007, 43: 537-541.
[23] BRUG G J, VAN DEN EEDEN A L G, SLUYTERS-REHBACH M, SLUYTERS J H. The analysis of electrode impedances complicated by the presence of a constant phase element [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1984, 176: 275-295.
[24] ARMSTRONG R D, HENDERSON M. Impedance plane display of a reaction with an adsorbed intermediate [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1972, 39: 81-90.
[25] LAI Yan-qing, LI Yuan, JIANG Liang-xing, XU Wang, LV Xiao-jun, LI Jie, LIU Ye-xiang. Electrochemical behaviors of co-deposited Pb/Pb-MnO2 composite anode in sulfuric acid solution—Tafel and EIS investigations [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2012, 671: 16-23.
[26] STERRATT D C. Nernst equation [M]. New York: Springer, 2015.
[27] SULCIUS A, GRISKONIS E, KANTMINIENE K, ZMUID- ZINAVICIENE N. Influence of different electrolysis parameters on electrodeposition of γ- and α-Mn from pure electrolytes—A review with special reference to Russian language literature [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 137: 33-37.
[28] SIDES W D, HUANG Q. Electrochemical nucleation and growth of antimony telluride binary compound on gold substrate [J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2018, 165: D568-D573.
[29] PALOMAR-PARDAVE M, SCHARIFKER B R, ARCE E M, ROMERO-ROMO M. Nucleation and diffusion-controlled growth of electroactive centers: Reduction of protons during cobalt electrodeposition [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2005, 50: 4736-4745.
[30] PEREIRA N M, PEREIRA C M, ARAUJO J P, SILVA A F. Electrodeposition of Mn and Mn-Sn alloy using choline chloride-based ionic liquids [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164: D486-D492.
[31] MILCHEV A, STOYANOV S, KAISCHEV R. Atomistic theory of electrolytic nucleation: I [J]. Thin Solid Films, 1974, 22: 255-265.
[32] ALVAREZ A E, SALINAS D R. Formation of Cu/Pd bimetallic crystals by electrochemical deposition [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55: 3714-3720.
[33] BOUDINAR S, BENBRAHIM N, BENFEDDA B, KADRI A, CHAINET E, HAMADOU L. Electrodeposition of heterogeneous Mn-Bi thin films from a sulfate-nitrate bath: Nucleation mechanism and morphology [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2014, 161: D227-D234.
[34] SCHARIFKER B R, MOSTANY J. Three-dimensional nucleation with diffusion controlled growth: Part I. Number density of active sites and nucleation rates per site [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1984, 177: 13-23.
[35] ALI N, ALI M, ALI E, ALI A. Electrocatalytic behaviour of Ni and NiCu alloy modified glassy carbon electrode in electro-oxidation of contraflam [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24: 1703-1712.
杨 凡,蒋良兴,于枭影,刘芳洋,赖延清,李 劼
中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:采用线性扫描伏安(LSV)、电化学阻抗谱(EIS)、恒电位极化、计时电流、扫描电镜(SEM)和X射线衍射(XRD)等方法,研究在不同电位区间硫酸铵浓度对不锈钢表面析氢和锰沉积反应的影响。结果表明,NH4+的放电反应可以加速整个阴极析氢反应动力学,NH4+的放电反应速率随硫酸铵浓度和过电位的增加而增加。锰在不锈钢表面的电结晶服从三维连续成核机理,晶核生长受扩散控制。增加过电位能加快形核速率,但使形核密度降低。在低电位区间,吸附于不锈钢表面的Mn2+优先放电;在中等电位区间,增加硫酸铵浓度能提高电流效率并生成更多块状晶体;在高电位区间,增加硫酸铵浓度会抑制形核过程,该条件下得到的晶体以柱状形态为主,且晶格中的氢含量更高。
关键词:硫酸铵;锰电沉积;析氢;不锈钢阴极
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (1053320170703) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University, China
Corresponding author: Liang-xing JIANG; Tel: +86-731-88830474; E-mail: lxjiang@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65149-6

