Mechanical properties and stress corrosion cracking behaviour of AZ31 magnesium alloy laser weldments
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2011年第1期
论文作者:P. B. SRINIVASAN S. RIEKEHR C. BLAWERT W. DIETZEL M. KOСAK
文章页码:1 - 8
关键词:镁合金;激光焊接;显微组织;力学性能;慢应变速率拉伸;应力腐蚀裂纹;断面分析
Key words:AZ31 magnesium alloy; laser welding; microstructure; mechanical properties; slow strain rate tensile test; stress corrosion cracking; fractography
摘 要:采用Nd-YAG激光对AZ31 HP镁合金进行激光自熔焊接。显微组织分析表明,使用或不使用填料(焊料)AZ61镁合金得到的激光焊接接头的平均晶粒尺寸大约为12 μm,显微硬度和拉伸强度与母材相近。然而,慢应变速率拉伸表明,在ASTM D1384溶液中两种焊接接头的抗应力腐蚀性能比母材略差。可观察到应力腐蚀裂纹在焊缝金属萌生并向热影响区(HAZ)扩展。然而,在以AZ61镁合金为填料(焊料)获得的焊接接头中,观察到裂纹起源及扩展出现在热影响区(HAZ)。在慢应变速率拉伸试验中,由于试样表面暴露在腐蚀环境中,在氢氧化镁/氧化镁层形成局部损伤,从而导致应力腐蚀裂纹的生成。
Abstract: An AZ31 HP magnesium alloy was laser beam welded in autogenous mode with AZ61 filler using Nd-YAG laser system. Microstructural examination revealed that the laser beam weld metals obtained with or without filler material had an average grain size of about 12 μm. The microhardness and the tensile strength of the weldments were similar to those of the parent alloy. However, the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behaviour of both the weldments assessed by slow strain rate tensile (SSRT) tests in ASTM D1384 solution was found to be slightly inferior to that of the parent alloy. It was observed that the stress corrosion cracks originated in the weld metal and propagated through the weld metal-HAZ regions in the autogenous weldment. On the other hand, in the weldment obtained with AZ61 filler material, the crack initiation and propagation was in the HAZ region. The localized damage of the magnesium hydroxide/oxide film formed on the surface of the specimens due to the exposure to the corrosive environment during the SSRT tests was found to be responsible for the SCC.

P. B. SRINIVASAN, S. RIEKEHR, C. BLAWERT, W. DIETZEL, M. KO?AK
Institute of Materials Research, GKSS-Forschungszentrum Geesthacht GmbH Geesthacht D-21502, Germany
Received 25 January 2010; accepted 7 April 2010
Abstract: An AZ31 HP magnesium alloy was laser beam welded in autogenous mode with AZ61 filler using Nd-YAG laser system. Microstructural examination revealed that the laser beam weld metals obtained with or without filler material had an average grain size of about 12 ?m. The microhardness and the tensile strength of the weldments were similar to those of the parent alloy. However, the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behaviour of both the weldments assessed by slow strain rate tensile (SSRT) tests in ASTM D1384 solution was found to be slightly inferior to that of the parent alloy. It was observed that the stress corrosion cracks originated in the weld metal and propagated through the weld metal-HAZ regions in the autogenous weldment. On the other hand, in the weldment obtained with AZ61 filler material, the crack initiation and propagation was in the HAZ region. The localized damage of the magnesium hydroxide/oxide film formed on the surface of the specimens due to the exposure to the corrosive environment during the SSRT tests was found to be responsible for the SCC.
Key words: AZ31 magnesium alloy; laser welding; microstructure; mechanical properties; slow strain rate tensile test; stress corrosion cracking; fractography
1 Introduction
Automobile and aircraft applications demand light weight and high performance materials, and wrought magnesium alloys are slowly replacing steels and aluminium alloys in those industries[1]. Magnesium alloys, in general, have excellent castability and moderate formability, and hence components are made from both cast and wrought Mg alloys. Even though the joining of magnesium alloys can be accomplished by gas tungsten arc welding[2-4]. Recently laser beam welding (LBW), electron beam welding (EBW) and friction stir welding (FSW) processes are widely employed for the joining of these alloys[5-9]. This is due to reduced defect levels and consequent higher joint efficiencies that result from the controlled power beam and FSW processing. While the FSW process is a solid state process that does not involve any filler materials, the LBW process can be used to produce magnesium alloy weldments with or without the employment of additional filler materials. For many applications, in addition to the mechanical properties, the corrosion resistance of materials must be taken into consideration. Magnesium alloys generally have been regarded as materials with a poor corrosion resistance[10]. However, the general corrosion resistance of magnesium alloys with controlled levels of impurities is claimed to be better than that of carbon steel in atmospheric exposure tests for 2 years at the Texas Gulf Coast[11].
The corrosion behaviour of magnesium alloys is significantly influenced by the impurities, especially those on the surface[12]. In the case of weldments, in addition to the surface impurities, the corrosion behaviour can be influenced by the grain size, weld metal composition, distribution of micro-constituents and residual stresses, etc. Furthermore, the problem of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is prominent in magnesium alloys[13]. The environmentally assisted cracking of magnesium alloys is reported to occur due to either the galvanically induced anodic dissolution of the matrix promoted by a more noble secondary phase or atomic hydrogen[13-15]. Researchers reported both intergranular and transgranular modes of cracking existed in magnesium alloys and their weldments[16-19]. There are a few publications by our group and other researchers which address the corrosion and SCC behaviour of weldments obtained by GTAW, FSW and autogenous LBW[20-22]. Joining of magnesium alloys by LBW is mostly done in autogenous mode. In this work, laser beam welds from an AZ31 HP magnesium alloy were produced in autogenous mode and with the introduction of an aluminium-rich (AZ61) filler material. As the published information was limited on the SCC behaviour laser beam weldments of magnesium alloys, an attempt was made to correlate the microstructure- mechanical property—SCC behaviour of these weldments.
2 Experimental
Rolled AZ31 HP magnesium alloy sheet of 2.5 mm in thickness with a nominal chemical composition of Mg-(2.5-3.5)%Al-(0.6-1.4)%Zn-(0.2-0.6)%Mn (mass fraction) was used in this experiment. Welds were produced by joining two pieces of size 200 mm×330 mm×2.5 mm with a Nd-YAG laser system in autogenous mode and with the use of a d1.2 mm AZ61 wire. The following optimized welding parameters were used: laser power 2.2 kW; welding speed 90 mm/s; focusing on surface; helium shielding 16 L/min at top side, 40 L/min at bottom side. The wire feed rate was 1.25 m/min while welding with AZ61 filler wire.
The metallographic specimens (cross-sections) were polished successively with 500, 1 200 and 2 500 grit emery sheets followed by final polishing with colloidal silica solution and etched in a solution containing 3.5 g picric acid, 6.5 mL acetic acid, 20 mL water and 100 mL ethanol. Microstructural examination was performed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Microhardness evaluation across the weldments was carried out under a load of 1 N with a loading dwell time of 20 s.
The SCC susceptibility of the parent alloy and the weldments was assessed by slow strain rate tensile tests (SSRT) in ASTM D1384 solution containing 148 mg/L Na2SO4, 165 mg/L NaCl and 138 mg/L NaHCO3 in 1 L distilled water at a nominal strain rate of 10-6 s-1 following the ISO standard 7359—Part 7[23]. The geometry and dimensions of the specimens employed for the SSRT tests are presented in Fig.1. The weld reinforcements in the face and root regions of both the weldment specimens were removed by grinding successively with 320, 500 and 1 200 grit emery sheets, and the same level of surface finish was given to the parent specimens before SSRT tests. Reference SSRT tests were performed on the parent alloy and weldment specimens in air at a strain rate of 10-5 s-1. The elongation of the specimens in the SSRT tests (in air and in ASTM solution) was measured by employing two linear variable displacement transducers (LVDTs). As the elongation values were measured with the LVDTs fitted to the specimen grips and not in the gauge section of specimens, it is referred as apparent strain in the discussion. The SSRT tested specimens were examined by an optical microscope to identify the fracture location, and the failed surfaces were investigated by SEM to assess the nature of fracture.
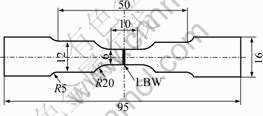
Fig.1 Dimensions of tensile specimen used in SSRT tests (Unit: mm)
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure
Scanning electron micrographs of the parent alloy, the autogenous weld metal and the weld metal obtained with AZ61 filler are shown in Figs.2(a)-(c), respectively. The parent alloy is an aluminium lean alloy, the secondary phase β particles were observed in very small quantities randomly distributed in the matrix. Both the weld metals had a finer grain size (average grain size of about 12 ?m) compared with the parent alloy. The weld metals were observed to contain a relatively large number of fine particles of size <1 ?m spread uniformly across the matrix and along the grain boundaries. It should be pointed out that the volume fraction of these particles was higher in the weld metal with AZ61 filler than in the autogenous weld metal. The formation of such particles was reported in laser beam and electron beam weld metals by other researchers[22, 24]. While BOBBY et al[22] reported the particles as Al rich phase in an autogenous AZ31 laser weld metal, COELHO and his co-workers[25] identified them as Mg17(Al,Zn)12 phase by using TEM diffraction patterns in yet another AZ31 magnesium alloy laser beam weld metal. CHI et al[24] also reported the particles were Mg17Al12 phase in the EB welds of AZ31, AZ61 and AZ91 alloys. The EDS point analysis made on the particles showed that they were richer in Al and Zn, which corroborated the reports of CHI et al[24] and COELHO et al[25].
3.2 Microhardness
Fig.3 shows the microhardness distribution in the weldments obtained with or without filler material. The hardness values were in the range of HV0.1 (70±10) in the entire weldment (parent, HAZ and weld metal regions). Neither the evolution of a fine grained structure nor the presence of the Al-Zn rich particles did influence the hardness of the weld metal. Similar observations on the hardness of laser beam weld metals of magnesium alloys

Fig.2 SEM images of AZ31 parent alloy (a), weld metal obtained without filler (b) and weld metal obtained with AZ61 filler (c)
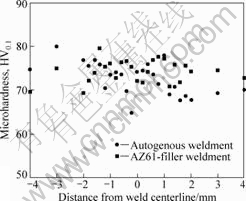
Fig.3 Microhardness profile across laser beam weldments
were reported in earlier investigations[22, 25].
3.3 Tensile properties
The plots of stress vs apparent strain presented in Fig.4 show that all the three specimens have an ultimate tensile strength value around 250 MPa. The parent alloy had registered an apparent strain value of about 55% against a value of about 46% registered for the two weldment specimens. After tensile tests, the weldment specimens were examined in the optical microscope to identify the fracture location. The optical macrograph of the autogenous weldment specimen SSRT tested shown in Fig.5(a) suggested the plastic deformation localized in the weld metal and a consequent fracture there. However, a close examination of the fractured region at a higher magnification revealed that the fracture initiated with the

Fig.4 Stress vs apparent strain plots for AZ31 parent alloy and weldment specimens at strain rate of 10-5 s-1 in air
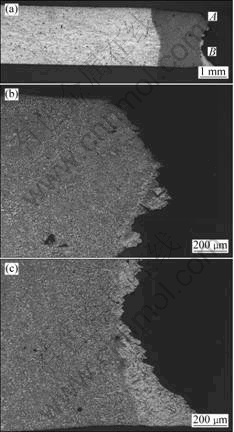
Fig.5 Optical graphs of SSRT tested autogenous weldment specimen in air: (a) Overview; (b-c) Fracture locations/path in weld metal (higher magnification of region marked A and B in Fig.5(a))
necking in the weld metal region close to the fusion boundary, it propagated through the weld metal–HAZ regions. The fracture in the face region of the weld metal and along the fusion boundary is evident in Fig.5(b). Similarly, the final fracture path in the HAZ-parent alloy in the root region is demonstrated in Fig.5(c). Considering the necking and fracture occurred in the weld metal region, it appears that this autogenous weldment was slightly under-matched despite the fact that the ultimate tensile strength values of this weldment and the parent alloy specimens were nearly the same.
In the case of the weldment specimen obtained with AZ61 filler, the tensile fracture was observed in the parent alloy at a location far away from the weld metal as seen in Fig.6(a). The weld metal and the HAZ regions did not show any sign of plastic deformation, and the fracture outside the weld metal/HAZ regions demonstrated the over-matched nature of this weldment. Optical micrographs of the parent alloy in the un-deformed region (Fig.6(b)) and the necked region
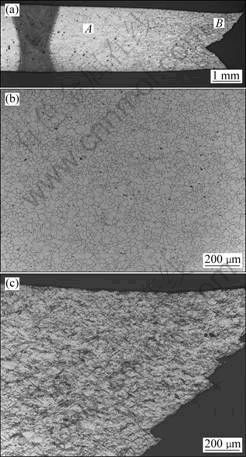
Fig.6 Optical graphs of SSRT tested weldment specimen obtained with AZ61 filler in air: (a) Overview (note fracture location is far away from weld metal); (b) Microstructure of unaffected base metal in weldment (region marked A in Fig.6(a)); (c) Micrograph showing extensive deformation in necked zone of parent alloy in weldment (region marked B in Fig.6(a))
(Fig.6(c)) clearly reveal the extent of plastic deformation in the parent alloy. The better mechanical behaviour of this weld metal is attributed to a potential solid solution strengthening effect provided by the increased aluminium content in the weld metal with the use of AZ61 filler. It is also plausible that the increased precipitation of β phase particles in the matrix could influence the mechanical properties. The fracture surface examination of the tensile tested parent alloy and the weldment specimens showed a fibrous-dimpled structure characteristic of ductile fracture.
3.4 Stress corrosion cracking
The environmental cracking susceptibility of the parent alloy and the weldments was assessed by slow strain rate tensile tests performed at a nominal strain rate of 10-6 s-1 in ASTM D1384 solution. The stress vs apparent strain plots of the parent alloy and the weldment specimens are presented in Fig.7. All the three specimens were found to fail at a much lower stress in the corrosive environment than in the tests performed in air. The much lower apparent strain values registered for the specimens indicate their stress corrosion cracking susceptibility. The parent alloy fractured after reaching a maximum stress level of about 195 MPa with an apparent strain value of around 6%. The autogenous weldment was found to fracture at around 185 MPa showing an apparent strain value of about 4.5% at the maximum stress. In the case of the weldment obtained with AZ61 alloy filler, the maximum stress and apparent strain at maximum stress were about 180 MPa and 4%, respectively. The reduction in cross section of all the three specimens was found to be around 7.5%. It is shown that magnesium alloys and their weldments exhibit a higher susceptibility to SCC at strain rates of 10-7 s-1 and 10-8 s-1 than in ASTM D1384 test environment[22, 26]. The ratio of tensile properties in
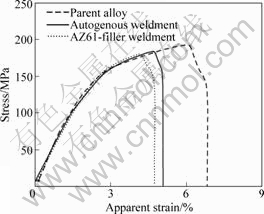
Fig.7 Plots of stress vs apparent strain for AZ31 parent alloy and two weldment specimens at strain rate of 10-6 s-1 in ASTM D1384 solution
the corrosive environment to that in air is addressed as SCC susceptibility index (ISCC). The SCC susceptibility index based on the ultimate tensile strength (ISCC(UTS)) values was (0.73±0.03) and the susceptibility index (ISCC-%e) based on apparent strain was (0.10±0.01) for the parent alloy and the two weldment specimens. BOBBY et al[17] reported only slightly higher SCC susceptibility indices for the AZ31 parent alloy and its friction stir weldment in ASTM D1384 solution based on the SSRT tests performed at a strain rate of 1×10-7 s-1.
An optical macrograph of the autogenous weldment specimen after the SSRT test in ASTM D1384 solution is shown in Fig.8(a). This specimen was found to fail at the weld metal and weld metal/HAZ interface. Also, it is evident that the weld metal underwent some degree of plastic deformation as observed in the root region of this micrograph. In addition, there was a micro-crack in the parent alloy (marked by arrow in Fig.8(a)). A closer examination of the region marked A (Fig.8(a)) in the root region of the weld metal showed the presence of a micro crack, indicating the SCC susceptibility of the weld
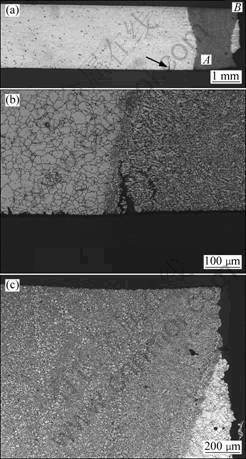
Fig.8 Optical graphs of SSRT tested autogenous weldment specimen: (a) Overview; (b) Region A marked in Fig.8(a) revealing crack in root region of weld metal; (c) Region B marked in Fig.8(a) showing fracture in face region of weld metal
metal. Even though the deformation is not obvious in the face region of this weld metal, it appears that another stress corrosion crack initiated at the face region of this weld metal and propagated through the weld metal and weld metal-HAZ regions, causing the final fracture. The crack/fracture path starting from the face region of the weld metal is clearly seen in Fig.8(c).
An optical macrograph of the AZ61-filler weldment specimen SSRT tested in ASTM D1384 solution is shown in Fig.9(a). The fracture of this specimen was observed to be at a location close to the fusion boundary in the face region of the weldment, marked as A. The higher magnification micrograph of this region shown in Fig.9(b) reveals that the SCC crack apparently initiated at the HAZ very close to the fusion boundary and propagated along the weld metal-HAZ interface before deviating into the parent alloy to cause the final rupture. A slight degree of necking in the parent alloy at about 0.5 mm from the fusion boundary in the root region was observed. However, the retention of the original grain structure in the fracture zone of the parent alloy clearly
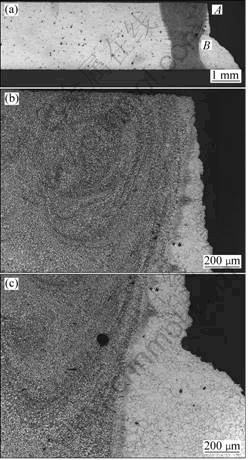
Fig.9 Optical graphs of SSRT tested weldment specimen obtained with AZ61 filler: (a) Overview; (b) Region A marked in Fig.9(a) showing cracking at HAZ close to fusion boundary; (c) Region B marked in Fig.9(a) showing pore in weld metal and grain structure in unaffected parent alloy
suggested that the extent of plastic deformation was insignificant and there was no significant work hardening (Fig.9(c)). It is pertinent to point out that the presence of a defect in the form of a pore in both the weld metals (autogenous and AZ61-filler) did neither influence the mechanical properties nor the SCC behaviour of this weldment.
It is apparent that both the weldments had a slightly higher SCC susceptibility than the parent alloy. BOBBY et al[22] reported that the laser weld metal had a nobler potential than the parent alloy in ASTM D1384 solution and thus attributed the SCC in the HAZ to the galvanically induced dissolution. However, in this work, the SCC was found to occur in the weld metal region and propagate through the weld metal-HAZ interface. It is well known that the dissolution of magnesium alloy in aqueous environments results in the formation of a magnesium oxide/hydroxide film on the surface. It appears that the straining/deformation of the weld metal region during the SSRT tests caused micro cracking on the layer formed on the surface and thus developed localized regions for the onset of SCC. On the other hand, the SCC in the AZ61-filler weldment was found to initiate and propagate through the HAZ of the weldment. An increase in aluminium content in the weld metal in this case is expected to provide a higher corrosion resistance. Also, as this aluminium enriched weld metal had a higher strength, this region did not undergo plastic deformation during straining. Hence, the cracking was observed in a region slightly away from the weld metal.
The weldment specimens were subjected to salt spray tests for 48 h as per ASTM B117 with 5% NaCl solution. Optical macrographs in Figs.10(a) and (b) show the extent of corrosion damage in the weldment specimens obtained in autogenous mode and with the use of AZ61-filler, respectively. In the autogenous weldment (Fig.10(a)), a few regions of localized damage can be observed in the weld metal. However, the extent of damage was quite high on the parent alloy. This observation suggests that the weld metal was nobler compared to the rest of the regions of this autogenous weldment. In the case of the weldment with AZ61-filler (Fig.10(b)), an extensive corrosion damage was observed near the fusion boundary (in the HAZ region). The parent alloy also had much higher corrosion damage, as can be seen in the above macrograph. From the salt spray test, the following two points are evident: 1) the weld metal region had a better corrosion resistance in both the weldments than the rest of the weldment, possibly on account of the formation of a relatively stable oxide film and/or the nobler potential, and 2) the enhanced corrosion damage in the region close to the fusion boundary in the HAZ of the weldment obtained with AZ61 filler metal due to the galvanic effect imposed by the apparently nobler corrosion potential of the aluminium rich weld metal.

Fig.10 Optical macrographs of specimens after salt spray test for 48 h: (a) Autogenous weldment; (b) Weldment obtained with AZ61-filler
The fracture surface of the parent alloy and the two weldment specimens SSRT tested in air and in ASTM D1384 solution had similar features, and the representative fractographs are presented in Figs.11(a) and (b), respectively. The surface of the specimen tested in air had numerous dimples, whilst the specimen tested in the corrosive environment exhibited brittle behaviour with a transgranular surface appearance. Even though WINZER et al[27] observed an intergranular fracture and BOBBY et al[22] reported a mixed mode of fracture (intergranular and transgranular) in GTA and LB weldments of AZ31 magnesium alloy, respectively. Many earlier investigations on the SCC of magnesium alloys reported a transgranular fracture, which was speculated to be assisted by hydrogen[13, 28-29]. In this investigation, all the specimens also exhibited a transgranular fracture suggesting hydrogen induced damage to be the possible mechanism. It is postulated that the cracking of the film formed on the surface of the specimens acted as sites for the generation and ingress of hydrogen, thus causing the damage[14, 22]. This investigation revealed that the weldment obtained with AZ61 filler material is better than the autogenous weldment in the context of its over-matched mechanical properties, but this weldment has a slightly higher susceptibility to SCC than both the parent alloy and autogenous weldment in ASTM D1384 solution.
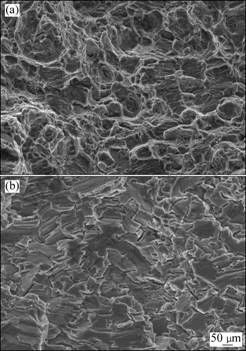
Fig.11 Fractographs of specimens SSRT tested in air (a) and ASTM D1384 solution (b)
4 Conclusions
1) Laser beam weldments with or without the addition of filler wires can be produced on AZ31HP magnesium alloy with acceptable mechanical properties. However, the parent alloy and the two weldments were found to be susceptible to stress corrosion cracking in ASTM D1384 solution even at a nominal strain rate of 10-6 s-1.
2) The formation of an oxide/hydroxide film on the surface of specimens exposed to the ASTM D1384 solution and the consequent localized breakdown in the film due to straining were found to be the reason for the SCC. The transgranular fracture mode observed in all the cases suggests the involvement of hydrogen in the SCC process.
3) The salt-spray tests demonstrated that the weld metal region was better in terms of general corrosion resistance in both the weldments. The enrichment of aluminium in the weld metal produced with AZ61-filler was found to inflict a galvanic damage in the HAZ region adjacent to the fusion boundary.
Acknowledgement
The authors express their sincere thanks to Mr. U. BURMESTER, Mr. V. HEITMANN and Mr. V. KREE for the technical support during the course of this work. P. B. SRINIVASAN thankfully acknowledges the Hermann-von-Helmholtz Association, Germany and DAAD, Germany for the award of fellowship.
References
[1] ELIEZER E, AGHION E, FROES F H. Magnesium science technology and applications [J]. Advanced Performance Materials, 1998, 5: 201-212.
[2] MARYA M, EDWARDS G R. Chloride contributions in flux-assisted GTA welding of magnesium alloys [J]. Welding Journal, 2002, 81: 291-298.
[3] LIU L M, CAI D H, ZHANG Z D. Gas tungsten arc welding of magnesium alloy using activated flux-coated wire [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57: 695-698.
[4] QUAN Y J, CHEN Z H, GONG X S, YU Z H. Characteristics of laser welded wrought Mg-Al-Mn alloy [J]. Materials Characterization, 2008, 59: 1799-1804.
[5] YU Z H, YAN H G, GONG X S, QUAN Y J, CHEN J H, CHEN Q. Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welded wrought ZK21 magnesium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 523: 220-225.
[6] CHI C T, CHAO C G. Characterization on electron beam welds and parameters for AZ31B-F extrusive plates [J]. Journal of Materials Processsing Technology, 2007, 182: 369-373.
[7] SU S F, HUANG J C, LIN H K, HO N J. Electron beam welding behaviour in Mg-Al based alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33: 1461-1473.
[8] MUNITZ A, COTLER C, SHAHAM H, KOHN G. Electron beam welding of magnesium AZ91D plates [J]. Welding Journal, 2009, 79: 202s-208s.
[9] PARK S H C, SATO Y S, KOKAWA H. Effect of micro-texture on fracture location in friction stir weld of Mg alloy AZ61 during tensile test [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2003, 49: 161-166.
[10] SONG G, ATRENS A. Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials,1999, 1: 11-33.
[11] HILLIS J E, REICHEK K N. High purity magnesium AM60 alloy: The critical contaminant limits and the salt water corrosion performance [R]. SAE Technical Paper Series #860288. Detroit, 1986.
[12] SONG G, ATRENS A. Understanding magnesium corrosion mechanism: A framework for improved alloy performance [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2003, 5: 837-858.
[13] WINZER N, ATRENS A, SONG G, GHALI E, DIETZEL W, KAINER K U, HORT N, BLAWERT C. A critical review of the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of magnesium alloys [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2005, 7: 659-693.
[14] CHEN J, WANG J, HAN E, KE W. Effect of hydrogen on stress corrosion of magnesium alloy in 0.1 M Na2SO4 solution [J]. Materials Science and Enginering A, 2008, 488: 428-434.
[15] WINZER N, ATRENS A, DIETZEL W, SONG G, KAINER K U. Evaluation of the delayed hydride cracking mechanism for transgranular stress corrosion cracking of magnesium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 466: 18-31.
[16] BALA S P, ZETTLER R, BLAWERT C, DIETZEL W. Stress corrosion cracking of AZ61 magnesium alloy friction stir weldments in ASTM D1384 Solution [J].Corrosion Engineering Science and Technology, 2009, 44: 477-480.
[17] BOBBY K M, DIETZEL W, ZENG R, ZETTLER R, DOS SANTOS J F. A study on the SCC susceptibility of friction stir welded AZ31 Mg sheet [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 460-461: 243-250.
[18] WINZER N, ATRENS A, DIETZEL W, SONG G, KAINER K U. Fractography of stress corrosion cracking of Mg-Al alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2008, 39: 1157-1173.
[19] BOBBY K M, DIETZEL W, BLAWERT C, ATRENS A, LYON P. Stress corrosion cracking of rare-earth containing magnesium alloys ZE41, QE22 and Elektron 21 (EV31A) compared with AZ80 [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 480: 529-539.
[20] BEN-HAMUA G, ELIEZER E, CROSS C E, B?LLINGHAUS T H. The relation between microstructure and corrosion behavior of GTA welded AZ31B magnesium sheet [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 452-453: 210-218.
[21] BALA S P, ZETTLER R, BLAWERT C, DIETZEL W. A study on the effect of plasma electrolytic oxidation on the stress corrosion cracking behaviour of a wrought AZ61 magnesium alloy and its friction stir weldment [J]. Materials Characterization, 2009, 60: 389-396.
[22] BOBBY K M, DIETZEL W, BLAWERT C, RIEKEHR S, KO?AK M. Stress corrosion cracking behavior of Nd:YAG laser butt welded AZ31 Mg sheet [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 444: 220-226.
[23] International Standard ISO 7539. Corrosion of metals and alloys—Stress corrosion testing (Part 7): Slow strain rate stress corrosion tests [S]. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization, 1989.
[24] CHI C T, CHAO C G, LIU T F, WANG C C. A study of weldability and fracture modes in electron beam weldments of AZ series magnesium alloys [J]. Materials Science Engineering A, 2006, 435/436: 672-680.
[25] COELHO R S, KOSTKA A, PINTO H, RIEKEHR S, KO?AK M, PYZALLA R. Microstructure and mechanical properties of magnesium alloy AZ31B laser beam welds [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 485: 20-30.
[26] BALA S P, BLAWERT C, DIETZEL W, KAINER K U. Stress corrosion cracking behaviour of a surface-modified magnesium alloys [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 59: 43-46.
[27] WINZER N, XU P, BENDER S, GROSS T, UNGER W E S, CROSS C E. Stress corrosion cracking of gas-tungsten arc welds in continuous-cast AZ31Mg alloy sheet [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51: 1950-1963.
[28] ARNON A, AGHION E. Stress corrosion cracking of nano/sub-micron E906 magnesium alloy [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2008, 10: 742-745.
[29] CHEN J, AI M, WANG J, HAN E, KE W. Stress corrosion cracking behaviors of AZ91 magnesium alloy in deicer solutions using constant load [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 515: 79-84.
P. B. SRINIVASAN, S. RIEKEHR, C. BLAWERT, W. DIETZEL, M. KO?AK
Institute of Materials Research, GKSS-Forschungszentrum Geesthacht GmbH Geesthacht D-21502, Germany
摘 要:采用Nd-YAG激光对AZ31 HP镁合金进行激光自熔焊接。显微组织分析表明,使用或不使用填料(焊料)AZ61镁合金得到的激光焊接接头的平均晶粒尺寸大约为12 μm,显微硬度和拉伸强度与母材相近。然而,慢应变速率拉伸表明,在ASTM D1384溶液中两种焊接接头的抗应力腐蚀性能比母材略差。可观察到应力腐蚀裂纹在焊缝金属萌生并向热影响区(HAZ)扩展。然而,在以AZ61镁合金为填料(焊料)获得的焊接接头中,观察到裂纹起源及扩展出现在热影响区(HAZ)。在慢应变速率拉伸试验中,由于试样表面暴露在腐蚀环境中,在氢氧化镁/氧化镁层形成局部损伤,从而导致应力腐蚀裂纹的生成。
关键词:镁合金;激光焊接;显微组织;力学性能;慢应变速率拉伸;应力腐蚀裂纹;断面分析
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
Corresponding author: P. B. SRINIVASAN; Tel: 00-49-4152-871997; Fax: 00-49-4152-871909; E-mail: bala.srinivasan@gkss.de
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60670-5

