Heat treatment process for improving ductility of Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C alloy
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2003年第5期
论文作者:雷力明 黄旭 孙福生 吴学仁 曹春晓 D Rugg W Voice
文章页码:1175 - 1180
Key words:non-burning; titanium alloy; heat treatment; mechanical properties; TiCr2
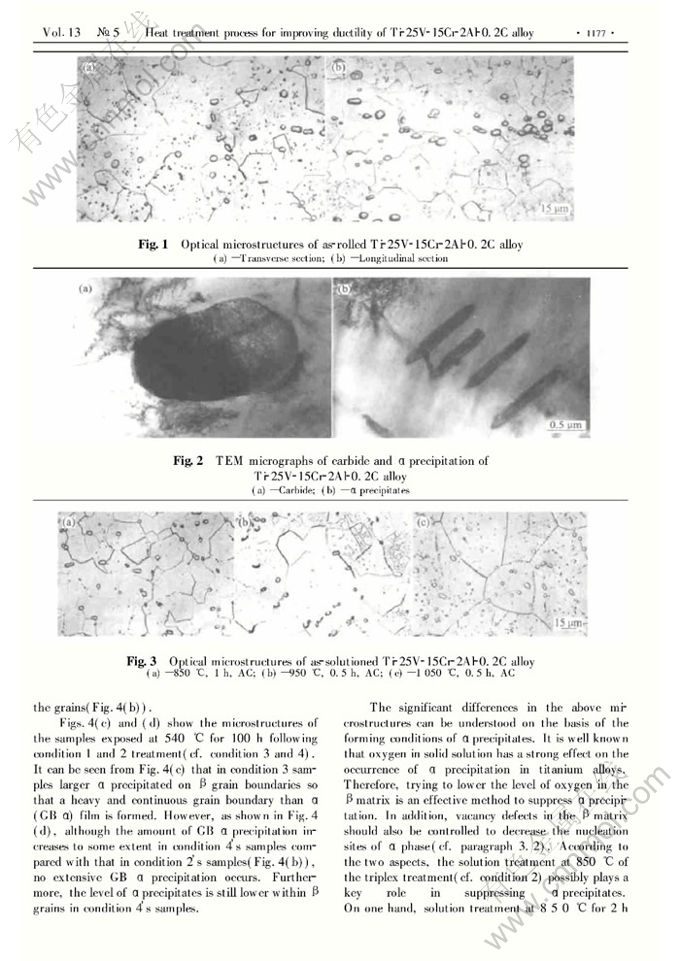
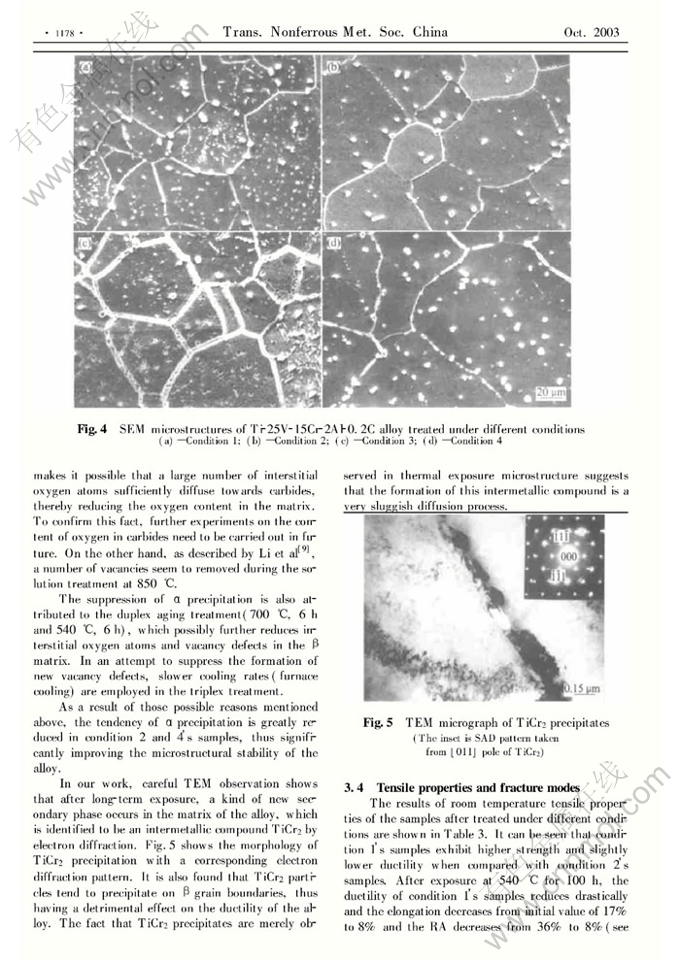
Abstract: The effect of heat treatment and thermal exposure on the microstructure and mechanical properties of non-burning β titanium alloy Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C (mass fraction, %) was investigated. It is found that the amount of α precipitation in samples after solution treatment followed by air cooling increases with increasing solution temperature. After solution treatment, the alloy was subjected to two different heat treatments to stabilize the material. The results show that the single ageing treatment(700℃, 4h, AC) leads to a large amount of α precipitation, while the triplex treatment(850℃, 2h, FC+700℃, 6h, FC+540℃, 6h, AC) significantly suppresses the formation of α precipitates. It is more important that after long-term exposure at 540℃(the expected application temperature) samples heat-treated by the triplex treatment have markedly higher ductility than those given the single aging treatment. The intermetallic compound TiCr2 is observed in samples after long-term exposure, which further degrades the ductility of the alloy.