DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2017.05.005
含Mo单晶镍基合金的高温蠕变及损伤行为
梁 爽1, 2,田素贵1,刘智鑫1, 2,薛永超1
(1. 沈阳工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,沈阳 110870;
2. 营口理工学院 机电工程系,营口 115000)
摘 要:通过蠕变性能测试及组织形貌观察,研究含3%和5%(质量分数)Mo无Re单晶镍基合金的高温蠕变和损伤行为。结果表明:与3%Mo单晶合金相比,5%Mo无Re单晶合金具有较好的蠕变抗力和较长的蠕变寿命,测定出5%Mo单晶合金在1040 ℃、137 MPa的蠕变寿命为556 h。在施加的温度和应力范围内,测定出合金在稳态蠕变期间的表观蠕变激活能Q=484.7 kJ/mol。合金在稳态蠕变期间的变形机制是位错在基体中滑移和攀移越过筏状γ′相;合金在蠕变较后阶段的变形机制是位错剪切进入筏状γ′相。随蠕变进行,位错的交替滑移致使合金中筏状γ′相发生扭曲,并在筏状γ′/γ两相界面发生裂纹的萌生和扩展,直至断裂,是合金在高温蠕变后期的损伤与断裂机制。
关键词:含Mo镍基单晶合金;显微组织;蠕变;变形机制;断裂特征
文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-05-0911-09 中图分类号:TG146.1 文献标志码:A
单晶镍基合金因在高温服役条件下具有强度高、抗氧化和抗腐蚀性能好等特点,可用于制作先进航空发动机及工业燃气机的热端叶片部件,并得到广泛应用[1-2]。单晶镍基合金的组织结构主要由γ和γ′两相组成,其中,Ni3Al-γ′相是具有Ll2有序结构的强化相[3],且随难熔元素(W+Ta+Mo)含量增加,合金中γ和γ′两相中难溶元素含量提高,可大幅度提高合金的高温力学及蠕变性能[4-6]。尽管高合金化程度的单晶镍基合金具有良好的高温力学及抗蠕变性能,但蠕变损伤仍是合金在服役期间的主要失效方式[7-9]。由于不同成分单晶镍基合金在不同条件具有不同的蠕变行为与断裂机制,因此,不同成分单晶镍基合金在不同条件的蠕变行为得到广泛研究。
研究结果表明[10],高温蠕变期间,合金中γ′相沿与应力轴垂直的方向转变为筏状结构,可阻碍位错运动,因此,位错攀移越过筏状γ′相是合金在高温稳态蠕变期间的变形机制,而蠕变后期,合金的变形机制为位错剪切进入γ′相。特别是在蠕变后期,位错的交替滑移,致使微裂纹及孔洞出现在筏状γ/γ′两相界面[11-12],在高温恒定载荷的作用下,随蠕变的进行,筏状γ/γ′两相的界面发生微小孔洞的聚集和长大,或形成宏观裂纹,并逐渐扩展,直至发生合金的蠕变断裂,是合金在蠕变后期的断裂机制。其中,断口表面分布许多近似正方形的小平面,小平面通过撕裂棱相互连接,是合金在中温/高应力蠕变断裂后的断口形貌特征[13]。
加入元素Re可大幅度提高合金的高温蠕变性能,其中,加入3%和6%(质量分数)的Re元素是第二代和第三代单晶镍基合金的成分特征[14],但元素Re价格昂贵,其Re的加入大幅度提高了合金的制备成本,故限制了单晶镍基合金的广泛应用。因此,研制高蠕变抗力无Re单晶镍基合金,使其蠕变性能达到含Re第二代单晶合金的水平,并大幅度降低合金的成本,可促进单晶镍基合金的广泛应用。在无Re合金中加入的元素Mo,主要溶入γ基体相,且随含量增加,可提高合金基体的固溶强化程度,改善合金的蠕变抗力。
本文作者设计和制备出两种分别含3%和5%Mo (质量分数)无Re单晶镍基合金,通过对合金进行高温蠕变性能测试,组织形貌观察,研究Mo含量对无Re单晶镍基合金高温蠕变行为的影响,并对高温蠕变期间的损伤与断裂机制进行分析和讨论,从而为无Re单晶镍基合金的开发与应用提供理论依据。
1 实验
采用选晶法在高温度梯度真空定向凝固炉中,分别将成分为Ni-6.0Al-3/5Mo-W-Ta-Cr-Co(质量分数,%)的母合金制备成两种[001]取向的镍基单晶合金试棒,单晶试棒的生长方向与[001]取向的偏差在7%以内。选取的热处理工艺为(1280 ℃,2 h)+(1300 ℃, 2 h)+(1315 ℃,6 h,AC)+(1080 ℃,4 h,AC)+(870 ℃,24 h,AC)。其中,含3%Mo单晶合金定义为合金1,5%Mo单晶合金定义为合金2,且两合金均具有负的晶格错配度。
试棒经完全热处理后,沿(100)晶面加工成宽4.5 mm、厚2.5 mm、标距为20 mm的片状拉伸蠕变试样,试样经机械研磨、抛光后,置入GTW504型高温蠕变试验机中,在高温不同条件下进行蠕变性能测试,并绘制蠕变曲线。不同状态合金的试样经研磨、抛光后,进行化学腐蚀(选用的腐蚀剂成分为:20 g CuSO4+5 mL H2SO4+100 mL HCl+80 mL H2O),然后,在S3400型扫描电子显微镜(SEM)下进行组织形貌观察。将蠕变不同阶段的样品经机械研磨,制成直径为3 mm、厚为50 μm的薄膜样品,选用成分为7%高氯酸+93%无水乙醇(体积分数)的电解液进行电解双喷减薄后,在型号为TECNA120的透射电子显微镜(TEM)下,进行显微组织形貌观察,研究合金在蠕变期间的微观变形机制。
2 实验结果
2.1 Mo含量对合金蠕变性能的影响
合金1和2在1040 ℃、137 MPa条件下测定的蠕变曲线,如图1所示,尽管两种合金在高温蠕变期间均具有初始阶段、稳态阶段和加速阶段特征,但表现出不同的蠕变行为。其中,合金1在稳态蠕变期间持续的时间较短,约为169 h,测定出稳态期间的应变速率为0.0087%/h,蠕变寿命仅为268 h。合金2在稳态蠕变期间的应变速率为0.0034%/h,稳态期间持续的时间约为430 h,蠕变寿命为556 h。表明在(1040 ℃,137 MPa)条件下,合金2具有较好的蠕变抗力和较长的蠕变寿命,与合金1相比较,合金2的蠕变寿命提高幅度达107.5%。由此得出结论,无Re单晶镍基合金中Mo含量由3%提高到5%,可大幅度提高合金的高温蠕变抗力。
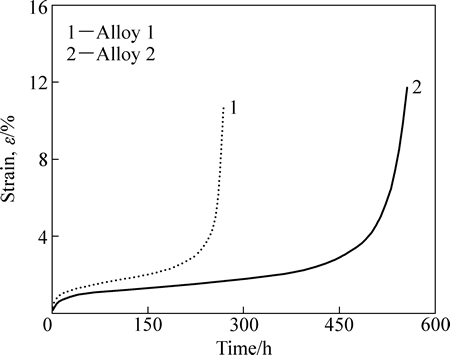
图1 合金在1040 ℃、137 MPa条件下的蠕变曲线
Fig. 1 Creep curves of alloys at 1040 ℃ and 137 MPa
2.2 合金的高温蠕变行为
与合金1比较,合金2具有更好的蠕变抗力,如图1所示,因此,本文作者主要对合金2进行蠕变性能测试和组织结构观察,研究合金2的高温蠕变行为。合金2在高温不同条件测定的蠕变曲线,如图2所示,其中,在不同温度施加137 MPa应力测定的蠕变曲线,如图2(a)所示。由图2(a)可以看出,合金在1040 ℃、137 MPa具有较好的蠕变抗力和较长的蠕变寿命,测定出合金在稳态蠕变期间的应变速率为0.0034%/h,蠕变556 h发生断裂。随温度提高到1060 ℃,合金在稳态蠕变期间的应变速率为0.0085%/h,稳态蠕变期间持续的时间约为200 h,335 h后发生蠕变断裂。随温度提高到1070 ℃,测定出合金在稳态蠕变期间的应变速率为0.0139%/h,稳态蠕变期间持续的时间约为150 h,蠕变寿命为239 h。特别是当施加应力为137 MPa,蠕变温度由1040 ℃提高到1060 ℃时,合金的蠕变寿命由556 h降低到335 h,蠕变寿命的降低幅度达66%。结果表明,施加应力为137 MPa,蠕变温度大于1040 ℃时,合金表现出明显的施加温度敏感性。

图2 合金在高温不同条件下的蠕变曲线
Fig. 2 Creep curves of alloy under different conditions and high temperature
合金在1070 ℃施加不同应力测定的蠕变曲线,如图2(b)所示,当施加应力为137 MPa时,合金在稳态蠕变期间具有较低的应变速率,蠕变200 h后,仍处于稳态阶段,蠕变寿命为239 h。当施加应力提高到147 MPa,合金在稳态蠕变期间的应变速率略有提高,测定出稳态蠕变期间的应变速率为0.0144%/h,持续的时间约为150 h,蠕变寿命为180 h。随施加应力进一步提高到160 MPa,测定出合金在稳态蠕变期间的应变速率为0.0316%/h,持续的时间约为80 h,蠕变寿命为110 h。特别是在1070 ℃,当施加应力由147 MPa提高到160 MPa时,合金的蠕变寿命由180 h降低到110 h,蠕变寿命的降低幅度达63.5%。结果表明,在1070 ℃蠕变期间,当施加应力大于147 MPa时,合金表现出明显的施加应力敏感性。
合金在高温施加载荷的瞬间,产生较大的瞬间应变,并在初始蠕变期间具有较大的应变速率,其对应的组织结构是大量位错在基体中滑移[12],其位错塞积产生的形变硬化作用,致使合金的应变速率降低,之后,合金的蠕变逐渐进入稳态阶段。在稳态蠕变期间,合金的蠕变速率保持恒定,其稳态期间的应变速率( )可用Norton- Baily定律描述:
)可用Norton- Baily定律描述:
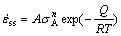 (1)
(1)
式中:A是与材料相关的常数;T是绝对温度;R是气体常数;Q是蠕变激活能;n是应力指数;σA为施加应力。
根据图2中蠕变曲线的数据,在施加温度和应力的范围内,测定出合金在稳态蠕变期间的应变速率,其稳态蠕变期间应变速率与施加温度、应力之间的关系,可表示为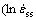 —
—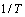 )和
)和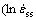 —
—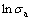 )曲线,如图3所示。由此,计算出稳态期间合金的蠕变激活能:Q=484.7 kJ/mol,可定量表明,该合金在施加的温度和应力范围内具有较好的蠕变抗力。此外,计算出合金在稳态蠕变期间的应力指数为n=4.3,由此可推断合金在稳态蠕变期间的变形机制是位错在基体通道中滑移和攀移越过γ′相。
)曲线,如图3所示。由此,计算出稳态期间合金的蠕变激活能:Q=484.7 kJ/mol,可定量表明,该合金在施加的温度和应力范围内具有较好的蠕变抗力。此外,计算出合金在稳态蠕变期间的应力指数为n=4.3,由此可推断合金在稳态蠕变期间的变形机制是位错在基体通道中滑移和攀移越过γ′相。
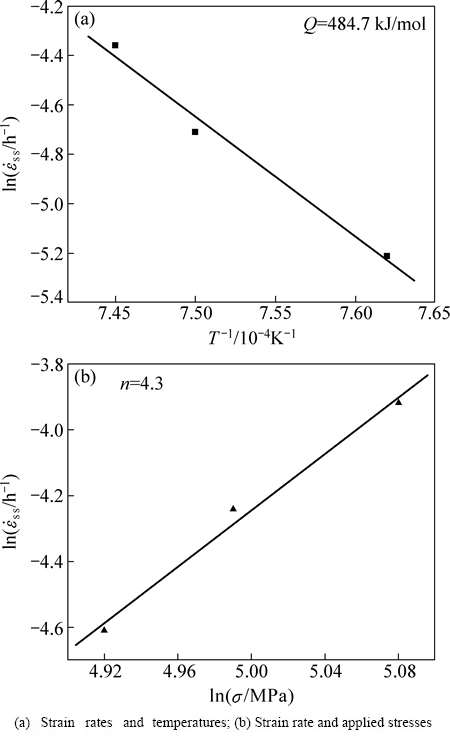
图3 合金在稳态蠕变期间的应变速率与温度、施加应力之间的关系
Fig. 3 Dependence of strain rates during steady state creep of alloy on temperatures and stresses
2.3 蠕变期间的组织演化
经1315 ℃固溶及完全热处理后,单晶镍基合金的组织结构由立方γ′相以共格方式镶嵌在g基体所组成,立方γ′相的边缘尺寸约为0.4~0.5 μm,且立方γ′相沿<100>方向规则排列,如图4所示。
合金经1070 ℃、137 MPa蠕变150 h已经进入稳态阶段,其组织形貌如图5所示,由于该合金具有负的晶格错配度,故合金中γ′相已沿垂直于应力轴方向转变为N-型筏状结构,并在筏状γ′/γ两相界面存在位错网(如图5中箭头所示),其方框区域的放大形貌示于照片的左上方。可以看出,有位错在γ基体中滑移,且位错网中存在位错割阶,但筏状γ′相内位错数量较少。合金在1070 ℃、137 MPa蠕变150 h,应变量已达2%(见图2),但剪切进入筏状γ′相位错数量较少的事实表明,合金在稳态蠕变期间的变形机制是位错在基体中滑移和攀移越过筏状γ′相。稳态蠕变期间,当基体中的蠕变位错运动至γ′/γ两相界面,蠕变位错与位错网发生反应,可改变原来的运动方向[15],促使位错攀移越过筏状γ′相。由此可以认为,合金中γ/γ′两相界面的位错网可以延缓蠕变期间引起的应力集中,对蠕变期间形成的加工硬化和回复软化起到协调的作用。
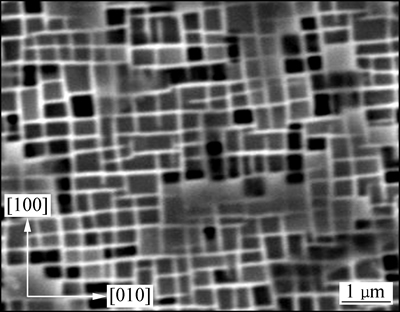
图4 单晶镍基合金经完全热处理后的组织形貌
Fig. 4 Microstructure of single crystal nickel based superalloy after fully heat treatment

图5 合金在1070 ℃、137 MPa蠕变150 h的组织形貌
Fig. 5 Microstructure of alloy crept at 1070 ℃ and 137 MPa for 150 h
合金经1070 ℃、137 MPa蠕变239 h 断裂后,样品表面的组织形貌,如图6所示,其中,图6(a)所示为标注观察区域的示意图。在试样中的区域A为无应变区域。由图6(a)可以看出,该区域的γ′相已沿垂直于应力轴方向形成了筏状结构,筏状γ′相的厚度尺寸约为0.5 μm,但沿平行于应力轴方向仍存在较多细小γ基体相,如图6(b)中箭头所示,表明该区域未形成完整的筏状结构。尽管区域B中γ′相已大部分转变成筏形结构,但局部区域沿平行于应力轴方向仍存在少量细小γ基体相,如图6(c)中箭头所示。在施加拉应力的区域C,合金中γ′相已完全转变成N-型筏状结构,筏状γ′相的厚度尺寸与前者相比,无明显差别,如图6(d)所示。由于区域D已接近断口,较大的塑性变形使该区域的筏状γ′相发生了明显的粗化和扭曲,使其厚度尺寸增加至0.6 μm,如图6(e)所示。在近断口的区域E,筏状γ′相的厚度已增加至0.7 μm,但长度尺寸减小,特别是该区域已发生颈缩,其较大的塑性变形使筏状γ′相的扭曲程度加剧,使其与应力轴的夹角约为45°,如图6(f)中箭头所示。
2.4 蠕变后期的变形特征
合金经1070 ℃、137 MPa蠕变239 h断裂后的组织形貌,如图7所示,在远离断口区域的显微组织形貌如图7(a)所示。可以看出,合金中γ′相已转变成筏形结构,位错网仍存在于筏状γ′/γ两相的界面,在区域A切入γ′相的位错数量较少,但在区域B切入γ′相的位错数量较多,切入筏状γ′相的位错,如箭头所示,由于该区域已发生较大的塑性变形,故筏状γ′相展示出扭曲的形态,如区域A所示。
在近断口区域的组织形貌如图7(b)所示,施加应力的方向如图中双箭头所示,部分筏状γ'相仍沿垂直于应力轴方向排列,但局部区域的筏状γ'相呈现扭曲形状,如区域C所示。其中,大量位错在基体通道中滑移,如图中区域D所示,且在γ基体中滑移位错的迹线方向与施加应力轴约呈45°角,为施加载荷的最大剪切应力所致,并有大量位错网分布在筏状γ'/γ两相界面,如图7(b)中区域E所示。大量位错已剪切进入筏状γ'相的事实表明,合金在该区域已失去蠕变抗力。
根据图7(b)的组织形貌及变形特征分析认为,合金在蠕变后期的变形机制是位错在基体中滑移和剪切筏状γ'相。在蠕变的较后阶段,合金的变形特征是主/次滑移位错的交替开动,首先是主滑移系开动,随后次滑移系开动,主/次滑移位错的交替开动,并剪切进入筏状γ'相,可致使筏状γ'/γ两相发生扭曲[16]。进一步,随蠕变的进行,合金中筏状γ'相的扭曲程度随应变量增加而增大,并促使在筏状γ'/γ两相界面发生微裂纹的萌生与扩展,是合金在蠕变后期的变形与损伤特征。
合金经1070 ℃、137 MPa蠕变239 h断裂后,裂纹的萌生与扩展发生在近断口区域的筏状γ'/γ两相界面,其形貌如图8所示,施加应力的方向如图8中双箭头所示。分析认为,在蠕变的较后阶段,大量位错在基体中滑移至筏状γ'相界面受阻,并在界面堆积产生应力集中,当应力集中的值超过合金的屈服强度时,筏状γ'/γ两相界面的位错网可破损[17],使蠕变位错沿筏状γ'/γ两相的界面剪切进入γ'相。其中,主/次滑移位错的交替滑移,致使筏状γ'相扭曲,并导致筏状γ'/γ两相的界面形成微孔,如图8(a)中区域A所示。随蠕变进行,筏状γ'/γ两相界面的微孔发生聚集和长大,形成微裂纹,并沿与应力轴垂直的方向,发生裂纹的扩展,如图8(b)中区域B所示。随蠕变的进行,裂纹尖端区域再次产生应力集中,可促使裂纹继续扩展,使其形成宏观大尺寸裂纹,如图8(c)所示,直至发生蠕变断裂,是合金在高温蠕变后期的断裂机制[18]。
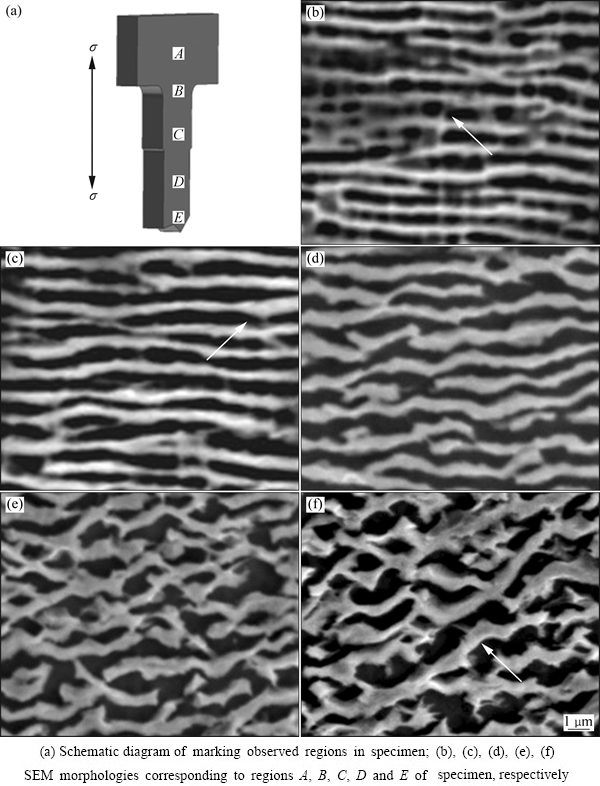
图6 合金经1070 ℃、137 MPa蠕变239 h断裂后样品不同区域的显微组织
Fig. 6 Microstructures in different regions of alloy crept at 1070 ℃ and 137 MPa for 239 h up to fracture
3 分析与讨论
单晶镍基合金的组织结构是高体积分数的立方γ'相以共格方式嵌镶在γ基体中,其中,γ'相是具有Ll2型有序结构的金属间化合物,是单晶合金中的重要强化相,对位错运动有阻碍作用。蠕变初期,合金的微观变形特征主要是位错在γ基体通道的八面体滑移系中运动。在垂直于应力轴的γ基体通道中,承受较大的剪切应力,故使位错在该通道中滑移距离较长,可以滑移穿越几个立方γ'相的距离。而在与应力轴平行的g基体通道中,由于立方γ'相的阻碍作用,位错在通道中滑移的距离较小,故该通道中的位错密度较低。其中,当蠕变位错在γ基体通道中运动至γ'相受阻时,可通过Orowan机制绕过γ'相,此时,位错运动克服Orowan阻力的临界切应力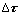 可表示为
可表示为
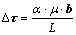 (2)
(2)
式中:μ为剪切模量;b为位错的柏氏矢量;L为位错在两立方γ'相之间的基体通道沿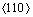 方向滑移的距离;α为与受力状态有关的常数。当蠕变期间沿[001]取向施加拉应力时,(001)晶面承受较大的有效应力;α=1,(100)和(010)晶面承受较小的有效应力;α>1,且随合金中立方γ'相的体积分数及尺寸增加,基体通道的尺寸(L)减小。由于实验用单晶合金中立方γ'相的体积分数大于65%,其高体积分数的γ'相和较小尺寸的g基体通道,使其位错在基体通道中运动具有较大的阻力,是合金在蠕变初期具有较好蠕变抗力的原因之一。另外,合金中加入5%的Mo元素,主要分布在合金的γ基体中,提高合金的固溶强化程度,可增加位错运动的阻力。
方向滑移的距离;α为与受力状态有关的常数。当蠕变期间沿[001]取向施加拉应力时,(001)晶面承受较大的有效应力;α=1,(100)和(010)晶面承受较小的有效应力;α>1,且随合金中立方γ'相的体积分数及尺寸增加,基体通道的尺寸(L)减小。由于实验用单晶合金中立方γ'相的体积分数大于65%,其高体积分数的γ'相和较小尺寸的g基体通道,使其位错在基体通道中运动具有较大的阻力,是合金在蠕变初期具有较好蠕变抗力的原因之一。另外,合金中加入5%的Mo元素,主要分布在合金的γ基体中,提高合金的固溶强化程度,可增加位错运动的阻力。
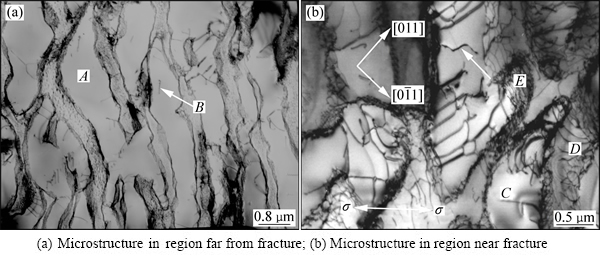
图7 经1070 ℃、137 MPa蠕变239 h断裂后合金中γ′/γ′两相的变形特征
Fig. 7 Deformation feature of γ′/γ phases in alloy crept at 1070 ℃ and 137 MPa for 239 h up to fracture
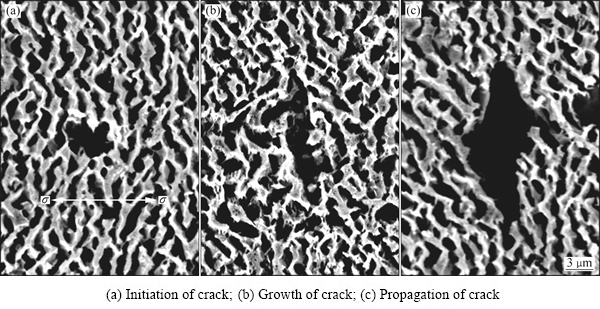
图8 合金经1070 ℃、137 MPa蠕变239 h断裂后在近断口区域的显微组织
Fig. 8 Microstructures in region near fracture of alloy crept at 1070 ℃ and 137 MPa for 239 h up to fracture
随蠕变进行至稳态阶段,合金中γ'相已转变成与应力轴垂直的筏形结构,其蠕变期间的变形机制是位错在基体中滑移和攀移越过筏状γ'相。随蠕变进行,合金基体中的位错密度增加,并产生应力集中,当应力集中值超过γ'相的屈服强度时,位错可剪切进入筏状γ'相。随位错剪切进入γ'相的数量增加,合金的蠕变抗力降低,应变速率增大,可加速合金的蠕变断裂。因此,合金中γ'相的强化水平与蠕变寿命密切相关。
分析认为,合金中γ'相的强化水平主要包括固溶强化、有序强化和γ'/γ两相共格界面强化,其合金中加入高浓度的元素Mo,可提高γ'/γ两相的强化程度,因此,合金具有较好的蠕变抗力。此外, 合金具有负的错配度,且随温度的提高,合金的错配度增大。在蠕变初期和稳态阶段,γ'/γ两相保持共格和半共格界面,其共格界面的应力场作用可增加位错运动的阻力,其共格界面应力场抑制位错剪切进入γ'相的阻力(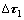 )可表示为
)可表示为
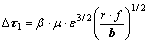 (3)
(3)
式中:β为与位错类型有关的常数,对刃位错β=3,对螺位错β=1;ε为共格界面的晶格应变;r为γ'相的半径尺寸;f为γ'相的体积分数。蠕变后期,当大量位错在合金基体中滑移产生应力集中时,[110]超位错可剪切进入筏状γ'有序相。进一步,剪切进入γ'相的位错可发生分解,形成反向畴界(ηAPB),增加位错运动的阻力,且随合金的固溶强化程度提高,位错剪切进入γ'相的阻力增大,因此,剪切进入γ'相的临界切应力(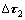 )可表示为
)可表示为
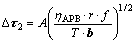 (4)
(4)
式中:ηAPB为单位面积的反向畴界能;T为位错线张力。式(3)和(4)表明,随合金强化程度提高,γ'相体积分数和尺寸增大,位错剪切进入γ'相所需的临界剪切应力提高。由于实验用单晶合金2具有较高的合金化程度、较高的体积分数和较大尺寸的γ'相,因此,合金具有良好的高温蠕变抗力,以上分析与实验结果相一致。
4 结论
1) 与3%Mo单晶合金相比,5%Mo无Re单晶合金具有较好的蠕变抗力和较长的蠕变寿命,测定出5%Mo单晶合金在1040 ℃、137 MPa的蠕变寿命为556 h。在试验的温度和施加应力范围内,测定出合金在稳态蠕变期间的表观蠕变激活能Q=484.7 kJ/mol。
2) 合金在稳态蠕变期间的变形机制是位错在基体中滑移和攀移越过筏状γ′相;合金在蠕变较后阶段的变形机制是位错剪切进入筏状γ′相。
3) 蠕变后期,位错的交替滑移致使合金中筏状γ′相发生扭曲,并在筏状γ′/γ两相的扭曲界面发生裂纹的萌生,随蠕变进行,裂纹沿垂直于应力轴的筏状γ′/γ两相界面发生扩展直至断裂,是合金在高温蠕变后期的损伤与断裂机制。
REFERENCES
[1] 郭建亭, 周兰章, 袁 超, 候介山, 秦学智.我国独创和独具特色的几种高温合金的组织和性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(2): 237-249.
GUO Jian-ting, ZHOU Lan-zhang, YUAN Chao, HOU Jie-shan, QIN Xue-zhi. Microstructure and properties of several originally invented and unique superalloys in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(2): 237-249.
[2] 项嘉义, 谢发勤, 吴向清, 姚小飞. 基于专利分析的中国高温合金发展趋势研究[J]. 材料导报, 2014, 28(2): 100-106.
XIANG Jia-yi, XIE Fa-qin, WU Xiang-qing, YAO Xiao-fei. Study on development trend of superalloy in China based on patent analysis[J]. Materials Review, 2014, 28(2): 100-106.
[3] THOMAS M C, HELMINK R C, FRASIER D J. Property and turbine engineering performance of CMSX-4 airfoils[J]. Materials for Advanced Power Engineering, 1994, 9: 1075-1098.
[4] MULLER L, GLATZEL U, FELLE-KNIEPMEIER M. Modeling thermal misfit stresses in nickel-base superalloy containing high volume fraction of γ′ phase[J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materiala, 1992, 40: 1321-1327.
[5] CARON P, HENDERSON P J, KHAN T, MCLEAN M. On the effects of heat treatment on the creep behaviour of a single crystal superalloy[J]. Scripta Metallurgice, 1986, 20(6): 875-880.
[6] FUCHS G E. Solution heat treatment response of a third generation single crystal Ni-base superalloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 300(1/2): 52-60.
[7] 王小蒙, 王天佑, 赵子华, 张 峥. 涡轮叶片蠕变损伤行为及固溶处理对叶片材料性能的影响[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(10): 2784-2793.
WANG Xiao-meng, WANG Tian-you, ZHAO Zi-hua, ZHANG Zheng. Creep damage behavior for serviced turbine blades and effects of solutioning on blade materials[J]. Acta Aeronautica Et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(10): 2784-2793.
[8] 于兴福, 杜洪强, 田素贵, 宁 英, 王铁军, 崔树森. 无铼二代镍基单晶高温合金中温高应力蠕变机制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(7): 1921-1928.
YU Xing-fu, DU Hong-qiang, TIAN Su-gui, NING Ying, WANG Tie-jun, CUI Shu-sen. Creep deformation mechanism in Re free second generation nickel-base single crystal superalloy during medium temperature and high stress[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(7): 1921-1928.
[9] YEH A C, SATO A, KOBAYASHI T, HARADA H. On the creep and phase stability of advanced Ni-based single crystal superalloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 490: 445-451.
[10] 史振学, 李嘉荣, 刘世忠, 王效光. 镍基单晶高温合金在不同条件下的蠕变性能和组织演化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(8): 2536-2543.
SHI Zhen-xue, LI Jia-rong, LIU Shi-zhong, WANG Xiao-guang. Creep properties and microstructure evolution of a nickel-based single crystal superalloy at different conditions[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(8): 2536-2543.
[11] 田素贵, 李秋阳, 郭忠革, 薛永超, 曾 征, 舒德龙, 谢 君. 固溶温度对单晶镍基合金成分偏析和蠕变行为的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(3): 668-677.
TIAN Su-gui, LI Qiu-yang, GUO Zhong-ge, XUE Yong-chao, SHU De-long, XIE Jun. Influence of solution temperature on composition segregation and creep behaviors of single crystal nickel based superalloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(3): 668-677.
[12] 田 宁, 田素贵, 于惠臣, 孟宪林. DZ125 镍基合金的显微组织与蠕变行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(5): 1232-1240.
TIAN Ning, TIAN Su-gui, YU Hui-chen, MENG Xian-lin. Microstructures and creep behavior of DZ125 nickel-based superalloy[J]. The Chinese Journal Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(5): 1232-1240.
[13] LIU Li-rong, JIN Tao, LIU Jin-lai, SUN Xiao-feng, HU Zhuang-qi. Effect of ruthenium on γ' precipitation behavior and evolution in single crystal superalloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(1): 14-22.
[14] 刘心刚,雷 强, 王 莉, 李相伟, 钱 宝, 楼琅洪. 第三代单晶高温合DD3固溶处理中组织的演变[J]. 材料研究学报, 2014, 28(6): 407-412.
LIU Xin-gang, LEI Qiang, WANG Li, LI Xiang-wei, QIAN Bao, LOU Lang-hong. Microstructural evolution of a third-generation single crystal superalloy DD33 during solution treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2014, 28(6): 407-412.
[15] TIAN Su-gui, ZHOU Hui-hua, ZNANG Jing-hua, YANG Hong-cai, XU Yong-bo, HU Zhuang-qi. Formation and role of dislocations networks during high temperature creep of a single crystal nickel-based superalloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 279: 160-165.
[16] TIAN Su-gui, SU Yong, QIAN Ben-jiang, YU Xing-fu, LIANG Fu-shun, LI An-an. Creep behavior of a single crystal nickel-based superalloy containing 4.2% Re[J]. Materials and Design, 2012, 37: 236-242.
[17] SATO A, HARADA H, YOKOKAWA T, MURAKUMO T, KOIZUNI Y, KOBAYASHI T, IMAI H. The effects of ruthenium on the phase stability of fourth generation Ni-base single crystal superalloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 54(9): 1679-1684.
[18] LIU J L, SUN X F, ZHANG Z H, GUAN H R, HU Z Q. Anisotropy of stress rupture properties of a Ni base single crystal superalloy at two temperature[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 479: 277-284.
Creep and damage behavior of containing Mo nickel-based single crystal superalloy at high temperature
LIANG Shuang1, 2, TIAN Su-gui1, LIU Zhi-xin1, 2, XUE Yong-chao1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shenyang University of Technology, Shenyang 110870, China;
2. Department of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Yingkou Institute of Technology, Yinkou 115000, China)
Abstract: By means of creep property measurement and microstructure observation, the creep and damage behaviors of containing 3% and 5% (mass fraction) Mo single crystal Ni-based superalloy at high temperature were investigated. The results show that, compared to 3%Mo single crystal superalloy, the 5%Mo superalloy displays a better creep resistance and longer creep life, the creep life of alloy at 1040 ℃ and 137 MPa is measured to be 556 h. The deformation mechanisms of the alloy during steady state creep are dislocation slipping in γ matrix and climbing over the rafted γ' phase. In the later stage of creep, the deformation mechanism of alloy is dislocation shearing into the rafted γ' phase. As the creep going on, the alternate activation of dislocations slipping resulted in the twisted of rafted γ' phase promotes the initiation and propagation of crack occurring in the interface of γ/γ' phase, until fracture, which is thought to be the damage and fracture mechanism of alloy during creep at high temperature.
Key words: Ni-based single crystal supperalloy containing Mo; microstructure; creep; deformation mechanism; fracture feature
Foundation item: Project(51271125) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2016-03-18; Accepted date: 2016-07-19
Corresponding author: TIAN Su-gui; Tel: +86-24-25494089; E-mail: tiansugui2003@163.com
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51271125)
收稿日期:2016-03-18;修订日期:2016-07-19
通信作者:田素贵,教授,博士;电话:024-25494089;E-mail:tiansugui2003@163.com